Feasibility of a Portable Electronic Nose for Detection of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Sudan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Materials
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Characteristics
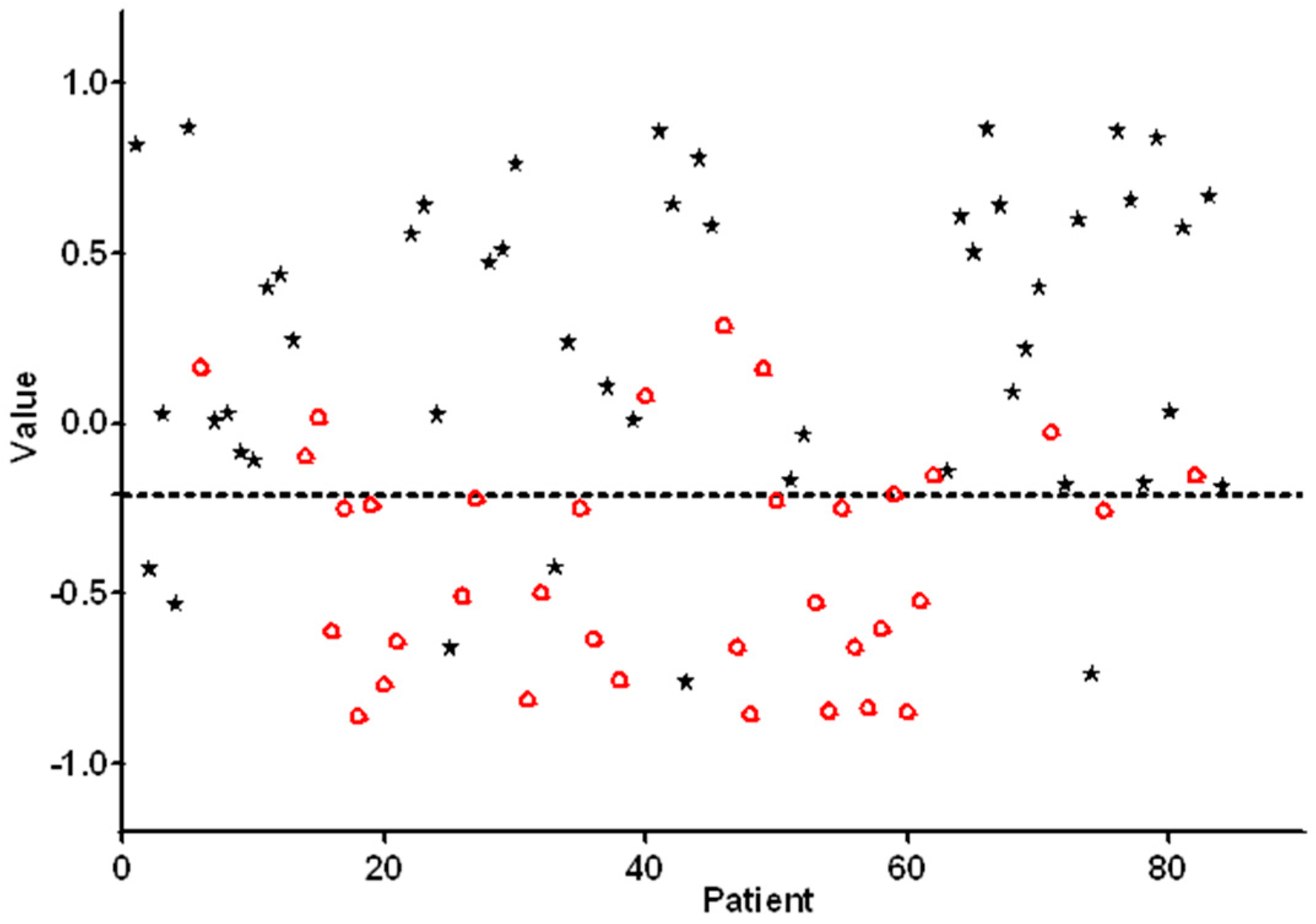
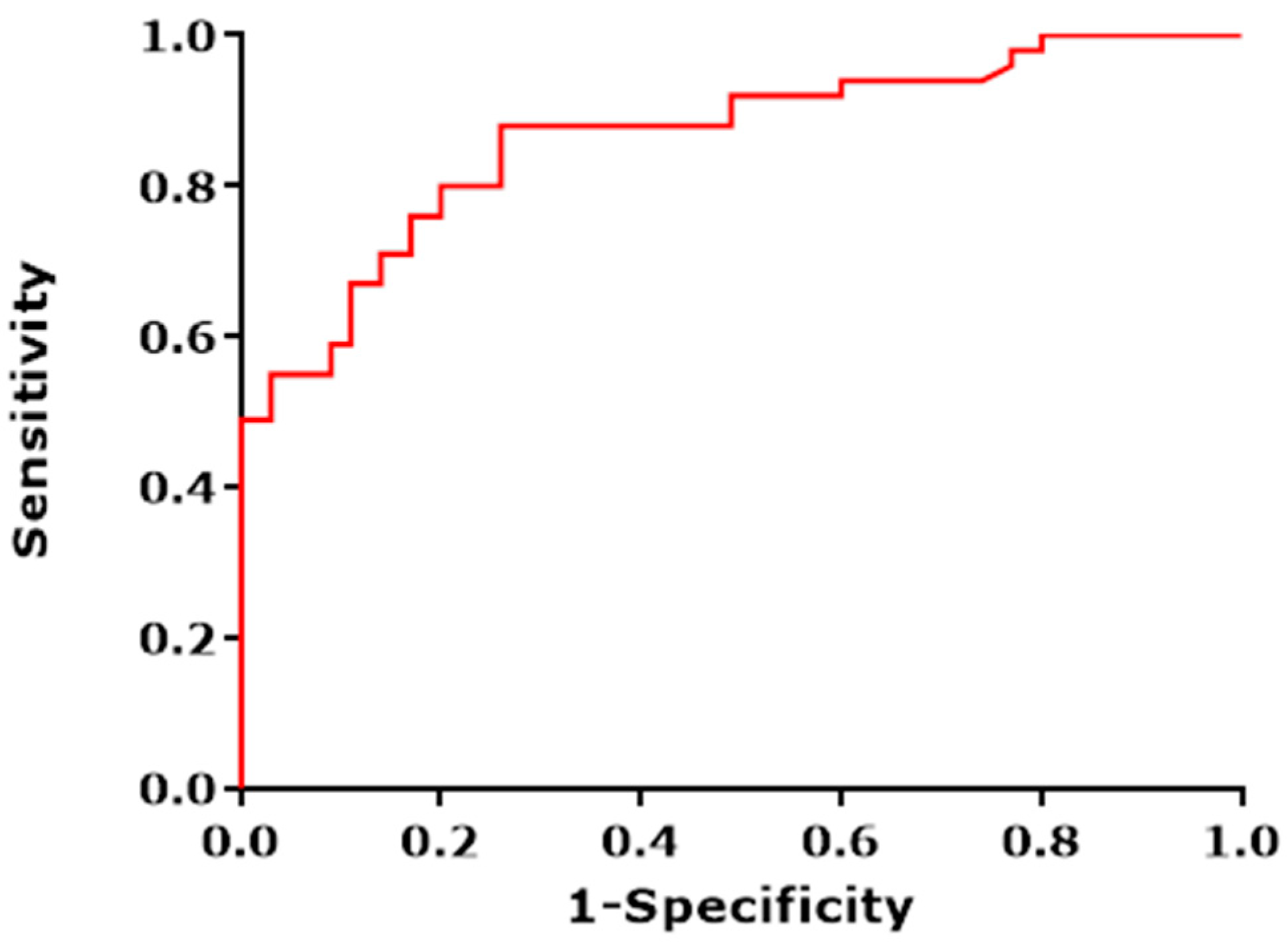
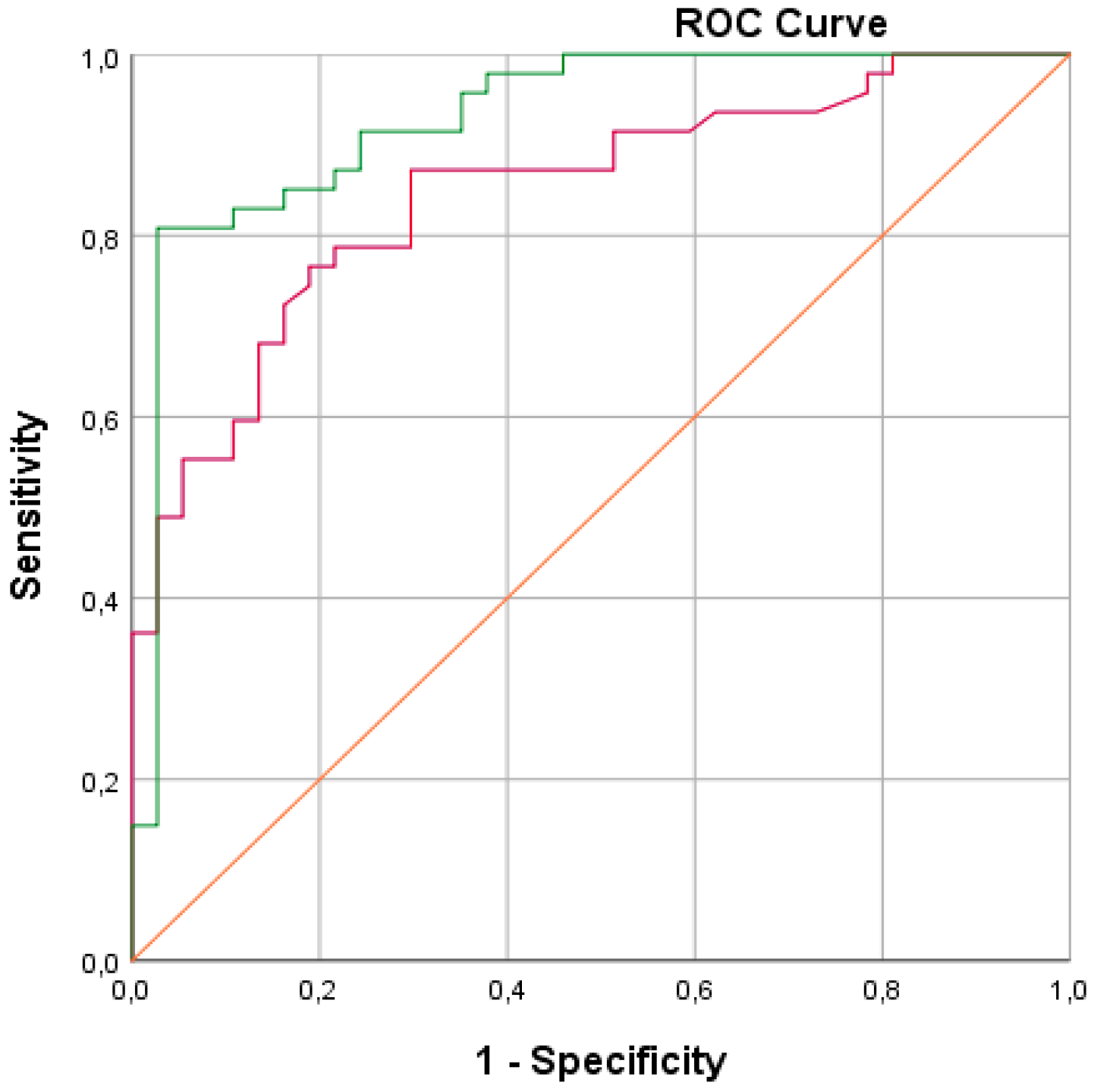
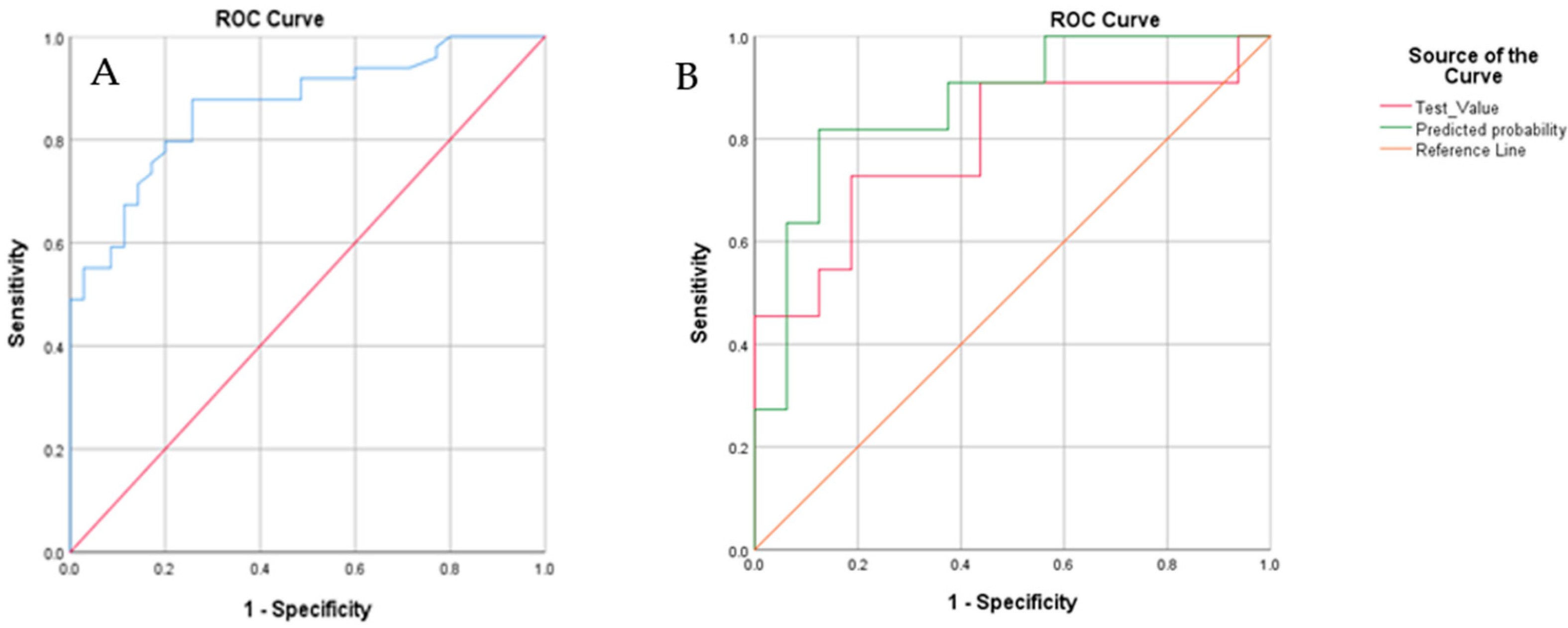
3.2. Feasibility Analysis of E-Nose Measurements
3.3. Blinded Control Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amann, A.; Costello, B.D.L.; Miekisch, W.; Schubert, J.; Buszewski, B.; Pleil, J.; Ratcliffe, N.; Risby, T. The human volatilome: Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in exhaled breath, skin emanations, urine, feces and saliva. J. Breath Res. 2014, 8, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruins, M.; van Belkum, A.; Bos, A. The Use of Electronic Nose Devices in Clinical Microbiology; Hays, J.P., van Leeuwen, W.B., Eds.; Bentham Science Publishers Ltd.: Bentham, UK, 2012; pp. 90–101. [Google Scholar]
- Pauling, L.; Robinson, A.B.; Teranishi, R.; Cary, P. Quantitative Analysis of Urine Vapor and Breath by Gas-Liquid Partition Chromatography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1971, 68, 2374–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattray, N.J.; Hamrang, Z.; Trivedi, D.K.; Goodacre, R.; Fowler, S.J. Taking your breath away: Metabolomics breathes life in to personalized medicine. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beale, D.J.; Jones, O.A.H.; Karpe, A.V.; Dayalan, S.; Oh, D.Y.; Kouremenos, K.A.; Ahmed, W.; Palombo, E.A. A Review of Analytical Techniques and Their Application in Disease Diagnosis in Breathomics and Salivaomics Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buszewski, B.; Grzywiński, D.; Ligor, T.; Stacewicz, T.; Bielecki, Z.; Wojtas, J. Detection of volatile organic compounds as biomarkers in breath analysis by different analytical techniques. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 2287–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.P.; Magan, N. Electronic noses and disease diagnostics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 2, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbacz, M.; Malec, A.; Duda-Saternus, S.; Suchorab, Z.; Guz, Ł.; Łagód, G. Methods for Early Detection of Microbiological Infestation of Buildings Based on Gas Sensor Technologies. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D.A.D. Recent progress in the design and clinical development of electronic-nose technologies. Nanobiosens. Dis. Diagn. 2016, 5, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D.; Baietto, M. Applications and Advances in Electronic-Nose Technologies. Sensors 2009, 9, 5099–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinek, R.; Jelen, H.; Malaga-Tobola, U.; Molenda, M.; Gancarz, M. Influence of Changes in the Level of Volatile Compounds Emitted during Rapeseed Quality Degradation on the Reaction of MOS Type Sensor-Array. Sensors 2020, 20, 3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slimani, S.; Bultel, E.; Cubizolle, T.; Herrier, C.; Rousselle, T.; Livache, T. Opto-Electronic Nose Coupled to a Silicon Micro Pre-Concentrator Device for Selective Sensing of Flavored Waters. Chemosens. 2020, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Mirzaei, A.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, H.J.; Vuong, P.Q.; Kim, S.S. A Novel X-Ray Radiation Sensor Based on Networked SnO2 Nanowires. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulczyński, B.; Gębicki, J. Currently Commercially Available Chemical Sensors Employed for Detection of Volatile Organic Compounds in Outdoor and Indoor Air. Environment 2017, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gancarz, M.; Malaga-Toboła, U.; Oniszczuk, A.; Tabor, S.; Oniszczuk, T.; Gawrysiak-Witulska, M.; Rusinek, R. Detection and measurement of aroma compounds with the electronic nose and a novel method for MOS sensor signal analysis during the wheat bread making process. Food Bioprod. Process. 2021, 127, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, C.D.; Ostheymer, G. Data analysis for chemical sensor arrays. In Advances in Sensing with Security Applications; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Distante, C.; Leo, M.; Siciliano, P.; Persaud, K.C. On the study of feature extraction methods for an electronic nose. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2002, 87, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, M.; Gardner, J.; Bartlett, P. Electronic noses—Development and future prospects. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 1996, 15, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D. Applications of Electronic-Nose Technologies for Noninvasive Early Detection of Plant, Animal and Human Diseases. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queralto, N.; Berliner, A.N.; Goldsmith, B.; Martino, R.; Rhodes, P.; Lim, S.H. Detecting cancer by breath volatile organic compound analysis: A review of array-based sensors. J. Breath Res. 2014, 8, 027112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haick, H.; Broza, Y.Y.; Mochalski, P.; Ruzsanyi, V.; Amann, A. Assessment, origin, and implementation of breath volatile cancer markers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 1423–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Goor, R.; van Hooren, M.R.; Henatsch, D.; Kremer, B.; Kross, K.W. Detecting head and neck squamous carcinoma using a portable handheld electronic nose. Head Neck 2020, 42, 2555–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.; Ward, E.; Brawley, J.; Ahmedin, J. Cancer statistics, 2011: The impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 212–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, V.; Mukherjee, R.; Ghost, A.K.; Routray, A.; Chakraborty, C. “Omics” in oral cancer: New approaches for biomarker discovery. Arch. Oral Biol. 2018, 87, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.E.M.; Lam, F.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. 2020. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/populations/729-sudan-fact-sheets.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Kujan, O.; Idrees, M.; Farah, C.S. Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancer in Arab Nations. In Handbook of Healthcare in the Arab World; Metzler, J.B., Ed.; Ismail Laher; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, T.; Satti, A.; Bøe, O.; Yang, Y.-H.; Ibrahim, S.; Suleiman, A.; Ta, O.; Aa, S.; Oe, B.; Yh, Y.; et al. Pattern of malignant tumors registered at a referral oral and maxillofacial hospital in Sudan during 2006 and 2007. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2010, 6, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendenhall, W.M.; Werning, J.W.; Pfister, D.G. Cancer of the Head and Neck. In Principles & Practice of Oncology (Cancer Principles and Practice of Oncology); DeVita, V.R., Rosenberg, S.A., Lawrence, T.S., Eds.; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 422–450. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrotra, R.; Gupta, D.K. Exciting new advances in oral cancer diagnosis: Avenues to early detection. Head Neck Oncol. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, J.B.; Güneri, P.; Boyacioglu, H.; Abt, E. The limitations of the clinical oral examination in detecting dysplastic oral lesions and oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2012, 143, 1332–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kujan, O.; Khattab, A.; Oliver, R.J.; Roberts, S.A.; Thakker, N.; Sloan, P. Why oral histopathology suffers inter-observer variability on grading oral epithelial dysplasia: An attempt to understand the sources of variation. Oral Oncol. 2007, 43, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leunis, N.; Boumans, M.-L.; Kremer, B.; Din, S.; Stobberingh, E.; Kessels, A.G.H.; Kross, K.W. Application of an electronic nose in the diagnosis of head and neck cancer. Laryngoscope 2013, 124, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costea, D.E.; Lukandu, O.; Bui, L.; Ibrahim, J.; Lygre, R.; Neppelberg, E.; Ibrahim, S.O.; Vintemyr, O.K.; Johannessen, A.C. Adverse effects of Sudanese toombak vs. Swedish snuff on human oral cells. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2010, 39, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitsma, M.B.; Fullman, N.; Ng, M.; Salama, J.S.; Abajobir, A.; Abate, K.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; Abraham, B.; Abyu, G.Y.; et al. Smoking prevalence and attributable disease burden in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1885–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.M.; Ahmed, H.M.; Mukhtar, I.B.; Gadir, A.F.; El-Beshir, I.E. Descriptive epidemiology of oral neoplasms in Sudan 1970–1985 and the role of toombak. Int. J. Cancer 1995, 61, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hooren, M.R.; Leonis, N.; Brandsma, D.S.; Dingemans, A.-M.; Kremmer, B.; Kross, K.W. Differentiating head and neck carcinoma from lung carcinoma with an electronic nose: A proof of concept study. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 3897–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Goor, R.; van Hooren, M.; Dingemans, A.-M.; Kremmer, B.; Kross, K. Training and Validating a Portable Electronic Nose for Lung Cancer Screening. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouza, M.; Gonzalez-Soto, J.; Pereiro, R.; De Vicente, J.C.; Sanz-Medel, A. Exhaled breath and oral cavity VOCs as potential biomarkers in oral cancer patients. J. Breath Res. 2017, 11, 016015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakim, M.; Billan, S.; Tisch, U.; Peng, G.; Dvrokind, I.; Marom, O.; Abdah-Bortnyak, R.; Kuten, A.; Haick, H. Diagnosis of head-and-neck cancer from exhaled breath. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigeyama, H.; Wang, T.; Ichinose, M.; Ansai, T.; Lee, S.-W. Identification of volatile metabolites in human saliva from patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma via zeolite-based thin-film microextraction coupled with GC–MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1104, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwig, S.; Raguse, J.D.; Pfitzner, D.; Preissner, R.; Paris, S.; Preissner, S. Volatile Organic Compounds in the Breath of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients: A Pilot Study. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2017, 157, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shield, K.D.; Ferlay, J.; Jemal, A.; Sankaranarayanan, R.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Bray, F.; Soerjomataram, I. The global incidence of lip, oral cavity, and pharyngeal cancers by subsite in 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 67, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Cohort Demographics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-OSCC Patients | OSCC Patients | |||||
| Number of individuals | 35 | 49 | ||||
| 82.9% males (29) | 49% males (24) | |||||
| 17.1% females (6) | 51% females (25) | |||||
| Age * | Males | 48.4 years (24–68 years) | 55.6 years (21–82 years) | |||
| Females | 33.5 years (27–64 years) | 52.2 years (27–80 years) | ||||
| Tobacco history and mean pack-years (PY) * | 65 | 35 | ||||
| Clinical findings for OSCC patients | ||||||
| Tumor location | Number of cases | Tumor stage | ||||
| Stage | Number (%) | |||||
| Buccal lower | 26.5% (13) | I | 2% (1) | |||
| Labial lower | 24.5% (12) | II | 2% (1) | |||
| Tongue | 14.3% (7) | III | 22.5% (11) | |||
| Palate | 8.2% (4) | IV | 63.3% (31) | |||
| Other sites | 12.2% (6) | Missing staging: 10.2% (5) | ||||
| Missing sites data | 14.3% (7) | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed, N.; van de Goor, R.; El-Sheikh, M.; Elrayah, O.; Osman, T.; Nginamau, E.S.; Johannessen, A.C.; Suleiman, A.; Costea, D.E.; Kross, K.W. Feasibility of a Portable Electronic Nose for Detection of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Sudan. Healthcare 2021, 9, 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9050534
Mohamed N, van de Goor R, El-Sheikh M, Elrayah O, Osman T, Nginamau ES, Johannessen AC, Suleiman A, Costea DE, Kross KW. Feasibility of a Portable Electronic Nose for Detection of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Sudan. Healthcare. 2021; 9(5):534. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9050534
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed, Nazar, Rens van de Goor, Mariam El-Sheikh, Osman Elrayah, Tarig Osman, Elisabeth Sivy Nginamau, Anne Christine Johannessen, Ahmed Suleiman, Daniela Elena Costea, and Kenneth W. Kross. 2021. "Feasibility of a Portable Electronic Nose for Detection of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Sudan" Healthcare 9, no. 5: 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9050534
APA StyleMohamed, N., van de Goor, R., El-Sheikh, M., Elrayah, O., Osman, T., Nginamau, E. S., Johannessen, A. C., Suleiman, A., Costea, D. E., & Kross, K. W. (2021). Feasibility of a Portable Electronic Nose for Detection of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Sudan. Healthcare, 9(5), 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9050534






