Bi-Allelic MARVELD2 Variant Identified with Exome Sequencing in a Consanguineous Multiplex Ghanaian Family Segregating Non-Syndromic Hearing Loss
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Family and Phenotype Description
2.2. WES Variant Identification
2.3. Validation of WES Variant
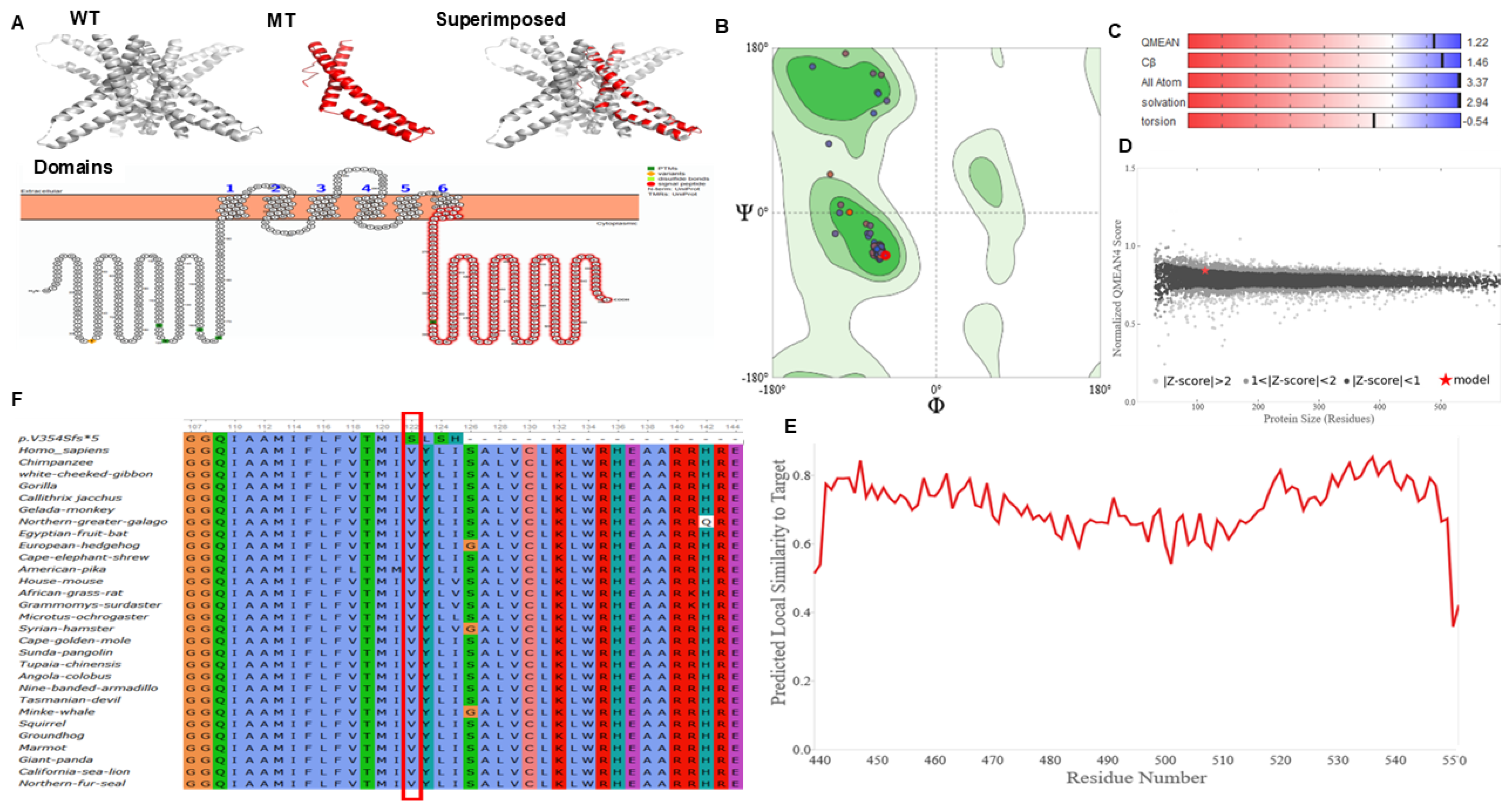
2.4. Evolutionary and Conservation Analysis of MARVELD2 Protein
2.5. MARVELD2 Protein Modeling Analysis
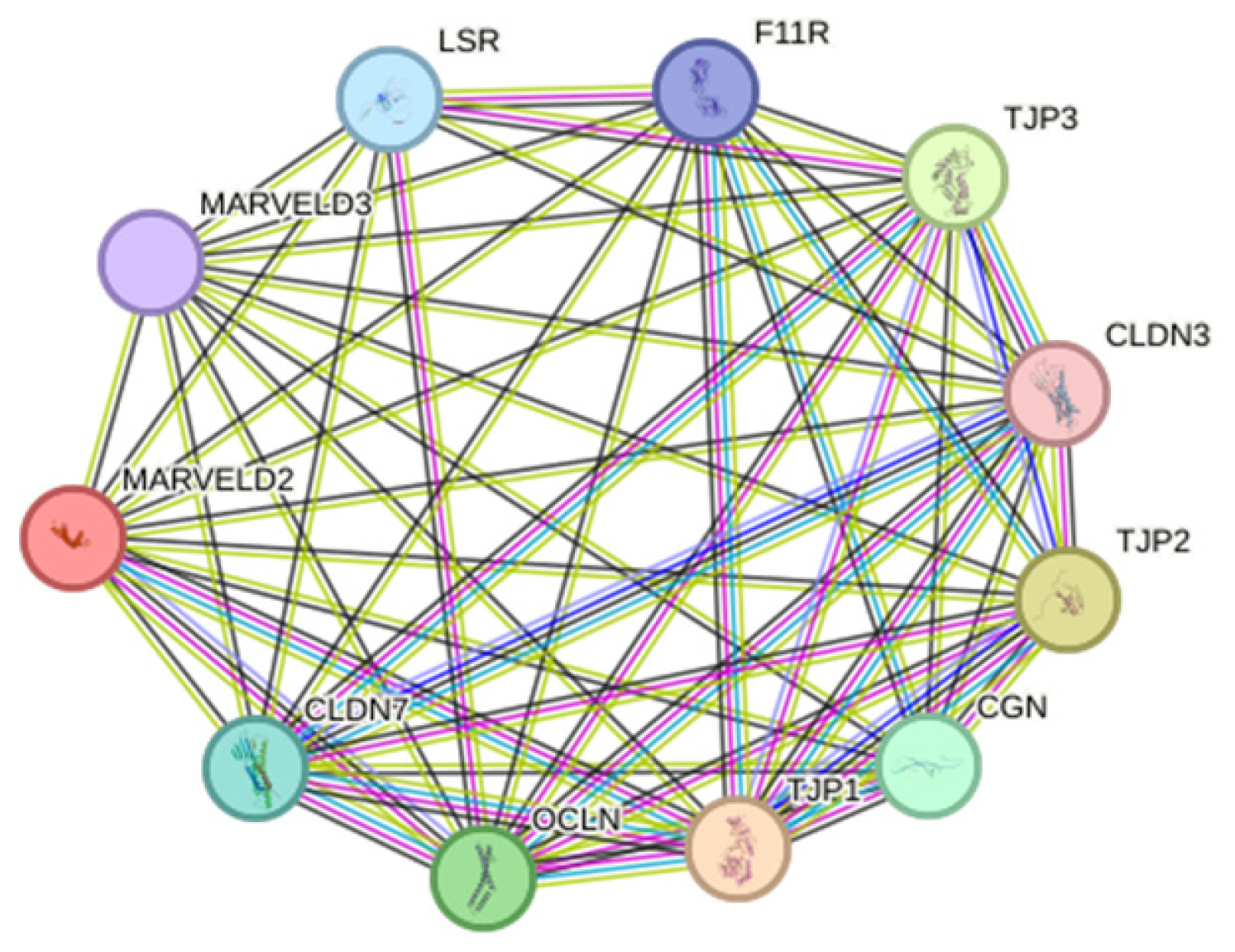
2.6. Investigating Variant MARVELD2 Truncation, Stability, and Protein-to-Protein Interactions
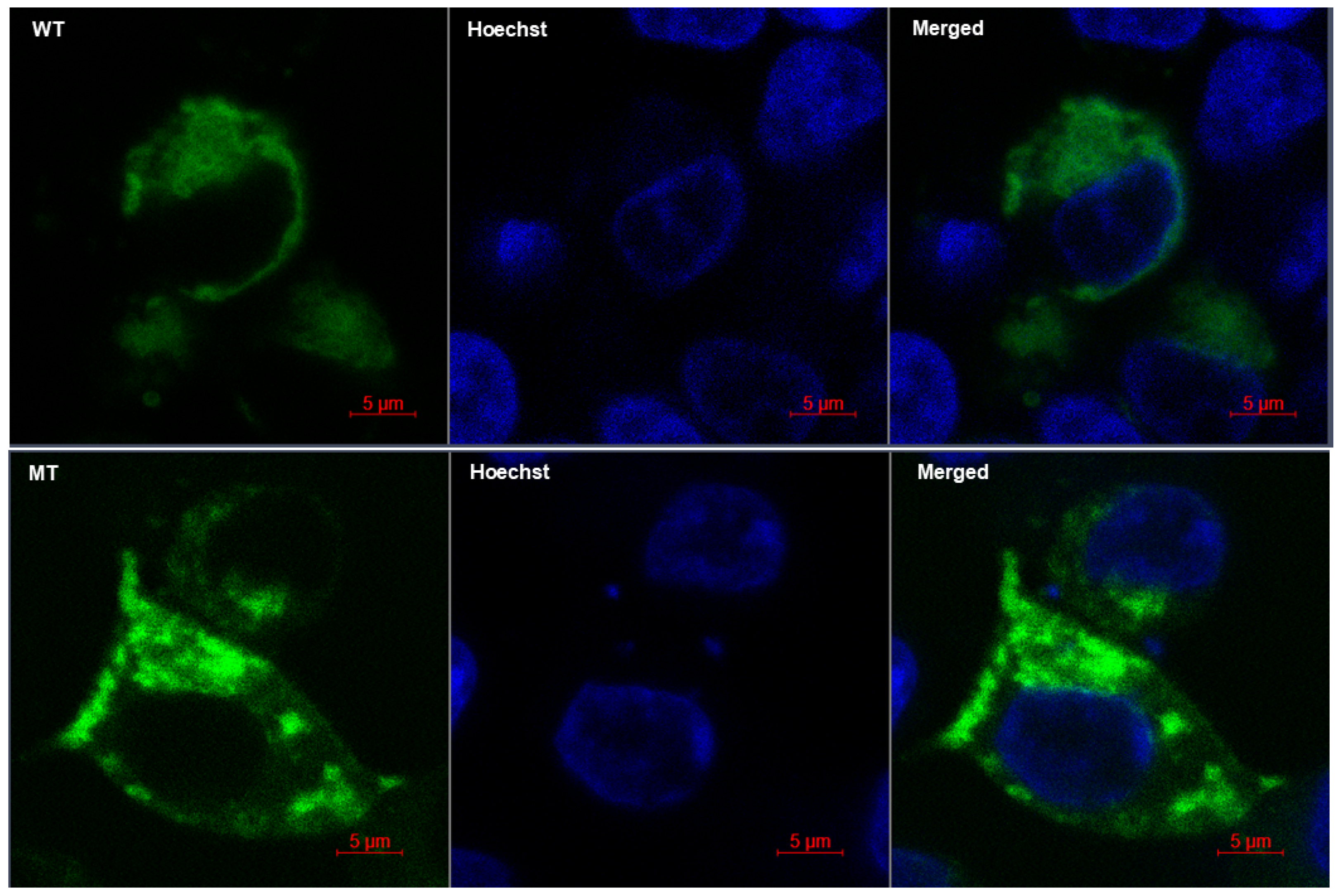
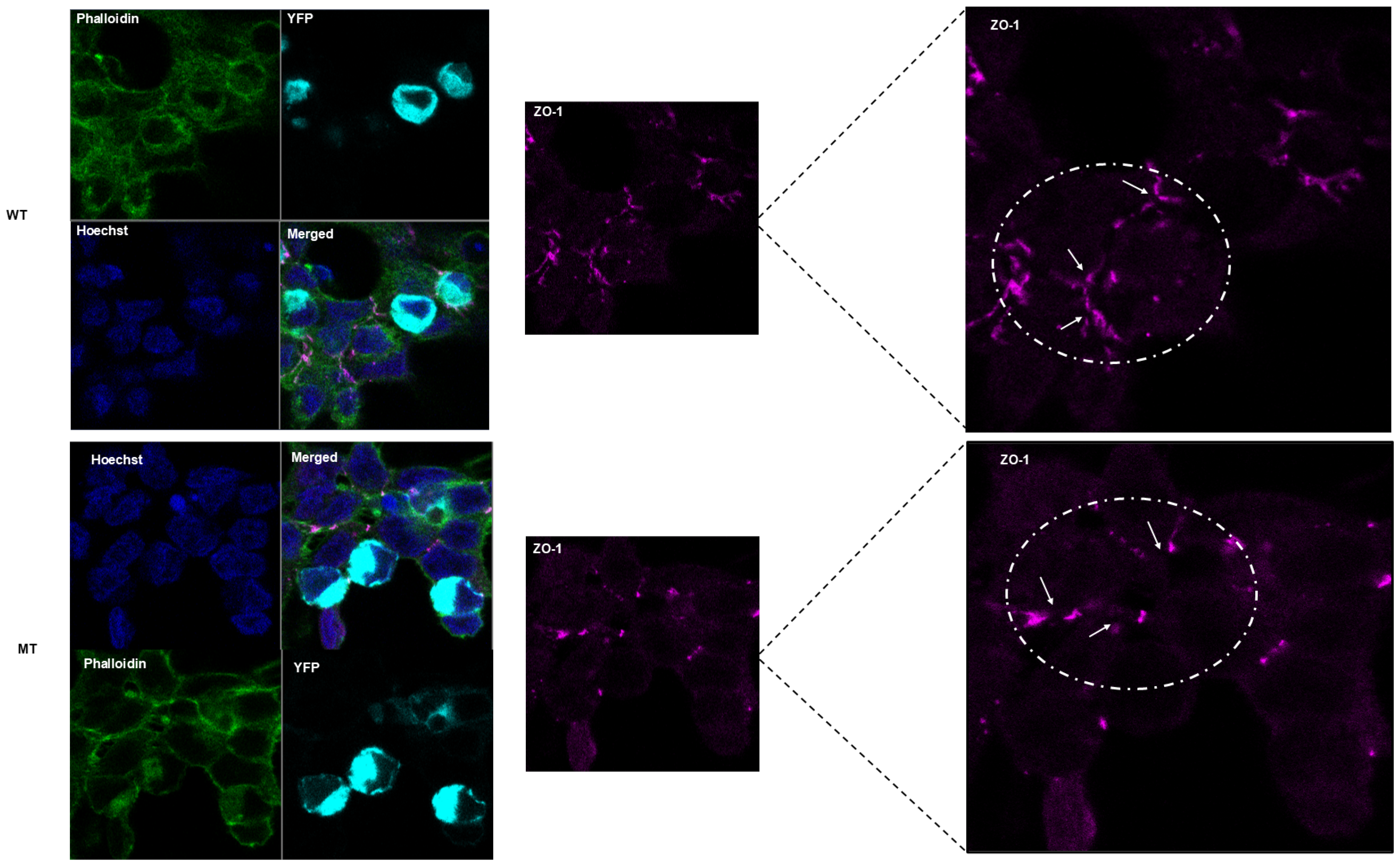
2.7. Cell Morphology, In Vitro Localization, and Cytoskeletal Arrangements
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Approvals
4.2. Participants’ Enrollment and Sample Collection
4.3. Whole Exome Sequencing
4.4. Annotation and Filtering Strategy
4.5. Sanger Sequencing
4.6. Evolutionary Conservation
4.7. MARVELD2 Protein Model Analysis
4.8. HEK-293 Cell In Vitro Functional Assay of the MARVELD2 Variant
4.8.1. Expression Vectors and Site-Directed Mutagenesis
4.8.2. Cell Cultures and Transfections
4.8.3. Western Blot Analysis
4.8.4. Co-Immunoprecipitation Assay
4.8.5. Fluorescent Microscopy
4.8.6. Immunocytochemistry
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAF | Alternative Allele Frequency |
| ACMG | American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics |
| AD | Autosomal Dominant |
| AR | Autosomal Recessive |
| BCA | Bicinchoninic acid |
| BLAST | Basic Local Alignment Search Tool |
| BSA | Bovine Serum Albumin |
| bTJs | Bicellular Tight Junctions |
| CADD | Combined Annotation Dependent Depletion |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| Co-IP | Co-immunoprecipitation |
| DANN | Deleterious Annotation of genetic variants using Neural Networks |
| DFNB29 | Deafness Autosomal Recessive 29 |
| DFNB42 | Deafness Autosomal Recessive 42 |
| DFNB49 | Deafness Autosomal Recessive 49 |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| dupT | Thymine duplication |
| ECL | Enhanced chemiluminescence |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| ENT | Ear, Nose, Throat |
| EP | Endocochlear Potential |
| EYFP | Exogenous Yellow Fluorescence Protein |
| GATK | Genome Analysis Tool Kits |
| GERP | Genomic Evolutionary Rate Profiling |
| GJB2 | Gap Junction Protein Beta 2 |
| GRCh | Human Genome Reference Consortium |
| GTEx | Genotype-Tissue Expression |
| gVCF | Genomic Variant Call Format |
| HEK | Human Embryonic Kidney |
| HHL | Hereditary Hearing Loss |
| HI | Hearing Impairment |
| HPO | Human Phenotype Ontology |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| ILDR1 | Angulin-2 |
| ILDR2 | Angulin-3 |
| JAMs | Junctional Adhesion Molecules |
| LoF | Loss of Function |
| LSR | Angulin-1 |
| MARVELD2 | MARVEL domain-containing protein 2 |
| M-CAP | Mendelian Clinically Applicable Pathogenicity |
| MT | Mutant |
| NCBI | National Center Biotechnology Information |
| NGS | Next-Generation Sequencing |
| NSHI | Non-syndromic hearing impairment |
| OMIM | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man |
| PBS | Phosphate Buffer Saline |
| PDB | Protein Database |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| PROVEAN | Protein Variation Effect Analyzer |
| PTA | Pure Tone Average |
| qPCR | Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| RT | Room Temperature |
| SDM | Site Directed Mutagenesis |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl-sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| SIFT | Sorting Intolerant From Tolerant |
| TJs | Tight Junctions |
| tTJs | Tricellular Tight Junctions |
| WB | Western blot |
| WES | Whole-Exome Sequencing |
| WT | Wild Type |
| YFP | Yellow Florescence Protein |
| ZO-1 | Zonula Occluden-1 |
| ZO-2 | Zonula Occluden-2 |
| ZO-3 | Zonula Occluden-3 |
| Zos | Zonula Occludens |
References
- World Health Organization Deafness and Hearing Loss; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Haile, L.M.; Kamenov, K.; Briant, P.S.; Orji, A.U.; Steinmetz, J.D.; Abdoli, A.; Abdollahi, M.; Abu-Gharbieh, E.; Afshin, A.; Ahmed, H.; et al. Hearing Loss Prevalence and Years Lived with Disability, 1990–2019: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2021, 397, 996–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shearer, A.E.; Hildebrand, M.S.; Sloan, C.M.; Smith, R.J.H. Deafness in the Genomics Era. Hear. Res. 2011, 282, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.J.; Bale Jr, J.F.; White, K.R. Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Children. Lancet 2005, 365, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morton, C.C.; Nance, W.E. Newborn Hearing Screening—A Silent Revolution. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2151–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, J.G.; Geers, A.E. Effects of Early Auditory Experience on the Spoken Language of Deaf Children at 3 Years of Age. Ear Hear. 2006, 27, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borre, E.D.; Kaalund, K.; Frisco, N.; Zhang, G.; Ayer, A.; Kelly-Hedrick, M.; Reed, S.D.; Emmett, S.D.; Francis, H.; Tucci, D.L.; et al. The Impact of Hearing Loss and Its Treatment on Health-Related Quality of Life Utility: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2023, 38, 456–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, A.; Smith, B.; Ray, J. The Impact of Rehabilitation on Quality of Life after Hearing Loss: A Systematic Review. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 275, 2435–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, E.; Jafari, Z.; Gholami, M. Effect of Early Intervention on Language Development in Hearing-Impaired Children. Iran. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 28, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wonkam, A.; Noubiap, J.J.N.; Djomou, F.; Fieggen, K.; Njock, R.; Toure, G.B. Aetiology of Childhood Hearing Loss in Cameroon (Sub-Saharan Africa). Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2013, 56, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adadey, S.M.; Manyisa, N.; Mnika, K.; De Kock, C.; Nembaware, V.; Quaye, O.; Amedofu, G.K.; Awandare, G.A.; Wonkam, A. GJB2 and GJB6 Mutations in Non-Syndromic Childhood Hearing Impairment in Ghana. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 841. [Google Scholar]
- Yalcouyé, A.; Traoré, O.; Taméga, A.; Maïga, A.B.; Kané, F.; Oluwole, O.G.; Guinto, C.O.; Kéita, M.; Timbo, S.K.; DeKock, C.; et al. Etiologies of Childhood Hearing Impairment in Schools for the Deaf in Mali. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 726776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dia, Y.; Loum, B.; Dieng, Y.J.K.B.; Diop, J.P.D.; Adadey, S.M.; Aboagye, E.T.; Ba, S.A.; Touré, A.A.; Niang, F.; Diaga Sarr, P.; et al. Childhood Hearing Impairment in Senegal. Genes 2023, 14, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, I.R.T.; Ceronio, D.; Swart, T.; Joubert, G. Age of Diagnosis of Congenital Hearing Loss: Private v. Public Healthcare Sector. S. Afr. Med. J. 2015, 105, 927–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, A.E.; Hildebrand, M.S.; Smith, R.J. Genetic Hearing Loss Overview. 1999 February 14 [Updated 2023 September 28]. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993–2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Angeli, S.; Lin, X.; Liu, X.Z. Genetics of Hearing and Deafness. Anat. Rec. Adv. Integr. Anat. Evol. Biol. 2012, 295, 1812–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, A.E.; Smith, R.J.H. Genetics: Advances in Genetic Testing for Deafness. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2012, 24, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, V.G.; Smith, R.J.H. Hereditary Hearing Loss Homepage. Available online: https://hereditaryhearingloss.org (accessed on 5 August 2019).
- Mikstiene, V.; Jakaitiene, A.; Byckova, J.; Gradauskiene, E.; Preiksaitiene, E.; Burnyte, B.; Tumiene, B.; Matuleviciene, A.; Ambrozaityte, L.; Uktveryte, I. The High Frequency of GJB2 Gene Mutation c. 313_326del14 Suggests Its Possible Origin in Ancestors of Lithuanian Population. BMC Genet. 2016, 17, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adadey, S.M.; Wonkam-Tingang, E.; Aboagye, E.T.; Quaye, O.; Awandare, G.A.; Wonkam, A. Hearing Loss in Africa: Current Genetic Profile. Hum. Genet. 2022, 141, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcouyé, A.; Schrauwen, I.; Traoré, O.; Bamba, S.; Aboagye, E.T.; Acharya, A.; Bharadwaj, T.; Latanich, R.; Esoh, K.; Fortes-Lima, C.A.; et al. Whole Exome Sequencing Reveals Known and Candidate Genes for Hearing Impairment in Mali. Hum. Genet. Genom. Adv. 2025, 6, 100391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonkam, A.; Adadey, S.M.; Schrauwen, I.; Aboagye, E.T.; Wonkam-Tingang, E.; Esoh, K.; Popel, K.; Manyisa, N.; Jonas, M.; deKock, C.; et al. Exome Sequencing of Families from Ghana Reveals Known and Candidate Hearing Impairment Genes. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergquist, T.; Stenton, S.L.; Nadeau, E.A.W.; Byrne, A.B.; Greenblatt, M.S.; Harrison, S.M.; Tavtigian, S.V.; O’Donnell-Luria, A.; Biesecker, L.G.; Radivojac, P.; et al. Calibration of Additional Computational Tools Expands ClinGen Recommendation Options for Variant Classification with PP3/BP4 Criteria. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejaver, V.; Byrne, A.B.; Feng, B.-J.; Pagel, K.A.; Mooney, S.D.; Karchin, R.; O’Donnell-Luria, A.; Harrison, S.M.; Tavtigian, S.V.; Greenblatt, M.S.; et al. Calibration of Computational Tools for Missense Variant Pathogenicity Classification and ClinGen Recommendations for PP3/BP4 Criteria. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 109, 2163–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, R.C.; Berg, J.S.; Grody, W.W.; Kalia, S.S.; Korf, B.R.; Martin, C.L.; McGuire, A.L.; Nussbaum, R.L.; O’daniel, J.M.; Ormond, K.E. American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. ACMG Recommendations for Reporting of Incidental Findings in Clinical Exome and Genome Sequencing. Genet. Med. 2013, 15, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isken, O.; Maquat, L.E. Quality Control of Eukaryotic mRNA: Safeguarding Cells from Abnormal mRNA Function. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 1833–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaiez, H.; Booth, K.T.; Ephraim, S.S.; Crone, B.; Black-Ziegelbein, E.A.; Marini, R.J.; Shearer, A.E.; Sloan-Heggen, C.M.; Kolbe, D.; Casavant, T.; et al. Genomic Landscape and Mutational Signatures of Deafness-Associated Genes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 103, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuse, M.; Hirase, T.; Itoh, M.; Nagafuchi, A.; Yonemura, S.; Tsukita, S.; Tsukita, S. Occludin: A Novel Integral Membrane Protein Localizing at Tight Junctions. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 123, 1777–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fanning, A.S.; Anderson, J.M.; Lavie, A. Structure of the Conserved Cytoplasmic C-Terminal Domain of Occludin: Identification of the ZO-1 Binding Surface. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 352, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazuddin, S.; Ahmed, Z.M.; Fanning, A.S.; Lagziel, A.; Kitajiri, S.; Ramzan, K.; Khan, S.N.; Chattaraj, P.; Friedman, P.L.; Anderson, J.M.; et al. Tricellulin Is a Tight-Junction Protein Necessary for Hearing. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 79, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozkova, D.S.; Lastuvkova, J.; Stepenkova, H.; Kurotova, M.; Trkova, M.; Myska, P.; Seeman, P. DFNB49 Is an Important Cause of Non-Syndromic Deafness in Czech Roma Patients but Not in the General Czech Population. Clin. Genet. 2012, 82, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chishti, M.S.; Bhatti, A.; Tamim, S.; Lee, K.; McDonald, M.L.; Leal, S.M.; Ahmad, W. Splice-Site Mutations in the TRIC Gene Underlie Autosomal Recessive Nonsyndromic Hearing Impairment in Pakistani Families. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 53, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikenouchi, J.; Furuse, M.; Furuse, K.; Sasaki, H.; Tsukita, S.; Tsukita, S. Tricellulin Constitutes a Novel Barrier at Tricellular Contacts of Epithelial Cells. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 171, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mašindová, I.; Šoltýsová, A.; Varga, L.; Mátyás, P.; Ficek, A.; Hučková, M.; Sůrová, M.; Šafka-Brožková, D.; Anwar, S.; Bene, J.; et al. MARVELD2 (DFNB49) Mutations in the Hearing Impaired Central European Roma Population—Prevalence, Clinical Impact and the Common Origin. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, G.; Varga, L.; Trincot, C.; Shahzad, M.; Friedman, P.L.; Klimes, I.; Greienwald, J.H., Jr. Molecular Genetics of MARVELD2 and Clinical Phenotype in Pakistani and Slovak Families Segregating DFNB49 Hearing Loss. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 176, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, Z.; Chavoshi Tarzjani, S.P.; Miri Moosavi, R.S.; Saber, S.; Ebrahimi, A. A Rare Mutation in the MARVELD2 Gene Can Cause Nonsyndromic Hearing Loss. Int. Med. Case Rep. J. 2020, 13, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabaiefar, M.A.; Alasti, F.; Zohour, M.M.; Shariati, L.; Farrokhi, E.; Farhud, D.D.; Camp, G.V.; Noori-Daloii, M.R.; Chaleshtori, M.H. Genetic Linkage Analysis of 15 DFNB Loci in a Group of Iranian Families with Autosomal Recessive Hearing Loss. Iran. J. Public Health 2011, 40, 34–48. [Google Scholar]
- Taghipour-Sheshdeh, A.; Nemati-Zargaran, F.; Zarepour, N.; Tahmasebi, P.; Saki, N.; Tabatabaiefar, M.A.; Mohammadi-Asl, J.; Hashemzadeh-Chaleshtori, M. A Novel Pathogenic Variant in the MARVELD2 Gene Causes Autosomal Recessive Non-Syndromic Hearing Loss in an Iranian Family. Genomics 2019, 111, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Meng, W.F.; Zhang, C.F.; Liu, H.Q.; Yao, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Guan, M.X. New SNP Variants of MARVELD2 (DFNB49) Associated with Non-Syndromic Hearing Loss in Chinese Population. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2019, 20, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamitani, T.; Sakaguchi, H.; Tamura, A.; Miyashita, T.; Yamazaki, Y.; Tokumasu, R.; Inamoto, R.; Matsubara, A.; Mori, N.; Hisa, Y.; et al. Deletion of Tricellulin Causes Progressive Hearing Loss Associated with Degeneration of Cochlear Hair Cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babanejad, M.; Fattahi, Z.; Bazazzadegan, N.; Nishimura, C.; Meyer, N.; Nikzat, N.; Sohrabi, E.; Najmabadi, A.; Jamali, P.; Habibi, F.; et al. A Comprehensive Study to Determine Heterogeneity of Autosomal Recessive Nonsyndromic Hearing Loss in Iran. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2012, 158, 2485–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, S.M.; Amasheh, S.; Richter, J.F.; Milatz, S.; Günzel, D.; Westphal, J.K.; Huber, O.; Schulzke, J.D.; Fromm, M. Tricellulin Forms a Barrier to Macromolecules in Tricellular Tight Junctions without Affecting Ion Permeability. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 3713–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, K.; Shaikh, R.S.; Ahmad, J.; Khan, S.N.; Riazuddin, S.; Ahmed, Z.M.; Friedman, T.B.; Wilcox, E.R.; Riazuddin, S. A New Locus for Nonsyndromic Deafness DFNB49 Maps to Chromosome 5q12.3-Q14.1. Hum. Genet. 2005, 116, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, T.; Lenz, D.R.; Furuse, M.; Avraham, K.B. A “Tric” to Tighten Cell-Cell Junctions in the Cochlea for Hearing. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3712–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikenouchi, J.; Sasaki, H.; Tsukita, S.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S. Loss of Occludin Affects Tricellular Localization of Tricellulin. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 4687–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-de Usera, A.; Lorenzo-Salazar, J.M.; Rubio-Rodríguez, L.A.; Muñoz-Barrera, A.; Guillen-Guio, B.; Marcelino-Rodríguez, I.; García-Olivares, V.; Mendoza-Alvarez, A.; Corrales, A.; Íñigo-Campos, A.; et al. Evaluation of Whole-Exome Enrichment Solutions: Lessons from the High-End of the Short-Read Sequencing Scale. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce Framework for Analyzing next-Generation DNA Sequencing Data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar]
- Oza, A.M.; DiStefano, M.T.; Hemphill, S.E.; Cushman, B.J.; Grant, A.R.; Siegert, R.K.; Shen, J.; Chapin, A.; Boczek, N.J.; Schimmenti, L.A.; et al. Expert Specification of the ACMG/AMP Variant Interpretation Guidelines for Genetic Hearing Loss. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 1593–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoffroy, V.; Herenger, Y.; Kress, A.; Stoetzel, C.; Piton, A.; Dollfus, H.; Muller, J. AnnotSV: An Integrated Tool for Structural Variations Annotation. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3572–3574. [Google Scholar]
- Smedley, D.; Haider, S.; Ballester, B.; Holland, R.; London, D.; Thorisson, G.; Kasprzyk, A. BioMart–Biological Queries Made Easy. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 22. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, J.R.; Ziman, R.; Yuen, R.K.; Feuk, L.; Scherer, S.W. The Database of Genomic Variants: A Curated Collection of Structural Variation in the Human Genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D986–D992. [Google Scholar]
- Okonechnikov, K.; Golosova, O.; Fursov, M. Unipro UGENE: A Unified Bioinformatics Toolkit. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1166–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuetz, A.; Radusheva, V.; Krug, S.M.; Heinemann, U. Crystal Structure of the Tricellulin C-Terminal Coiled-Coil Domain Reveals a Unique Mode of Dimerization. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1405, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasini, M.; Bienert, S.; Waterhouse, A.; Arnold, K.; Studer, G.; Schmidt, T.; Kiefer, F.; Gallo Cassarino, T.; Bertoni, M.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Modelling Protein Tertiary and Quaternary Structure Using Evolutionary Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W252–W258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Twumasi Aboagye, E.; Adadey, S.M.; Alves de Souza Rios, L.; Esoh, K.K.; Wonkam-Tingang, E.; Xhakaza, L.; De Kock, C.; Schrauwen, I.; Amenga-Etego, L.; Lang, D.; et al. Bi-Allelic MARVELD2 Variant Identified with Exome Sequencing in a Consanguineous Multiplex Ghanaian Family Segregating Non-Syndromic Hearing Loss. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073337
Twumasi Aboagye E, Adadey SM, Alves de Souza Rios L, Esoh KK, Wonkam-Tingang E, Xhakaza L, De Kock C, Schrauwen I, Amenga-Etego L, Lang D, et al. Bi-Allelic MARVELD2 Variant Identified with Exome Sequencing in a Consanguineous Multiplex Ghanaian Family Segregating Non-Syndromic Hearing Loss. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073337
Chicago/Turabian StyleTwumasi Aboagye, Elvis, Samuel Mawuli Adadey, Leonardo Alves de Souza Rios, Kevin K. Esoh, Edmond Wonkam-Tingang, Lettilia Xhakaza, Carmen De Kock, Isabelle Schrauwen, Lucas Amenga-Etego, Dirk Lang, and et al. 2025. "Bi-Allelic MARVELD2 Variant Identified with Exome Sequencing in a Consanguineous Multiplex Ghanaian Family Segregating Non-Syndromic Hearing Loss" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073337
APA StyleTwumasi Aboagye, E., Adadey, S. M., Alves de Souza Rios, L., Esoh, K. K., Wonkam-Tingang, E., Xhakaza, L., De Kock, C., Schrauwen, I., Amenga-Etego, L., Lang, D., Awandare, G. A., Leal, S. M., Mowla, S., & Wonkam, A. (2025). Bi-Allelic MARVELD2 Variant Identified with Exome Sequencing in a Consanguineous Multiplex Ghanaian Family Segregating Non-Syndromic Hearing Loss. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3337. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073337






