Morphogenetic Variability and Hypertension in Ischemic Stroke Patients—Preliminary Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Group
2.2. Tested Determinants
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Francis, J.; Raghunathan, S.; Khanna, P. The role of genetics in stroke. Postgrad. Med. J. 2007, 83, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razvi, S.S.; Bone, I. Single gene disorders causing ischaemic stroke. J. Neurol. 2006, 253, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dichgans, M. Genetics of ischaemic stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier-Lasserve, E. New players in the genetics of stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1711–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oline Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM). Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 16 April 2018).
- Brass, L.M.; Isaacsohn, J.L.; Merikangas, K.R.; Robinette, C.D. A study of twins and stroke. Stroke 1992, 23, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brass, L.M.; Shaker, L.A. Family history in patients with transient ischemic attacks. Stroke 1991, 22, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettehad, D.; Emdin, C.A.; Kiran, A.; Anderson, S.G.; Callender, T.; Emberson, J.; Chalmers, J.; Rodgers, A.; Rahimi, K. Blood pressure lowering for prevention of cardiovascular disease and death: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2016, 387, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanos, A.H.; Filippatou, A.; Manios, E.; Deftereos, S.; Parissis, J.; Frogoudaki, A.; Vrettou, A.R.; Ikonomidis, I.; Pikilidou, M.; Kargiotis, O.; et al. Blood Pressure Reduction and Secondary Stroke Prevention: A Systematic Review and Metaregression Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Hypertension 2017, 69, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinkovic, D.; Ilic, M.; Spremo, B. Studies of human population—Genetic variation. Comparasion of homozygously recessive traits in attendants of special and regular schools in Serbia. Arh. Biol. Nauka 1990, 42, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Marinković, D.; Cvjetićanin, S. Studes of human population genetic. The frequencies of ABO blood types and homozygously recessive traits among top sportsmen and young intelectuals. Arh. Biol. Nauka 1991, 43, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Marinkovic, D.; Cvjeticanin, S. Anthropogenetic Homozygosity and Adaptive Variability. HRC-Test in Studies of Human Populations; Monographs DCLXXII, Book 8; Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts: Belgrade, Serbia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cvjeticanin, S.; Marinkovic, D. Genetic variability in the group of patients with congenital hip dislocation. Genetika 2005, 41, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cvjeticanin, S.; Marinkovic, D. Genetic variability and frequencies of ABO blood types among different samples of patients from Serbia. Korean J. Genet. 2005, 27, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Marinkovic, D.; Cvjeticanin, S.; Stanojevic, M. Population genetic analyses of susceptibility to developing alcohol dependence. Addict. Res. Theory 2008, 16, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petricevic, B.; Cvjeticanin, S. Morphogenetic variability and handedness in Montenegro and Serbia. Russ. J. Genet. 2011, 43, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branković, S.; Cvjetićanin, S. Anthropogenetic variability in groups of children from regular and special schools from different localities in Serbia. Genetika 2016, 48, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, D.; Cvjeticanin, S.; Petronic, I.; Milincic, Z.; Brdar, R.; Karan, R.; Konstantinovic, L.; Dragin, A.; Cutovic, M. Population genetic analyses of susceptibility to increased body weight. Arch. Med. Sci. 2012, 8, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cvjeticanin, S.; Marinkovic, D. Morphogenetic variability during selection of elite water polo players. J. Sports Sci. 2009, 27, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Blaha, M.J.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; Deo, R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Floyd, J.; Fornage, M.; Gillespie, C.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2017 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e146–e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.; Markus, H.S. Genetics and ischaemic stroke. Brain 2000, 123 Pt 9, 1784–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamzi, K.; Tazzite, A.; Nadifi, S. Large-scale meta-analysis of genetic studies in ischemic stroke: Five genes involving 152,797 individuals. Indian J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 17, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, J.P.; Hingorani, A.D.; Bautista, L.E.; Sharma, P. Meta-analysis of Genetic Studies in Ischemic StrokeThirty-two Genes Involving Approximately 18 000 Cases and 58 000 Controls. Arch. Neurol. 2004, 61, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munshi, A.; Sharma, V. Genetic signatures in the treatment of stroke. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, R.; Chauhan, G.; Traylor, M.; Sargurupremraj, M.; Okada, Y.; Mishra, A.; Rutten-Jacobs, L.; Giese, A.K.; van der Laan, S.W.; Gretarsdottir, S.; et al. Multiancestry genome-wide association study of 520,000 subjects identifies 32 loci associated with stroke and stroke subtypes. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachiya, T.; Kamatani, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Hata, J.; Furukawa, R.; Shiwa, Y.; Yamaji, T.; Hara, M.; Tanno, K.; Ohmomo, H.; et al. Genetic Predisposition to Ischemic Stroke: A Polygenic Risk Score. Stroke 2017, 48, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milašinović, S.; Cvjetićanin, S.; Brdar, R.; Nikolić, D. Morphogenetic variability and genetic loads among patients with different expression of developmental hip dysplasia. Genetika 2017, 49, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, R.; Obrenovic-Kircanski, B.; Cvjeticanin, S.; Kovacevic-Kostic, N.; Velinovic, M.; Milicevic, V.; Vranes-Stoimirov, M.; Nikolic, D. The Gender Impact on Morphogenetic Variability in Coronary Artery Disease: A Preliminary Study. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

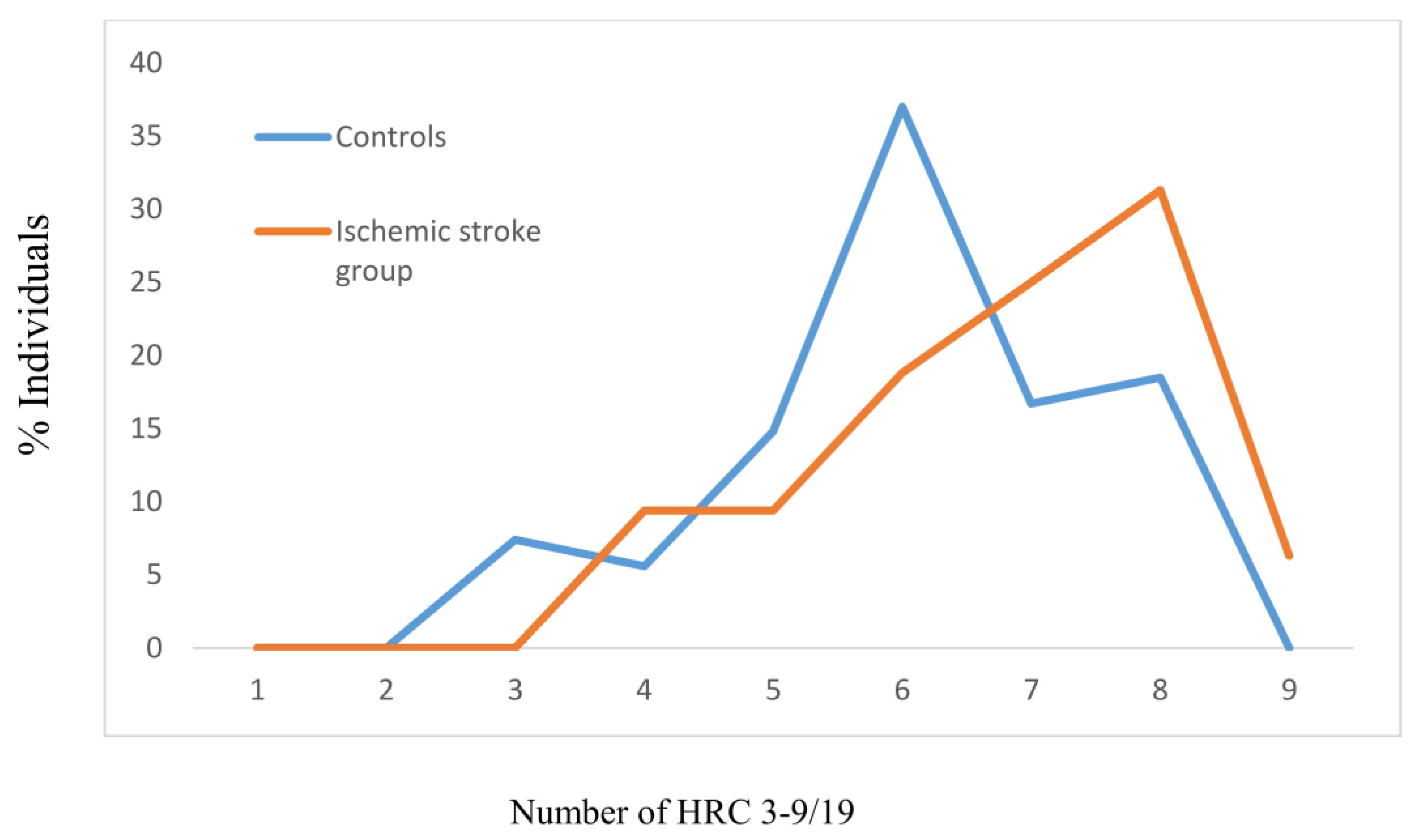
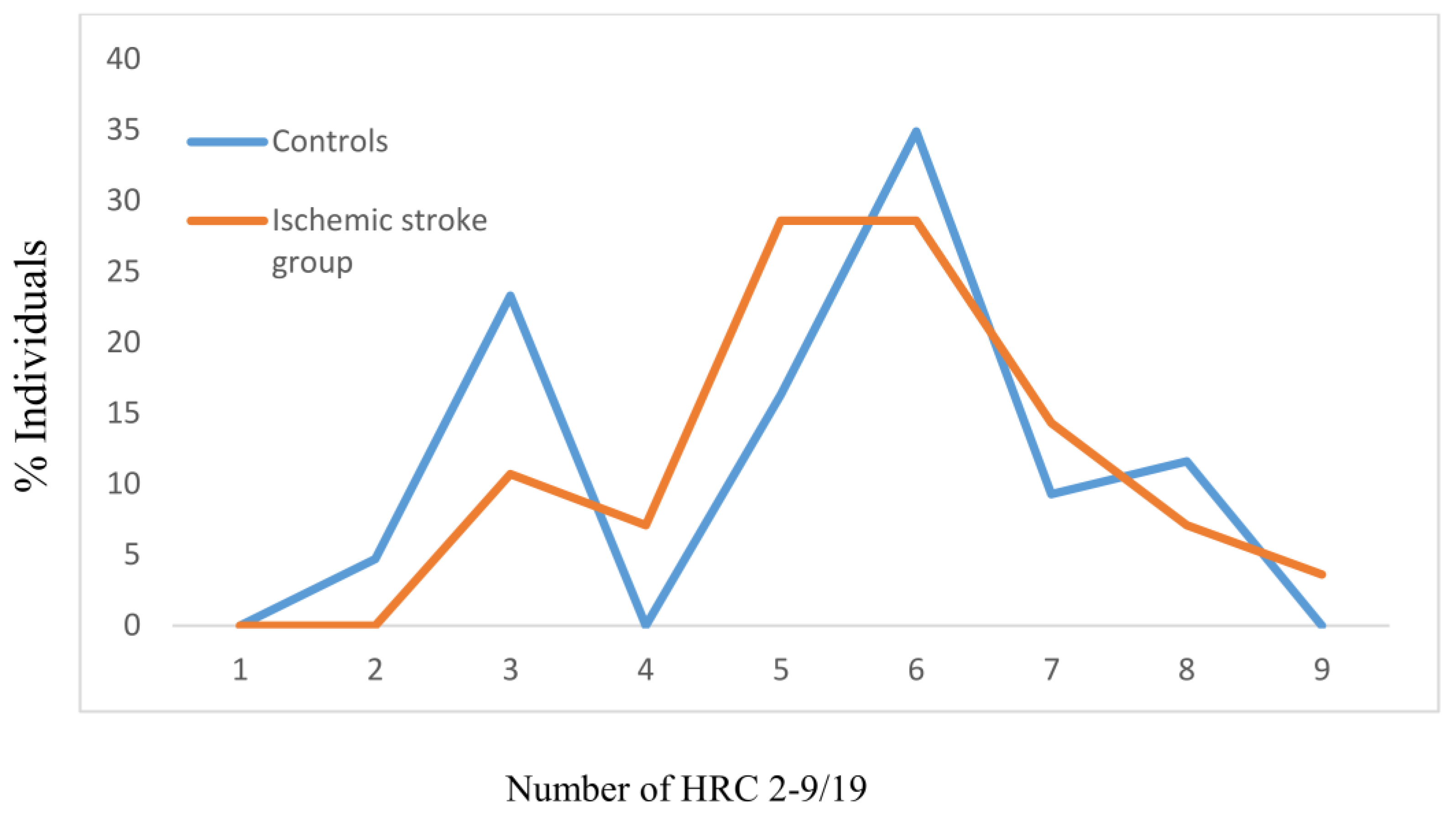
| Parameters | Controls N = 194 | Ischemic Stroke Group N = 120 | p Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, N (%) | Males | 82 (42.27%) | 44 (36.67%) | 0.325 * |
| Females | 112 (57.73%) | 76 (63.33%) | ||
| Age, years (MV ± SD) | 67.49 ± 7.12 | 71.32 ± 6.92 | 0.000 ** | |
| BMI (MV ± SD) | 26.34 ± 8.28 | 29.14 ± 7.18 | 0.002 ** | |
| Hypertension, N (%) | 86 (44.33%) | 56 (46.67%) | 0.686 * | |
| Diabetes mellitus, N (%) | 52 (26.80%) | 49 (40.83%) | 0.010 * | |
| Non-insulin dependent, N (%) | 38 (19.59%) | 42 (35.00%) | 0.002 * | |
| Insulin dependent, N (%) | 14 (7.22%) | 7 (5.83%) | 0.634 * | |
| Dyslipidemia, N (%) | 128 (65.98%) | 86 (71.67%) | 0.293 * | |
| Family history of hypertension, N (%) | 104 (53.61%) | 81 (67.50%) | 0.015 * | |
| Family history of MI, N (%) | 78 (40.21%) | 63 (52.50%) | 0.033 * | |
| Prior PCI, N (%) | 84 (43.30%) | 26 (21.67%) | 0.000 * | |
| Prior stroke, N (%) | 0 (0%) | 31 (25.83%) | - | |
| Homozygously Recessive Characteristics | Controls N = 194, n (%) | Ischemic Stroke Group N = 120, n (%) | χ2 | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blond Hair | 52 (26.80) | 29 (24.17) | 0.258 | 0.87 (0.51–1.47) |
| Straight Hair | 121 (62.37) | 88 (73.33) | 1.930 | 1.64 (0.99–2.69) |
| Double Hair Whorl | 19 (9.79) | 12 (10.00) | 0.005 | 1.02 (0.48–2.19) |
| Opposite Hair Whorl Orientation | 40 (20.62) | 29 (24.17) | 0.611 | 1.23 (0.71–2.11) |
| Soft Hair | 92 (47.42) | 73 (60.83) | 3.792 | 1.72 * (1.08–2.73) |
| Continuous Hair Line | 96 (49.48) | 36 (30.00) | 7.669 ** | 0.44 ** (0.27–0.71) |
| Attached Ear Lobe | 31 (15.98) | 14 (11.67) | 1.162 | 0.69 (0.35–1.37) |
| Ear Without Darwinian notch | 18 (9.28) | 17 (14.17) | 2.577 | 1.61 (0.80–3.27) |
| Blue Eyes | 57 (29.38) | 68 (56.67) | 25.349 ** | 3.14 ** (1.95–5.06) |
| Speaking deficiency -guttural “r” | 12 (6.19) | 8 (6.67) | 0.037 | 1.08 (0.43–2.73) |
| Inability to Transversally Tongue Roll | 52 (26.80) | 51 (42.50) | 9.197 ** | 2.02 ** (1.25–3.27) |
| Inability to Longitudinally Tongue Roll | 73 (37.63) | 49 (40.83) | 0.272 | 1.14 (0.72–1.82) |
| Right Thumb over Left Thumb | 97 (50.00) | 78 (65.00) | 4.500 * | 1.86 ** (1.16–2.97) |
| Top Joint of the Thumb >45° | 47 (24.23) | 21 (17.50) | 1.869 | 0.66 (0.37–1.18) |
| Hypermobility of proximal thumb joint | 21 (10.82) | 14 (11.67) | 0.067 | 1.09 (0.53–2.23) |
| Proximal thumb extensibility | 69 (35.57) | 38 (31.67) | 0.428 | 0.84 (0.52–1.36) |
| Three tendons in the wrist | 84 (43.30) | 56 (46.67) | 0.262 | 1.15 (0.73–1.81) |
| Left-handedness | 29 (14.95) | 16 (13.33) | 0.176 | 0.88 (0.45–1.69) |
| Index finger longer than the ring finger | 86 (44.33) | 53 (44.17) | 0.001 | 0.99 (0.63–1.57) |
| ∑χ2 = 60.162 ** | ||||
| Groups | With/Without Hypertension | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Z * | p | Cohen’s d (%) | |
| Controls | −2.943 | <0.003 | 46.70 |
| Ischemic stroke group | 4.037 | <0.001 | 79.14 |
| No. of HRCs | OR (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controls (with/without Hypertension) | Ischemic Stroke Group (with/without Hypertension) | With Hypertension (Ischemic Stroke Group/Controls) | Without Hypertension (Ischemic Stroke Group/Controls) | |
| 2 | - | - | - | - |
| 3 | 3.79 ** (1.58–9.10) | - | 0.40 (0.15–1.06) | - |
| 4 | - | 0.74 (0.20–2.78) | - | 1.76 (0.54–5.70) |
| 5 | 1.12 (0.51–2.44) | 3.87 ** (1.39–10.73) | 2.06 (0.91–4.65) | 0.59 (0.22–1.61) |
| 6 | 0.91 (0.50–1.64) | 1.73 (0.74–4.07) | 0.75 (0.36–1.55) | 0.39 * (0.19–0.82) |
| 7 | 0.51 (0.21–1.24) | 0.50 (0.20–1.28) | 1.63 (0.57–4.62) | 1.67 (0.78–3.56) |
| 8 | 0.58 (0.26–1.31) | 0.17 ** (0.05–0.53) | 0.58 (0.17–1.96) | 2.00 (0.98–4.10) |
| 9 | - | 0.56 (0.10–3.16) | - | 2.74 * (1.14–6.62) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Savic, M.; Cvjeticanin, S.; Lazovic, M.; Nikcevic, L.; Nikolic, D. Morphogenetic Variability and Hypertension in Ischemic Stroke Patients—Preliminary Study. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7070162
Savic M, Cvjeticanin S, Lazovic M, Nikcevic L, Nikolic D. Morphogenetic Variability and Hypertension in Ischemic Stroke Patients—Preliminary Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2018; 7(7):162. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7070162
Chicago/Turabian StyleSavic, Milan, Suzana Cvjeticanin, Milica Lazovic, Ljubica Nikcevic, and Dejan Nikolic. 2018. "Morphogenetic Variability and Hypertension in Ischemic Stroke Patients—Preliminary Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 7, no. 7: 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7070162
APA StyleSavic, M., Cvjeticanin, S., Lazovic, M., Nikcevic, L., & Nikolic, D. (2018). Morphogenetic Variability and Hypertension in Ischemic Stroke Patients—Preliminary Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(7), 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7070162





