Apelin/APJ: Another Player in the Cancer Biology Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Apelin/APJ System in Cancer
2.1. Role of Apelin/APJ as a Prognostic Marker in Different Human Cancers
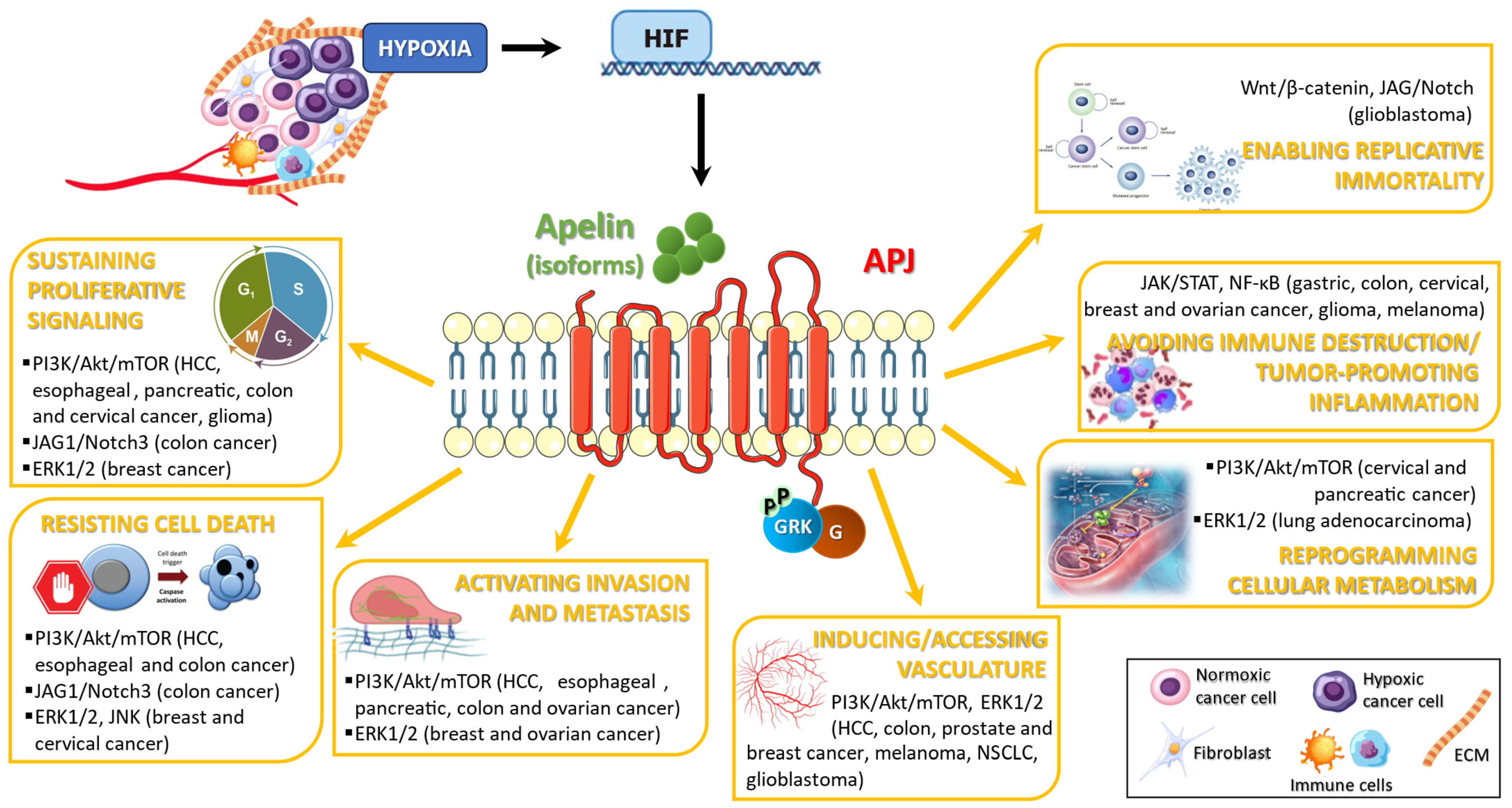
2.2. Apelin/APJ Affects the Hallmarks of Cancer: Evidence from In Vitro and In Vivo Models
2.2.1. Sustaining Proliferative Signaling
2.2.2. Resisting Cell Death
2.2.3. Activating Invasion and Metastasis
2.2.4. Inducing/Accessing Vasculature
2.2.5. Reprogramming Cellular Metabolism
2.2.6. Avoiding Immune Destruction and Tumor-Promoting Inflammation
2.2.7. Enabling Replicative Immortality
3. Apelin/APJ and Drug Resistance in Cancer
3.1. Main Mechanisms of Drug Resistance in Cancer: The Interplay of the Apelin/APJ System
3.2. The Apelinergic System as a Risk Factor and Drug Resistance: Evidence from Experimental Models and Clinical Studies
3.2.1. Lung Cancer
3.2.2. Colon Cancer
3.2.3. Gastric Cancer
3.2.4. Hepatocellular Cancer (HCC)
3.2.5. Breast Cancer
3.2.6. Glioblastoma
3.2.7. Chondrosarcoma
3.2.8. Prostate Cancer
3.2.9. Ovarian Cancer
4. Apelin/APJ System Inhibitors and Antagonists
5. MiRNA Expression and the Apelin System in Cancer
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Dowd, B.F.; Heiber, M.; Chan, A.; Heng, H.H.; Tsui, L.C.; Kennedy, J.L.; Shi, X.; Petronis, A.; George, S.R.; Nguyen, T. A Human Gene That Shows Identity with the Gene Encoding the Angiotensin Receptor Is Located on Chromosome 11. Gene 1993, 136, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durham, A.L.; Speer, M.Y.; Scatena, M.; Giachelli, C.M.; Shanahan, C.M. Role of Smooth Muscle Cells in Vascular Calcification: Implications in Atherosclerosis and Arterial Stiffness. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, H.; Chen, L. Apelin/APJ System: A Critical Regulator of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 5180–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.K.; Cheng, R.; Nguyen, T.; Fan, T.; Kariyawasam, A.P.; Liu, Y.; Osmond, D.H.; George, S.R.; O’Dowd, B.F. Characterization of Apelin, the Ligand for the APJ Receptor. J. Neurochem. 2000, 74, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antushevich, H.; Wójcik, M. Review: Apelin in Disease. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2018, 483, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughal, A.; O’Rourke, S.T. Vascular Effects of Apelin: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 190, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Prabhavalkar, K.S.; Bhatt, L.K. Elabela Peptide: An Emerging Target in Therapeutics. Curr. Drug Targets 2022, 23, 1304–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.; Tan, S.Y.X.; Wee, S.; Wu, Y.; Tan, S.J.C.; Ramakrishna, N.B.; Chng, S.C.; Nama, S.; Szczerbinska, I.; Chan, Y.-S.; et al. ELABELA Is an Endogenous Growth Factor That Sustains HESC Self-Renewal via the PI3K/AKT Pathway. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 17, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurowska, P.; Barbe, A.; Różycka, M.; Chmielińska, J.; Dupont, J.; Rak, A. Apelin in Reproductive Physiology and Pathology of Different Species: A Critical Review. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 9170480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Chen, R.; Jiang, Y.; Bai, B.; Yang, T.; Liu, H. The Protective Effects and Mechanisms of Apelin/APJ System on Ischemic Stroke: A Promising Therapeutic Target. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, B.; Li, G.; Bai, B. Temporal Expression of Apelin/Apelin Receptor in Ischemic Stroke and Its Therapeutic Potential. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibbi, B.; Marroncini, G.; Naldi, L.; Peri, A. The Yin and Yang Effect of the Apelinergic System in Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medhurst, A.D.; Jennings, C.A.; Robbins, M.J.; Davis, R.P.; Ellis, C.; Winborn, K.Y.; Lawrie, K.W.M.; Hervieu, G.; Riley, G.; Bolaky, J.E.; et al. Pharmacological and Immunohistochemical Characterization of the APJ Receptor and Its Endogenous Ligand Apelin. J. Neurochem. 2003, 84, 1162–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorli, S.C.; Le Gonidec, S.; Knibiehler, B.; Audigier, Y. Apelin Is a Potent Activator of Tumour Neoangiogenesis. Oncogene 2007, 26, 7692–7699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Wang, G.; Qi, X.; Lee, H.M.; Englander, E.W.; Greeley, G.H.J. A Possible Role for Hypoxia-Induced Apelin Expression in Enteric Cell Proliferation. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 294, R1832–R1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lv, S.-Y.; Ye, W.; Zhang, L. Apelin/APJ System and Cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 457, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Q.; Jiao, X.; Ye, J.; Hao, Y.; Gao, Q.; Ma, G.; et al. APLN Promotes the Proliferation, Migration, and Glycolysis of Cervical Cancer through the PI3K/AKT/MTOR Pathway. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 755, 109983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, X.; Zheng, J.; Chen, J.; Xue, H.; Zheng, X. APLN: A Potential Novel Biomarker for Cervical Cancer. Sci. Prog. 2021, 104, 368504211011341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinkaya, S.O.; Nergiz, S.; Küçük, M.; Yüksel, H. Apelin Levels Are Higher in Obese Patients with Endometrial Cancer. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2015, 41, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Cui, Z.; Peng, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X. Apelin Is Associated with Clinicopathological Parameters and Prognosis in Breast Cancer Patients. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2022, 306, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grupińska, J.; Budzyń, M.; Brzeziński, J.J.; Gryszczyńska, B.; Kasprzak, M.P.; Kycler, W.; Leporowska, E.; Iskra, M. Association between Clinicopathological Features of Breast Cancer with Adipocytokine Levels and Oxidative Stress Markers before and after Chemotherapy. Biomed. Rep. 2021, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wong, C.-C.; Liu, D.; Go, M.Y.Y.; Wu, B.; Peng, S.; Kuang, M.; Wong, N.; Yu, J. APLN Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Activating PI3K/Akt Pathway and Is a Druggable Target. Theranostics 2019, 9, 5246–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.; Park, C.-K.; Ha, S.Y. Prognostic Role of Apelin Receptor Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated With Curative Surgical Resection. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 3025–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Zhu, X.; Pan, T.; Liu, Z.; Shangguan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Q. Apelin (APLN) Is a Biomarker Contributing to the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakowska, D.; Markocka-Mączka, K.; Szelachowski, P.; Grabowski, K. Serum Levels of Resistin, Adiponectin, and Apelin in Gastroesophageal Cancer Patients. Dis. Mark. 2014, 2014, 619649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Yun, D.; Cui, Q.; Wu, X.; Lu, W.; Yang, X.; Zhang, M. Inhibition of APLN Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Migration and Promotes Cell Apoptosis in Esophageal Cancer Cells In Vitro, through Activating PI3K/MTOR Signaling Pathway. Eur. J. Histochem. 2022, 66, 3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Yao, G.; Yu, H.; Qing, Y.; Wang, K. Tumor Apelin, Not Serum Apelin, Is Associated with the Clinical Features and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berta, J.; Kenessey, I.; Dobos, J.; Tovari, J.; Klepetko, W.; Jan Ankersmit, H.; Hegedus, B.; Renyi-Vamos, F.; Varga, J.; Lorincz, Z.; et al. Apelin Expression in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Role in Angiogenesis and Prognosis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.; Ehrlich, L.; Venter, J.; O’Brien, A.; White, T.; Zhou, T.; Dang, T.; Meng, F.; Invernizzi, P.; Bernuzzi, F.; et al. Inhibition of the Apelin/Apelin Receptor Axis Decreases Cholangiocarcinoma Growth. Cancer Lett. 2017, 386, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soylu, H.; Unal, B.; Aksu, K.; Avci, S.; Caylan, A.E.; Ustunel, I.I. Evaluation of Angiogenic Apelin/Apelin Receptor Axis in Normal Prostate, High Grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Prostatic Adenocarcinoma. Malays. J. Pathol. 2022, 44, 461–467. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Xi, M.; Wan, S.; Hua, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, H.; Jiang, F.; Zhong, W. Dysregulated MicroRNA-224/Apelin Axis Associated with Aggressive Progression and Poor Prognosis in Patients with Prostate Cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelakantan, D.; Dogra, S.; Devapatla, B.; Jaiprasart, P.; Mukashyaka, M.C.; Janknecht, R.; Dwivedi, S.K.D.; Bhattacharya, R.; Husain, S.; Ding, K.; et al. Multifunctional APJ Pathway Promotes Ovarian Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 1378–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podgórska, M.; Diakowska, D.; Pietraszek-Gremplewicz, K.; Nienartowicz, M.; Nowak, D. Evaluation of Apelin and Apelin Receptor Level in the Primary Tumor and Serum of Colorectal Cancer Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-P.; Sun, X.-Q.; Yuan, S.-J. APLNR Stimulates the Development of Glioma via the NFAT5/AKT Feedback Loop. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 10594–10600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, Y.-L.; Li, X.-Q.; Zhang, Z. High Apelin Level Indicates a Poor Prognostic Factor in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Dis. Mark. 2019, 2019, 4586405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktan, M.; Ozmen, H.K. A Preliminary Study of Serum Apelin Levels in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer. Eurasian J. Med. 2019, 51, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, K.; Kim, Y.H.; Sung, H.J.; Li, H.Y.; Yoo, C.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, U.L.; Nam, B.H.; Kim, E.O.; et al. Hypoxia-Induced up-Regulation of Apelin Is Associated with a Poor Prognosis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, T.; Demir, L.; Varol, U.; Akyol, M.; Oflazoglu, U.; Yildiz, Y.; Taskaynatan, H.; Cengiz, H.; Guvendi, G.; Kucukzeybek, Y.; et al. Serum Apelin Levels and Body Composition Changes in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with an Aromatase Inhibitor. J. Buon. 2016, 21, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar]
- Maden, M.; Pamuk, O.N.; Pamuk, G.E. High Apelin Levels Could Be Used as a Diagnostic Marker in Multiple Myeloma: A Comparative Study. Cancer Biomark. 2016, 17, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Su, T.; Lv, D.; Xie, F.; Liu, W.; Cao, J.; Sheikh, I.A.; Qin, X.; Li, L.; Chen, L. ERK1/2 Mediates Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Proliferation and Autophagy Induced by Apelin-13. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2014, 46, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; An, Y.; Dong, H.; Xie, L.; Zheng, H.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Teng, T.; Wang, Q.; Yan, Z.; et al. High APLN Expression Predicts Poor Prognosis for Glioma Patients. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 8393336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harford-Wright, E.; Andre-Gregoire, G.; Jacobs, K.A.; Treps, L.; Le Gonidec, S.; Leclair, H.M.; Gonzalez-Diest, S.; Roux, Q.; Guillonneau, F.; Loussouarn, D.; et al. Pharmacological Targeting of Apelin Impairs Glioblastoma Growth. Brain 2017, 140, 2939–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacquaniti, A.; Altavilla, G.; Picone, A.; Donato, V.; Chirico, V.; Mondello, P.; Aloisi, C.; Marabello, G.; Loddo, S.; Buemi, A.; et al. Apelin beyond Kidney Failure and Hyponatremia: A Useful Biomarker for Cancer Disease Progression Evaluation. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 15, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acik, D.Y.; Bankir, M.; Baylan, F.A.; Aygun, B. Can ELABELA Be a Novel Target in the Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia? BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, D.; Cai, C.; Sims, M.M.; Yang, C.H.; Thomas, M.; Cheng, J.; Saad, A.G.; Pfeffer, L.M. APELA Expression in Glioma, and Its Association with Patient Survival and Tumor Grade. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawauchi, K.; Ogasawara, T.; Yasuyama, M.; Otsuka, K.; Yamada, O. The PI3K/Akt Pathway as a Target in the Treatment of Hematologic Malignancies. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wei, J.; Liu, P. Attacking the PI3K/Akt/MTOR Signaling Pathway for Targeted Therapeutic Treatment in Human Cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 85, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Almagro, C.; Auriau, J.; Dortignac, A.; Clerc, P.; Lulka, H.; Deleruyelle, S.; Projetti, F.; Nakhlé, J.; Frances, A.; Berta, J.; et al. Upregulated Apelin Signaling in Pancreatic Cancer Activates Oncogenic Signaling Pathways to Promote Tumor Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picault, F.-X.; Chaves-Almagro, C.; Projetti, F.; Prats, H.; Masri, B.; Audigier, Y. Tumour Co-Expression of Apelin and Its Receptor Is the Basis of an Autocrine Loop Involved in the Growth of Colon Adenocarcinomas. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, N.; Xu, G.-M.; Liu, T.-J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Huo, S.-B.; Zhang, K. Apelin13/APJ Promotes Proliferation of Colon Carcinoma by Activating Notch3 Signaling Pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 101697–101706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Li, F.; Wang, P.; Jia, S.; Sun, L.; Huo, H. Apelin-13 Induces MCF-7 Cell Proliferation and Invasion via Phosphorylation of ERK1/2. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchelaghem, R.; Mader, S.; Gaboury, L.; Messarah, M.; Boumendjel, M.; Boumendjel, A. Estrogens Desensitize MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells to Apelin-Induced Autophagy and Enhanced Growth under Estrogen Starvation: A Possible Implication in Endocrine Resistance. Cell Mol. Biol. 2022, 68, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Gogola, J.; Ptak, A. Apelin Abrogates the Stimulatory Effects of 17β-Estradiol and Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 on Proliferation of Epithelial and Granulosa Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines via Crosstalk between APLNR and ERα/IGF1R. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 6325–6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Tsai, S.-H.; Cheng, J.-C.; Wang, E.Y.; Anglesio, M.S.; Cochrane, D.R.; Fuller, M.; Gibb, E.A.; Wei, W.; Huntsman, D.G.; et al. APELA Promotes Tumour Growth and Cell Migration in Ovarian Cancer in a P53-Dependent Manner. Gynecol. Oncol. 2017, 147, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, M.S. Targeting BCL-2 in B-Cell Lymphomas. Blood 2017, 130, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Chen, L. Novel Pathogenesis: Regulation of Apoptosis by Apelin/APJ System. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2017, 49, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.; Deng, X. Nicotine Inactivation of the Proapoptotic Function of Bax through Phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 10781–10789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgering, B.M.T.; Medema, R.H. Decisions on Life and Death: FOXO Forkhead Transcription Factors Are in Command When PKB/Akt Is off Duty. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2003, 73, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, L.D.; Donner, D.B. The PTEN, Mdm2, P53 Tumor Suppressor-Oncoprotein Network. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berta, J.; Hoda, M.A.; Laszlo, V.; Rozsas, A.; Garay, T.; Torok, S.; Grusch, M.; Berger, W.; Paku, S.; Renyi-Vamos, F.; et al. Apelin Promotes Lymphangiogenesis and Lymph Node Metastasis. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 4426–4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, N.K.; Sharma, D.; Ding, X.; Lin, S.; Marra, F.; Merlin, D.; Anania, F.A. Concomitant Activation of the JAK/STAT, PI3K/AKT, and ERK Signaling Is Involved in Leptin-Mediated Promotion of Invasion and Migration of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2497–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PodgÓrska, M.; Pietraszek-Gremplewicz, K.; OlszaŃska, J.; Nowak, D. The Role of Apelin and Apelin Receptor Expression in Migration and Invasiveness of Colon Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoumi, J.; Jafarzadeh, A.; Khorramdelazad, H.; Abbasloui, M.; Abdolalizadeh, J.; Jamali, N. Role of Apelin/APJ Axis in Cancer Development and Progression. Adv. Med. Sci. 2020, 65, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrella, G.; Hou, M.; Li, M.; Stoecklein, V.M.; Zdouc, N.; Volmar, M.N.M.; Miletic, H.; Reinhard, S.; Herold-Mende, C.C.; Kleber, S.; et al. Targeting APLN/APLNR Improves Antiangiogenic Efficiency and Blunts Proinvasive Side Effects of VEGFA/VEGFR2 Blockade in Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 2298–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kälin, R.E.; Kretz, M.P.; Meyer, A.M.; Kispert, A.; Heppner, F.L.; Brändli, A.W. Paracrine and Autocrine Mechanisms of Apelin Signaling Govern Embryonic and Tumor Angiogenesis. Dev. Biol. 2007, 305, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Li, L.; Lu, Q.; Li, Y.; Xie, F.; Li, H.; Cao, J.; Liu, M.; Wu, D.; He, L.; et al. PAK1-Cofilin Phosphorylation Mediates Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells Migration Induced by Apelin-13. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2016, 43, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehnman, M.; Larsson, O. Microenvironmental Targets in Sarcoma. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, Y.; Saito, K.; Iioka, H.; Sakamoto, I.; Kanda, Y.; Sakaguchi, M.; Horii, A.; Kondo, E. PLOD2 Is Essential to Functional Activation of Integrin Β1 for Invasion/Metastasis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. iScience 2020, 23, 100850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Xu, R. Roles of PLODs in Collagen Synthesis and Cancer Progression. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, N.T.N.; Lai, C.-Y.; Tsai, H.-C.; Huang, Y.-L.; Liu, S.-C.; Tsai, C.-H.; Fong, Y.-C.; Tzeng, H.-E.; Tang, C.-H. Apelin Promotes Osteosarcoma Metastasis by Upregulating PLOD2 Expression via the Hippo Signaling Pathway and Hsa_circ_0000004/MiR-1303 Axis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.K.; Qin, R.-Y. Mechanism and Its Regulation of Tumor-Induced Angiogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 9, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Jiménez, F.; Pérez-Pérez, A.; de la Cruz-Merino, L.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Obesity and Breast Cancer: Role of Leptin. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribesalgo, I.; Hoffmann, D.; Zhang, Y.; Kavirayani, A.; Lazovic, J.; Berta, J.; Novatchkova, M.; Pai, T.-P.; Wimmer, R.A.; László, V.; et al. Apelin Inhibition Prevents Resistance and Metastasis Associated with Anti-Angiogenic Therapy. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e9266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-T.; Mu, L.-Q.; Dai, W.; Wang, C.-B.; Liu, X.-Y.; Xiang, D.-X. Preparation, Characterization, and Evaluation of Antitumor Effect of Brucea Javanica Oil Cationic Nanoemulsions. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2515–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernier-Latmani, J.; Cisarovsky, C.; Mahfoud, S.; Ragusa, S.; Dupanloup, I.; Barras, D.; Renevey, F.; Nassiri, S.; Anderle, P.; Squadrito, M.L.; et al. Apelin-Driven Endothelial Cell Migration Sustains Intestinal Progenitor Cells and Tumor Growth. Nat. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 1, 476–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Huo, X.; Ling, Y.; Lv, X.; Lin, S.; Song, H. Single-Cell and Spatial Transcriptomics Reveal Apelin/APJ Pathway’s Role in Microvessel Formation and Tumour Progression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e70152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidoya, H.; Kunii, N.; Naito, H.; Muramatsu, F.; Okamoto, Y.; Nakayama, T.; Takakura, N. The Apelin/APJ System Induces Maturation of the Tumor Vasculature and Improves the Efficiency of Immune Therapy. Oncogene 2012, 31, 3254–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakariassen, P.Ø.; Prestegarden, L.; Wang, J.; Skaftnesmo, K.-O.; Mahesparan, R.; Molthoff, C.; Sminia, P.; Sundlisaeter, E.; Misra, A.; Tysnes, B.B.; et al. Angiogenesis-Independent Tumor Growth Mediated by Stem-like Cancer Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16466–16471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talasila, K.M.; Soentgerath, A.; Euskirchen, P.; Rosland, G.V.; Wang, J.; Huszthy, P.C.; Prestegarden, L.; Skaftnesmo, K.O.; Sakariassen, P.Ø.; Eskilsson, E.; et al. EGFR Wild-Type Amplification and Activation Promote Invasion and Development of Glioblastoma Independent of Angiogenesis. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 125, 683–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, A.; Kälin, S.; Monk, R.; Radke, J.; Heppner, F.L.; Kälin, R.E. Apelin Controls Angiogenesis-Dependent Glioblastoma Growth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Qin, Y.; Ji, S.; Xu, W.; Liu, W.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, M.; Ni, Q.; Yu, X.; et al. UHRF1 Promotes Aerobic Glycolysis and Proliferation via Suppression of SIRT4 in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 452, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, X.; Xu, L.; Batu, W.; Li, Y.; Guo, B.; et al. RSL3 Enhances the Antitumor Effect of Cisplatin on Prostate Cancer Cells via Causing Glycolysis Dysfunction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 192, 114741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatenby, R.A.; Gillies, R.J. Glycolysis in Cancer: A Potential Target for Therapy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; He, X.; Chen, J.-X. Endothelial Sirtuin 3 Dictates Glucose Transport to Cardiomyocyte and Sensitizes Pressure Overload-Induced Heart Failure. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e015895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, Q.; Huang, W.; Li, L.; Xie, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Meng, Y. Apelin-13 Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses and Acute Lung Injury by Regulating PFKFB3-Driven Glycolysis Induced by NOX4-Dependent ROS. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 2121–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, Q.; Wan, H.; Hu, Y.; Xing, S.; Yang, H.; Gao, Y.; He, Z. PI3K-Akt-MTOR/PFKFB3 Pathway Mediated Lung Fibroblast Aerobic Glycolysis and Collagen Synthesis in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Lab. Investig. 2020, 100, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massari, F.; Ciccarese, C.; Santoni, M.; Iacovelli, R.; Mazzucchelli, R.; Piva, F.; Scarpelli, M.; Berardi, R.; Tortora, G.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; et al. Metabolic Phenotype of Bladder Cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2016, 45, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashmi, R.; DeSelm, C.; Helms, C.; Bowcock, A.; Rogers, B.E.; Rader, J.L.; Rader, J.; Grigsby, P.W.; Schwarz, J.K. AKT Inhibitors Promote Cell Death in Cervical Cancer through Disruption of MTOR Signaling and Glucose Uptake. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanan, P.; Srikumar, I.F.; Talwar, P. Autophagy: The Spotlight for Cellular Stress Responses. Life Sci. 2017, 188, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Coussens, L.M. Accessories to the Crime: Functions of Cells Recruited to the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Fan, Y.; Yu, X.; Mao, X.; Jin, F. PTBP1 Promotes the Growth of Breast Cancer Cells through the PTEN/Akt Pathway and Autophagy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 8930–8939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera-Ramirez, L.; Vodnala, S.K.; Nini, R.; Hunter, K.W.; Green, J.E. Autophagy Promotes the Survival of Dormant Breast Cancer Cells and Metastatic Tumour Recurrence. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, M.; Xu, C.; Liu, F.; Bian, L.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Li, D. Autophagy Inhibition Enhances Celecoxib-Induced Apoptosis in Osteosarcoma. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, J.; Glogowska, A.; Thliveris, J.; Kalantari, F.; Shojaei, S.; Hombach-Klonisch, S.; Klonisch, T.; Ghavami, S. Autophagy Modulates Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2018, 1865, 749–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, L.; Zong, Z.; Hua, X.; Su, D.; Li, H.; et al. Autophagy Promotes Metastasis and Glycolysis by Upregulating MCT1 Expression and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway Activation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.-F.; Shi, Y.-H.; Ding, Z.-B.; Ke, A.-W.; Gu, C.-Y.; Hui, B.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, S.-J.; Dai, Z.; Fan, J. Autophagy Inhibition Suppresses Pulmonary Metastasis of HCC in Mice via Impairing Anoikis Resistance and Colonization of HCC Cells. Autophagy 2013, 9, 2056–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z.; Xie, X.; Cao, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.D.; Fan, H.; Liu, Z. Autophagy Facilitates TLR4- and TLR3-Triggered Migration and Invasion of Lung Cancer Cells through the Promotion of TRAF6 Ubiquitination. Autophagy 2014, 10, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Luo, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Huang, S.; Tang, M.; Yang, L.; Lu, L.; et al. Apelin/APJ Signaling Activates Autophagy to Promote Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Migration. Life Sci. 2021, 281, 119763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, R.; Edberg, D.D.; Li, Y. Architectural Transcription Factor HMGI(Y) Promotes Tumor Progression and Mesenchymal Transition of Human Epithelial Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 575–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resar, L.; Chia, L.; Xian, L. Lessons from the Crypt: HMGA1-Amping up Wnt for Stem Cells and Tumor Progression. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1890–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, T.-K.; Her, N.-G.; Lee, M.-G.; Ryu, B.-K.; Lee, J.-H.; Han, J.; Jeong, S.-I.; Kang, M.-J.; Kim, N.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; et al. Caveolin-1 Increases Aerobic Glycolysis in Colorectal Cancers by Stimulating HMGA1-Mediated GLUT3 Transcription. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 4097–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.D.; Zhang, X.; Belton, A.S.; Xian, L.; Huso, T.; Park, J.-J.; Siems, W.F.; Gang, D.R.; Resar, L.M.S.; Reeves, R.; et al. HMGA1 Drives Metabolic Reprogramming of Intestinal Epithelium during Hyperproliferation, Polyposis, and Colorectal Carcinogenesis. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 1420–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. High Mobility Group Proteins and Their Post-Translational Modifications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1784, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Bu, H.; Huang, H.; Chen, H.; Ran, J.; Qin, L.; Ni, Y.; Yao, M.; Song, T.; et al. Apelin-Mediated Deamidation of HMGA1 Promotes Tumorigenesis by Enhancing SREBP1 Activity and Lipid Synthesis. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 3722–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsumi, T.; Singh, R.; Sabharwal, L.; Bando, H.; Meng, J.; Arima, Y.; Yamada, M.; Harada, M.; Jiang, J.-J.; Kamimura, D.; et al. Inflammation Amplifier, a New Paradigm in Cancer Biology. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, D.; Cang, H.; Guo, B. Crosstalk between Cancer and Immune Cells: Role of Tumor-Associated Macrophages in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 4709–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, E.; Astsaturov, I.; Cukierman, E.; DeNardo, D.G.; Egeblad, M.; Evans, R.M.; Fearon, D.; Greten, F.R.; Hingorani, S.R.; Hunter, T.; et al. A Framework for Advancing Our Understanding of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, X. Characteristics and Significance of the Pre-Metastatic Niche. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNardo, D.G.; Coussens, L.M. Inflammation and Breast Cancer. Balancing Immune Response: Crosstalk between Adaptive and Innate Immune Cells during Breast Cancer Progression. Breast Cancer Res. 2007, 9, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcellos-Hoff, M.H.; Akhurst, R.J. Transforming Growth Factor-Beta in Breast Cancer: Too Much, Too Late. Breast Cancer Res. 2009, 11, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Wang, G.; Qi, X.; Englander, E.W.; Greeley, G.H.J. Involvement of a Stat3 Binding Site in Inflammation-Induced Enteric Apelin Expression. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 295, G1068–G1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeper, N.J.; Tedesco, M.M.; Kojima, Y.; Schultz, G.M.; Kundu, R.K.; Ashley, E.A.; Tsao, P.S.; Dalman, R.L.; Quertermous, T. Apelin Prevents Aortic Aneurysm Formation by Inhibiting Macrophage Inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 296, H1329–H1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, H.; Farzan, M.; Konkel, M.; Martin, K.; Sun, Y.; Marcon, L.; Cayabyab, M.; Berman, M.; Dorf, M.E.; Gerard, N.; et al. The Orphan Seven-Transmembrane Receptor Apj Supports the Entry of Primary T-Cell-Line-Tropic and Dualtropic Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 6113–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edinger, A.L.; Hoffman, T.L.; Sharron, M.; Lee, B.; Yi, Y.; Choe, W.; Kolson, D.L.; Mitrovic, B.; Zhou, Y.; Faulds, D.; et al. An Orphan Seven-Transmembrane Domain Receptor Expressed Widely in the Brain Functions as a Coreceptor for Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 and Simian Immunodeficiency Virus. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 7934–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, Y.; Fujii, T.; Kamimura, Y.; Kawashima, K. The Endogenous, Immunologically Active Peptide Apelin Inhibits Lymphocytic Cholinergic Activity during Immunological Responses. J. Neuroimmunol. 2003, 144, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, X.; Yang, H.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Ason, B.; Liu, S.; Hu, L.A. APLNR Regulates IFN-γ Signaling via β-Arrestin 1 Mediated JAK-STAT1 Pathway in Melanoma Cells. Biochem. J. 2022, 479, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alspach, E.; Lussier, D.M.; Schreiber, R.D. Interferon γ and Its Important Roles in Promoting and Inhibiting Spontaneous and Therapeutic Cancer Immunity. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2019, 11, a028480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Hu-Lieskovan, S.; Wargo, J.A.; Ribas, A. Primary, Adaptive, and Acquired Resistance to Cancer Immunotherapy. Cell 2017, 168, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, F.; Cardoso, A.P.; Gonçalves, R.M.; Serre, K.; Oliveira, M.J. Interferon-Gamma at the Crossroads of Tumor Immune Surveillance or Evasion. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Mezzadra, R.; Schumacher, T.N. Regulation and Function of the PD-L1 Checkpoint. Immunity 2018, 48, 434–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, X. Primary and Acquired Resistance to PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade in Cancer Treatment. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 46, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, F.; Wei, F.; Ren, X. The Role of Toll-like Receptor 4 in Tumor Microenvironment. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 66656–66667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Liu, G.; Chen, G.; Guo, D.; Xu, L.; Hang, M.; Jin, M. Apelin Protects against Sepsis-induced Cardiomyopathy by Inhibiting the TLR4 and NLRP3 Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Guo, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, Z.; Duan, W.; Zeng, B. Apelin-13 Regulates LPS-Induced N9 Microglia Polarization Involving STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Neuropeptides 2019, 76, 101938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, W.H.; Pagès, F.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Galon, J. The Immune Contexture in Human Tumours: Impact on Clinical Outcome. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, M.C.A.; Nelson, B.H. Prognostic Significance of Tumor-Infiltrating B Cells and Plasma Cells in Human Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 6125–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, F.S.; Güneş, C.E.; Yavuz, E.; Kurar, E. Apelin Triggers Macrophage Polarization to M2 Type in Head and Neck Cancer. Immunobiology 2023, 228, 152353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kälin, R.E.; Glass, R. APLN/APLNR Signaling Controls Key Pathological Parameters of Glioblastoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Noma, K.; Ohara, T.; Kashima, H.; Katsura, Y.; Sato, H.; Komoto, S.; Katsube, R.; Ninomiya, T.; Tazawa, H.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Affect Intratumoral CD8(+) and FoxP3(+) T Cells Via IL6 in the Tumor Microenvironment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4820–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singel, K.L.; Segal, B.H. Neutrophils in the Tumor Microenvironment: Trying to Heal the Wound That Cannot Heal. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 273, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egelston, C.A.; Avalos, C.; Tu, T.Y.; Simons, D.L.; Jimenez, G.; Jung, J.Y.; Melstrom, L.; Margolin, K.; Yim, J.H.; Kruper, L.; et al. Human Breast Tumor-Infiltrating CD8(+) T Cells Retain Polyfunctionality despite PD-1 Expression. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.Y.; Martini, C.; Fridlender, Z.G.; Bonder, C.S.; Brown, M.P.; Ebert, L.M. Control of Immune Cell Entry through the Tumour Vasculature: A Missing Link in Optimising Melanoma Immunotherapy? Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2017, 6, e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Hayashi, Y.; Kidoya, H.; Takakura, N. Endothelial Cell-Derived Apelin Inhibits Tumor Growth by Altering Immune Cell Localization. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loetscher, P.; Seitz, M.; Clark-Lewis, I.; Baggiolini, M.; Moser, B. Monocyte Chemotactic Proteins MCP-1, MCP-2, and MCP-3 Are Major Attractants for Human CD4+ and CD8+ T Lymphocytes. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, T.H.; Deyev, V.V.; Rosenblatt, J.D.; Podack, E.R. Tumor-Induced Suppression of CTL Expansion and Subjugation by Gp96-Ig Vaccination. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2026–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, C.L.; Camire, R.B.; Jones, M.C.; Luster, A.D. The Chemokine Receptor CCR8 Promotes the Migration of Dendritic Cells into the Lymph Node Parenchyma to Initiate the Allergic Immune Response. Immunity 2018, 49, 449–463.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, E.; Clevers, H. Cancer Stem Cells Revisited. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devic, E.; Paquereau, L.; Vernier, P.; Knibiehler, B.; Audigier, Y. Expression of a New G Protein-Coupled Receptor X-Msr Is Associated with an Endothelial Lineage in Xenopus Laevis. Mech. Dev. 1996, 59, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devic, E.; Rizzoti, K.; Bodin, S.; Knibiehler, B.; Audigier, Y. Amino Acid Sequence and Embryonic Expression of Msr/Apj, the Mouse Homolog of Xenopus X-Msr and Human APJ. Mech. Dev. 1999, 84, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C.M.; D’Agostino, S.L.; Miller, M.K.; Heimark, R.L.; Krieg, P.A. Apelin, the Ligand for the Endothelial G-Protein-Coupled Receptor, APJ, Is a Potent Angiogenic Factor Required for Normal Vascular Development of the Frog Embryo. Dev. Biol. 2006, 296, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vodyanik, M.A.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Tian, S.; Stewart, R.; Thomson, J.A.; Slukvin, I.I. A Mesoderm-Derived Precursor for Mesenchymal Stem and Endothelial Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 7, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.C.; Hirst, C.E.; Costa, M.; Ng, E.S.; Schiesser, J.V.; Gertow, K.; Stanley, E.G.; Elefanty, A.G. APELIN Promotes Hematopoiesis from Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Blood 2012, 119, 6243–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; McKay, R.M.; Parada, L.F. Malignant Glioma: Lessons from Genomics, Mouse Models, and Stem Cells. Cell 2012, 149, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harford-Wright, E.; Gavard, J. Apelin, the Devil Inside Brain Tumors. J. Exp. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 1179069518759680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannampuzha, S.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V. Cancer Chemoresistance and Its Mechanisms: Associated Molecular Factors and Its Regulatory Role. Med. Oncol. 2023, 40, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.; Sadeghi, S.; Tabatabaeian, H. Battling Chemoresistance in Cancer: Root Causes and Strategies to Uproot Them. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.P.; Bartek, J. The DNA-Damage Response in Human Biology and Disease. Nature 2009, 461, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez, G.T. DNA Injury and Repair Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housman, G.; Byler, S.; Heerboth, S.; Lapinska, K.; Longacre, M.; Snyder, N.; Sarkar, S. Drug Resistance in Cancer: An Overview. Cancers 2014, 6, 1769–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, W.P.; Kaina, B. DNA Damage-Induced Cell Death: From Specific DNA Lesions to the DNA Damage Response and Apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2013, 332, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, L.; Cui, X.; Wang, J.; Pan, L.; Ye, Z.; Liu, P.; Wu, L. Apelin Induces Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Migration via a PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a/MMP-2 Pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 69, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagamajalu, S.; Rex, D.A.B.; Philem, P.D.; Rainey, J.K.; Keshava Prasad, T.S. A Network Map of Apelin-Mediated Signaling. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 16, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Gu, C.; Hu, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L. Protective Effect of Apelin-13 in Lens Epithelial Cells via Inhibiting Oxidative Stress-Induced Apoptosis. BMC Ophthalmol. 2024, 24, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Cao, L.; Tang, D.; Dai, X. Endogenous Ligand of the APJ Receptor Apelin-13 Inhibits Cell Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress of Cardiomyocytes. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2023, 69, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Cui, Y.; Hu, K.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y. Silencing APLNR Enhances the Radiosensitivity of Prostate Cancer by Modulating the PI3K/AKT/MTOR Signaling Pathway. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2024. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibue, T.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT, CSCs, and Drug Resistance: The Mechanistic Link and Clinical Implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzyn, K.; Kiezun, M.; Kopij, G.; Zarzecka, B.; Gudelska, M.; Kisielewska, K.; Zaobidna, E.; Makowczenko, K.G.; Dall’Aglio, C.; Kamiński, T.; et al. Correction: Apelin-13 Modulates the Endometrial Transcriptome of the Domestic Pig during Implantation. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Zhu, W.F.; Shen, W.C.; Xia, Y.; Wu, X.F.; Zhang, H.J.; Liu, W.; Cui, Z.L.; Zheng, X.W.; Chen, G. Expression of Apelin and Snail protein in breast cancer and their prognostic significance. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi Chin. J. Pathol. 2018, 47, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, A.; Rahman, H.; Ambudkar, S.V. Advances in the Structure, Mechanism and Targeting of Chemoresistance-Linked ABC Transporters. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2023, 23, 762–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, K.; Katayama, K.; Sugimoto, Y. Human ABC Transporter ABCG2/BCRP Expression in Chemoresistance: Basic and Clinical Perspectives for Molecular Cancer Therapeutics. Pharmgenom. Pers. Med. 2014, 7, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.-Y.; Lu, Q.; Ouyang, X.-P.; Tang, S.-L.; Zhao, G.-J.; Lv, Y.-C.; He, P.-P.; Kuang, H.-J.; Tang, Y.-Y.; Fu, Y.; et al. Apelin-13 Increases Expression of ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter A1 via Activating Protein Kinase C α Signaling in THP-1 Macrophage-Derived Foam Cells. Atherosclerosis 2013, 226, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Jiang, P.; Liu, L.-Y.; Gao, Y.; Yang, X.-X.; Cai, Z.-C.; Fan, X.-F.; Gong, Y.-S.; Mao, S.-Z. Apelin attenuates hypoxia induced pulmonary hypertension of mice through regulation of lipid metabolism. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi Zhongguo Yingyong Shenglixue Zazhi Chin. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 33, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junttila, M.R.; de Sauvage, F.J. Influence of Tumour Micro-Environment Heterogeneity on Therapeutic Response. Nature 2013, 501, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H Al-Zuaini, H.; Rafiq Zahid, K.; Xiao, X.; Raza, U.; Huang, Q.; Zeng, T. Hypoxia-Driven NcRNAs in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1207253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Li, Q.; Wang-Gillam, A.; Yu, J.; Head, R.; Liu, J.; Ruzinova, M.B.; Lim, K.-H. Tumor-Stroma IL1β-IRAK4 Feedforward Circuitry Drives Tumor Fibrosis, Chemoresistance, and Poor Prognosis in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, A.; Wang, D.; Luo, Z.; Ping, Y.; Zhou, B.; Liu, S.; Li, H.; Yue, D.; et al. IL6 Derived from Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promotes Chemoresistance via CXCR7 in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oncogene 2018, 37, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintani, Y.; Fujiwara, A.; Kimura, T.; Kawamura, T.; Funaki, S.; Minami, M.; Okumura, M. IL-6 Secreted from Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Mediates Chemoresistance in NSCLC by Increasing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Signaling. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1482–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, C.; Karachaliou, N.; Bulotta, A.; Viganó, M.; Mirabile, A.; Brioschi, E.; Santarpia, M.; Gianni, L.; Rosell, R.; Gregorc, V. Combination of Immunotherapy with Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy in Lung Cancer: Is This the Beginning of the End for Cancer? Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10, 1758835918762094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.C.; Formenti, S.C. Integration of Radiation and Immunotherapy in Breast Cancer—Treatment Implications. Breast 2018, 38, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrilovich, D.I.; Nagaraj, S. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells as Regulators of the Immune System. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarzadeh, A.; Naseri, B.; Khorramdelazad, H.; Jafarzadeh, S.; Ghorbaninezhad, F.; Asgari, Z.; Masoumi, J.; Nemati, M. Reciprocal Interactions Between Apelin and Noncoding RNAs in Cancer Progression. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2024, 42, e4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, M.; Qiu, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W. The Apelin/APLNR System Modulates Tumor Immune Response by Reshaping the Tumor Microenvironment. Gene 2022, 834, 146564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, L. Roles of Apelin/APJ System in Cancer: Biomarker, Predictor, and Emerging Therapeutic Target. J. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 237, 3734–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagenaar, G.T.M.; Moll, G.N. Advances in the Therapeutic Potentials of Ligands of the Apelin Receptor APJ. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 991, 177302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, A.K.; Campbell, K.R.; Zhabyeyev, P.; Oudit, G.Y.; Moore, R.B.; Murray, A.G. Loss of Apelin Blocks the Emergence of Sprouting Angiogenesis in Experimental Tumors. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chen, X.; Pan, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, X.; Ma, S. Proteins Associated with EGFR-TKIs Resistance in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Revealed by Mass Spectrometry. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 4823–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermin, S.; Çok, G.; Veral, A.; Köse, T. The Role of Apelin in the Assessment of Response to Chemotherapyand Prognosis in Stage 4 Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 46, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Karuniawati, H.; Jairoun, A.A.; Urbi, Z.; Ooi, D.J.; John, A.; Lim, Y.C.; Kibria, K.M.K.; Mohiuddin, A.K.M.; Ming, L.C.; et al. Colorectal Cancer: A Review of Carcinogenesis, Global Epidemiology, Current Challenges, Risk Factors, Preventive and Treatment Strategies. Cancers 2022, 14, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuurbier, L.; Rahman, A.; Cordes, M.; Scheick, J.; Wong, T.J.; Rustenburg, F.; Joseph, J.C.; Dynoodt, P.; Casey, R.; Drillenburg, P.; et al. Apelin: A Putative Novel Predictive Biomarker for Bevacizumab Response in Colorectal Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 42949–42961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Takara, K.; Yamakawa, D.; Kidoya, H.; Takakura, N. Apelin as a Marker for Monitoring the Tumor Vessel Normalization Window during Antiangiogenic Therapy. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gombodorj, N.; Yokobori, T.; Yoshiyama, S.; Kawabata-Iwakawa, R.; Rokudai, S.; Horikoshi, I.; Nishiyama, M.; Nakano, T. Inhibition of Ubiquitin-Conjugating Enzyme E2 May Activate the Degradation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factors and, Thus, Overcome Cellular Resistance to Radiation in Colorectal Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 2425–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.-Z.; Li, M.-L.; Ning, F.-L.; Wang, X.-W. APJ Is Associated with Treatment Response in Gastric Cancer Patients Receiving Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy and Endostar Therapy. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2017, 32, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmedt, C.; Fornili, M.; Clatot, F.; Demicheli, R.; De Bortoli, D.; Di Leo, A.; Viale, G.; de Azambuja, E.; Crown, J.; Francis, P.A.; et al. Differential Benefit of Adjuvant Docetaxel-Based Chemotherapy in Patients With Early Breast Cancer According to Baseline Body Mass Index. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2883–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourgue, F.; Derouane, F.; van Marcke, C.; Villar, E.; Dano, H.; Desmet, L.; Bouzin, C.; Duhoux, F.P.; Cani, P.D.; Jordan, B.F. Tumor Apelin and Obesity Are Associated with Reduced Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Response in a Cohort of Breast Cancer Patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, L.M.; Fell, G.; Arfe, A.; Sharma, C.; Greenup, R.; Reynolds, K.L.; Smith, B.L.; Alexander, B.; Moy, B.; Isakoff, S.J.; et al. Pathologic Complete Response after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Impact on Breast Cancer Recurrence and Survival: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2838–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wu, S.; Jiang, L.; Gao, Z.; Li, X.; Duan, Y.; Li, N.; Sun, T. Network-Based Approach to Identify Biomarkers Predicting Response and Prognosis for HER2-Negative Breast Cancer Treatment with Taxane-Anthracycline Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wculek, S.K.; Cueto, F.J.; Mujal, A.M.; Melero, I.; Krummel, M.F.; Sancho, D. Dendritic Cells in Cancer Immunology and Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, J.; Jafarzadeh, A.; Tavakoli, T.; Basirjafar, P.; Zandvakili, R.; Javan, M.R.; Taghipour, Z.; Moazzeni, S.M. Inhibition of Apelin/APJ Axis Enhances the Potential of Dendritic Cell-Based Vaccination to Modulate TH1 and TH2 Cell-Related Immune Responses in an Animal Model of Metastatic Breast Cancer. Adv. Med. Sci. 2022, 67, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, J.; Zainodini, N.; Basirjafar, P.; Tavakoli, T.; Zandvakili, R.; Nemati, M.; Ramezani, M.; Rezayati, M.-T.; Ayoobi, F.; Khademalhosseini, M.; et al. Apelin Receptor Antagonist Boosts Dendritic Cell Vaccine Efficacy in Controlling Angiogenic, Metastatic and Apoptotic-Related Factors in 4T1 Breast Tumor-Bearing Mice. Med. Oncol. 2023, 40, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semreen, A.M.; Alsoud, L.O.; Semreen, M.H.; Ahmed, M.; Al-Hroub, H.M.; El-Awady, R.; Ramadan, W.S.; Abuhelwa, A.; Bustanji, Y.; Soares, N.C.; et al. Multi-Omics Analysis Revealed Significant Metabolic Changes in Brain Cancer Cells Treated with Paclitaxel and/or Topotecan. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, W.A. Chondrosarcoma: Biology, Genetics, and Epigenetics. F1000Research 2018, 7, F1000-Faculty. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-C.; Shih, H.-C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Guo, J.-H.; Huang, C.; Huang, H.-C.; Chong, Z.-Y.; Tang, C.-H. MicroRNA-631 Resensitizes Doxorubicin-Resistant Chondrosarcoma Cells by Targeting Apelin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogra, S.; Neelakantan, D.; Patel, M.M.; Griesel, B.; Olson, A.; Woo, S. Adipokine Apelin/APJ Pathway Promotes Peritoneal Dissemination of Ovarian Cancer Cells by Regulating Lipid Metabolism. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 1534–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.; Carter, C.; Lynch, M.; Lowinger, T.; Dumas, J.; Smith, R.A.; Schwartz, B.; Simantov, R.; Kelley, S. Discovery and Development of Sorafenib: A Multikinase Inhibitor for Treating Cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiprasart, P.; Dogra, S.; Neelakantan, D.; Devapatla, B.; Woo, S. Identification of Signature Genes Associated with Therapeutic Resistance to Anti-VEGF Therapy. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.G.; Berger, C.; Feldner, A.; Yang, W.-J.; Wüstehube-Lausch, J.; Herberich, S.E.; Pinder, M.; Gesierich, S.; Hammes, H.-P.; Augustin, H.G.; et al. Synaptojanin-2 Binding Protein Stabilizes the Notch Ligands DLL1 and DLL4 and Inhibits Sprouting Angiogenesis. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 1206–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Tan, Y.; Chen, T.; Wang, Q.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, J. Sempervirine Inhibits Proliferation, Invasion and Metastasis of Ovarian Cancer Cells and Induces Ultrastructural Changes In Vivo. J. Ovarian Res. 2025, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, X.; Mukhtar, M.; Lu, Z.; Fang, J.; DuBois, G.C.; Pomerantz, R.J. Structural and Functional Study of the Apelin-13 Peptide, an Endogenous Ligand of the HIV-1 Coreceptor, APJ. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 10163–10168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-Almagro, C.; Castan-Laurell, I.; Dray, C.; Knauf, C.; Valet, P.; Masri, B. Apelin Receptors: From Signaling to Antidiabetic Strategy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 763, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.K.; Saldivia, V.R.; Nguyen, T.; Cheng, R.; George, S.R.; O’Dowd, B.F. Modification of the Terminal Residue of Apelin-13 Antagonizes Its Hypotensive Action. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Jiang, Y.-R.; Qian, J.; Tao, Y. Apelin-13 Regulates Proliferation, Migration and Survival of Retinal Müller Cells under Hypoxia. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 99, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, J.; Shirabe, K.; Yoshizumi, T.; Ikegami, T.; Aishima, S.; Ishigami, K.; Yonemitsu, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Soejima, Y.; Maehara, Y. The Apelin-APJ System Induces Tumor Arteriogenesis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 5313–5320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gourgue, F.; Mignion, L.; Van Hul, M.; Dehaen, N.; Bastien, E.; Payen, V.; Leroy, B.; Joudiou, N.; Vertommen, D.; Bouzin, C.; et al. Obesity and Triple-Negative-Breast-Cancer: Is Apelin a New Key Target? J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 10233–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, B.; Nail, V.; Nachar, O.; Bouhlel, A.; Moyon, A.; Balasse, L.; Simoncini, S.; Chabert, A.; Fernandez, S.; Brige, P.; et al. Design and Preclinical Evaluation of a Novel Apelin-Based PET Radiotracer Targeting APJ Receptor for Molecular Imaging of Angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 2023, 26, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, P.R.; Khan, P.; Hedrick, M.; Gosalia, P.; Milewski, M.; Li, L.; Roth, G.P.; Sergienko, E.; Suyama, E.; Sugarman, E.; et al. Discovery of 4-Oxo-6-((Pyrimidin-2-Ylthio)Methyl)-4H-Pyran-3-Yl 4-Nitrobenzoate (ML221) as a Functional Antagonist of the Apelin (APJ) Receptor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 6656–6660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawid, M.; Mlyczynska, E.; Kurowska, P.; Sierpowski, M.; Rak, A. Apelin Decreased Placental Hormone Secretion by Human Trophoblast BeWo Cells via Apelin Receptor, Protein Kinase A and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinases 1/2 Activation. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 70, 95–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ying, H.; Yu, Z.; Chang, L.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Chang, S.-J.; Qiu, Y.; Lin, X. Apelin Receptor Can Act as a Specific Marker and Promising Therapeutic Target for Infantile Hemangioma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 143, 566–577.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gonidec, S.; Chaves-Almagro, C.; Bai, Y.; Kang, H.J.; Smith, A.; Wanecq, E.; Huang, X.-P.; Prats, H.; Knibiehler, B.; Roth, B.L.; et al. Protamine Is an Antagonist of Apelin Receptor, and Its Activity Is Reversed by Heparin. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 2507–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAnally, D.; Siddiquee, K.; Gomaa, A.; Szabo, A.; Vasile, S.; Maloney, P.R.; Divlianska, D.B.; Peddibhotla, S.; Morfa, C.J.; Hershberger, P.; et al. Repurposing Antimalarial Aminoquinolines and Related Compounds for Treatment of Retinal Neovascularization. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berta, J.; Török, S.; Tárnoki-Zách, J.; Drozdovszky, O.; Tóvári, J.; Paku, S.; Kovács, I.; Czirók, A.; Masri, B.; Megyesfalvi, Z.; et al. Apelin Promotes Blood and Lymph Vessel Formation and the Growth of Melanoma Lung Metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Bu, P. Non-Coding RNA in Cancer. Essays Biochem. 2021, 65, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasiadou, E.; Jacob, L.S.; Slack, F.J. Non-Coding RNA Networks in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, F.; Shen, A.; Islam, W.; Saleem, M.Z.; Muthu, R.; Xie, Q.; Wu, M.; Cheng, Y.; Chu, J.; Lin, W.; et al. Role of MicroRNAs and Their Corresponding ACE2/Apelin Signaling Pathways in Hypertension. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 162, 105361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wang, A.; Cao, J.; Chen, L. Apelin/APJ System: An Emerging Therapeutic Target for Respiratory Diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 2919–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, M.; et al. MicroRNA-122-5p Aggravates Angiotensin II-Mediated Myocardial Fibrosis and Dysfunction in Hypertensive Rats by Regulating the Elabela/Apelin-APJ and ACE2-GDF15-Porimin Signaling. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2022, 15, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.-S.; Hsi, E.; Chang, M.-H.; You, Y.-Z.; Juo, S.-H.H. MicroRNA-765 Influences Arterial Stiffness through Modulating Apelin Expression. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 411, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Ren, Z.; Zou, W.; Jiang, Y. MiR-497 Accelerates Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein-Induced Lipid Accumulation in Macrophages by Repressing the Expression of Apelin. Cell Biol. Int. 2017, 41, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Dong, B.; Zhang, N.; Liu, S.; Zhao, H. MicroRNA-182 Negatively Influences the Neuroprotective Effect of Apelin Against Neuronal Injury in Epilepsy. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.-L.; Li, S.-M.; Hou, J.-Y.; Hong, Y.-H.; Chen, X.-X.; Zhou, C.-Q.; Wu, H.; Zheng, G.-H.; Zeng, C.-T.; Wu, H.-D.; et al. Elabela, a Novel Peptide, Exerts Neuroprotective Effects Against Ischemic Stroke Through the APJ/MiR-124-3p/CTDSP1/AKT Pathway. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 43, 2989–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.-K.; Wang, Y.-H.; Kuo, S.-J.; Wang, S.-W.; Tsai, C.-H.; Fong, Y.-C.; Wu, N.-L.; Liu, S.-C.; Tang, C.-H. Apelin Enhances IL-1β Expression in Human Synovial Fibroblasts by Inhibiting MiR-144-3p through the PI3K and ERK Pathways. Aging 2020, 12, 9224–9239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.-K.; Zhong, Y.-H.; Liu, S.-C.; Huang, C.-C.; Tsai, C.-H.; Lee, H.-P.; Wang, S.-W.; Hsu, C.-J.; Tang, C.-H. Apelin Promotes Endothelial Progenitor Cell Angiogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease via the MiR-525-5p/Angiopoietin-1 Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 737990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.-Y.; Huang, Y.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Han, Z.-D.; He, H.-C.; Ling, X.-H.; Fu, X.; Dai, Q.-S.; Cai, C.; Chen, J.-H.; et al. MicroRNA-224 Inhibits Progression of Human Prostate Cancer by Downregulating TRIB1. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegedus, Z.; Czibula, A.; Kiss-Toth, E. Tribbles: A Family of Kinase-like Proteins with Potent Signalling Regulatory Function. Cell. Signal. 2007, 19, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angius, A.; Uva, P.; Pira, G.; Muroni, M.R.; Sotgiu, G.; Saderi, L.; Uleri, E.; Caocci, M.; Ibba, G.; Cesaraccio, M.R.; et al. Integrated Analysis of MiRNA and MRNA Endorses a Twenty MiRNAs Signature for Colorectal Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Xu, J.-L.; Chen, W.-Q.; Xu, W.-X.; Song, Y.-X.; Tang, W.-J.; Xu, D.; Jiang, M.-P.; Tang, J. Roles and Mechanisms of MiR-195-5p in Human Solid Cancers. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 112885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, M.; Du, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, G.; Ye, L.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; et al. MicroRNA-195 Suppresses the Progression of Lung Adenocarcinoma by Directly Targeting Apelin. Thorac. Cancer 2019, 10, 1419–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, G.; Cai, J.; Du, Y.; Li, H.; Duan, L.; Zhao, G.; Huang, Y. Exosomal Transfer of MiR-195-5p Restrains Lung Adenocarcinoma Progression. Exp. Cell Res. 2023, 424, 113485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Bian, Z.; Xu, P.; Sun, S.; Huang, Z. MicroRNA-204-5p: A Pivotal Tumor Suppressor. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 3185–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Yang, Y.; Guan, J.; Lv, T.; Qu, S.; Fu, Q.; Zhao, H. LncRNA UCA1 Sponges MiR-204-5p to Promote Migration, Invasion and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Glioma Cells via Upregulation of ZEB1. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 1474–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Yin, Y.; Jin, G.; Li, D.; Li, M.; Hu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bian, Z.; Wang, X.; et al. Exosome-Mediated Delivery of MiR-204-5p Inhibits Tumor Growth and Chemoresistance. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 5989–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Yao, S.; Hu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Li, M.; Bian, Z.; Zhang, J.; Qin, Y.; Qi, X.; Zhou, L.; et al. The Immune-Microenvironment Confers Chemoresistance of Colorectal Cancer through Macrophage-Derived IL6. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 7375–7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Lv, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, J.; Huo, X.; Guo, M.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Overcoming Multi-Drug Resistance in SCLC: A Synergistic Approach with Venetoclax and Hydroxychloroquine Targeting the LncRNA LYPLAL1-DT/BCL2/BECN1 Pathway. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, R.; Luo, J.; Li, X.; Zhong, Y.; Sun, Z. Dysregulation of MiR-204-5p/APLN Axis Affects Malignant Progression and Cell Stemness of Esophageal Cancer. Mutat. Res. 2022, 825, 111791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Liu, B.; Zang, L.E.; Jiang, H. MiR-631/ZAP70: A Novel Axis in the Migration and Invasion of Prostate Cancer Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 469, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liao, Z.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Su, C.; Liang, H.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X. MiR-631 Inhibits Intrahepatic Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting PTPRE. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 565266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Li, L.; Du, J.; An, R.; Fan, R.; Lu, J.; Wu, Y.-X.; Wu, S.-X.; Hou, J.; Zhao, L.-M. Hsa-MiR-631 Resensitizes Bortezomib-Resistant Multiple Myeloma Cell Lines by Inhibiting UbcH10. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, A.E.; Gall, T.M.H.; Castellano, L.; Stebbing, J.; Jiao, L.R.; Krell, J. Towards a Clinical Use of MiRNAs in Pancreatic Cancer Biopsies. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2013, 13, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drahos, J.; Schwameis, K.; Orzolek, L.D.; Hao, H.; Birner, P.; Taylor, P.R.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Schoppmann, S.F.; Cook, M.B. MicroRNA Profiles of Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: Differences in Glandular Non-Native Epithelium. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2016, 25, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-C.; Chen, T.-Y.; Tsai, K.-J.; Lin, M.-W.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Wu, D.-C.; Tsai, E.-M.; Hsieh, T.-H. NF-ΚB/MiR-18a-3p and MiR-4286/BZRAP1 Axis May Mediate Carcinogenesis in Helicobacter Pylori-Associated Gastric Cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tian, H.; Li, R.; Yan, W.; Xu, R. MicroRNA-4286 Promotes Esophageal Carcinoma Development by Targeting INPP4A to Evoke the JAK2/STAT3 Pathway Activation. Pharmazie 2018, 73, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, C.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Tang, H.; Du, W.; Zeng, Y.; Sun, L.; Huang, J.-A.; Liu, Z. MicroRNA-4286 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion via PTEN Regulation of the PI3K/Akt Pathway in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 3520–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, K.-H.; Chen, P.-H.; Shih, C.-M.; Lee, Y.-T.; Cheng, C.-H.; Liu, A.-J.; Lee, C.-C.; Chen, K.-C. MiR-4286 Is Involved in Connections Between IGF-1 and TGF-β Signaling for the Mesenchymal Transition and Invasion by Glioblastomas. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 42, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komina, A.; Palkina, N.; Aksenenko, M.; Tsyrenzhapova, S.; Ruksha, T. Antiproliferative and Pro-Apoptotic Effects of MiR-4286 Inhibition in Melanoma Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, N.; Jiang, Y.-Y.; Pan, Z.-P.; Wan, J. Forkhead Box M1 Regulates the Proliferation, Invasion, and Drug Resistance of Gastric Cancer Cells via circ_NOTCH1. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2023, 45, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhong, Q.; Cheng, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, R.; Leng, X.; Shao, L. MiR-449c-5p Availability Is Antagonized by Circ-NOTCH1 for MYC-Induced NOTCH1 Upregulation as Well as Tumor Metastasis and Stemness in Gastric Cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 4052–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Song, W.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, L.; Lu, H. C-Myc-Induced Circ-NOTCH1 Promotes Aggressive Phenotypes of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells by Regulating the MiR-34c-5p/c-Myc Axis. Cell Biol. Int. 2021, 45, 1436–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, E.; Xu, X.; Xue, F. Circ-NOTCH1 Acts as a Sponge of MiR-637 and Affects the Expression of Its Target Gene Apelin to Regulate Gastric Cancer Cell Growth. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 98, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Mai, S.-R.; Zhang, L. Circ-ZNF264 Promotes the Growth of Glioma Cells by Upregulating the Expression of MiR-4493 Target Gene Apelin. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 69, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Huang, Y.; Liu, T. Long Non-Coding RNA BACE1-AS Is a Novel Target for Anisomycin-Mediated Suppression of Ovarian Cancer Stem Cell Proliferation and Invasion. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1916–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, C.; Ku, J.-L.; Kim, W.; Yoon, S.K.; Kuh, H.-J.; Lee, J.-H.; Nam, S.W.; Lee, E.K. A Long Non-Coding RNA SnaR Contributes to 5-Fluorouracil Resistance in Human Colon Cancer Cells. Mol. Cells 2014, 37, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Tang, L.; Huang, H.; Xu, M.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, L.; Ho, L.; Lu, J.; Ai, X. LncRNA BACE1-AS Enhances the Invasive and Metastatic Capacity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through Mediating MiR-377-3p/CELF1 Axis. Life Sci. 2021, 275, 119288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, T.; Yang, L.; Na, X.; Qu, Y. LncRNA BACE1-AS Promotes the Progression of Osteosarcoma through MiR-762/SOX7 Axis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 5853–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Yan, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, Y. Long Non-Coding RNA BACE1-AS Plays an Oncogenic Role in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells through MiR-214-3p/APLN Axis. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2021, 53, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; You, Z.; Bai, Z.; Xie, J. Machine Learning-Based Construction of a Ferroptosis and Necroptosis Associated LncRNA Signature for Predicting Prognosis and Immunotherapy Response in Hepatocellular Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1171878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yu, L.; Si, Z. M6A Modified BACE1-AS Contributes to Liver Metastasis and Stemness-like Properties in Colorectal Cancer through TUFT1 Dependent Activation of Wnt Signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Jiang, C.; Liu, B.; Fang, S.; Kuang, M. MicroRNA-15a-5p Suppresses Cancer Proliferation and Division in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting BDNF. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2016, 37, 5821–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chava, S.; Reynolds, C.P.; Pathania, A.S.; Gorantla, S.; Poluektova, L.Y.; Coulter, D.W.; Gupta, S.C.; Pandey, M.K.; Challagundla, K.B. MiR-15a-5p, MiR-15b-5p, and MiR-16-5p Inhibit Tumor Progression by Directly Targeting MYCN in Neuroblastoma. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.H.; Li, W.X.; Hu, C.; Zhang, B. Upregulation of SNHG12 Accelerates Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion and Restrain Cell Apoptosis in Breast Cancer by Enhancing Regulating SALL4 Expression via Sponging MiR-15a-5p. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J. MiR-15a-5p Regulates Liver Cancer Cell Migration, Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Progression by Targeting Transcription Factor E2F3. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2022, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-M.; Wan, X.-H.; Sang, G.-Y.; Zhao, J.-D.; Zhu, Q.-Y.; Wang, D.-M. MiR-15a-5p Suppresses Endometrial Cancer Cell Growth via Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway by Inhibiting WNT3A. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 4810–4818. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ergun, S.; Güney, S.; Temiz, E.; Petrovic, N.; Gunes, S. Significance of MiR-15a-5p and CNKSR3 as Novel Prognostic Biomarkers in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Li, Y.; He, T.; Hu, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Z.; Gui, Y.; Mao, X.; Yang, S.; et al. MiR-15a-5p Acts as an Oncogene in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontos, C.K.; Tsiakanikas, P.; Avgeris, M.; Papadopoulos, I.N.; Scorilas, A. MiR-15a-5p, A Novel Prognostic Biomarker, Predicting Recurrent Colorectal Adenocarcinoma. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2017, 21, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, K.; Song, J.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, Z. MiR-15a-5p Targets PHLPP2 in Gastric Cancer Cells to Modulate Platinum Resistance and Is a Suitable Serum Biomarker for Oxaliplatin Resistance. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandewalle, V.; Essaghir, A.; Bollaert, E.; Lenglez, S.; Graux, C.; Schoemans, H.; Saussoy, P.; Michaux, L.; Valk, P.J.M.; Demoulin, J.-B.; et al. MiR-15a-5p and MiR-21-5p Contribute to Chemoresistance in Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukaemia by Targeting PDCD4, ARL2 and BTG2. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollaert, E.; Claus, M.; Vandewalle, V.; Lenglez, S.; Essaghir, A.; Demoulin, J.-B.; Havelange, V. MiR-15a-5p Confers Chemoresistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia by Inhibiting Autophagy Induced by Daunorubicin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, M.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, L.; Yan, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, W.; et al. MicroRNA-15a-5p Suppresses Hypoxia-Induced Tumor Growth and Chemoresistance in Bladder Cancer by Binding to EIF5A2. Neoplasma 2024, 71, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Ni, Y.; Huang, H.; Liu, Z.; Miao, Z.; Zhang, L. Apelin Enhances Biological Functions in Lung Cancer A549 Cells by Downregulating Exosomal MiR-15a-5p. Carcinogenesis 2021, 42, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y.; Sailike, D.; Luo, K.; Du, G.; Xiang, X.; Jiafu, G.D. MicroRNA-106a-5p Facilitates Human Glioblastoma Cell Proliferation and Invasion by Targeting Adenomatosis Polyposis Coli Protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 481, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, W.; Zhou, Z.; Ni, X.; Xia, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; Xu, B. Long Non-Coding RNA H19 Promotes Glucose Metabolism and Cell Growth in Malignant Melanoma via MiR-106a-5p/E2F3 Axis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, F.; Zhou, G.; Shao, N.; Xia, X.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Xue, L.; Wang, S.; et al. MiR-106a-5p Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Astrocytoma Cells and Promotes Apoptosis by Targeting FASTK. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Yin, M.; Cheng, N.; Yin, J. Long Non-Coding RNA Fer-1-like Protein 4 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor via MiR-106a-5p and Predicts Good Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2017, 20, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Dong, K.; Ma, Y.; Jin, Q.; Yin, S.; Zhu, X.; Wang, S. Effects of FER1L4-MiR-106a-5p/MiR-372-5p-E2F1 Regulatory Axis on Drug Resistance in Liver Cancer Chemotherapy. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 24, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, J.; Yuan, Y.; Ju, H.; Liao, H.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, T.; et al. Exosomal MiR-106a-5p from Highly Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Cells Drives Liver Metastasis by Inducing Macrophage M2 Polarization in the Tumor Microenvironment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingyue, S.; Xiao, W.; Juanmin, Z.; Wei, L.; Daoming, L.; Hong, X. TFAP2E Methylation Promotes 5-fluorouracil Resistance via Exosomal MiR-106a-5p and MiR-421 in Gastric Cancer MGC-803 Cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, D. MiR-106a-5p Promotes 5-FU Resistance and the Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer by Targeting TGFβR2. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 5622–5634. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, T.; Wang, L.-X.; Yang, M.-L.; Zhang, R.-M. LncRNA TPTEP1 Inhibits Stemness and Radioresistance of Glioma through MiR-106a-5p-mediated P38 MAPK Signaling. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 4857–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Guo, J.; Yang, H.; Yuan, D.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z. Exosomes Derived from Hypoxic Glioma Cells Reduce the Sensitivity of Glioma Cells to Temozolomide Through Carrying MiR-106a-5p. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2022, 16, 3589–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Dou, D.; Zhang, T.; Wang, B. HOTAIR Promotes Cisplatin Resistance of Osteosarcoma Cells by Regulating Cell Proliferation, Invasion, and Apoptosis via MiR-106a-5p/STAT3 Axis. Cell Transplant. 2020, 29, 963689720948447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, X.; Yu, X. MicroRNA-106a-5p Alleviated the Resistance of Cisplatin in Lung Cancer Cells by Targeting Jumonji Domain Containing 6. Transpl. Immunol. 2021, 69, 101478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.-H.; Chang, S.L.-Y.; Khanh, P.M.; Trang, N.T.N.; Liu, S.-C.; Tsai, H.-C.; Chang, A.-C.; Lin, J.-Y.; Chen, P.-C.; Liu, J.-F.; et al. Apelin Promotes Prostate Cancer Metastasis by Downregulating TIMP2 via Increases in MiR-106a-5p Expression. Cells 2022, 11, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoey, C.; Ray, J.; Jeon, J.; Huang, X.; Taeb, S.; Ylanko, J.; Andrews, D.W.; Boutros, P.C.; Liu, S.K. MiRNA-106a and Prostate Cancer Radioresistance: A Novel Role for LITAF in ATM Regulation. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 1324–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Effects of Apelin/APJ System in Cancer Patients and in Experimental Models of Cancer | |
|---|---|
| Modulation of Apelin/APJ and Impact on Prognosis | Resistance to Anticancer Treatments |
| Lung cancer | |
| Apelin expression in tissue positively correlates with more advanced disease and poorer outcomes in NSCLC [28] Apelin expression in tissue and circulating apelin positively correlate with a higher tumor stage, a higher probability of distant metastasis, and a shorter PFS and OS in lung adenocarcinoma [40] Apelin expression in tissue correlates with disease stage in lung cancer [43] | Resistance to TKIs [74,160,176,178] -increased apelin expression in EGFR-TKI-resistant patients compared to EGFR-TKI-sensitive subjects -inhibition of apelin in combination with sunitinib delays cancer growth and reduces the density of tumor vessels and microvessel remodeling Resistance to doxorubicin and razoxane [67] -overexpression of apelin-13 and APJ inhibits the cytotoxic effect of the drugs by activating the PAK1/LIMK1/cofilin pathway and promoting cell invasion and migration Resistance to cisplatin [233,281,282] -miR-106a-5p and miR-204-5 are downregulated in resistant lung cancer cells Resistant to etoposide and paclitaxel [233] -miR-204-5 is downregulated in resistant lung cancer cells Apelin expression in tissue predicts cancer progression independently of other potential confounders in patients affected by lung cancer and treated with one or more lines of chemotherapy, surgery, and/or radiotherapy [43] |
| Colorectal cancer | |
| Circulating apelin positively correlates with more advanced TNM stages, and lymph node and distant metastasis [33] Apelin expression in tissue correlates with disease stage [43] | Resistance to bevacizumab [180,181] -high apelin levels in bevacizumab-resistant patients with reduced progression-free survival -apelin mRNA expression and circulating levels decrease on the fifth day after bevacizumab treatment and are associated with reduction of tumor growth, blood vessel density, and tumor hypoxia Resistance to 5-fluorouracile [252,278] -expression of BACE1-AS is downregulated in resistant cells -expression of miR-106a-5p is associated with drug resistance Apelin expression in tissue predicts cancer progression independently of other potential confounders in patients affected by gastrointestinal cancer and treated with one or more lines of chemotherapy, surgery, and/or radiotherapy [43] Resistance to radiation [182] -apelin mediates HIF1α-dependent cellular resistance to radiation |
| Gastric cancer | |
| Apelin expression in tissue positively correlates with more advanced disease and poorer outcomes [27] Apelin expression in tissue correlates with disease stage in gastrointestinal cancer [43] | Resistance to endostar + chemiotherapy [183] -high levels of APJ expression in patients are associated with a poorer response (significantly shorter overall survival) to the combined treatment than patients with low APJ expression Resistance to 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin [226,277] -miR-195–5p enhances sensitivity in drug-resistant cells by targeting ZNF139 -expression of miR-106a-5p is associated with 5-fluorouracile resistance Resistance to doxorubicin [246] -overexpression of circ-NOTCH1 is correlated to resistance to doxorubicin Resistance to cisplatin [266] -overexpression of miR-15a-5p is associated with cisplatin resistance by promoting Akt phosphorylation Apelin expression in tissue correlates with disease stage and predicts cancer progression independently of other potential confounders in patients affected by gastrointestinal cancer and treated with one or more lines of chemotherapy, surgery, and/or radiotherapy [43] |
| Esophageal cancer | |
| Apelin expression in tissue positively correlates with a lower 3000-day survival rate [26] | |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) | |
| Apelin expression in tissue: -is an independent prognostic factor of shorter overall survival [22] -is associated with a more rapid progression from T2 to advanced stages (T3 and T4) [24] APJ expression in tissue [23]: -is associated with the presence of intrahepatic metastasis, early recurrence, and shorter PFS and OS -is an independent predictor of shorter PFS | Resistance to immunotherapy [77,256] -apelin/APJ correlates with immune suppression in high-risk HCC and non-responsiveness to immunotherapic drugs -BACE1-AS levels directly correlate with response to immunotherapy |
| Cholangiocarcinoma | |
| Apelin expression in tissue positively correlates with more advanced disease and poorer outcomes [29] | |
| Breast cancer | |
| Apelin expression in tissue: -significantly correlates with tumor size and stage, microvessel density, lymph node metastasis, and worse disease-free and overall survival [20,38] -is an independent predictor of HER-2/neu expression and a more aggressive breast cancer phenotype [21] -correlates with disease stage and predicts cancer progression independently of other potential confounders in patients affected by gastrointestinal cancer and treated with one or more lines of chemotherapy, surgery, and/or radiotherapy [43] -together with Snail, is positively associated with lymph node metastases and TNM staging, thus correlating with a poor prognosis [159] Circulating apelin positively correlates with a higher tumor stage, a higher probability of distant metastasis, and a shorter PFS and OS [38] | Resistance to chemotherapy [38,185,186] -high tumor expression of apelin/APJ is associated with a reduced rate of pathological complete response to chemotherapy and a worse progression-free survival Resistance to trastuzumab [226] -expression of miR-195–5p was inversely associated with drug resistance Resistance to immunotherapy [189,190] -combined therapy with the APJ antagonist ML221 and a dendritic cell vaccine (DCV) is more effective than single therapies in reducing tumor growth, vascular density and vessel diameter, preventing lung metastases, and improving survival rates through an increase of Th1/Th2 ratio in the spleen Resistance to RTK inhibitors [74] -apelin inhibition prevents resistance to the anti-angiogenetic RTK inhibitors treatment and reduced tumor progression in vivo |
| Glioblastoma/glioma | |
| APJ expression in tissue is associated with advanced stage and worse prognosis [34] Apelin expression in tissue and circulating apelin positively correlate with a higher tumor stage, a higher probability of distant metastases, and a shorter PFS and OS [41,42] Increased expression of Elabela is associated with poor prognosis [45] | Resistance to bevacizumab [65] -bevacizumab reduces apelin expression levels but increases the invasive activity of APJ-expressing cells -treatment with a mutant form of apelin that sequesters APJ reduces angiogenic and invasive activity with synergistic effects to bevacizumab Resistance to temozolomide [42,279,280] -APJ antagonist MM54 enhances cancer stem cell sensitivity to the drug by affecting the GSK3β pathway -expression of miR-106a-5p is associated with radio and temozolomide resistance Resistance to topotecan [191] -apelin expression is altered after topotecan treatment and paclitaxel+topotecan combination ttherapy |
| Head and neck cancer | |
| Apelin expression in tissue and circulating apelin positively correlate with a higher tumor stage, a higher probability of distant metastasis, and a shorter PFS and OS [36,37] | |
| Prostate cancer | |
| Apelin upregulation in tissue more frequently occurs in prostate cancer tissues with advanced tumor stage and metastasis and is associated with a shorter biochemical recurrence-free survival [31] Apelin expression in tissue correlates with disease stage [43] | APLN silencing enhances the radiosensitivity of prostate cancer by downregulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and the Bcl-2 protein family, and by promoting apoptosis mediated by Bax and caspase-3 [156] Apelin expression in tissue predicts cancer progression independently of other potential confounders in patients treated with one or more lines of chemotherapy, surgery, and/or radiotherapy [43] |
| Muscle-invasive bladder cancer | |
| Apelin expression in tissue and circulating apelin positively correlate with a higher tumor stage, a higher probability of distant metastasis, and a shorter PFS and OS [35] | Resistance to doxorubicin [269] -miR-15a-5p promotes sensitization of cells to doxorubicin |
| Chondrosarcoma | |
| Resistance to doxorubicin [193] -apelin is more expressed in doxorubicin-resistant tumor cells -apelin expression is higher in high-grade cancer tissues than in low-grade ones -miR-631 is a key regulator of apelin expression in doxorubicin-resistant cells | |
| Multiple myeloma | |
| Apelin expression in tissue and circulating apelin positively correlate with a higher tumor stage, a higher probability of distant metastasis, and a shorter PFS and OS [39] | Resistance to doxorubicin [193] -apelin is more expressed in doxorubicin-resistant tumor cells -apelin expression is higher in high-grade cancer tissues than in low-grade ones -miR-631 is a key regulator of apelin expression in doxorubicin-resistant cells Resistance to bortexomib [237] -miR-631 is downregulated in resistant cells |
| Ovarian cancer | |
| APJ expression in tissue significantly correlates with a decreased OS (14.7 months) in patients with high-grade cancer [32] Apelin expression in tissue correlates with disease stage [43] | Resistance to bevacizumab [174,196] -increased apelin expression is associated with reduced disease-free survival and a poor prognosis Resistance to sorafenib [194,195] -overexpression of apelin/APJ reduces the response of cancer cells to sorafenib Resistance to cisplatin [226] -overexpression of miR-195–5p downregulates cisplatin resistance by targeting PSAT1 and inhibiting the GSK3β/β-catenin pathway Resistance to anisomycin [251] -BACE1-AS silencing results in drug resistance Apelin expression in tissue predicts cancer progression independently of other potential confounders in patients treated with one or more lines of chemotherapy, surgery, and/or radiotherapy [43] |
| Cervical cancer | |
| Apelin expression in tissue positively correlates with advanced clinicopathologic features, poor therapy outcomes, and short survival [17,18,19] Apelin expression in tissue correlates with disease stage [43] | Resistance to bevacizumab [174] -increased apelin expression is associated with reduced disease-free survival Resistance to sorafenib [194,195] -overexpression of apelin/APJ reduces the response of cancer cells to sorafenib Apelin expression in tissue predicts cancer progression independently of other potential confounders in patients treated with one or more lines of chemotherapy, surgery, and/or radiotherapy [43] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naldi, L.; Peri, A.; Fibbi, B. Apelin/APJ: Another Player in the Cancer Biology Network. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072986
Naldi L, Peri A, Fibbi B. Apelin/APJ: Another Player in the Cancer Biology Network. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):2986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072986
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaldi, Laura, Alessandro Peri, and Benedetta Fibbi. 2025. "Apelin/APJ: Another Player in the Cancer Biology Network" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 2986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072986
APA StyleNaldi, L., Peri, A., & Fibbi, B. (2025). Apelin/APJ: Another Player in the Cancer Biology Network. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 2986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072986





