Auxin and Target of Rapamycin Spatiotemporally Regulate Root Organogenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
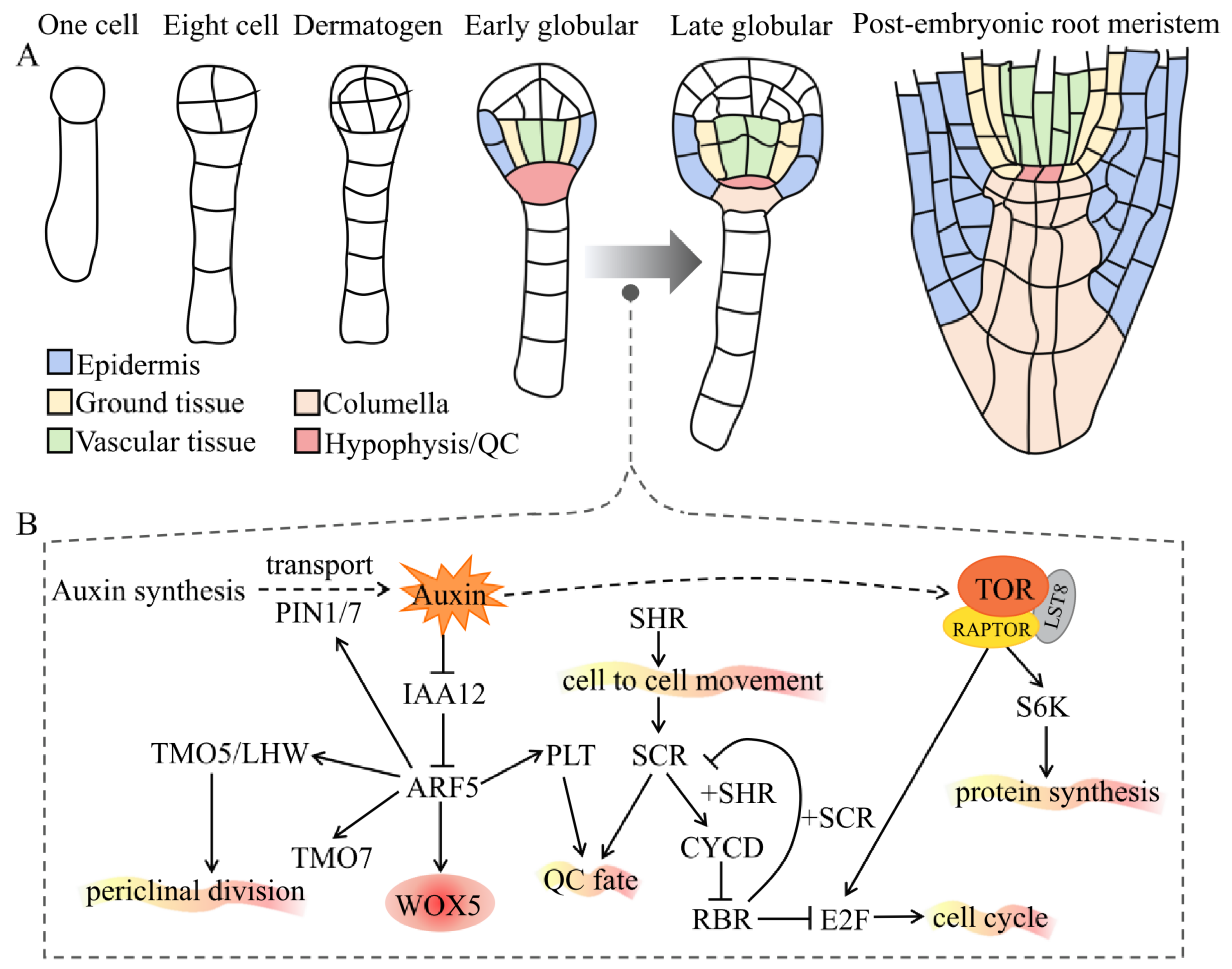
2. Auxin and TOR Interplay Regulates the Formation of Embryonic Roots
3. Auxin and TOR Interact to Regulate the Development of Primary Roots
4. Auxin and TOR Spatiotemporally Regulate Lateral Roots Organogenesis
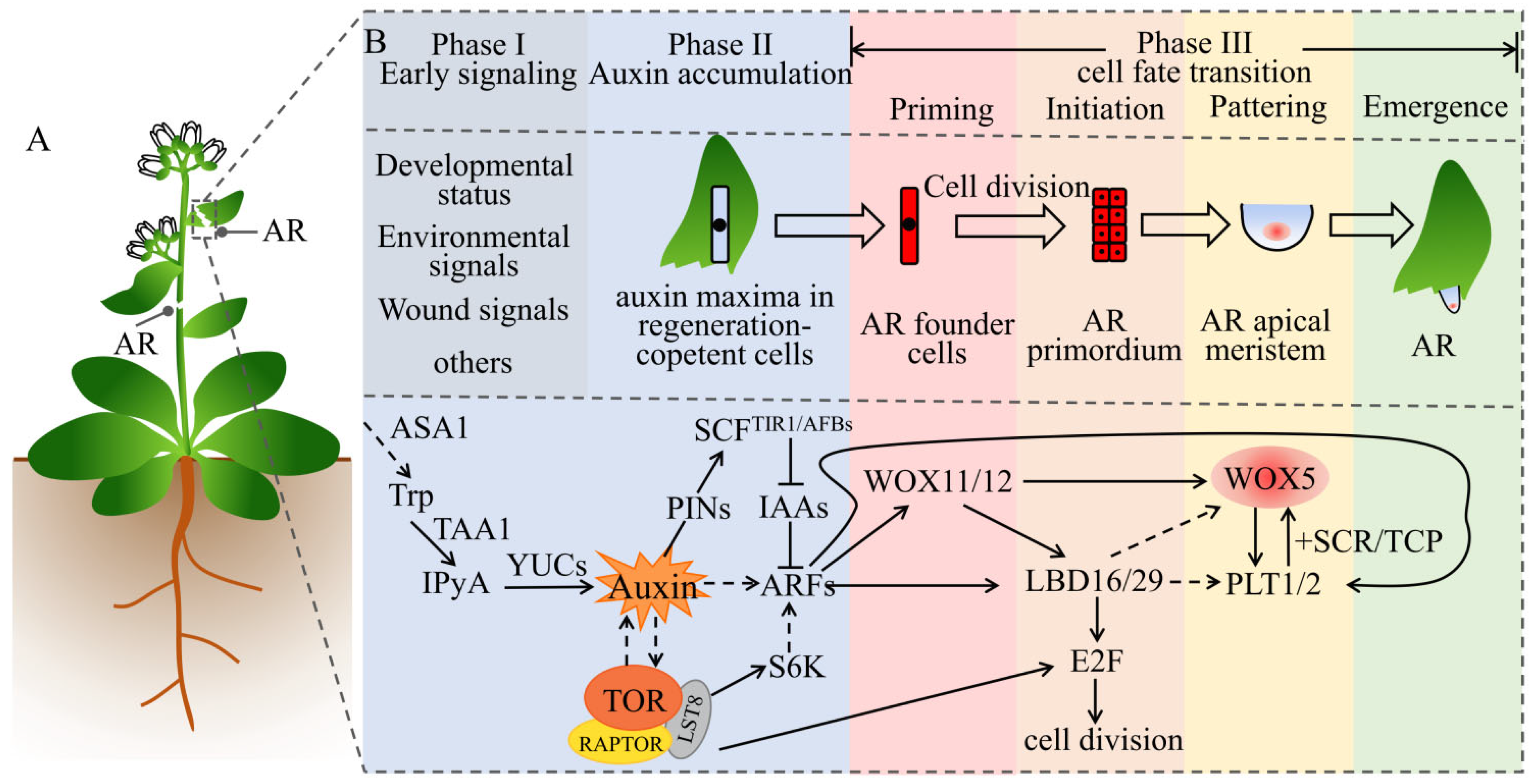
5. Auxin and TOR Synergistically Regulate the Regeneration of Adventitious Roots
6. Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABCB/MDR/PGP | ATP-binding cassette/multidrug resistance/P-glycoprotein |
| ABP1 | auxin-binding protein 1 |
| amiR | artificial microRNA |
| AR | adventitious root |
| ARF | auxin response factor |
| ASA1 | anthranilate synthase 1 |
| AUX/IAA | auxin/indole-3-acetic acid |
| AUX1/LAX | auxin resistant1/like AUX1 |
| CYC | cyclin |
| DSC | distal stem cell |
| E2F | early 2 factor |
| ER | embryonic root |
| EZ | elongation zone |
| FKBP12 | FK506-binding protein 12 |
| IAA | indole-3-acetic acid |
| IPyA | indole-3-pyruvic acid |
| LBD | lateral organ boundaries domain |
| LR | lateral root |
| LRP | lateral root primordium |
| LST | lethal with SEC13 protein 8 |
| MZ | meristem zone |
| NAA | naphthaleneacetic acid |
| PIN | PIN-formed |
| PLT | plethora |
| PR | primary root |
| QC | quiescent center |
| RAM | root apical meristem |
| RAPTOR | regulatory-associated protein of TOR |
| RBR | retinoblastoma related |
| RC | root cap |
| RGF | root meristem growth factor |
| RNAi | RNA interference |
| ROP2 | GTPase Rho-related protein 2 |
| S6K | S6 kinase |
| SCF | SKP1, Cullin, and F-box complex |
| SCN | stem-cell niche |
| SCR | scarecrow |
| SHR | short root |
| TAA1/TAR | tryptophan aminotransferase of Arabidopsis 1/Tryptophan aminotransferase-related |
| TCP | teosinte-branched cycloidea PCNA |
| TIR1/AFB | transport inhibitor response 1/auxin signaling F box |
| TMO5/LHW | target of monopteros 5/Lonesome highway |
| TOR | target of rapamycin |
| TORC | target of rapamycin complex |
| WOX5 | Wuschel-related homeobox5 |
| YUC | yucca |
References
- Ge, Y.; Fang, X.; Liu, W.; Sheng, L.; Xu, L. Adventitious lateral rooting: The plasticity of root system architecture. Physiol. Plant 2019, 165, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winnicki, K. The winner takes it all: Auxin-the main player during plant embryogenesis. Cells 2020, 9, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, P.; Fatima, M.; Ma, X.; Liu, J.; Ming, R. Auxin regulation involved in gynoecium morphogenesis of papaya flowers. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Friml, J. Auxin guides roots to avoid obstacles during gravitropic growth. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balla, J.; Medvedova, Z.; Kalousek, P.; Matijescukova, N.; Friml, J.; Reinohl, V.; Prochazka, S. Auxin flow-mediated competition between axillary buds to restore apical dominance. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Rodriguez, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Friml, J. Functional innovations of PIN auxin transporters mark crucial evolutionary transitions during rise of flowering plants. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc8895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Bhat, J.A.; Singh, V.P.; Corpas, F.J.; Yadav, S.R. Auxin metabolic network regulates the plant response to metalloids stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielach, A.; Hrtyan, M.; Tognetti, V.B. Plants under stress: Involvement of auxin and cytokinin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casanova-Saez, R.; Voss, U. Auxin metabolism controls developmental decisions in land plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2019, 24, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, N.R. YUC and TAA1/TAR proteins function in the same pathway for auxin biosynthesis. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugawara, S.; Hishiyama, S.; Jikumaru, Y.; Hanada, A.; Nishimura, T.; Koshiba, T.; Zhao, Y.; Kamiya, Y.; Kasahara, H. Biochemical analyses of indole-3-acetaldoxime-dependent auxin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5430–5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morffy, N.; Strader, L.C. Old Town Roads: Routes of auxin biosynthesis across kingdoms. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2020, 55, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, O.; Henykova, E.; Sairanen, I.; Kowalczyk, M.; Pospisil, T.; Ljung, K. Tissue-specific profiling of the Arabidopsis thaliana auxin metabolome. Plant J. 2012, 72, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Yang, H.; Shang, C.; Ma, S.; Liu, L.; Cheng, J. The roles of auxin biosynthesis YUCCA gene family in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y. Essential roles of local auxin biosynthesis in plant development and in adaptation to environmental changes. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, Y.; Nemoto, K. The pathway of auxin biosynthesis in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 2853–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrison, C.J. Auxin transport in the evolution of branching forms. New Phytol. 2017, 215, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leyser, O. Auxin signaling. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, S.; Luschnig, C.; Friml, J. Pho-view of auxin: Reversible protein phosphorylation in auxin biosynthesis, transport and signaling. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavy, M.; Estelle, M. Mechanisms of auxin signaling. Development 2016, 143, 3226–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korasick, D.A.; Enders, T.A.; Strader, L.C. Auxin biosynthesis and storage forms. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 2541–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, A.; Hall, M.N. Nutrient sensing and TOR signaling in yeast and mammals. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, A.; Hall, M.N.; Lin, S.C.; Hardie, D.G. AMPK and TOR: The Yin and Yang of cellular nutrient sensing and growth control. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 472–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, H.; Kong, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Luo, T.; Jiang, Y. Targeting mTOR for cancer therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisman, R. Target of rapamycin (TOR) regulates growth in response to nutritional signals. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, K.; Wang, W.; Feng, L.; Yin, H.; Xiong, F.; Ren, M. Target of rapamycin regulates potassium uptake in Arabidopsis and potato. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 155, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Alyafei, M.S.; Masmoudi, K.; Jaleel, A.; Ren, M. Contributions of TOR signaling on photosynthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Xiong, F.; Que, Y.; Wang, K.; Yu, L.; Li, Z.; Ren, M. Expression profiling and functional analysis reveals that TOR is a key player in regulating photosynthesis and phytohormone signaling pathways in Arabidopsi. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, L.; Wang, P.; Xiong, Y. Target of rapamycin signaling in plant stress responses. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Shi, L.; Li, L.; Fu, L.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Sheen, J. Integration of nutrient, energy, light, and hormone signalling via TOR in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 2227–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, A.; Moin, M.; Madhav, M.S.; Kirti, P.B. Target of rapamycin, a master regulator of multiple signalling pathways and a potential candidate gene for crop improvement. Plant Biol. 2019, 21, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.Q. The hot issue: TOR signalling network in plants. Funct. Plant Biol. 2020, 48, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, M.; Venglat, P.; Qiu, S.; Feng, L.; Cao, Y.; Wang, E.; Xiang, D.; Wang, J.; Alexander, D.; Chalivendra, S.; et al. Target of rapamycin signaling regulates metabolism, growth, and life span in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 4850–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Menand, B.; Desnos, T.; Nussaume, L.; Berger, F.; Bouchez, D.; Meyer, C.; Robaglia, C. Expression and disruption of the Arabidopsis TOR (target of rapamycin) gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6422–6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deprost, D.; Yao, L.; Sormani, R.; Moreau, M.; Leterreux, G.; Nicolai, M.; Bedu, M.; Robaglia, C.; Meyer, C. The Arabidopsis TOR kinase links plant growth, yield, stress resistance and mRNA translation. EMBO Rep. 2007, 8, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caldana, C.; Li, Y.; Leisse, A.; Zhang, Y.; Bartholomaeus, L.; Fernie, A.R.; Willmitzer, L.; Giavalisco, P. Systemic analysis of inducible target of rapamycin mutants reveal a general metabolic switch controlling growth in Arabidopsis thalian. Plant J. 2013, 73, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zheng, L.; Zhuo, F.; Yin, H.; Ge, X.; et al. Target of rapamycin (TOR) regulates the expression of incRNAs in response to abiotic stresses in cotton. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, K.; Dong, P.; Wang, W.; Feng, L.; Xiong, F.; Wang, K.; Zhang, S.; Feng, S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; et al. The TOR pathway is involved in adventitious root formation in Arabidopsis and potato. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, F.; Zhang, R.; Meng, Z.; Deng, K.; Que, Y.; Zhuo, F.; Feng, L.; Guo, S.; Datla, R.; Ren, M. Brassinosteriod Insensitive 2 (BIN2) acts as a downstream effector of the Target of Rapamycin (TOR) signaling pathway to regulate photoautotrophic growth in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahfouz, M.M.; Kim, S.; Delauney, A.J.; Verma, D.P. Arabidopsis TARGET OF RAPAMYCIN interacts with RAPTOR, which regulates the activity of S6 kinase in response to osmotic stress signals. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brumos, J.; Robles, L.M.; Yun, J.; Vu, T.C.; Jackson, S.; Alonso, J.M.; Stepanova, A.N. Local auxin biosynthesis is a key regulator of plant development. Dev. Cell 2018, 47, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olatunji, D.; Geelen, D.; Verstraeten, I. Control of endogenous auxin levels in plant root development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quilichini, T.D.; Gao, P.; Pandey, P.K.; Xiang, D.; Ren, M.; Datla, R. A role for TOR signaling at every stage of plant life. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 2285–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vleesschauwer, D.; Filipe, O.; Hoffman, G.; Seifi, H.S.; Haeck, A.; Canlas, P.; Van Bockhaven, J.; De Waele, E.; Demeestere, K.; Ronald, P.; et al. Target of rapamycin signaling orchestrates growth-defense trade-offs in plants. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schepetilnikov, M.; Ryabova, L.A. Recent discoveries on the role of TOR (Target of Rapamycin) signaling in translation in plants. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.; Li, L.; Feng, L.; Mo, H.; Ren, M. Target of rapamycin regulates genome methylation reprogramming to control plant growth in Arabidopsis. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bogre, L.; Henriques, R.; Magyar, Z. TOR tour to auxin. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 1069–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retzer, K.; Weckwerth, W. The TOR-auxin connection upstream of root hair growth. Plants 2021, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Yu, L.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, W.; Dong, P.; Zhang, J.; Ren, M. Target of rapamycin is a key player for auxin signaling transduction in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armenta-Medina, A.; Gillmor, C.S.; Gao, P.; Mora-Macias, J.; Kochian, L.V.; Xiang, D.; Datla, R. Developmental and genomic architecture of plant embryogenesis: From model plant to crops. Plant Commun. 2021, 2, 100136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Chen, H.; Miao, Y.; Bayer, M. Square one: Zygote polarity and early embryogenesis in flowering plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2020, 53, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresselhaus, T.; Jurgens, G. Comparative embryogenesis in angiosperms: Activation and patterning of embryonic cell lineages. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2021, 72, 641–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce, M.R.; Micol, J.L. A cornucopia of mutants for understanding plant embryo development. New Phytol. 2020, 226, 306–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, S.; Attuluri, S.; Robert, H.S. An essential function for auxin in embryo development. CSH Perspect. Biol. 2021, 13, a039966. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, H.S.; Park, C.; Gutierrez, C.L.; Wojcikowska, B.; Pencik, A.; Novak, O.; Chen, J.; Grunewald, W.; Dresselhaus, T.; Friml, J.; et al. Maternal auxin supply contributes to early embryo patterning in Arabidopsis. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Liu, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Ren, D. The RAF-like mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinases RAF22 and RAF28 are required for the regulation of embryogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2018, 96, 734–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlereth, A.; Moller, B.; Liu, W.; Kientz, M.; Flipse, J.; Rademacher, E.H.; Schmid, M.; Jurgens, G.; Weijers, D. MONOPTEROS controls embryonic root initiation by regulating a mobile transcription factor. Nature 2010, 464, 913–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi-Ito, K.; Iwamoto, K.; Nagashima, Y.; Kojima, M.; Sakakibara, H.; Fukuda, H. A positive feedback loop comprising LHW-TMO5 and local auxin biosynthesis regulates initial vascular development in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 2684–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundu, S.; Tabassum, N.; Blilou, I. Moving with purpose and direction: Transcription factor movement and cell fate determination revisited. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2020, 57, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolters, H.; Jurgens, G. Survival of the flexible: Hormonal growth control and adaptation in plant development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Jiao, H.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, Y.X. Two-step functional innovation of the stem-cell factors WUS/WOX5 during plant evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Engstrom, E.M.; Nimchuk, Z.L.; Pruneda-Paz, J.L.; Tarr, P.T.; Yan, A.; Kay, S.A.; Meyerowitz, E.M. Control of plant stem cell function by conserved interacting transcriptional regulators. Nature 2015, 517, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kong, X.; Lu, S.; Tian, H.; Ding, Z. WOX5 is shining in the root stem cell niche. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 601–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheres, B.; Krizek, B.A. Coordination of growth in root and shoot apices by AIL/PLT transcription factors. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 41, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, M.E.; Weijers, D. The role of auxin signaling in early embryo pattern formation. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 28, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, B.; Weijers, D. Auxin control of embryo patterning. CSH Perspect Biol. 2009, 1, a001545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deprost, D.; Truong, H.N.; Robaglia, C.; Meyer, C. An Arabidopsis homolog of RAPTOR/KOG1 is essential for early embryo development. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 326, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.A.; Li, Y.; Wiszniewski, A.; Giavalisco, P. Regulatory-associated protein of TOR (RAPTOR) alters the hormonal and metabolic composition of Arabidopsis seeds, controlling seed morphology, viability and germination potential. Plant J. 2017, 92, 525–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obomighie, I.; Lapenas, K.; Murphy, B.E.; Bowles, A.M.C.; Bechtold, U.; Prischi, F. The role of ribosomal protein S6 kinases in plant homeostasis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 636560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardal, R.; Heidstra, R. Root stem cell niche networks: It’s complexed! A review on gene networks regulating the Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 6727–6738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naramoto, S. Polar transport in plants mediated by membrane transporters: Focus on mechanisms of polar auxin transport. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 40, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, I.C.R.; Hammes, U.Z.; Schwechheimer, C. Activation and polarity control of PIN-FORMED auxin transporters by phosphorylation. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.S.; Park, J.M.; Cho, H.S.; Jeon, J.H. PIN-mediated polar auxin transport facilitates root-obstacle avoidance. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, M.; Kleine-Vehn, J. PIN-FORMED and PIN-LIKES auxin transport facilitators. Development 2019, 146, dev168088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swarup, R.; Bhosale, R. Developmental roles of AUX1/LAX auxin influx carriers in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zwiewka, M.; Bilanovicova, V.; Seifu, Y.W.; Nodzynski, T. The nuts and bolts of PIN auxin efflux carriers. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimotohno, A.; Heidstra, R.; Blilou, I.; Scheres, B. Root stem cell niche organizer specification by molecular convergence of PLETHORA and SCARECROW transcription factor modules. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 1085–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liebsch, D.; Palatnik, J.F. MicroRNA miR396, GRF transcription factors and GIF co-regulators: A conserved plant growth regulatory module with potential for breeding and biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2020, 53, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillotin, B.; Birnbaum, K.D. Just passing through: The auxin gradient of the root meristem. Curr. Top Dev. Biol. 2020, 137, 433–454. [Google Scholar]
- Santuari, L.; Sanchez-Perez, G.F.; Luijten, M.; Rutjens, B.; Terpstra, I.; Berke, L.; Gorte, M.; Prasad, K.; Bao, D.; Timmermans-Hereijgers, J.L.; et al. The PLETHORA gene regulatory network guides growth and cell differentiation in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 2937–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Nagawa, S.; Yang, Z. Uniform auxin triggers the Rho GTPase-dependent formation of interdigitation patterns in pavement cells. Small GTPases 2011, 2, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schepetilnikov, M.; Makarian, J.; Srour, O.; Geldreich, A.; Yang, Z.; Chicher, J.; Hammann, P.; Ryabova, L.A. GTPase ROP2 binds and promotes activation of target of rapamycin, TOR, in response to auxin. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 886–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepetilnikov, M.; Dimitrova, M.; Mancera-Martinez, E.; Geldreich, A.; Keller, M.; Ryabova, L.A. TOR and S6K1 promote translation reinitiation of uORF-containing mRNAs via phosphorylation of eIF3h. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 1087–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, Z.; Magyar, Z.; Bogre, L.; Papdi, C. Cell cycle control by the target of rapamycin signalling pathway in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 2275–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forzani, C.; Aichinger, E.; Sornay, E.; Willemsen, V.; Laux, T.; Dewitte, W.; Murray, J.A. WOX5 suppresses CYCLIN D activity to establish quiescence at the center of the root stem cell niche. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 1939–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Xu, P.; Yu, Y.; Xiong, Y. Glucose-TOR signaling regulates PIN2 stability to orchestrate auxin gradient and cell expansion in Arabidopsis root. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2020, 117, 32223–32225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motte, H.; Beeckman, T. The evolution of root branching: Increasing the level of plasticity. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiatante, D.; Rost, T.; Bryant, J.; Scippa, G.S. Regulatory networks controlling the development of the root system and the formation of lateral roots: A comparative analysis of the roles of pericycle and vascular cambium. Ann. Bot. 2018, 122, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torres-Martinez, H.H.; Rodriguez-Alonso, G.; Shishkova, S.; Dubrovsky, J.G. Lateral root primordium morphogenesis in angiosperms. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Martinez, H.H.; Hernandez-Herrera, P.; Corkidi, G.; Dubrovsky, J.G. From one cell to many: Morphogenetic field of lateral root founder cells in Arabidopsis thaliana is built by gradual recruitment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2020, 117, 20943–20949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mitsuda, N.; Yoshizumi, T.; Horii, Y.; Oshima, Y.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Matsui, M.; Kakimoto, T. Two types of bHLH transcription factor determine the competence of the pericycle for lateral root initiation. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Scheres, B. Lateral root formation and the multiple roles of auxin. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yu, J.; Ge, Y.; Qin, P.; Xu, L. Pivotal role of LBD16 in root and root-like organ initiation. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 3329–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soyano, T.; Shimoda, Y.; Kawaguchi, M.; Hayashi, M. A shared gene drives lateral root development and root nodule symbiosis pathways in Lotus. Science 2019, 366, 1021–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiessl, K.; Lilley, J.L.S.; Lee, T.; Tamvakis, I.; Kohlen, W.; Bailey, P.C.; Thomas, A.; Luptak, J.; Ramakrishnan, K.; Carpenter, M.D.; et al. NODULE INCEPTION recruits the lateral root developmental program for symbiotic nodule organogenesis in medicago truncatula. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 3657–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Yadav, S.; Singh, A.; Mahima, M.; Singh, A.; Gautam, V.; Sarkar, A.K. Auxin signaling modulates LATERAL ROOT PRIMORDIUM1 (LRP1) expression during lateral root development in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2020, 101, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Scheres, B. PLETHORA transcription factors orchestrate de novo organ patterning during Arabidopsis lateral root outgrowth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2017, 114, 11709–11714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teixeira, J.S.; Ten Tusscher, K.H. The systems biology of lateral root formation: Connecting the dots. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 784–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berckmans, B.; Vassileva, V.; Schmid, S.P.; Maes, S.; Parizot, B.; Naramoto, S.; Magyar, Z.; Alvim Kamei, C.L.; Koncz, C.; Bogre, L.; et al. Auxin-dependent cell cycle reactivation through transcriptional regulation of Arabidopsis E2Fa by lateral organ boundary proteins. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 3671–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magyar, Z.; Horvath, B.; Khan, S.; Mohammed, B.; Henriques, R.; De Veylder, L.; Bako, L.; Scheres, B.; Bogre, L. Arabidopsis E2FA stimulates proliferation and endocycle separately through RBR-bound and RBR-free complexes. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 1480–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nanjareddy, K.; Blanco, L.; Arthikala, M.K.; Alvarado-Affantranger, X.; Quinto, C.; Sanchez, F.; Lara, M. A legume TOR protein kinase regulates rhizobium symbiosis and is essential for infection and nodule development. Plant Physiol. 2016, 172, 2002–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez-Gomez, M.; Castro-Mercado, E.; Pena-Uribe, C.A.; Reyes-de la Cruz, H.; Lopez-Bucio, J.; Garcia-Pineda, E. TARGET OF RAPAMYCIN signaling plays a role in Arabidopsis growth promotion by Azospirillum brasilense Sp245. Plant Sci. 2020, 293, 110416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthikala, M.K.; Nanjareddy, K.; Blanco, L.; Alvarado-Affantranger, X.; Lara, M. Target of rapamycin, PvTOR, is a key regulator of arbuscule development during mycorrhizal symbiosis in Phaseolus. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardon, R.; Geelen, D. Natural variation in plant pluripotency and regeneration. Plants 2020, 9, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L. De novo root regeneration from leaf explants: Wounding, auxin, and cell fate transition. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 41, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Qin, P.; Xu, L. Auxin control of root organogenesis from callus in tissue culture. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Sheng, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Huang, H.; Xu, L. WOX11 and 12 are involved in the first-step cell fate transition during de novo root organogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Xu, L. Transcription factors WOX11/12 directly activate WOX5/7 to promote root primordia initiation and organogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2016, 172, 2363–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Hu, X.; Qin, P.; Prasad, K.; Hu, Y.; Xu, L. The WOX11-LBD16 pathway promotes pluripotency acquisition in callus cells during de novo shoot regeneration in tissue culture. Plant Cell Physiol. 2018, 59, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Street, I.H.; Mathews, D.E.; Yamburkenko, M.V.; Sorooshzadeh, A.; John, R.T.; Swarup, R.; Bennett, M.J.; Kieber, J.J.; Schaller, G.E. Cytokinin acts through the auxin influx carrier AUX1 to regulate cell elongation in the root. Development 2016, 143, 3982–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shu, W.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, C.; Zhao, S.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Yang, Z.; Groover, A.; Lu, M.Z. The auxin receptor TIR1 homolog (PagFBL 1) regulates adventitious rooting through interactions with Aux/IAA28 in Populus. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, S.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Wen, P.; Ma, X.; Shi, Y.; Qi, R.; Yang, Y.; et al. Genomes of the banyan tree and pollinator wasp provide insights into Fig-Wasp coevolution. Cell 2020, 183, 875–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, X.; Wang, Y.; Datla, R.; Ren, M. Auxin and Target of Rapamycin Spatiotemporally Regulate Root Organogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111357
Xie X, Wang Y, Datla R, Ren M. Auxin and Target of Rapamycin Spatiotemporally Regulate Root Organogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(21):11357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111357
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Xiulan, Ying Wang, Raju Datla, and Maozhi Ren. 2021. "Auxin and Target of Rapamycin Spatiotemporally Regulate Root Organogenesis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 21: 11357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111357





