Outcomes Vary by Pre-Operative Physical Activity Levels in Total Knee Arthroplasty Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
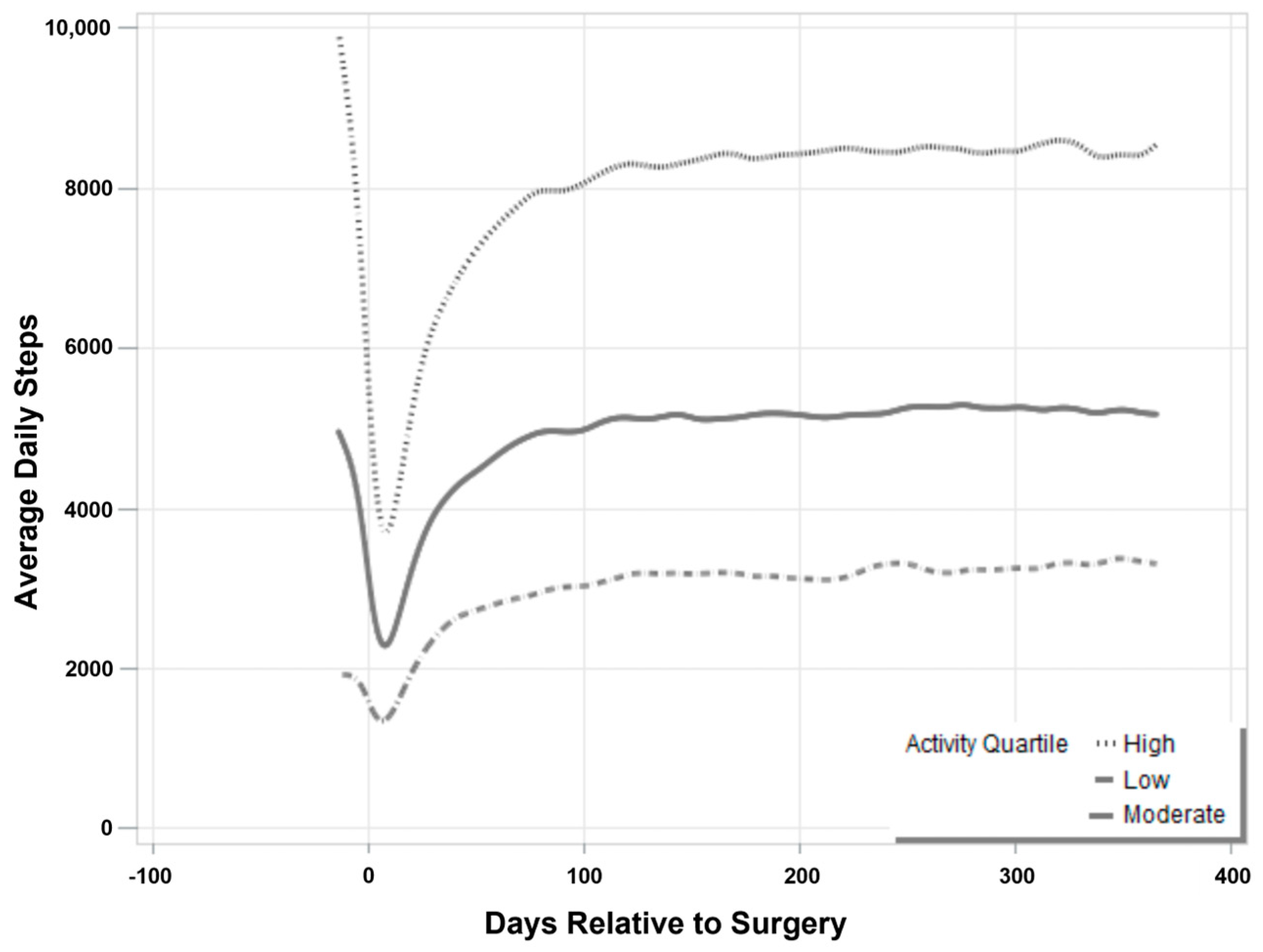
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, A.; Li, H.; Wang, D.; Zhong, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H. Global, regional prevalence, incidence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis in population-based studies. eClinicalMedicine 2020, 29–30, 100587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingsbury, S.R.; Gross, H.J.; Isherwood, G.; Conaghan, P.G. Osteoarthritis in Europe: Impact on health status, work productivity and use of pharmacotherapies in five European countries. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conley, B.; Bunzli, S.; Bullen, J.; O’Brien, P.; Persaud, J.; Gunatillake, T.; Dowsey, M.M.; Choong, P.F.M.; Lin, I. Core Recommendations for Osteoarthritis Care: A Systematic Review of Clinical Practice Guidelines. Arthritis Care Res. 2023, 75, 1897–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Raya, S.; Abou-Raya, A.; Kareem, A.A. SAT0314 Effects of Physical Activity on Inflammation, Skeletal Muscle Strength/Function (Sarcopenia) and Fat Infiltration (Sarcopenic Obesity) in Older Adults With Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, A690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Han, D.; Nevitt, M.C.; Wise, B.L.; Segal, N.A. Longitudinal Relationship Between Physical Activity and Joint Space Narrowing: Forty-Eight-Month Follow-Up Data From the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Arthritis Care Res. 2022, 74, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, M.; Klokker, L.; Graven-Nielsen, T.; Bartholdy, C.; Schjødt Jørgensen, T.; Bandak, E.; Danneskiold-Samsøe, B.; Christensen, R.; Bliddal, H. Association of Exercise Therapy and Reduction of Pain Sensitivity in Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arthritis Care Res. 2014, 66, 1836–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, V.B.; Sprow, K.; Powell, K.E.; Buchner, D.; Bloodgood, B.; Piercy, K.; George, S.M.; Kraus, W.E. Effects of Physical Activity in Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Umbrella Review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 1324–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, T.; Eek, F.; Dell’Isola, A.; Dahlberg, L.E.; Ekvall Hansson, E. The Better Management of Patients with Osteoarthritis Program: Outcomes after evidence-based education and exercise delivered nationwide in Sweden. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, M.V.; Mitchell, H.L.; Walsh, N. In Osteoarthritis, the Psychosocial Benefits of Exercise Are as Important as Physiological Improvements. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2003, 31, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sašek, M.; Kozinc, Ž.; Löfler, S.; Hofer, C.; Šarabon, N. Objectively Measured Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior and Functional Performance before and after Lower Limb Joint Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-H.; Waring, M.E.; Eaton, C.B.; Lapane, K.L. Association of Objectively Measured Physical Activity and Metabolic Syndrome among US Adults with Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2015, 67, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holla, J.F.; Sanchez-Ramirez, D.C.; van der Leeden, M.; Ket, J.C.; Roorda, L.D.; Lems, W.F.; Steultjens, M.P.; Dekker, J. The avoidance model in knee and hip osteoarthritis: A systematic review of the evidence. J. Behav. Med. 2014, 37, 1226–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunn, A.H.; Schwartz, T.A.; Arbeeva, L.S.; Callahan, L.F.; Golightly, Y.; Goode, A.; Hill, C.H.; Huffman, K.; Iversen, M.D.; Pathak, A.; et al. Fear of Movement and Associated Factors Among Adults With Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2017, 69, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponzio, D.Y.; Chiu, Y.F.; Salvatore, A.; Lee, Y.Y.; Lyman, S.; Windsor, R.E. An Analysis of the Influence of Physical Activity Level on Total Knee Arthroplasty Expectations, Satisfaction, and Outcomes: Increased Revision in Active Patients at Five to Ten Years. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2018, 100, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, K.; Falchi, B.; Duckett, C.; Naylor, J. Minimal change in physical activity after lower limb joint arthroplasty, but the outcome measure may be contributing to the problem: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Physiotherapy 2019, 105, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxton, R.J.; Melanson, E.L.; Stevens-Lapsley, J.E.; Christiansen, C.L. Physical activity after total knee arthroplasty: A critical review. World J. Orthop. 2015, 6, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kersten, R.F.; Stevens, M.; van Raay, J.J.; Bulstra, S.K.; van den Akker-Scheek, I. Habitual physical activity after total knee replacement. Phys. Ther. 2012, 92, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieter, C.; Carlien, S.; Kuijer, P.P. Knee arthroplasty: A window of opportunity to improve physical activity in daily life, sports and work. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2020, 6, e000822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, F.; Snyder-Mackler, L.; Zeni, J. Physical exercise after knee arthroplasty: A systematic review of controlled trials. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2013, 49, 877–892. [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi, M.; Sawano, S.; Kugo, M.; Maegawa, S.; Kawasaki, T.; Ichihashi, N. Physical Activity Promotes Gait Improvement in Patients With Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2016, 31, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffet, H.; Collet, J.P.; Shapiro, S.H.; Paradis, G.; Marquis, F.; Roy, L. Effectiveness of intensive rehabilitation on functional ability and quality of life after first total knee arthroplasty: A single-blind randomized controlled trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valtonen, A.; Pöyhönen, T.; Sipilä, S.; Heinonen, A. Effects of aquatic resistance training on mobility limitation and lower-limb impairments after knee replacement. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 91, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hepperger, C.; Gföller, P.; Hoser, C.; Ulmer, H.; Fischer, F.; Schobersberger, W.; Fink, C. The effects of a 3-month controlled hiking programme on the functional abilities of patients following total knee arthroplasty: A prospective, randomized trial. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2017, 25, 3387–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papalia, R.; Campi, S.; Vorini, F.; Zampogna, B.; Vasta, S.; Papalia, G.; Fossati, C.; Torre, G.; Denaro, V. The Role of Physical Activity and Rehabilitation Following Hip and Knee Arthroplasty in the Elderly. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, J.C.; Blackburn, B.E.; Anderson, L.A.; Gililland, J.M.; Peters, C.L.; Archibeck, M.J.; Pelt, C.E. Recovery Curve for Patient Reported Outcomes and Objective Physical Activity after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty—A Multicenter Study Using Wearable Technology. J. Arthroplast. 2023, 38, S94–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yocum, D.; Elashoff, B.; Verta, P.; Armock, G.; Yergler, J. Patient reported outcomes do not correlate to functional knee recovery and range of motion in total knee arthroplasty. J. Orthop. 2023, 43, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crizer, M.P.; Kazarian, G.S.; Fleischman, A.N.; Lonner, J.H.; Maltenfort, M.G.; Chen, A.F. Stepping Toward Objective Outcomes: A Prospective Analysis of Step Count After Total Joint Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, S162–S165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, I.E.; Kehlet, H.; Peterson, B.; Wede, H.R.; Hoevsgaard, S.J.; Aasvang, E.K. Early patient-reported outcomes versus objective function after total hip and knee arthroplasty: A prospective cohort study. Bone Jt. J. 2017, 99B, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höll, S.; Blum, A.; Gosheger, G.; Dieckmann, R.; Winter, C.; Rosenbaum, D. Clinical outcome and physical activity measured with StepWatch 3™ Activity Monitor after minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2018, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, M.; Ringling, M.; Winter, C.; Hillmann, A.; Rosenbaum, D. Changes in physical activity and health-related quality of life during the first year after total knee arthroplasty. Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Sheeha, B.; Granat, M.; Williams, A.; Johnson, D.S.; Jones, R. Does free-living physical activity improve one-year following total knee arthroplasty in patients with osteoarthritis: A prospective study. Osteoarthr. Cartil. Open 2020, 2, 100065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frimpong, E.; van der Jagt, D.R.; Mokete, L.; Pietrzak, J.; Kaoje, Y.S.; Smith, A.; McVeigh, J.A.; Meiring, R.M. Improvements in Objectively Measured Activity Behaviors Do Not Correlate With Improvements in Patient-Reported Outcome Measures Following Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratford, P.W.; Kennedy, D.M.; Woodhouse, L.J. Performance measures provide assessments of pain and function in people with advanced osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. Phys. Ther. 2006, 86, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratford, P.W.; Kennedy, D.M. Does parallel item content on WOMAC’s pain and function subscales limit its ability to detect change in functional status? BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2004, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Stratford, P.; Kennedy, D.; Clarke, H. Confounding pain and function: The WOMAC’s failure to accurately predict lower extremity function. Arthroplast. Today 2018, 4, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gränicher, P.; Stöggl, T.; Fucentese, S.F.; Adelsberger, R.; Swanenburg, J. Preoperative exercise in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Arch. Physiother. 2020, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calatayud, J.; Casaña, J.; Ezzatvar, Y.; Jakobsen, M.D.; Sundstrup, E.; Andersen, L.L. High-intensity preoperative training improves physical and functional recovery in the early post-operative periods after total knee arthroplasty: A randomized controlled trial. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2017, 25, 2864–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.D.; O’Brien, J.; Mulford, J.; Mathew, R.; Thapa, D.K.; Hamilton, K.; Cheney, M.; Schmidt, M.; Wu, S.; Bird, M.L. Effect of combined exercise training and behaviour change counselling versus usual care on physical activity in patients awaiting hip and knee arthroplasty: A randomised controlled trial. Osteoarthr. Cartil. Open 2022, 4, 100308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berliner, J.L.; Brodke, D.J.; Chan, V.; SooHoo, N.F.; Bozic, K.J. Can Preoperative Patient-reported Outcome Measures Be Used to Predict Meaningful Improvement in Function After TKA? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017, 475, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, G.S.; Baker, C.M.; Tarabichi, S.; Clark, S.C.; Austin, M.S.; Lonner, J.H. The Paradox of Patient-Reported Outcome Measures: Should We Prioritize “Feeling Better” or “Feeling Good” After Total Knee Arthroplasty? J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, 1751–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, S.; Lee, Y.Y.; McLawhorn, A.S.; Islam, W.; MacLean, C.H. What Are the Minimal and Substantial Improvements in the HOOS and KOOS and JR Versions After Total Joint Replacement? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2018, 476, 2432–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leichtenberg, C.S.; van Tol, F.R.; Gademan, M.G.J.; Krom, T.; Tilbury, C.; Horemans, H.L.D.; Bussmann, J.B.J.; Verdegaal, S.H.M.; Marijnissen, W.; Nelissen, R.; et al. Are pain, functional limitations and quality of life associated with objectively measured physical activity in patients with end-stage osteoarthritis of the hip or knee? Knee 2021, 29, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, G.J.; Irrgang, J.J.; Fitzgerald, G.K.; Jakicic, J.M.; Piva, S.R. Reliability of Physical Activity Measures During Free-Living Activities in People After Total Knee Arthroplasty. Phys. Ther. 2016, 96, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, D.J.; Heslop, P.S.; Chandler, C.; Pinder, I.M. Measured ambulation and self-reported health status following total joint replacement for the osteoarthritic knee. Rheumatology 2002, 41, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- de Groot, I.B.; Bussmann, H.J.; Stam, H.J.; Verhaar, J.A. Small increase of actual physical activity 6 months after total hip or knee arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2008, 466, 2201–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughn, N.H.; Dunklebarger, M.F.; Mason, M.W. Individual Patient-reported Activity Levels Before and After Joint Arthroplasty Are Neither Accurate nor Reproducible. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2019, 477, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, T.L.; Schwarzkopf, R. Does Total Knee Arthroplasty Affect Physical Activity Levels? Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. J. Arthroplast. 2015, 30, 1521–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudor-Locke, C.; Washington, T.L.; Hart, T.L. Expected values for steps/day in special populations. Prev. Med. 2009, 49, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twiggs, J.; Salmon, L.; Kolos, E.; Bogue, E.; Miles, B.; Roe, J. Measurement of physical activity in the pre- and early post-operative period after total knee arthroplasty for Osteoarthritis using a Fitbit Flex device. Med. Eng. Phys. 2018, 51, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsonga, T.; Kapetanakis, S.; Papadopoulos, C.; Papathanasiou, J.; Mourgias, N.; Georgiou, N.; Fiska, A.; Kazakos, K. Evaluation of improvement in quality of life and physical activity after total knee arthroplasty in greek elderly women. Open Orthop. J. 2011, 5, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cooper, N.A.; Rakel, B.A.; Zimmerman, B.; Tonelli, S.M.; Herr, K.A.; Clark, C.R.; Noiseux, N.O.; Callaghan, J.J.; Sluka, K.A. Predictors of multidimensional functional outcomes after total knee arthroplasty. J. Orthop. Res. 2017, 35, 2790–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezzadeh, K.; Behery, O.A.; Kester, B.S.; Long, W.J.; Schwarzkopf, R. The Effect of Total Knee Arthroplasty on Physical Activity and Body Mass Index: An Analysis of the Osteoarthritis Initiative Cohort. Geriatr. Orthop. Surg. Rehabil. 2019, 10, 2151459318816480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, P.; Holland, A.E.; Delany, C.; Hinman, R.S. Do activity levels increase after total hip and knee arthroplasty? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 1502–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, P.D.; McLaughlin, J.; Boisvert, C.B.; Li, W.; Ayers, D.C. Pilot study of methods to document quantity and variation of independent patient exercise and activity after total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2006, 21, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, D.A.; Watts, M.C.; Anderson, L.J.; Walsh, W.R. Knee arthroplasty: A cross-sectional study assessing energy expenditure and activity. ANZ J. Surg. 2011, 81, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vissers, M.M.; Bussmann, J.B.; de Groot, I.B.; Verhaar, J.A.; Reijman, M. Physical functioning four years after total hip and knee arthroplasty. Gait Posture 2013, 38, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubin, J.A.; Westrich, G.H. Preoperative activity levels are an important indicator of postoperative activity in cementless TKAs. J. Orthop. 2020, 22, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutzner, C.; Beyer, F.; Kirschner, S.; Lutzner, J. How Much Improvement in Patient Activity Can Be Expected After TKA? Orthopedics 2016, 39, S18–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, S.M.; Birmingham, T.B.; Callaghan, J.P.; Jones, G.R.; Chesworth, B.M.; Maly, M.R. Association of pain with frequency and magnitude of knee loading in knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, J.T.; Wu, H.H.; Chung, C.C.; Bendich, I.; Barry, J.J.; Bini, S.A. Wearable activity sensors and early pain after total joint arthroplasty. Arthroplast. Today 2020, 6, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langenberger, B.; Schrednitzki, D.; Halder, A.M.; Busse, R.; Pross, C.M. Predicting whether patients will achieve minimal clinically important differences following hip or knee arthroplasty. Bone Jt. Res. 2023, 12, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seetharam, A.; Deckard, E.R.; Ziemba-Davis, M.; Meneghini, R.M. The AAHKS Clinical Research Award: Are Minimum Two-Year Patient-Reported Outcome Measures Necessary for Accurate Assessment of Patient Outcomes after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty? J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, S716–S720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| All Activity Levels | Low Pre-Operative Activity | Moderate Pre-Operative Activity | High Pre-Operative Activity | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 64.5 ± 8.9 | 66.4 ± 8.8 | 64.2 ± 9.0 | 63.2 ± 8.5 | <0.0001 |
| BMI | 31.4 ± 6.3 | 33.1 ± 6.7 | 31.8 ± 6.2 | 29.0 ± 5.5 | <0.0001 |
| Sex—female | 1178 (60.7) | 344 (70.8) | 577 (59.6) | 257 (52.9) | <0.0001 |
| All Activity Levels | Low Pre-Operative Activity | Moderate Pre-Operative Activity | High Pre-Operative Activity | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-operative step count | 5211 ± 2943 | 2025 ± 726 | 4817 ± 1034 | 9180 ± 2392 | <0.0001 |
| 4 weeks | 4144 ± 2442 | 2356 ± 1523 | 3931 ± 1851 | 6277 ± 2617 | <0.0001 |
| 6 weeks | 4601 ± 2538 | 2679 ± 1647 | 4345 ± 1862 | 6937 ± 2631 | <0.0001 |
| 3 months | 5280 ± 2880 | 3058 ± 1910 | 4948 ± 2079 | 7949 ± 2911 | <0.0001 |
| 6 months | 5529 ± 3126 | 3071 ± 2074 | 5186 ± 2295 | 8378 ± 3106 | <0.0001 |
| 12 months | 5730 ± 3390 | 3281 ± 2481 | 5225 ± 2522 | 8749 ± 3341 | <0.0001 |
| Percent recovery | |||||
| 4 weeks | 94.4 ± 133.7 | 145.1 ± 258.4 | 82.6 ± 39.2 | 69.7 ± 27.1 | <0.0001 |
| 6 weeks | 105.1 ± 128.7 | 164.3 ± 246.5 | 91.3 ± 40.0 | 77.1 ± 40.0 | <0.0001 |
| 3 months | 116.9 ± 129.3 | 176.7 ± 247.3 | 104.0 ± 43.8 | 87.7 ± 29.4 | <0.0001 |
| 6 months | 121.6 ± 147.9 | 181.3 ± 287.7 | 109.5 ± 49.8 | 92.0 ± 32.9 | <0.0001 |
| 12 months | 121.3 ± 88.4 | 175.2 ± 154 | 108.6 ± 51.2 | 94.6 ± 32.4 | <0.0001 |
| Step Count Change from Pre-Operative | Low Pre-Operative Activity | p Value | Moderate Pre-Operative Activity | p Value | High Pre-Operative Activity | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 weeks | 306 ± 1586 | <0.0001 | −907 ± 1838 | <0.0001 | −2902 ± 2885 | <0.0001 |
| 6 weeks | 632 ± 1698 | <0.0001 | −491 ± 1811 | <0.0001 | −2245 ± 2864 | <0.0001 |
| 3 months | 966 ± 1916 | <0.0001 | 125 ± 1954 | 0.07 | −1277 ± 2880 | <0.0001 |
| 6 months | 1016 ± 2071 | <0.0001 | 365 ± 2221 | <0.0001 | −938 ± 3108 | <0.0001 |
| 12 months | 1213 ± 2424 | <0.0001 | 399 ± 2399 | 0.0001 | −653 ± 3040 | 0.0003 |
| KOOS JR | All Activity Levels | Low Pre-Operative Activity | Moderate Pre-Operative Activity | High Pre-Operative Activity | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-operative | 51.71 ± 12.20 | 49.26 ± 12.53 | 51.54 ± 11.86 | 54.38 ± 12.02 | <0.0001 |
| 1 month | 63.03 ± 10.28 | 62.67 ± 11.11 | 62.97 ± 10.31 | 63.51 ± 9.34 | 0.45 |
| 3 months | 70.36 ± 12.03 | 69.97 ± 11.68 | 70.31 ± 12.28 | 70.80 ± 11.85 | 0.60 |
| 6 months | 74.61 ± 13.49 | 73.56 ± 13.49 | 74.65 ± 13.97 | 75.53 ± 12.54 | 0.12 |
| 12 months | 80.32 ± 14.20 | 78.38 ± 15.34 | 81.43 ± 13.55 | 79.90 ± 14.23 | 0.01 |
| Δ 1 month | 11.29 ± 13.78 | 13.27 ± 14.51 | 11.42 ± 13.82 | 9.15 ± 12.66 | <0.0001 |
| Δ 3 months | 18.48 ± 14.86 | 20.17 ± 14.23 | 18.80 ± 15.15 | 16.38 ± 14.64 | 0.0008 |
| Δ 6 months | 22.83 ± 15.67 | 23.67 ± 15.96 | 23.19 ± 15.75 | 21.34 ± 15.15 | 0.08 |
| Δ 12 months | 28.70 ± 16.96 | 29.7 ± 17.84 | 29.89 ± 16.67 | 25.56 ± 16.37 | 0.0007 |
| All Activity Levels | Low Pre-Operative Activity | Moderate Pre-Operative Activity | High Pre-Operative Activity | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pain | |||||
| Pre-operative | 5.62 ± 2.08 | 5.95 ± 1.96 | 5.63 ± 2.11 | 5.28 ± 2.07 | <0.0001 |
| 30 days | 3.82 ± 2.03 | 4.10 ± 2.14 | 3.73 ± 2.02 | 3.74 ± 1.93 | 0.01 |
| 90 days | 2.65 ± 2.12 | 2.80 ± 2.26 | 2.56 ± 2.08 | 2.68 ± 2.04 | 0.18 |
| Δ 30 days | −1.73 ± 2.48 | −1.92 ± 2.45 | −1.80 ± 2.57 | −1.45 ± 2.33 | 0.02 |
| Δ 90 days | −2.89 ± 2.63 | −3.15 ± 2.50 | −2.94 ± 2.71 | −2.59 ± 2.58 | 0.01 |
| KSS Satisfaction | |||||
| Pre-operative | 13.4 ± 7.6 | 12.1 ± 7.2 | 13.2 ± 7.6 | 14.7 ± 7.8 | <0.0001 |
| 30 days | 23.6 ± 11.0 | 22.4 ± 11.6 | 23.8 ± 11.0 | 24.4 ± 10.0 | 0.02 |
| 90 days | 28.8 ± 9.5 | 27.9 ± 10.0 | 29.0 ± 9.4 | 29.2 ± 9.2 | 0.09 |
| Δ 30 days | 10.7 ± 12.3 | 11.2 ± 12.5 | 11.1 ± 12.4 | 9.7 ± 11.7 | 0.11 |
| Δ 90 days | 15.2 ± 11.3 | 15.6 ± 11.3 | 15.6 ± 11.7 | 14.0 ± 10.7 | 0.051 |
| EQ-5D-5L | |||||
| Pre-operative | 0.572 ± 0.250 | 0.506 ± 0.281 | 0.569 ± 0.242 | 0.638 ± 0.214 | <0.0001 |
| 30 days | 0.689 ± 0.191 | 0.668 ± 0.196 | 0.695 ± 0.192 | 0.699 ± 0.183 | 0.03 |
| 90 days EQ-5D-5L | 0.803 ± 0.167 | 0.781 ± 0.168 | 0.808 ± 0.168 | 0.812 ± 0.162 | 0.02 |
| 6 months | 0.833 ± 0.176 | 0.812 ± 0.195 | 0.832 ± 0.176 | 0.853 ± 0.154 | 0.007 |
| 12 months | 0.864 ± 0.169 | 0.828 ± 0.216 | 0.872 ± 0.156 | 0.879 ± 0.139 | 0.0003 |
| Δ 30 days | 0.112 ± 0.262 | 0.165 ± 0.261 | 0.118 ± 0.268 | 0.053 ± 0.243 | <0.0001 |
| Δ 90 days | 0.223 ± 0.248 | 0.269 ± 0.247 | 0.231 ± 0.256 | 0.170 ± 0.224 | <0.0001 |
| Δ 6 months | 0.256 ± 0.256 | 0.305 ± 0.265 | 0.258 ± 0.261 | 0.211 ± 0.229 | <0.0001 |
| Δ 12 months | 0.281 ± 0.236 | 0.328 ± 0.250 | 0.289 ± 0.241 | 0.228 ± 0.199 | <0.0001 |
| EQ-VAS | |||||
| Pre-operative | 75.46 ± 15.7 | 71.53 ± 17.2 | 75.72 ± 15.5 | 78.72 ± 13.7 | <0.0001 |
| 30 days | 77.22 ± 14.64 | 76.22 ± 14.65 | 77.38 ± 14.77 | 77.84 ± 14.38 | 0.26 |
| 90 days | 82.6 ± 12.6 | 80.8 ± 13.4 | 82.8 ± 12.6 | 83.8 ± 11.7 | 0.004 |
| 6 months | 83.67 ± 12.46 | 81.65 ± 14.28 | 83.48 ± 12.17 | 85.79 ± 10.85 | <0.0001 |
| 12 months | 85.09 ± 12.49 | 82.94 ± 15.19 | 85.06 ± 11.45 | 87.0 ± 11.58 | 0.0005 |
| Δ 30 days | 1.65 ± 16.54 | 5.12 ± 17.19 | 1.60 ± 16.10 | −1.31 ± 16.23 | <0.0001 |
| Δ 90 days | 6.89 ± 15.5 | 9.22 ± 16.1 | 6.75 ± 15.5 | 5.18 ± 14.9 | 0.002 |
| Δ 6 months | 8.11 ± 15.32 | 11.01 ± 18.03 | 7.45 ± 14.84 | 6.84 ± 13.23 | 0.0007 |
| Δ 12 months | 8.87 ± 15.48 | 10.73 ± 17.98 | 8.81 ± 14.36 | 7.46 ± 15.24 | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Redfern, R.E.; Crawford, D.A.; Lombardi, A.V., Jr.; Tripuraneni, K.R.; Van Andel, D.C.; Anderson, M.B.; Cholewa, J.M. Outcomes Vary by Pre-Operative Physical Activity Levels in Total Knee Arthroplasty Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010125
Redfern RE, Crawford DA, Lombardi AV Jr., Tripuraneni KR, Van Andel DC, Anderson MB, Cholewa JM. Outcomes Vary by Pre-Operative Physical Activity Levels in Total Knee Arthroplasty Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(1):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010125
Chicago/Turabian StyleRedfern, Roberta E., David A. Crawford, Adolph V. Lombardi, Jr., Krishna R. Tripuraneni, David C. Van Andel, Mike B. Anderson, and Jason M. Cholewa. 2024. "Outcomes Vary by Pre-Operative Physical Activity Levels in Total Knee Arthroplasty Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 1: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010125
APA StyleRedfern, R. E., Crawford, D. A., Lombardi, A. V., Jr., Tripuraneni, K. R., Van Andel, D. C., Anderson, M. B., & Cholewa, J. M. (2024). Outcomes Vary by Pre-Operative Physical Activity Levels in Total Knee Arthroplasty Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(1), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010125







