Strategies to Overcome Resistance to Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Lung Cancer
2. EGFR-Mutated NSCLC: The Rise of TKI Treatments
3. Acquired Resistance to Osimertinib
4. Strategies to Overcome On-Target Resistance to Osimertinib (See Table 2)
4.1. Fourth-Generation EGFR TKIs
4.2. Combining Osimertinib with Other EGFR TKIs
4.3. PROTACs
5. Strategies to Overcome Off-Target Resistance to Osimertinib (See Table 2)
5.1. MET
5.2. HER2
5.3. HER3
5.4. AXL
5.5. FGFR
5.6. VEGF/VEGFR
5.7. IGF1R
5.8. Other Strategies
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Laversanne, M.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today (Version 1.0); International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2024; Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Yatabe, Y.; Austin, J.H.M.; Beasley, M.B.; Chirieac Lucian, R.; Dacic, S.; Duhig, E.; Flieder, D.B.; et al. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, A.A.; Solomon, B.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Gainor, J.F.; Heist, R.S. Lung Cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barta, J.A.; Powell, C.A.; Wisnivesky, J.P. Global Epidemiology of Lung Cancer. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbula, B.R.; Gasalberti, D.P.; Mukkamalla, S.K.R.; Anjum, F. Squamous Cell Lung Cancer; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, T.J.; Bell, D.W.; Sordella, R.; Gurubhagavatula, S.; Okimoto, R.A.; Brannigan, B.W.; Harris, P.L.; Haserlat, S.M.; Supko, J.G.; Haluska, F.G.; et al. Activating Mutations in the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Underlying Responsiveness of Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer to Gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pao, W.; Miller, V.; Zakowski, M.; Doherty, J.; Politi, K.; Sarkaria, I.; Singh, B.; Heelan, R.; Rusch, V.; Fulton, L.; et al. EGF Receptor Gene Mutations Are Common in Lung Cancers from “Never Smokers” and Are Associated with Sensitivity of Tumors to Gefitinib and Erlotinib. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13306–13311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collisson, E.A.; Campbell, J.D.; Brooks, A.N.; Berger, A.H.; Lee, W.; Chmielecki, J.; Beer, D.G.; Cope, L.; Creighton, C.J.; Danilova, L.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Profiling of Lung Adenocarcinoma: The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Nature 2014, 511, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotow, J.; Bivona, T.G. Understanding and Targeting Resistance Mechanisms in NSCLC. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 637–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, P.K.; Arcila, M.E.; Fara, M.; Sima, C.S.; Miller, V.A.; Kris, M.G.; Ladanyi, M.; Riely, G.J. Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Lung Adenocarcinomas Harboring BRAF Mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2046–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergethon, K.; Shaw, A.T.; Ou, S.H.I.; Katayama, R.; Lovly, C.M.; McDonald, N.T.; Massion, P.P.; Siwak-Tapp, C.; Gonzalez, A.; Fang, R.; et al. ROS1 Rearrangements Define a Unique Molecular Class of Lung Cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, M.; Choi, Y.L.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujiwara, S.I.; Watanabe, H.; Kurashina, K.; Hatanaka, H.; et al. Identification of the Transforming EML4-ALK Fusion Gene in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nature 2007, 448, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, R.P.; Treece, A.L.; Lindeman, N.I.; Vasalos, P.; Shan, M.; Jennings, L.J.; Rimm, D.L. Worldwide Frequency of Commonly Detected EGFR Mutations. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, D.; Raez, L.E.; Russo, A.; Rolfo, C. Neuregulin 1 Gene (NRG1). A Potentially New Targetable Alteration for the Treatment of Lung Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraud, J.-S.; Jouinot, A.; Pasmant, E.; Tlemsani, C. NF1 Mutations as Biomarker of Response to Immune Checkpoint Blockades for Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, L.; Tiu, R.; Smyth, E.N.; Willard, M.D.; Li, L.; Beyrer, J.; Han, Y.; Singh, A. Clinical Characteristics, Treatments, and Concurrent Mutations in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with NF1 Mutations. Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, 32–41.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, L. NF1-Mutant Cancer and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Large Database Analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, 480–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Nadal, E.; Gray, J.E.; Ardizzoni, A.; Caria, N.; Puri, T.; Grohe, C. Overall Treatment Strategy for Patients with Metastatic NSCLC with Activating EGFR Mutations. Clin. Lung Cancer 2022, 23, e69–e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, M.L.; Marrocco, I.; Yarden, Y. EGFR in Cancer: Signaling Mechanisms, Drugs, and Acquired Resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlizza, E.; Romaniello, D.; Borrelli, F.; Pagano, F.; Girone, C.; Gelfo, V.; Kuhre, R.S.; Morselli, A.; Mazzeschi, M.; Sgarzi, M.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Activation: Interplay of Drivers in Cancer Progression. Cancers 2023, 15, 2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zeng, F.; Forrester, S.J.; Eguchi, S.; Zhang, M.Z.; Harris, R.C. Expression and Function of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Physiology and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1025–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citri, A.; Yarden, Y. EGF-ERBB Signalling: Towards the Systems Level. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.T.; Akita, R.W.; Sliwkowski, M.X. Binding Specificities and Affinities of Egf Domains for ErbB Receptors. FEBS Lett. 1999, 447, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarden, Y.; Sliwkowski, M.X. Untangling the ErbB Signalling Network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Yan, H.; Yang, J.; Dong, Z.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X.; et al. Molecular Characteristics and Clinical Outcomes of EGFR Exon 19 Indel Subtypes to EGFR TKIs in NSCLC Patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 111246–111257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beau-Faller, M.; Prim, N.; Ruppert, A.M.; Nanni-Metéllus, I.; Lacave, R.; Lacroix, L.; Escande, F.; Lizard, S.; Pretet, J.L.; Rouquette, I.; et al. Rare EGFR Exon 18 and Exon 20 Mutations in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer on 10 117 Patients: A Multicentre Observational Study by the French ERMETIC-IFCT Network. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcila, M.E.; Nafa, K.; Chaft, J.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Lau, C.; Reva, B.A.; Zakowski, M.F.; Kris, M.G.; Ladanyi, M. EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations in Lung Adenocarcinomas: Prevalence, Molecular Heterogeneity, and Clinicopathologic Characteristics. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Mitsudomi, T. Not All Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutations in Lung Cancer Are Created Equal: Perspectives for Individualized Treatment Strategy. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, A.; Mok, T.; Peters, S.; Popat, S.; Ahn, M.J.; de Marinis, F. Recent Advances on the Role of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in the Management of NSCLC with Uncommon, Non Exon 20 Insertions, EGFR Mutations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Brown, B.P.; Kim, S.; Ferguson, D.; Pavlick, D.C.; Jayakumaran, G.; Benayed, R.; Gallant, J.N.; Zhang, Y.K.; Yan, Y.; et al. Structure–Function Analysis of Oncogenic EGFR Kinase Domain Duplication Reveals Insights into Activation and a Potential Approach for Therapeutic Targeting. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copia Sperandio, R.; Luiza Teixeira Tostes, F.; Vidal Campregher, P.; Ribeiro Paes, V.; Moura, F.; Schvartsman, G. EGFR-RAD51 Fusion in Lung Adenocarcinoma with Systemic and Intracranial Response to Osimertinib: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Lung Cancer 2022, 166, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.T.; Vyse, S.; Huang, P.H. Rare Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 61, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miyauchi, E.; Inoue, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Maemondo, M.; Sugawara, S.; Oizumi, S.; Isobe, H.; Gemma, A.; Saijo, Y.; Yoshizawa, H.; et al. Efficacy of Chemotherapy after First-Line Gefitinib Therapy in EGFR Mutation-Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer--Data from a Randomized Phase III Study Comparing Gefitinib with Carboplatin plus Paclitaxel (NEJ002). Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 45, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Maemondo, M.; Sugawara, S.; Oizumi, S.; Isobe, H.; Gemma, A.; Harada, M.; Yoshizawa, H.; Kinoshita, I.; et al. Updated Overall Survival Results from a Randomized Phase III Trial Comparing Gefitinib with Carboplatin–Paclitaxel for Chemo-Naïve Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Sensitive EGFR Gene Mutations (NEJ002). Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, M.; Wu, Y.-L.; Thongprasert, S.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Leong, S.-S.; Sriuranpong, V.; Chao, T.-Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Chu, D.-T.; Saijo, N.; et al. Biomarker Analyses and Final Overall Survival Results From a Phase III, Randomized, Open-Label, First-Line Study of Gefitinib Versus Carboplatin/Paclitaxel in Clinically Selected Patients with Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer in Asia (IPASS). J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2866–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.-L.; Thongprasert, S.; Yang, C.-H.; Chu, D.-T.; Saijo, N.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Han, B.; Margono, B.; Ichinose, Y.; et al. Gefitinib or Carboplatin–Paclitaxel in Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudomi, T.; Morita, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Negoro, S.; Okamoto, I.; Tsurutani, J.; Seto, T.; Satouchi, M.; Tada, H.; Hirashima, T.; et al. Gefitinib versus Cisplatin plus Docetaxel in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harbouring Mutations of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (WJTOG3405): An Open Label, Randomised Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, H.; Shimokawa, M.; Seto, T.; Morita, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Okamoto, I.; Tsurutani, J.; Satouchi, M.; Hirashima, T.; Atagi, S.; et al. Final Overall Survival Results of WJTOG3405, a Randomized Phase III Trial Comparing Gefitinib versus Cisplatin with Docetaxel as the First-Line Treatment for Patients with Stage IIIB/IV or Postoperative Recurrent EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1978–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Y.-L.; Chen, G.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.-Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Ren, S.; et al. Erlotinib versus Chemotherapy as First-Line Treatment for Patients with Advanced EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Randomised, Phase 3 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Y.L.; Chen, G.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.-Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Ren, S.; et al. Final Overall Survival Results from a Randomised, Phase III Study of Erlotinib versus Chemotherapy as First-Line Treatment of EGFR Mutation-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802). Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1877–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, R.; Carcereny, E.; Gervais, R.; Vergnenegre, A.; Massuti, B.; Felip, E.; Palmero, R.; Garcia-Gomez, R.; Pallares, C.; Sanchez, J.M.; et al. Erlotinib versus Standard Chemotherapy as First-Line Treatment for European Patients with Advanced EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (EURTAC): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Randomised Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.-H.; Wu, Y.-L.; Schuler, M.; Sebastian, M.; Popat, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.-P.; O’Byrne, K.; Feng, J.; et al. Afatinib versus Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy for EGFR Mutation-Positive Lung Adenocarcinoma (LUX-Lung 3 and LUX-Lung 6): Analysis of Overall Survival Data from Two Randomised, Phase 3 Trials. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequist, L.V.; Yang, J.C.H.; Yamamoto, N.; O’Byrne, K.; Hirsh, V.; Mok, T.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Tsai, C.M.; Boyer, M.; et al. Phase III Study of Afatinib or Cisplatin plus Pemetrexed in Patients with Metastatic Lung Adenocarcinoma with EGFR Mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.-P.; Feng, J.; Lu, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Hou, M.; Shi, J.H.; Lee, K.Y.; et al. Afatinib versus Cisplatin plus Gemcitabine for First-Line Treatment of Asian Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harbouring EGFR Mutations (LUX-Lung 6): An Open-Label, Randomised Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Mok, T.S.; Han, J.-Y.; Ahn, M.-J.; Delmonte, A.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Kim, S.W.; Shepherd, F.A.; Laskin, J.; He, Y.; et al. Osimertinib versus Platinum–Pemetrexed for Patients with EGFR T790M Advanced NSCLC and Progression on a Prior EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor: AURA3 Overall Survival Analysis. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1536–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.-L.; Ahn, M.-J.; Garassino, M.C.; Kim, H.R.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Shepherd, F.A.; He, Y.; Akamatsu, H.; Theelen, W.S.M.E.; et al. Osimertinib or Platinum–Pemetrexed in EGFR T790M–Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.-C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR -Mutated Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR -Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Tsuji, F.; Linke, R.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; et al. Dacomitinib versus Gefitinib as First-Line Treatment for Patients with EGFR-Mutation-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (ARCHER 1050): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Lee, M.; Linke, R.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; et al. Improvement in Overall Survival in a Randomized Study That Compared Dacomitinib with Gefitinib in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and EGFR-Activating Mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2244–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Chawla, A.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; Migliorino, M.R.; et al. Updated Overall Survival in a Randomized Study Comparing Dacomitinib with Gefitinib as First-Line Treatment in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and EGFR-Activating Mutations. Drugs 2021, 81, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Tang, K.-J.; Cho, B.C.; Liu, B.; Paz-Ares, L.; Cheng, S.; Kitazono, S.; Thiagarajan, M.; Goldman, J.W.; Sabari, J.K.; et al. Amivantamab plus Chemotherapy in NSCLC with EGFR Exon 20 Insertions. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2039–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Haura, E.B.; Leighl, N.B.; Mitchell, P.; Shu, C.A.; Girard, N.; Viteri, S.; Han, J.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, C.K.; et al. Amivantamab in EGFR Exon 20 Insertion-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Progressing on Platinum Chemotherapy: Initial Results From the CHRYSALIS Phase I Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3391–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besse, B.; Goto, K.; Wang, Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Marmarelis, M.E.; Ohe, Y.; Caro, R.B.; Kim, D.-W.; Lee, J.-S.; Cousin, S.; et al. Amivantamab Plus Lazertinib in Patients with EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) After Progression on Osimertinib and Platinum-Based Chemotherapy: Results From CHRYSALIS-2 Cohort A. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2025, in press. [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.C.; Lu, S.; Felip, E.; Spira, A.I.; Girard, N.; Lee, J.-S.; Lee, S.-H.; Ostapenko, Y.; Danchaivijitr, P.; Liu, B.; et al. Amivantamab plus Lazertinib in Previously Untreated EGFR -Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1486–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, A.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Melosky, B.; Shih, J.-Y.; Wang, J.; Azuma, K.; Juan-Vidal, O.; Cobo, M.; et al. Amivantamab plus Chemotherapy with and without Lazertinib in EGFR-Mutant Advanced NSCLC after Disease Progression on Osimertinib: Primary Results from the Phase III MARIPOSA-2 Study. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, S.-W.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Riely, G.J.; Mekhail, T.; Nguyen, D.; Garcia Campelo, M.R.; Felip, E.; et al. Treatment Outcomes and Safety of Mobocertinib in Platinum-Pretreated Patients with EGFR Exon 20 Insertion–Positive Metastatic Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, e214761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazandjian, D.; Blumenthal, G.M.; Yuan, W.; He, K.; Keegan, P.; Pazdur, R. FDA Approval of Gefitinib for the Treatment of Patients with Metastatic EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.H.; Johnson, J.R.; Chen, Y.-F.; Sridhara, R.; Pazdur, R. FDA Drug Approval Summary: Erlotinib (Tarceva®) Tablets. Oncologist 2005, 10, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, L.; Yuan, X.; Sun, Y. Icotinib, a Selective EGF Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, for the Treatment of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Future Oncol. 2015, 11, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, H.J.; Sun, Y.; Dirix, L.Y.; Jiang, Z.; Paridaens, R.; Tan, A.R.; Awada, A.; Ranade, A.; Jiao, S.; Schwartz, G.; et al. Neratinib, an Irreversible ErbB Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced ErbB2-Positive Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maemondo, M.; Inoue, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Sugawara, S.; Oizumi, S.; Isobe, H.; Gemma, A.; Harada, M.; Yoshizawa, H.; Kinoshita, I.; et al. Gefitinib or Chemotherapy for Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer with Mutated EGFR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sos, M.L.; Rode, H.B.; Heynck, S.; Peifer, M.; Fischer, F.; Klüter, S.; Pawar, V.G.; Reuter, C.; Heuckmann, J.M.; Weiss, J.; et al. Chemogenomic Profiling Provides Insights into the Limited Activity of Irreversible EGFR Inhibitors in Tumor Cells Expressing the T790M EGFR Resistance Mutation. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, Y.N.; Scott, L.J. Osimertinib: A Review in T790M-Positive Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Target. Oncol. 2017, 12, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greig, S.L. Osimertinib: First Global Approval. Drugs 2016, 76, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaid, A.K.; Gupta, A.; Momi, G. Overall Survival in Stage IV EGFR Mutation-Positive NSCLC: Comparing First-, Second- And Third-Generation EGFR-TKIs (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2021, 58, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Milone, M.; Seetharamu, N. Osimertinib in Egfr-Mutated Lung Cancer: A Review of the Existing and Emerging Clinical Data. Onco Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 4579–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatineni, V.; O’Shea, P.J.; Ozair, A.; Khosla, A.A.; Saxena, S.; Rauf, Y.; Jia, X.; Murphy, E.S.; Chao, S.T.; Suh, J.H.; et al. First- versus Third-Generation EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Brain Metastases. Cancers 2023, 15, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, N.; Nagasaka, M. Amivantamab plus Lazertinib vs. Osimertinib in First-Line EGFR -Mutant Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2025, 19, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Jänne, P.A.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Yanagitani, N.; Kim, S.-W.; Sugawara, S.; Yu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Geater, S.L.; et al. Osimertinib with or without Chemotherapy in EGFR -Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1935–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrocco, I.; Giri, S.; Simoni-Nieves, A.; Gupta, N.; Rudnitsky, A.; Haga, Y.; Romaniello, D.; Sekar, A.; Zerbib, M.; Oren, R.; et al. L858R Emerges as a Potential Biomarker Predicting Response of Lung Cancer Models to Anti-EGFR Antibodies: Comparison of Osimertinib vs. Cetuximab. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 101142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Chen, L.; Sangji, N.; Okabe, T.; Yonesaka, K.; Francis, J.M.; Flavin, R.J.; Johnson, W.; Kwon, J.; Yu, S.; et al. Cetuximab Response of Lung Cancer-Derived EGF Receptor Mutants Is Associated with Asymmetric Dimerization. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 6770–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, M.J.; Aredo, J.V.; Starrett, J.H.; Stockhammer, P.; van Alderwerelt van Rosenburgh, I.K.; Wurtz, A.; Piper-Valillo, A.J.; Piotrowska, Z.; Falcon, C.; Yu, H.A.; et al. Efficacy of Osimertinib in Patients with Lung Cancer Positive for Uncommon EGFR Exon 19 Deletion Mutations. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 2123–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robichaux, J.P.; Le, X.; Vijayan, R.S.K.; Hicks, J.K.; Heeke, S.; Elamin, Y.Y.; Lin, H.Y.; Udagawa, H.; Skoulidis, F.; Tran, H.; et al. Structure-Based Classification Predicts Drug Response in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC. Nature 2021, 597, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendrell, J.A.; Quantin, X.; Aussel, A.; Solassol, I.; Serre, I.; Solassol, J. EGFR-Dependent Mechanisms of Resistance to Osimertinib Determined by CtDNA NGS Analysis Identify Patients with Better Outcome. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 4084–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, A.; Sharma, S.; Minari, R.; Perego, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Tiseo, M. Resistance Mechanisms to Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 725–737. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Yang, B.; An, Q.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Cao, X.; Xia, J. Acquired Resistance to Third-Generation EGFR-TKIs and Emerging next-Generation EGFR Inhibitors. Innovation 2021, 2, 100103. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.-Y.; Tsai, C.-L.; Huang, H.-P. Optimizing Osimertinib for NSCLC: Targeting Resistance and Exploring Combination Therapeutics. Cancers 2025, 17, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielecki, J.; Gray, J.E.; Cheng, Y.; Ohe, Y.; Imamura, F.; Cho, B.C.; Lin, M.C.; Majem, M.; Shah, R.; Rukazenkov, Y.; et al. Candidate Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance to First-Line Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielecki, J.; Mok, T.; Wu, Y.L.; Han, J.Y.; Ahn, M.J.; Ramalingam, S.S.; John, T.; Okamoto, I.; Yang, J.C.H.; Shepherd, F.A.; et al. Analysis of Acquired Resistance Mechanisms to Osimertinib in Patients with EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer from the AURA3 Trial. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, D.A.E.; Ashton, S.E.; Ghiorghiu, S.; Eberlein, C.; Nebhan, C.A.; Spitzler, P.J.; Orme, J.P.; Finlay, M.R.V.; Ward, R.A.; Mellor, M.J.; et al. AZD9291, an Irreversible EGFR TKI, Overcomes T790M-Mediated Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors in Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1046–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, N.; Ou, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wu, X.; Bao, H.; Tong, X.; Wang, X.; Shao, Y.W.; et al. Investigating Novel Resistance Mechanisms to Third-Generation EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Osimertinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3097–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Mao, T.; Wang, J.; Zheng, H.; Hu, Z.; Cao, P.; Yang, S.; Zhu, L.; Guo, S.; Zhao, X.; et al. Toward the next Generation EGFR Inhibitors: An Overview of Osimertinib Resistance Mediated by EGFR Mutations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cell Commun. Signal 2023, 21, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenfeld, A.J.; Chan, J.M.; Kubota, D.; Sato, H.; Rizvi, H.; Daneshbod, Y.; Chang, J.C.; Paik, P.K.; Offin, M.; Arcila, M.E.; et al. Tumor Analyses Reveal Squamous Transformation and Off-Target Alterations As Early Resistance Mechanisms to First-Line Osimertinib in EGFR -Mutant Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2654–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starrett, J.H.; Guernet, A.A.; Cuomo, M.E.; Poels, K.E.; van Alderwerelt van Rosenburgh, I.K.; Nagelberg, A.; Farnsworth, D.; Price, K.S.; Khan, H.; Ashtekar, K.D.; et al. Drug Sensitivity and Allele Specificity of First-Line Osimertinib Resistance EGFR Mutations. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.P.; Zhang, Y.-K.; Westover, D.; Yan, Y.; Qiao, H.; Huang, V.; Du, Z.; Smith, J.A.; Ross, J.S.; Miller, V.A.; et al. On-Target Resistance to the Mutant-Selective EGFR Inhibitor Osimertinib Can Develop in an Allele-Specific Manner Dependent on the Original EGFR-Activating Mutation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3341–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enrico, D.H.; Lacroix, L.; Rouleau, E.; Scoazec, J.-Y.; Loriot, Y.; Tselikas, L.; Jovelet, C.; Planchard, D.; Gazzah, A.; Mezquita, L.; et al. Multiple Synchronous Mechanisms May Contribute to Osimertinib Resistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients: Insights of the MATCH-R Study. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nukaga, S.; Yasuda, H.; Tsuchihara, K.; Hamamoto, J.; Masuzawa, K.; Kawada, I.; Naoki, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Mimaki, S.; Ikemura, S.; et al. Amplification of EGFR Wild-Type Alleles in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells Confers Acquired Resistance to Mutation-Selective EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2078–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonetti, A.; Minari, R.; Mazzaschi, G.; Gnetti, L.; La Monica, S.; Alfieri, R.; Campanini, N.; Verzè, M.; Olivani, A.; Ventura, L.; et al. Small Cell Lung Cancer Transformation as a Resistance Mechanism to Osimertinib in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma: Case Report and Literature Review. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 642190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Patel, D.; Jofre, S.; Fidvi, S.; Suhrland, M.; Cohen, P.; Cheng, H. Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Transformation as a Mechanism of Acquired Resistance to Osimertinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Case Report and Literature Review. Clin. Lung Cancer 2022, 23, e276–e282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Kuno, Y.; Hayai, S.; Teramachi, R.; Yamashita, R.; Saito, Y.; Higuchi, K.; Nara, Y.; Ikeda, T. An EGFR T790M-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma Undergoing Large-Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma Transformation after Osimertinib Therapy: A Case Report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, H.; Yamasaki, A.; Ueda, Y.; Sumikawa, T.; Maeta, H.; Nakamoto, S.; Shimizu, E. Squamous Cell Carcinoma Transformation from EGFR-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report and Literature Review. Clin. Lung Cancer 2018, 19, e63–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoni-Rugiu, E.; Melchior, L.C.; Urbanska, E.M.; Jakobsen, J.N.; de Stricker, K.; Grauslund, M.; Sørensen, J.B. Intrinsic Resistance to EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Differences and Similarities with Acquired Resistance. Cancers 2019, 11, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Lee, C.K.; Kurata, T.; Kim, D.-W.; John, T.; Nogami, N.; Ohe, Y.; Mann, H.; Rukazenkov, Y.; et al. Osimertinib As First-Line Treatment of EGFR Mutation-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Oxnard, G.R.; Cohen, E.F.; Mahadevan, N.R.; Alessi, J.V.; Hung, Y.P.; Bertram, A.A.; Heppner, D.E.; Ribeiro, M.F.; Sacardo, K.P.; et al. Genomic and Biological Study of Fusion Genes as Resistance Mechanisms to EGFR Inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Wel, J.W.T.; Jebbink, M.; van den Broek, D.; Steinbusch, L.C.; Theelen, W.S.M.E.; Ruiter, G.; Buikhuisen, W.; Burgers, J.A.; Baas, P.; Vermeulen, M.; et al. Combined Analysis of Circulating Tumor DNA and Tumor Tissue to Overcome Osimertinib Resistance (OSIRIS); the Second Line Osimertinib Cohort. Lung Cancer 2024, 198, 107972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, A.; Leighl, N.; Blackhall, F.; Popat, S.; Kerr, K.; Ahn, M.J.; Arcila, M.E.; Arrieta, O.; Planchard, D.; de Marinis, F.; et al. ESMO Expert Consensus Statements on the Management of EGFR Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 466–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Yun, C.-H.; Park, E.; Ercan, D.; Manuia, M.; Juarez, J.; Xu, C.; Rhee, K.; Chen, T.; Zhang, H.; et al. Overcoming EGFR(T790M) and EGFR(C797S) Resistance with Mutant-Selective Allosteric Inhibitors. Nature 2016, 534, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- To, C.; Jang, J.; Chen, T.; Park, E.; Mushajiang, M.; De Clercq, D.J.H.; Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Cameron, M.D.; Heppner, D.E.; et al. Single and Dual Targeting of Mutant EGFR with an Allosteric Inhibitor. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 926–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyett, T.S.; To, C.; Heppner, D.E.; Rana, J.K.; Schmoker, A.M.; Jang, J.; De Clercq, D.J.H.; Gomez, G.; Scott, D.A.; Gray, N.S.; et al. Molecular Basis for Cooperative Binding and Synergy of ATP-Site and Allosteric EGFR Inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eno, M.S.; Brubaker, J.D.; Campbell, J.E.; De Savi, C.; Guzi, T.J.; Williams, B.D.; Wilson, D.; Wilson, K.; Brooijmans, N.; Kim, J.; et al. Discovery of BLU-945, a Reversible, Potent, and Wild-Type-Sparing Next-Generation EGFR Mutant Inhibitor for Treatment-Resistant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 9662–9677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.M.; Schalm, S.S.; Lee, E.J.; Park, S.; Conti, C.; Millet, Y.A.; Woessner, R.; Zhang, Z.; Tavera-Mendoza, L.E.; Stevison, F.; et al. BLU-945, a Potent and Selective next-Generation EGFR TKI, Has Antitumor Activity in Models of Osimertinib-Resistant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2024, 16, 17588359241280689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elamin, Y.Y.; Nagasaka, M.; Shum, E.; Bazhenova, L.; Ross Camidge, D.; Chul Cho, B.; Felip, E.; Goto, K.; Lin, C.-C.; Piotrowska, Z.; et al. Rapid Abstract Session BLU-945 Monotherapy and in Combination with Osimertinib (OSI) in Previously Treated Patients with Advanced EGFR-Mutant (EGFRm) NSCLC in the Phase 1/2 SYMPHONY Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blueprint Medicines Blueprint Medicines Highlights 2024 Corporate Strategy and Business Priorities at 42nd Annual J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference. Available online: https://ir.blueprintmedicines.com/news-releases/news-release-details/blueprint-medicines-highlights-2024-corporate-strategy-and (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Tavera, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wardwell, S.; Job, E.; McGinn, K.; Chen, M.; Iliou, M.; Albayya, F.; Campbell, J.; Eno, M.; et al. BLU-701 Tumour Suppression and Intracranial Activity as a Single Agent and in Combination with BLU-945 in Models of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Driven by EGFR Mutations. Lung Cancer 2022, 165, S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavera, L.; Schalm, S.; Campbell, J.; Guo, J.; Medendorp, C.; Chen, M.; Albayya, F.; Dineen, T.; Zhang, Z.; Iliou, M.; et al. Antitumor Activity of BLU-945 and BLU-701 as Single Agents and in Combination in EGFR L858R-Driven Models of NSCLC. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 3328. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.L.; Henry, J.T.; Spira, A.I.; Battiste, J.; Alnahhas, I.; Ahluwalia, S.; Barve, M.A.; Edenfield, W.J.; Nam, D.-H.; Eathiraj, S.; et al. TPS9156 Poster Session A Phase 1 Study to Assess BDTX-1535, an Oral EGFR Inhibitor, in Patients with Glioblastoma or Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, TPS9156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black Diamond Therapeutics Announces Initial Phase 2 Data Demonstrating Robust Anti-Tumor Activity of BDTX-1535 in Patients with Recurrent EGFRm NSCLC Who Present with a Broad Spectrum of Classical, Non-Classical, and C797S Resistance Mutations. 2024. Available online: https://investors.blackdiamondtherapeutics.com/news-releases/news-release-details/black-diamond-therapeutics-announces-initial-phase-2-data/ (accessed on 22 March 2025).
- Niederst, M.J.; Hu, H.; Mulvey, H.E.; Lockerman, E.L.; Garcia, A.R.; Piotrowska, Z.; Sequist, L.V.; Engelman, J.A. The Allelic Context of the C797S Mutation Acquired upon Treatment with Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitors Impacts Sensitivity to Subsequent Treatment Strategies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3924–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, J.-J.; Huang, J.; Ye, J.-Y.; Zhang, X.-C.; Tu, H.-Y.; Han-Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.-L. Lung Adenocarcinoma Harboring EGFR T790M and In Trans C797S Responds to Combination Therapy of First- and Third-Generation EGFR TKIs and Shifts Allelic Configuration at Resistance. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1723–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulananda, S.; Do, H.; Musafer, A.; Mitchell, P.; Dobrovic, A.; John, T. Combination Osimertinib and Gefitinib in C797S and T790M EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1728–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangachari, D.; To, C.; Shpilsky, J.E.; VanderLaan, P.A.; Kobayashi, S.S.; Mushajiang, M.; Lau, C.J.; Paweletz, C.P.; Oxnard, G.R.; Jänne, P.A.; et al. EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancers Resistant to Osimertinib through EGFR C797S Respond to First-Generation Reversible EGFR Inhibitors but Eventually Acquire EGFR T790M/C797S in Preclinical Models and Clinical Samples. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotow, J.K.; Costa, D.B.; Paweletz, C.P.; Awad, M.M.; Marcoux, P.; Rangachari, D.; Barbie, D.A.; Sands, J.; Cheng, M.L.; Johnson, B.E.; et al. Concurrent Osimertinib plus Gefitinib for First-Line Treatment of EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 9507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.A.; Goldberg, S.B.; Le, X.; Piotrowska, Z.; Goldman, J.W.; De Langen, A.J.; Okamoto, I.; Cho, B.C.; Smith, P.; Mensi, I.; et al. Biomarker-Directed Phase II Platform Study in Patients with EGFR Sensitizing Mutation-Positive Advanced/Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Whose Disease Has Progressed on First-Line Osimertinib Therapy (ORCHARD). Clin. Lung Cancer 2021, 22, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, K.M.; Kim, K.B.; Kumagai, A.; Mercurio, F.; Crews, C.M.; Deshaies, R.J. Protacs: Chimeric Molecules That Target Proteins to the Skp1-Cullin-F Box Complex for Ubiquitination and Degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8554–8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burslem, G.M.; Crews, C.M. Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeras as Therapeutics and Tools for Biological Discovery. Cell 2020, 181, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneekloth, A.R.; Pucheault, M.; Tae, H.S.; Crews, C.M. Targeted Intracellular Protein Degradation Induced by a Small Molecule: En Route to Chemical Proteomics. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 5904–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Wang, E.S.; Donovan, K.A.; Liang, Y.; Fischer, E.S.; Zhang, T.; Gray, N.S. Development of Dual and Selective Degraders of Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 4 and 6. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 6321–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cromm, P.M.; Samarasinghe, K.T.G.; Hines, J.; Crews, C.M. Addressing Kinase-Independent Functions of Fak via PROTAC-Mediated Degradation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 17019–17026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondeson, D.P.; Mares, A.; Smith, I.E.D.; Ko, E.; Campos, S.; Miah, A.H.; Mulholland, K.E.; Routly, N.; Buckley, D.L.; Gustafson, J.L.; et al. Catalytic in Vivo Protein Knockdown by Small-Molecule PROTACs. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, M.; Crews, C.M. PROteolysis TArgeting Chimeras (PROTACs)—Past, Present and Future. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2019, 31, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Hu, B.; Wang, M.; Xu, F.; Miao, B.; Yang, C.-Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Hayes, D.F.; Chinnaswamy, K.; et al. Discovery of ERD-308 as a Highly Potent Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC) Degrader of Estrogen Receptor (ER). J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 1420–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Hu, J.; Xu, F.; Chen, Z.; Bai, L.; Fernandez-Salas, E.; Lin, M.; Liu, L.; Yang, C.-Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Discovery of a Small-Molecule Degrader of Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal (BET) Proteins with Picomolar Cellular Potencies and Capable of Achieving Tumor Regression. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 462–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cui, J.; Chen, H.; Yu, B.; Long, S. Recent Progress in Degradation of Membrane Proteins by PROTACs and Alternative Targeted Protein Degradation Techniques. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 262, 115911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, E.P.; Ma, C.; De Laurentiis, M.; Iwata, H.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Wander, S.A.; Danso, M.; Lu, D.R.; Perkins Smith, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. VERITAC-2: A Phase III Study of Vepdegestrant, a PROTAC ER Degrader, versus Fulvestrant in ER+/HER2- Advanced Breast Cancer. Future Oncol. 2024, 20, 2447–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burslem, G.M.; Smith, B.E.; Lai, A.C.; Jaime-Figueroa, S.; McQuaid, D.C.; Bondeson, D.P.; Toure, M.; Dong, H.; Qian, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. The Advantages of Targeted Protein Degradation Over Inhibition: An RTK Case Study. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 67–77.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Du, Y.; Huang, L.; Cui, J.; Niu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, Q. Discovery of Novel Potent Covalent Inhibitor-Based EGFR Degrader with Excellent in Vivo Efficacy. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 120, 105605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Zheng, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Discovery and Biological Evaluation of Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras (PROTACs) as an EGFR Degraders Based on Osimertinib and Lenalidomide. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; To, C.; De Clercq, D.J.H.; Park, E.; Ponthier, C.M.; Shin, B.H.; Mushajiang, M.; Nowak, R.P.; Fischer, E.S.; Eck, M.J.; et al. Mutant-Selective Allosteric EGFR Degraders Are Effective Against a Broad Range of Drug-Resistant Mutations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 14481–14489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Li, A.; Zheng, L.; Chen, S.; Li, Y. EGFR Degraders in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Breakthrough and Unresolved Issue. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2024, 103, e14517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchibori, K.; Inase, N.; Araki, M.; Kamada, M.; Sato, S.; Okuno, Y.; Fujita, N.; Katayama, R. Brigatinib Combined with Anti-EGFR Antibody Overcomes Osimertinib Resistance in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ye, G.; Zhang, G. HJM-561, a Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable EGFR PROTAC That Overcomes Osimertinib-Resistant EGFR Triple Mutations. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xie, R.; Ai-Furas, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, J.; Xu, F.; Xu, T. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Novel EGFR PROTACs Targeting Del19/T790M/C797S Mutation. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartak, R.; Deore, B.; Sanhueza, C.A.; Patel, K. Cetuximab-Based PROteolysis Targeting Chimera for Effectual Downregulation of NSCLC with Varied EGFR Mutations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 252, 126413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, J.A.; Zejnullahu, K.; Mitsudomi, T.; Song, Y.; Hyland, C.; Park, J.O.; Lindeman, N.; Gale, C.-M.; Zhao, X.; Christensen, J.; et al. MET Amplification Leads to Gefitinib Resistance in Lung Cancer by Activating ERBB3 Signaling. Science 2007, 316, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehlman, C.; Swalduz, A.; Monnet, I.; Morin, C.; Wislez, M.; Guisier, F.; Curcio, H.; Du Rusquec, P.; Cortot, A.B.; Gounant, V.; et al. COMPOSIT Study: Evaluating Osimertinib Combination with Targeted Therapies in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncologist 2024, 26, oyae312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanska, E.M.; Grauslund, M.; Koffeldt, P.R.; Truelsen, S.L.B.; Löfgren, J.O.; Costa, J.C.; Melchior, L.C.; Sørensen, J.B.; Santoni-Rugiu, E. Real-World Data on Combined EGFR-TKI and Crizotinib Treatment for Acquired and De Novo MET Amplification in Patients with Metastatic EGFR-Mutated NSCLC. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmaier, R.J.; Markovets, A.A.; Ahn, M.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Han, J.-Y.; Cho, B.C.; Yu, H.A.; Kim, S.-W.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; et al. Osimertinib + Savolitinib to Overcome Acquired MET-Mediated Resistance in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated, MET-Amplified Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: TATTON. Cancer Discov. 2023, 13, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.A.; Ambrose, H.; Baik, C.; Cho, B.C.; Cocco, E.; Goldberg, S.B.; Goldman, J.W.; Kraljevic, S.; de Langen, A.J.; Okamoto, I.; et al. 1239P ORCHARD Osimertinib + Savolitinib Interim Analysis: A Biomarker-Directed Phase II Platform Study in Patients (Pts) with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Whose Disease Has Progressed on First-Line (1L) Osimertinib. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S978–S979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.; De Marinis, F.; Bonanno, L.; Cho, B.C.; Kim, T.-M.; Cheng, S.; Novello, S.; Proto, C.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, J.S.; et al. EP08.02-140 MET Biomarker-Based Preliminary Efficacy Analysis in SAVANNAH: Savolitinib+osimertinib in EGFRm NSCLC Post-Osimertinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S469–S470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Guarneri, V.; Voon, P.J.; Lim, B.K.; Yang, J.-J.; Wislez, M.; Huang, C.; Liam, C.K.; Mazieres, J.; Tho, L.M.; et al. Tepotinib plus Osimertinib in Patients with EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with MET Amplification Following Progression on First-Line Osimertinib (INSIGHT 2): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamori, S.; Seto, T.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kinoshita, F.; Fujishita, T.; Ito, K.; Toyozawa, R.; Shoji, F.; Okamoto, T. Case Report: Success of Tepotinib Therapy in Overcoming Resistance to Osimertinib in a Patient with EGFR-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma with a Potential Acquired MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutation. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 965741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzawa, K.; Offin, M.; Schoenfeld, A.J.; Plodkowski, A.J.; Odintsov, I.; Lu, D.; Lockwood, W.W.; Arcila, M.E.; Rudin, C.M.; Drilon, A.; et al. Acquired MET Exon 14 Alteration Drives Secondary Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, PO.19.00011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghawy, O.; Barsouk, A.; Reed-Guy, L.; Stalker, M.; Sussman, J.; Robinson, K.; Kosteva, J.; Singh, A.; Cohen, R.B.; Langer, C.; et al. Brief Report: Osimertinib Plus Capmatinib for Patients with MET-Altered EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Following Progression on Front Line Therapy. Clin. Lung Cancer 2024, 26, 158–163.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, K.; Larkins, E.; Chatterjee, S.; Mishra-Kalyani, P.S.; Aungst, S.; Wearne, E.; Subramaniam, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, J.; et al. FDAApproval Summary: Amivantamab for the Treatment of Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 3262–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moores, S.L.; Chiu, M.L.; Bushey, B.S.; Chevalier, K.; Luistro, L.; Dorn, K.; Brezski, R.J.; Haytko, P.; Kelly, T.; Wu, S.J.; et al. A Novel Bispecific Antibody Targeting EGFR and CMet Is Effective against EGFR Inhibitor-Resistant Lung Tumors. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3942–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayaraghavan, S.; Lipfert, L.; Chevalier, K.; Bushey, B.S.; Henley, B.; Lenhart, R.; Sendecki, J.; Beqiri, M.; Millar, H.J.; Packman, K.; et al. Amivantamab (JNJ-61186372), an Fc Enhanced EGFR/CMet Bispecific Antibody, Induces Receptor Downmodulation and Antitumor Activity by Monocyte/Macrophage Trogocytosis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 2044–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besse, B.; Baik, C.S.; Marmarelis, M.E.; Sabari, J.K.; Goto, K.; Shu, C.A.; Lee, J.-S.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Cho, B.C.; Waqar, S.N.; et al. Predictive Biomarkers for Treatment with Amivantamab plus Lazertinib among EGFR-Mutated NSCLC in the Post-Osimertinib Setting: Analysis of Tissue IHC and CtDNA NGS. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 9013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Anderson, M.G.; Oleksijew, A.; Vaidya, K.S.; Boghaert, E.R.; Tucker, L.; Zhang, Q.; Han, E.K.; Palma, J.P.; Naumovski, L.; et al. ABBV-399, a c-Met Antibody-Drug Conjugate That Targets Both MET-Amplified and c-Met-Overexpressing Tumors, Irrespective of MET Pathway Dependence. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horinouchi, H.; Cho, B.C.; Camidge, D.R.; Goto, K.; Tomasini, P.; Li, Y.; Vasilopoulos, A.; Brunsdon, P.; Hoffman, D.; Shi, W.; et al. Results from a Phase 1b Study of Telisotuzumab Vedotin in Combination with Osimertinib in Patients with C-Met Protein-Overexpressing, EGFR-Mutated Locally Advanced/Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) after Progression on Prior Osimertinib. Ann. Oncol. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takezawa, K.; Pirazzoli, V.; Arcila, M.E.; Nebhan, C.A.; Song, X.; de Stanchina, E.; Ohashi, K.; Janjigian, Y.Y.; Spitzler, P.J.; Melnick, M.A.; et al. HER2 Amplification: A Potential Mechanism of Acquired Resistance to EGFR Inhibition in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers That Lack the Second-Site EGFRT790M Mutation. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, A.; Jänne, P.A.; Mok, T.; Peters, S. Overcoming Therapy Resistance in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romaniello, D.; Mazzeo, L.; Mancini, M.; Marrocco, I.; Noronha, A.; Kreitman, M.; Srivastava, S.; Ghosh, S.; Lindzen, M.; Salame, T.M.; et al. A Combination of Approved Antibodies Overcomes Resistance of Lung Cancer to Osimertinib by Blocking Bypass Pathways. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5610–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrocco, I.; Romaniello, D.; Vaknin, I.; Drago-Garcia, D.; Oren, R.; Uribe, M.L.; Belugali Nataraj, N.; Ghosh, S.; Eilam, R.; Salame, T.-M.; et al. Upfront Admixing Antibodies and EGFR Inhibitors Preempts Sequential Treatments in Lung Cancer Models. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e13144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Monica, S.; Cretella, D.; Bonelli, M.; Fumarola, C.; Cavazzoni, A.; Digiacomo, G.; Flammini, L.; Barocelli, E.; Minari, R.; Naldi, N.; et al. Trastuzumab Emtansine Delays and Overcomes Resistance to the Third-Generation EGFR-TKI Osimertinib in NSCLC EGFR Mutated Cell Lines. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebbink, M.; de Langen, A.J.; Monkhorst, K.; Boelens, M.C.; van den Broek, D.; van der Noort, V.; de Gooijer, C.J.; Mahn, M.; van der Wekken, A.J.; Hendriks, L.; et al. Trastuzumab-Emtansine and Osimertinib Combination Therapy to Target HER2 Bypass Track Resistance in EGFR Mutation-Positive NSCLC. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2023, 4, 100481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-C.; Liao, B.-C.; Liao, W.-Y.; Markovets, A.; Stetson, D.; Thress, K.; Yang, J.C.-H. Exon 16–Skipping HER2 as a Novel Mechanism of Osimertinib Resistance in EGFR L858R/T790M–Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, G.U.; Vellanki, P.J.; Ren, Y.; Amatya, A.K.; Mishra-Kalyani, P.S.; Pan, L.; Zirkelbach, J.F.; Pan, Y.; Liu, J.; Aungst, S.L.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Fam-Trastuzumab Deruxtecan-Nxki for Unresectable or Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Activating HER2 Mutations. Oncologist 2024, 29, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, H.M.; Lee, C.B.; Chen, K.Y. Fam-Trastuzumab-Deruxtecan and Osimertinib Combination to Target HER2 Driven Resistance in a NSCLC Patient Following Osimertinib Progression: Case Report. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2025, 6, 100787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, O.; Sasaki, H.; Endo, K.; Suzuki, E.; Haneda, H.; Yukiue, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yano, M.; Fujii, Y. ErbB3 MRNA Expression Correlated with Specific Clinicopathologic Features of Japanese Lung Cancers. J. Surg. Res. 2008, 146, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Tidow, C.; Diederichs, S.; Bulk, E.; Pohle, T.; Steffen, B.; Schwäble, J.; Plewka, S.; Thomas, M.; Metzger, R.; Schneider, P.M.; et al. Identification of Metastasis-Associated Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 1778–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharpenseel, H.; Hanssen, A.; Loges, S.; Mohme, M.; Bernreuther, C.; Peine, S.; Lamszus, K.; Goy, Y.; Petersen, C.; Westphal, M.; et al. EGFR and HER3 Expression in Circulating Tumor Cells and Tumor Tissue from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.; Gal, H.; Gaborit, N.; Mazzeo, L.; Romaniello, D.; Salame, T.M.; Lindzen, M.; Mahlknecht, G.; Enuka, Y.; Ga Burton, D.; et al. An Oligoclonal Antibody Durably Overcomes Resistance of Lung Cancer to Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitors. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romaniello, D.; Marrocco, I.; Nataraj, N.B.; Ferrer, I.; Drago-Garcia, D.; Vaknin, I.; Oren, R.; Lindzen, M.; Ghosh, S.; Kreitman, M.; et al. Targeting Her3, a Catalytically Defective Receptor Tyrosine Kinase, Prevents Resistance of Lung Cancer to a Third-Generation Egfr Kinase Inhibitor. Cancers 2020, 12, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonesaka, K.; Tanizaki, J.; Maenishi, O.; Haratani, K.; Kawakami, H.; Tanaka, K.; Hayashi, H.; Sakai, K.; Chiba, Y.; Tsuya, A.; et al. HER3 Augmentation via Blockade of EGFR/AKT Signaling Enhances Anticancer Activity of HER3-Targeting Patritumab Deruxtecan in EGFR-Mutated Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, M.; Gaborit, N.; Lindzen, M.; Salame, T.M.; Dall’Ora, M.; Sevilla-Sharon, M.; Abdul-Hai, A.; Downward, J.; Yarden, Y. Combining Three Antibodies Nullifies Feedback-Mediated Resistance to Erlotinib in Lung Cancer. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, ra53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bacco, F.; Orzan, F.; Erriquez, J.; Casanova, E.; Barault, L.; Albano, R.; D’Ambrosio, A.; Bigatto, V.; Reato, G.; Patanè, M.; et al. ERBB3 Overexpression Due to MiR-205 Inactivation Confers Sensitivity to FGF, Metabolic Activation, and Liability to ERBB3 Targeting in Glioblastoma. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Gao, L.; Wang, S.; McManaman, J.L.; Thor, A.D.; Yang, X.H.; Esteva, F.J.; Liu, B. Heterotrimerization of the Growth Factor Receptors ErbB2, ErbB3, and Insulin-like Growth Factor-I Receptor in Breast Cancer Cells Resistant to Herceptin. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, H.; Yamada, T.; Wang, R.; Tanimura, K.; Adachi, Y.; Nishiyama, A.; Tanimoto, A.; Takeuchi, S.; Araujo, L.H.; Boroni, M.; et al. AXL Confers Intrinsic Resistance to Osimertinib and Advances the Emergence of Tolerant Cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Jia, S.; Ren, Y.; Cao, B.; Zha, X.; He, J.; Chen, C. ErbB3 Ligand Heregulin1 Is a Major Mitogenic Factor for Uncontrolled Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation. Neoplasia 2019, 21, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwanji, D.; Trenker, R.; Thaker, T.M.; Wang, F.; Agard, D.A.; Verba, K.A.; Jura, N. Structures of the HER2–HER3–NRG1β Complex Reveal a Dynamic Dimer Interface. Nature 2021, 600, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonesaka, K.; Hirotani, K.; Kawakami, H.; Takeda, M.; Kaneda, H.; Sakai, K.; Okamoto, I.; Nishio, K.; Jänne, P.A.; Nakagawa, K. Anti-HER3 Monoclonal Antibody Patritumab Sensitizes Refractory Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer to the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor Erlotinib. Oncogene 2016, 35, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Pawel, J.; Tseng, J.; Dediu, M.; Schumann, C.; Moritz, B.; Mendell-Harary, J.; Jin, X.; Feng, W.; Copigneaux, C.; Beckman, R.A. Phase 2 HERALD Study of Patritumab (P) with Erlotinib (E) in Advanced NSCLC Subjects (SBJs). J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 8045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koganemaru, S.; Kuboki, Y.; Koga, Y.; Kojima, T.; Yamauchi, M.; Maeda, N.; Kagari, T.; Hirotani, K.; Yasunaga, M.; Matsumura, Y.; et al. U3-1402, a Novel HER3-Targeting Antibody–Drug Conjugate, for the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Koyama, K.; Kamai, Y.; Hirotani, K.; Ogitani, Y.; Zembutsu, A.; Abe, M.; Kaneda, Y.; Maeda, N.; Shiose, Y.; et al. A Novel HER3-Targeting Antibody–Drug Conjugate, U3-1402, Exhibits Potent Therapeutic Efficacy through the Delivery of Cytotoxic Payload by Efficient Internalization. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 7151–7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonesaka, K.; Takegawa, N.; Watanabe, S.; Haratani, K.; Kawakami, H.; Sakai, K.; Chiba, Y.; Maeda, N.; Kagari, T.; Hirotani, K.; et al. An HER3-Targeting Antibody–Drug Conjugate Incorporating a DNA Topoisomerase I Inhibitor U3-1402 Conquers EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Resistant NSCLC. Oncogene 2019, 38, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänne, P.A.; Baik, C.; Su, W.C.; Johnson, M.L.; Hayashi, H.; Nishio, M.; Kim, D.W.; Koczywas, M.; Gold, K.A.; Steuer, C.E.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Patritumab Deruxtecan (HER3-DXd) in EGFR Inhibitor– Resistant, EGFR-Mutated Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.A.; Goto, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Felip, E.; Chih-Hsin Yang, J.; Reck, M.; Yoh, K.; Lee, S.-H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Besse, B.; et al. HERTHENA-Lung01, a Phase II Trial of Patritumab Deruxtecan (HER3-DXd) in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer After Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy and Platinum-Based Chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 5363–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.; Jänne, P.A.; Nishio, M.; Novello, S.; Reck, M.; Steuer, C.; Wu, Y.L.; Fougeray, R.; Fan, P.D.; Meng, J.; et al. HERTHENA-Lung02: Phase III Study of Patritumab Deruxtecan in Advanced EGFR-Mutated NSCLC after a Third-Generation EGFR TKI. Future Oncol. 2024, 20, 969–980. [Google Scholar]
- Janne, P.A.; Mostillo, J.; Shrestha, P.; Zhang, R.; Fan, P.-D. TPS3161 Poster Session Phase 1 Study of Patritumab Deruxtecan (HER3-DXd; U3-1402) in Combination with Osimertinib in Patients with Advanced EGFR-Mutated NSCLC. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, TPS3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schram, A.M.; Goto, K.; Kim, D.-W.; Macarulla, T.; Hollebecque, A.; O’Reilly, E.M.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Rodon, J.; Rha, S.Y.; Nishino, K.; et al. Efficacy of Zenocutuzumab in NRG1 Fusion–Positive Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, C.; Armstrong, E.A.; Peet, C.R.; Saker, J.; Amler, L.C.; Sliwkowski, M.X.; Harari, P.M. Dual Targeting of EGFR and HER3 with MEHD7945A Overcomes Acquired Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors and Radiation. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayette, J.; Wirth, L.; Oprean, C.; Udrea, A.; Jimeno, A.; Rischin, D.; Nutting, C.; Harari, P.M.; Csoszi, T.; Cernea, D.; et al. Randomized Phase II Study of Duligotuzumab (MEHD7945A) vs. Cetuximab in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (MEHGAN Study). Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimeno, A.; Machiels, J.P.; Wirth, L.; Specenier, P.; Seiwert, T.Y.; Mardjuadi, F.; Wang, X.; Kapp, A.V.; Royer-Joo, S.; Penuel, E.; et al. Phase Ib Study of Duligotuzumab (MEHD7945A) plus Cisplatin/5-Fluorouracil or Carboplatin/Paclitaxel for First-Line Treatment of Recurrent/Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Cancer 2016, 122, 3803–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieu, C.H.; Hidalgo, M.; Berlin, J.D.; Ko, A.H.; Cervantes, A.; LoRusso, P.; Gerber, D.E.; Eder, J.P.; Eckhardt, S.G.; Kapp, A.V.; et al. A Phase Ib Dose-Escalation Study of the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Cobimetinib and Duligotuzumab in Patients with Previously Treated Locally Advanced or Metastatic Cancers with Mutant KRAS. Oncologist 2017, 22, 1024-e89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juric, D.; Dienstmann, R.; Cervantes, A.; Hidalgo, M.; Messersmith, W.; Blumenschein, G.R.; Tabernero, J.; Roda, D.; Calles, A.; Jimeno, A.; et al. Safety and Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics of the First-in-Class Dual Action HER3/EGFR Antibody MEHD7945A in Locally Advanced or Metastatic Epithelial Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2462–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogier, C.; Colombo, P.E.; Bousquet, C.; Canterel-Thouennon, L.; Sicard, P.; Garambois, V.; Thomas, G.; Gaborit, N.; Jarlier, M.; Pirot, N.; et al. Targeting the NRG1/HER3 Pathway in Tumor Cells and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts with an Anti-Neuregulin 1 Antibody Inhibits Tumor Growth in Pre-Clinical Models of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 432, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, G.V.; De La Cruz, C.C.; Chiu, C.; Alag, N.; Schaefer, G.; Crocker, L.; Ross, S.; Goldenberg, D.; Merchant, M.; Tien, J.; et al. Blocking NRG1 and Other Ligand-Mediated Her4 Signaling Enhances the Magnitude and Duration of the Chemotherapeutic Response of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 171ra18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H.; Cui, W. Function of Axl Receptor Tyrosine Kinase in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 2726–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Suda, K.; Shimizu, S.; Sakai, K.; Mizuuchi, H.; Tomizawa, K.; Takemoto, T.; Nishio, K.; Mitsudomi, T. Clinical, Pathological, and Molecular Features of Lung Adenocarcinomas with AXL Expression. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xia, H.; Zhuang, Z.; Miao, L.; Chen, X.; Cai, H. Axl-Altered MicroRNAs Regulate Tumorigenicity and Gefitinib Resistance in Lung Cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Bai, F.; Fan, L.; Pang, W.; Han, R.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Yan, X.; Duan, H.; Xing, L. Coexpression of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase AXL and EGFR in Human Primary Lung Adenocarcinomas. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lee, J.C.; Lin, L.; Olivas, V.; Au, V.; LaFramboise, T.; Abdel-Rahman, M.; Wang, X.; Levine, A.D.; Rho, J.K.; et al. Activation of the AXL Kinase Causes Resistance to EGFR-Targeted Therapy in Lung Cancer. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.Y.; Hong, J.-Y.; Lee, H.-J.; Park, H.J.; Lee, S.K. Targeting the Degradation of AXL Receptor Tyrosine Kinase to Overcome Resistance in Gefitinib-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 10146–10160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namba, K.; Shien, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Torigoe, H.; Sato, H.; Yoshioka, T.; Takeda, T.; Kurihara, E.; Ogoshi, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; et al. Activation of AXL as a Preclinical Acquired Resistance Mechanism Against Osimertinib Treatment in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okura, N.; Nishioka, N.; Yamada, T.; Taniguchi, H.; Tanimura, K.; Katayama, Y.; Yoshimura, A.; Watanabe, S.; Kikuchi, T.; Shiotsu, S.; et al. ONO-7475, a Novel AXL Inhibitor, Suppresses the Adaptive Resistance to Initial EGFR-TKI Treatment in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2244–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Niu, X. EMT-Mediated Acquired EGFR-TKI Resistance in NSCLC: Mechanisms and Strategies. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, D.; Zambre, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Ghoshdastidar, S.; Jiang, Y.; Joshi, T.; Upendran, A.; Kannan, R. Silencing AXL by Covalent SiRNA-Gelatin-Antibody Nanoconjugate Inactivates MTOR/EMT Pathway and Stimulates P53 for TKI Sensitization in NSCLC. Nanomedicine 2019, 20, 102007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Li, J.; Jang, C.; Wang, J.; Xiong, J. The Role of Axl in Drug Resistance and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 6653–6661. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haga, Y.; Marrocco, I.; Noronha, A.; Uribe, M.L.; Nataraj, N.B.; Sekar, A.; Drago-Garcia, D.; Borgoni, S.; Lindzen, M.; Giri, S.; et al. Host-Dependent Phenotypic Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 3862–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, A.N.; Niederst, M.J.; Archibald, H.L.; Gomez-Caraballo, M.; Siddiqui, F.M.; Mulvey, H.E.; Maruvka, Y.E.; Ji, F.; Bhang, H.C.; Krishnamurthy Radhakrishna, V.; et al. Tumor Cells Can Follow Distinct Evolutionary Paths to Become Resistant to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.V.; Lee, D.Y.; Li, B.; Quinlan, M.P.; Takahashi, F.; Maheswaran, S.; McDermott, U.; Azizian, N.; Zou, L.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. A Chromatin-Mediated Reversible Drug-Tolerant State in Cancer Cell Subpopulations. Cell 2010, 141, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrocco, I.; Yarden, Y. Resistance of Lung Cancer to EGFR-Specific Kinase Inhibitors: Activation of Bypass Pathways and Endogenous Mutators. Cancers 2023, 15, 5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntzifa, A.; Strati, A.; Kallergi, G.; Kotsakis, A.; Georgoulias, V.; Lianidou, E. Gene Expression in Circulating Tumor Cells Reveals a Dynamic Role of EMT and PD-L1 during Osimertinib Treatment in NSCLC Patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Bartholdy, B.A.; Cheng, H.; Halmos, B. Blockade of AXL Activation Overcomes Acquired Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 2425–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noronha, A.; Belugali Nataraj, N.; Lee, J.S.; Zhitomirsky, B.; Oren, Y.; Oster, S.; Lindzen, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Will, R.; Ghosh, S.; et al. AXL and Error-Prone DNA Replication Confer Drug Resistance and Offer Strategies to Treat EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 2666–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoni-Nieves, A.; Lindzen, M.; Giri, S.; Gupta, N.; Chatterjee, R.; Selvadurai, B.-R.; Van Daele, M.; Love, D.; Haga, Y.; Romaniello, D.; et al. A Bispecific Antibody Targeting EGFR and AXL Delays Resistance to Osimertinib. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Gu, Z.; Yu, X.; Cheng, T.; Liu, B. Research Progress on the Role of Bypass Activation Mechanisms in Resistance to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1447678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beenken, A.; Mohammadi, M. The FGF Family: Biology, Pathophysiology and Therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, M.; Nakagama, H. FGF Receptors: Cancer Biology and Therapeutics. Med. Res. Rev. 2014, 34, 280–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, R.; Borea, R.; Coelho, A.; Khan, S.; Araújo, A.; Reclusa, P.; Franchina, T.; Van Der Steen, N.; Van Dam, P.; Ferri, J.; et al. FGFR a Promising Druggable Target in Cancer: Molecular Biology and New Drugs. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 113, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornitz, D.M.; Itoh, N. The Fibroblast Growth Factor Signaling Pathway. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2015, 4, 215–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienstmann, R.; Rodon, J.; Prat, A.; Perez-Garcia, J.; Adamo, B.; Felip, E.; Cortes, J.; Iafrate, A.J.; Nuciforo, P.; Tabernero, J. Genomic Aberrations in the FGFR Pathway: Opportunities for Targeted Therapies in Solid Tumors. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, M.; Costa, D.B.; Kobayashi, S.S. Targeting of Drug-Tolerant Persister Cells as an Approach to Counter Drug Resistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2024, 194, 107885. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raoof, S.; Mulford, I.J.; Frisco-Cabanos, H.; Nangia, V.; Timonina, D.; Labrot, E.; Hafeez, N.; Bilton, S.J.; Drier, Y.; Ji, F.; et al. Targeting FGFR Overcomes EMT-Mediated Resistance in EGFR Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncogene 2019, 38, 6399–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Oeck, S.; Zhang, G.J.; Schramm, A.; Glazer, P.M. Hypoxia Induces Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors in Lung Cancer Cells via Upregulation of FGFR1 and the MAPK Pathway. Cancer Res. 2021, 80, 4655–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terp, M.G.; Jacobsen, K.; Molina, M.A.; Karachaliou, N.; Beck, H.C.; Bertran-Alamillo, J.; Giménez-Capitán, A.; Cardona, A.F.; Rosell, R.; Ditzel, H.J. Combined FGFR and Akt Pathway Inhibition Abrogates Growth of FGFR1 Overexpressing EGFR-TKI-Resistant NSCLC Cells. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2021, 5, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, R.; Yamada, T.; Tokuda, S.; Morimoto, K.; Katayama, Y.; Matsui, Y.; Hirai, S.; Ishida, M.; Kawachi, H.; Sawada, R.; et al. Triple Combination Therapy Comprising Osimertinib, an AXL Inhibitor, and an FGFR Inhibitor Improves the Efficacy of EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2024, 598, 217124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanal-Villalonga, A.; Molina-Pinelo, S.; Cirauqui, C.; Ojeda-Márquez, L.; Marrugal, Á.; Suarez, R.; Conde, E.; Ponce-Aix, S.; Enguita, A.B.; Carnero, A.; et al. FGFR1 Cooperates with EGFR in Lung Cancer Oncogenesis, and Their Combined Inhibition Shows Improved Efficacy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yue, L.; Leng, Q.Q.; Chang, C.; Gan, C.; Ye, T.; Cao, D. Targeting FGFR for Cancer Therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 17, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Deng, J.; Li, X. Clinical Advances and Challenges in Targeting FGF/FGFR Signaling in Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haura, E.B.; Hicks, J.K.; Boyle, T.A. Erdafitinib Overcomes FGFR3-TACC3–Mediated Resistance to Osimertinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, e154–e156. [Google Scholar]
- Raphael, A.; Dudnik, E.; Hershkovitz, D.; Jain, S.; Olsen, S.; Soussan-Gutman, L.; Ben-Shitrit, T.; Dvir, A.; Nechushtan, H.; Peled, N.; et al. FGFR Fusions as an Acquired Resistance Mechanism Following Treatment with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (EGFR TKIs) and a Suggested Novel Target in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (ANSCLC). J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N.; Adamis, A.P. Ten Years of Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 385–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.A.; Kamal, M.A.; Akhtar, S. Tumor Angiogenesis and VEGFR-2: Mechanism, Pathways and Current Biological Therapeutic Interventions. Curr. Drug Metab. 2020, 22, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, A.; Montanino, A.; Carillio, G.; Costanzo, R.; Sandomenico, C.; Normanno, N.; Piccirillo, M.C.; Daniele, G.; Perrone, F.; Rocco, G.; et al. Angiogenesis Inhibitors in NSCLC. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.; Nilsson, M.; Goldman, J.; Reck, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Kato, T.; Ares, L.P.; Frimodt-Moller, B.; Wolff, K.; Visseren-Grul, C.; et al. Dual EGFR-VEGF Pathway Inhibition: A Promising Strategy for Patients With EGFR-Mutant NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, N.; Seto, T.; Nishio, M.; Goto, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Okamoto, I.; Yamanaka, T.; Tanaka, M.; Takahashi, K.; Fukuoka, M. Erlotinib plus Bevacizumab vs Erlotinib Monotherapy as First-Line Treatment for Advanced EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Squamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Survival Follow-up Results of the Randomized JO25567 Study. Lung Cancer 2021, 151, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Garon, E.B.; Seto, T.; Nishio, M.; Ponce Aix, S.; Paz-Ares, L.; Chiu, C.-H.; Park, K.; Novello, S.; Nadal, E.; et al. Ramucirumab plus Erlotinib in Patients with Untreated, EGFR-Mutated, Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (RELAY): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.A.; Schoenfeld, A.J.; Makhnin, A.; Kim, R.; Rizvi, H.; Tsui, D.; Falcon, C.; Houck-Loomis, B.; Meng, F.; Yang, J.L.; et al. Effect of Osimertinib and Bevacizumab on Progression-Free Survival for Patients with Metastatic EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers: A Phase 1/2 Single-Group Open-Label Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soo, R.A.; Han, J.-Y.; Dafni, U.; Cho, B.C.; Yeo, C.M.; Nadal, E.; Carcereny, E.; de Castro, J.; Sala, M.A.; Bernabé, R.; et al. A Randomised Phase II Study of Osimertinib and Bevacizumab versus Osimertinib Alone as Second-Line Targeted Treatment in Advanced NSCLC with Confirmed EGFR and Acquired T790M Mutations: The European Thoracic Oncology Platform (ETOP 10-16) BOOSTER Trial. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenmotsu, H.; Wakuda, K.; Mori, K.; Kato, T.; Sugawara, S.; Kirita, K.; Yoneshima, Y.; Azuma, K.; Nishino, K.; Teraoka, S.; et al. Randomized Phase 2 Study of Osimertinib Plus Bevacizumab Versus Osimertinib for Untreated Patients with Nonsquamous NSCLC Harboring EGFR Mutations: WJOG9717L Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenmotsu, H.; Sakai, K.; Mori, K.; Kato, T.; Sugawara, S.; Kirita, K.; Yoneshima, Y.; Azuma, K.; Nishino, K.; Teraoka, S.; et al. Final Analysis Data and Exploratory Biomarker Analysis of a Randomized Phase 2 Study of Osimertinib Plus Bevacizumab Versus Osimertinib Monotherapy for Untreated Patients with Nonsquamous NSCLC Harboring EGFR Mutations: The WJOG9717L Study. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2024, 5, 100716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Li, J.; Cang, S.-D.; Lin, J.-X.; Tu, H.-Y.; Du, Y.; Qin, J.-W.; Liang, X.-H.; Yu, Y.; Lan, H.-T.; et al. FLAIR: A Phase II, Open Label, Randomized Study of Osimertinib Plus Bevacizumab Versus Osimertinib in Recurrent or Metastatic Treatment-Naïve NSCLC Patients Harboring EGFR 21L858R Mutation. Clin. Lung Cancer 2025, 26, 152–157.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, X.; Patel, J.D.; Shum, E.; Baik, C.; Sanborn, R.E.; Shu, C.A.; Kim, C.; Fidler, M.J.; Hall, R.; Elamin, Y.Y.; et al. A Multicenter Open-Label Randomized Phase II Study of Osimertinib with and Without Ramucirumab in Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Naïve EGFR-Mutant Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (RAMOSE Trial). J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manabe, T.; Yasuda, H.; Terai, H.; Kagiwada, H.; Hamamoto, J.; Ebisudani, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Masuzawa, K.; Ikemura, S.; Kawada, I.; et al. IGF2 Autocrine-Mediated IGF1R Activation Is a Clinically Relevant Mechanism of Osimertinib Resistance in Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, T.; Ohmori, T.; Ohba, M.; Arata, S.; Murata, Y.; Kusumoto, S.; Ando, K.; Ishida, H.; Ohnishi, T.; Sasaki, Y. Distinct Afatinib Resistance Mechanisms Identified in Lung Adenocarcinoma Harboring an EGFR Mutation. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makimoto, G.; Ninomiya, K.; Kubo, T.; Sunami, R.; Kato, Y.; Ichihara, E.; Ohashi, K.; Rai, K.; Hotta, K.; Tabata, M.; et al. A Novel Osimertinib-Resistant Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Line Harbouring Mutant EGFR and Activated IGF1R. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 51, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, D.; Takahashi, F.; Mitsuishi, Y.; Tajima, K.; Hidayat, M.; Winardi, W.; Ihara, H.; Kanamori, K.; Matsumoto, N.; Asao, T.; et al. Activation of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Receptor Confers Acquired Resistance to Osimertinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR T790M Mutation. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.-E.; Sung, K.J.; Park, S.; Kim, W.S.; Song, J.S.; Choi, C.-M.; Sung, Y.H.; et al. Activation of the IGF1R Pathway Potentially Mediates Acquired Resistance to Mutant-Selective 3rd-Generation EGF Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 22005–22015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Q.; Zheng, J.; Chen, B.; Xie, B.; Zhang, W.-M. Implication of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in IGF1R-Induced Resistance to EGFR-TKIs in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 44332–44345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortot, A.B.; Repellin, C.E.; Shimamura, T.; Capelletti, M.; Zejnullahu, K.; Ercan, D.; Christensen, J.G.; Wong, K.-K.; Gray, N.S.; Jänne, P.A. Resistance to Irreversible EGF Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors through a Multistep Mechanism Involving the IGF1R Pathway. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yamada, T.; Kita, K.; Taniguchi, H.; Arai, S.; Fukuda, K.; Terashima, M.; Ishimura, A.; Nishiyama, A.; Tanimoto, A.; et al. Transient IGF-1R Inhibition Combined with Osimertinib Eradicates AXL-Low Expressing EGFR Mutated Lung Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Wang, Y.; James, M.; Jeong, J.H.; You, M. Inhibition of IGF1R Signaling Abrogates Resistance to Afatinib (BIBW2992) in EGFR T790M Mutant Lung Cancer Cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 55, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leighl, N.B.; Rizvi, N.A.; de Lima, L.G.; Arpornwirat, W.; Rudin, C.M.; Chiappori, A.A.; Ahn, M.-J.; Chow, L.Q.M.; Bazhenova, L.; Dechaphunkul, A.; et al. Phase 2 Study of Erlotinib in Combination with Linsitinib (OSI-906) or Placebo in Chemotherapy-Naive Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Activating Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutations. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, 34–42.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offin, M.; Somwar, R.; Rekhtman, N.; Benayed, R.; Chang, J.C.; Plodkowski, A.; Lui, A.J.W.; Eng, J.; Rosenblum, M.; Li, B.T.; et al. Acquired ALK and RET Gene Fusions as Mechanisms of Resistance to Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, PO.18.00126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lormans, M.; Van Haecke, P.; Demedts, I. An Acquired CCDC6::RET Gene Fusion as Resistance Mechanism for Osimertinib in Exon 21 EGFR(L858R)-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Its Successful Management with Osimertinib and Selpercatinib: A Case Report and Review of Literature. J. Chemother. 2025, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, R.; Meng, Y.; Wang, L.; Zheng, L.; You, J. Case Report: Durable Response of Ensartinib Targeting EML4-ALK Fusion in Osimertinib-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1359403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanska, E.M.; Sørensen, J.B.; Melchior, L.C.; Costa, J.C.; Santoni-Rugiu, E. Durable Response to Combined Osimertinib and Pralsetinib Treatment for Osimertinib Resistance Due to Novel Intergenic ANK3-RET Fusion in EGFR -Mutated Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, e2200040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotow, J.; Patel, J.D.; Hanley, M.P.; Yu, H.; Awad, M.; Goldman, J.W.; Nechushtan, H.; Scheffler, M.; Kuo, C.-H.S.; Rajappa, S.; et al. Osimertinib and Selpercatinib Efficacy, Safety, and Resistance in a Multicenter, Prospectively Treated Cohort of EGFR-Mutant and RET Fusion-Positive Lung Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 2979–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Tse, V.; Altaie, G.; Husain, H. Efficacy and Tolerability of Osimertinib with Dabrafenib and Trametinib in BRAF V600E Acquired EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Case Series. J. Thorac. Dis. 2024, 16, 5379–5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Man, J.; Lord, S.; Cooper, W.; Links, M.; Gebski, V.; Herbst, R.S.; Gralla, R.J.; Mok, T.; Yang, J.C.-H. Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Associated with Survival Among Patients Treated with Checkpoint Inhibitors for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; He, Y.; Wang, W.; Cai, Q.; Ge, F.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, H.; Chen, Y.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Individuals with Advanced EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Who Progressed on EGFR Tyrosine-Kinase Inhibitors: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Network Meta-Analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.-H.; Shepherd, F.A.; Kim, D.-W.; Lee, G.-W.; Lee, J.S.; Chang, G.-C.; Lee, S.S.; Wei, Y.-F.; Lee, Y.G.; Laus, G.; et al. Osimertinib Plus Durvalumab versus Osimertinib Monotherapy in EGFR T790M-Positive NSCLC Following Previous EGFR TKI Therapy: CAURAL Brief Report. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Yu, H.; Kim, S.-W.; Saka, H.; Horn, L.; Goto, K.; Ohe, Y.; Mann, H.; Thress, K.S.; et al. TATTON: A Multi-Arm, Phase Ib Trial of Osimertinib Combined with Selumetinib, Savolitinib, or Durvalumab in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
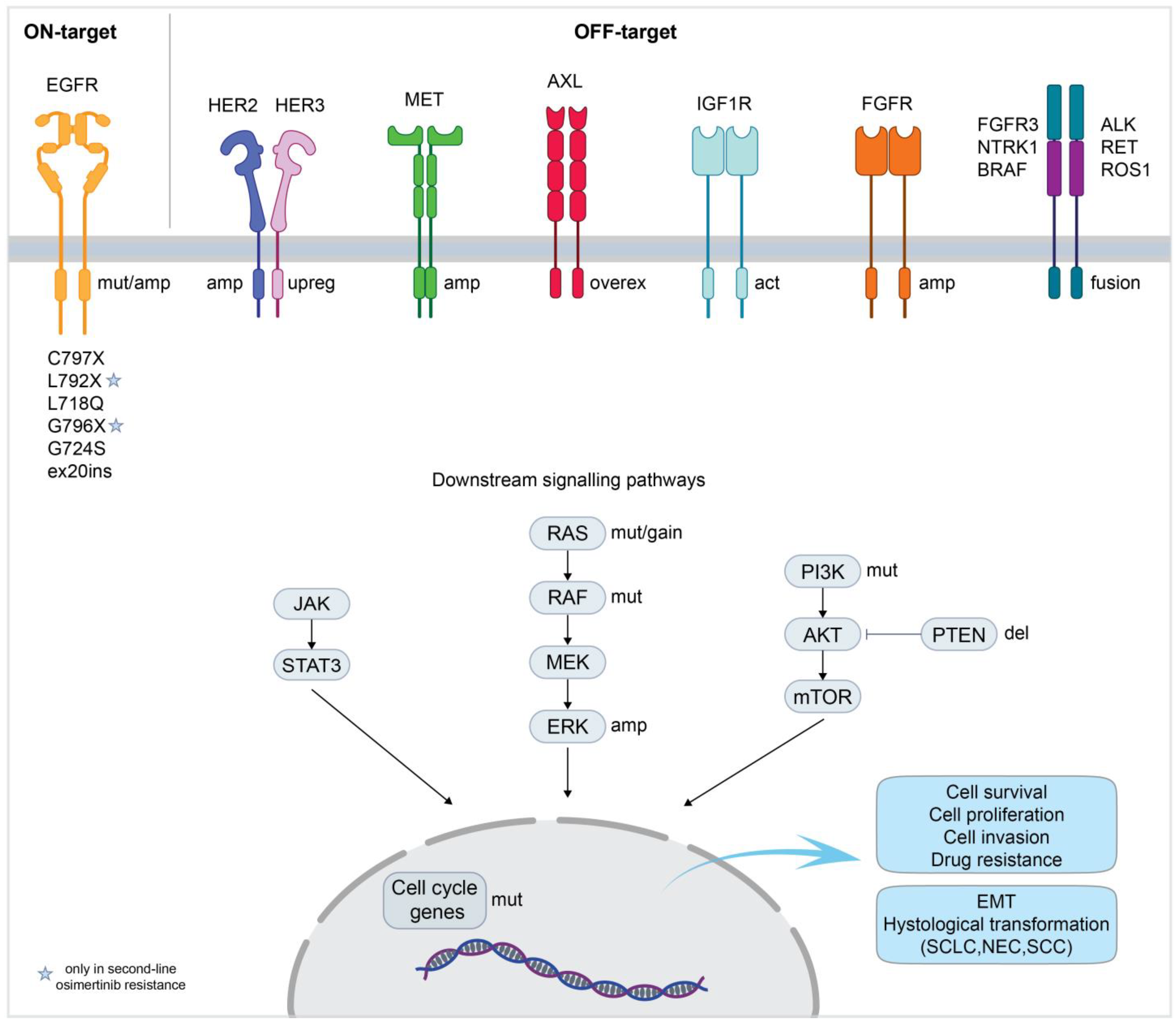
| Name of the Molecule | Trade Name | Class | Year of FDA Approval | Company | Indication | Key Clinical Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gefitinib | Iressa | 1st generation TKI | 2003 | AstraZeneca | Del19/L858R-EGFR positive NSCLC | NEJ002 [34,35] IPASS [36,37] WJTOG3405 [38,39] |
| Erlotinib | Tarceva | 1st generation TKI | 2004 | OSI Pharms | Del19/L858R-EGFR positive NSCLC | OPTIMAL [40,41] EUTARC [42] |
| Afatinib | Gilotrif | 2nd generation TKI | 2013 | Boehringer Ingelheim | Del19/L858R-EGFR positive NSCLC | LUX-Lung3 [43,44] LUX-Lung6 [43,45] |
| Osimertinib | Tagrisso | 3rd generation TKI | 2015 | AstraZeneca | Del19/L858R/T790M-EGFR positive NSCLC | AURA3 [46,47] FLAURA [48,49] |
| Dacomitinib | Vizimpro | 2nd generation TKI | 2018 | Pfizer | Del19/L858R-EGFR positive NSCLC | ARCHER1050 [50,51,52] |
| Amivantamab | Rybrevant | Bispecific Antibody | 2021 | Janssen Biotech | Ins20/Del19/L858R-EGFR positive NSCLC | PAPILLON [53] CHRYSALIS [54] CHRYSALIS2 [55] MARIPOSA [56] MARIPOSA2 [57] |
| Mobocertinib | Exkivity | TKI | 2021 (withdrawn in 2024) | Takeda Pharms | Ins20-EGFR positive NSCLC | NCT02716116 [58] |
| Lazertinib | Lazcluze | 3rd generation TKI | 2024 | Janssen Biotech | Del19/L858R-EGFR positive NSCLC | MARIPOSA [56] MARIPOSA2 [57] |
| Mechanism of Resistance | Player of Resistance | Strategy to Overcome Resistance | Drugs | Status | Relevant Studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ON-TARGET | EGFR | EGFR TKI (4th generation) | JIN-A02 | Phase 1–2 (recruiting) | NCT05394831 |
| HS-10375 | Phase 1–2 (recruiting) | NCT05435248 | |||
| WJ13405 | Phase 1–2 (recruiting) | NCT05662670 | |||
| BLU-945 | Phase 1–2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT04862780 (SYMPHONY) | |||
| BPI-361175 | Phase 1–2 (not yet recruiting) | NCT05393466 | |||
| BDTX-1535 | Phase 1–2 (recruiting) | NCT05256290 | |||
| QLH11811 | Phase 1 (recruiting) | NCT05555212 | |||
| H002 | Phase 1–2 (recruiting) | NCT05552781 | |||
| EGFR/HER2 TKI | BAY2927088 | Phase 1–2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT05099172 | ||
| 1st- + 3rd-generation EGFR TKI | Osimertinib + gefitinib | Phase 1–2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT03122717 | ||
| 1st- + 3rd-generation EGFR TKI | Osimertinib + gefitinib | Phase 2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT03944772 (ORCHARD) | ||
| 2nd- + 3rd-generation EGFR TKI | Osimertinib + dacomitinib | Early phase 1 (completed) | NCT03755102 | ||
| 3rd-generation EGFR TKI + EGFR mAb | Osimertinib + necitumumab | Phase 2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT03944772 (ORCHARD) | ||
| EGFR PROTAC | HSK40118 | Phase 1 (recruiting) | NCT06050980 | ||
| OFF-TARGET | MET | MET TKI | Osimertinib + savolitinib | Phase 1 (active, not recruiting) | NCT02143466 (TATTON) |
| Osimertinib + savolitinib | Phase 2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT03778229 (SAVANNAH) | |||
| Osimertinib + savolitinib | Phase 3 (recruiting) | NCT05015608 (SACHI) | |||
| Osimertinib + savolitinib | Phase 2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT03944772 (ORCHARD) | |||
| Osimertinib + savolitinib | Phase 2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT05163249 (FLOWERS) | |||
| Osimertinib + savolitinib | Phase 3 (recruiting) | NCT05261399 (SAFFRON) | |||
| Osimertinib + savolitinib | Phase 2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT04606771 | |||
| Osimertinib + savolitinib | Phase 3 (recruiting) | NCT05009836 (SANOVO) | |||
| Osimertinib + tepotinib | Phase 2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT03940703 (INSIGHT 2) | |||
| Osimertinib + vebreltinib | Phase 1–2 (recruiting) | NCT04743505 | |||
| Osimertinib + glumetinib | Phase 1–2 (unknown status) | NCT04338243 | |||
| Osimertinib + capmatinib | Phase 3 (terminated) | NCT04816214 (GEOMETRY-E) | |||
| Osimertinib + capmatinib ± ramucirumab | Phase 2 (recruiting) | NCT05642572 | |||
| Bispecific antibody (EGFR-MET) | Lazertinib + amivantamab + bevacizumab | Phase 2 (recruiting) | NCT05601973 (AMAZE-Lung) | ||
| Osimertinib + EMB-01 | Phase 1–2 (not yet recruiting) | NCT05498389 | |||
| MCLA-129 + Befotertinib (3rd-generation EGFR TKI) | Phase 1 (not yet recruiting) | NCT06015568 | |||
| MET ADC | Osimertinib + telisotuzumab vedotin | Phase 1 (active, not recruiting) | NCT02099058 | ||
| HER2 | HER2 ADC | Osimertinib + trastuzumab-emtansine | Phase 2 (terminated) | NCT03784599 (TRAEMOS) | |
| HER2 mAb | Osimertinib + necitumumab + trastuzumab | Phase 1–2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT04285671 | ||
| HER3 | HER3 ADC | Patritumab deruxtecan | Phase 1 (recruiting) | NCT03260491 | |
| Patritumab deruxtecan | Phase 2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT04619004 (HERTHENA-Lung01) | |||
| Patritumab deruxtecan | Phase 3 (active, not recruiting) | NCT05338970 (HERTHENA-Lung02) | |||
| Osimertinib + patritumab deruxtecan | Phase 1 (active, not recruiting) | NCT04676477 | |||
| Bispecific antibody (EGFR-HER3) | Osimertinib + izalontamab | Phase 2–3 (recruiting) | NCT05020769 | ||
| EGFR-HER3 ADC (bispecific antibody) | Osimertinib + BL-B01D1 | Phase 2 (recruiting) | NCT05880706 | ||
| Osimertinib + BMS-986507 | Phase 1–2 (recruiting) | NCT06618287 | |||
| AXL | AXL TKI | Dubermatinib (TP-0903) | Phase 1 (completed) | NCT02729298 | |
| Osimertinib + DS-1205c | Phase 1 (terminated) | NCT03255083 | |||
| Downstream molecules | BRAF + MEK inhibitor | Dabrafenib + trametinib | Phase 2 (completed) | NCT04452877 | |
| mTOR inhibitor | Osimertinib + sapanisertib | Phase 1 (active, not recruiting) | NCT02503722 | ||
| Osimertinib + sapanisertib | Phase 1 (completed) | NCT04479306 | |||
| JAK inhibitor | Osimertinib + itacitinib | Phase 1–2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT02917993 | ||
| Osimertinib + golidocitinib | Phase 1–2 (completed) | NCT03450330 (JACKPOT1) | |||
| MEK inhibitor | Osimertinib + selumetinib | Phase 1 (active, not recruiting) | NCT02143466 | ||
| Osimertinib + selumetinib | Phase 2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT03392246 | |||
| Osimertinib + selumetinib | Phase 2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT03944772 (ORCHARD) | |||
| PI3K inhibitor | Osimertinib + TQ-B3525 | Phase 1–2 (unknown status) | NCT05284994 | ||
| ALK | ALK TKI | Osimertinib + alectinib | Phase 2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT03944772 (ORCHARD) | |
| RET | RET TKI | Osimertinib + selpercatinib | Phase 2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT03944772 (ORCHARD) | |
| Cell cycle/apoptosis regulators | CDK 4/6 inhibitor | Osimertinib + G1738 (lerociclib) | Phase 1–2 (completed) | NCT03455829 | |
| Osimertinib + abemaciclib | Phase 2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT04545710 | |||
| Bcl-2 inhibitor | Osimertinib + navitoclax | Phase 1 (completed) | NCT02520778 | ||
| Osimertinib + pelcitoclax | Phase 1 (recruiting) | NCT04001777 | |||
| Aurora Kinase A inhibitor | Osimertinib + VIC-1911 | Phase 1 (recruiting) | NCT05489731 | ||
| Osimertinib + alisertib | Phase 1 (completed) | NCT04479306 | |||
| Osimertinib + alisertib | Phase 1 (recruiting) | NCT04085315 | |||
| Osimertinib + LY3295668 | Phase 1–2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT05017025 | |||
| VEGF/VEGFR | VEGF mAb | Osimertinib + bevacizumab | Phase 2 (completed) | NCT03133546 (BOOSTER) | |
| Osimertinib + bevacizumab | Phase 1–2 (completed) | NCT02803203 | |||
| Osimertinib + bevacizumab | Phase 3 (recruiting) | NCT04181060 | |||
| Osimertinib + bevacizumab | Phase 3 (recruiting) | NCT05104281 | |||
| Osimertinib + bevacizumab | Phase 2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT02971501 | |||
| Osimertinib + bevacizumab | Phase 2 (not yet recruiting) | NCT04988607 | |||
| VEGFR mAb | Osimertinib + ramucirumab | Phase 2 (active, not recruiting) | NCT03909334 (RAMOSE) | ||
| Osimertinib + ramucirumab or necitumumab | Phase 1 (completed) | NCT02789345 | |||
| Osimertinib + ramucirumab | Phase 3 (active, not recruiting) | NCT02411448 (RELAY) | |||
| Others | VEGFR-PDGFR-FGFR-cKIT TKI | Osimertinib + Anlotinib | Phase 1–2 (completed) | NCT04770688 (AUTOMAN) | |
| MERTK and FLT3 TKI | Osimertinib + MRX-2843 | Phase 1 (recruiting) | NCT04762199 | ||
| ROS1/TRK/ALK TKI | Osimertinib + repotrectinib | Phase 1 (recruiting) | NCT04772235 (TOTEM) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romaniello, D.; Morselli, A.; Marrocco, I. Strategies to Overcome Resistance to Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072957
Romaniello D, Morselli A, Marrocco I. Strategies to Overcome Resistance to Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072957
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomaniello, Donatella, Alessandra Morselli, and Ilaria Marrocco. 2025. "Strategies to Overcome Resistance to Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072957
APA StyleRomaniello, D., Morselli, A., & Marrocco, I. (2025). Strategies to Overcome Resistance to Osimertinib in EGFR-Mutated Lung Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072957








