CXCR2 Mediates Distinct Neutrophil Behavior in Brain Metastatic Breast Tumor
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
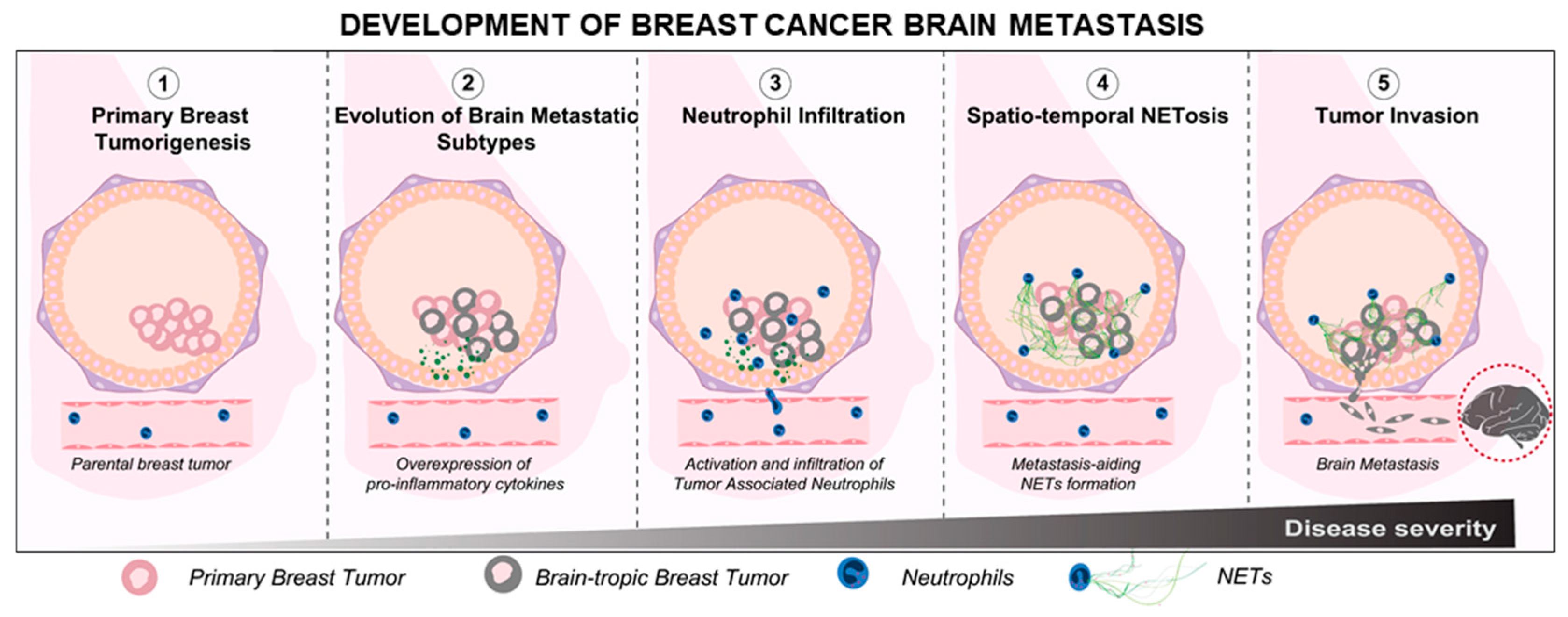
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Isolation of Neutrophils
2.2.1. Microfluidic Neutrophil Chemotaxis Assays
2.2.2. Neutrophil-Tumor Spheroid Interaction Assay
2.3. Immunostaining
2.4. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.5. Cohort Analysis
2.6. Imaging and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
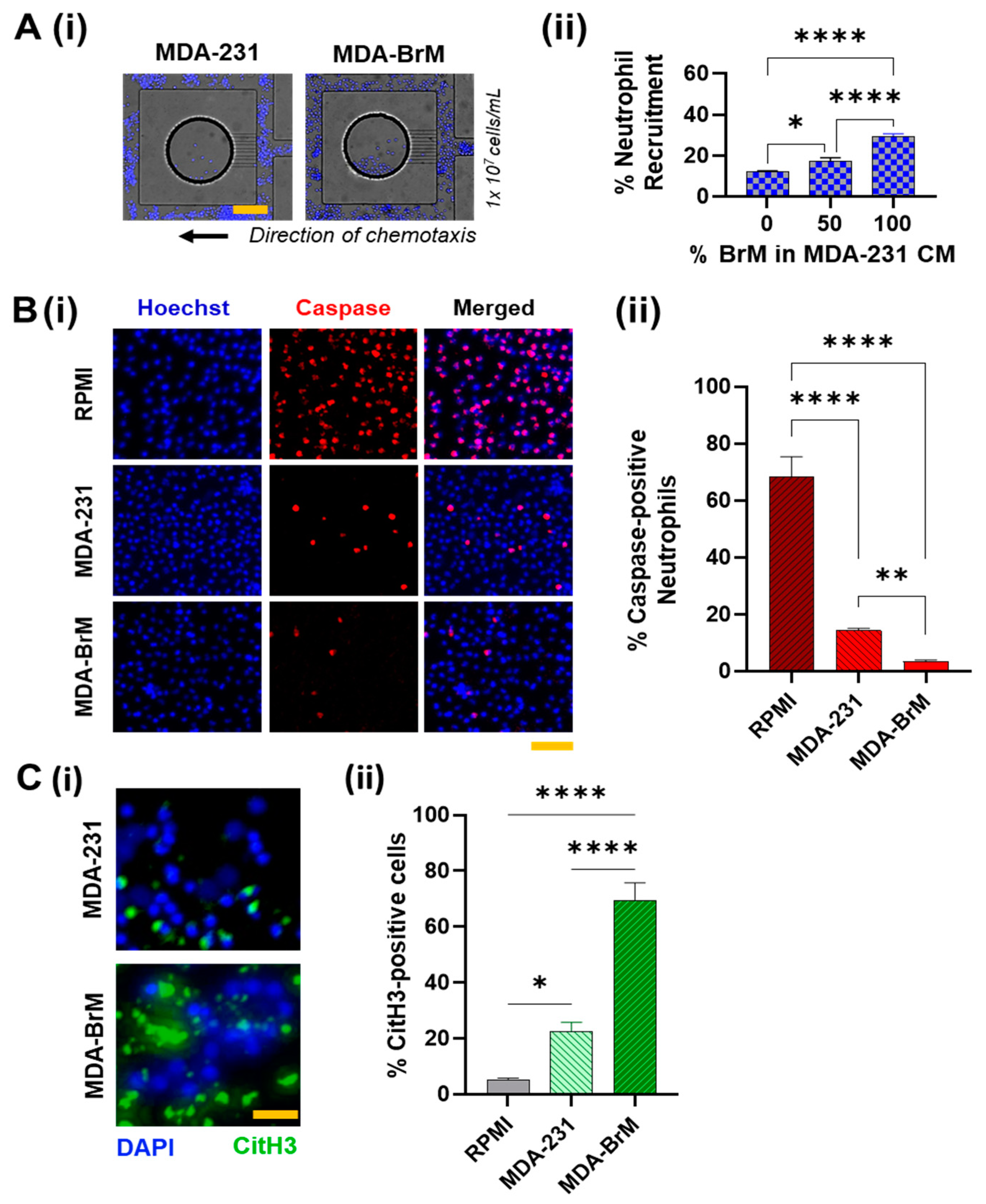
3.1. Comparison of Neutrophil Responses to Conditioned Media Derived from MDA-BrM and MDA-231
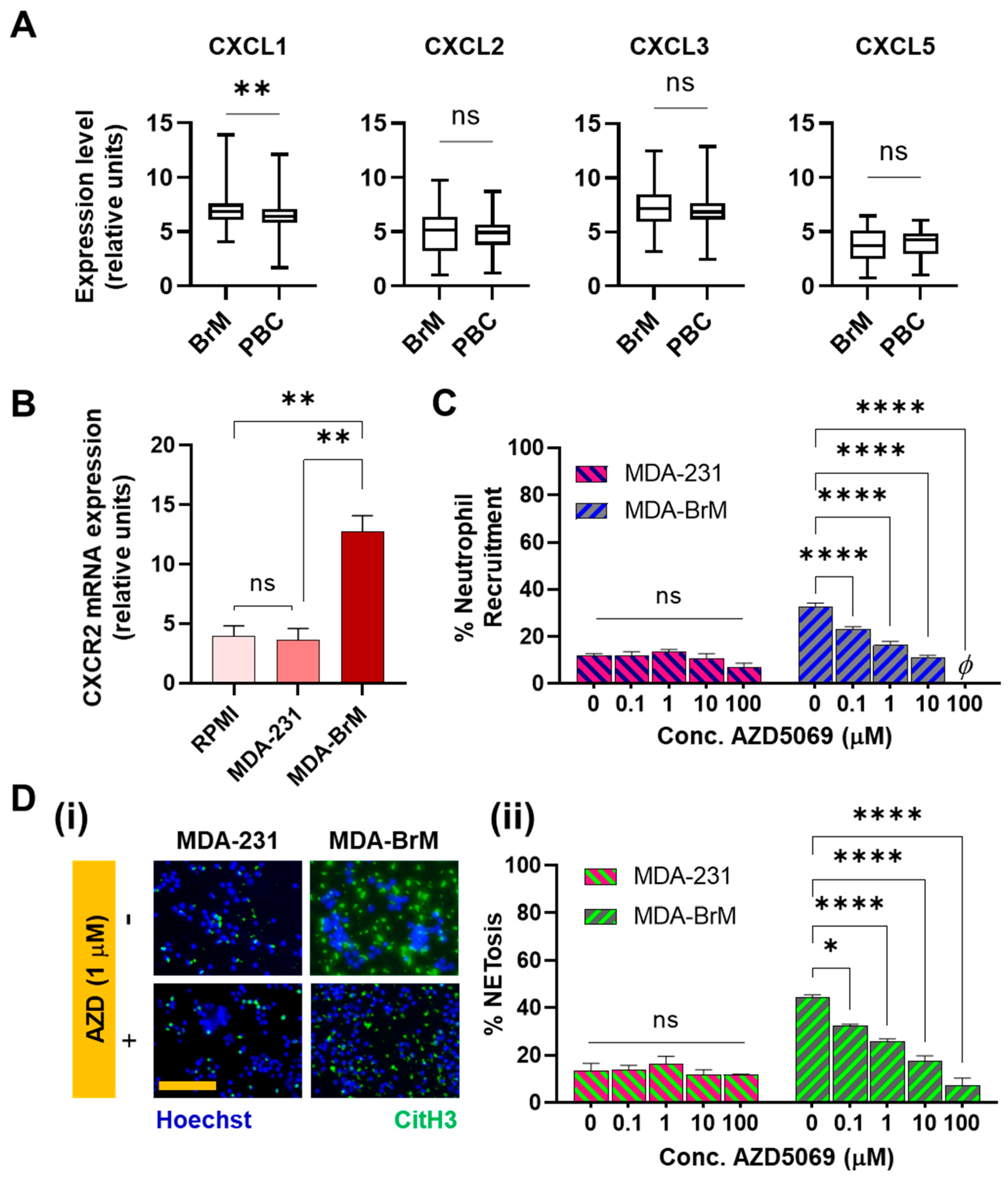
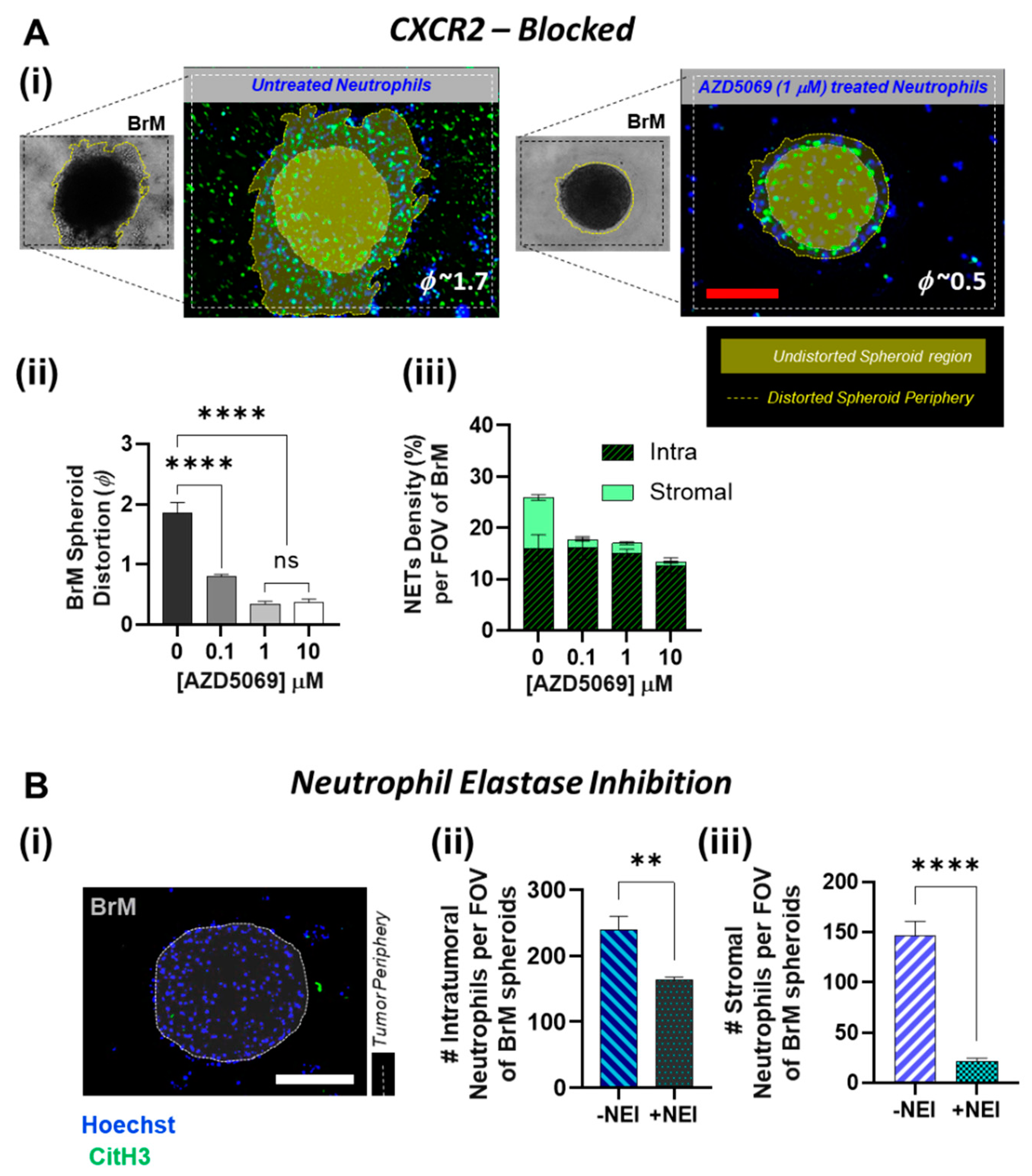
3.2. Involvement of CXCR2 in BrM-Neutrophils Interactions
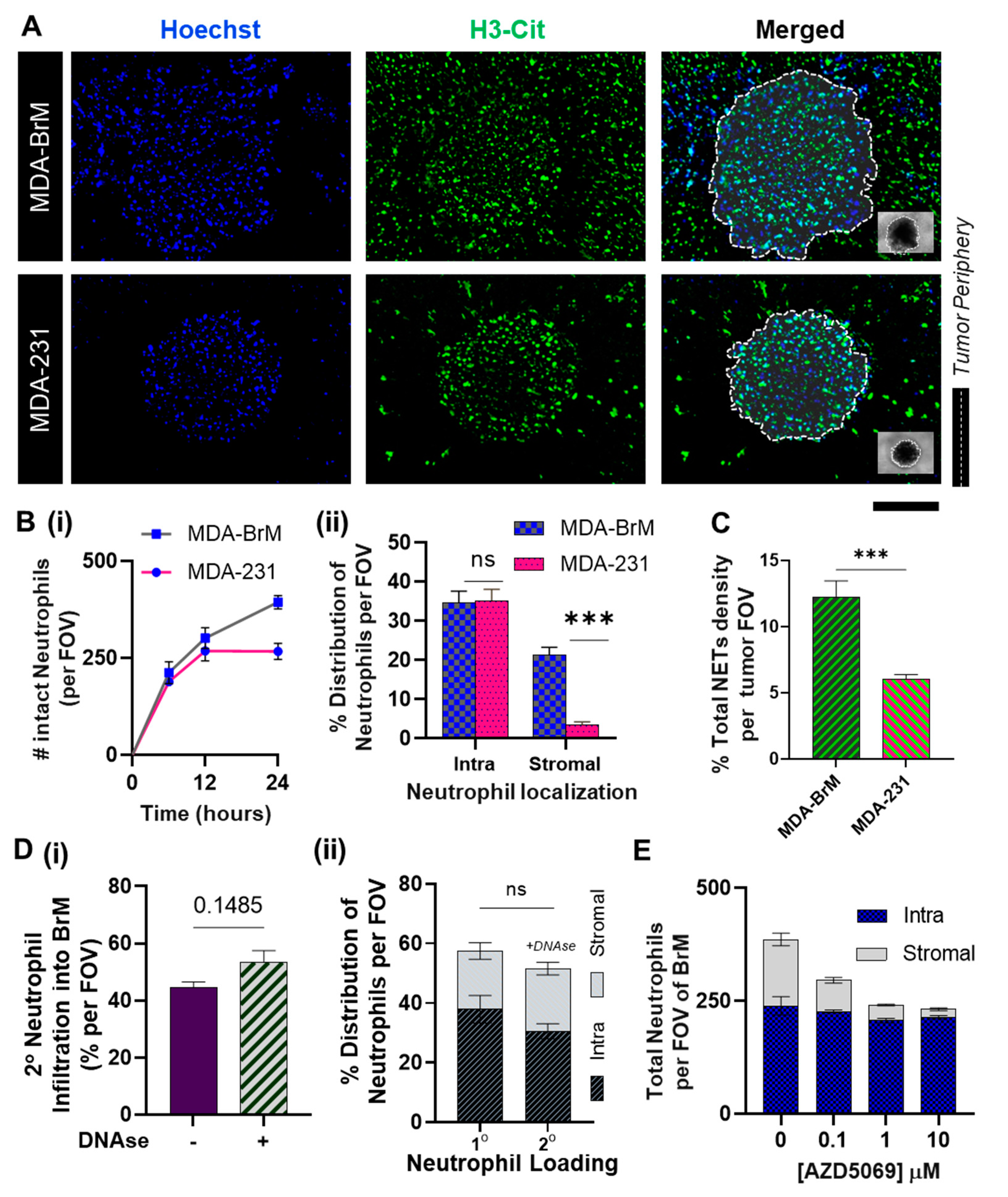
3.3. Distinct Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Tumor-Associated Neutrophils in BrM
3.4. Inhibition of NETs in BrM Limits Tumor-Associated Neutrophil Infiltration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- You, H.; Baluszek, S.; Kaminska, B. Immune Microenvironment of Brain Metastases-Are Microglia and Other Brain Macrophages Little Helpers? Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacho-Díaz, B.; García-Botello, D.R.; Wegman-Ostrosky, T.; Reyes-Soto, G.; Ortiz-Sánchez, E.; Herrera-Montalvo, L.A. Tumor Microenvironment Differences between Primary Tumor and Brain Metastases. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosnan, E.M.; Anders, C.K. Understanding Patterns of Brain Metastasis in Breast Cancer and Designing Rational Therapeutic Strategies. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabouret, E.; Chinot, O.; Metellus, P.; Tallet, A.; Viens, P.; Gonçalves, A. Recent Trends in Epidemiology of Brain Metastases: An Overview. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 4655–4662. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, N.U.; Bellon, J.R.; Winer, E.P. CNS Metastases in Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 3608–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aversa, C.; Rossi, V.; Geuna, E.; Martinello, R.; Milani, A.; Redana, S.; Valabrega, G.; Aglietta, M.; Montemurro, F. Metastatic Breast Cancer Subtypes and Central Nervous System Metastases. Breast 2014, 23, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendell, J.C.; Domchek, S.M.; Burstein, H.J.; Harris, L.; Younger, J.; Kuter, I.; Bunnell, C.; Rue, M.; Gelman, R.; Winer, E. Central Nervous System Metastases in Women Who Receive Trastuzumab-Based Therapy for Metastatic Breast Carcinoma. Cancer 2003, 97, 2972–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.U.; Claus, E.; Sohl, J.; Razzak, A.R.; Arnaout, A.; Winer, E.P. Sites of Distant Recurrence and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: High Incidence of Central Nervous System Metastases. Cancer 2008, 113, 2638–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Ma, X.; Du, Y.; Feng, J. Understanding Patterns of Brain Metastasis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer and Exploring Potential Therapeutic Targets. OncoTargets Ther. 2021, 14, 589–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Cao, Y. Exosomes Derived from Brain Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells Destroy the Blood-Brain Barrier by Carrying LncRNA GS1-600G8.5. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 7461727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Kim, I.A. Evolving Treatment Strategies of Brain Metastases from Breast Cancer: Current Status and Future Direction. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920936117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surendran, V.; Rutledge, D.; Colmon, R.; Chandrasekaran, A. A Novel Tumor-Immune Microenvironment (TIME)-on-Chip Mimics Three Dimensional Neutrophil-Tumor Dynamics and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs)-Mediated Collective Tumor Invasion. Biofabrication 2021, 13, 035029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayes, R.F.; Mouhanna, J.G.; Nicolau, I.; Bourdeau, F.; Giannias, B.; Rousseau, S.; Quail, D.; Walsh, L.; Sangwan, V.; Bertos, N.; et al. Primary Tumors Induce Neutrophil Extracellular Traps with Targetable Metastasis-Promoting Effects. JCI insight 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnewies, M.; Roberts, E.W.; Kersten, K.; Chan, V.; Fearon, D.F.; Merad, M.; Coussens, L.M.; Gabrilovich, D.I.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Hedrick, C.C.; et al. Understanding the Tumor Immune Microenvironment (TIME) for Effective Therapy. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, D.R.; Huttenlocher, A. Neutrophils in the Tumor Microenvironment. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, Y.; Okabe, H.; Yamashita, Y.-I.; Nakagawa, S.; Saito, Y.; Umezaki, N.; Tsukamoto, M.; Yamao, T.; Yamamura, K.; Arima, K.; et al. Tumour-Infiltrating Inflammatory and Immune Cells in Patients with Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramatsu, S.; Tanaka, H.; Nishimura, J.; Sakimura, C.; Tamura, T.; Toyokawa, T.; Muguruma, K.; Yashiro, M.; Hirakawa, K.; Ohira, M. Neutrophils in Primary Gastric Tumors Are Correlated with Neutrophil Infiltration in Tumor-Draining Lymph Nodes and the Systemic Inflammatory Response. BMC Immunol. 2018, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Wu, L.; Yang, H.; Yang, H. Prognostic Significance of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) in Patients with Ovarian Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e17475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swierczak, A.; Mouchemore, K.A.; Hamilton, J.A.; Anderson, R.L. Neutrophils: Important Contributors to Tumor Progression and Metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015, 34, 735–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catena, R.; Bhattacharya, N.; El Rayes, T.; Wang, S.; Choi, H.; Gao, D.; Ryu, S.; Joshi, N.; Bielenberg, D.; Lee, S.B.; et al. Bone Marrow-Derived Gr1+ Cells Can Generate a Metastasis-Resistant Microenvironment via Induced Secretion of Thrombospondin-1. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finisguerra, V.; Di Conza, G.; Di Matteo, M.; Serneels, J.; Costa, S.; Thompson, A.A.R.; Wauters, E.; Walmsley, S.; Prenen, H.; Granot, Z.; et al. MET Is Required for the Recruitment of Anti-Tumoural Neutrophils. Nature 2015, 522, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granot, Z.; Henke, E.; Comen, E.A.; King, T.A.; Norton, L.; Benezra, R. Tumor Entrained Neutrophils Inhibit Seeding in the Premetastatic Lung. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Perez-de-Celis, E.; Chavarri-Guerra, Y.; Leon-Rodriguez, E.; Gamboa-Dominguez, A. Tumor-Associated Neutrophils in Breast Cancer Subtypes. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 18, 2689–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Saxena, S.; Goel, P.; Prajapati, D.R.; Wang, C.; Singh, R.K. Breast Cancer Cell-Neutrophil Interactions Enhance Neutrophil Survival and pro-Tumorigenic Activities. Cancers 2020, 12, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.A.; Katara, G.K.; Kulshrestha, A.; Jaiswal, M.K.; Amin, M.A.; Beaman, K.D. Breast Cancer Associated A2 Isoform Vacuolar ATPase Immunomodulates Neutrophils: Potential Role in Tumor Progression. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 33033–33045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wculek, S.K.; Malanchi, I. Neutrophils Support Lung Colonization of Metastasis-Initiating Breast Cancer Cells. Nature 2015, 528, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Li, Q.; Ferrara, N. Metastatic Growth Instructed by Neutrophil-Derived Transferrin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 11060–11065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S.; Baba, T.; Muranaka, H.; Tanabe, Y.; Takahashi, C.; Matsugo, S.; Mukaida, N. Involvement of Prokineticin 2–Expressing Neutrophil Infiltration in 5-Fluorouracil–Induced Aggravation of Breast Cancer Metastasis to Lung. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, J.; Morton, J.P.; Sansom, O.J. Neutrophils: Homing in on the Myeloid Mechanisms of Metastasis. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 110, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Saxena, S.; Awaji, M.; Singh, R.K. Tumor-Associated Neutrophils in Cancer: Going Pro. Cancers 2019, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, K.; Sépult, C.; Rocks, N.; Blacher, S.; Gérard, C.; Noel, A.; Cataldo, D. Neutrophil-Derived Interleukin 16 in Premetastatic Lungs Promotes Breast Tumor Cell Seeding. Cancer Growth Metastasis 2017, 10, 1179064417738513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queen, M.M.; Ryan, R.E.; Holzer, R.G.; Keller-Peck, C.R.; Jorcyk, C.L. Breast Cancer Cells Stimulate Neutrophils to Produce Oncostatin M: Potential Implications for Tumor Progression. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 8896–8904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowanetz, M.; Wu, X.; Lee, J.; Tan, M.; Hagenbeek, T.; Qu, X.; Yu, L.; Ross, J.; Korsisaari, N.; Cao, T.; et al. Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor Promotes Lung Metastasis through Mobilization of Ly6G+ Ly6C+ Granulocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21248–21255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffelt, S.B.; Kersten, K.; Doornebal, C.W.; Weiden, J.; Vrijland, K.; Hau, C.-S.; Verstegen, N.J.M.; Ciampricotti, M.; Hawinkels, L.J.A.C.; Jonkers, J.; et al. IL-17-Producing Γδ T Cells and Neutrophils Conspire to Promote Breast Cancer Metastasis. Nature 2015, 522, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharyya, S.; Oskarsson, T.; Vanharanta, S.; Malladi, S.; Kim, J.; Morris, P.G.; Manova-Todorova, K.; Leversha, M.; Hogg, N.; Seshan, V.E.; et al. A CXCL1 Paracrine Network Links Cancer Chemoresistance and Metastasis. Cell 2012, 150, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.-Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Kitamura, T.; Zhang, J.; Campion, L.R.; Kaiser, E.A.; Snyder, L.A.; Pollard, J.W. CCL2 Recruits Inflammatory Monocytes to Facilitate Breast-Tumour Metastasis. Nature 2011, 475, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Zhang, H.; Hu, G. Cancer and Microenvironment Plasticity: Double-Edged Swords in Metastasis. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Kill Bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrengues, J.; Shields, M.A.; Ng, D.; Park, C.G.; Ambrico, A.; Poindexter, M.E.; Upadhyay, P.; Uyeminami, D.L.; Pommier, A.; Küttner, V.; et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Produced during Inflammation Awaken Dormant Cancer Cells in Mice. Science 2018, 361, eaao4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cools-Lartigue, J.; Spicer, J.; McDonald, B.; Gowing, S.; Chow, S.; Giannias, B.; Bourdeau, F.; Kubes, P.; Ferri, L. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Sequester Circulating Tumor Cells and Promote Metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3446–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohme, S.; Yazdani, H.O.; Al-Khafaji, A.B.; Chidi, A.P.; Loughran, P.; Mowen, K.; Wang, Y.; Simmons, R.L.; Huang, H.; Tsung, A. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote the Development and Progression of Liver Metastases after Surgical Stress. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demers, M.; Krause, D.S.; Schatzberg, D.; Martinod, K.; Voorhees, J.R.; Fuchs, T.A.; Scadden, D.T.; Wagner, D.D. Cancers Predispose Neutrophils to Release Extracellular DNA Traps That Contribute to Cancer-Associated Thrombosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13076–13081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.S.; Gu, J.; Kim, J.-E.; Nam, Y.; Song, J.W.; Kim, H.K. Cancer Cell-Induced Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promote Both Hypercoagulability and Cancer Progression. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Ko, S.Y.; Mohamed, M.S.; Kenny, H.A.; Lengyel, E.; Naora, H. Neutrophils Facilitate Ovarian Cancer Premetastatic Niche Formation in the Omentum. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Wysocki, R.W.; Amoozgar, Z.; Maiorino, L.; Fein, M.R.; Jorns, J.; Schott, A.F.; Kinugasa-Katayama, Y.; Lee, Y.; Won, N.H.; et al. Cancer Cells Induce Metastasis-Supporting Neutrophil Extracellular DNA Traps. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, ra138–ra361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teijeira, Á.; Garasa, S.; Gato, M.; Alfaro, C.; Migueliz, I.; Cirella, A.; de Andrea, C.; Ochoa, M.C.; Otano, I.; Etxeberria, I.; et al. CXCR1 and CXCR2 Chemokine Receptor Agonists Produced by Tumors Induce Neutrophil Extracellular Traps That Interfere with Immune Cytotoxicity. Immunity 2020, 52, 856–871.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, B.; Chen, J.; Huang, D.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Chen, F.; et al. DNA of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promotes Cancer Metastasis via CCDC25. Nature 2020, 583, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuya, K.; Nakasu, Y.; Kurakane, T.; Hayashi, N.; Harada, H.; Nozaki, K. Elevated Preoperative Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor of Worse Survival after Resection in Patients with Brain Metastasis. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 127, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yao, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Li, P.; Qu, J.; Badu-Nkansah, A.; Yuan, X.; Huang, Y.-W.; Fukumura, K.; et al. Blocking Immunosuppressive Neutrophils Deters PY696-EZH2-Driven Brain Metastases. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaz5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpinati, L.; Kaisar-Iluz, N.; Shaul, M.E.; Groth, C.; Umansky, V.; Fridlender, Z.G. Tumor-Derived Factors Differentially Affect the Recruitment and Plasticity of Neutrophils. Cancers 2021, 13, 5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, F.; Liu, Y.; Sharma, S.; Wu, K.; Chan, M.D.; Lo, H.-W.; Carpenter, R.L.; Metheny-Barlow, L.J.; Zhou, X.; Qasem, S.A.; et al. Activation of the C-Met Pathway Mobilizes an Inflammatory Network in the Brain Microenvironment to Promote Brain Metastasis of Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4970–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekaran, A.; Ellett, F.; Jorgensen, J.; Irimia, D. Temporal Gradients Limit the Accumulation of Neutrophils towards Sources of Chemoattractant. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2017, 3, 16067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Mok, S.; Moraes, C. Micropocket Hydrogel Devices for All-in-One Formation, Assembly, and Analysis of Aggregate-Based Tissues. Biofabrication 2019, 11, 045013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SenGupta, S.; Hein, L.E.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Konwerski, J.R.; Li, Y.; Johnson, C.; Cai, D.; Smith, J.L.; Parent, C.A. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells Recruit Neutrophils by Secreting TGF-β and CXCR2 Ligands. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 659996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, P.V.; Janka-Junttila, M.; Lee, Y.J.; McCann, C.P.; Oliver, C.M.; Aamer, K.A.; Losert, W.; Cicerone, M.T.; Parent, C.A. LTB4 Is a Signal-Relay Molecule during Neutrophil Chemotaxis. Dev. Cell 2012, 22, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Luo, H.R.; Kambara, H. Heterogeneity of Neutrophil Spontaneous Death. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, E156–E159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschnek, S.; Vier, J.; Gautam, S.; Frankenberg, T.; Rangelova, S.; Eitz-Ferrer, P.; Grespi, F.; Ottina, E.; Villunger, A.; Häcker, H.; et al. Molecular Analysis of Neutrophil Spontaneous Apoptosis Reveals a Strong Role for the Pro-Apoptotic BH3-Only Protein Noxa. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1805–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.R.; Loison, F. Constitutive Neutrophil Apoptosis: Mechanisms and Regulation. Am. J. Hematol. 2008, 83, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loison, F.; Zhu, H.; Karatepe, K.; Kasorn, A.; Liu, P.; Ye, K.; Zhou, J.; Cao, S.; Gong, H.; Jenne, D.E.; et al. Proteinase 3-Dependent Caspase-3 Cleavage Modulates Neutrophil Death and Inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4445–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christenson, K.; Björkman, L.; Karlsson, J.; Sundqvist, M.; Movitz, C.; Speert, D.P.; Dahlgren, C.; Bylund, J. In Vivo-Transmigrated Human Neutrophils Are Resistant to Antiapoptotic Stimulation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 90, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlomovitz, I.; Speir, M.; Gerlic, M. Flipping the dogma—phosphatidylserine in non-apoptotic cell death. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzouz, D.; Palaniyar, N. ApoNETosis: Discovery of a Novel Form of Neutrophil Death with Concomitant Apoptosis and NETosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazennec, G.; Richmond, A. Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors: New Insights into Cancer-Related Inflammation. Trends Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bièche, I.; Chavey, C.; Andrieu, C.; Busson, M.; Vacher, S.; Le Corre, L.; Guinebretière, J.-M.; Burlinchon, S.; Lidereau, R.; Lazennec, G. CXC Chemokines Located in the 4q21 Region Are Up-Regulated in Breast Cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2007, 14, 1039–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavey, C.; Bibeau, F.; Gourgou-Bourgade, S.; Burlinchon, S.; Boissière, F.; Laune, D.; Roques, S.; Lazennec, G. Oestrogen Receptor Negative Breast Cancers Exhibit High Cytokine Content. Breast Cancer Res. 2007, 9, R15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freund, A.; Chauveau, C.; Brouillet, J.-P.; Lucas, A.; Lacroix, M.; Licznar, A.; Vignon, F.; Lazennec, G. IL-8 Expression and Its Possible Relationship with Estrogen-Receptor-Negative Status of Breast Cancer Cells. Oncogene 2003, 22, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timaxian, C.; Vogel, C.F.A.; Orcel, C.; Vetter, D.; Durochat, C.; Chinal, C.; NGuyen, P.; Aknin, M.-L.; Mercier-Nomé, F.; Davy, M.; et al. Pivotal Role for Cxcr2 in Regulating Tumor-Associated Neutrophil in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.; Rosowski, S.; Huttenlocher, E.E. Neutrophil Migration in Infection and Wound Repair: Going Forward in Reverse. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Betts, C.; Robinson, I.; Malmgren, A.; Humfrey, C. The Chemokine CXCR2 Antagonist (AZD5069) Preserves Neutrophil-Mediated Host Immunity in Non-Human Primates. Haematologica 2017, 102, e65–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sody, S.; Uddin, M.; Grüneboom, A.; Görgens, A.; Giebel, B.; Gunzer, M.; Brandau, S. Distinct Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Tumor-Associated Neutrophils in Small Tumor Lesions. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommerswinkel, N.; Niggemann, B.; Keil, S.; Zänker, K.S.; Dittmar, T. Analysis of Cell Migration within a Three-Dimensional Collagen Matrix. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 92, e51963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinci, M.; Box, C.; Eccles, S.A. Three-Dimensional (3D) Tumor Spheroid Invasion Assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 99, e52686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okeke, E.B.; Louttit, C.; Fry, C.; Najafabadi, A.H.; Han, K.; Nemzek, J.; Moon, J.J. Inhibition of Neutrophil Elastase Prevents Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation and Rescues Mice from Endotoxic Shock. Biomaterials 2020, 238, 119836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayes, R.F.; Vourtzoumis, P.; Bou Rjeily, M.; Seth, R.; Bourdeau, F.; Giannias, B.; Berube, J.; Huang, Y.-H.; Rousseau, S.; Camilleri-Broet, S.; et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Trap-Associated CEACAM1 as a Putative Therapeutic Target to Prevent Metastatic Progression of Colon Carcinoma. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 2285–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, B.E.; Tabariès, S.; Johnson, R.M.; Andrzejewski, S.; Senecal, J.; Lehuédé, C.; Annis, M.G.; Ma, E.H.; Völs, S.; Ramsay, L.; et al. Immature Low-Density Neutrophils Exhibit Metabolic Flexibility That Facilitates Breast Cancer Liver Metastasis. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 3902–3915.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groth, C.; Weber, R.; Lasser, S.; Özbay, F.G.; Kurzay, A.; Petrova, V.; Altevogt, P.; Utikal, J.; Umansky, V. Tumor Promoting Capacity of Polymorphonuclear Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Neutralization. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 1628–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Ma, M.; Tan, Z.; Zheng, H.; Liu, X. Neutrophil: A New Player in Metastatic Cancers. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 565165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Dong, L.; Cheng, L. Neutrophils in Cancer Carcinogenesis and Metastasis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwicki, M.; Pittet, M.J. Versatile Neutrophil Functions in Cancer. In Semin. Immuno; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; p. 101538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guoqiang, L.; Sun, M.; Lu, X. Targeting and Exploitation of Tumor-Associated Neutrophils to Enhance Immunotherapy and Drug Delivery for Cancer Treatment. Cancer Biol. Med. 2020, 17, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaul, M.E.; Fridlender, Z.G. Neutrophils as Active Regulators of the Immune System in the Tumor Microenvironment. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 102, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaunisto, A.; Henry, W.S.; Montaser-Kouhsari, L.; Jaminet, S.-C.; Oh, E.-Y.; Zhao, L.; Luo, H.R.; Beck, A.H.; Toker, A. NFAT1 Promotes Intratumoral Neutrophil Infiltration by Regulating IL8 Expression in Breast Cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1140–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, T.; Furth, E.E.; Vonderheide, R.H. CXCR2-Dependent Accumulation of Tumor-Associated Neutrophils Regulates T-Cell Immunity in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 968–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highfill, S.L.; Cui, Y.; Giles, A.J.; Smith, J.P.; Zhang, H.; Morse, E.; Kaplan, R.N.; Mackall, C.L. Disruption of CXCR2-Mediated MDSC Tumor Trafficking Enhances Anti-PD1 Efficacy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 237ra67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, H.; Wang, D.; Daikoku, T.; Sun, H.; Dey, S.K.; Dubois, R.N. CXCR2-Expressing Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Are Essential to Promote Colitis-Associated Tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashar, H.K.; Pulavendran, S.; Rudd, J.M.; Maram, P.; Achanta, M.; Chow, V.T.K.; Malayer, J.R.; Snider, T.A.; Teluguakula, N. Administration of a CXC Chemokine Receptor 2 (CXCR2) Antagonist, SCH527123, Together with Oseltamivir Suppresses NETosis and Protects Mice from Lethal Influenza and Piglets from Swine-Influenza Infection. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtmann, A.; Zarbock, A. CXCR2: From Bench to Bedside. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.F.; Huang, Y.; Han, Y.Y.; Lin, L.Y.; Sun, W.H.; Rabson, A.B.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.F. TNFα-Activated Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Promote Breast Cancer Metastasis by Recruiting CXCR2+ Neutrophils. Oncogene 2017, 36, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, A.; Tian, Y.; Wu, J.D.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Wu, K. The CXCL8-CXCR1/2 Pathways in Cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016, 31, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, S.; Reyes-Aldasoro, C.C.; Candel, S.; Renshaw, S.A.; Mulero, V.; Calado, Â. Cxcl8 (IL-8) mediates neutrophil recruitment and behavior in the zebrafish inflammatory response. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 4349–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Mo, F.; Li, Q.; Han, X.; Shi, H.; Chen, S.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. Targeting CXCR2 inhibits the progression of lung cancer and promotes therapeutic effect of cisplatin. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ma, X.-L.; Wei, Y.-Q.; Wei, X.-W. Potential Roles and Targeted Therapy of the CXCLs/CXCR2 Axis in Cancer and Inflammatory Diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2019, 1871, 289–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eash, K.J.; Greenbaum, A.M.; Gopalan, P.K.; Link, D.C. CXCR2 and CXCR4 Antagonistically Regulate Neutrophil Trafficking from Murine Bone Marrow. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 2423–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Liu, Y.; Dai, N.; Hoffmann, C.; Hudock, K.M.; Zhang, P.; Guttentag, S.H.; Kolls, J.K.; Oliver, P.M.; Bushman, F.D.; et al. Cxcr2 and Cxcl5 Regulate the IL-17/G-CSF Axis and Neutrophil Homeostasis in Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 974–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurcevic, S.; Humfrey, C.; Uddin, M.; Warrington, S.; Larsson, B.; Keen, C. The Effect of a Selective CXCR2 Antagonist (AZD5069) on Human Blood Neutrophil Count and Innate Immune Functions: Effects of CXCR2 Antagonism on Human Neutrophils. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 80, 1324–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockman, P.R.; Mittapalli, R.K.; Taskar, K.S.; Rudraraju, V.; Gril, B.; Bohn, K.A.; Adkins, C.E.; Roberts, A.; Thorsheim, H.R.; Gaasch, J.A.; et al. Heterogeneous Blood-Tumor Barrier Permeability Determines Drug Efficacy in Experimental Brain Metastases of Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5664–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, R.; Berghoff, A.S.; Vogl, U.; Rudas, M.; Bergen, E.; Dubsky, P.; Dieckmann, K.; Pinker, K.; Bago-Horvath, Z.; Galid, A.; et al. Activity of T-DM1 in Her2-Positive Breast Cancer Brain Metastases. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2015, 32, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, F.; Delaloge, S.; Barrios, C.H.; Wuerstlein, R.; Anton, A.; Brain, E.; Hatschek, T.; Kelly, C.M.; Peña-Murillo, C.; Yilmaz, M.; et al. Trastuzumab Emtansine (T-DM1) in Patients with HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer and Brain Metastases: Exploratory Final Analysis of Cohort 1 from KAMILLA, a Single-Arm Phase IIIb Clinical Trial. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, S.; Ashley, S.; Miles, D.; Chan, S.; Wardley, A.; Davidson, N.; Bhatti, R.; Shehata, M.; Nouras, H.; Camburn, T.; et al. Treatment of HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer with Lapatinib and Capecitabine in the Lapatinib Expanded Access Programme, Including Efficacy in Brain Metastases-the UK Experience. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, R.A.; Gelman, R.S.; Anders, C.K.; Melisko, M.E.; Parsons, H.A.; Cropp, A.M.; Silvestri, K.; Cotter, C.M.; Componeschi, K.P.; Marte, J.M.; et al. Translational Breast Cancer Research Consortium. TBCRC 022: A Phase II Trial of Neratinib and Capecitabine for Patients with Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive Breast Cancer and Brain Metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.U.; Borges, V.; Anders, C.; Murthy, R.K.; Paplomata, E.; Hamilton, E.; Hurvitz, S.; Loi, S.; Okines, A.; Abramson, V.; et al. Intracranial Efficacy and Survival with Tucatinib plus Trastuzumab and Capecitabine for Previously Treated HER2-Positive Breast Cancer with Brain Metastases in the HER2CLIMB Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2610–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailleux, C.; Eberst, L.; Bachelot, T. Treatment Strategies for Breast Cancer Brain Metastases. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Soyza, A.; Pavord, I.; Elborn, J.S.; Smith, D.; Wray, H.; Puu, M.; Larsson, B.; Stockley, R. A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Study of the CXCR2 Antagonist AZD5069 in Bronchiectasis. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Byrne, P.M.; Metev, H.; Puu, M.; Richter, K.; Keen, C.; Uddin, M.; Larsson, B.; Cullberg, M.; Nair, P. Efficacy and Safety of a CXCR2 Antagonist, AZD5069, in Patients with Uncontrolled Persistent Asthma: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsten, A.M.; Förster, K.; Radeczky, E.; Linnhoff, A.; Balint, B.; Watz, H.; Wray, H.; Salkeld, L.; Cullberg, M.; Larsson, B. The Safety and Tolerability of Oral AZD5069, a Selective CXCR2 Antagonist, in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe COPD. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 31, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-J.; Wei, K.-C.; Chen, P.-Y.; Lim, M.; Hwang, T.-L. Roles of Neutrophils in Glioma and Brain Metastases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 701383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüönd, F.; Tiede, S.; Christofori, G. Breast Cancer as an Example of Tumour Heterogeneity and Tumour Cell Plasticity during Malignant Progression. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zardavas, D.; Irrthum, A.; Swanton, C.; Piccart, M. Clinical Management of Breast Cancer Heterogeneity. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragomeni, S.M.; Sciallis, A.; Jeruss, J.S. Molecular Subtypes and Local-Regional Control of Breast Cancer. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 27, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, S.; Broglio, K.; Esteva, F.J.; Ibrahim, N.K.; Kau, S.-W.; Islam, R.; Aldape, K.D.; Yu, T.-K.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M. Defining Prognosis for Women with Breast Cancer and CNS Metastases by HER2 Status. Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yipp, B.G.; Petri, B.; Salina, D.; Jenne, C.N.; Scott, B.N.; Zbytnuik, L.D.; Pittman, K.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Wu, K.; Meijndert, H.C.; et al. Dynamic NETosis is carried out by live neutrophils in human and mouse bacterial abscesses and during severe gram-positive infection. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamaru, R.; Ohzawa, H.; Miyato, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Haruta, H.; Kurashina, K.; Saito, S.; Hosoya, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; Yamashita, H.; et al. Low Density Neutrophils (LDN) in Postoperative Abdominal Cavity Assist the Peritoneal Recurrence through the Production of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monjezi, M.; Rismanian, M.; Jamaati, H.; Kashaninejad, N. Anti-Cancer Drug Screening with Microfluidic Technology. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, A.; Abduljawad, M.; Moraes, C. Have Microfluidics Delivered for Drug Discovery? Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2016, 11, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changirwa, D.; Schlechte, J.; McDonald, B. A Multi-Modal Toolkit for Studying Neutrophils in Cancer and Beyond. Cancers 2021, 13, 5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, X.; Wang, J.; Lu, D.; Xu, X. Targeting Tumor-Associated Macrophages to Synergize Tumor Immunotherapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Mu, J.; Zeng, Q.; Deng, S.; Zhou, H. Signaling Pathways in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Targeted Therapy for Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Safarulla, S.; Madan, A.; Xing, F.; Chandrasekaran, A. CXCR2 Mediates Distinct Neutrophil Behavior in Brain Metastatic Breast Tumor. Cancers 2022, 14, 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030515
Safarulla S, Madan A, Xing F, Chandrasekaran A. CXCR2 Mediates Distinct Neutrophil Behavior in Brain Metastatic Breast Tumor. Cancers. 2022; 14(3):515. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030515
Chicago/Turabian StyleSafarulla, Simrit, Ankit Madan, Fei Xing, and Arvind Chandrasekaran. 2022. "CXCR2 Mediates Distinct Neutrophil Behavior in Brain Metastatic Breast Tumor" Cancers 14, no. 3: 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030515
APA StyleSafarulla, S., Madan, A., Xing, F., & Chandrasekaran, A. (2022). CXCR2 Mediates Distinct Neutrophil Behavior in Brain Metastatic Breast Tumor. Cancers, 14(3), 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030515





