Metabolite Changes Associated with Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.4. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Participant Demographics
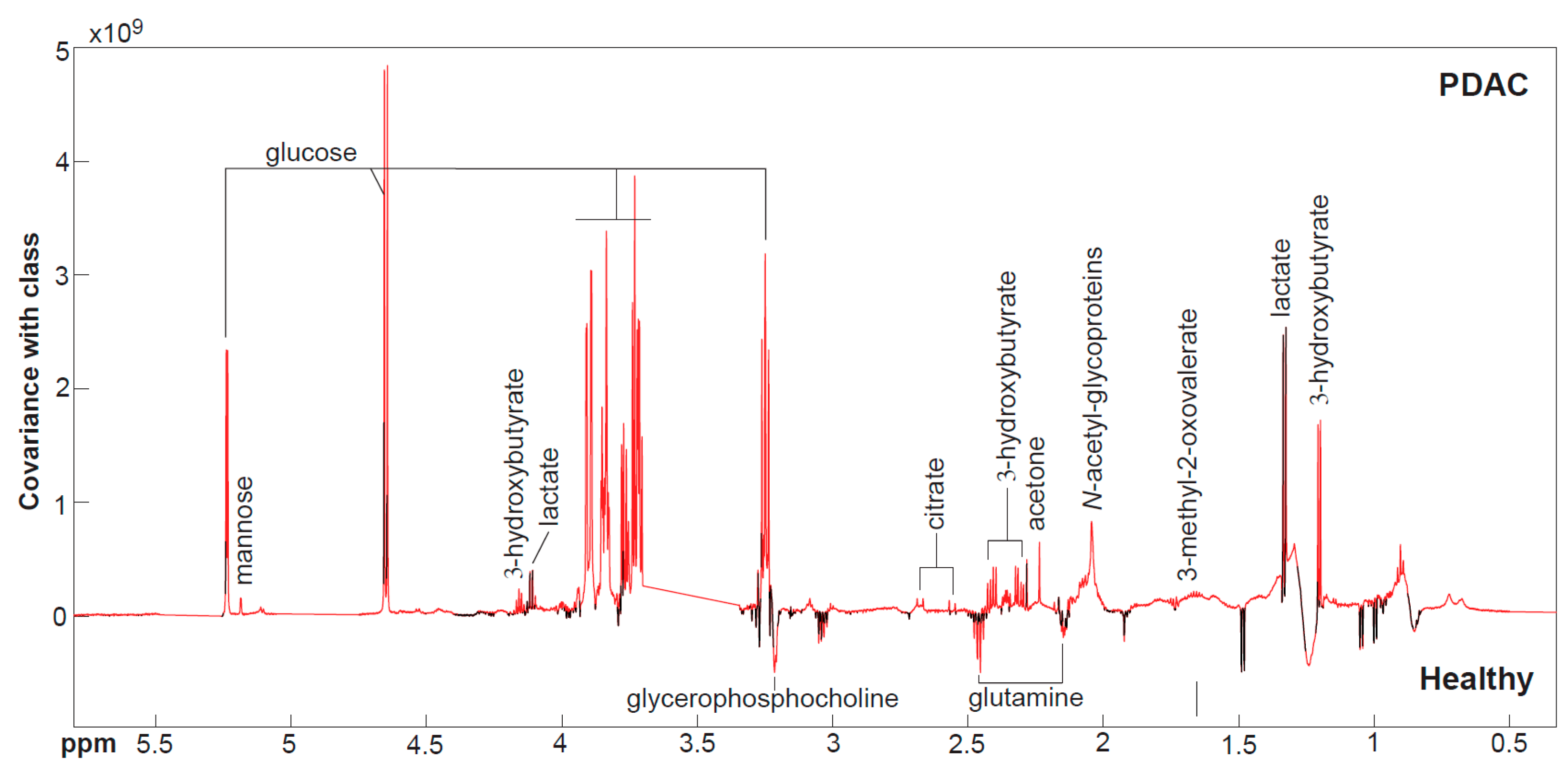
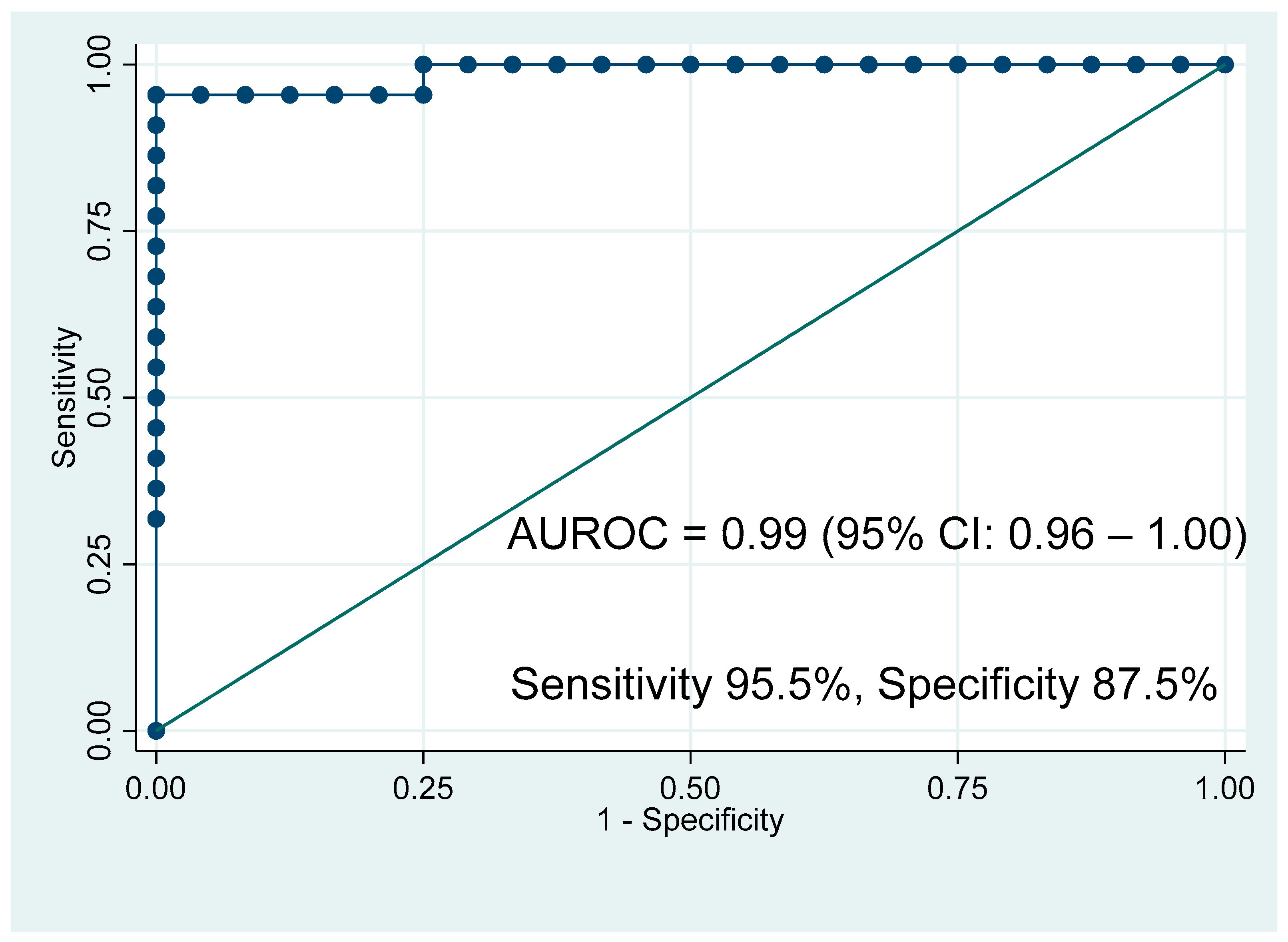
3.2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Results
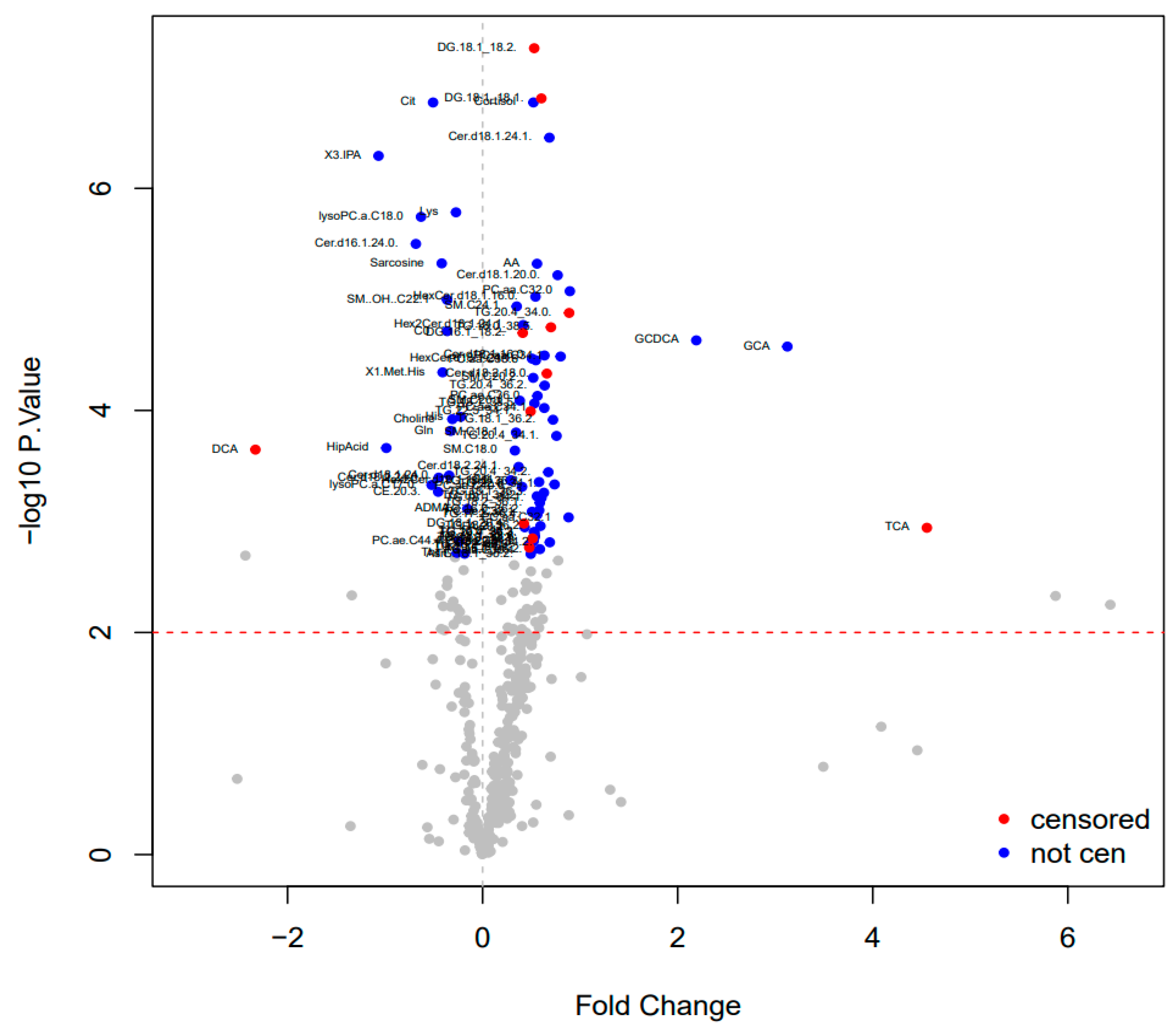
3.3. Mass Spectrometry Results
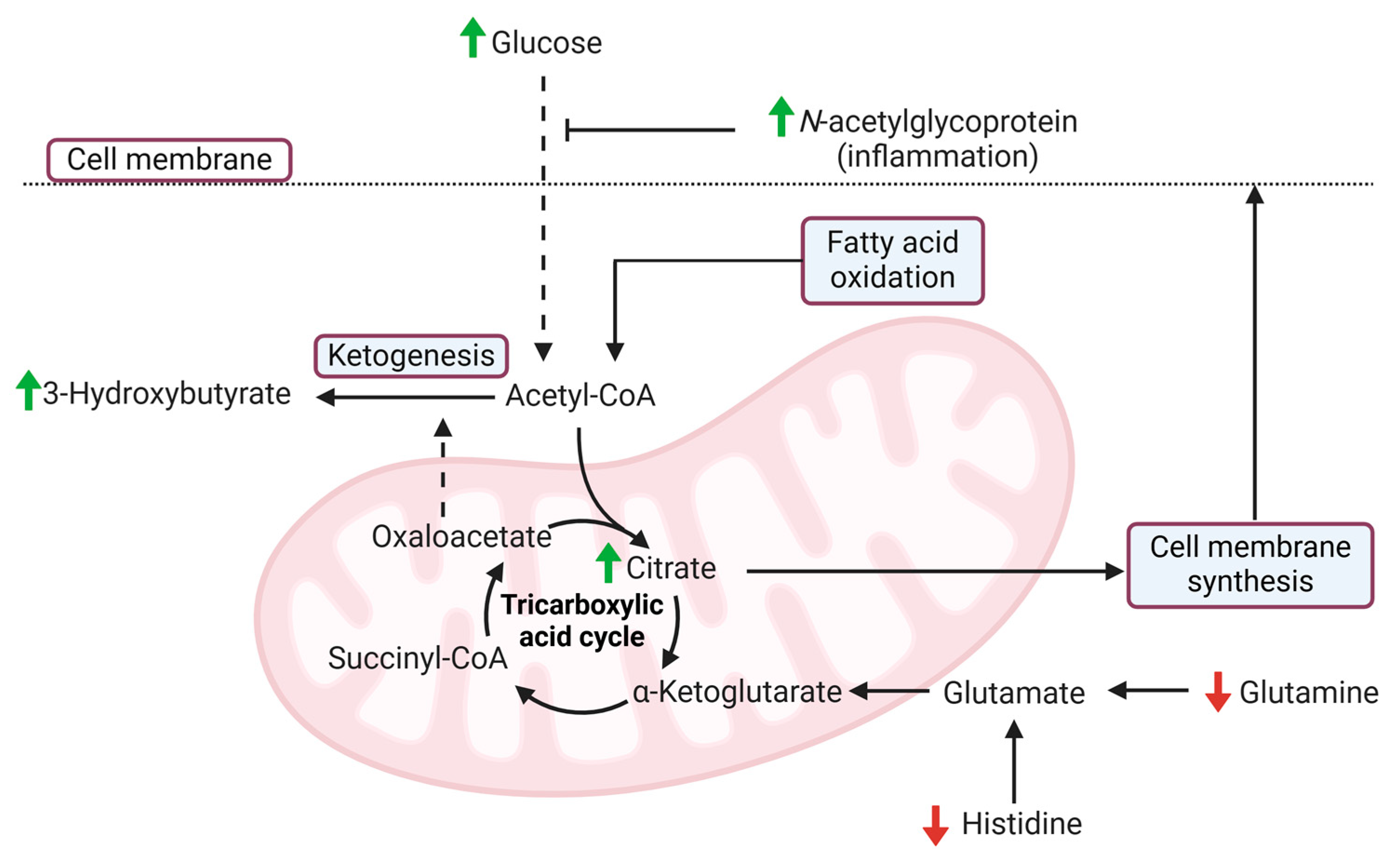
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shinde, R.S.; Bhandare, M.; Chaudhari, V.; Shrikhande, S.V. Cutting-edge strategies for borderline resectable pancreatic cancer. Ann. Gastroenterol. Surg. 2019, 3, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bilimoria, K.Y.; Bentrem, D.J.; Ko, C.Y.; Stewart, A.K.; Winchester, D.P.; Talamonti, M.S. National failure to operate on early stage pancreatic cancer. Ann. Surg. 2007, 246, 173–180. [Google Scholar]
- Prattico, F.; Garajova, I. Focus on Pancreatic Cancer Microenvironment. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 4241–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feig, C.; Gopinathan, A.; Neesse, A.; Chan, D.S.; Cook, N.; Tuveson, D.A. The pancreas cancer microenvironment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4266–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P.A.; Bellin, M.D.; Andersen, D.K.; Bradley, D.; Cruz-Monserrate, Z.; Forsmark, C.E.; Goodarzi, M.O.; Habtezion, A.; Korc, M.; Kudva, Y.C.; et al. Type 3c (pancreatogenic) diabetes mellitus secondary to chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 226–237. [Google Scholar]
- Halbrook, C.J.; Lyssiotis, C.A. Employing Metabolism to Improve the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ji, S.; Shi, S.; Xu, W.; Liu, J.; Xiang, J.; Liang, D.; Hu, Q.; et al. Metabolic plasticity in heterogeneous pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1866, 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- Sarvepalli, D.; Rashid, M.U.; Rahman, A.U.; Ullah, W.; Hussain, I.; Hasan, B.; Jehanzeb, S.; Khan, A.K.; Jain, A.G.; Khetpal, N.; et al. Gemcitabine: A Review of Chemoresistance in Pancreatic Cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2019, 24, 199–212. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Hegde, S.; Knolhoff, B.L.; Zhu, Y.; Herndon, J.M.; Meyer, M.A.; Nywening, T.M.; Hawkins, W.G.; Shapiro, I.M.; Weaver, D.T.; et al. Targeting focal adhesion kinase renders pancreatic cancers responsive to checkpoint immunotherapy. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 851–860. [Google Scholar]
- Sciano, F.; Terrana, F.; Pecoraro, C.; Parrino, B.; Cascioferro, S.; Diana, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Carbone, D. Exploring the therapeutic potential of focal adhesion kinase inhibition in overcoming chemoresistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Future Med. Chem. 2024, 16, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Baer, J.M.; Stone, M.L.; Knolhoff, B.L.; Hogg, G.D.; Turner, M.C.; Kao, Y.L.; Weinstein, A.G.; Ahmad, F.; Chen, J.; et al. Stromal reprogramming overcomes resistance to RAS-MAPK inhibition to improve pancreas cancer responses to cytotoxic and immune therapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2024, 16, eado2402. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Creeden, J.F.; Alganem, K.; Imami, A.S.; Henkel, N.D.; Brunicardi, F.C.; Liu, S.H.; Shukla, R.; Tomar, T.; Naji, F.; McCullumsmith, R.E. Emerging Kinase Therapeutic Targets in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Pancreatic Cancer Desmoplasia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, D.; Pecoraro, C.; Panzeca, G.; Xu, G.; Roeten, M.S.F.; Cascioferro, S.; Giovannetti, E.; Diana, P.; Parrino, B. 1,3,4-Oxadiazole and 1,3,4-Thiadiazole Nortopsentin Derivatives against Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Synthesis, Cytotoxic Activity, and Inhibition of CDK1. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Feng, J.; Qi, L.; Jin, Y. Stromal Reprogramming Optimizes KRAS-Specific Chemotherapy Inducing Antitumor Immunity in Pancreatic Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 61583–61598. [Google Scholar]
- Wishart, D.S.; Cheng, L.L.; Copie, V.; Edison, A.S.; Eghbalnia, H.R.; Hoch, J.C.; Gouveia, G.J.; Pathmasiri, W.; Powers, R.; Schock, T.B.; et al. NMR and Metabolomics—A Roadmap for the Future. Metabolites 2022, 12, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazzoli, G.; Garcia-Valdeavero, O.M.; Pena, M.; Prados, J.; Melguizo, C.; Jimenez-Luna, C. Evaluating Metabolite-Based Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review. Metabolites 2023, 13, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, H.E.; Powers, R. Meta-Analysis Reveals Both the Promises and the Challenges of Clinical Metabolomics. Cancers 2022, 14, 3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jin, H.; Guo, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Tang, S.; Mo, P.; Wu, K.; Nie, Y.; Pan, Y.; et al. Distinguishing pancreatic cancer from chronic pancreatitis and healthy individuals by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabonomic profiles. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Lu, L.; Qiu, Y.; Ni, Q.; Zhang, W.; Gao, Y.T.; Risch, H.A.; Yu, H.; Jia, W. Plasma metabolite biomarkers for the detection of pancreatic cancer. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar]
- Fukutake, N.; Ueno, M.; Hiraoka, N.; Shimada, K.; Shiraishi, K.; Saruki, N.; Ito, T.; Yamakado, M.; Ono, N.; Imaizumi, A.; et al. A Novel Multivariate Index for Pancreatic Cancer Detection Based On the Plasma Free Amino Acid Profile. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalkova, L.; Hornik, S.; Sykora, J.; Habartova, L.; Setnicka, V.; Bunganic, B. Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Based on 1H NMR Metabolomics. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 1744–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OuYang, D.; Xu, J.; Huang, H.; Chen, Z. Metabolomic profiling of serum from human pancreatic cancer patients using 1H NMR spectroscopy and principal component analysis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 165, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afolabi, P.R.; McDonnell, D.; Byrne, C.D.; Wilding, S.; Goss, V.; Walters, J.; Hamady, Z.Z. DEPEND study protocol: Early detection of patients with pancreatic cancer—A pilot study to evaluate the utility of faecal elastase-1 and (13)C-mixed triglyceride breath test as screening tools in high-risk individuals. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e057271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, D.; Afolabi, P.R.; Wilding, S.; Griffiths, G.O.; Swann, J.R.; Byrne, C.D.; Hamady, Z.Z. Utilising Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency in the Detection of Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagana Gowda, G.A.; Gowda, Y.N.; Raftery, D. Expanding the limits of human blood metabolite quantitation using NMR spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloarec, O.; Dumas, M.E.; Trygg, J.; Craig, A.; Barton, R.H.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E. Evaluation of the orthogonal projection on latent structure model limitations caused by chemical shift variability and improved visualization of biomarker changes in 1H NMR spectroscopic metabonomic studies. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MATLAB, version 9.4.0.949201 (R2018a); The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2018.
- StataCorp, version 16.0. Stata Statistical Software. StataCorp LLC: College Station, TX, USA, 2019.
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, B.; Gelman, A.; Hoffman, M.D.; Lee, D.; Goodrich, B.; Betancourt, M.; Brubaker, M.A.; Guo, J.; Li, P.; Riddell, A. Stan: A Probabilistic Programming Language. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 76, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.B. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- StataCorp. Stata 18 User’s Guide; Stata Press: College Station, TX, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gelman, A. Bayesian Data Analysis, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Stan Development Team. Stan Modeling Language Users Guide and Reference Manual 2024 [VERSION 2.36]. Available online: https://mc-stan.org (accessed on 30 August 2024).
- McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. Testing significance relative to a fold-change threshold is a TREAT. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, R.P.; Nagpal, S.J.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Chari, S.T. New insights into pancreatic cancer-induced paraneoplastic diabetes. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, S.T.; Zapiach, M.; Yadav, D.; Rizza, R.A. Beta-cell function and insulin resistance evaluated by HOMA in pancreatic cancer subjects with varying degrees of glucose intolerance. Pancreatology 2005, 5, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Delitto, D.; Black, B.S.; Sorenson, H.L.; Knowlton, A.E.; Thomas, R.M.; Sarosi, G.A.; Moldawer, L.L.; Behrns, K.E.; Liu, C.; George, T.J.; et al. The inflammatory milieu within the pancreatic cancer microenvironment correlates with clinicopathologic parameters, chemoresistance and survival. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 783. [Google Scholar]
- Permert, J.; Ihse, I.; Jorfeldt, L.; von Schenck, H.; Arnquist, H.J.; Larsson, J. Improved glucose metabolism after subtotal pancreatectomy for pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Surg. 1993, 80, 1047–1050. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Karimi, R.; Yanovich, A.; Elbarbry, F.; Cleven, A. Adaptive Effects of Endocrine Hormones on Metabolism of Macronutrients during Fasting and Starvation: A Scoping Review. Metabolites 2024, 14, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.Y.; Choe, W.; Yoon, K.S.; Ha, J.; Kim, S.S.; Yeo, E.J.; Kang, I. Molecular Mechanisms for Ketone Body Metabolism, Signaling Functions, and Therapeutic Potential in Cancer. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, K.P.; Mackowska-Kedziora, A.; Sobolewski, B.; Wozniak, P. Key Roles of Glutamine Pathways in Reprogramming the Cancer Metabolism. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 964321. [Google Scholar]
- Yuneva, M.O.; Fan, T.W.; Allen, T.D.; Higashi, R.M.; Ferraris, D.V.; Tsukamoto, T.; Mates, J.M.; Alonso, F.J.; Wang, C.; Seo, Y.; et al. The metabolic profile of tumors depends on both the responsible genetic lesion and tissue type. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 157–170. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, K.; Iwadate, D.; Kato, H.; Nakai, Y.; Tateishi, K.; Fujishiro, M. Targeting the Metabolic Rewiring in Pancreatic Cancer and Its Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2022, 14, 4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrer, A.; Trefely, S.; Zhao, S.; Campbell, S.L.; Norgard, R.J.; Schultz, K.C.; Sidoli, S.; Parris, J.L.D.; Affronti, H.C.; Sivanand, S.; et al. Acetyl-CoA Metabolism Supports Multistep Pancreatic Tumorigenesis. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 416–435. [Google Scholar]
- Longo, R.; Peri, C.; Cricri, D.; Coppi, L.; Caruso, D.; Mitro, N.; De Fabiani, E.; Crestani, M. Ketogenic Diet: A New Light Shining on Old but Gold Biochemistry. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otvos, J.D.; Shalaurova, I.; Wolak-Dinsmore, J.; Connelly, M.A.; Mackey, R.H.; Stein, J.H.; Tracy, R.P. GlycA: A Composite Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Biomarker of Systemic Inflammation. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, C.; Saldova, R.; Wormald, M.R.; Rudd, P.M.; McElvaney, N.G.; Reeves, E.P. The role and importance of glycosylation of acute phase proteins with focus on alpha-1 antitrypsin in acute and chronic inflammatory conditions. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 3131–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafaqat, S.; Khurshid, H.; Hafeez, R.; Arif, M.; Zafar, A.; Gilani, M.; Ashraf, H.; Rafaqat, S. Role of Interleukins in Pancreatic Cancer: A Literature Review. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2024, 55, 1498–1510. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Qiao, S.; Zhang, G.; Lu, A.; Li, F. Inflammatory Processes: Key Mediators of Oncogenesis and Progression in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, N.P.; Yoon, S.J.; Anh, N.H.; Nghi, T.D.; Lim, D.K.; Hong, Y.J.; Hong, S.S.; Kwon, S.W. A systematic review on metabolomics-based diagnostic biomarker discovery and validation in pancreatic cancer. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Nishiumi, S.; Yamanaka, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Fujigaki, S.; Iemoto, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Okusaka, T.; Nakamori, S.; et al. Identification of highly sensitive biomarkers that can aid the early detection of pancreatic cancer using GC/MS/MS-based targeted metabolomics. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 468, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Kanarek, N.; Keys, H.R.; Cantor, J.R.; Lewis, C.A.; Chan, S.H.; Kunchok, T.; Abu-Remaileh, M.; Freinkman, E.; Schweitzer, L.D.; Sabatini, D.M. Histidine catabolism is a major determinant of methotrexate sensitivity. Nature 2018, 559, 632–636. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Rachagani, S.; Natarajan, G.; Crook, A.; Gopal, T.; Rajamanickam, V.; Kaushal, J.B.; Nagabhishek, S.N.; Powers, R.; Batra, S.K.; et al. Histidine Enhances the Anticancer Effect of Gemcitabine against Pancreatic Cancer via Disruption of Amino Acid Homeostasis and Oxidant-Antioxidant Balance. Cancers 2023, 15, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holeček, M. Histidine in Health and Disease: Metabolism, Physiological Importance, and Use as a Supplement. Nutrients 2020, 12, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosnan, M.E.; Brosnan, J.T. Histidine Metabolism and Function. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 2570S–2575S. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Zhao, R.; Guo, K.; Ren, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Tian, L.; Li, T.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z. Potential Metabolite Biomarkers for Early Detection of Stage-I Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 744667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, G.; Berezhnoy, G.; Flores, A.; Cannet, C.; Schafer, H.; Dahlke, M.H.; Michl, P.; Loffler, M.W.; Konigsrainer, A.; Trautwein, C. Quantitative Metabolomics and Lipoprotein Analysis of PDAC Patients Suggests Serum Marker Categories for Pancreatic Function, Pancreatectomy, Cancer Metabolism, and Systemic Disturbances. J. Proteome Res. 2024, 23, 1249–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Participant Characteristics | Healthy Volunteers (n = 24) | Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (n = 22) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, Years *, | 63 (58–71) | 68 (56–75) | 0.62 |
| Sex †, Men (%) | 13 (54.2%) | 16 (69.6%) | 0.17 |
| Weight, kg # | 81.3 ± 19.9 | 77.1 ± 9.6 | 0.70 |
| Body Mass Index, kg/m2 # | 28.3 ± 6.5 | 26.0 ± 3.7 | 0.36 |
| Metabolite | Healthy Volunteers (n = 24) (µM) | Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (n = 22) (µM) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-Hydroxybutyrate, median (IQR) | 374 (309–414) | 423 (378–747) | 0.019 |
| N-Acetylglycoproteins, median (IQR) | 462 (426–641) | 640 (582–789) | <0.001 |
| Glutamine, median (IQR) | 894 (841–954) | 809 (723–891) | 0.0049 |
| Citrate, median (IQR) | 168 (154–193) | 213 (178–242) | 0.0011 |
| Glucose, median (IQR) | 3810 (3585–4215) | 4469 (4080–7020) | <0.001 |
| Histidine, median (IQR) | 368 (356–396) | 323 (270–357) | 0.002 |
| Metabolite | Fold Change | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Taurocholic acid | 4.55 | 0.001 |
| Glycocholic acid | 3.12 | <0.001 |
| Glycochenodeoxycholic acid | 2.19 | <0.001 |
| Deoxycholic acid | −2.32 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McDonnell, D.; Afolabi, P.R.; Niazi, U.; Wilding, S.; Griffiths, G.O.; Swann, J.R.; Byrne, C.D.; Hamady, Z.Z. Metabolite Changes Associated with Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071150
McDonnell D, Afolabi PR, Niazi U, Wilding S, Griffiths GO, Swann JR, Byrne CD, Hamady ZZ. Metabolite Changes Associated with Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(7):1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071150
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcDonnell, Declan, Paul R. Afolabi, Umar Niazi, Sam Wilding, Gareth O. Griffiths, Jonathan R. Swann, Christopher D. Byrne, and Zaed Z. Hamady. 2025. "Metabolite Changes Associated with Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma" Cancers 17, no. 7: 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071150
APA StyleMcDonnell, D., Afolabi, P. R., Niazi, U., Wilding, S., Griffiths, G. O., Swann, J. R., Byrne, C. D., & Hamady, Z. Z. (2025). Metabolite Changes Associated with Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers, 17(7), 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071150





