Down-Regulation of HLA-C Expression on Melanocytes May Contribute to the Therapeutic Efficacy of UVB Phototherapy in Psoriasis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. UVB Irradiation of Melanocytes Suppresses Their Ability to Stimulate the Vα3S1/Vβ13S1 TCR
2.2. The Effect of UVB on Melanocyte Immunogenicity Can Be Reproduced Using HLA-C*06:02-Positive Melanoma Cell Lines
2.3. UVB Suppresses IFN-γ-Induced HLA-Class I and HLA-C Expression on Melanocytes
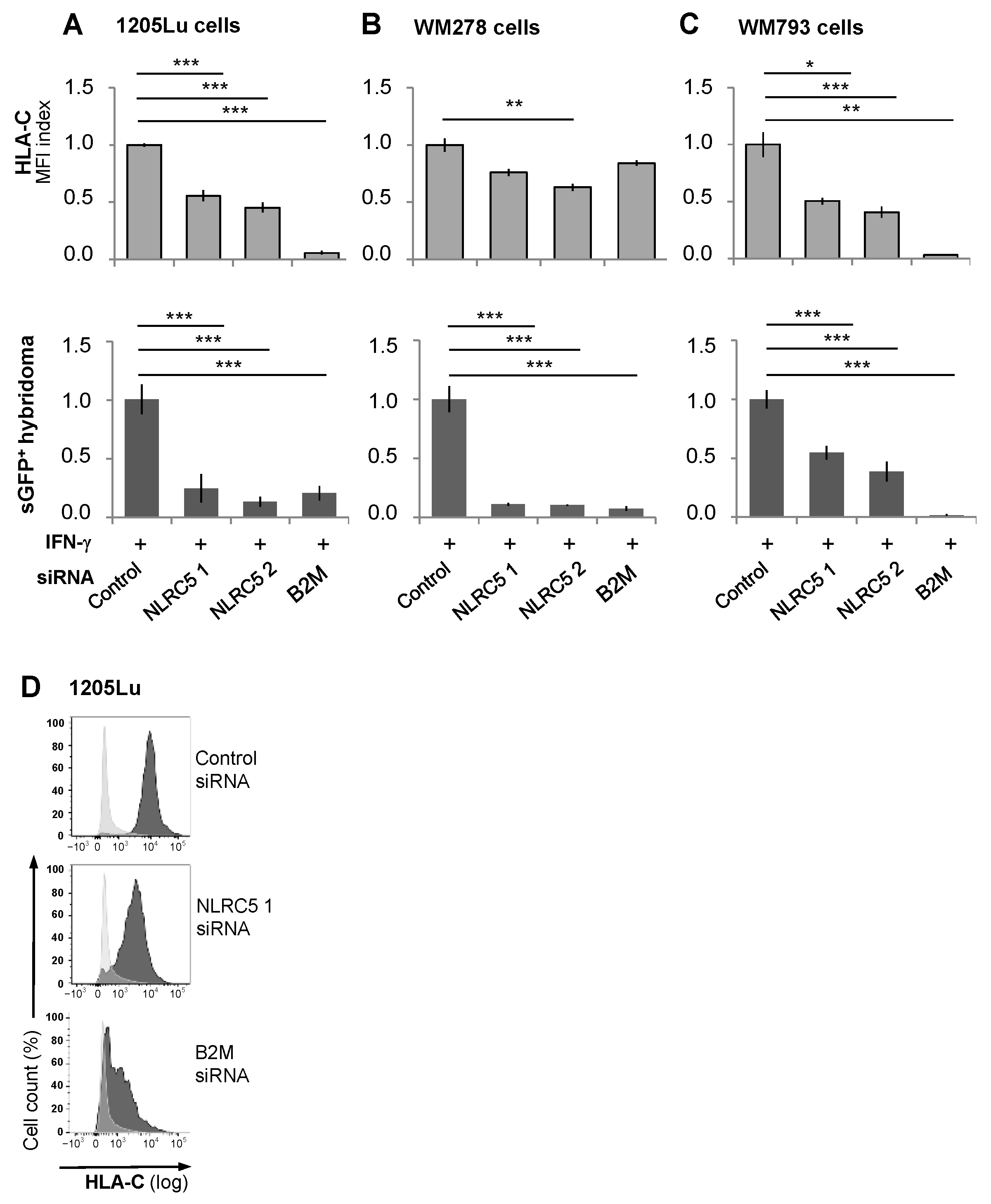
2.4. UVB Down-Regulates IFN-γ-Induced Translational and Posttranscriptional Regulators of HLA-Class I and HLA-C Expression
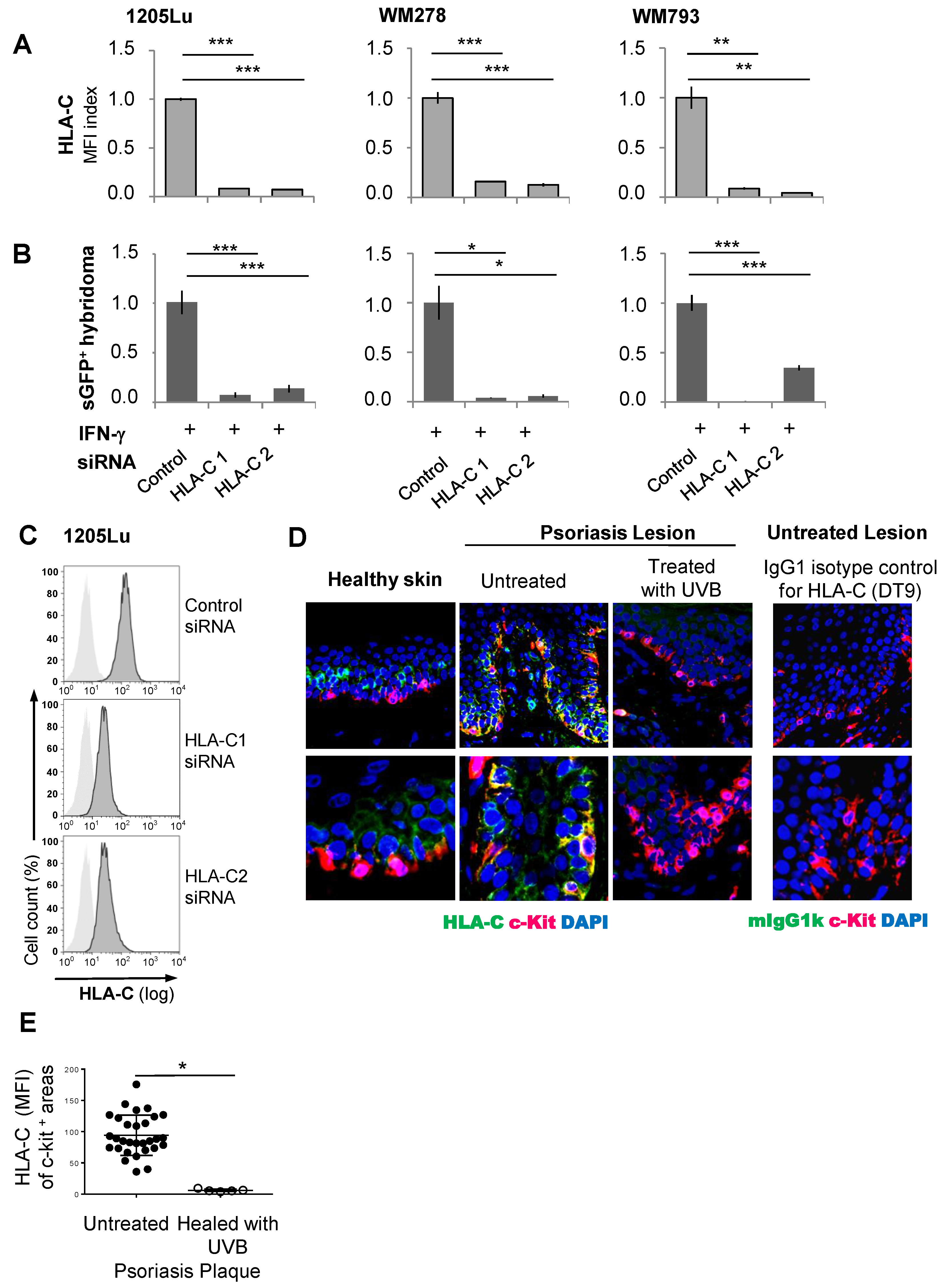
2.5. The Immunogenicity of Melanocytes for the Vα3S1/Vβ13S1 TCR Is Lost with Suppression of HLA-C Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Cells and Cell Lines
4.3. UVB and UVA Irradiation of PHMs or Melanoma Cell Lines
4.4. Cell Viability and Apoptosis Assay
4.5. Vα3S1/Vβ13S1-TCR Hybridoma Activation Assays and Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.6. Evaluation of HLA Expression
4.7. RNA Isolation, Reverse Transcription, and Real-Time PCR
4.8. siRNA Knockdown Experiments
4.9. Immunofluorescence Staining of Paraffin Sections
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PHMs | Primary human melanocytes |
| B2M | β2-microglobulin |
| ADAMTSL5 | ADAMTS-like protein 5 |
| TCR | T-cell receptor |
References
- Bernard, J.J.; Gallo, R.L.; Krutmann, J. Photoimmunology: How ultraviolet radiation affects the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 688–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wolf, P. How It Works: The Immunology Underlying Phototherapy. Dermatol. Clin. 2020, 38, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzinger, T.; Berneburg, M.; Ghoreschi, K.; Gollnick, H.; Holzle, E.; Honigsmann, H.; Lehmann, P.; Peters, T.; Rocken, M.; Scharffetter-Kochanek, K.; et al. S1-Guidelines on UV phototherapy and photochemotherapy. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2016, 14, 853–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, D.; Lim, H.W. Ultraviolet B Phototherapy for Psoriasis: Review of Practical Guidelines. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2016, 17, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, T. 25 years of UV-induced immunosuppression mediated by T cells-from disregarded T suppressor cells to highly respected regulatory T cells. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.P.; Stuart, P.E.; Nistor, I.; Hiremagalore, R.; Chia, N.V.; Jenisch, S.; Weichenthal, M.; Abecasis, G.R.; Lim, H.W.; Christophers, E.; et al. Sequence and haplotype analysis supports HLA-C as the psoriasis susceptibility 1 gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 78, 827–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Cao, H.; Zuo, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, R.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; et al. Deep sequencing of the MHC region in the Chinese population contributes to studies of complex disease. Nat Genet. 2016, 48, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, T.; Christophers, E. Psoriasis of early and late onset: Characterization of two types of psoriasis vulgaris. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1985, 13, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, M.; Winchester, R.; Giles, J.T.; Heffernan, E.; FitzGerald, O. Certain class I HLA alleles and haplotypes implicated in susceptibility play a role in determining specific features of the psoriatic arthritis phenotype. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; He, F.; Zhao, X.; Hou, R.; Lin, H.; Shen, J.; Wu, X.; Liao, Q.; Xing, J.; et al. Cross-sectional study reveals that HLA-C*07:02 is a potential biomarker of early onset/lesion severity of psoriasis. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Huang, H.; Hu, Z.; Yuan, T.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Zhang, X. Two Variants in the NOTCH4 and HLA-C Genes Contribute to Familial Clustering of Psoriasis. Int. J. Genomics 2020, 2020, 6907378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabuchi, T.; Ota, T.; Manabe, Y.; Ikoma, N.; Ozawa, A.; Terui, T.; Ikeda, S.; Inoko, H.; Oka, A. HLA-C*12:02 is a susceptibility factor in late-onset type of psoriasis in Japanese. J. Dermatol. 2014, 41, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, V.; Bull, S.B.; Pellett, F.J.; Ayearst, R.; Rahman, P.; Gladman, D.D. Human leukocyte antigen alleles and susceptibility to psoriatic arthritis. Hum. Immunol. 2013, 74, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Meglio, P.; Villanova, F.; Navarini, A.A.; Mylonas, A.; Tosi, I.; Nestle, F.O.; Conrad, C. Targeting CD8(+) T cells prevents psoriasis development. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 274–276.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Bhonsle, L.; Besgen, P.; Nickel, J.; Backes, A.; Held, K.; Vollmer, S.; Dornmair, K.; Prinz, J.C. Analysis of the paired TCR alpha- and beta-chains of single human T cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37338. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.C.; Smith, L.R.; Froning, K.J.; Schwabe, B.J.; Laxer, J.A.; Caralli, L.L.; Kurland, H.H.; Karasek, M.A.; Wilkinson, D.I.; Carlo, D.J.; et al. CD8+ T cells in psoriatic lesions preferentially use T-cell receptor V beta 3 and/or V beta 13.1 genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 9282–9286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Plazyo, O.; Billi, A.C.; Tsoi, L.C.; Xing, X.; Wasikowski, R.; Gharaee-Kermani, M.; Hile, G.; Jiang, Y.; Harms, P.W.; et al. Single cell and spatial sequencing define processes by which keratinocytes and fibroblasts amplify inflammatory responses in psoriasis. Nat. Comm. 2023, 14, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, C.; Fernandez, A.S.; Carrillo, J.M.; Romero, P.; Molina, I.J.; Moreno, J.C.; Santamaria, M. IL-17-producing CD8+ T lymphocytes from psoriasis skin plaques are cytotoxic effector cells that secrete Th17-related cytokines. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chang, H.W.; Huang, Z.M.; Nakamura, M.; Sekhon, S.; Ahn, R.; Munoz-Sandoval, P.; Bhattarai, S.; Beck, K.M.; Sanchez, I.M.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing of psoriatic skin identifies pathogenic Tc17 cell subsets and reveals distinctions between CD8(+) T cells in autoimmunity and cancer. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 2370–2380. [Google Scholar]
- Vural, S.; Kerl, K.; Ertop Dogan, P.; Vollmer, S.; Puchta, U.; He, M.; Arakawa, Y.; Heper, A.O.; Karal-Oktem, A.; Hartmann, D.; et al. Lesional activation of Tc 17 cells in Behcet disease and psoriasis supports HLA class I-mediated autoimmune responses. Brit. J. Dermatol. 2021, 185, 1209–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheuk, S.; Schlums, H.; Gallais Serezal, I.; Martini, E.; Chiang, S.C.; Marquardt, N.; Gibbs, A.; Detlofsson, E.; Introini, A.; Forkel, M.; et al. CD49a Expression Defines Tissue-Resident CD8(+) T Cells Poised for Cytotoxic Function in Human Skin. Immunity 2017, 46, 287–300. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Q.F.; Akalu, Y.T.; Suarez-Farinas, M.; Gonzalez, J.; Mitsui, H.; Lowes, M.A.; Orlow, S.J.; Manga, P.; Krueger, J.G. IL-17 and TNF synergistically modulate cytokine expression while suppressing melanogenesis: Potential relevance to psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 2741–2752. [Google Scholar]
- Loite, U.; Raam, L.; Reimann, E.; Reemann, P.; Prans, E.; Traks, T.; Vasar, E.; Silm, H.; Kingo, K.; Koks, S. The Expression Pattern of Genes Related to Melanogenesis and Endogenous Opioids in Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinz, J.C. The Woronoff Ring in Psoriasis and the Mechanisms of Postinflammatory Hypopigmentation. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00031. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Racz, E.; Prens, E.P.; Kurek, D.; Kant, M.; de Ridder, D.; Mourits, S.; Baerveldt, E.M.; Ozgur, Z.; van Ijcken, W.F.; Laman, J.D.; et al. Effective treatment of psoriasis with narrow-band UVB phototherapy is linked to suppression of the IFN and Th17 pathways. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson-Huang, L.M.; Suarez-Farinas, M.; Sullivan-Whalen, M.; Gilleaudeau, P.; Krueger, J.G.; Lowes, M.A. Effective narrow-band UVB radiation therapy suppresses the IL-23/IL-17 axis in normalized psoriasis plaques. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 2654–2663. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piskin, G.; Koomen, C.W.; Picavet, D.; Bos, J.D.; Teunissen, M.B. Ultraviolet-B irradiation decreases IFN-gamma and increases IL-4 expression in psoriatic lesional skin in situ and in cultured dermal T cells derived from these lesions. Exp. Dermatol. 2003, 12, 172–180. [Google Scholar]
- Coimbra, S.; Oliveira, H.; Reis, F.; Belo, L.; Rocha, S.; Quintanilha, A.; Figueiredo, A.; Teixeira, F.; Castro, E. Interleukin (IL)-22, IL-17, IL-23, IL-8, vascular endothelial growth factor and tumour necrosis factor-alpha levels in patients with psoriasis before, during and after psoralen-ultraviolet A and narrowband ultraviolet B therapy. Brit. J. Dermatol. 2010, 163, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar]
- Krueger, J.G.; Wolfe, J.T.; Nabeya, R.T.; Vallat, V.P.; Gilleaudeau, P.; Heftler, N.S.; Austin, L.M.; Gottlieb, A.B. Successful ultraviolet B treatment of psoriasis is accompanied by a reversal of keratinocyte pathology and by selective depletion of intraepidermal T cells. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 2057–2068. [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa, M.; Ferenczi, K.; Kikuchi, T.; Cardinale, I.; Austin, L.M.; Coven, T.R.; Burack, L.H.; Krueger, J.G. 312-nanometer ultraviolet B light (narrow-band UVB) induces apoptosis of T cells within psoriatic lesions. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 711–718. [Google Scholar]
- Vacharanukrauh, P.; Meephansan, J.; Ponnikorn, S.; Tangtanatakul, P.; Soonthornchai, W.; Wongpiyabovorn, J.; Ingkaninanda, P.; Morita, A. Transcriptome profiling in psoriasis: NB-UVB treatment-associated transcriptional changes and modulation of autoinflammation in perilesional skin in early-phase disease. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2022, 107, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Boonpethkaew, S.; Meephansan, J.; Charoensuksira, S.; Jumlongpim, O.; Tangtanatakul, P.; Wongpiyabovorn, J.; Komine, M.; Akimichi, M. Elucidating the NB-UVB mechanism by comparing transcriptome alteration on the edge and center of psoriatic plaques. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4384. [Google Scholar]
- Seitz, S.; Schneider, C.K.; Malotka, J.; Nong, X.; Engel, A.G.; Wekerle, H.; Hohlfeld, R.; Dornmair, K. Reconstitution of paired T cell receptor alpha- and beta-chains from microdissected single cells of human inflammatory tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12057–12062. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, A.; Siewert, K.; Stohr, J.; Besgen, P.; Kim, S.M.; Ruhl, G.; Nickel, J.; Vollmer, S.; Thomas, P.; Krebs, S.; et al. Melanocyte antigen triggers autoimmunity in human psoriasis. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 2203–2212. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, S.; Littler, D.R.; Mobbs, J.I.; Braun, A.; Baker, D.G.; Tennant, L.; Purcell, A.W.; Vivian, J.P.; Rossjohn, J. Complimentary electrostatics dominate T-cell receptor binding to a psoriasis-associated peptide antigen presented by human leukocyte antigen C *06:02. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104930. [Google Scholar]
- Ishimoto, T.; Arakawa, Y.; Vural, S.; Stohr, J.; Vollmer, S.; Galinski, A.; Siewert, K.; Ruhl, G.; Poluektov, Y.; Delcommenne, M.; et al. Multiple environmental antigens may trigger autoimmunity in psoriasis through T-cell receptor polyspecificity. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1374581. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Qiu, J.; Lin, Z.T.; Li, W.; Haley, C.; Mui, U.N.; Ning, J.; Tyring, S.K.; Wu, T. Identification of Novel Autoantibodies Associated with Psoriatic Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 941–951. [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa, A.; Reeves, E.; Vollmer, S.; Arakawa, Y.; He, M.; Galinski, A.; Stohr, J.; Dornmair, K.; James, E.; Prinz, J.C. ERAP1 Controls the Autoimmune Response against Melanocytes in Psoriasis by Generating the Melanocyte Autoantigen and Regulating Its Amount for HLA-C*06:02 Presentation. J. Immunol. 2021, 207, 2235–2244. [Google Scholar]
- Strange, A.; Capon, F.; Spencer, C.C.; Knight, J.; Weale, M.E.; Allen, M.H.; Barton, A.; Band, G.; Bellenguez, C.; Bergboer, J.G.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies new psoriasis susceptibility loci and an interaction between HLA-C and ERAP1. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 985–990. [Google Scholar]
- Carlen, L.; Sakuraba, K.; Stahle, M.; Sanchez, F. HLA-C expression pattern is spatially different between psoriasis and eczema skin lesions. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 342–348. [Google Scholar]
- Bjerke, J.R.; Livden, J.K.; Degre, M.; Matre, R. Interferon in suction blister fluid from psoriatic lesions. Brit. J. Dermatol. 1983, 108, 295–299. [Google Scholar]
- Prinz, J.C. Melanocytes: Target Cells of an HLA-C*06:02-Restricted Autoimmune Response in Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar]
- Siewert, K.; Malotka, J.; Kawakami, N.; Wekerle, H.; Hohlfeld, R.; Dornmair, K. Unbiased identification of target antigens of CD8+ T cells with combinatorial libraries coding for short peptides. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saric, T.; Chang, S.C.; Hattori, A.; York, I.A.; Markant, S.; Rock, K.L.; Tsujimoto, M.; Goldberg, A.L. An IFN-gamma-induced aminopeptidase in the ER, ERAP1, trims precursors to MHC class I-presented peptides. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- York, I.A.; Chang, S.C.; Saric, T.; Keys, J.A.; Favreau, J.M.; Goldberg, A.L.; Rock, K.L. The ER aminopeptidase ERAP1 enhances or limits antigen presentation by trimming epitopes to 8–9 residues. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Snary, D.; Barnstable, C.J.; Bodmer, W.F.; Crumpton, M.J. Molecular structure of human histocompatibility antigens: The HLA-C series. Eur. J. Immunol. 1977, 7, 580–585. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, K.S.; van den Elsen, P.J. NLRC5: A key regulator of MHC class I-dependent immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 813–820. [Google Scholar]
- Staehli, F.; Ludigs, K.; Heinz, L.X.; Seguin-Estevez, Q.; Ferrero, I.; Braun, M.; Schroder, K.; Rebsamen, M.; Tardivel, A.; Mattmann, C.; et al. NLRC5 deficiency selectively impairs MHC class I- dependent lymphocyte killing by cytotoxic T cells. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3820–3828. [Google Scholar]
- Carey, B.S.; Poulton, K.V.; Poles, A. Factors affecting HLA expression: A review. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2019, 46, 307–320. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, G.P.; Koebel, C.M.; Schreiber, R.D. Interferons, immunity and cancer immunoediting. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 836–848. [Google Scholar]
- Vince, N.; Li, H.; Ramsuran, V.; Naranbhai, V.; Duh, F.M.; Fairfax, B.P.; Saleh, B.; Knight, J.C.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrington, M. HLA-C Level Is Regulated by a Polymorphic Oct1 Binding Site in the HLA-C Promoter Region. Am. J. Hum. Gen. 2016, 99, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, S.; Qi, Y.; O’HUigin, C.; Pereyra, F.; Ramsuran, V.; McLaren, P.; Fellay, J.; Nelson, G.; Chen, H.; Liao, W.; et al. Genetic interplay between HLA-C and MIR148A in HIV control and Crohn disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20705–20710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neefjes, J.; Jongsma, M.L.; Paul, P.; Bakke, O. Towards a systems understanding of MHC class I and MHC class II antigen presentation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dendrou, C.A.; Petersen, J.; Rossjohn, J.; Fugger, L. HLA variation and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apps, R.; Qi, Y.; Carlson, J.M.; Chen, H.; Gao, X.; Thomas, R.; Yuki, Y.; Del Prete, G.Q.; Goulder, P.; Brumme, Z.L.; et al. Influence of HLA-C expression level on HIV control. Science 2013, 340, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, R.; Apps, R.; Qi, Y.; Gao, X.; Male, V.; O’HUigin, C.; O’Connor, G.; Ge, D.; Fellay, J.; Martin, J.N.; et al. HLA-C cell surface expression and control of HIV/AIDS correlate with a variant upstream of HLA-C. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1290–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rene, C.; Lozano, C.; Eliaou, J.F. Expression of classical HLA class I molecules: Regulation and clinical impacts: Julia Bodmer Award Review 2015. HLA 2016, 87, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oestreicher, J.L.; Walters, I.B.; Kikuchi, T.; Gilleaudeau, P.; Surette, J.; Schwertschlag, U.; Dorner, A.J.; Krueger, J.G.; Trepicchio, W.L. Molecular classification of psoriasis disease-associated genes through pharmacogenomic expression profiling. Pharmacogenom. J. 2001, 1, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowcock, A.M.; Shannon, W.; Du, F.; Duncan, J.; Cao, K.; Aftergut, K.; Catier, J.; Fernandez-Vina, M.A.; Menter, A. Insights into psoriasis and other inflammatory diseases from large-scale gene expression studies. Hum. Mol. Gen. 2001, 10, 1793–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hald, A.; Andres, R.M.; Salskov-Iversen, M.L.; Kjellerup, R.B.; Iversen, L.; Johansen, C. STAT1 expression and activation is increased in lesional psoriatic skin. Brit. J. Dermatol. 2013, 168, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.X.; Vijayan, S.; Yoo, J.S.; Watanabe, T.; Ouda, R.; An, N.; Kobayashi, K.S. MHC class I transactivator NLRC5 in host immunity, cancer and beyond. Immunology 2020, 162, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzi, S.; Forloni, M.; Cifaldi, L.; Antonucci, C.; Citti, A.; Boldrini, R.; Pezzullo, M.; Castellano, A.; Russo, V.; van der Bruggen, P.; et al. IRF1 and NF-kB restore MHC class I-restricted tumor antigen processing and presentation to cytotoxic T cells in aggressive neuroblastoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doody, G.M.; Stephenson, S.; McManamy, C.; Tooze, R.M. PRDM1/BLIMP-1 modulates IFN-gamma-dependent control of the MHC class I antigen-processing and peptide-loading pathway. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 7614–7623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludigs, K.; Seguin-Estevez, Q.; Lemeille, S.; Ferrero, I.; Rota, G.; Chelbi, S.; Mattmann, C.; MacDonald, H.R.; Reith, W.; Guarda, G. NLRC5 exclusively transactivates MHC class I and related genes through a distinctive SXY module. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, T.B.; Li, A.; Biswas, A.; Lee, K.H.; Liu, Y.J.; Bayir, E.; Iliopoulos, D.; van den Elsen, P.J.; Kobayashi, K.S. NLR family member NLRC5 is a transcriptional regulator of MHC class I genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13794–13799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczak, F.; Alvelos, M.I.; Marin-Canas, S.; Castela, A.; Demine, S.; Colli, M.L.; Op de Beeck, A.; Thomaidou, S.; Marselli, L.; Zaldumbide, A.; et al. Transcription and splicing regulation by NLRC5 shape the interferon response in human pancreatic beta cells. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotarenko, A.; Chekalin, E.; Mesentsev, A.; Kiseleva, L.; Gribanova, E.; Mehta, R.; Baranova, A.; Tatarinova, T.V.; Piruzian, E.S.; Bruskin, S. Integrated computational approach to the analysis of RNA-seq data reveals new transcriptional regulators of psoriasis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrone, S.; Marincola, F.M. Loss of HLA class I antigens by melanoma cells: Molecular mechanisms, functional significance and clinical relevance. Immunol. Today 1995, 16, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, R.; Rodriguez, T.; Del Campo, A.; Monge, E.; Maleno, I.; Aptsiauri, N.; Jimenez, P.; Pedrinaci, S.; Pawelec, G.; Ruiz-Cabello, F.; et al. Characterization of HLA class I altered phenotypes in a panel of human melanoma cell lines. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2008, 57, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, J.C. Human Leukocyte Antigen-Class I Alleles and the Autoreactive T Cell Response in Psoriasis Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marco, M.; Schuster, H.; Backert, L.; Ghosh, M.; Rammensee, H.G.; Stevanovic, S. Unveiling the Peptide Motifs of HLA-C and HLA-G from Naturally Presented Peptides and Generation of Binding Prediction Matrices. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 2639–2651. [Google Scholar]
- Menter, A.; Korman, N.J.; Elmets, C.A.; Feldman, S.R.; Gelfand, J.M.; Gordon, K.B.; Gottlieb, A.; Koo, J.Y.M.; Lebwohl, M.; Lim, H.W.; et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: Section 5. Guidelines of care for the treatment of psoriasis with phototherapy and photochemotherapy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 62, 114–135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Tsai, T.F. HLA-Cw6 and psoriasis. Brit. J. Dermatol. 2018, 178, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuchacovich, R.; Garcia-Valladares, I.; Espinoza, L.R. Combination biologic treatment of refractory psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hsu, M.Y.; Herlyn, M. Cultivation of normal human epidermal melanocytes. Methods Mol. Med. 1996, 2, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Pawlikowski, B.; Schlessinger, A.; More, S.S.; Stryke, D.; Johns, S.J.; Portman, M.A.; Chen, E.; Ferrin, T.E.; Sali, A.; et al. Role of organic cation transporter 3 (SLC22A3) and its missense variants in the pharmacologic action of metformin. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2010, 20, 687–699. [Google Scholar]


| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
| IRF 1 | 5′ ggc aca tcc cag tgg aag 3′ | 5′ ccc ttc ctc atc ctc atc tgt 3′ |
| Oct1 | 5′ tcc tct tcc tgc tct act act gg | 5′ tgg tcc att atc ttt att gct tca 3′ |
| B2M | 5′ ttc tgg cct gga ggc tat c 3′ | 5′ tca gga aat ttg act ttc cat tc 3′ |
| ADAMTSL5 | 5′ tac cag tgg gtg ccc ttc 3′ | 5′ ggc cga agc tgt ggt aga 3′ |
| ERAP 1 | 5′ gtc act gtg aag atg agc acc ta 3′ | 5′ tgt ctg gca cag cat aaa cag 3′ |
| NLRC5 | 5′ ggt gct gct gag tac ttt 3′ | 5′ ggt tgg ctt ttc ccc tca 3′ |
| STAT 1 | 5′ gag ctt cac tcc ct tagt ttt ga 3′ | 5′ cac aac ggg cag aga ggt 3′ |
| Gene | Product details | Locator |
| miR-148a | Assay ID Hs04273238_s1 | See Thermo Fisher Scientific—TaqMan Search (last accessed 22 February 2025) |
| HLA-C | Assay ID Hs03044135_m1 | See Thermo Fisher Scientific—TaqMan Search (last accessed 22 February 2025) |
| siRNA | Sense Strand | Antisense Strand | siRNA Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| NRLC5-1 | GCUGAUCUUUGAUGGGCUAtt | UAGCCCAUCAAAGAUCAGCag | Chr.16: 56989547-57083524 on Build GRCh38 |
| NRLC5-2 | GAGCUGGACUUGUCUAACAtt | UGUUAGACAAGUCCAGCUCct | Chr.16: 56989547-57083524 on Build GRCh38 |
| HLA-C-1 | GUCAAUUCCUAGAAGUUGAtt | UCAACUUCUAGGAAUUGACtt | Chr.6: 31268749-31272136 on Build GRCh38 |
| HLA-C-2 | GUUGAGAGAGCAAAUAAAGtt | CUUUAUUUGCUCUCUCAACtt | Chr.6: 31268749-31272136 on Build GRCh38 |
| B2M | CAUCCGACAUUGAAGUUGAtt | UCAACUUCAAUGUCGGAUGga | Chr.15: 44711487-44718159 on Build GRCh38 |
| Antibody | Origin | Isotype | Designation | Distributor | Order Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HLA-C | PE | mouse | IgG2b, k | DT-9 | Bio Legend, Inc | AB-2650941 |
| HLA-ABC | PE | mouse | IgG2a, k | W6/32 | Bio Legend, Inc | 311406 |
| c-kit | Rabbit | Dako | A4502 | |||
| Anti-mouse IgG | Alexa 488 | Goat | Invitrogen | A11001 | ||
| Anti-rabbit IgG | Alexa 594 | Goat | Invitrogen | A11037 | ||
| Mouse IgG2b, k Isotype | PE | mouse | IgG2b, k | MG2b-57 | Bio Legend, Inc | 401208 |
| Mouse IgGa, k Isotype | PE | mouse | IgG2a, k | eBM2a | eBiosience | 12-4724-42 |
| Mouse IgG1, k Isotype | mouse | IgG1, k | MG1-45 | Bio Legend, Inc | 401402 | |
| Human BD Fc Block | BD Bioscience | 564219 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arakawa, Y.; Arakawa, A.; Vural, S.; He, M.; Vollmer, S.; Prinz, J.C. Down-Regulation of HLA-C Expression on Melanocytes May Contribute to the Therapeutic Efficacy of UVB Phototherapy in Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072858
Arakawa Y, Arakawa A, Vural S, He M, Vollmer S, Prinz JC. Down-Regulation of HLA-C Expression on Melanocytes May Contribute to the Therapeutic Efficacy of UVB Phototherapy in Psoriasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072858
Chicago/Turabian StyleArakawa, Yukiyasu, Akiko Arakawa, Seçil Vural, Mengwen He, Sigrid Vollmer, and Jörg C. Prinz. 2025. "Down-Regulation of HLA-C Expression on Melanocytes May Contribute to the Therapeutic Efficacy of UVB Phototherapy in Psoriasis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072858
APA StyleArakawa, Y., Arakawa, A., Vural, S., He, M., Vollmer, S., & Prinz, J. C. (2025). Down-Regulation of HLA-C Expression on Melanocytes May Contribute to the Therapeutic Efficacy of UVB Phototherapy in Psoriasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072858







