Serum and Plasma miRNA Expression Levels in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Abstract
:1. Introduction
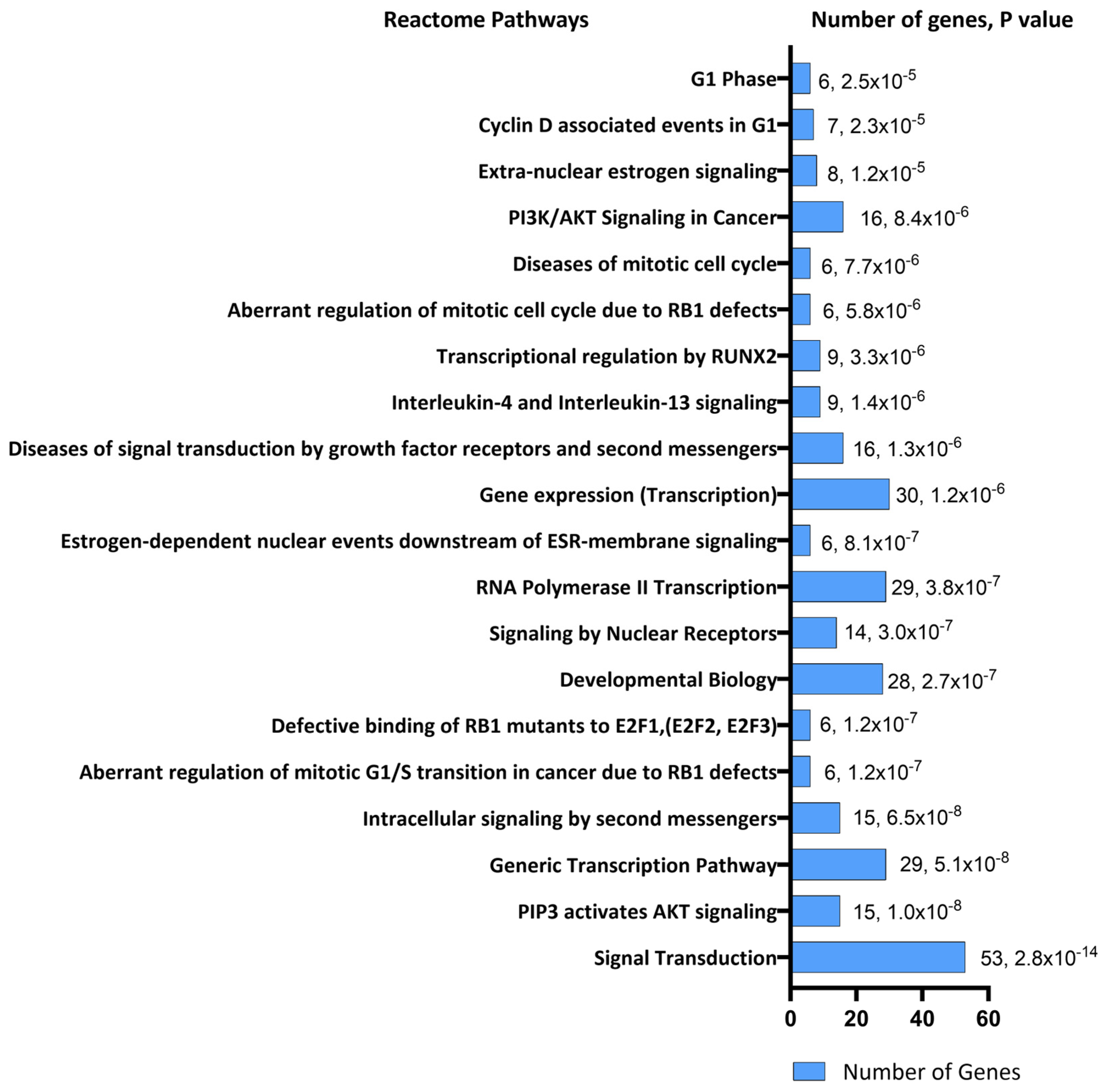
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Populations and Sampling
4.2. Clinical Examination and Patient Recruitment
4.3. Blood Collection, MicroRNA Extraction, and Reverse Transcription
4.4. MicroRNA Real-Time PCR
4.5. Statistical Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Tsai Do, B.S.; Schwartz, S.R.; Bontempo, L.J.; Faucett, E.A.; Finestone, S.A.; Hollingsworth, D.B.; Kelley, D.M.; Kmucha, S.T.; Moonis, G.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Sudden Hearing Loss (Update). Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2019, 161, S1–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, T.H.; Harris, J.P. Incidence of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Otol. Neurotol. 2013, 34, 1586–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, T.; Sato, H.; Gyo, K.; Hato, N.; Yoshida, T.; Shimono, M.; Teranishi, M.; Sone, M.; Fukunaga, Y.; Kobashi, G.; et al. Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Japan. Acta Otolaryngol. 2014, 134, 1158–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondal, T.; Nielsen, S.J.; Baker, A.; Andreasen, D.; Mouritzen, P.; Teilum, M.W.; Dahlsveen, I.K. Assessing Sample and miRNA Profile Quality in Serum and Plasma or Other Biofluids. Methods 2013, 59, S1–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Garcia, I.; Miska, E.A. MicroRNA Functions in Animal Development and Human Disease. Development 2005, 132, 4653–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumathipala, M.; Weiss, S.T. Predicting miRNA-Based Disease-Disease Relationships through Network Diffusion on Multi-Omics Biological Data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szelenberger, R.; Kacprzak, M.; Saluk-Bijak, J.; Zielinska, M.; Bijak, M. Plasma MicroRNA as a Novel Diagnostic. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 499, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, M.A.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Ferdin, J.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs in Body Fluids—The Mix of Hormones and Biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Du, X.; Ma, K.; Li, G.; Liu, Z.; Rong, W.; Miao, H.; Zhu, F.; Cui, Q.; Wu, S.; et al. Circulating miRNAs Related to Long-Term Adverse Cardiovascular Events in STEMI Patients: A Nested Case-Control Study. Can. J. Cardiol. 2021, 37, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Ochiya, T. Circulating microRNA in Body Fluid: A New Potential Biomarker for Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 2087–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, S.; Weber, J.; Baxter, D.; Galas, D.J. Export of microRNAs and microRNA-Protective Protein by Mammalian Cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 7248–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesinghe, P.; Xi, J.; Cui, J.; Campbell, M.; Pham, W.; Matsubara, J.A. MicroRNAs in Tear Fluids Predict Underlying Molecular Changes Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease. Life Sci. Alliance 2023, 6, e202201757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, L.M.; Dror, A.A.; Mor, E.; Tenne, T.; Toren, G.; Satoh, T.; Biesemeier, D.J.; Shomron, N.; Fekete, D.M.; Hornstein, E.; et al. MicroRNAs Are Essential for Development and Function of Inner Ear Hair Cells in Vertebrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7915–7920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushakov, K.; Rudnicki, A.; Avraham, K.B. MicroRNAs in Sensorineural Diseases of the Ear. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesinghe, P.; Nunez, D.A.; Garnis, C. MicroRNA Signature and Cellular Characterization of Undifferentiated and Differentiated House Ear Institute-Organ of Corti 1 (HEI-OC1) Cells. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2022, 23, 467–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Peng, X.; Huang, H.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, J. RNA Sequencing Uncovers the Key microRNAs Potentially Contributing to Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Medicine 2017, 96, e8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunez, D.A.; Wijesinghe, P.; Nabi, S.; Yeh, D.; Garnis, C. microRNAs in Sudden Hearing Loss. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, E416–E422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, B. MicroRNA-186-5p Is Expressed Highly in Ethanol-induced Cardiomyocytes and Regulates Apoptosis via the Target Gene XIAP. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 3179–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Pan, J.; Jin, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, M. MiR-195-5p Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells by Targeting CEP55. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 11465–11474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Dou, X.; Li, S.; Jia, Q.; Ling, P.; Liu, H.; Han, Q.; Sun, S. miR-590-5p Affects Chondrocyte Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Inflammation by Targeting FGF18 in Osteoarthritis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 8728–8741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Jiang, J.; Deng, H.; Wang, Z.; Gu, R.; Wang, F. miR-140-3p Aggregates Osteoporosis by Targeting PTEN and Activating PTEN/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Hum. Cell 2020, 33, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhou, X.; Long, Q.; Zeng, H.; Sun, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wu, D.; Liu, L. Small Extracellular Vesicles Containing miR-30a-3p Attenuate the Migration and Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting SNAP23 Gene. Oncogene 2021, 40, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-Mediated Transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs Is a Novel Mechanism of Genetic Exchange between Cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collino, F.; Deregibus, M.C.; Bruno, S.; Sterpone, L.; Aghemo, G.; Viltono, L.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Microvesicles Derived from Adult Human Bone Marrow and Tissue Specific Mesenchymal Stem Cells Shuttle Selected Pattern of miRNAs. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, J.D.; Chevillet, J.R.; Kroh, E.M.; Ruf, I.K.; Pritchard, C.C.; Gibson, D.F.; Mitchell, P.S.; Bennett, C.F.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Stirewalt, D.L.; et al. Argonaute2 Complexes Carry a Population of Circulating microRNAs Independent of Vesicles in Human Plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5003–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiam, K.; Mayne, G.C.; Wang, T.; Watson, D.I.; Irvine, T.S.; Bright, T.; Smith, L.T.; Ball, I.A.; Bowen, J.M.; Keefe, D.M.; et al. Serum Outperforms Plasma in Small Extracellular Vesicle microRNA Biomarker Studies of Adenocarcinoma of the Esophagus. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Yuan, Y.; Cho, J.-H.; McClarty, S.; Baxter, D.; Galas, D.J. Comparing the MicroRNA Spectrum between Serum and Plasma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foye, C.; Yan, I.K.; David, W.; Shukla, N.; Habboush, Y.; Chase, L.; Ryland, K.; Kesari, V.; Patel, T. Comparison of miRNA Quantitation by Nanostring in Serum and Plasma Samples. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLellan, S.A.; MacAulay, C.; Lam, S.; Garnis, C. Pre-Profiling Factors Influencing Serum microRNA Levels. BMC Clin. Pathol. 2014, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.G. Uses and Abuses of Hearing Loss Classification. Asha 1981, 23, 493–500. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.-D.; Cui, S.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xu, J.; Bao, J.; Li, Y.; Wen, J.; Zuo, H.; et al. miRTarBase Update 2022: An Informative Resource for Experimentally Validated miRNA–Target Interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. DAVID: A Web Server for Functional Enrichment Analysis and Functional Annotation of Gene Lists (2021 Update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, S.M.; Hwang, K.R.; Park, I.H.; Park, S.; Choi, J.S.; Park, D.J.; Park, J.-E.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Seo, Y.J. Circulating microRNAs as Potentially New Diagnostic Biomarkers of Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Acta Otolaryngol. 2020, 140, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, H.; Yang, G.; Ke, J.; Sun, W.; Yang, L.; Kuang, S.; Li, H.; Yuan, W. Differentially Expressed miRNA Profiles of Serum-Derived Exosomes in Patients with Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1177988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, N.B.; Ng, E.K.; Lo, Y.D. Stability of Endogenous and Added RNA in Blood Specimens, Serum, and Plasma. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisco, K.L. Is RNA in Serum Bound to Nucleoprotein Complexes? Clin. Chem. 2001, 47, 1744–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; MacIntyre, D.A.; Sykes, L.; Arianoglou, M.; Bennett, P.R.; Terzidou, V. Whole Blood Holding Time Prior to Plasma Processing Alters microRNA Expression Profile. Front. Genet. 2022, 12, 818334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mompeón, A.; Ortega-Paz, L.; Vidal-Gómez, X.; Costa, T.J.; Pérez-Cremades, D.; Garcia-Blas, S.; Brugaletta, S.; Sanchis, J.; Sabate, M.; Novella, S.; et al. Disparate miRNA Expression in Serum and Plasma of Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic and Paired Comparative Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachler, R.J.; Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Archer, S.M.; Rosenfeld, R.M.; Schwartz, S.R.; Barrs, D.M.; Brown, S.R.; Fife, T.D.; Ford, P.; Ganiats, T.G.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Sudden Hearing Loss. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2012, 146, S1–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings-Goss, R.A.; Campbell, M.C.; Tishkoff, S.A. Global Population-Specific Variation in miRNA Associated with Cancer Risk and Clinical Biomarkers. BMC Med. Genom. 2014, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshua, T.G.; Ayub, A.; Wijesinghe, P.; Nunez, D.A. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Patients with Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2022, 148, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abgoon, R.; Wijesinghe, P.; Garnis, C.; Nunez, D.A. The Expression Levels of MicroRNAs Differentially Expressed in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Patients’ Serum Are Unchanged for up to 12 Months after Hearing Loss Onset. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing Real-Time PCR Data by the Comparative CT Method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
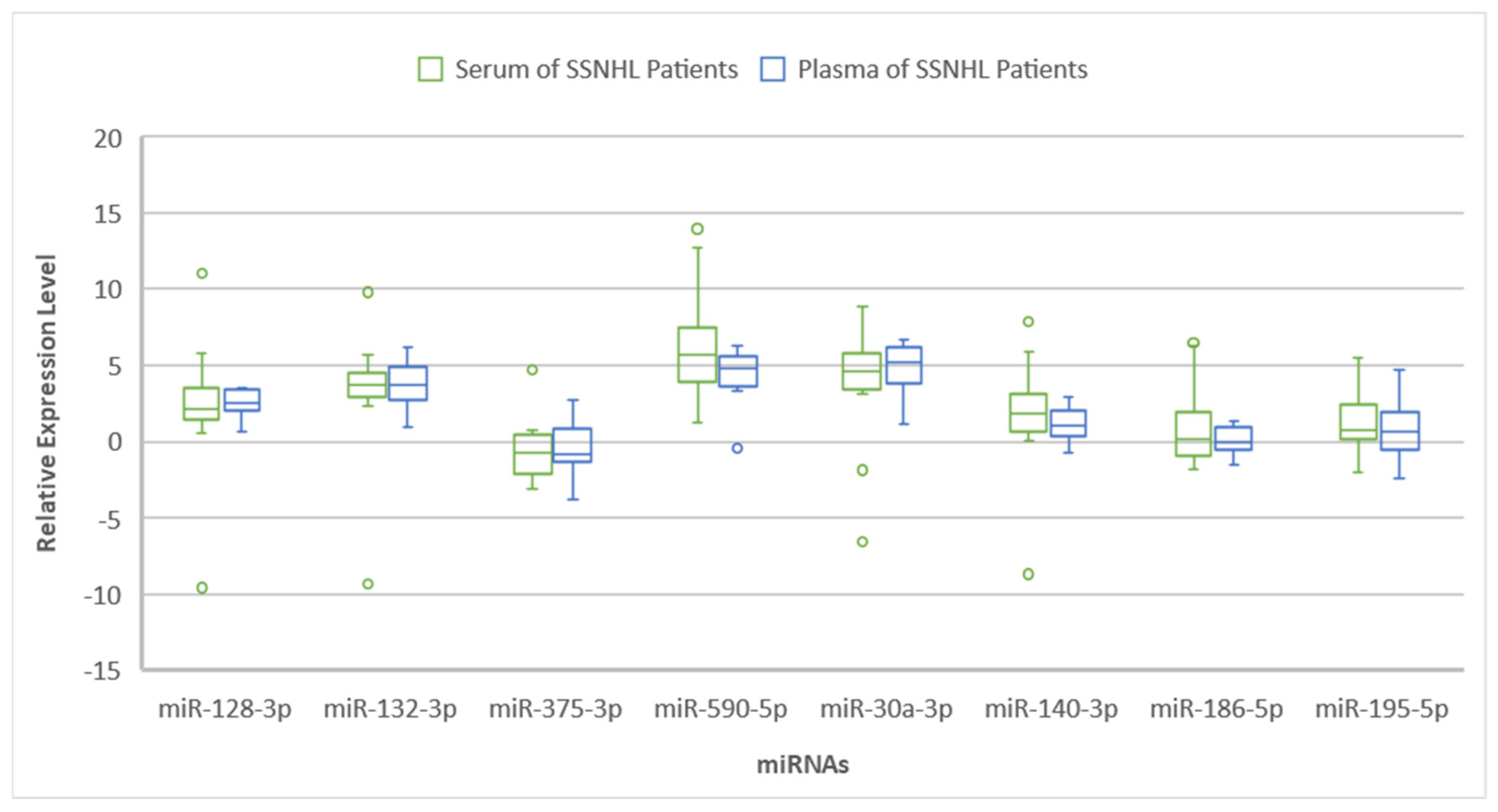
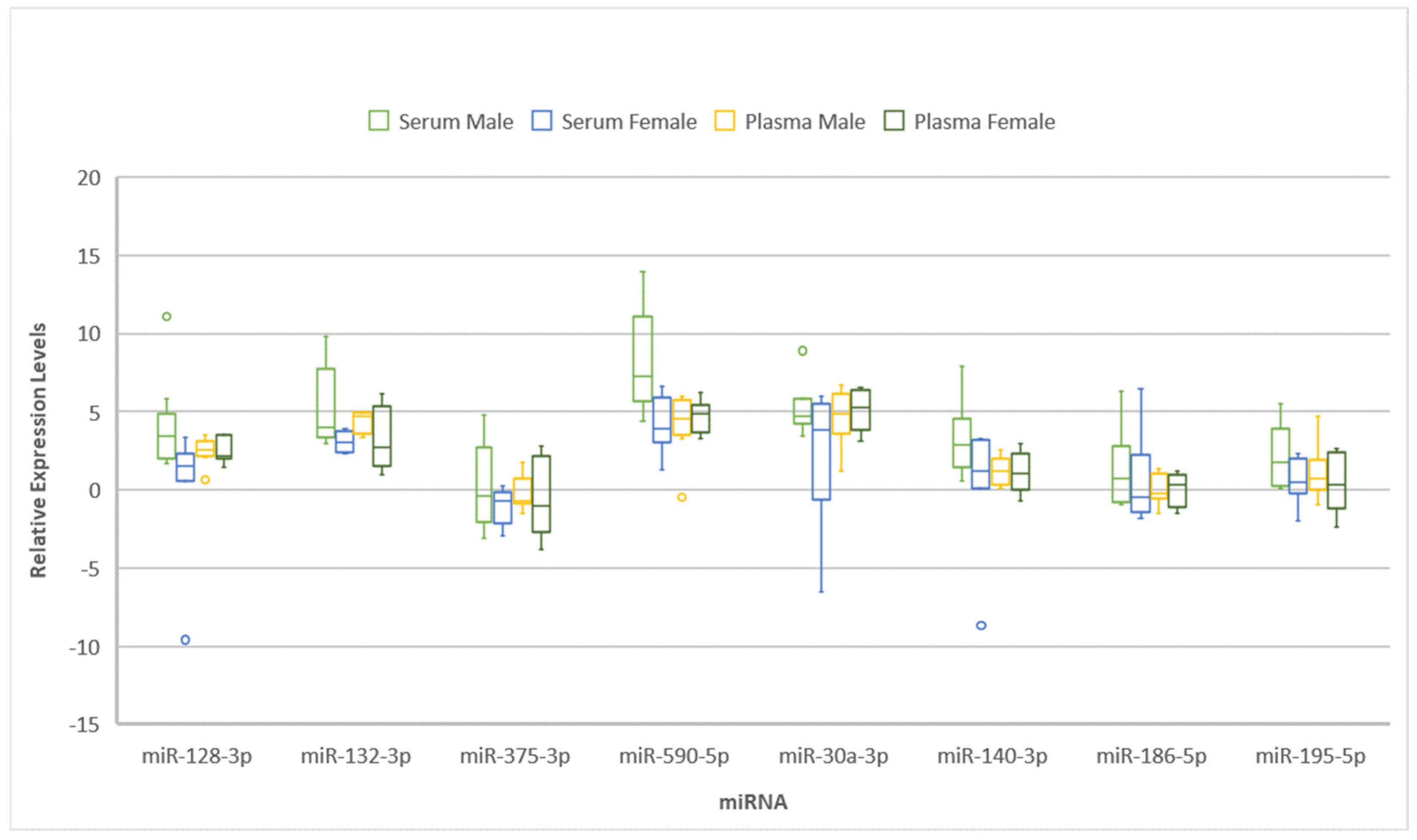
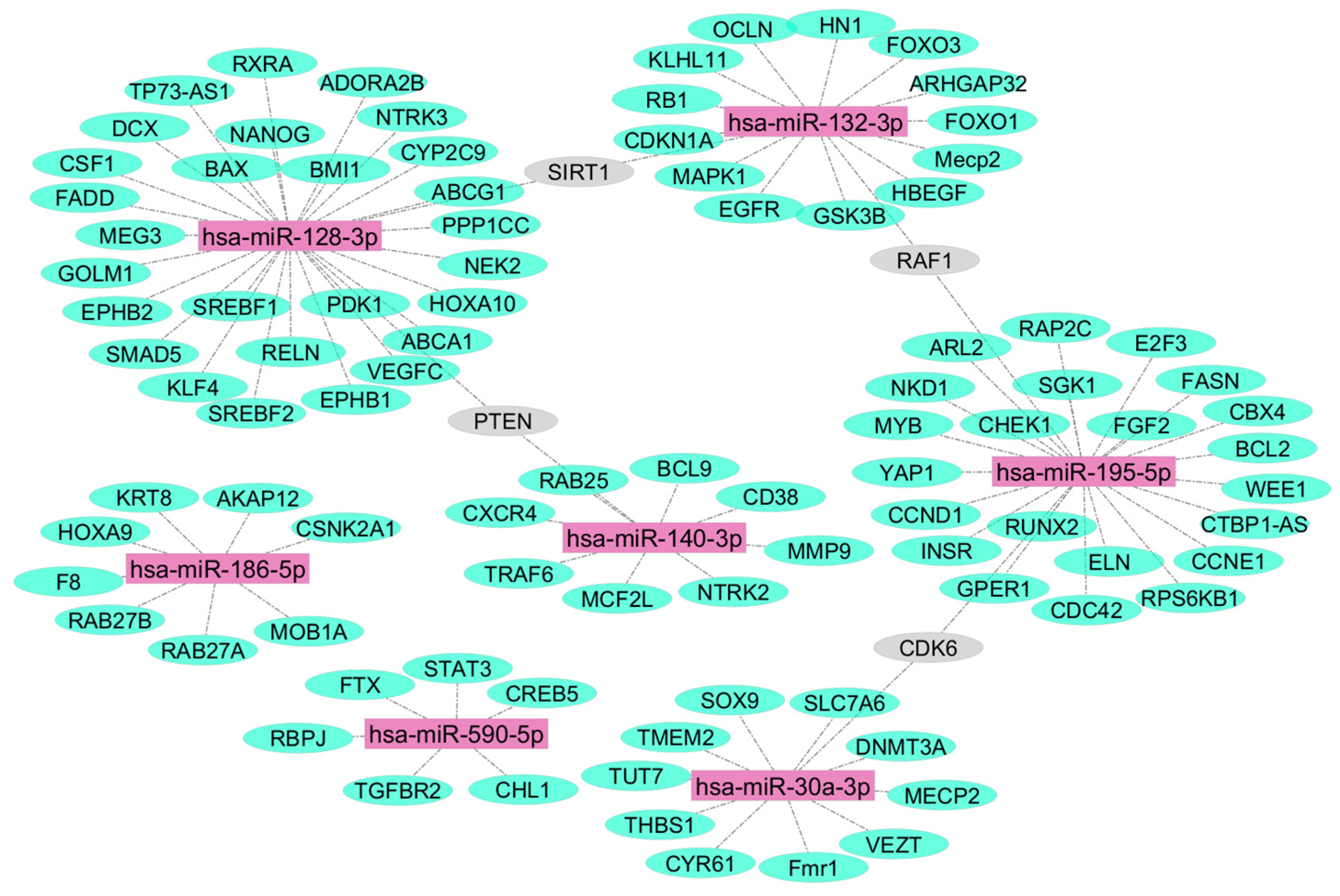
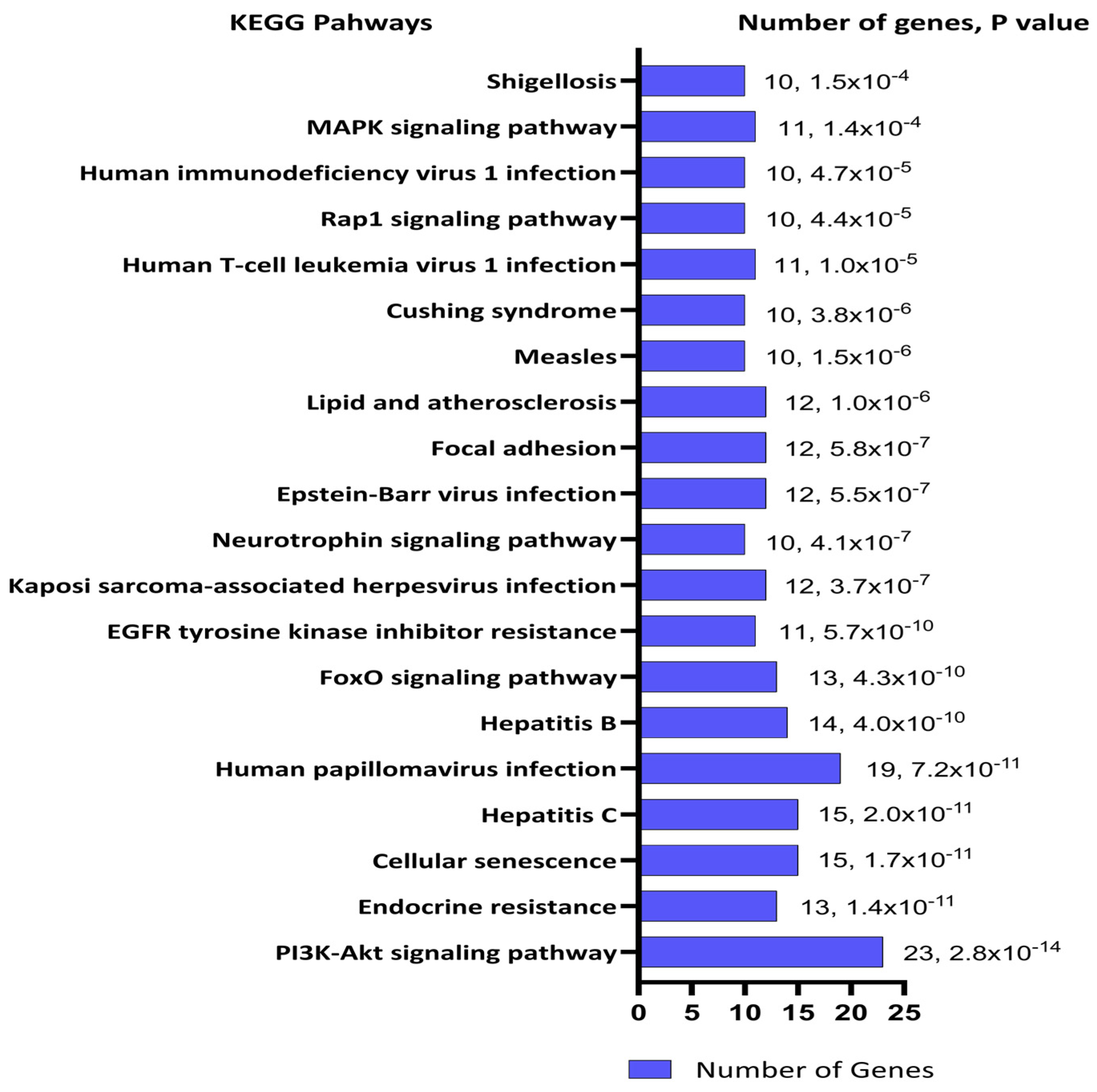
| Features | SSNHL Patients |
|---|---|
| Hearing loss site, n (%) Right ear Left ear | 10 (58.8) 7 (41.2) |
| Initial PTA of the affected ear (mean ± SD in dB) | 60.7 ± 22.85 |
| Age in years (mean ± SD) | 51.9 ± 13.9 |
| Sex (male: female) | 9:8 |
| Dizziness (with dizziness: without dizziness) | 1:16 |
| miRNA Name | Accession Number MiRBase | Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-128-3p | MIMAT0000424 | UCACAGUGAACCGGUCUCUUU |
| hsa-miR-132-3p | MIMAT0000426 | UAACAGUCUACAGCCAUGGUCG |
| hsa-miR-375-3p | MIMAT0000728 | UUUGUUCGUUCGGCUCGCGUGA |
| hsa-miR-590-5p | MIMAT0003258 | GAGCUUAUUCAUAAAAGUGCAG |
| hsa-miR-30a-3p | MIMAT0000088 | CUUUCAGUCGGAUGUUUGCAGC |
| hsa-miR-140-3p | MIMAT0004597 | UACCACAGGGUAGAACCACGG |
| hsa-miR-186-5p | MIMAT0000456 | CAAAGAAUUCUCCUUUUGGGCU |
| hsa-miR-195-5p | MIMAT0000461 | UAGCAGCACAGAAAUAUUGGC |
| has-miR-191-5p | MIMAT0000440 | CAACGGAAUCCCAAAAGCAGCUG |
| hsa-miR-16-5p | MIMAT0000069 | UAGCAGCACGUAAAUAUUGGCG |
| hsa-miR-103a-3p | MIMAT0000101 | AGCAGCAUUGUACAGGGCUAUGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nunez, D.A.; Abgoon, R.; Wijesinghe, P.; Garnis, C. Serum and Plasma miRNA Expression Levels in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031245
Nunez DA, Abgoon R, Wijesinghe P, Garnis C. Serum and Plasma miRNA Expression Levels in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(3):1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031245
Chicago/Turabian StyleNunez, Desmond A., Reyhaneh Abgoon, Printha Wijesinghe, and Cathie Garnis. 2025. "Serum and Plasma miRNA Expression Levels in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 3: 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031245
APA StyleNunez, D. A., Abgoon, R., Wijesinghe, P., & Garnis, C. (2025). Serum and Plasma miRNA Expression Levels in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(3), 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031245







