Treatment with Intravenous Methylprednisolone in Patients with Graves’ Orbitopathy Significantly Affects Adrenal Function: Assessment of Serum, Salivary Cortisol and Serum Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Study Design and Treatment
2.3. Assays
2.4. Statistical Analysis
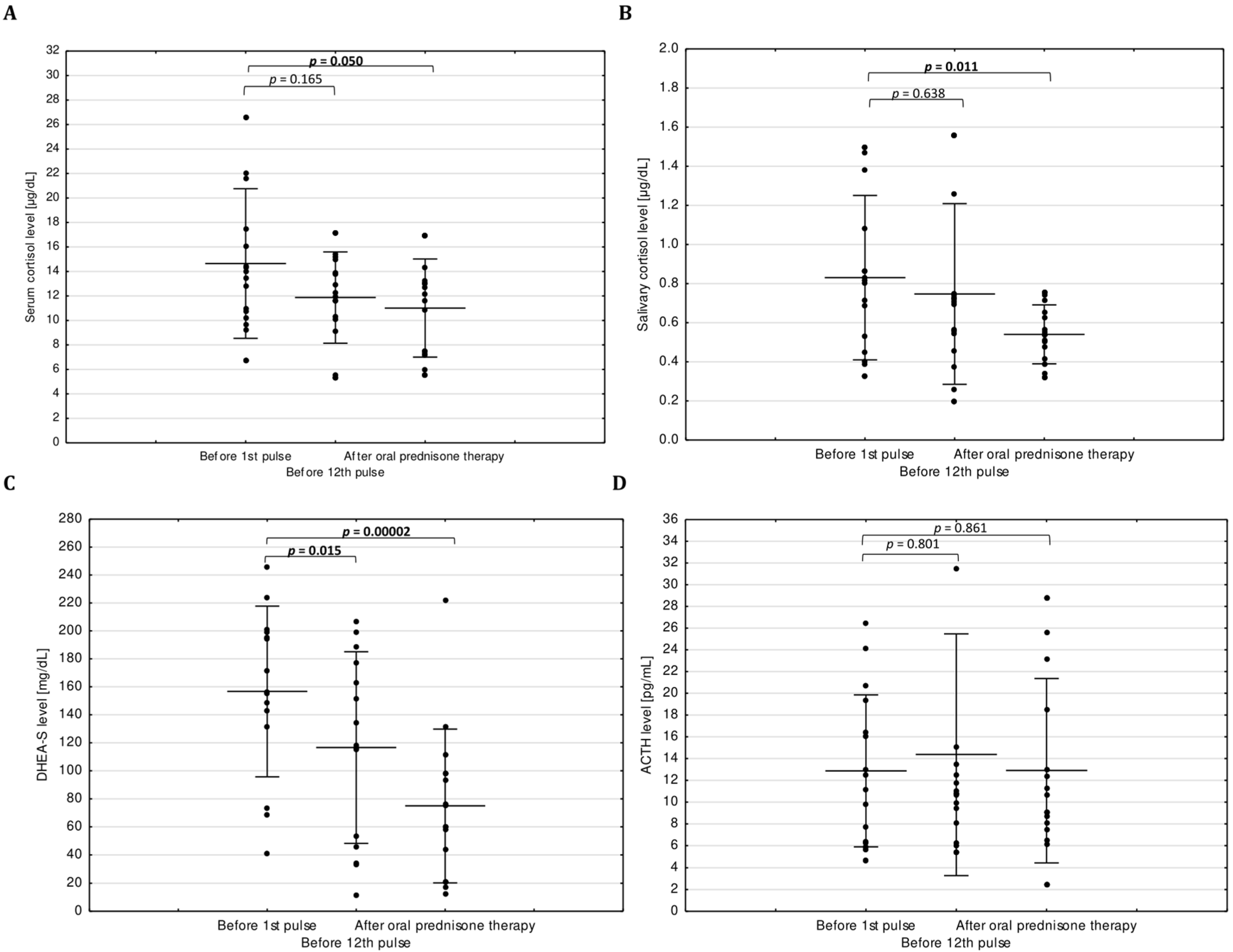
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartalena, L.; Baldeschi, L.; Boboridis, K.; Eckstein, A.; Kahaly, G.J.; Marcocci, C.; Perros, P.; Salvi, M.; Wiersinga, W.M. The 2016 European Thyroid Association/European Group on Graves’ Orbitopathy Guidelines for the Management of Graves’ Orbitopathy. Eur. Thyroid J. 2016, 5, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartalena, L.; Baldeschi, L.; Dickinson, A.; Eckstein, A.; Kendall-Taylor, P.; Marcocci, C.; Mourits, M.; Perros, P.; Boboridis, K.; Boschi, A.; et al. Consensus statement of the European Group on Graves’ orbitopathy (EUGOGO) on management of GO. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 158, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miśkiewicz, P.; Kryczka, A.; Ambroziak, U.; Rutkowska, B.; Główczyńska, R.; Opolski, G.; Kahaly, G.; Bednarczuk, T. Is high dose intravenous methylprednisolone pulse therapy in patients with Graves’ orbitopathy safe? Endokrynol. Pol. 2014, 65, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornstein, S.R.; Allolio, B.; Arlt, W.; Barthel, A.; Don-wauchope, A.; Hammer, G.D.; Husebye, E.S.; Merke, D.P.; Murad, H.; Stratakis, C.A.; et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Primary Adrenal Insufficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 364–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendel, C.M.; Kuhn, R.W.; Weisiger, R.A.; Cavalieri, R.R.; Siiteri, P.K.; Cunha, G.R.; Murai, J.T. Uptake of cortisol by the perfused rat liver: Validity of the free hormone hypothesis applied to cortisol. Endocrinology 1989, 124, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendel, C.M.; Miller, M.B.; Siiteri, P.K.; Murai, J.T. Rates of dissociation of steroid and thyroid hormones from human serum albumin. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1990, 37, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenke, M.A.; Zeng, A.; Meyer, E.J.; Lewis, J.G.; Rankin, W.; Johnston, J.; Kireta, S.; Jesudason, S.; Torpy, D.J. Differential Effects of Estrogen on Corticosteroid-Binding Globulin Forms Suggests Reduced Cleavage in Pregnancy. J. Endocr. Soc. 2017, 1, 202–210. [Google Scholar]
- Ceccato, F.; Marcelli, G.; Martino, M.; Concettoni, C.; Brugia, M.; Trementino, L.; Michetti, G.; Arnaldi, G. The diagnostic accuracy of increased late night salivary cortisol for Cushing’s syndrome: A real-life prospective study. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2019, 42, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langelaan, M.L.P.; Kisters, J.M.H.; Oosterwerff, M.M.; Boer, A.K. Salivary cortisol in the diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency: Cost efficient and patient friendly. Endocr. Connect. 2018, 7, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haning, R.V.; Hackett, R.J.; Boothroid, R.I.; Canick, J.A. Steroid sulphatase activity in the human ovarian corpus luteum, stroma, and follicle: Comparison to activity in other tissues and the placenta. J. Steroid Biochem. 1990, 36, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambroziak, U.; Bluszcz, G.; Bednarczuk, T.; Miśkiewicz, P. The influence of Graves’ orbitopathy treatment with intravenous glucocorticoids on adrenal function. Endokrynol. Pol. 2017, 68, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jespersen, S.; Nygaard, B.; Kristensen, L.Ø. Methylprednisolone Pulse Treatment of Graves’ Ophthalmopathy is Not Associated with Secondary Adrenocortical Insufficiency. Eur. Thyroid J. 2015, 4, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giotaki, Z.; Fountas, A.; Tsirouki, T.; Bargiota, A.; Tigas, S.; Tsatsoulis, A. Adrenal reserve following treatment of graves’ orbitopathy with intravenous glucocorticoids. Thyroid 2015, 25, 462–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ospina, N.S.; Al Nofal, A.; Bancos, I.; Javed, A.; Benkhadra, K.; Kapoor, E.; Lteif, A.N.; Natt, N.; Murad, H. ACTH Stimulation Tests for the Diagnosis of Adrenal Insufficiency: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Aridi, R.; Abdelmannan, D.; Arafah, B.M. Biochemical diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency: The added value of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate measurements. Endocr. Pract. 2011, 17, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charoensri, S.; Chailurkit, L.; Muntham, D.; Bunnag, P. Serum dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate in assessing the integrity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2017, 7, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.S.; Shaw, S.R.; McIntyre, H.E.; McGarry, G.W.; Wallace, A.M. Morning salivary cortisol versus short Synacthen test as a test of adrenal suppression. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2004, 41, 408–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulhaq, I.; Ahmad, T.; Khoja, A.; Islam, N. Morning cortisol as an alternative to short synecthan test for the diagnosis of primary adrenal insufficiency. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 35, 1413–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, Y.J.; Gaudl, A.; Jaeger, S.; Stadelmann, S.; Hiemisch, A.; Kiess, W.; Willenberg, A.; Schaab, M.; Von Klitzing, K.; Thiery, J.; et al. Immunoassay or LC-MS/MS for the measurement of salivary cortisol in children? Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutschbein, T.; Broecker-Preuss, M.; Flitsch, J.; Jaeger, A.; Althoff, R.; Walz, M.K.; Mann, K.; Petersenn, S. Salivary cortisol as a diagnostic tool for Cushing’s syndrome and adrenal insufficiency: Improved screening by an automatic immunoassay. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 166, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, N.; Fréchette, I.; Mallet, P.L.; Dubé, J.; Houde, G.; Fink, G.D. Establishment of reference intervals for the salivary cortisol circadian cycle, by electrochemiluminescence (ECLIA), in healthy adults. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 54, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogeser, M.; Kratzsch, J.; Bae, Y.J.; Bruegel, M.; Ceglarek, U.; Fiers, T.; Gaudl, A.; Kurka, H.; Milczynski, C.; Prat Knoll, C.; et al. Multicenter performance evaluation of a second generation cortisol assay. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Before 1st Pulse | Before 12th Pulse | After Oral Prednisone Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|
| TSC (µg/dL) | 14.46 ± 5.72 | 11.93 ± 3.56 | 10.90 ± 3.98 a |
| SC (µg/dL) | 0.82 ± 0.40 | 0.73 ± 0.43 | 0.54 ± 0.14 b |
| DHEA-S (µg/dL) | 155.60 ± 66.17 | 115.2 ± 74.18 a | 76.1 ± 58.97 c |
| ACTH (pg/mL) | 12.99 ± 7.48 | 13.49 ± 10.04 | 9.1 ± 8.72 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pelewicz, K.; Szewczyk, S.; Miśkiewicz, P. Treatment with Intravenous Methylprednisolone in Patients with Graves’ Orbitopathy Significantly Affects Adrenal Function: Assessment of Serum, Salivary Cortisol and Serum Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3233. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103233
Pelewicz K, Szewczyk S, Miśkiewicz P. Treatment with Intravenous Methylprednisolone in Patients with Graves’ Orbitopathy Significantly Affects Adrenal Function: Assessment of Serum, Salivary Cortisol and Serum Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(10):3233. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103233
Chicago/Turabian StylePelewicz, Katarzyna, Sebastian Szewczyk, and Piotr Miśkiewicz. 2020. "Treatment with Intravenous Methylprednisolone in Patients with Graves’ Orbitopathy Significantly Affects Adrenal Function: Assessment of Serum, Salivary Cortisol and Serum Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 10: 3233. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103233
APA StylePelewicz, K., Szewczyk, S., & Miśkiewicz, P. (2020). Treatment with Intravenous Methylprednisolone in Patients with Graves’ Orbitopathy Significantly Affects Adrenal Function: Assessment of Serum, Salivary Cortisol and Serum Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(10), 3233. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103233





