Imaging of Joints and Bones in Autoinflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
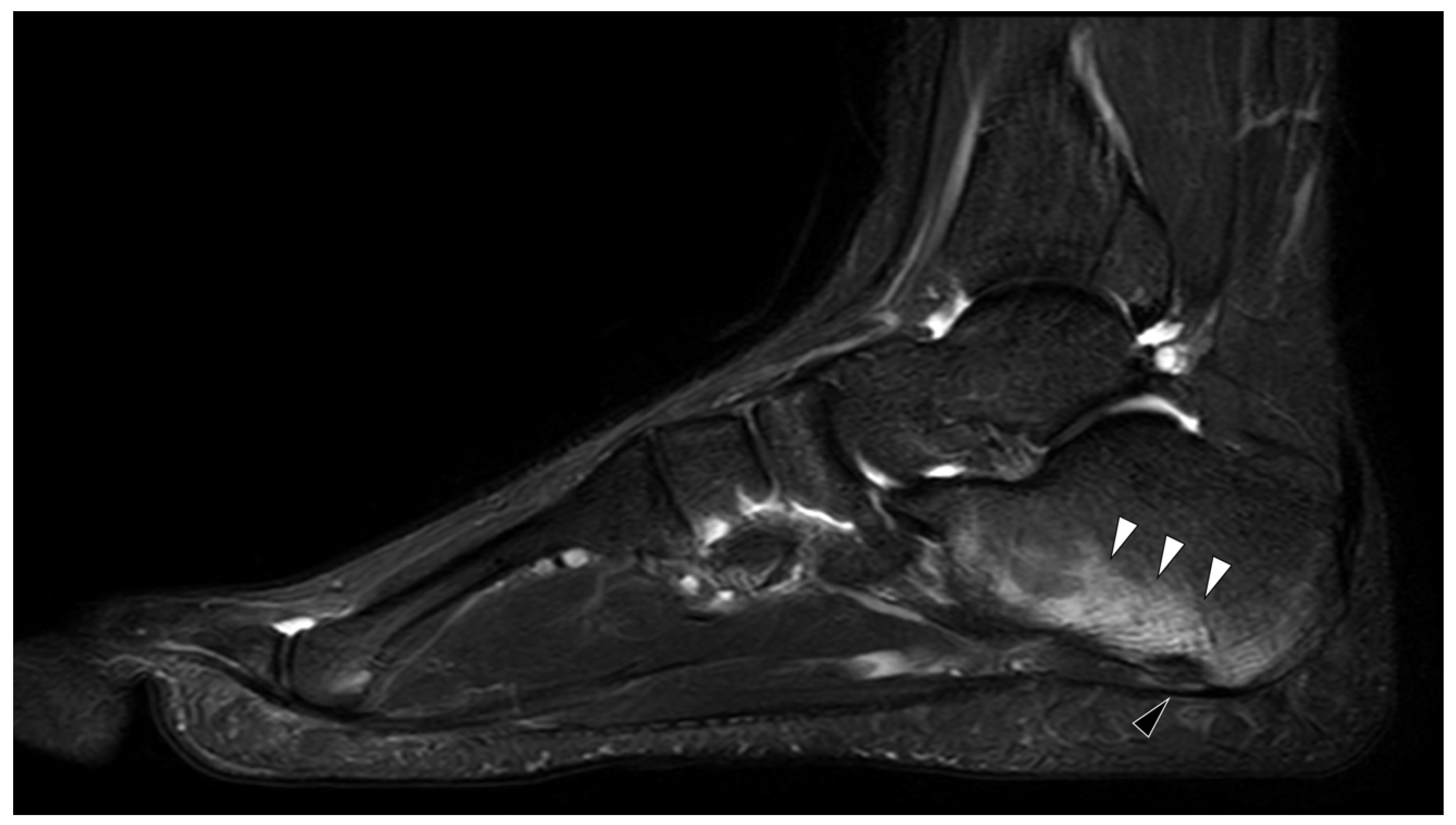
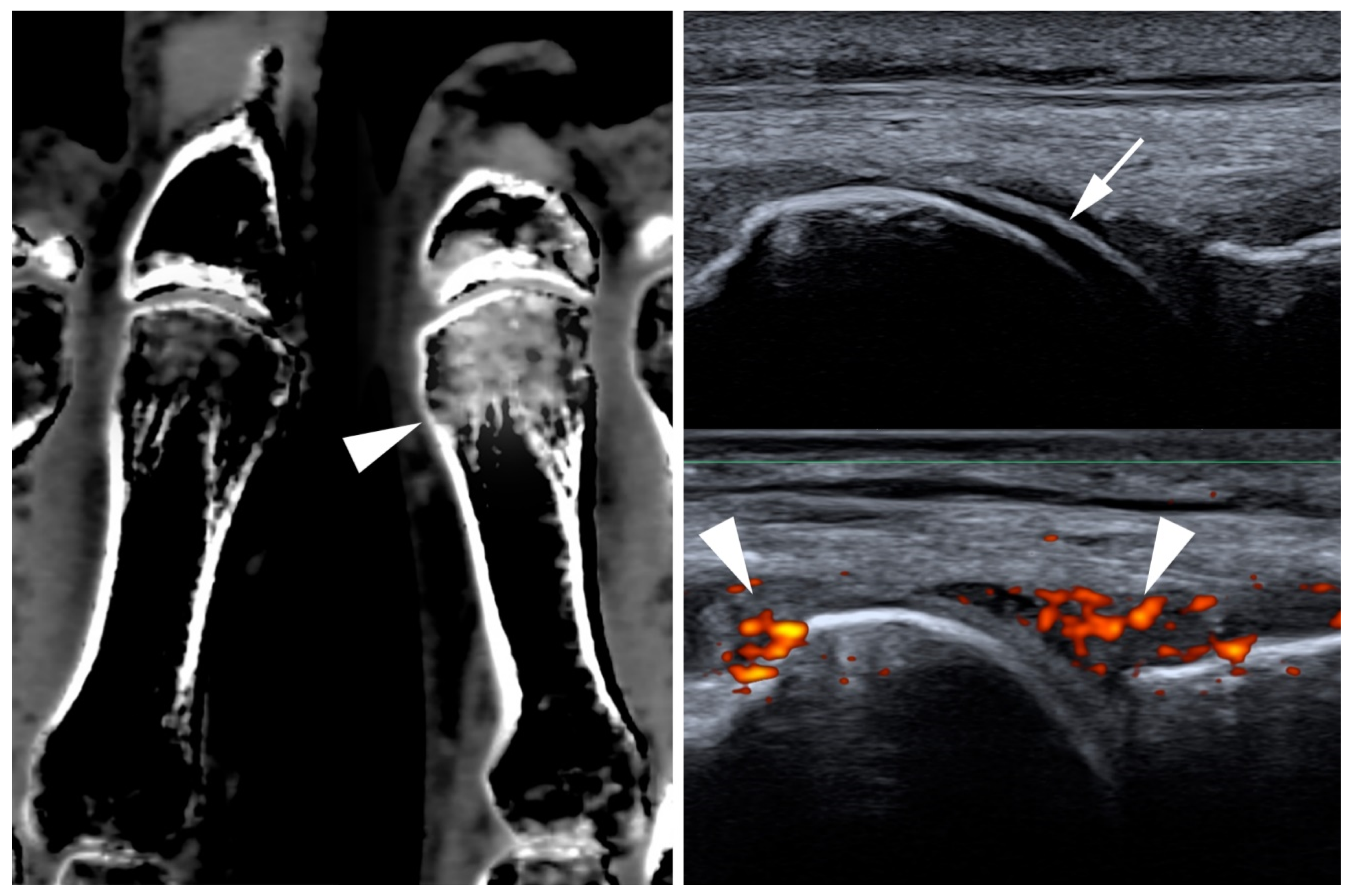
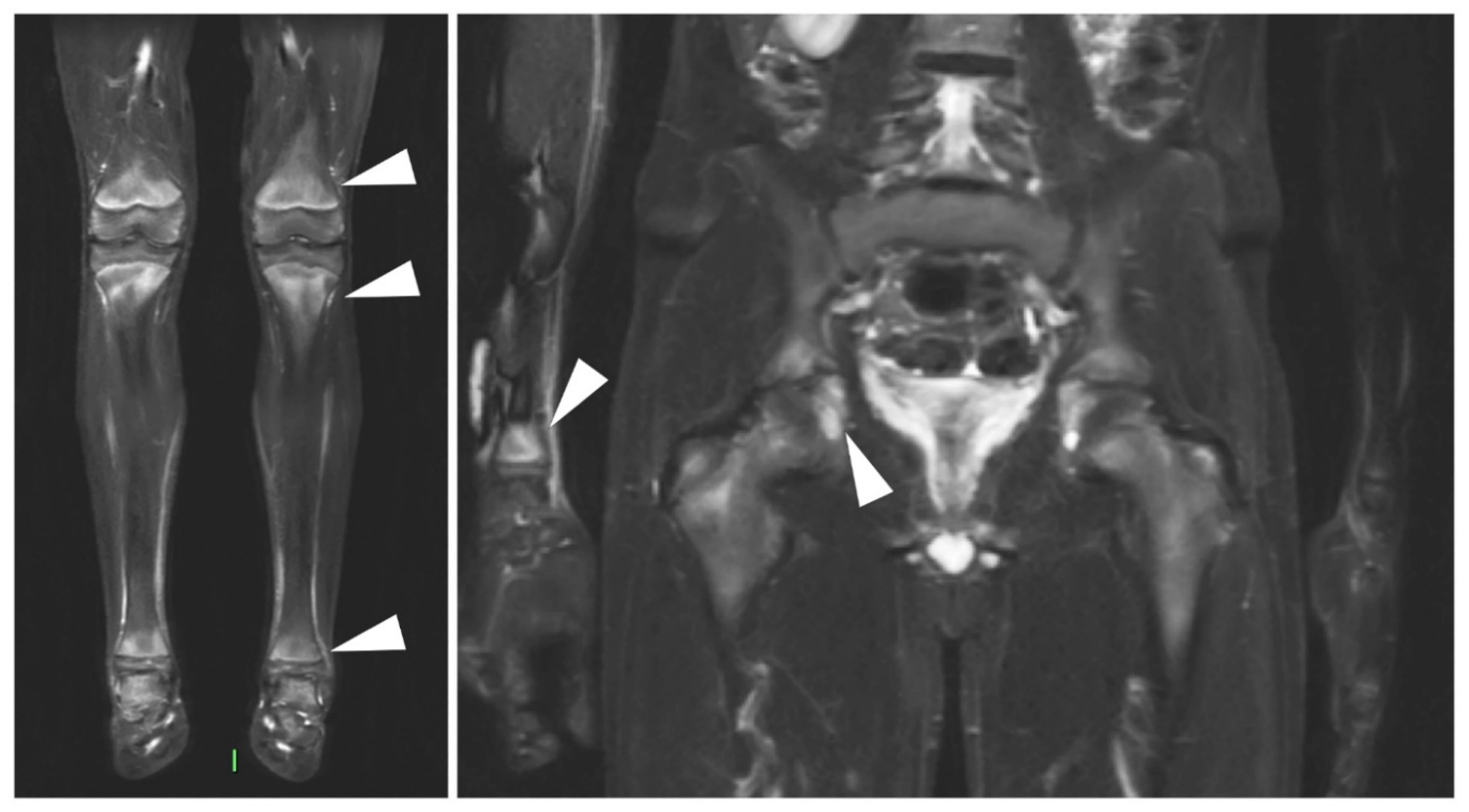
2. Familial Mediterranean Fever
3. Behçet Disease
4. Crystal Deposition
5. Gout
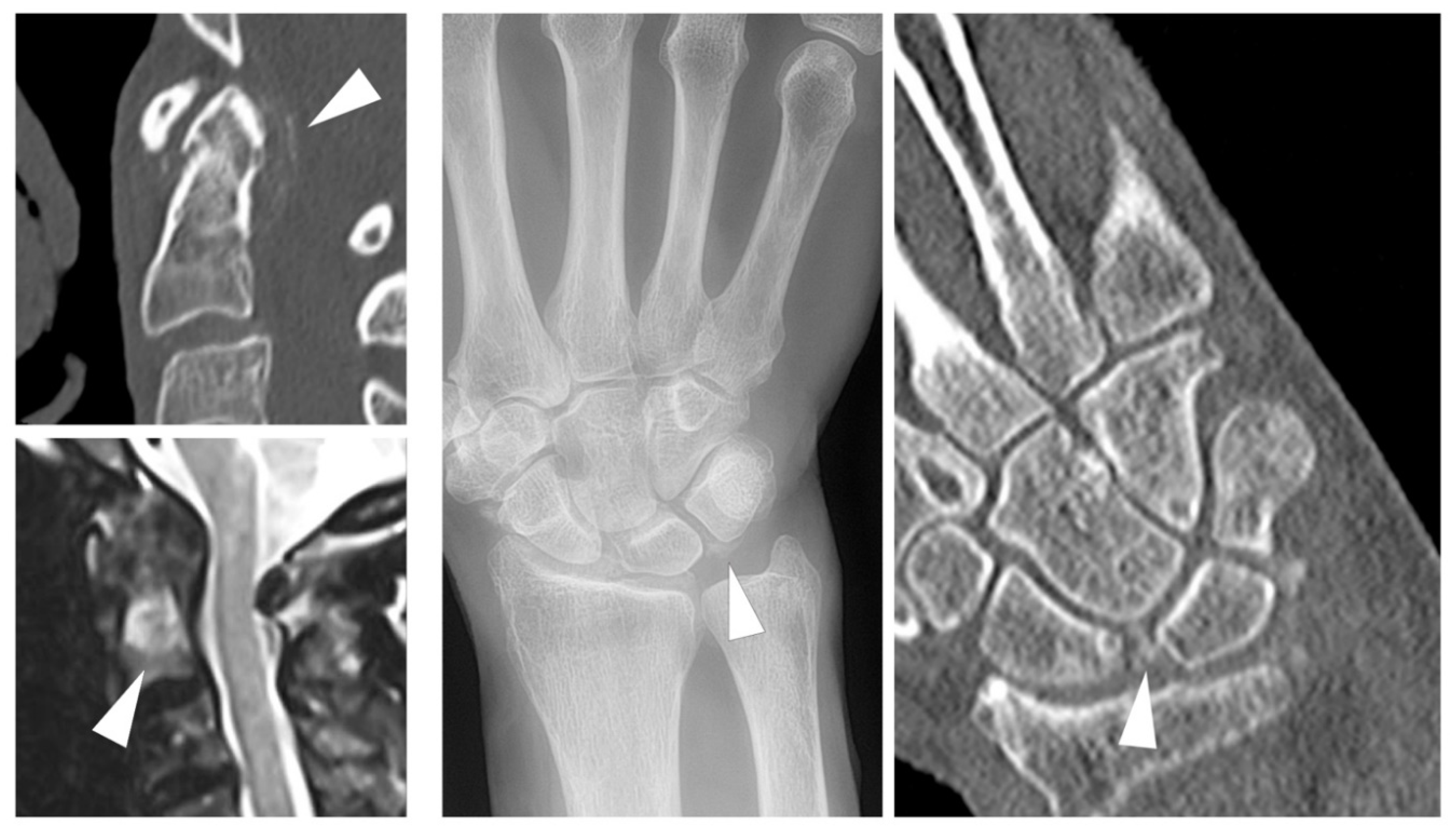
6. Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Deposition (CPPD)
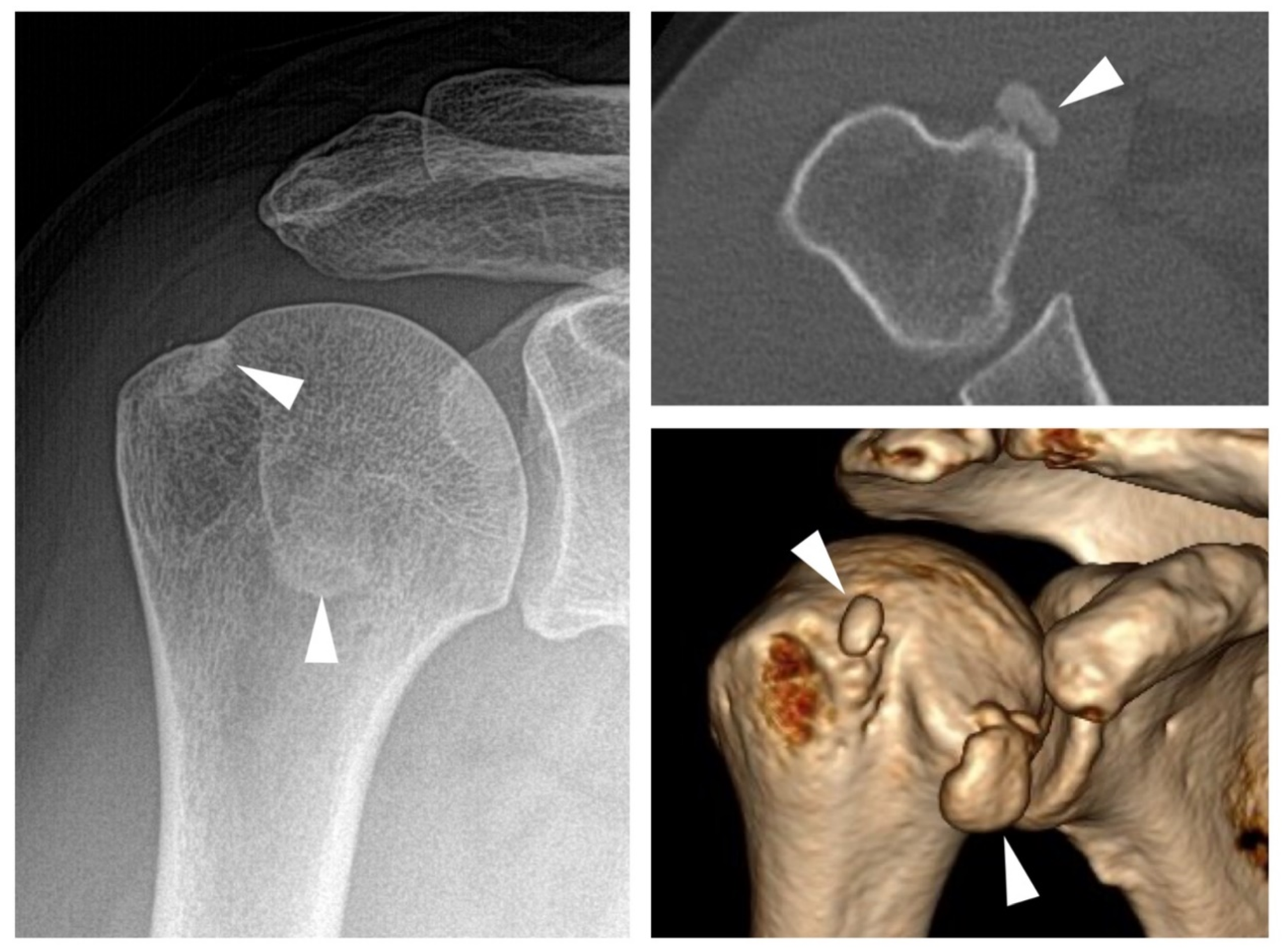
7. BCP and Mixed Crystal Disease
8. Adult-Onset Still’s Disease (AOSD)
9. SAPHO and CRMO
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGonagle, D.; McDermott, M.F. A Proposed Classification of the Immunological Diseases. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedrich, C.M. Shaping the spectrum—From autoinflammation to autoimmunity. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 165, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozdogan, H.; Ugurlu, S. Familial Mediterranean Fever. Press. Méd. 2019, 48, e61–e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touitou, I. The spectrum of Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) mutations. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 9, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaşifoğlu, T.; Çalışır, C.; Cansu, D.Ü.; Korkmaz, E.H.C. The frequency of sacroiliitis in familial Mediterranean fever and the role of HLA-B27 and MEFV mutations in the development of sacroiliitis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2008, 28, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosan, F.; Üstek, D.; Oku, B.; Duymaz-Tozkir, J.; Cakiris, A.; Abaci, N.; Ocal, L.; Aral, O.; Gul, A. Association of familial Mediterranean fever-related MEFV variations with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 3232–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshed, I.; Rosman, Y.; Livneh, A.; Kedem, R.; Langevitz, P.; Lidar, M.; Ben-Zvi, I. Exertional Leg Pain in Familial Mediterranean Fever: A Manifestation of an Underlying Enthesopathy and a Marker of More Severe Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 3221–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshed, I.; Bollow, M.; McGonagle, D.G.; Tan, A.L.; Althoff, C.; Asbach, P.; Hermann, K.-G. MRI of enthesitis of the appendicular skeleton in spondyloarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshed, I.; Kushnir, T.; Livneh, A.; Langevitz, P.; Ben-Zvi, I.; Konen, E.; Lidar, M. Exertional leg pain as a manifestation of occult spondyloarthropathy in familial Mediterranean fever: An MRI evaluation. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 41, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigenbaum, A. Description of Behcet’s Syndrome in the Hippocratic Third Book of Endemic Diseases. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1956, 40, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Menthon, M.; LaValley, M.P.; Maldini, C.; Guillevin, L.; Mahr, A. HLA-B51/B5and the risk of Behçet’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control genetic association studies. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaklamani, V.G.; Vaiopoulos, G.; Kaklamanis, P.G. Behçet’s Disease. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 27, 197–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, A.; Goyal, A.; Bansal, P.; Quint, J.M. Behcet Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H. Clinical Analysis of Behcet Disease; Arthritic Manifestations in Behcet Disease may present as Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis or Palindromic Rheumatism. Korean J. Intern. Med. 1999, 14, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bicer, A. Musculoskeletal Findings in Behcet’s Disease. Pathol. Res. Int. 2011, 2012, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazici, H.; Tuzlaci, M.; Yurdakul, S. A controlled survey of sacroiliitis in Behcet’s disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1981, 40, 558–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatemi, G.; Fresko, I.; Tascilar, K.; Yazici, H. Increased enthesopathy among Behçet’s syndrome patients with acne and arthritis: An ultrasonography study. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehlin, M.; Jacobsson, L.; Roddy, E. Global epidemiology of gout: Prevalence, incidence, treatment patterns and risk factors. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punzi, L.; Scanu, A.; Ramonda, R.; Oliviero, F. Gout as autoinflammatory disease: New mechanisms for more appropriated treatment targets. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 12, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Evans, J.E.; Rock, K.L. Molecular identification of a danger signal that alerts the immune system to dying cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 425, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnason, I.; O’Morain, C.; Levi, A.; Peters, T.J. Absorption of 151chromium-labeled ethylenediaminetetraacetate in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 1983, 85, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, G.M.; Dunne, A. Calcium crystals and auto-inflammation. Rheumatology 2019, 59, 247–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliviero, F.; Bindoli, S.; Scanu, A.; Feist, E.; Doria, A.; Galozzi, P.; Sfriso, P. Autoinflammatory Mechanisms in Crystal-Induced Arthritis. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richette, P.; Doherty, M.; Pascual, E.; Barskova, V.; Becce, F.; Castaneda, J.; Coyfish, M.; Guillo, S.; Jansen, T.; Janssens, H.; et al. 2018 updated European League Against Rheumatism evidence-based recommendations for the diagnosis of gout. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Doherty, M.; Bardini, T.; Barskova, V.; Guerne, P.-A.; Jansen, T.L.; Leeb, B.F.; Perez-Ruiz, F.; Pimentao, J.; Punzi, L.; et al. European League Against Rheumatism recommendations for calcium pyrophosphate deposition. Part I: Terminology and diagnosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neame, R.L.; Carr, A.J.; Muir, K.; Doherty, M. UK community prevalence of knee chondrocalcinosis: Evidence that correlation with osteoarthritis is through a shared association with osteophyte. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felson, D.T.; Anderson, J.J.; Naimark, A.; Kannel, W.; Meenan, R.F. The prevalence of chondrocalcinosis in the elderly and its association with knee osteoarthritis: The Framingham Study. J. Rheumatol. 1989, 16, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Salaffi, F.; De Angelis, R.; Grassi, W.; Prevalence, M.P.; INvestigation Group (MAPPING) study. Prevalence of musculoskeletal conditions in an Italian population sample: Results of a regional community-based study. I. The MAPPING study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2005, 23, 819–828. [Google Scholar]
- Koto, R.; Nakajima, A.; Horiuchi, H.; Yamanaka, H. Real-world treatment of gout and asymptomatic hyperuricemia: A cross-sectional study of Japanese health insurance claims data. Mod. Rheumatol. 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, W.; Ding, J.; Khorshed, D.; Shojania, K.; Nicolaou, S. Unravelling the mysteries of gout by multimodality imaging. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, S17–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checa, A. Consistency of the sonographic image (double contour sign) in patients with gout after ambulation. J. Med. Ultrasound 2019, 27, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogdie, A.; Taylor, W.; Neogi, T.; Fransen, J.; Jansen, T.L.; Schumacher, H.R.; Louthrenoo, W.; Vazquez-Mellado, J.; Eliseev, M.; McCarthy, G.; et al. Performance of Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Gout in a Multicenter Study: Comparison with Monosodium Urate Monohydrate Crystal Analysis as the Gold Standard. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogdie, A.; Taylor, W.J.; Weatherall, M.; Fransen, J.; Jansen, T.L.; Neogi, T.; Schumacher, H.R.; Dalbeth, N. Imaging modalities for the classification of gout: Systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1868–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiteado, D.; Villalba, A.; Martín-Mola, E.; Balsa, A.; De Miguel, E. Ultrasound sensitivity to changes in gout: A longitudinal study after two years of treatment. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Löffler, C.; Sattler, H.; Peters, L.; Tuleweit, A.; Löffler, U.; Wadsack, D.; Uppenkamp, M.; Bergner, R. In arthritis the Doppler based degree of hypervascularisation shows a positive correlation with synovial leukocyte count and distinguishes joints with leukocytes greater and less than 5/nL. Jt. Bone Spine 2016, 83, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Song, G.G. Diagnostic accuracy of dual-energy computed tomography in patients with gout: A meta-analysis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2017, 47, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamala, M.; Jacobs, J.W.G.; Van Laar, J.M. The diagnostic performance of dual energy CT for diagnosing gout: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 2117–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongartz, T.; Glazebrook, K.N.; Kavros, S.J.; Murthy, N.S.; Merry, S.P.; Franz, W.B.; Michet, C.J.; Veetil, B.M.A.; Davis, J.M.I.; Ii, T.G.M.; et al. Dual-energy CT for the diagnosis of gout: An accuracy and diagnostic yield study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlyarov, M.; Hermann, K.G.A.; Mews, J.; Hamm, B.; Diekhoff, T. Development and validation of a quantitative method for estimation of the urate burden in patients with gouty arthritis using dual-energy computed tomography. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalbeth, N.; Choi, H.K. Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Gout Diagnosis and Management. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2013, 15, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekhoff, T.; Scheel, M.; Hermann, S.; Mews, J.; Hamm, B.; Hermann, K.-G.A. Osteitis: A retrospective feasibility study comparing single-source dual-energy CT to MRI in selected patients with suspected acute gout. Skelet. Radiol. 2017, 46, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippou, G.; Scirè, C.A.; Adinolfi, A.; Damjanov, N.S.; Carrara, G.; Bruyn, G.A.W.; Cazenave, T.; D’Agostino, M.A.; Sedie, A.D.; Di Sabatino, V.; et al. Identification of calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD) by ultrasound: Reliability of the OMERACT definitions in an extended set of joints—An international multiobserver study by the OMERACT Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease Ultrasound Subtask Force. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippou, G.; Scirè, C.A.; Damjanov, N.; Adinolfi, A.; Carrara, G.; Picerno, V.; Toscano, C.; Bruyn, G.A.; D’Agostino, M.A.; Sedie, A.D.; et al. Definition and Reliability Assessment of Elementary Ultrasonographic Findings in Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease: A Study by the OMERACT Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease Ultrasound Subtask Force. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 1744–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.Y.; Lim, W.Y.; Wolfson, T.; Gamst, A.; Chung, C.B.; Bae, W.C.; Resnick, D.L. Frequency of Atlantoaxial Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Deposition at CT. Radiology 2013, 269, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegeler, K.; Diekhoff, T.; Hermann, S.; Hamm, B.; Hermann, K.G. Low-dose computed tomography as diagnostic tool in calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease arthropathy: Focus on ligamentous calcifications of the wrist. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37, 826–833. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, D.; Guermazi, A.; Sieren, J.P.; Lynch, J.A.; Torner, J.C.; Neogi, T.; Felson, D. CT imaging for evaluation of calcium crystal deposition in the knee: Initial experience from the Multicenter Osteoarthritis (MOST) study. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekhoff, T.; Kiefer, T.; Stroux, A.; Pilhofer, I.; Juran, R.; Mews, J.; Blobel, J.; Tsuyuki, M.; Ackermann, B.; Hamm, B.; et al. Detection and Characterization of Crystal Suspensions Using Single-Source Dual-Energy Computed Tomography. Investig. Radiol. 2015, 50, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascart, T.; Falgayrac, G.; Norberciak, L.; Lalanne, C.; Legrand, J.; Houvenagel, E.; Ea, H.-K.; Becce, F.; Budzik, J.-F. Dual-energy computed-tomography-based discrimination between basic calcium phosphate and calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition in vivo. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2020, 12, 1759720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascart, T.; Norberciak, L.; Legrand, J.; Becce, F.; Budzik, J. Dual-energy computed tomography in calcium pyrophosphate deposition: Initial clinical experience. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2019, 27, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippou, G.; Pascart, T.; Iagnocco, A. Utility of Ultrasound and Dual Energy CT in Crystal Disease Diagnosis and Management. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2020, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegeler, K.; Hermann, S.; Hermann, K.G.A.; Hamm, B.; Diekhoff, T. Dual-energy CT in the differentiation of crystal depositions of the wrist: Does it have added value? Skelet. Radiol. 2019, 49, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegeler, K.; Richter, S.-T.; Hermann, S.; Hermann, K.G.A.; Hamm, B.; Diekhoff, T. Dual-energy CT collagen density mapping of wrist ligaments reveals tissue remodeling in CPPD patients: First results from a clinical cohort. Skelet. Radiol. 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshrif, A.; Laredo, J.D.; Bassiouni, H.; Abdelkareem, M.; Richette, P.; Rigon, M.R.; Bardin, T. Spinal involvement with calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease in an academic rheumatology center: A series of 37 patients. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 48, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hongsmatip, P.; Cheng, K.Y.; Kim, C.; Lawrence, D.A.; Rivera, R.; Smitaman, E. Calcium hydroxyapatite deposition disease: Imaging features and presentations mimicking other pathologies. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 120, 108653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianca, V.; Albano, D.; Messina, C.; Midiri, F.; Mauri, G.; Aliprandi, A.; Catapano, M.; Pescatori, L.C.; Monaco, C.G.; Gitto, S.; et al. Rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy: From diagnosis to treatment. Acta Biomed. 2018, 89, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jacques, T.; Michelin, P.; Badr, S.; Nasuto, M.; Lefebvre, G.; Larkman, N.; Cotten, A. Conventional Radiology in Crystal Arthritis. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 55, 967–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, N.S.; Lee, B.G.; Rhee, Y.G. Radiologic course of the calcific deposits in calcific tendinitis of the shoulder: Does the initial radiologic aspect affect the final results? J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2010, 19, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhthoff, H.; Sarkar, K. Calcifying tendinitis. Baillières Clin. Rheumatol. 1989, 3, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greis, A.C.; Derrington, S.M.; McAuliffe, M. Evaluation and Nonsurgical Management of Rotator Cuff Calcific Tendinopathy. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 46, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ea, H.; Lioté, F. Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate and basic calcium phosphate crystalinduced arthropathies: Update on pathogenesis, clinical features, and Therapy. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2004, 6, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, D.J. Milwaukee shoulder syndrome. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 1991, 102, 271–283, discussion 283–274. [Google Scholar]
- Santiago, T.; Coutinho, M.; Malcata, A.; Da Silva, J.A.P. Milwaukee shoulder (and knee) syndrome. BMJ Case Rep. 2014, 2014, bcr2013202183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feist, E.; Mitrovic, S.; Fautrel, B. Mechanisms, biomarkers and targets for adult-onset Still’s disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fautrel, B. Adult-onset Still disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2008, 22, 773–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouchot, J.; Sampalis, J.S.; Beaudet, F.; Carette, S.; Decary, F.; Salusinsky-Sternbach, M.; Hill, R.O.; Gutkowski, A.; Harth, M.; Myhal, D.; et al. Adult Still’s disease: Manifestations, disease course, and outcome in 62 patients. Medicine 1991, 70, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belghali, S.; El Amri, N.; Baccouche, K.; Laataoui, S.; Bouzaoueche, M.; Zeglaoui, H.; Bouajina, E. Atypical form of Adult-onset Still’s Disease with Distal Interphalangeal Joints Involvement. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2018, 14, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelušić, M.; Čekada, N.; Frković, M.; Potočki, K.; Skerlev, M.; Murat-Sušić, S.; Husar, K.; Đapić, T.; Šmigovec, I.; Bajramović, D. Chronic Recurrent Multifocal Osteomyelitis (CRMO) and Synovitis Acne Pustulosis Hyperostosis Osteitis (SAPHO) Syndrome—Two Presentations of the Same Disease? Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. 2018, 26, 212–219. [Google Scholar]
- Jansson, M.A.; Renner, E.D.; Ramser, J.; Mayer, A.; Haban, M.; Meindl, A.; Grote, V.; Diebold, J.; Schneider, K.; Belohradsky, B.H. Classification of Non-Bacterial Osteitis: Retrospective study of clinical, immunological and genetic aspects in 89 patients. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klicman, R.F.; Simoni, P.; Robinson, P.; Teh, J.; Jurik, A.G. SAPHO and CRMO: The Value of Imaging. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2018, 22, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falip, C.; Alison, M.; Boutry, N.; Job-Deslandre, C.; Cotten, A.; Azoulay, R.; Adamsbaum, C. Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis (CRMO): A longitudinal case series review. Pediatr. Radiol. 2013, 43, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurik, A.G. Chronic Recurrent Multifocal Osteomyelitis. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2004, 8, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePasquale, R.; Kumar, N.; Lalam, R.; Tins, B.; Tyrrell, P.; Singh, J.; Cassar-Pullicino, V. SAPHO: What radiologists should know. Clin. Radiol. 2012, 67, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andronikou, S.; Kraft, J.K.; Offiah, A.C.; Jones, J.; Douis, H.; Thyagarajan, M.; Barrera, C.A.; Zouvani, A.; Ramanan, A.V. Whole-body MRI in the diagnosis of paediatric CNO/CRMO. Rheumatology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buch, K.; Thuesen, A.C.B.; Brøns, C.; Schwarz, P. Chronic Non-bacterial Osteomyelitis: A Review. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2019, 104, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimenti, M.S.; Caso, F.; Alivernini, S.; De Martino, E.; Costa, L.; Tolusso, B.; Triggianese, P.; Conigliaro, P.; Gremese, E.; Scarpa, R.; et al. Amplifying the concept of psoriatic arthritis: The role of autoimmunity in systemic psoriatic disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himuro, H.; Kurata, S.; Nagata, S.; Sumi, A.; Tsubaki, F.; Matsuda, A.; Fujimoto, K.; Abe, T. Imaging features in patients with SAPHO/CRMO: A pictorial review. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2020, 38, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ziegeler, K.; Eshed, I.; Diekhoff, T.; Hermann, K.G. Imaging of Joints and Bones in Autoinflammation. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 4074. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124074
Ziegeler K, Eshed I, Diekhoff T, Hermann KG. Imaging of Joints and Bones in Autoinflammation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(12):4074. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124074
Chicago/Turabian StyleZiegeler, Katharina, Iris Eshed, Torsten Diekhoff, and Kay Geert Hermann. 2020. "Imaging of Joints and Bones in Autoinflammation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 12: 4074. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124074
APA StyleZiegeler, K., Eshed, I., Diekhoff, T., & Hermann, K. G. (2020). Imaging of Joints and Bones in Autoinflammation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(12), 4074. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124074






