A Two-Phage Cocktail Modulates Gut Microbiota Composition and Metabolic Profiles in an Ex Vivo Colon Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
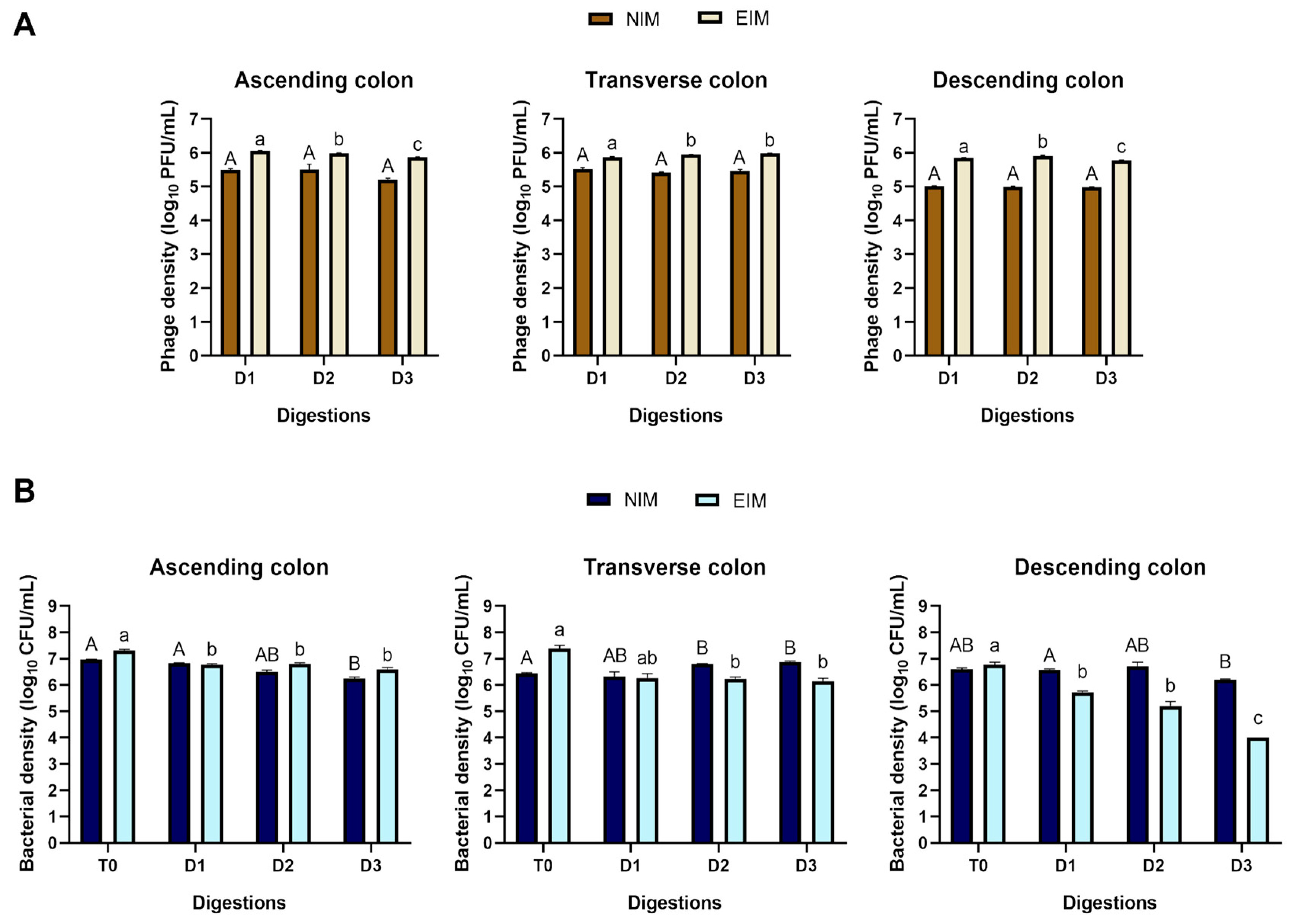
2.1. Microbiological Analysis
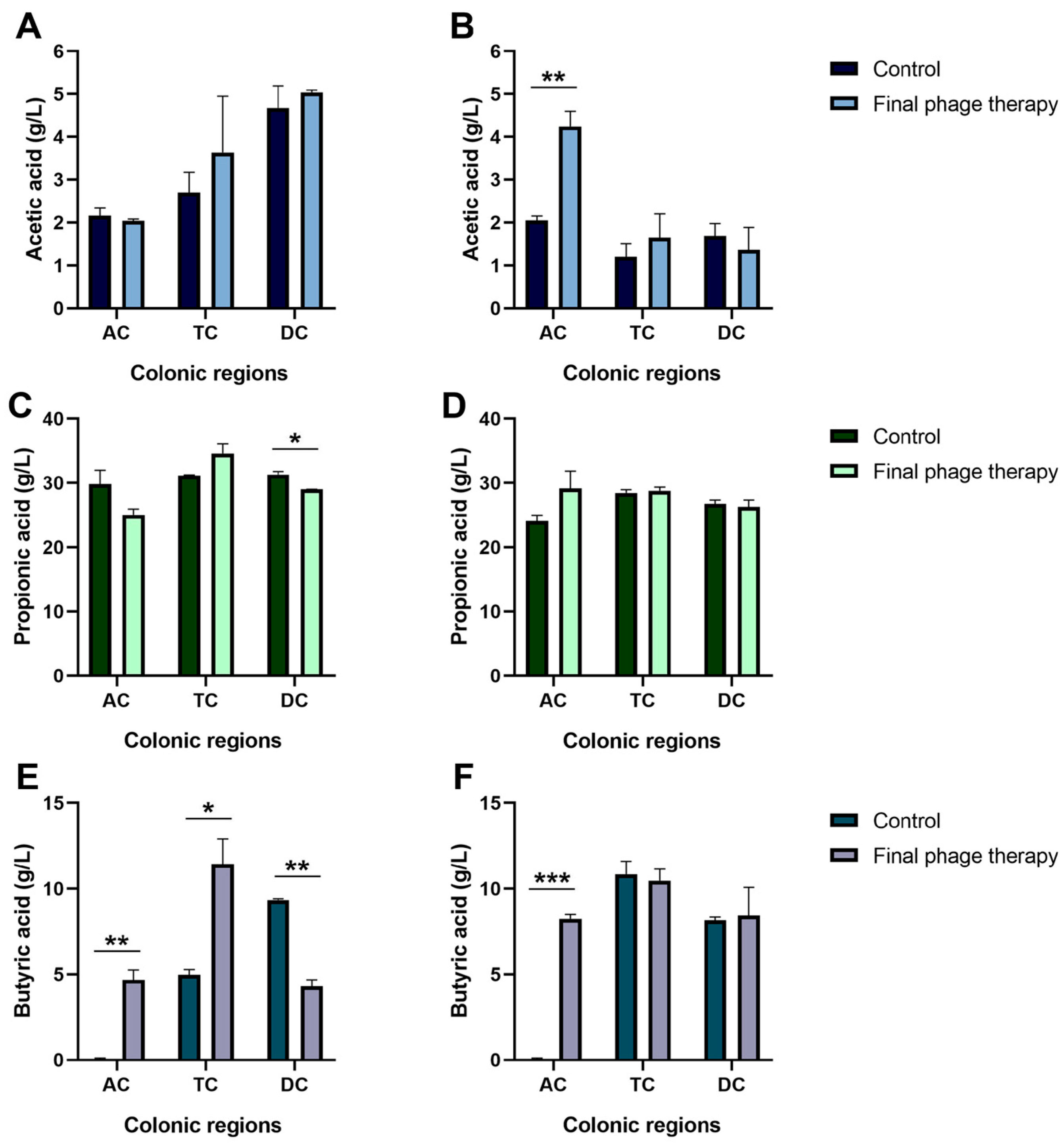
2.2. Production of Short-Chain Fatty Acids
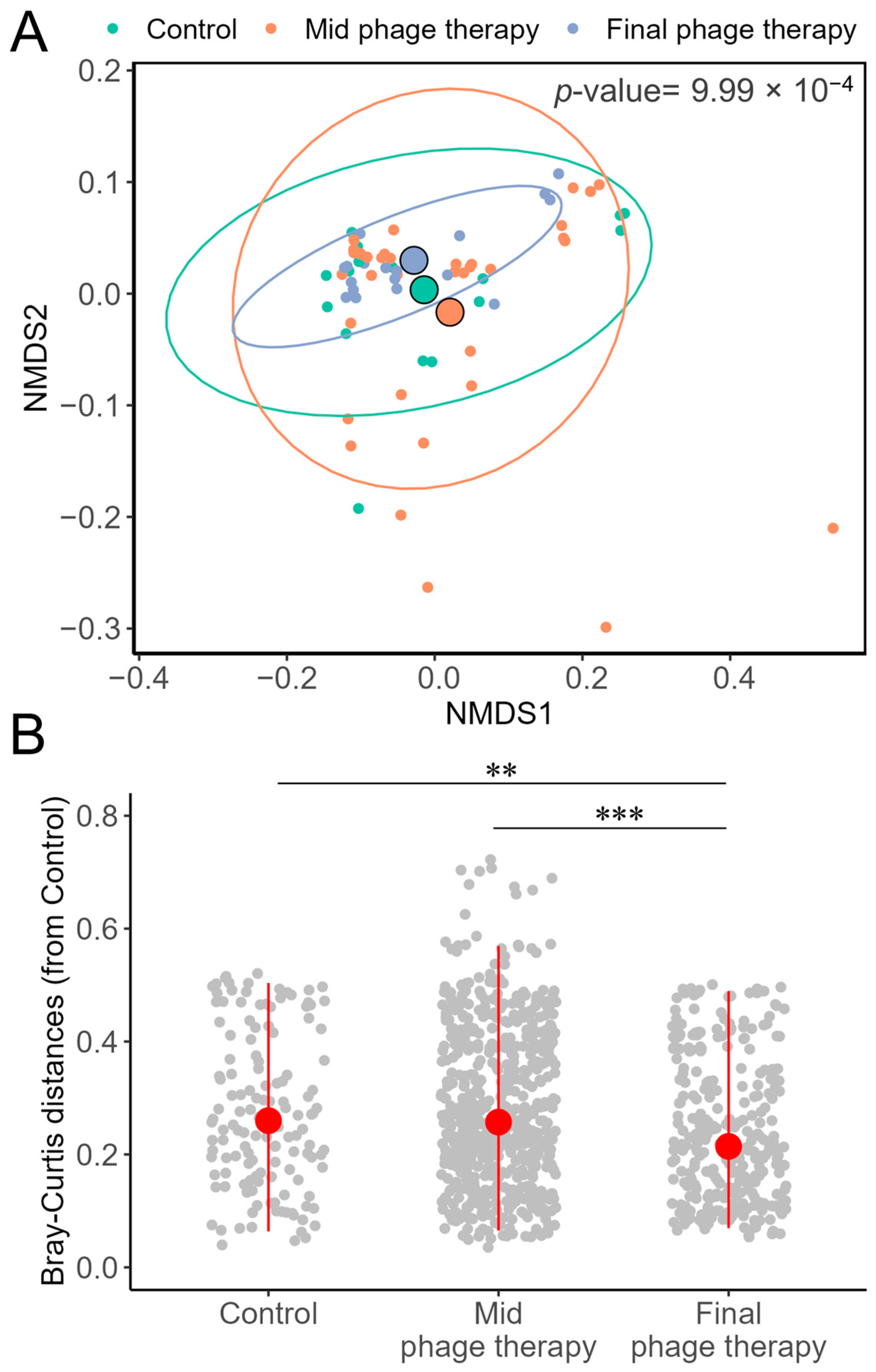
2.3. Comparative Analysis of Alpha Diversity
2.4. Comparative Analysis of Beta Diversity
2.5. Taxonomic Diversity
2.6. Enterobacter cloacae 16S rRNA Gene Sequences
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Adaptation of the Microbiota in the Automatic Robotic Intestinal System
4.3. Fecal Inoculum
4.4. Digestion of the Characteristic Diet of Individuals with Obesity in Bioreactors
4.5. Characteristics of the Bacteriophage Cocktail and Its Inoculation
4.6. Bacteriophage and Bacteria Density in Bioreactor Samples
4.7. Quantification of Short-Chain Fatty Acids
4.8. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Metabarcoding Profile
4.9. Bioinformatic Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sender, R.; Fuchs, S.; Milo, R. Revised Estimates for the Number of Human and Bacteria Cells in the Body. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, A.; Wu, M.; McNulty, N.P.; Rohwer, F.L.; Gordon, J.I. Gnotobiotic Mouse Model of Phage–Bacterial Host Dynamics in the Human Gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20236–20241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manor, O.; Dai, C.L.; Kornilov, S.A.; Smith, B.; Price, N.D.; Lovejoy, J.C.; Gibbons, S.M.; Magis, A.T. Health and Disease Markers Correlate with Gut Microbiome Composition across Thousands of People. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, B.B.; Gibson, T.E.; Yeliseyev, V.; Liu, Q.; Lyon, L.; Bry, L.; Silver, P.A.; Gerber, G.K. Dynamic Modulation of the Gut Microbiota and Metabolome by Bacteriophages in a Mouse Model. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 803–814.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, S.V.; Pedersen, O. The Human Intestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, W.; Lan, P.; Mou, X. The Microbiome in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: From Pathogenesis to Therapy. Protein Cell 2021, 12, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komaroff, A.L. The Microbiome and Risk for Obesity and Diabetes. JAMA 2017, 317, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.-N.; Liu, X.-T.; Liang, Z.-H.; Wang, J.-H. Gut Microbiota in Obesity. WJG 2021, 27, 3837–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Zheng, L.; Wei, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, D.; Yan, S.; Qin, H.; Wang, Q.; Ci, X.; Feng, H. Enterobacter cloacae Aggravates Metabolic Disease by Inducing Inflammation and Lipid Accumulation. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 90, 103819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskitalo, A.; Munukka, E.; Toivonen, R.; Hollmén, M.; Kainulainen, H.; Huovinen, P.; Jalkanen, S.; Pekkala, S. Enterobacter cloacae Administration Induces Hepatic Damage and Subcutaneous Fat Accumulation in High-Fat Diet Fed Mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konturek, P.C.; Haziri, D.; Brzozowski, T.; Hess, T.; Heyman, S.; Kwiecien, S.; Konturek, S.J.; Koziel, J. Emerging Role of Fecal Microbiota Therapy in the Treatment of Gastrointestinal and Extra-Gastrointestinal Diseases. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Airola, C.; Severino, A.; Porcari, S.; Fusco, W.; Mullish, B.H.; Gasbarrini, A.; Cammarota, G.; Ponziani, F.R.; Ianiro, G. Future Modulation of Gut Microbiota: From Eubiotics to FMT, Engineered Bacteria, and Phage Therapy. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.-M.; Flemer, B.; Joyce, S.A.; Zulquernain, A.; Sheehan, D.; Shanahan, F.; O’Toole, P.W. Changes in Microbiota Composition, Bile and Fatty Acid Metabolism, in Successful Faecal Microbiota Transplantation for Clostridioides Difficile Infection. BMC Gastroenterol. 2018, 18, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.-X.; Zhang, X.-Z. Bacteriophage-Mediated Modulation of Microbiota for Diseases Treatment. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 176, 113856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordillo Altamirano, F.L.; Barr, J.J. Phage Therapy in the Postantibiotic Era. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00066-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichet, M.C.; Adderley, J.; Avellaneda-Franco, L.; Magnin-Bougma, I.; Torriero-Smith, N.; Gearing, L.J.; Deffrasnes, C.; David, C.; Pepin, G.; Gantier, M.P.; et al. Mammalian Cells Internalize Bacteriophages and Use Them as a Resource to Enhance Cellular Growth and Survival. PLoS Biol. 2023, 21, e3002341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febvre, H.P.; Rao, S.; Gindin, M.; Goodwin, N.D.M.; Finer, E.; Vivanco, J.S.; Lu, S.; Manter, D.K.; Wallace, T.C.; Weir, T.L. PHAGE Study: Effects of Supplemental Bacteriophage Intake on Inflammation and Gut Microbiota in Healthy Adults. Nutrients 2019, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüssow, H. Hurdles for Phage Therapy to Become a Reality—An Editorial Comment. Viruses 2019, 11, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeckx, K.; Cotter, P.D.; López-Expósito, I.; Kleiveland, C.; Lea, T.; Mackie, A.; Requena, T.; Swiatecka, D.; Wichers, H. The Impact of Food Bioactives on Gut Health: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Models; Springer Open: Cham, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-16104-4. [Google Scholar]
- Molly, K.; Woestyne, M.V.; Smet, I.D.; Verstraete, W. Validation of the Simulator of the Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem (SHIME) Reactor Using Microorganism-Associated Activities. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 1994, 7, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gamboa, R.; Gradilla-Hernández, M.S.; Ortiz-Basurto, R.I.; García-Reyes, R.A.; González-Avila, M. Assessment of Intermediate and Long Chains Agave Fructan Fermentation on the Growth of Intestinal Bacteria Cultured in a Gastrointestinal Tract Simulator. Rev. Mex. Ing. Quim. 2019, 19, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verthé, K.; Possemiers, S.; Boon, N.; Vaneechoutte, M.; Verstraete, W. Stability and Activity of an Enterobacter aerogenes-Specific Bacteriophage under Simulated Gastro-Intestinal Conditions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 65, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moye, Z.D.; Woolston, J.; Abbeele, P.V.D.; Duysburgh, C.; Verstrepen, L.; Das, C.R.; Marzorati, M.; Sulakvelidze, A. A Bacteriophage Cocktail Eliminates Salmonella Typhimurium from the Human Colonic Microbiome While Preserving Cytokine Signaling and Preventing Attachment to and Invasion of Human Cells by Salmonella In Vitro. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 1336–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, S.; Kredo-Russo, S.; Valdés-Mas, R.; Kviatcovsky, D.; Weinstock, E.; Matiuhin, Y.; Silberberg, Y.; Atarashi, K.; Furuichi, M.; Oka, A.; et al. Targeted Suppression of Human IBD-Associated Gut Microbiota Commensals by Phage Consortia for Treatment of Intestinal Inflammation. Cell 2022, 185, 2879–2898.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Gómez, J.P.; Rodríguez-Arellano, S.N.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Vergara-Jiménez, M.D.J.; Chaidez, C. Genomic and Biological Characterization of Bacteriophages against Enterobacter cloacae, a High-Priority Pathogen. Virology 2024, 595, 110100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, R.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Behare, P.V.; Jain, S.; Yadav, H. Probiotics, Their Health Benefits and Applications for Developing Healthier Foods: A Review. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 334, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeser, R.F.; Arbeeva, L.; Kelley, K.; Fodor, A.A.; Sun, S.; Ulici, V.; Longobardi, L.; Cui, Y.; Stewart, D.A.; Sumner, S.J.; et al. Association of Increased Serum Lipopolysaccharide, But Not Microbial Dysbiosis, with Obesity-Related Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, S.; Xue, Y.; Lu, H.; Jia, X.; Wang, S. Association of the Gut Microbiome with Fecal Short-Chain Fatty Acids, Lipopolysaccharides, and Obesity in Young Chinese College Students. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1057759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdomo, C.M.; Cohen, R.V.; Sumithran, P.; Clément, K.; Frühbeck, G. Contemporary Medical, Device, and Surgical Therapies for Obesity in Adults. Lancet 2023, 401, 1116–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, K.; Chaudhari, D.; Dhotre, D.; Shouche, Y.; Saroj, S. Restoration of Dysbiotic Human Gut Microbiome for Homeostasis. Life Sci. 2021, 278, 119622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paule, A.; Frezza, D.; Edeas, M. Microbiota and Phage Therapy: Future Challenges in Medicine. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brives, C.; Pourraz, J. Phage Therapy as a Potential Solution in the Fight against AMR: Obstacles and Possible Futures. Palgrave Commun. 2020, 6, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, A.J.; West, N.P.; Cripps, A.W. Obesity, Inflammation, and the Gut Microbiota. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.-M.; Jeong, J.-J.; Woo, K.H.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.-H. Lactobacillus Sakei OK67 Ameliorates High-Fat Diet–Induced Blood Glucose Intolerance and Obesity in Mice by Inhibiting Gut Microbiota Lipopolysaccharide Production and Inducing Colon Tight Junction Protein Expression. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, A.P.B.; Texeira, T.F.S.; Ferreira, A.B.; Do Carmo Gouveia Peluzio, M.; De Cássia Gonçalves Alfenas, R. Influence of a High-Fat Diet on Gut Microbiota, Intestinal Permeability and Metabolic Endotoxaemia. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, S.I.; Gu Liu, C.; Yu, X.; Gibson, S.; Salmen, W.; Rajan, A.; Carter, H.E.; Clark, J.R.; Song, X.; Ramig, R.F.; et al. Targeting of Mammalian Glycans Enhances Phage Predation in the Gastrointestinal Tract. mBio 2021, 12, e03474-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, M.; Nakamoto, N.; Kredo-Russo, S.; Weinstock, E.; Weiner, I.N.; Khabra, E.; Ben-Ishai, N.; Inbar, D.; Kowalsman, N.; Mordoch, R.; et al. Bacteriophage Therapy against Pathological Klebsiella Pneumoniae Ameliorates the Course of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Feng, Y.; Du, B.; Fu, H.; Tian, Z.; Xue, G.; Yan, C.; Cui, X.; Zhang, R.; Cui, J.; et al. Bacteriophage Targeting Microbiota Alleviates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Induced by High Alcohol-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, C.; Cui, J.; Lu, J.; Yan, C.; Wei, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, N.; Li, S.; Xue, G.; et al. Fatty Liver Disease Caused by High-Alcohol-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 675–688.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Llorente, C.; Lang, S.; Brandl, K.; Chu, H.; Jiang, L.; White, R.C.; Clarke, T.H.; Nguyen, K.; Torralba, M.; et al. Bacteriophage Targeting of Gut Bacterium Attenuates Alcoholic Liver Disease. Nature 2019, 575, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gindin, M.; Febvre, H.P.; Rao, S.; Wallace, T.C.; Weir, T.L. Bacteriophage for Gastrointestinal Health (PHAGE) Study: Evaluating the Safety and Tolerability of Supplemental Bacteriophage Consumption. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2019, 38, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubb, D.S.; Wrigley, S.D.; Freedman, K.E.; Wei, Y.; Vazquez, A.R.; Trotter, R.E.; Wallace, T.C.; Johnson, S.A.; Weir, T.L. PHAGE-2 Study: Supplemental Bacteriophages Extend Bifidobacterium Animalis Subsp. Lactis BL04 Benefits on Gut Health and Microbiota in Healthy Adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titécat, M.; Rousseaux, C.; Dubuquoy, C.; Foligné, B.; Rahmouni, O.; Mahieux, S.; Desreumaux, P.; Woolston, J.; Sulakvelidze, A.; Wannerberger, K.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of an AIEC-Targeted Bacteriophage Cocktail in a Mice Colitis Model. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2022, 16, 1617–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiki, J.; Schnabl, B. Phage Therapy: Targeting Intestinal Bacterial Microbiota for the Treatment of Liver Diseases. JHEP Rep. 2023, 5, 100909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Li, N.; Lu, Z.; Li, L.; Hui, S.; Xu, H. Gut Microbiota and Short Chain Fatty Acids Partially Mediate the Beneficial Effects of Inulin on Metabolic Disorders in Obese Ob/Ob Mice. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, D.J.; Preston, T. Formation of Short Chain Fatty Acids by the Gut Microbiota and Their Impact on Human Metabolism. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, N.H.T.; Joglekar, M.V.; Wong, W.K.M.; Nassif, N.T.; Simpson, A.M.; Hardikar, A.A. Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Insulin Sensitivity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2024, 82, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overby, H.B.; Ferguson, J.F. Gut Microbiota-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids Facilitate Microbiota: Host Cross Talk and Modulate Obesity and Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2021, 23, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laforêt, F.; Antoine, C.; Lebrun, S.; Gonza, I.; Goya-Jorge, E.; Douny, C.; Duprez, J.-N.; Scippo, M.-L.; Taminiau, B.; Daube, G.; et al. Impact Assessment of vB_KpnP_K1-ULIP33 Bacteriophage on the Human Gut Microbiota Using a Dynamic In Vitro Model. Viruses 2023, 15, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallavali, R.R.; Degati, V.L.; Lomada, D.; Reddy, M.C.; Durbaka, V.R.P. Isolation and in Vitro Evaluation of Bacteriophages against MDR-Bacterial Isolates from Septic Wound Infections. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, R.; Wang, S.; Ahmadi, S.; Hayes, J.; Gagliano, J.; Subashchandrabose, S.; Kitzman, D.W.; Becton, T.; Read, R.; Yadav, H. Human-Origin Probiotic Cocktail Increases Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production via Modulation of Mice and Human Gut Microbiome. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A Rapid DNA Isolation Procedure for Small Quantities of Fresh Leaf Tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Huse, S.M.; Dethlefsen, L.; Huber, J.A.; Welch, D.M.; Relman, D.A.; Sogin, M.L. Exploring Microbial Diversity and Taxonomy Using SSU rRNA Hypervariable Tag Sequencing. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An Ultra-Fast All-in-One FASTQ Preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME Improves Sensitivity and Speed of Chimera Detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, D.E.; Lu, J.; Langmead, B. Improved Metagenomic Analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Breitwieser, F.P.; Thielen, P.; Salzberg, S.L. Bracken: Estimating Species Abundance in Metagenomics Data. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2017, 3, e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Colonic Regions | Index | Control | Mid Phage Therapy | Final Phage Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending | Chao1 | 23.67 ± 6.50 a | 27.33 ± 6.68 a | 18.33 ± 0.57 a |
| Shannon | 1.67 ± 0.13 a | 1.87 ± 1.31 a | 1.57 ± 0.07 a | |
| Transverse | Chao1 | 24.50 ± 5.76 a | 32.41 ± 6.27 a | 23.67 ± 4.72 a |
| Shannon | 1.59 ± 0.14 a | 1.72 ± 0.06 a | 1.66 ± 0.14 a | |
| Descending | Chao1 | 41.52 ± 15.51 a | 42.47 ± 4.10 a | 33.91 ± 3.39 a |
| Shannon | 2.12 ± 0.13 a | 2.12 ± 0.07 a | 2.13 ± 0.06 a |
| Colonic Regions | Index | Control | Mid Phage Therapy | Final Phage Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending | Chao1 | 53.23 ± 5.06 a | 51.75 ± 13.66 a | 29.50 ± 5.89 b |
| Shannon | 2.05± 0.07 ab | 2.35 ± 0.32 a | 1.60 ± 0.03 b | |
| Transverse | Chao1 | 44.97 ± 7.20 a | 43.29 ± 9.15 a | 34.08 ± 1.18 a |
| Shannon | 1.62 ± 0.03 a | 1.60 ± 0.08 a | 1.82 ± 0.06 b | |
| Descending | Chao1 | 52.20 ± 8.25 a | 46.04 ± 4.82 a | 53.40 ± 5.7 a |
| Shannon | 2.27 ± 0.01 a | 2.26 ± 0.05 a | 2.27 ± 0.02 a |
| Intervention Time | Ascending Colon | Transverse Colon | Descending Colon |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 7 ± 5.00 a | 79.67 ± 10.00 a | 18 ± 8.88 a |
| Mid phage therapy | 2.33 ± 1.63 ab | 28.67 ± 13.45 b | 12.17 ± 6.73 ab |
| Final phage therapy | 0.33 ± 0.57 b | 21.67 ± 7.63 b | 2.33 ± 1.52 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Arellano, S.N.; González-Gómez, J.P.; Gomez-Gil, B.; González-Ávila, M.; Palomera-Hernández, J.R.; Barrón-Cabrera, E.; Vergara-Jiménez, M.d.J.; Chaidez, C. A Two-Phage Cocktail Modulates Gut Microbiota Composition and Metabolic Profiles in an Ex Vivo Colon Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062805
Rodríguez-Arellano SN, González-Gómez JP, Gomez-Gil B, González-Ávila M, Palomera-Hernández JR, Barrón-Cabrera E, Vergara-Jiménez MdJ, Chaidez C. A Two-Phage Cocktail Modulates Gut Microbiota Composition and Metabolic Profiles in an Ex Vivo Colon Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062805
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Arellano, Sthefhany Nohemí, Jean Pierre González-Gómez, Bruno Gomez-Gil, Marisela González-Ávila, Juan Ramón Palomera-Hernández, Elisa Barrón-Cabrera, Marcela de Jesús Vergara-Jiménez, and Cristobal Chaidez. 2025. "A Two-Phage Cocktail Modulates Gut Microbiota Composition and Metabolic Profiles in an Ex Vivo Colon Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062805
APA StyleRodríguez-Arellano, S. N., González-Gómez, J. P., Gomez-Gil, B., González-Ávila, M., Palomera-Hernández, J. R., Barrón-Cabrera, E., Vergara-Jiménez, M. d. J., & Chaidez, C. (2025). A Two-Phage Cocktail Modulates Gut Microbiota Composition and Metabolic Profiles in an Ex Vivo Colon Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2805. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062805







