Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Trypanosomatids: The Key to Decoding Host–Parasite Communication
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Key Challenges in the Study of Trypanosomatid-Derived EVs
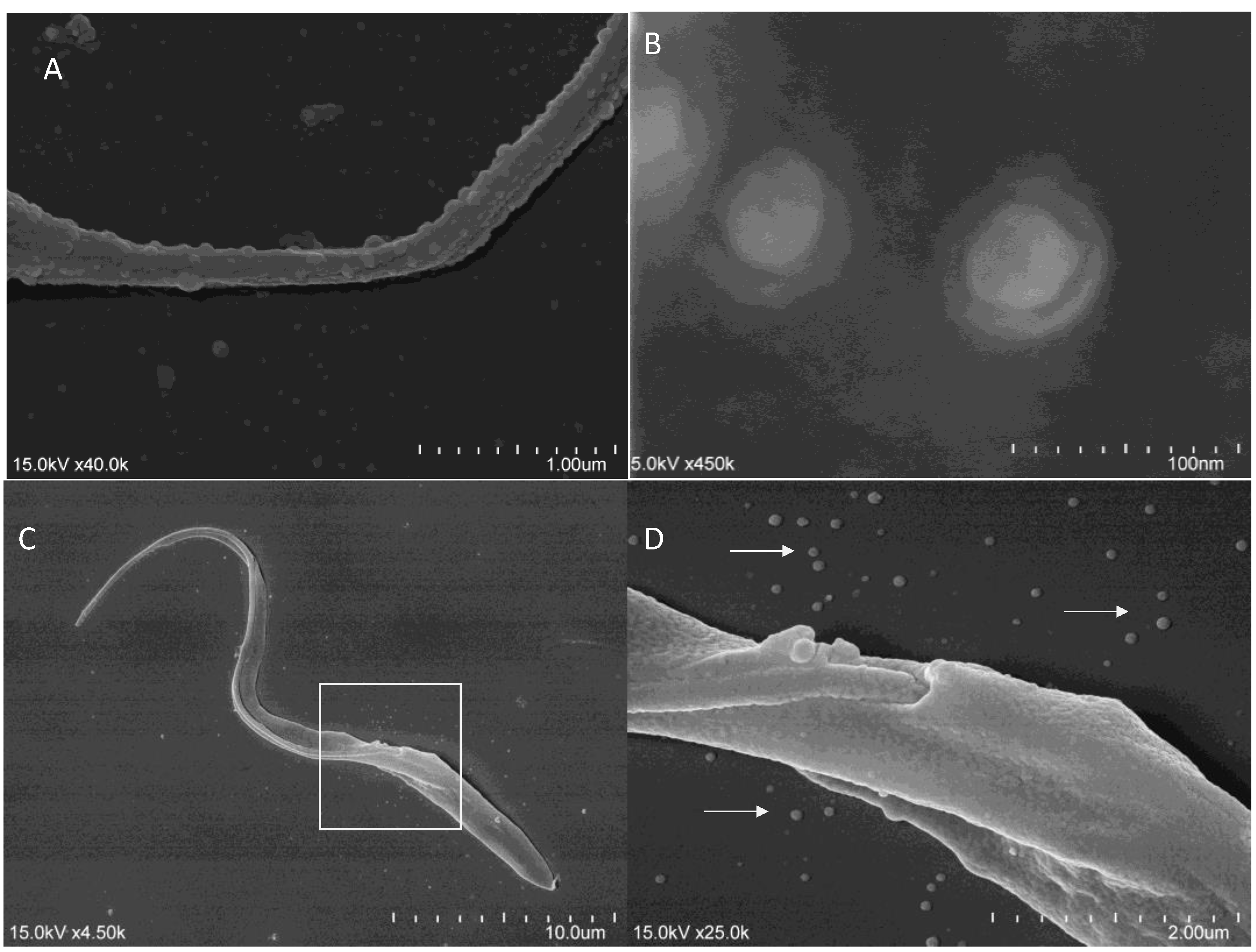
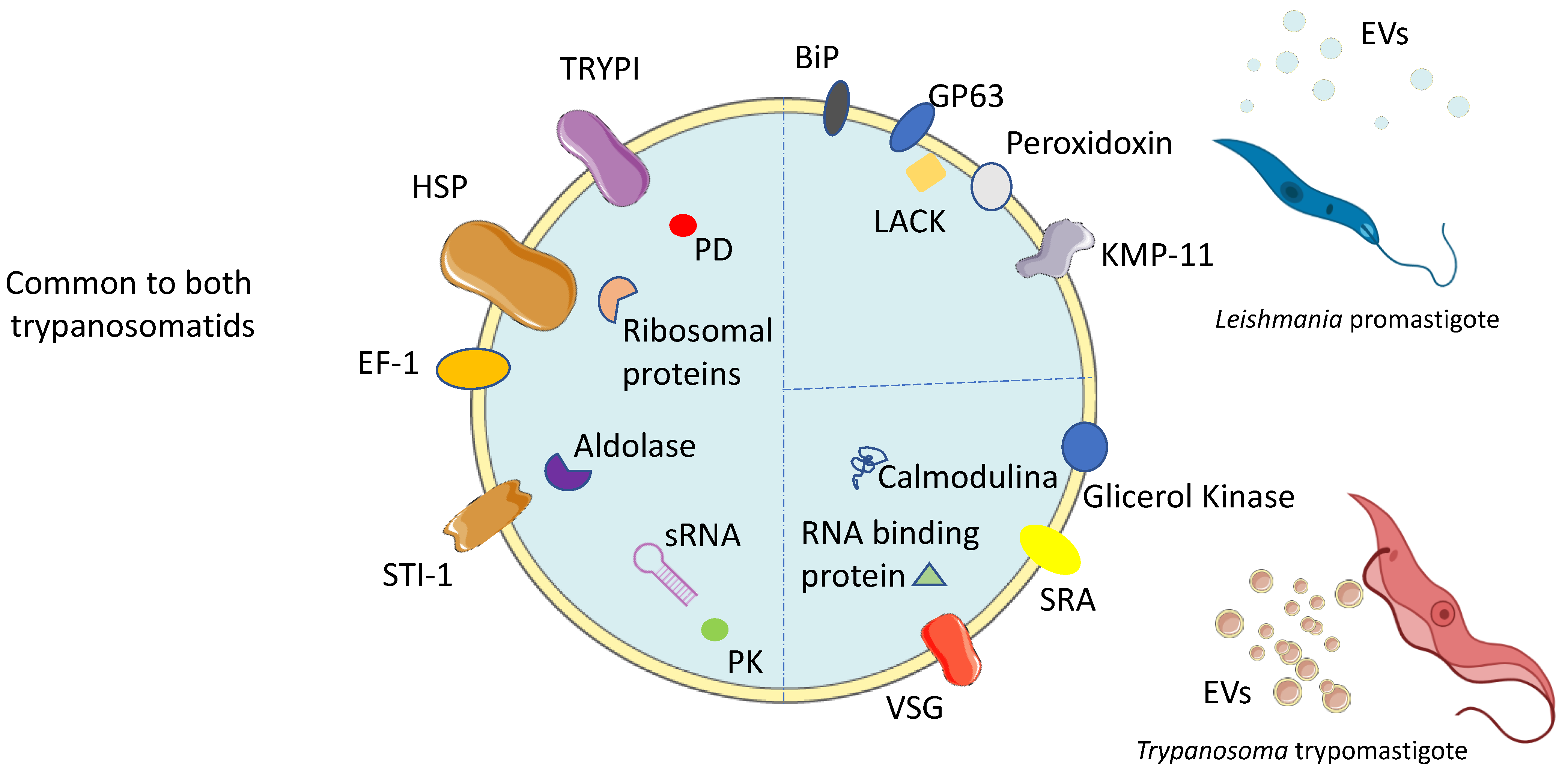
3. Composition of EVs Derived from Trypanosomatids
3.1. Leishmania-Derived EVs
3.2. Trypanosoma-Derived EVs
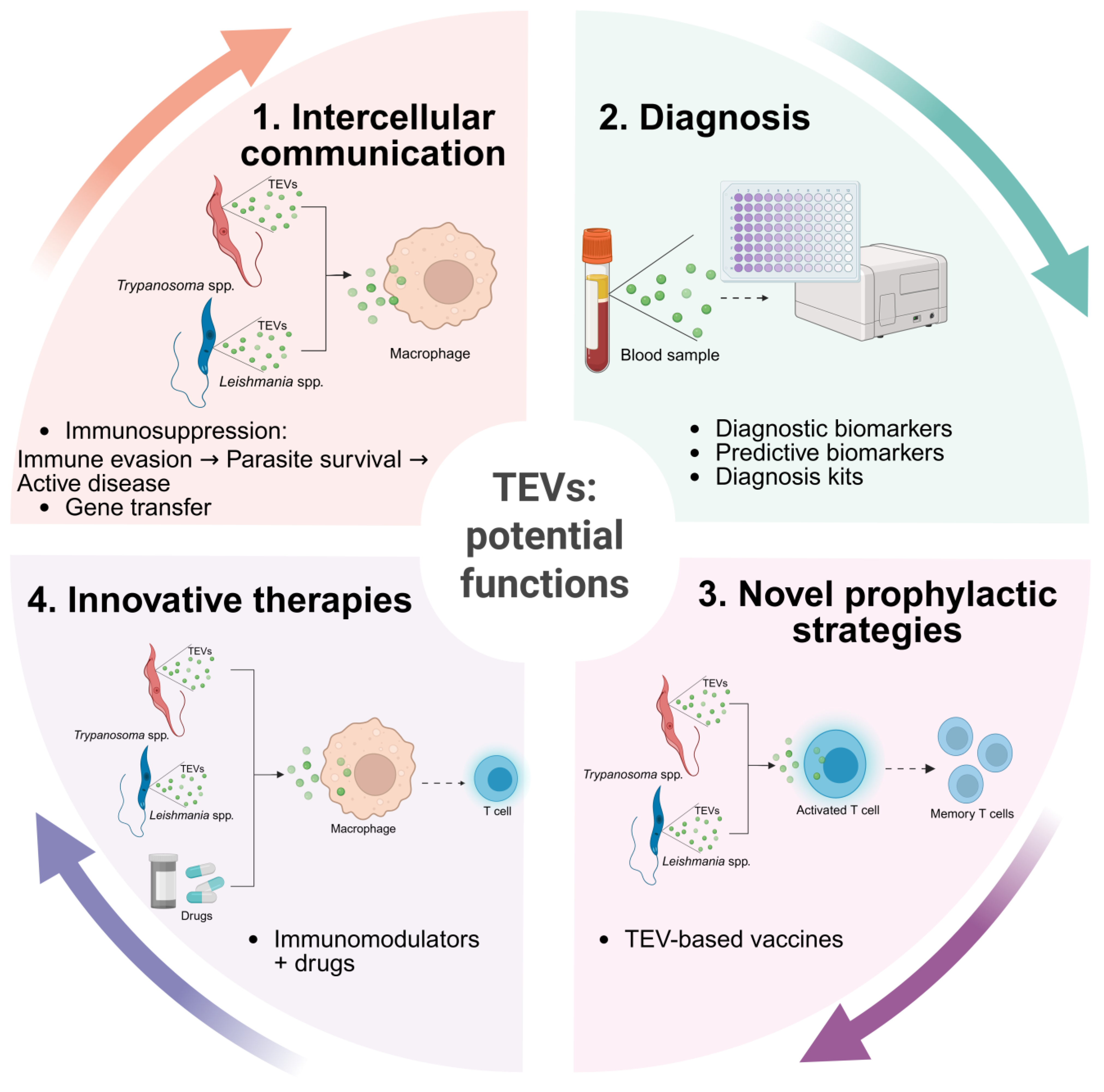
4. TEVs as Key Players in Host Immunomodulation
4.1. Host Immunomodulation by Leishmania-Derived EVs
4.2. Host Modulation by Trypanosoma-Derived EVs
5. EVs Implicated in Trypanosomatid Evolution by Horizontal Gene Transfer
6. Potential of TEVs as Emerging Diagnostic Biomarkers
7. Exploiting TEVs as an Innovative Approach to Controlling Trypanosomatid Diseases
8. Conclusions and Future Perspectives for TEVs
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NTDs | Neglected tropical diseases |
| NZDs | Neglected zoonotic diseases |
| VL | Visceral leishmaniasis |
| CL | Cutaneous leishmaniasis |
| CanL | Canine leishmaniasis |
| EV | Extracellular vesicle |
| ISEV | International Society for Extracellular Vesicles |
| MISEV | Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles |
| TEVs | Extracellular vesicles from trypanosomatids |
| MØ | Macrophage |
| HSP | Heat shock protein |
| TRYPI | Tryparedoxin peroxidase |
| LACK | Activated protein kinase c receptor |
| STI 1 | Stress-induced protein 1 |
| SRA | Serum-resistance-associated protein |
| FCaBP | Flagellum calcium-binding protein |
| SAPA | Shed acute-phase antigen |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| TcTASV-C | Trypomastigote Alanine-, Valine-, and Serine-rich proteins |
| PPG | Proteophosphoglycan |
| SAP | Secreted acid phosphatase |
| TF | Transcription factor |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| PTP | Protein tyrosine phosphatase |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| HGT | Horizontal Gene Transfer |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| MASP | Mucin-associated surface protein |
| RH | Retrotransposon hot spot protein family |
References
- World Health Organization. Global Report on Neglected Tropical Diseases; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jannin, J.; Gabrielli, A.F. Neurological Aspects of Neglected Tropical Diseases. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 114, pp. 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bouteille, B.; Oukem, O.; Bisser, S.; Dumas, M. Treatment Perspectives for Human African Trypanosomiasis. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 17, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmige, V.; Tanowitz, H.; Sethi, A. Trypanosoma cruzi Infection: A Review with Emphasis on Cutaneous Manifestations. Int. J. Dermatol. 2012, 51, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaum, K.; Honek, J.; C.v.C. Cadmus, C.M.; Efferth, T. Trypanosomatid Parasites Causing Neglected Diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 1594–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassi, A.; Rassi, A.; Marcondes de Rezende, J. American Trypanosomiasis (Chagas Disease). Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 26, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewardson, A.J.; Leder, K.; Torresi, J.; Johnson, D.F. Two Cases of Old World Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Australian Travelers Visiting Morocco. J. Travel. Med. 2010, 17, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickerman, K. The Evolutionary Expansion of the Trypanosomatid Flagellates. Int. J. Parasitol. 1994, 24, 1317–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Research Priorities for Chagas Disease, Human African Trypanosomiasis and Leishmaniasis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Marcili, A.; Sperança, M.A.; da Costa, A.P.; Madeira, M.d.F.; Soares, H.S.; Sanches, C.d.O.C.C.; Acosta, I.d.C.L.; Girotto, A.; Minervino, A.H.H.; Horta, M.C.; et al. Phylogenetic Relationships of Leishmania Species Based on Trypanosomatid Barcode (SSU RDNA) and GGAPDH Genes: Taxonomic Revision of Leishmania (L.) infantum Chagasi in South America. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 25, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoundi, M.; Kuhls, K.; Cannet, A.; Votýpka, J.; Marty, P.; Delaunay, P.; Sereno, D. A Historical Overview of the Classification, Evolution, and Dispersion of Leishmania Parasites and Sandflies. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, R.; Blum, J.; Chappuis, F.; Burri, C. Human African Trypanosomiasis. Lancet 2010, 375, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Utzinger, J.; Saric, J.; Li, J.V.; Burckhardt, J.; Dirnhofer, S.; Nicholson, J.K.; Singer, B.H.; Brun, R.; Holmes, E. Global Metabolic Responses of Mice to Trypanosoma brucei brucei Infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6127–6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereno, D. Leishmania (mundinia) spp.: From Description to Emergence as New Human and Animal Leishmania Pathogens. New Microbes New Infect. 2019, 30, 100540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebhodaghe, F.; Isaac, C.; Ohiolei, J.A. A Meta-Analysis of the Prevalence of Bovine Trypanosomiasis in Some African Countries from 2000 to 2018. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 160, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebhodaghe, F.; Ohiolei, J.A.; Isaac, C. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Small Ruminant and Porcine Trypanosomiasis Prevalence in Sub-Saharan Africa (1986 to 2018). Acta Trop. 2018, 188, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, J.R.C. Zoonoses Emergentes e Reemergentes e Sua Importância Para Saúde e Produção Animal. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2016, 51, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamond, N.; Cosson, A.; Blom-Potar, M.C.; Jouvion, G.; D’Archivio, S.; Medina, M.; Droin-Bergère, S.; Huerre, M.; Goyard, S.; Minoprio, P. Trypanosoma vivax Infections: Pushing Ahead with Mouse Models for the Study of Nagana. I. Parasitological, Hematological and Pathological Parameters. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, H.R.; Selby, R.; Mumba, C.; Napier, G.B.; Guitian, J. Assessment of animal African trypanosomiasis (AAT) vulnerability in cattle-owning communities of sub-Saharan Africa. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization—Human African Trypanosomiasis. Available online: https://www.afro.who.int/health-topics/human-african-trypanosomiasis (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Toor, J.; Adams, E.R.; Aliee, M.; Amoah, B.; Anderson, R.M.; Ayabina, D.; Bailey, R.; Basáñez, M.-G.; Blok, D.J.; Blumberg, S.; et al. Predicted Impact of COVID-19 on Neglected Tropical Disease Programs and the Opportunity for Innovation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 1463–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, M. Climate Change and the Neglected Tropical Diseases. Adv. Parasitol. 2018, 100, 39–126. [Google Scholar]
- Pitt, S.J.; Gunn, A. The One Health Concept. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2024, 81, 12366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stijlemans, B.; Guilliams, M.; Raes, G.; Beschin, A.; Magez, S.; De Baetselier, P. African Trypanosomosis: From Immune Escape and Immunopathology to Immune Intervention. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 148, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, P.; Scott, P. Leishmaniasis: Complexity at the Host–Pathogen Interface. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solano-Gallego, L.; Koutinas, A.; Miró, G.; Cardoso, L.; Pennisi, M.G.; Ferrer, L.; Bourdeau, P.; Oliva, G.; Baneth, G. Directions for the Diagnosis, Clinical Staging, Treatment and Prevention of Canine Leishmaniosis. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 165, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luckheeram, R.V.; Zhou, R.; Verma, A.D.; Xia, B. CD4+T Cells: Differentiation and Functions. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 925135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, K.L.; Reits, E.; Neefjes, J. Present Yourself! By MHC Class I and MHC Class II Molecules. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitson, J.P.; Grainger, J.R.; Maizels, R.M. Helminth Immunoregulation: The Role of Parasite Secreted Proteins in Modulating Host Immunity. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2009, 167, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, P.D.; Morelli, A.E. Regulation of Immune Responses by Extracellular Vesicles. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Théry, C. Biogenesis, Secretion, and Intercellular Interactions of Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantel, P.-Y.; Marti, M. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Plasmodium and Other Protozoan Parasites. Cell Microbiol. 2014, 16, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro-Ibáñez, E.; Sanz-Garcia, A.; Visakorpi, T.; Escobedo-Lucea, C.; Siljander, P.; Ayuso-Sacido, A.; Yliperttula, M. Different GDNA Content in the Subpopulations of Prostate Cancer Extracellular Vesicles: Apoptotic Bodies, Microvesicles, and Exosomes. Prostate 2014, 74, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Balkom, B.W.M.; Eisele, A.S.; Pegtel, D.M.; Bervoets, S.; Verhaar, M.C. Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis of Small RNAs in Human Endothelial Cells and Exosomes Provides Insights into Localized RNA Processing, Degradation and Sorting. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 26760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreimer, S.; Belov, A.M.; Ghiran, I.; Murthy, S.K.; Frank, D.A.; Ivanov, A.R. Mass-Spectrometry-Based Molecular Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles: Lipidomics and Proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 2367–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, H.; Drummen, G.; Mathivanan, S. Focus on Extracellular Vesicles: Introducing the Next Small Big Thing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, G.; Filho, A.L.; Olivier, M. Modulation of Host-Pathogen Communication by Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) of the Protozoan Parasite Leishmania. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, J.M.; Clos, J.; Horakova, E.; Wang, A.Y.; Wiesgigl, M.; Kelly, I.; Lynn, M.A.; McMaster, W.R.; Foster, L.J.; Levings, M.K.; et al. Leishmania Exosomes Modulate Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses through Effects on Monocytes and Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 5011–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atayde, V.D.; Aslan, H.; Townsend, S.; Hassani, K.; Kamhawi, S.; Olivier, M. Exosome Secretion by the Parasitic Protozoan Leishmania within the Sand Fly Midgut. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loria, A.D.; Dattilo, V.; Santoro, D.; Guccione, J.; De Luca, A.; Ciaramella, P.; Pirozzi, M.; Iaccino, E. Expression of Serum Exosomal MiRNA 122 and Lipoprotein Levels in Dogs Naturally Infected by Leishmania infantum: A Preliminary Study. Animals 2020, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atayde, V.D.; da Silva Lira Filho, A.; Chaparro, V.; Zimmermann, A.; Martel, C.; Jaramillo, M.; Olivier, M. Exploitation of the Leishmania Exosomal Pathway by Leishmania RNA Virus 1. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akers, J.C.; Gonda, D.; Kim, R.; Carter, B.S.; Chen, C.C. Biogenesis of Extracellular Vesicles (EV): Exosomes, Microvesicles, Retrovirus-like Vesicles, and Apoptotic Bodies. J. Neurooncol 2013, 113, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.-J.; Maghsoudi, T.; Wang, T. Exosomes Mediate the Intercellular Communication after Myocardial Infarction. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 13, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Zitvogel, L.; Amigorena, S. Exosomes: Composition, Biogenesis and Function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell 2016, 164, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Zhao, W.-L.; Ye, Y.-Y.; Bai, X.-C.; Liu, R.-Q.; Chang, L.-F.; Zhou, Q.; Sui, S.-F. Cellular Internalization of Exosomes Occurs through Phagocytosis. Traffic 2010, 11, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos-Amador, P.; Pérez-Cabezas, B.; Izquierdo-Useros, N.; Puertas, M.C.; Martinez-Picado, J.; Pujol-Borrell, R.; Naranjo-Gómez, M.; Borràs, F.E. Capture of Cell-Derived Microvesicles (Exosomes and Apoptotic Bodies) by Human Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 91, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, S.J.; Raposo, G. As We Wait: Coping with an Imperfect Nomenclature for Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atayde, V.D.; Hassani, K.; da Silva Lira Filho, A.; Borges, A.R.; Adhikari, A.; Martel, C.; Olivier, M. Leishmania Exosomes and Other Virulence Factors: Impact on Innate Immune Response and Macrophage Functions. Cell Immunol. 2016, 309, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, P.; Wang, S.; Didenko, V.V. Apoptotic Bodies: Selective Detection in Extracellular Vesicles. In Signal Transduction Immunohistochemistry; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1554, pp. 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular Vesicles: Exosomes, Microvesicles, and Friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateescu, B.; Kowal, E.J.K.; van Balkom, B.W.M.; Bartel, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Buzás, E.I.; Buck, A.H.; de Candia, P.; Chow, F.W.N.; Das, S.; et al. Obstacles and Opportunities in the Functional Analysis of Extracellular Vesicle RNA—An ISEV Position Paper. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1286095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A Position Statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and Update of the MISEV2014 Guidelines. J. Extracell Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, M.Z.; Ratajczak, J. Extracellular Microvesicles/Exosomes: Discovery, Disbelief, Acceptance, and the Future? Leukemia 2020, 34, 3126–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Silva, M.R.; Cura das Neves, R.F.; Cabrera-Cabrera, F.; Sanguinetti, J.; Medeiros, L.C.; Robello, C.; Naya, H.; Fernandez-Calero, T.; Souto-Padron, T.; de Souza, W.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Shed by Trypanosoma cruzi Are Linked to Small RNA Pathways, Life Cycle Regulation, and Susceptibility to Infection of Mammalian Cells. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambertz, U.; Oviedo Ovando, M.E.; Vasconcelos, E.J.; Unrau, P.J.; Myler, P.J.; Reiner, N.E. Small RNAs Derived from TRNAs and RRNAs Are Highly Enriched in Exosomes from Both Old and New World Leishmania Providing Evidence for Conserved Exosomal RNA Packaging. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliaz, D.; Kannan, S.; Shaked, H.; Arvatz, G.; Tkacz, I.D.; Binder, L.; Waldman Ben-Asher, H.; Okalang, U.; Chikne, V.; Cohen-Chalamish, S.; et al. Exosome Secretion Affects Social Motility in Trypanosoma brucei. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrales, R.M.; Sereno, D.; Mathieu-Daudé, F. Deciphering the Leishmania Exoproteome: What We Know and What We Can Learn. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 58, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, J.M.; Chan, S.K.; Robinson, D.P.; Dwyer, D.M.; Nandan, D.; Foster, L.J.; Reiner, N.E. Proteomic Analysis of the Secretome of Leishmania donovani. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, G.; Bruno, F.; Saieva, L.; Alessandro, R.; Galluzzi, L.; Diotallevi, A.; Vitale, F. Exosome Secretion by Leishmania infantum Modulate the Chemotactic Behavior and Cytokinic Expression Creating an Environment Permissive for Early Infection. Exp. Parasitol. 2019, 198, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, J.M.; Clos, J.; de’Oliveira, C.C.; Shirvani, O.; Fang, Y.; Wang, C.; Foster, L.J.; Reiner, N.E. An Exosome-Based Secretion Pathway Is Responsible for Protein Export from Leishmania and Communication with Macrophages. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, K.; Shio, M.T.; Martel, C.; Faubert, D.; Olivier, M. Absence of Metalloprotease GP63 Alters the Protein Content of Leishmania Exosomes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, K.; Antoniak, E.; Jardim, A.; Olivier, M. Temperature-Induced Protein Secretion by Leishmania mexicana Modulates Macrophage Signalling and Function. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Serna, L.E.; Diupotex, M.; Zamora-Chimal, J.; Ruiz-Remigio, A.; Delgado-Domínguez, J.; Cervantes-Sarabia, R.B.; Méndez-Bernal, A.; Escalona-Montaño, A.R.; Aguirre-García, M.M.; Becker, I. Leishmania mexicana: Novel Insights of Immune Modulation through Amastigote Exosomes. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 8894549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarém, N.; Racine, G.; Silvestre, R.; Cordeiro-da-Silva, A.; Ouellette, M. Exoproteome Dynamics in Leishmania infantum. J. Proteom. 2013, 84, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valério-Bolas, A.; Meunier, M.; Palma-Marques, J.; Rodrigues, A.; Santos, A.M.; Nunes, T.; Ferreira, R.; Armada, A.; Alves, J.C.; Antunes, W.; et al. Exploiting Leishmania—Primed Dendritic Cells as Potential Immunomodulators of Canine Immune Response. Cells 2024, 13, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.I.; Rodrigues, A.V.; Valério-Bolas, A.; Nunes, T.; Carvalheiro, M.; Antunes, W.; Alexandre-Pires, G.; da Fonseca, I.P.; Santos-Gomes, G. Insights on Host–Parasite Immunomodulation Mediated by Extracellular Vesicles of Cutaneous Leishmania shawi and Leishmania guyanensis. Cells 2023, 12, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, D.M.; Batista, M.; Marchini, F.K.; Tempone, A.J.; Traub-Csekö, Y.M. Proteomic Analysis of Exosomes Derived from Procyclic and Metacyclic-like Cultured Leishmania infantum chagasi. J. Proteom. 2020, 227, 103902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiweshe, S.M.; Steketee, P.C.; Jayaraman, S.; Paxton, E.; Neophytou, K.; Erasmus, H.; Labuschagne, M.; Cooper, A.; MacLeod, A.; Grey, F.E.; et al. Parasite Specific 7SL-Derived Small RNA Is an Effective Target for Diagnosis of Active Trypanosomiasis Infection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz Lozano, I.M.; De Pablos, L.M.; Longhi, S.A.; Zago, M.P.; Schijman, A.G.; Osuna, A. Immune Complexes in Chronic Chagas Disease Patients Are Formed by Exovesicles from Trypanosoma cruzi Carrying the Conserved MASP N-Terminal Region. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szempruch, A.J.; Sykes, S.E.; Kieft, R.; Dennison, L.; Becker, A.C.; Gartrell, A.; Martin, W.J.; Nakayasu, E.S.; Almeida, I.C.; Hajduk, S.L.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Trypanosoma brucei Mediate Virulence Factor Transfer and Cause Host Anemia. Cell 2016, 164, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungri, A.M.; dos Santos Sabatke, B.F.; Rossi, I.V.; das Neves, G.B.; Marques, J.; Ribeiro, B.G.; Borges, G.K.; Moreira, R.S.; Ramírez, M.I.; Miletti, L.C. Extracellular Vesicles Released by Trypanosoma evansi: Induction Analysis and Proteomics. Parasitol. Res. 2024, 123, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyekwelu, K.C. Life Cycle of Trypanosoma cruzi in the Invertebrate and the Vertebrate Hosts. In Biology of Trypanosoma cruzi; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan, K.T.; Ames, J.B.; Asfaw, S.H.; Wingard, J.N.; Olson, C.L.; Campana, P.T.; Araújo, A.P.U.; Engman, D.M. A Flagellum-Specific Calcium Sensor. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 40104–40111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-López, N.L.; Ndao, M.; Camargo, F.V.; Nara, T.; Annoura, T.; Hardie, D.B.; Borchers, C.H.; Jardim, A. Characterization and Diagnostic Application of Trypanosoma cruzi Trypomastigote Excreted-Secreted Antigens Shed in Extracellular Vesicles Released from Infected Mammalian Cells. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 744–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.J.M.; Colli, W. Role of the Gp85/Trans-Sialidase Superfamily of Glycoproteins in the Interaction of Trypanosoma cruzi with Host Structures. Subcell. Biochem. 2008, 47, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seco-Hidalgo, V.; Osuna, A.; de Pablos, L.M. Characterizing Cell Heterogeneity Using PCR Fingerprinting of Surface Multigene Families in Protozoan Parasites. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1745, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, B.C.; Uehara, I.A.; Dias, L.O.S.; Brígido, P.C.; da Silva, C.V.; Silva, M.J.B. Mechanisms of Infectivity and Evasion Derived from Microvesicles Cargo Produced by Trypanosoma cruzi. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, B.K.; Varikuti, S.; Seidler, G.R.; Volpedo, G.; Satoskar, A.R.; McGwire, B.S. MicroRNA-155 Deficiency Exacerbates Trypanosoma cruzi Infection. Infect. Immun. 2020, 88, e00948-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornet-Gomez, A.; Retana Moreira, L.; Kronenberger, T.; Osuna, A. Extracellular Vesicles of Trypomastigotes of Trypanosoma cruzi Induce Changes in Ubiquitin-Related Processes, Cell-Signaling Pathways and Apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecilhas, A.C.; Schumacher, R.I.; Alves, M.J.M.; Colli, W. Vesicles as Carriers of Virulence Factors in Parasitic Protozoan Diseases. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecilhas, A.C.; Soares, R.P.; Schenkman, S.; Fernández-Prada, C.; Olivier, M. Extracellular Vesicles in Trypanosomatids: Host Cell Communication. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 602502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maspi, N.; Abdoli, A.; Ghaffarifar, F. Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines in Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: A Review. Pathog. Glob. Health 2016, 110, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorey, J.S.; Cheng, Y.; Singh, P.P.; Smith, V.L. Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles in Host-Pathogen Interactions. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, J.M.; Reiner, N.E. Leishmania Exosomes Deliver Preemptive Strikes to Create an Environment Permissive for Early Infection. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 1, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, M.; Gomez, M.A.; Larsson, O.; Shio, M.T.; Topisirovic, I.; Contreras, I.; Luxenburg, R.; Rosenfeld, A.; Colina, R.; McMaster, R.W.; et al. Leishmania Repression of Host Translation through MTOR Cleavage Is Required for Parasite Survival and Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 9, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, M.A.; Contreras, I.; Hallé, M.; Tremblay, M.L.; McMaster, R.W.; Olivier, M. Leishmania GP63 Alters Host Signaling through Cleavage-Activated Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases. Sci. Signal 2009, 2, ra58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, F.M.C.; Dupin, T.V.; Toledo, M.D.S.; Reis, N.F.D.C.; Ribeiro, K.; Cronemberger-Andrade, A.; Rugani, J.N.; De Lorenzo, B.H.P.; Novaes E Brito, R.R.; Soares, R.P.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Released by Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis Promote Disease Progression and Induce the Production of Different Cytokines in Macrophages and B-1 Cells. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyllie, M.P.; Ramirez, M.I. Microvesicles Released during the Interaction between Trypanosoma cruzi TcI and TcII Strains and Host Blood Cells Inhibit Complement System and Increase the Infectivity of Metacyclic Forms of Host Cells in a Strain-Independent Process. Pathog. Dis. 2017, 75, ftx077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, P.M.; de Menezes-Neto, A.; Borges, V.M.; Descoteaux, A.; Torrecilhas, A.C.; Xander, P.; Revach, O.Y.; Regev-Rudzki, N.; Soares, R.P. Immunomodulatory Properties of Leishmania Extracellular Vesicles During Host-Parasite Interaction: Differential Activation of TLRs and NF-ΚB Translocation by Dermotropic and Viscerotropic Species. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zandbergen, G.; Klinger, M.; Mueller, A.; Dannenberg, S.; Gebert, A.; Solbach, W.; Laskay, T. Cutting Edge: Neutrophil Granulocyte Serves as a Vector for Leishmania Entry into Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 6521–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.A.; Alexandre-Pires, G.; Câmara, M.; Santos, M.; Martins, C.; Rodrigues, A.; Adriana, J.; Passero, L.F.D.; Pereira da Fonseca, I.; Santos-Gomes, G. Canine Neutrophils Cooperate with Macrophages in the Early Stages of Leishmania infantum in Vitro Infection. Parasite Immunol. 2019, 41, e12617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paranaiba, L.F.; Guarneri, A.A.; Torrecilhas, A.C.; Melo, M.N.; Soares, R.P. Extracellular Vesicles Isolated from Trypanosoma cruzi Affect Early Parasite Migration in the Gut of Rhodnius prolixus but Not in Triatoma infestans. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2019, 114, e190217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias-Guerreiro, T.; Palma-Marques, J.; Mourata-Gonçalves, P.; Alexandre-Pires, G.; Valério-Bolas, A.; Gabriel, Á.; Nunes, T.; Antunes, W.; Fonseca, I.P.d.; Sousa-Silva, M.; et al. African Trypanosomiasis: Extracellular Vesicles Shed by Trypanosoma brucei brucei Manipulate Host Mononuclear Cells. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.R.; Lima, L.; de Almeida, L.A.; Monteiro, J.; Moreno, C.J.G.; Nascimento, J.D.; de Araújo, R.F.; Mello, F.; Martins, L.P.A.; Graminha, M.A.S.; et al. Biological and Molecular Characterization of Trypanosoma cruzi Strains from Four States of Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, I.V.; Gavinho, B.; Ramirez, M.I. Isolation and Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Trypanosoma cruzi. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1955, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, P.J.; Palmer, J.D. Horizontal Gene Transfer in Eukaryotic Evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emamalipour, M.; Seidi, K.; Zununi Vahed, S.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, A.; Jaymand, M.; Majdi, H.; Amoozgar, Z.; Chitkushev, L.T.; Javaheri, T.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, R.; et al. Horizontal Gene Transfer: From Evolutionary Flexibility to Disease Progression. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancurel, C.; Legrand, L.; Danchin, E.G.J. Alienness: Rapid Detection of Candidate Horizontal Gene Transfers across the Tree of Life. Genes 2017, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, A.O.; Palmer, J.D. Horizontal Gene Transfer in Plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Defourny, K.A.Y.; Smid, E.J.; Abee, T. Gram-Positive Bacterial Extracellular Vesicles and Their Impact on Health and Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Annunziata, F.; Folliero, V.; Giugliano, R.; De Filippis, A.; Santarcangelo, C.; Izzo, V.; Daglia, M.; Galdiero, M.; Arciola, C.R.; Franci, G. Gene Transfer Potential of Outer Membrane Vesicles of Gram-Negative Bacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Han, Y.; Ren, H.; Chen, C.; He, D.; Zhou, L.; Eisner, G.M.; Asico, L.D.; Jose, P.A.; Zeng, C. Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Transfer of Donor Genomic DNA to Recipient Cells Is a Novel Mechanism for Genetic Influence between Cells. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 5, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wu, G.; Tan, X.; Han, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; Wang, N.; Zou, X.; Chen, X.; Zhou, F.; et al. Transferred BCR/ABL DNA from K562 Extracellular Vesicles Causes Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Immunodeficient Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douanne, N.; Dong, G.; Amin, A.; Bernardo, L.; Blanchette, M.; Langlais, D.; Olivier, M.; Fernandez-Prada, C. Leishmania Parasites Exchange Drug-Resistance Genes through Extracellular Vesicles. Cell Rep. 2022, 40, 111121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, M.; Lafleur, A.; Villalba-Guerrero, C.; Beaulieu, M.; Lira, A.B.; Olivier, M. Extracellular Vesicles in Parasitic Protozoa: Impact of Leishmania Exosomes Containing Leishmania RNA Virus 1 (LRV1) on Leishmania Infectivity and Disease Progression. Curr. Top. Membr. 2024, 94, 157–186. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanam, J.; Chetty, V.K.; Barthel, L.; Reinhardt, D.; Hoyer, P.-F.; Thakur, B.K. DNA in Extracellular Vesicles: From Evolution to Its Current Application in Health and Disease. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douanne, N.; Dong, G.; Douanne, M.; Olivier, M.; Fernandez-Prada, C. Unravelling the Proteomic Signature of Extracellular Vesicles Released by Drug-Resistant Leishmania infantum Parasites. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, R.; Jiménez, M.; García-Martínez, J.; San Martín, J.V.; Carrillo, E.; Sánchez, C.; Moreno, J.; Alves, F.; Alvar, J. Role of Asymptomatic and Symptomatic Humans as Reservoirs of Visceral Leishmaniasis in a Mediterranean Context. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luquetti, A.O.; Schmuñis, G.A. Diagnosis of Trypanosoma cruzi Infection. In American Trypanosomiasis Chagas Disease; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 687–730. [Google Scholar]
- Sudarshan, M.; Singh, T.; Chakravarty, J.; Sundar, S. A Correlative Study of Splenic Parasite Score and Peripheral Blood Parasite Load Estimation by Quantitative PCR in Visceral Leishmaniasis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 3905–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gummery, L.; Jallow, S.; Raftery, A.G.; Bennet, E.; Rodgers, J.; Sutton, D.G.M. Comparison of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) and PCR for the Diagnosis of Infection with Trypanosoma brucei ssp. in Equids in The Gambia. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, A.J.; Colburn, W.A.; DeGruttola, V.G.; DeMets, D.L.; Downing, G.J.; Hoth, D.F.; Oates, J.A.; Peck, C.C.; Schooley, R.T.; Spilker, B.A.; et al. Biomarkers and Surrogate Endpoints: Preferred Definitions and Conceptual Framework. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 69, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeijon, C.; Alves, F.; Monnerat, S.; Mbui, J.; Viana, A.G.; Almeida, R.M.; Bueno, L.L.; Fujiwara, R.T.; Campos-Neto, A. Urine-Based Antigen Detection Assay for Diagnosis of Visceral Leishmaniasis Using Monoclonal Antibodies Specific for Six Protein Biomarkers of Leishmania infantum/Leishmania donovani. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo, F.F.; Lakhal-Naouar, I.; Koles, N.; Raiciulescu, S.; Mody, R.; Aronson, N. Potential Biomarkers for Asymptomatic Visceral Leishmaniasis among Iraq-Deployed U.S. Military Personnel. Pathogens 2023, 12, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, Z.; Dabo, N.T. Erythrocytic, Enzymatic, and Histological Markers of Oxidative Stress in Subacute and Chronic Stage Infections in Wistar Rats (Rattus norvegicus) Infected with Trypanosoma brucei brucei. Dis. Markers 2023, 2023, 3590893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njamnshi, A.K.; Seke Etet, P.F.; Ngarka, L.; Perrig, S.; Olivera, G.C.; Nfor, L.N.; Njamnshi, W.Y.; Acho, A.; Muyembe, J.-J.; Bentivoglio, M.; et al. The Actigraphy Sleep Score: A New Biomarker for Diagnosis, Disease Staging, and Monitoring in Human African Trypanosomiasis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 2244–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnadas-Carceller, B.; del Portillo, H.A.; Fernandez-Becerra, C. Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers in Parasitic Disease Diagnosis. Curr. Top. Membr. 2024, 94, 187–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zanette, M.F.; de Lima, V.M.F.; Laurenti, M.D.; Rossi, C.N.; Vides, J.P.; da Costa Vieira, R.F.; Biondo, A.W.; Marcondes, M. Serological Cross-Reactivity of Trypanosoma cruzi, Ehrlichia canis, Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum and Babesia canis to Leishmania infantum chagasi Tests in Dogs. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2014, 47, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daltro, R.T.; Leony, L.M.; Freitas, N.E.M.; Silva, Â.A.O.; Santos, E.F.; Del-Rei, R.P.; Brito, M.E.F.; Brandão-Filho, S.P.; Gomes, Y.M.; Silva, M.S.; et al. Cross-Reactivity Using Chimeric Trypanosoma cruzi Antigens: Diagnostic Performance in Settings Where Chagas Disease and American Cutaneous or Visceral Leishmaniasis Are Coendemic. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e00762-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, Z.C.; Sousa, O.E.; Marques, W.P.; Saez-Alquezar, A.; Umezawa, E.S. Evaluation of Serological Tests To Identify Trypanosoma cruzi Infection in Humans and Determine Cross-Reactivity with Trypanosoma rangeli and Leishmania spp. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2007, 14, 1045–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo, M.d.S.; Cronemberger-Andrade, A.; Barbosa, F.M.C.; Reis, N.F.d.C.; Dupin, T.V.; Soares, R.P.; Torrecilhas, A.C.; Xander, P. Effects of Extracellular Vesicles Released by Peritoneal B-1 Cells on Experimental Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis Infection. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 1803–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballinas-Verdugo, M.A.; Jiménez-Ortega, R.F.; Martínez-Martínez, E.; Rivas, N.; Contreras-López, E.A.; Carbó, R.; Sánchez, F.; Bojalil, R.; Márquez-Velasco, R.; Sánchez-Muñoz, F.; et al. Circulating MiR-146a as a Possible Candidate Biomarker in the Indeterminate Phase of Chagas Disease. Biol. Res. 2021, 54, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja-Cabrera, G.P.; Correia Pontes, N.N.; Da Silva, V.O.; Paraguai De Souza, E.; Santos, W.R.; Gomes, E.M.; Luz, K.G.; Palatnik, M.; Palatnik De Sousa, C.B. Long Lasting Protection against Canine Kala-Azar Using the FML-QuilA Saponin Vaccine in an Endemic Area of Brazil (São Gonçalo Do Amarante, RN). Vaccine 2002, 20, 3277–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.P.; Costa, M.M.S.; Coelho, E.A.F.; Michalick, M.S.M.; de Freitas, E.; Melo, M.N.; Luiz Tafuri, W.; Resende, D.d.M.; Hermont, V.; Abrantes, C.d.F.; et al. Protective Immunity against Challenge with Leishmania (Leishmania) chagasi in Beagle Dogs Vaccinated with Recombinant A2 Protein. Vaccine 2008, 26, 5888–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, G.; Nieto, J.; Foglia Manzillo, V.; Cappiello, S.; Fiorentino, E.; Di Muccio, T.; Scalone, A.; Moreno, J.; Chicharro, C.; Carrillo, E.; et al. A Randomised, Double-Blind, Controlled Efficacy Trial of the LiESP/QA-21 Vaccine in Naïve Dogs Exposed to Two Leishmania infantum Transmission Seasons. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Cotrina, J.; Iniesta, V.; Monroy, I.; Baz, V.; Hugnet, C.; Marañon, F.; Fabra, M.; Gómez-Nieto, L.C.; Alonso, C. A Large-Scale Field Randomized Trial Demonstrates Safety and Efficacy of the Vaccine LetiFend® against Canine Leishmaniosis. Vaccine 2018, 36, 1972–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valério-Bolas, A.; Meunier, M.; Rodrigues, A.; Palma-Marques, J.; Ferreira, R.; Cardoso, I.; Lobo, L.; Monteiro, M.; Nunes, T.; Armada, A.; et al. Unveiling the Interplay Between Dendritic Cells and Natural Killer Cells as Key Players in Leishmania Infection. J. Immunol. Res. 2025, 2025, 3176927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serna, C.; Lara, J.A.; Rodrigues, S.P.; Marques, A.F.; Almeida, I.C.; Maldonado, R.A. A Synthetic Peptide from Trypanosoma cruzi Mucin-like Associated Surface Protein as Candidate for a Vaccine against Chagas Disease. Vaccine 2014, 32, 3525–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Costa, K.M.; da Fonseca, L.M.; dos Reis, J.S.; Santos, M.A.R.d.C.; Previato, J.O.; Mendonça-Previato, L.; Freire-de-Lima, L. Trypanosoma cruzi Trans-Sialidase as a Potential Vaccine Target Against Chagas Disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 768450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.; Almeida, F. Exosome-Based Vaccines: History, Current State, and Clinical Trials. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 711565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigues, A.; Weber, J.I.; Durães-Oliveira, J.; Moreno, C.; Ferla, M.; Aires Pereira, M.d.; Valério-Bolas, A.; Freitas, B.E.d.; Nunes, T.; Antunes, W.T.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Trypanosomatids: The Key to Decoding Host–Parasite Communication. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094302
Rodrigues A, Weber JI, Durães-Oliveira J, Moreno C, Ferla M, Aires Pereira Md, Valério-Bolas A, Freitas BEd, Nunes T, Antunes WT, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Trypanosomatids: The Key to Decoding Host–Parasite Communication. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094302
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigues, Armanda, Juliana Inês Weber, João Durães-Oliveira, Cláudia Moreno, Micheli Ferla, Maria de Aires Pereira, Ana Valério-Bolas, Bruna Eugênia de Freitas, Telmo Nunes, Wilson T. Antunes, and et al. 2025. "Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Trypanosomatids: The Key to Decoding Host–Parasite Communication" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094302
APA StyleRodrigues, A., Weber, J. I., Durães-Oliveira, J., Moreno, C., Ferla, M., Aires Pereira, M. d., Valério-Bolas, A., Freitas, B. E. d., Nunes, T., Antunes, W. T., Alexandre-Pires, G., Pereira da Fonseca, I., & Santos-Gomes, G. M. (2025). Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Trypanosomatids: The Key to Decoding Host–Parasite Communication. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4302. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094302










