The Detection of Lung Cancer Cell Profiles in Mediastinal Lymph Nodes Using a Hematological Analyzer and Flow Cytometry Method
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Materials
2.3. Analysis Using a Hematology Analyzer
2.4. Flow-Cytometric Analyses
- CD64-FITC (catalog number: 555527, clone number: 10.1 RUO, BD Biosciences, Herlev, Denmark);
- Fibroblasts Monoclonal Antibody (FMA)-PE (catalog number: MA5 16642, clone number: D7-FIB, Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA);
- CD146-PE-Cy7 (catalog number: 562135, clone number: P1H12, BD Biosciences, Herlev, Denmark);
- CD19-PE-DyLight 594 (catalog number: AQ335127, clone number: LT19, Sysmex, Norderstedt, Germany);
- CD3-PC-5.5 (catalog number: B49203, clone number: UCHT1, Beckman Coulter);
- CD8-APC (catalog number: IM2469, clone number: B9.11, Beckman Coulter);
- CD326 (Ep-CAM)-AF700 (catalog number: 324244, clone number: 9C4);
- CD16-APC-H7 (catalog number: 560195, clone number: 3G8, BD Biosciences, Herlev, Denmark);
- HLA-DR-V450 (catalog number: 655874, clone number: L243, BD Biosciences, Herlev, Denmark);
- CD45-V500 (catalog number: 655873, clone number: 2D1, BD Biosciences, Herlev, Denmark);
- CD4-BV650 (catalog number: 300536, clone number: RPA-T4, BioLegend, San Diego, CA, USA).
- CD326 (EpCAM)-BV 605 (catalog number: 324224, clone number: 9C4, BioLegend);
- MUC-1-APC (catalog number: 355608, clone number: 16A, BioLegend);
- TTF-1-Alexa Fluor 700 (catalog number: NBP3-21041AF700, clone number: 8143R, NovusBio, Centennial, CO, USA);
- Ki67-FITC (catalog number: F7268, clone number: MIB-1, Dako);
- Cytokeratin-PE (catalog number: 347204, clone number: CAM 5.2, BD Biosciences);
- CD56-ECD (catalog number: B49214, clone number: N901, Beckman Coulter);
- CD38-ECD (catalog number: C86903, clone number: LS198-4-3, Beckman Coulter);
- HLA-DR-BV 605 (catalog number: 307640, clone number: L243, BioLegend);
- HER-2-PE (catalog number: 340552, clone number: Neu 24.7, BD Biosciences);
- CD39-PerCP-Cy 5.5 (catalog number: 564899, clone number: TU66, BD Biosciences);
- CD73-BV785 (catalog number: 344028, clone number: AD2, BioLegend);
- CD90-PE Cy-7 (catalog number: 561558, clone number: 5E10, BD Biosciences);
- CD184-APC (catalog number: 555976, clone number: 12G5, BD Biosciences);
- PD-L1-PE (catalog number: 557924, clone number: MIH1, BD Biosciences);
- PD-L2-BV421 (catalog number: 563842, clone number: MIH18, BD Biosciences);
- CD152 (CTLA-4)-PE-Cy 5 (catalog number: 555854, clone number: BNI3, BD Biosciences);
2.5. Statistic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Clinical Characteristics
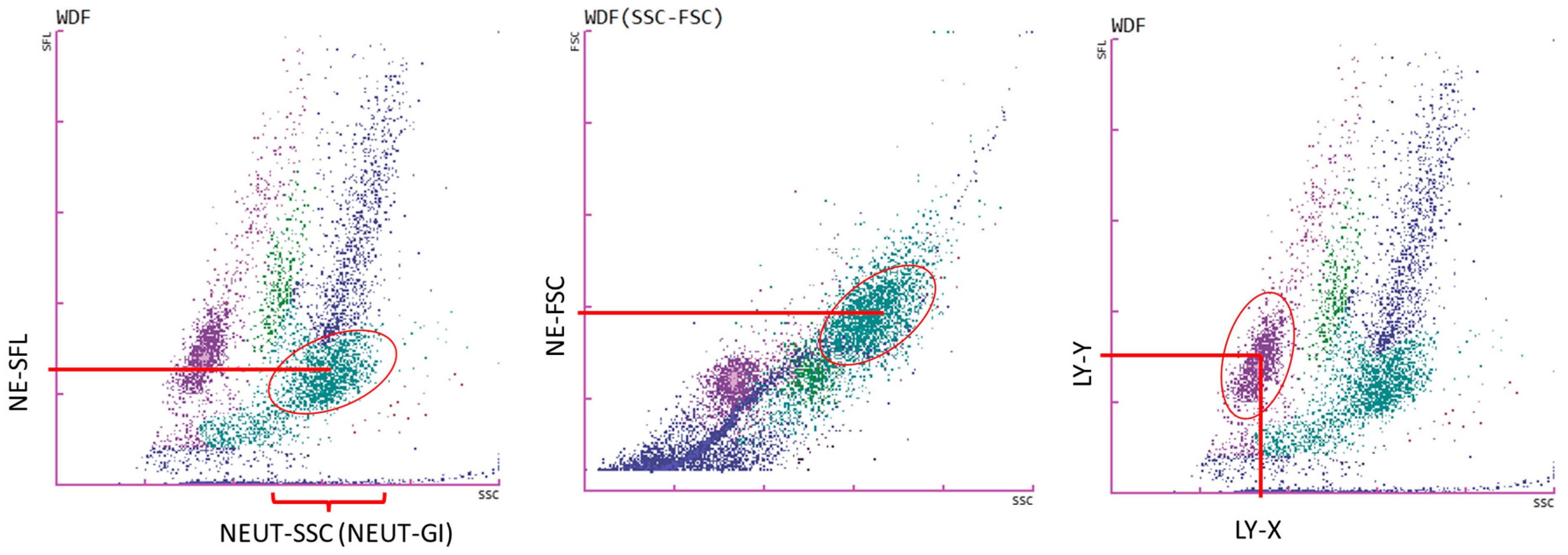
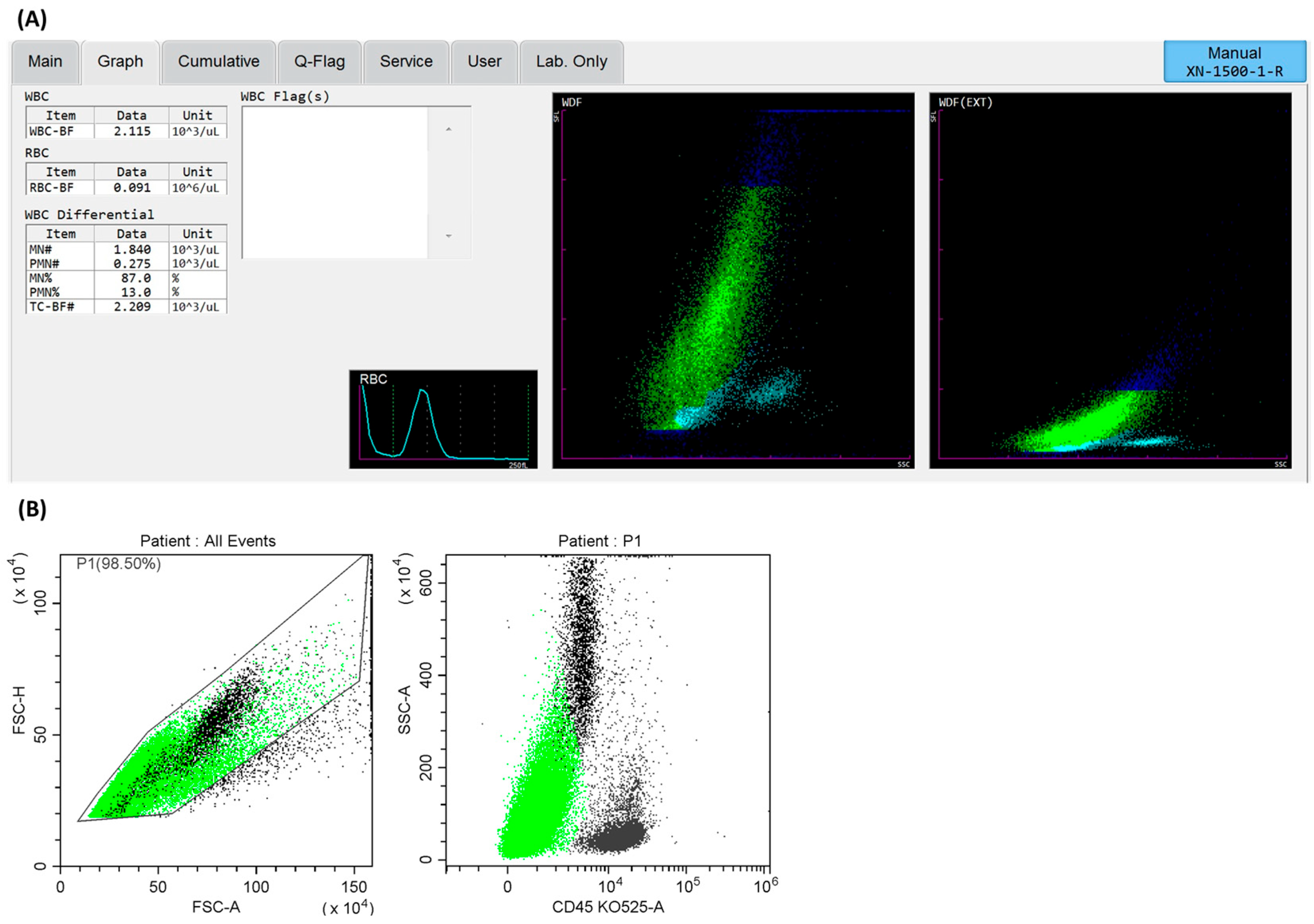
3.2. Cells Analysis of Lymph Node Aspirates Using a Hematological Analyzer
3.3. Cellular Characterization of Lymph Nodes via Flow Cytometry Methods
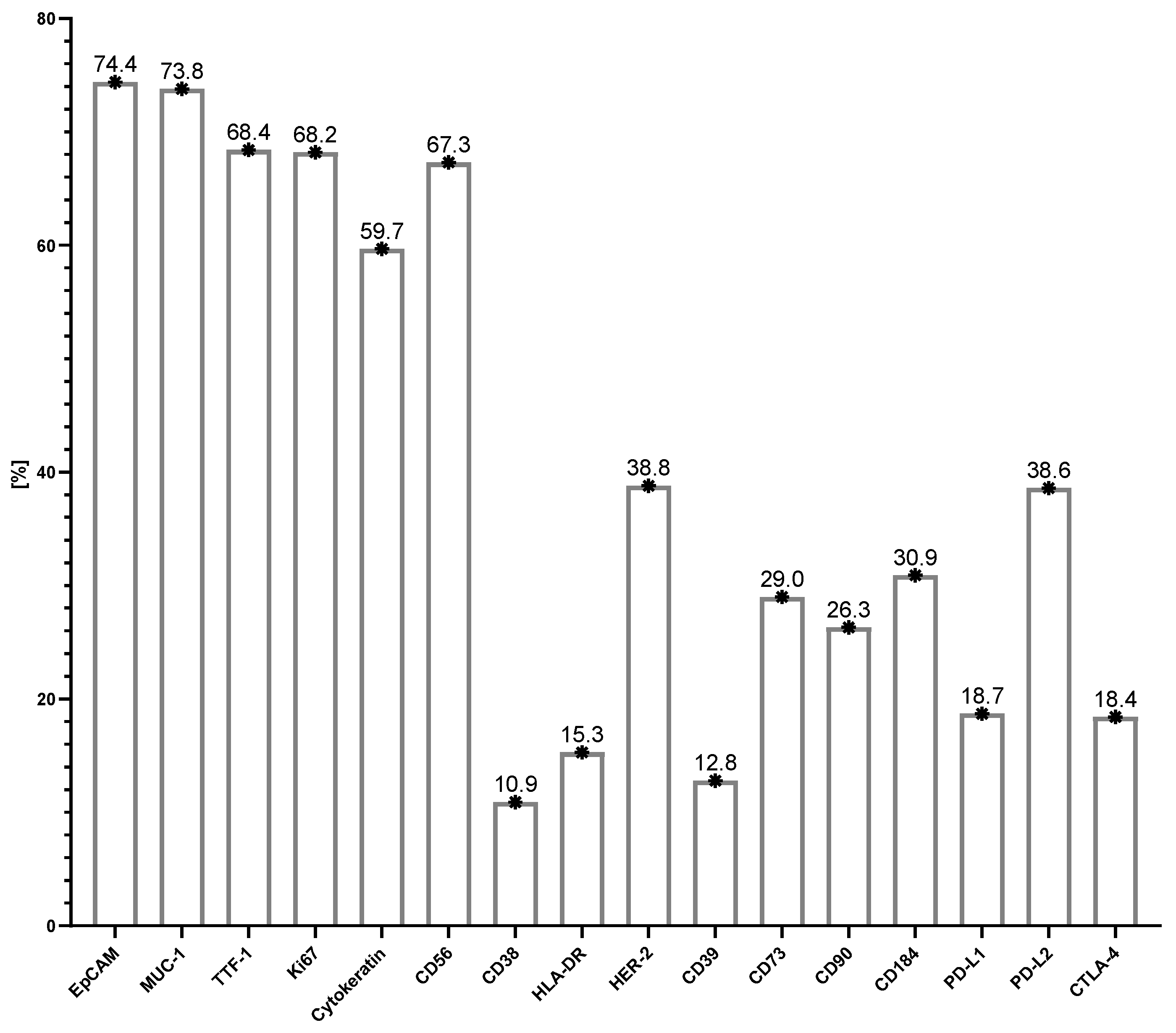
3.4. Antigenic Profile of Tumor Cells in Metastatic Lymph Nodes
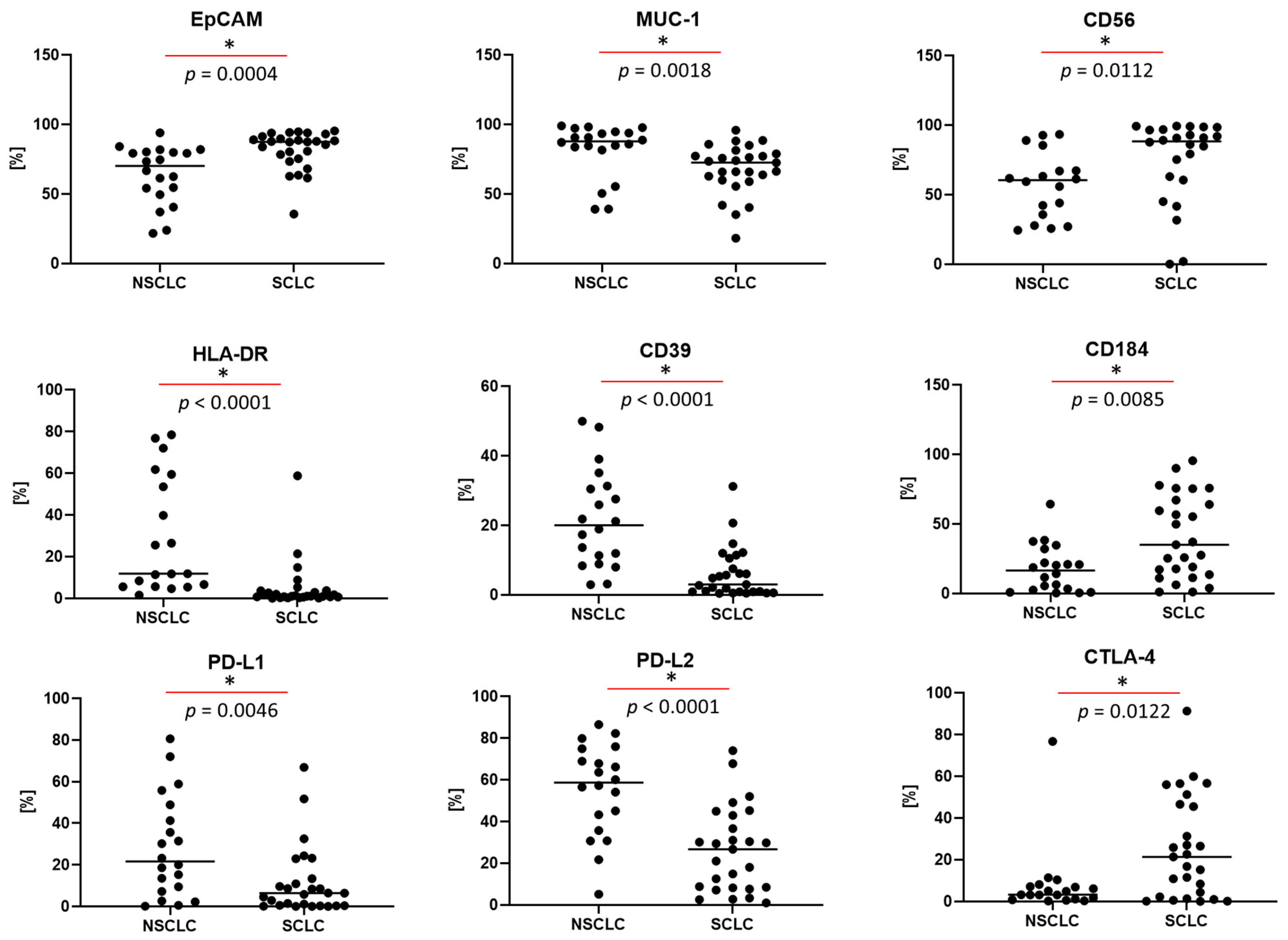
3.5. Differences in the Antigen Profile of Tumor Cells, Depending on the Type of Cancer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bade, B.C.; Dela Cruz, C.S. Lung Cancer 2020: Epidemiology, Etiology, and Prevention. Clin. Chest Med. 2020, 41, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araghi, M.; Mannani, R.; Heidarnejad Maleki, A.; Hamidi, A.; Rostami, S.; Safa, S.H.; Faramarzi, F.; Khorasani, S.; Alimohammadi, M.; Tahmasebi, S.; et al. Recent advances in non-small cell lung cancer targeted therapy; an update review. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alduais, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fan, F.; Chen, J.; Chen, B. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A review of risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Medicine 2023, 102, e32899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, K.; Higashiyama, M.; Okami, J.; Tokunaga, T.; Imamura, F.; Nakayama, T.; Inoue, A.; Kuriyama, K. Oncologic Outcomes of Segmentectomy Versus Lobectomy for Clinical T1a N0 M0 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 101, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, F.; Shehata, M.; Ghazal, M.; Contractor, S.; El-Baz, A. Lung Cancer Subtyping: A Short Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Yatabe, Y.; Austin, J.H.M.; Beasley, M.B.; Chirieac, L.R.; Dacic, S.; Duhig, E.; Flieder, D.B.; et al. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Genetic, Clinical and Radiologic Advances Since the 2004 Classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.S.; Baldwin, D.R. Recent advances in the management of lung cancer. Clin. Med. 2018, 18, s41–s46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ose, N.; Takeuchi, Y.; Sakamaki, Y.; Kadota, Y.; Urasaki, K.; Tsuji, H.; Kawahara, K.; Noguchi, M.; Shintani, Y. Detection of lymph node metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer using the new system of one-step nucleic acid amplification assay. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqutub, S.; Alqutub, A.; Bakhshwin, A.; Mofti, Z.; Alqutub, S.; Alkhamesi, A.A.; Nujoom, M.A.; Rammal, A.; Merdad, M.; Marzouki, H.Z. Histopathological predictors of lymph node metastasis in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1401211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herth, F.J.; Rabe, K.F.; Gasparini, S.; Annema, J.T. Transbronchial and transoesophageal (ultrasound-guided) needle aspirations for the analysis of mediastinal lesions. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raniszewska, A.; Kwiecien, I.; Sokolowski, R.; Rutkowska, E.; Domagala-Kulawik, J. Immunomodulatory Molecules on Lung Cancer Stem Cells From Lymph Nodes Aspirates. Cancers 2020, 12, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raniszewska, A.; Vroman, H.; Dumoulin, D.; Cornelissen, R.; Aerts, J.; Domagala-Kulawik, J. PD-L1(+) lung cancer stem cells modify the metastatic lymph-node immunomicroenvironment in nsclc patients. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raniszewska, A.; Polubiec-Kownacka, M.; Rutkowska, E.; Domagala-Kulawik, J. PD-L1 Expression on Lung Cancer Stem Cells in Metastatic Lymph Nodes Aspirates. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2019, 15, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fielding, D.; Lakis, V.; Dalley, A.J.; Chittoory, H.; Newell, F.; Koufariotis, L.T.; Patch, A.M.; Kazakoff, S.; Bashirzadeh, F.; Son, J.H.; et al. Evaluation of Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) Samples from Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer for Whole Genome, Whole Exome and Comprehensive Panel Sequencing. Cancers 2024, 16, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domagala-Kulawik, J. New Frontiers for Molecular Pathology. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaritakis, I.; Stoltidis, D.; Kotsakis, A.; Dermitzaki, E.K.; Koinis, F.; Lagoudaki, E.; Koutsopoulos, A.; Politaki, E.; Apostolaki, S.; Souglakos, J.; et al. TTF-1- and/or CD56-positive Circulating Tumor Cells in patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, J.; Tang, M.; Li, G.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y. Expression of Mucin Family Proteins in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and its Role in Evaluation of Prognosis. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 4181658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutic, M.; Vukic, A.; Baranasic, J.; Forsti, A.; Dzubur, F.; Samarzija, M.; Jakopovic, M.; Brcic, L.; Knezevic, J. Diagnostic, Predictive, and Prognostic Biomarkers in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Management. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barak, V.; Goike, H.; Panaretakis, K.W.; Einarsson, R. Clinical utility of cytokeratins as tumor markers. Clin. Biochem. 2004, 37, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugalho, A.; Martins, C.; Dias, S.S.; Nunes, G.; Silva, Z.; Correia, M.; Marques Gomes, M.J.; Videira, P.A. Cytokeratin 19, carcinoembryonic antigen, and epithelial cell adhesion molecule detect lung cancer lymph node metastasis in endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial aspiration samples. Clin. Lung Cancer 2013, 14, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martowicz, A.; Seeber, A.; Untergasser, G. The role of EpCAM in physiology and pathology of the epithelium. Histol. Histopathol. 2016, 31, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gires, O.; Pan, M.; Schinke, H.; Canis, M.; Baeuerle, P.A. Expression and function of epithelial cell adhesion molecule EpCAM: Where are we after 40 years? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 969–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, F.; Pan, C.; He, Z.; Pan, X.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, W.; Chen, L. Tumor cell proliferation (Ki-67) expression and its prognostic significance in histological subtypes of lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2021, 154, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, M.V.; Kala, M.; Nivsarkar, M. CD90 a potential cancer stem cell marker and a therapeutic target. Cancer Biomark. 2016, 16, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, L.; Li, Q.; Dong, Z. MUC1: An emerging target in cancer treatment and diagnosis. Bull. Cancer 2022, 109, 1202–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.; Dong, C.; Liang, S. Mucin1 as a potential molecule for cancer immunotherapy and targeted therapy. J. Cancer 2024, 15, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iso, H.; Hisakane, K.; Mikami, E.; Suzuki, T.; Matsuki, S.; Atsumi, K.; Nagata, K.; Seike, M.; Hirose, T. Thyroid transcription factor-1 (TTF-1) expression and the efficacy of combination therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors and cytotoxic chemotherapy in non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2023, 12, 1850–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, B.J.; Han, B.; Choi, D.R.; Kwon, J.H. Prognostic Impact of TTF-1 Expression in Non-Squamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 4279–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Jang, S.H.; Kim, H.I.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.; Hwang, Y.I.; Jung, K.S.; Seo, J.; Lee, C.Y.; Ko, Y.; et al. Thyroid transcription factor-1 as a prognostic indicator for stage IV lung adenocarcinoma with and without EGFR-sensitizing mutations. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegsmann, K.; Zgorzelski, C.; Muley, T.; Christopoulos, P.; Thomas, M.; Winter, H.; Eichhorn, M.; Eichhorn, F.; von Winterfeld, M.; Herpel, E.; et al. Role of Synaptophysin, Chromogranin and CD56 in adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the lung lacking morphological features of neuroendocrine differentiation: A retrospective large-scale study on 1170 tissue samples. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, R.; Chen, L.; Wu, S. CD38 as an immunomodulator in cancer. Future Oncol. 2020, 16, 2853–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, H.; Chavan, S.S.; Chow, A.; Chan, J.M.; Mukae, H.; Rudin, C.M.; Sen, T. Role of CD38 in anti-tumor immunity of small cell lung cancer. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1348982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, N.; Winzer, R.; Tolosa, E.; Fiedler, W.; Brauneck, F. The Clinical Significance of CD73 in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Kurabe, N.; Kahyo, T.; Kawase, A.; Tanahashi, M.; Ogawa, H.; Inui, N.; Funai, K.; Shinmura, K.; et al. Prognostic impact of CD73 and A2A adenosine receptor expression in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 8738–8751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passarelli, A.; Aieta, M.; Sgambato, A.; Gridelli, C. Targeting Immunometabolism Mediated by CD73 Pathway in EGFR-Mutated Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: A New Hope for Overcoming Immune Resistance. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, M.; Glodek, A.; Hartmann, T.; Schmitt-Graff, A.; Silberstein, L.E.; Fujii, N.; Kipps, T.J.; Burger, J.A. Functional expression of CXCR4 (CD184) on small-cell lung cancer cells mediates migration, integrin activation, and adhesion to stromal cells. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8093–8101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Kang, K.; Zhao, A.; Wu, Y. Dual blockade immunotherapy targeting PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 in lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 17, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmaninejad, A.; Valilou, S.F.; Shabgah, A.G.; Aslani, S.; Alimardani, M.; Pasdar, A.; Sahebkar, A. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: Basic biology and role in cancer immunotherapy. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 16824–16837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camidge, D.R.; Doebele, R.C.; Kerr, K.M. Comparing and contrasting predictive biomarkers for immunotherapy and targeted therapy of NSCLC. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yan, X.; Bai, X.; Yang, J.; Song, J. Programmed cell death-ligand 2: New insights in cancer. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1359532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchbinder, E.I.; Desai, A. CTLA-4 and PD-1 Pathways: Similarities, Differences, and Implications of Their Inhibition. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 39, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uy, N.F.; Merkhofer, C.M.; Baik, C.S. HER2 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Review of Emerging Therapies. Cancers 2022, 14, 4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, A.G.; Tsao, M.S.; Beasley, M.B.; Borczuk, A.C.; Brambilla, E.; Cooper, W.A.; Dacic, S.; Jain, D.; Kerr, K.M.; Lantuejoul, S.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Advances Since 2015. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 362–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaliawala, H.A.; Farooqui, S.M.; Harris, K.; Abdo, T.; Keddissi, J.I.; Youness, H.A. Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration (EBUS-TBNA): Technical Updates and Pathological Yield. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornet, E.; Boubaya, M.; Troussard, X. Contribution of the new XN-1000 parameters NEUT-RI and NEUT-WY for managing patients with immature granulocytes. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2015, 37, e123–e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinsdale, R.J.; Devi, A.; Hampson, P.; Wearn, C.M.; Bamford, A.L.; Hazeldine, J.; Bishop, J.; Ahmed, S.; Watson, C.; Lord, J.M.; et al. Changes in novel haematological parameters following thermal injury: A prospective observational cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furundarena, J.R.; Uranga, A.; Sainz, M.R.; Gonzalez, C.; Uresandi, N.; Argoitia, N.; Araiz, M. Usefulness of the lymphocyte positional parameters in the Sysmex XN haematology analyser in lymphoproliferative disorders and mononucleosis syndrome. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2018, 40, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poutakidou, D.; Ruth, I.; Gulbis, B. Differential diagnosis of lymphocytosis in routine laboratory practice: Contribution of lymphocyte parameters using the Sysmex-XN9000 haematology analyzer. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2023, 45, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Brambilla, E.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Sage, J. Small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodak, O.; Peris-Diaz, M.D.; Olbromski, M.; Podhorska-Okolow, M.; Dziegiel, P. Current Landscape of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Epidemiology, Histological Classification, Targeted Therapies, and Immunotherapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, L.E.L.; Remon, J.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Garassino, M.C.; Heymach, J.V.; Kerr, K.M.; Tan, D.S.W.; Veronesi, G.; Reck, M. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2024, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrone, J.; Jackups, R., Jr.; Eby, C.S.; Shimer, G.; Anderson, J.; Frater, J.L. Blast flagging of the Sysmex XN-10 hematology analyzer with supervised cell image analysis: Impact on quality parameters. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2019, 41, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantanate, C.; Klinbua, C. Performance Evaluation of High Fluorescence Lymphocyte Count: Comparability to Atypical Lymphocyte Count and Clinical Significance. Lab. Med. 2018, 49, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.S.; Tailor, H.; Liesner, R.; Machin, S.J.; Briggs, C.J. The value of the white precursor cell channel (WPC) on the Sysmex XN-1000 analyser in a specialist paediatric hospital. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 68, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.U.; Chi, H.S.; Park, S.H.; Jang, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, C.J. Body fluid cellular analysis using the Sysmex XN-2000 automatic hematology analyzer: Focusing on malignant samples. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2015, 37, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, A.; Sareen, R.; Gupta, G. High Fluorescent Cells on Automated Body Fluid Analysis as Discriminator for Malignant Cell Detection. S. Asian J. Cancer 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuff-Werner, P.; Kohlschein, P.; Maroz, A.; Linssen, J.; Dreissiger, K.; Burstein, C. Performance of the XN-2000 WPC channel-flagging to differentiate reactive and neoplastic leukocytosis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 1503–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, N.; Wada, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Gondo, K.; Seto, T.; Maruki, Y.; Kondo, T.; Asai, S.; Matsushita, H.; Miyachi, H. Evaluation of Assay Performance of the Body Fluid Mode on the Automated Hematology Analyzer XN-2000. Sysmex J. Web 2012, 31, 13. [Google Scholar]
- D’Andrilli, A.; Maurizi, G.; Venuta, F.; Rendina, E.A. Mediastinal staging: When and how? Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 68, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, M.; Reda, M.; Musso, V.; Danuzzo, F.; Mohamed, S.; Conforti, S. Diagnostic accuracy of endobronchial ultrasound-transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) for mediastinal lymph node staging of lung cancer. Mediastinum 2021, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, V.R.; Cardoso, P.F.G.; Jacomelli, M.; Santos, L.M.; Minata, M.; Terra, R.M. EBUS-TBNA versus surgical mediastinoscopy for mediastinal lymph node staging in potentially operable non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2020, 46, e20190221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Nakayama, M. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA): Revolutionizing the landscape of lung disease diagnostics. J. Med. Ultrason. 2024, 51, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gostomczyk, K.; Lukaszewska, E.; Borowczak, J.; Bator, A.; Zdrenka, M.; Bodnar, M.; Szylberg, L. Flow cytometry in the detection of circulating tumor cells in neoplastic effusions. Clin. Chim. Acta 2024, 552, 117651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Li, J.; Jiang, H.G.; Ge, L.P.; Wang, Y. Diagnostic value of MUC1 and EpCAM mRNA as tumor markers in differentiating benign from malignant pleural effusion. QJM Int. J. Med. 2014, 107, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Wu, D.; Wang, J.; Li, F. The combination therapy with EpCAM/CD3 BsAb and MUC-1/CD3 BsAb elicited antitumor immunity by T-cell adoptive immunotherapy in lung cancer. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 3380–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, P.; Wu, Z.; Li, B.; Li, W.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Liu, W.; et al. Circulating CD45+EpCAM+ cells as a diagnostic marker for early-stage primary lung cancer. Front. Med. Technol. 2022, 4, 982308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misch, D.; Blum, T.; Boch, C.; Weiss, T.; Crolow, C.; Griff, S.; Mairinger, T.; Bauer, T.T.; Kollmeier, J. Value of thyroid transcription factor (TTF)-1 for diagnosis and prognosis of patients with locally advanced or metastatic small cell lung cancer. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, L. Histopathologic classification of lung cancer: Relevance of cytokeratin and TTF-1 immunophenotyping. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2004, 8, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemieux, M.E.; Reveles, X.T.; Rebeles, J.; Bederka, L.H.; Araujo, P.R.; Sanchez, J.R.; Grayson, M.; Lai, S.C.; DePalo, L.R.; Habib, S.A.; et al. Detection of early-stage lung cancer in sputum using automated flow cytometry and machine learning. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.Y.; Hu, X.F.; Fang, K.X.; Kong, Q.Q.; Cui, R.; Li, H.F.; He, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.K.; Le, H.B. Prognostic value of mutant p53, Ki-67, and TTF-1 and their correlation with EGFR mutation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Histol. Histopathol. 2019, 34, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Ettinger, D.S.; Maleki, Z. Utility of the quantitative Ki-67 proliferation index and CD56 together in the cytologic diagnosis of small cell lung carcinoma and other lung neuroendocrine tumors. Acta Cytol. 2013, 57, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danbara, M.; Yoshida, M.; Kanoh, Y.; Jiang, S.X.; Masuda, N.; Akahoshi, T.; Higashihara, M. Flow cytometric detection of small cell lung cancer cells with aberrant CD45 expression in micrometastatic bone marrow. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 39, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X. A Comprehensive Review of HER2 in Cancer Biology and Therapeutics. Genes 2024, 15, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, N.; Iqbal, N. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) in Cancers: Overexpression and Therapeutic Implications. Mol. Biol. Int. 2014, 2014, 852748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wopereis, S.; Walter, L.O.; Vieira, D.S.C.; Ribeiro, A.A.B.; Fernandes, B.L.; Wilkens, R.S.; Santos-Silva, M.C. Evaluation of ER, PR and HER2 markers by flow cytometry for breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 523, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krencz, I.; Sztankovics, D.; Danko, T.; Sebestyen, A.; Khoor, A. Progression and metastasis of small cell lung carcinoma: The role of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and metabolic alterations. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021, 40, 1141–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Winslow, M.M.; Sage, J. Mechanisms of small cell lung cancer metastasis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e13122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Federico, A.; Hong, L.; Elkrief, A.; Thummalapalli, R.; Cooper, A.J.; Ricciuti, B.; Digumarthy, S.; Alessi, J.V.; Gogia, P.; Pecci, F.; et al. Lung adenocarcinomas with mucinous histology: Clinical, genomic, and immune microenvironment characterization and outcomes to immunotherapy-based treatments and KRAS(G12C) inhibitors. Ann. Oncol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raso, M.G.; Bota-Rabassedas, N.; Wistuba, I.I. Pathology and Classification of SCLC. Cancers 2021, 13, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppensteiner, L.; Mathieson, L.; Pattle, S.; Dorward, D.A.; O’Connor, R.; Akram, A.R. Location of CD39+ T cell subpopulations within tumors predict differential outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giatromanolaki, A.; Kouroupi, M.; Pouliliou, S.; Mitrakas, A.; Hasan, F.; Pappa, A.; Koukourakis, M.I. Ectonucleotidase CD73 and CD39 expression in non-small cell lung cancer relates to hypoxia and immunosuppressive pathways. Life Sci. 2020, 259, 118389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, C.; Yin, S.; To, K.K.W.; Fu, L. CD39/CD73/A2AR pathway and cancer immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streicher, K.; Higgs, B.; Wu, S.; Coffman, K.; Damera, G.; Durham, N.; Greenlees, L.; Lazdun, Y.; Cheng, L.; Cooper, Z.; et al. Increased CD73 and reduced IFNG signature expression in relation to response rates to anti-PD-1(L1) therapies in EGFR-mutant NSCLC. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 11505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliger, B.; Kloor, M.; Ferrone, S. HLA class II antigen-processing pathway in tumors: Molecular defects and clinical relevance. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1171447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.; Jiang, G.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wan, Y.; Chen, R.; Liu, F.; Mao, W.; Zheng, M.; Xu, J. HLA class II molecule HLA-DRA identifies immuno-hot tumors and predicts the therapeutic response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in NSCLC. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Fan, Y. Shaping the tumor immune microenvironment of SCLC: Mechanisms, and opportunities for immunotherapy. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2023, 120, 102606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yuan, P.; Mao, B.; Li, N.; Ying, J.; Tao, X.; Tang, W.; Zhang, L.; Geng, X.; Zhang, F.; et al. Genomic features and tumor immune microenvironment alteration in NSCLC treated with neoadjuvant PD-1 blockade. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotte, A. Combination of CTLA-4 and PD-1 blockers for treatment of cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulsen, E.E.; Kilvaer, T.K.; Rakaee, M.; Richardsen, E.; Hald, S.M.; Andersen, S.; Busund, L.T.; Bremnes, R.M.; Donnem, T. CTLA-4 expression in the non-small cell lung cancer patient tumor microenvironment: Diverging prognostic impact in primary tumors and lymph node metastases. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 1449–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkowska, E.; Kwiecien, I.; Raniszewska, A.; Sokolowski, R.; Bednarek, J.; Jahnz-Rozyk, K.; Chcialowski, A.; Rzepecki, P. New Neutrophil Parameters in Diseases with Various Inflammatory Processes. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, I.S.; Yi, J.; Chang, C.L.; Lee, E.Y. Cell Population Data NE-SFL and MO-WX From Sysmex XN-3000 Can Provide Additional Information for Exclusion of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia from Other Acute Myeloid Leukemias: A Preliminary Study. Ann. Lab. Med. 2016, 36, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, W.; Wang, C.; Ma, Z.; Zhu, S.; Hu, X. Heterogeneity in peripheral blood immune lymphocyte subsets predicts the response of immunotherapy or chemoradiotherapy in advanced lung cancer: An analysis across different pathological types, treatment modalities and age. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1464728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| All Studies Groups | ||
|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 47 | |
| Sex f/m (n) | 24/23 | |
| Age (mean ± SD years) | 68.1 ± 8.4 | |
| LNs: 4R/4L/7/10R/10L/11R/11L/ * | 12/7/9/0/1/1/1/4/12 | |
| Stage: I/II/III/IV (n) | 2/3/22/20 | |
| Tumor cells % (mean ± SD years) | 70.4% ± 25.1 | |
| Tumor cells events (mean ± SD years) | 66,300 ± 107,839 | |
| Histological types: | ||
| NSCLC | SCLC | |
| Number of patients | 20 | 27 |
| Age (mean ± SD years) | 69.2 ± 8.8 | 67.3 ± 8.2 |
| Sex f/m (n) | 10/10 | 14/13 |
| Histological subtypes: | ||
| SQCLC | 6 | n/a |
| ADC | 9 | n/a |
| NOS | 4 | n/a |
| LCC | 1 | n/a |
| Leukocytes Subpopulation and Tumor Cells: (via Flow Cytometry Methods) [% of All Cells] | Lung Cancer Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Lymphocytes | 11.6 ± 14.8 |
| Lymphocytes T | 7.9 ± 10.5 |
| CD4 | 5.0 ± 7.5 |
| CD8 | 3.0 ± 3.7 |
| Ratio CD4/CD8 | 1.9 ± 1.5 |
| Lymphocytes B | 3.0 ± 5.0 |
| Natural killer cells | 1.1 ± 2.6 |
| Neutrophils | 13.2 ± 16.4 |
| Eosinophiles | 0.1 ± 0.4 |
| Basophiles | 0.0 ± 0.0 |
| Monocytes | 0.6 ± 1.3 |
| Dendritic cells | 0.1 ± 0.4 |
| Fibroblasts | 1.9 ± 3.7 |
| Endothelium | 1.9 ± 4.9 |
| Tumor cells (%) | 70.4 ± 25.1 |
| Tumor cells (events) | 66,300 ± 107,839 |
| All cells (events) | 113,762 ± 248,646 |
| White blood cells [cells/µ] (by hematological analyzer) | 3325 ± 4855.3 |
| Leukocytes Subpopulation and Tumor Cells [% of All Cells] | NSCLC Median (Q1–Q3) | SCLC Median (Q1–Q3) | * p < 0.05 Mann–Whitney U Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lymphocytes | 8.5 (7.1–32.4) | 4.0 (1.0–8.4) | * p = 0.0249 |
| Lymphocytes T | 6.3 (3.3–20.5) | 3.2 (0.8–6.4) | * p = 0.0296 |
| CD4 | 3.5 (1.5–8.4) | 1.2 (0.4–4.0) | p = 0.1041 |
| CD8 | 3.2 (0.9–5.5) | 1.4 (0.3–2.2) | * p = 0.0241 |
| Ratio CD4/CD8 | 1.1 (0.8–1.9) | 1.3 (1.0–2.3) | p = 0.3515 |
| Lymphocytes B | 1.8 (0.5–6.3) | 0.6 (0.3–1.7) | * p = 0.0331 |
| NK cells | 0.4 (0.0–1.2) | 0.2 (0.0–0.9) | p = 0.3990 |
| Neutrophils | 11.1 (2.0–22.2) | 2.9 (0.8–17.8) | p = 0.4747 |
| Eosinophiles | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | p = 0.8396 |
| Basophiles | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | - |
| Monocytes | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.0 (0.0–1.4) | p = 0.4359 |
| Dendritic cells | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | p = 0.5291 |
| Fibroblasts | 1.2 (0.2–4.8) | 0.4 (0.1–1.0) | * p = 0.0313 |
| Endothelium | 0.6 (0.1–1.8) | 0.1 (0.0–1.4) | p = 0.2025 |
| Tumor cells (%) | 62.5 (32.3–78.4) | 88.5 (65.7–94.6) | * p = 0.0127 |
| Tumor cells (events) | 13,792 (3712–33,484) | 50,829 (7018–136,923) | * p = 0.0350 |
| All cells (events) | 25,245 (7737–76,001) | 59,925 (13045–144,124) | * p = 0.0185 |
| White blood cells [cells/µ] (by hematological analyzer) | 757 (333–1752) | 2115 (765–6499) | * p = 0.0249 |
| Scheme 1 | NSCLC Median (Q1–Q3) | SCLC Median (Q1–Q3) | * p < 0.05 Mann–Whitney U Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| [% of Tumor Cells] | |||
| EpCAM | 70.1 (51.9–80.1) | 87.5 (75.5–91.4) | * p = 0.0004 |
| MUC-1 | 88.0 (82.7–94.3) | 72.6 (59.9–79.0) | * p = 0.0018 |
| TTF-1 | 77.0 (48.2–85.0) | 78.5 (65.6–85.3) | p = 0.6621 |
| Ki67 | 72.7 (57.1–90.9) | 65.5 (54.2–77.8) | p = 0.1735 |
| Cytokeratin | 82.3 (43.9–89.9) | 72.8 (15.1–89.0) | p = 0.3203 |
| CD56 | 60.4 (35.6–67.3) | 88.5 (61.9–96.7) | * p = 0.0112 |
| CD38 | 8.0 (4.2–12.7) | 2.4 (0.7–13.3) | p = 0.1194 |
| HLA-DR | 11.8 (5.7–59.4) | 1.1 (0.6–3.7) | * p < 0.0001 |
| HER-2 | 24.7 (16.8–50.0) | 40.8 (5.6–64.0) | p = 0.7251 |
| CD39 | 20.0 (10.1–30.9) | 3.0 (0.9–10.5) | * p < 0.0001 |
| CD73 | 25.8 (16.2–58.6) | 18.1 (12.5–32.9) | p = 0.1950 |
| CD90 | 9.8 (3.1–19.1) | 26.3 (5.4–54.0) | p = 0.3660 |
| CD184 | 16.5 (2.9–27.1) | 35.1 (13.6–67.2) | * p = 0.0085 |
| PD-L1 | 21.6 (8.3–45.1) | 6.4 (0.3–13.4) | * p = 0.0046 |
| PD-L2 | 58.7 (39.5–71.9) | 26.7 (8.2–42.9) | * p < 0.0001 |
| CTLA-4 | 3.2 (1.1–7.1) | 21.4 (2.2–46.6) | * p = 0.0122 |
| [GMF of tumor cells] | |||
| EpCAM | 4769.2 (2503.3–7279.3) | 30,007.9 (9817.8–56,446.9) | * p < 0.0001 |
| MUC-1 | 8965.3 (4320.0–21,780.5) | 2412.0 (2072.7–4270.2) | * p = 0.0003 |
| TTF-1 | 4260.8 (1969.7–6719.4) | 3725.7 (2706.6–5928.6) | p = 0.9405 |
| Ki67 | 1912.2 (1433.3–2748.2) | 1657.1 (1429.8–1927.1) | p = 0.1735 |
| Cytokeratin | 3831.0 (1384.0–6446.8) | 2545.1 (1041.4–7083.0) | p = 0.3203 |
| CD56 | 3803.5 (2421.2–4995.8) | 15,059.8 (52,360.0–30,566.3) | * p = 0.0111 |
| CD38 | 1350.4 (809.5–1570.4) | 1073.3 (555.2–1864.1) | p = 0.5866 |
| HLA-DR | 1690.0 (988.4–4748.0) | 655.3 (401.0–809.0) | * p = 0.0008 |
| HER | 1373.0 (954.1–2796.2) | 1945.3 (745.8–4348.7) | p = 0.6621 |
| CD39 | 1825.1 (1380.9–2286.2) | 927.4 (565.0–1406.9) | * p < 0.0001 |
| CD73 | 1108.8 (826.1–3055.8) | 919.7 (778.9–1099.0) | p = 0.0872 |
| CD90 | 593.3 (192.6–924.9) | 2851.4 (171.4–7822.3) | p = 0.1807 |
| CD184 | 981.5 (171.3–2219.6) | 3396.1 (1389.2–8300.6) | * p = 0.0014 |
| PD-L1 | 837.8 (515.5–1109.7) | 419.2 (265.7–506.4) | *p = 0.0045 |
| PD-L2 | 967.0 (652.8–1352.5) | 525.1 (376.4–667.4) | * p < 0.0001 |
| CTLA-4 | 1340.1 (1001.6–1597.5) | 2979.7 (885.6–8482.2) | *p = 0.0371 |
| Hematological Parameters | NSCLC Median (Q1–Q3) | SCLC Median (Q1–Q3) | * p < 0.05 Mann–Whitney U Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| NE-SSC [ch] (or NE-GI) | 150.6 (134.4–153.7) | 119.1 (113.3–152.3) | * p = 0.0296 |
| NE-SFL [ch] | 45.9 (43.1–47.7) | 48.1 (45.0–50.6) | p = 0.1358 |
| NE-FSC [ch] | 72.4 (48.4–81.9) | 66.0 (53.3–86.7) | p = 0.8563 |
| LY-X [ch] | 83.9 (82.3–89.7) | 95.0 (84.4–100.4) | * p = 0.0075 |
| LY-Y [ch] | 53.8 (42.7–65.0) | 48.7 (44.8–57.6) | p = 0.3990 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwiecień, I.; Rutkowska, E.; Raniszewska, A.; Sokołowski, R.; Bednarek, J.; Jahnz-Różyk, K.; Rzepecki, P. The Detection of Lung Cancer Cell Profiles in Mediastinal Lymph Nodes Using a Hematological Analyzer and Flow Cytometry Method. Cancers 2025, 17, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030431
Kwiecień I, Rutkowska E, Raniszewska A, Sokołowski R, Bednarek J, Jahnz-Różyk K, Rzepecki P. The Detection of Lung Cancer Cell Profiles in Mediastinal Lymph Nodes Using a Hematological Analyzer and Flow Cytometry Method. Cancers. 2025; 17(3):431. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030431
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwiecień, Iwona, Elżbieta Rutkowska, Agata Raniszewska, Rafał Sokołowski, Joanna Bednarek, Karina Jahnz-Różyk, and Piotr Rzepecki. 2025. "The Detection of Lung Cancer Cell Profiles in Mediastinal Lymph Nodes Using a Hematological Analyzer and Flow Cytometry Method" Cancers 17, no. 3: 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030431
APA StyleKwiecień, I., Rutkowska, E., Raniszewska, A., Sokołowski, R., Bednarek, J., Jahnz-Różyk, K., & Rzepecki, P. (2025). The Detection of Lung Cancer Cell Profiles in Mediastinal Lymph Nodes Using a Hematological Analyzer and Flow Cytometry Method. Cancers, 17(3), 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030431







