The Role of Immunoglobulin G4 in Outcomes of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
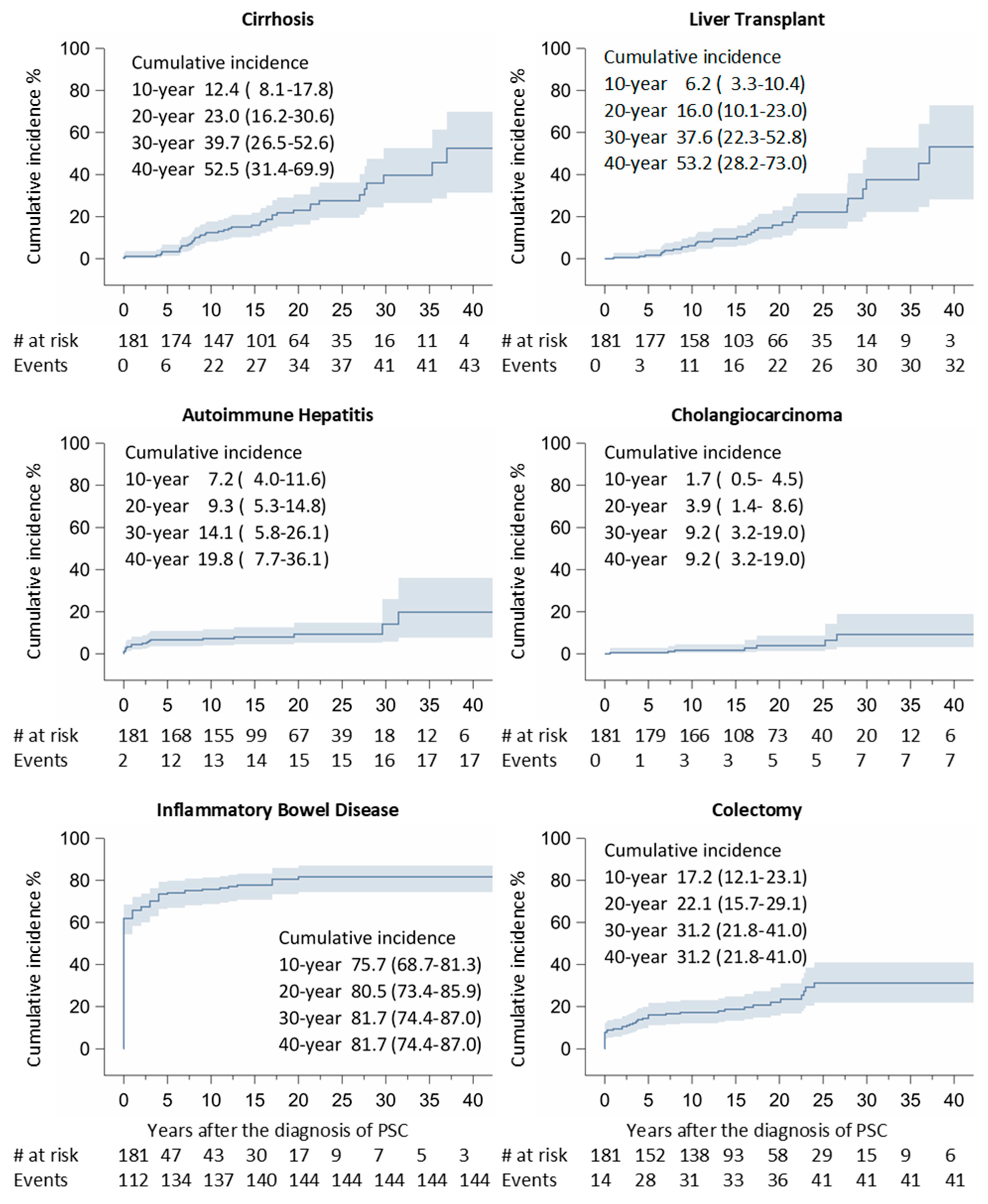
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIH | autoimmune hepatitis |
| EASL | European Association for the Study of the Liver |
| ERCP | endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography |
| HLA | human leukocyte antigen |
| IBD | inflammatory bowel disease |
| IgG | immunoglobulin G |
| IgGs | IgG subclass |
| PBC | primary biliary cholangitis |
| PSC | primary sclerosing cholangitis |
References
- EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of cholestatic liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 237–267. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manganis, C.D.; Chapman, R.W.; Culver, E.L. Review of primary sclerosing cholangitis with increased IgG4 levels. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 3126–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergquist, A.; Ekbom, A.; Olsson, R.; Kornfeldt, D.; Lööf, L.; Danielsson, A.; Hultcrantz, R.; Lindgren, S.; Prytz, H.; Sandberg-Gertzén, H.; et al. Hepatic and extrahepatic malignancies in primary sclerosing cholangitis. J. Hepatol. 2002, 36, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boberg, K.M.; Fausa, O.; Haaland, T.; Holter, E.; Mellbye, O.J.; Spurkland, A.; Schrumpf, E. Features of autoimmune hepatitis in primary sclerosing cholangitis: An evaluation of 114 primary sclerosing cholangitis patients according to a scoring system for the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 1996, 23, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujasinovic, M.; Maier, P.; Maetzel, H.; Valente, R.; Pozzi-Mucelli, R.; Moro, C.F.; Haas, S.L.; Said, K.; Verbeke, C.S.; Maisonneuve, P.; et al. Immunoglobulin G subtypes-1 and 2 differentiate immunoglobulin G4-associated sclerosing cholangitis from primary sclerosing cholangitis. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2020, 8, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, P.; Wu, D.; Xu, D.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, F.; et al. Serum IgG subclasses in autoimmune diseases. Medicine 2015, 94, e387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.G.; Li, J.M. IgG subclass serum levels in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Clin. Rheumatol. 2009, 28, 1315–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Jiang, F.; Shan, J.; Wang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Guo, Q.; Lou, J.; Zhao, Y. Levels of serum IgG subclasses in patients with liver disease: A retrospective study. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, F.D.; Jorgensen, R.; Keach, J.; Katzmann, J.A.; Smyrk, T.; Donlinger, J.; Chari, S.; Lindor, K.D. Elevated serum IgG4 concentration in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnsson, E.; Chari, S.; Silveira, M.; Gossard, A.; Takahashi, N.; Smyrk, T.; Lindor, K. Primary sclerosing cholangitis associated with elevated immunoglobulin G4: Clinical characteristics and response to therapy. Am. J. Ther. 2011, 18, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alswat, K.; Al-Harthy, N.; Mazrani, W.; Alshumrani, G.; Jhaveri, K.; Hirschfield, G.M. The spectrum of sclerosing cholangitis and the relevance of IgG4 elevations in routine practice. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parhizkar, B.; Mohammad Alizadeh, A.H.; Asadzadeh Aghdaee, H.; Malekpour, H.; Entezari, A.H. Primary sclerosing cholangitis associated with elevated immunoglobulin-g4: A preliminary study. ISRN Gastroenterol. 2012, 2012, 325743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Navaneethan, U.; Venkatesh, P.G.; Choudhary, M.; Shen, B.; Kiran, R.P. Elevated immunoglobulin G4 level is associated with reduced colectomy-free survival in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis and ulcerative colitis. J. Crohns Colitis 2013, 7, e35–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Benito de Valle, M.; Müller, T.; Björnsson, E.; Otten, M.; Volkmann, M.; Guckelberger, O.; Wiedenmann, B.; Sadik, R.; Schott, E.; Andersson, M.; et al. The impact of elevated serum IgG4 levels in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, S.A.; Majd, S.K.; Sianati, M.; Sepehrimanesh, M. Prevalence of IgG-4-associated cholangiopathy based on serum IgG-4 levels in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis and its relationship with inflammatory bowel disease. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 27, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Tazuma, S.; Nakazawa, T.; Isayama, H.; Tsuyuguchi, T.; Inui, K.; Takikawa, H. No negative impact of serum IgG4 levels on clinical outcome in 435 patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis from Japan. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Sci. 2017, 24, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhr, J.M.; Beuers, U.; Vujasinovic, M.; Alvaro, D.; Frøkjær, J.B.; Buttgereit, F.; Capurso, G.; Culver, E.L.; de-Madaria, E.; Della-Torre, E.; et al. European Guideline on IgG4-related digestive disease—UEG and SGF evidence-based recommendations. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2020, 8, 637–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, K.T.; Park, J.K.; Lee, J.K. Clinical Utility of Personalized Serum IgG Subclass Ratios for the Differentiation of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis (IgG4-SC) from Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) and Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA). J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhr, J.M.; Vujasinovic, M.; Rosendahl, J.; Stone, J.H.; Beuers, U. IgG4-related diseases of the digestive tract. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujasinovic, M.; Valente, R.; Maier, P.; von Beckerath, V.; Haas, S.L.; Arnelo, U.; Del Chiaro, M.; Kartalis, N.; Pozzi-Mucelli, R.M.; Fernandez-Moro, C.; et al. Diagnosis, treatment and long-term outcome of autoimmune pancreatitis in Sweden. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boberg, K.M.; Egeland, T.; Schrumpf, E. Long-term effect of corticosteroid treatment in primary sclerosing cholangitis patients. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 38, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schramm, C.; Schirmacher, P.; Helmreich-Becker, I.; Gerken, G.; zum Büschenfelde, K.H.; Lohse, A.W. Combined therapy with azathioprine, prednisolone, and ursodiol in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. A case series. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 131, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fosby, B.; Melum, E.; Bjøro, K.; Bennet, W.; Rasmussen, A.; Andersen, I.M.; Castedal, M.; Olausson, M.; Wibeck, C.; Gotlieb, M.; et al. Liver transplantation in the Nordic countries—An intention to treat and post-transplant analysis from The Nordic Liver Transplant Registry 1982-2013. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lewis, J.T.; Abraham, S.C.; Smyrk, T.C.; Leung, S.; Chari, S.T.; Poterucha, J.J.; Rosen, C.B.; Lohse, C.M.; Katzmann, J.A.; et al. IgG4+ plasma cell infiltrates in liver explants with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippchen, T.; Sauer, P.; Göppert, B.; Schirmacher, P.; Gotthardt, D.N.; Weiss, K.H.; Stremmel, W.; Rupp, C. Association between serum IgG level and clinical course in primary sclerosing cholangitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| All | Sex | Age at Diagnosis of PSC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | Males | Females | 0–19 | 20–29 | 30–39 | 40–49 | 50+ | |
| (n = 181) | (n = 120) | (n = 61) | (n = 25) | (n = 40) | (n = 61) | (n = 31) | (n = 24) | |
| IgG total (g/L) | 13.8 ± 3.7 | 14.1 ± 3.5 | 13.2 ± 4.1 | 14.6 ± 3.3 | 14.4 ± 3.7 | 13.5 ± 4.1 | 13.6 ± 3.3 | 13.0 ± 3.6 |
| IgG-1 (g/L) | 8.1 ± 3.0 | 8.3 ± 2.8 | 7.7 ± 3.4 | 8.9 ± 2.5 | 8.6 ± 3.1 | 7.8 ± 3.0 | 7.8 ± 3.1 | 7.6 ± 3.1 |
| IgG-2 (g/L) | 3.5 ± 1.3 | 3.6 ± 1.2 | 3.3 ± 1.4 | 3.4 ± 1.7 | 3.4 ± 1.2 | 3.5 ± 1.3 | 3.5 ± 1.2 | 3.6 ± 1.3 |
| IgG-3 (g/L) | 0.83 ± 0.52 | 0.85 ± 0.56 | 0.80 ± 0.41 | 1.06 ± 0.82 | 0.82 ± 0.48 | 0.83 ± 0.43 | 0.83 ± 0.48 | 0.63 ± 0.36 |
| IgG-4 (g/L) | 0.43 ± 0.40 | 0.47 ± 0.44 | 0.34 ± 0.30 | 0.34 ± 0.32 | 0.43 ± 0.38 | 0.46 ± 0.46 | 0.42 ± 0.34 | 0.45 ± 0.43 |
| IgG4/IgG (%) | 3.06 ± 2.62 | 3.24 ± 2.67 | 2.71 ± 2.53 | 2.22 ± 1.80 | 2.88 ± 2.10 | 3.37 ± 3.06 | 3.11 ± 2.47 | 3.42 ± 3.07 |
| IgG4/IgG1 (%) | 5.49 ± 5.05 | 5.75 ± 5.05 | 4.99 ± 5.06 | 3.76 ± 1.10 | 5.07 ± 4.02 | 6.10 ± 5.89 | 5.83 ± 5.35 | 6.02 ± 5.43 |
| Total | No Previous IBD | Previous IBD | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 181 (100.0) | 93 (100.0) | 88 (100.0) | |
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 61 (33.7) | 33 (35.5) | 28 (31.8) | |
| Male | 120 (66.3) | 60 (64.5) | 60 (68.2) | 0.60 |
| Age | ||||
| <20 | 25 (13.8) | 18 (19.4) | 7 (8.0) | |
| 20–29 | 40 (22.1) | 20 (21.5) | 20 (22.7) | |
| 30–39 | 61 (33.7) | 32 (34.4) | 29 (33.0) | |
| 40–49 | 31 (17.1) | 15 (16.1) | 16 (18.2) | |
| 50+ | 24 (13.3) | 8 (8.6) | 16 (18.2) | 0.11 |
| IgG (g/L) * | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 13.8 ± 3.7 | 13.9 ± 3.6 | 13.7 ± 3.8 | 0.69 |
| Low (<6.7 g/L) | 1 (0.6) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.1) | |
| Normal (6.7–14.5 g/L) | 118 (65.2) | 58 (62.4) | 61 (69.3) | |
| High (>14.5 g/L) | 62 (34.3) | 35 (37.6) | 27 (30.7) | 0.39 |
| IgG1 (g/L) * | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 8.1 ± 3.0 | 8.3 ± 3.1 | 7.9 ± 2.9 | 0.35 |
| Low (<2.8 g/L) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Normal (2.8–8.0 g/L) | 107 (59.1) | 53 (57.0) | 54 (61.4) | |
| High (>8.0 g/L) | 74 (40.9) | 40 (43.0) | 34 (38.6) | 0.55 |
| IgG2 (g/L) * | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 3.5 ± 1.3 | 3.5 ± 1.4 | 3.5 ± 1.2 | 0.95 |
| Low (<1.15 g/L) | 3 (1.7) | 2 (2.2) | 1 (1.1) | |
| Normal (1.15–5.7 g/L) | 168 (92.8) | 84 (90.3) | 84 (95.5) | |
| High (>5.7 g/L) | 10 (5.5) | 7 (7.5) | 3 (3.4) | 0.50 |
| IgG3 (g/L) * | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 0.83 ± 0.52 | 0.88 ± 0.53 | 0.78 ± 0.50 | 0.19 |
| Low (<0.24 g/L) | 10 (5.5) | 5 (5.4) | 5 (5.7) | |
| Normal (0.24–1.25 g/L) | 145 (80.1) | 73 (78.5) | 72 (81.8) | |
| High (>1.25 g/L) | 26 (14.4) | 15 (16.1) | 11 (12.5) | 0.81 |
| IgG4 (g/L) * | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 0.43 ± 0.40 | 0.46 ± 0.41 | 0.39 ± 0.39 | 0.25 |
| Low (<0.05 g/L) | 16 (8.8) | 5 (5.4) | 11 (12.5) | |
| Normal (0.05–1.25 g/L) | 156 (86.2) | 82 (88.2) | 74 (84.1) | |
| High (>1.25 g/L) | 9 (5.0) | 6 (6.5) | 3 (3.4) | 0.17 |
| IgG4/IgG ratio (%) * | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 3.06 ± 2.62 | 3.36 ± 2.90 | 2.75 ± 2.27 | 0.11 |
| Low (<median 2.40) | 91 (50.3) | 48 (51.6) | 43 (48.9) | |
| High (>median 2.40) | 90 (49.7) | 45 (48.4) | 45 (51.1) | 0.71 |
| IgG4/IgG1 (%) * | ||||
| Mean ± SD | 5.49 ± 5.05 | 6.01 ± 5.69 | 4.95 ± 4.25 | 0.15 |
| Low (<median 4.06) | 91 (50.3) | 47 (50.5) | 44 (50.0) | |
| High (>median 4.06) | 90 (49.7) | 46 (49.5) | 44 (50.0) | 0.94 |
| Autoimmune Hepatitis | Cirrhosis | Cholangio-Carcinoma | Liver Transplant | Colectomy | IBD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Events (% per Year) | Events (% per Year) | Events (% per Year) | Events (% per Year) | Events (% per Year) | Events (% per Year) | |
| ALL | 4 (6.06) | 37 (6.07) | 7 (6.93) | 29 (6.13) | 11 (8.15) | 8 (8.16) |
| IgG (g/L) * | ||||||
| Low (<6.7 g/L) | - | - | - | - | 1 (100.0) | - |
| Normal (6.7–14.5 g/L) | 2 (6.06) | 20 (7.55) | 6 (8.00) | 14 (7.87) | 1 (5.26) | 6 (8.57) |
| High (>14.5 g/L) | 2 (5.88) | 17 (4.91) | 1 (3.70) | 15 (5.08) | 9 (7.83) | 2 (7.14) |
| Log-rank test | 0.69 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.007 | 0.99 |
| IgG1 (g/L) * | ||||||
| Low (<2.8 g/L) | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Normal (2.8–8.0 g/L) | 1 (3.33) | 18 (7.23) | 5 (10.20) | 15 (6.49) | 3 (11.54) | 1 (25.00) |
| High (>8.0 g/L) | 3 (8.11) | 19 (5.26) | 2 (3.85) | 14 (5.79) | 8 (7.34) | 7 (7.45) |
| Log-rank test | 0.92 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.41 | 0.31 | 0.008 |
| IgG2 (g/L) * | ||||||
| Low (<1.15 g/L) | - | 1 (11.11) | - | - | 1 (100.0) | - |
| Normal (1.15–5.7 g/L) | 4 (6.06) | 34 (5.91) | 7 (6.93) | 28 (6.05) | 9 (8.04) | 8 (8.16) |
| High (>5.7 g/L) | - | 2 (7.41) | - | 1 (9.09) | 1 (4.35) | - |
| Log-rank test | - | 0.63 | - | 0.50 | 0.006 | - |
| IgG3 (g/L) * | ||||||
| Low (<0.24 g/L) | - | 4 (5.56) | - | 2 (9.09) | - | 1 (25.00) |
| Normal (0.24–1.25 g/L) | 4 (6.06) | 28 (6.18) | 5 (10.20) | 23 (5.84) | 6 (12.24) | 7 (7.45) |
| High (>1.25 g/L) | - | 5 (5.88) | 2 (3.85) | 4 (7.02) | 5 (5.81) | - |
| Log-rank test | - | 0.96 | 0.04 | 0.43 | 0.08 | 0.008 |
| IgG4 (g/L) * | ||||||
| Low (<0.05 g/L) | - | 2 (3.77) | 1 (100.0) | 3 (6.52) | 1 (100.) | - |
| Normal (0.05–1.25 g/L) | 4 (6.06) | 31 (6.14) | 6 (5.94) | 21 (6.05) | 10 (7.46) | 8 (8.16) |
| High (>1.25 g/L) | - | 4 (7.55) | - | 5 (6.25) | - | - |
| Log-rank test | - | 0.52 | 0.01 | 0.93 | 0.002 | - |
| IgG4/IgG (%) * | ||||||
| Low (<median 2.47) | 3 (4.69) | 17 (5.25) | 6 (6.45) | 12 (5.48) | 7 (7.07) | 2 (7.14) |
| High (>median 2.47) | 1 (50.00) | 20 (6.97) | 1 (12.50) | 17 (6.69) | 4 (11.11) | 6 (8.57) |
| Log-rank test | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.45 | 0.56 | 0.64 | 0.99 |
| IgG4/IgG1 (%) * | ||||||
| Low (<median 4.06) | 4 (6.06) | 19 (5.46) | 6 (6.45) | 13 (5.70) | 8 (7.69) | 3 (6.67) |
| High (>median 4.06) | - | 18 (6.87) | 1 (12.50) | 16 (6.53) | 3 (9.68) | 5 (9.43) |
| p-value | - | 0.28 | 0.45 | 0.76 | 0.86 | 0.71 |
| a | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cholangitis | ERCP | |||||
| No | Yes | p-Value * | No | Yes | p-Value * | |
| ALL | 111 | 71 (38.8) | 78 | 103 (56.9) | ||
| IgG4 (g/L) | ||||||
| Low (<0.05 g/L) | 8 | 8 (50.0) | 5 | 11 (68.8) | ||
| Normal (0.05–1.25 g/L) | 101 | 55 (35.3) | 73 | 83 (53.2) | ||
| High (>1.25 g/L) | 2 | 7 (77.8) | 0.02 | 0 | 9 (100.) | 0.009 |
| IgG4/IgG (%) * | ||||||
| Low (<median 2.47) | 55 | 36 (39.6) | 40 | 51 (56.0) | ||
| High (>median 2.47) | 56 | 34 (37.8) | 0.81 | 38 | 52 (57.8) | 0.81 |
| IgG4/IgG1 (%) * | ||||||
| Low (<median 4.06) | 42 | 49 (53.9) | 54 | 37 (40.7) | ||
| High (>median 4.06) | 36 | 54 (60.0) | 0.40 | 57 | 33 (36.7) | 0.58 |
| b Association of IgG4 values with cholangitis and ERCP (IgG evaluated before ERCP) | ||||||
| ERCP | ||||||
| No | Yes | p-value * | ||||
| ALL | 78 | 32 | ||||
| IgG4 (g/L) | ||||||
| Low (<0.05 g/L) | 5 | 2 | ||||
| Normal (0.05–1.25 g/L) | 73 | 30 | ||||
| High (>1.25 g/L) | 0 | 0 | 0.98 | |||
| c Association of IgG4 values with cholangitis and ERCP (IgG evaluated after ERCP) | ||||||
| ERCP | ||||||
| No | Yes | p-value * | ||||
| ALL | 78 | 71 | ||||
| IgG4 (g/L) | ||||||
| Low (<0.05 g/L) | 5 | 9 | ||||
| Normal (0.05–1.25 g/L) | 73 | 53 | ||||
| High (>1.25 g/L) | 0 | 9 | 0.002 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vujasinovic, M.; Said, K.; Villard, C.; Carlsson, J.; Poli, C.; Maisonneuve, P.; Löhr, J.-M. The Role of Immunoglobulin G4 in Outcomes of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010079
Vujasinovic M, Said K, Villard C, Carlsson J, Poli C, Maisonneuve P, Löhr J-M. The Role of Immunoglobulin G4 in Outcomes of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(1):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010079
Chicago/Turabian StyleVujasinovic, Miroslav, Karouk Said, Christina Villard, Jennifer Carlsson, Christopher Poli, Patrick Maisonneuve, and J.-Matthias Löhr. 2024. "The Role of Immunoglobulin G4 in Outcomes of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 1: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010079
APA StyleVujasinovic, M., Said, K., Villard, C., Carlsson, J., Poli, C., Maisonneuve, P., & Löhr, J.-M. (2024). The Role of Immunoglobulin G4 in Outcomes of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(1), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010079






