Triple Enhancement for Sensitive Immunochromatographic Assay: A Case Study for Human Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- (2)
- increased quantity of nanoparticles bound to the formed immune complex, by aggregation of different functionalized nanoparticles in the course of their movement to the binding zone and directly at this zone of test strip [15];
- (3)
- growth of the detected analytical signal by increasing size of nanoparticle labels after their attaching to the binding zone of the test strip [6].
- (1)
- the use of gold nanoparticles with branched surfaces, namely, gold nanoflowers (GNFs), instead of traditional spherical gold nanoparticles (sGNPs) [16];
- (2)
- the use of several kinds of nanoparticles functionalized by a biotin–streptavidin interacting module for their aggregation in the course of ICA [17]; and
- (3)
- in situ growth of bound gold nanoparticles by their catalysis of cationic gold reduction [18].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Synthesis of the Abs-Biotin and BSA-Biotin Derivatives
2.3. Preparation of sGNPs and Their Conjugates with Proteins
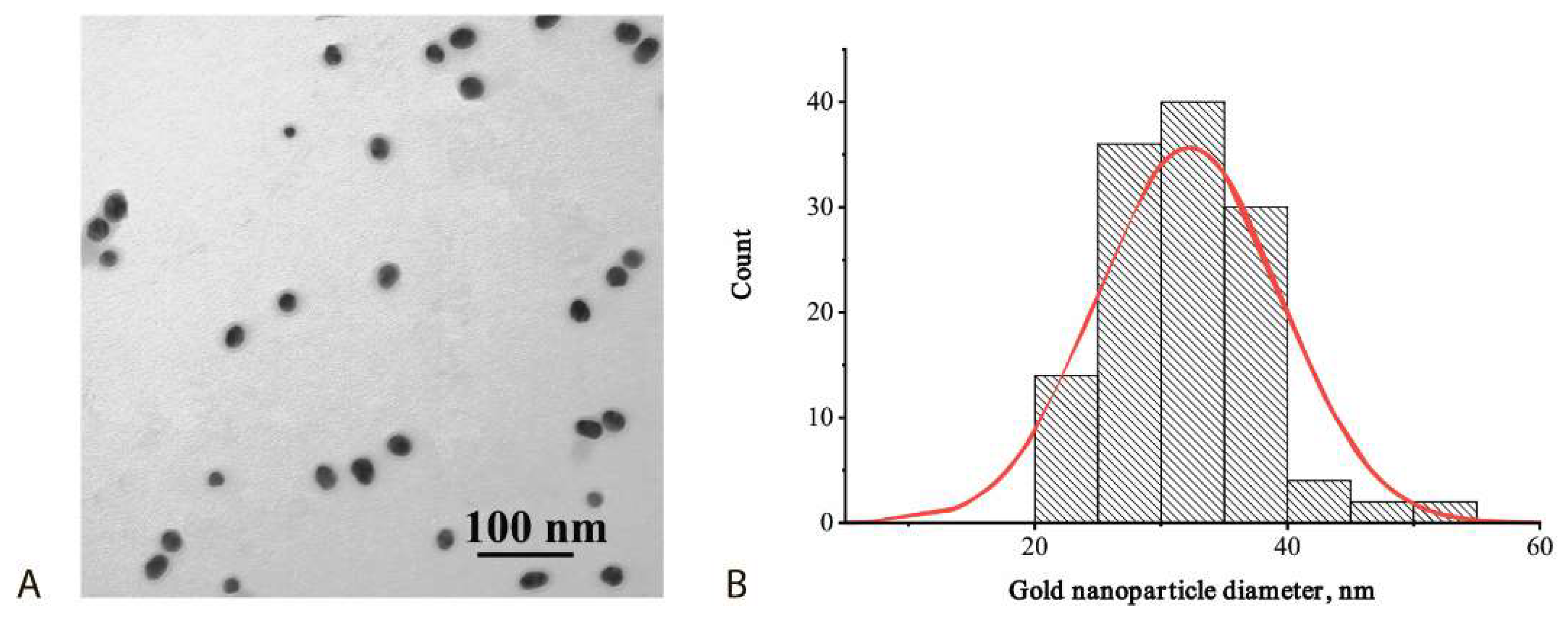
2.4. GNPs Characterization
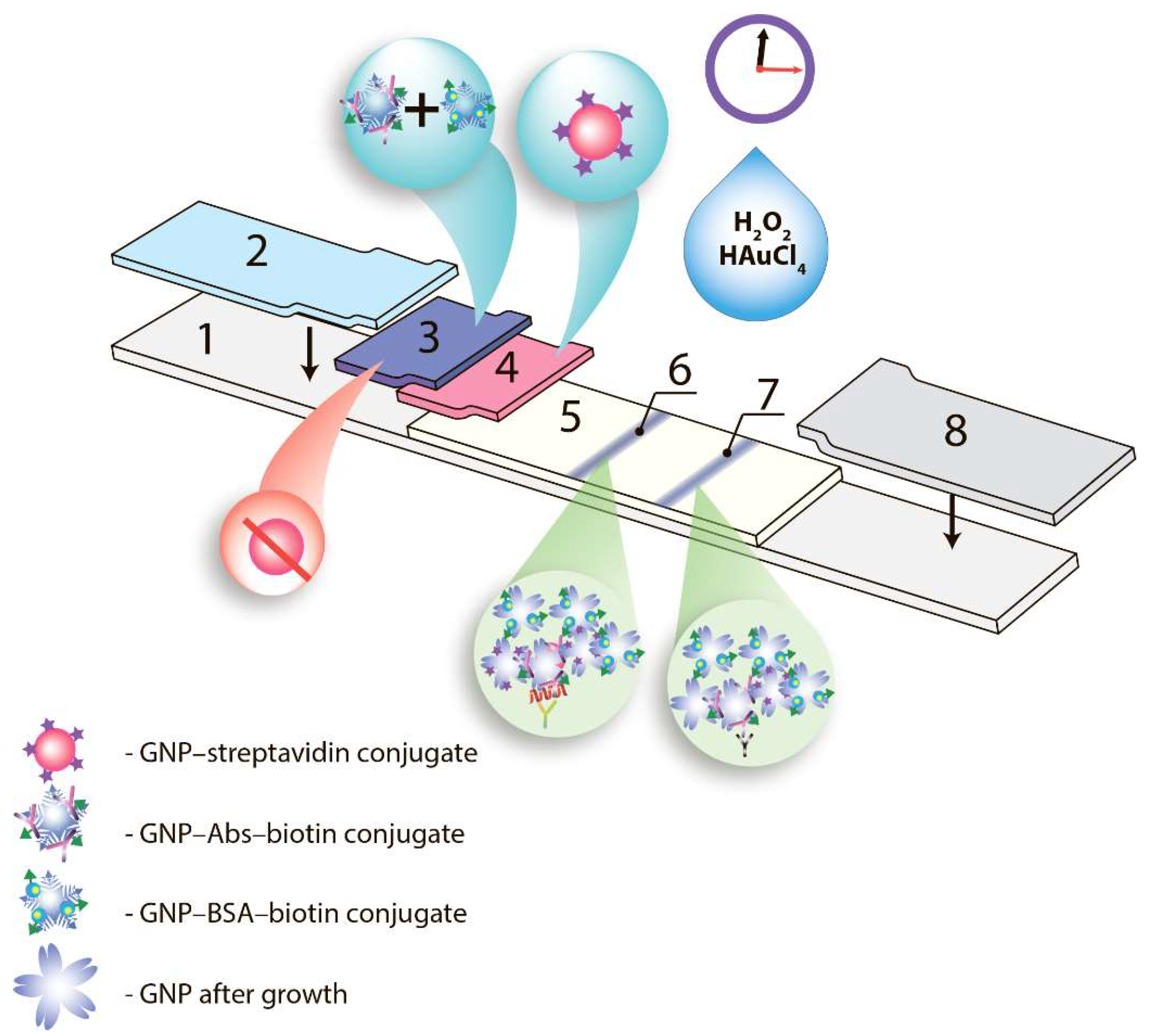
2.5. Fabrication of Immunochromatographic Tests
2.6. Immunochromatographic Assay and Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Common Test System
3.2. Test System with Changed Label
3.3. Test System with Nanoparticles Aggregation
3.4. Triple Enhanced Test System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Di Nardo, F.; Chiarello, M.; Cavalera, S.; Baggiani, C.; Anfossi, L. Ten years of lateral flow immunoassay technique applications: Trends, challenges and future perspectives. Sensors 2021, 21, 5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, K.-Y.; Shan, S.; Liu, D.-F.; Lai, W.-H. Recent advances of lateral flow immunoassay for mycotoxins detection. TrAC 2020, 133, 116087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.N.; Hawker-Bond, G.W.; Georgiou, P.G.; Dedola, S.; Field, R.A.; Gibson, M.I. Glycosylated gold nanoparticles in point of care diagnostics: From aggregation to lateral flow. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 7238–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Lv, X. Recent advances in sensitivity enhancement for lateral flow assay. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Sun, X.; Li, N.; Li, X.; Wu, T.; Wang, F. New Advances in Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFI) Technology for Food Safety Detection. Molecules 2022, 27, 6596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Recent advances of lateral flow immunoassay components as “point of need”. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2022, 43, 579–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzantiev, B.B.; Byzova, N.A.; Urusov, A.E.; Zherdev, A.V. Immunochromatographic methods in food analysis. TrAC 2014, 55, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.D.; Hsieh, H.V.; Gasperino, D.J.; Weigl, B.H. Sensitivity enhancement in lateral flow assays: A systems perspective. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 2486–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirshahi, V.; Liu, G. Enhancing the analytical performance of paper lateral flow assays: From chemistry to engineering. TrAC 2021, 136, 116200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Chen, S.; Guo, J.; Ma, X. Nanomaterial labels in lateral flow immunoassays for point-of-care-testing. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 60, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, E.; Lu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Dai, Z. Simultaneous and ultrasensitive detection of three pesticides using a surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based lateral flow assay test strip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 181, 113149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khlebtsov, B.; Khlebtsov, N. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based lateral-flow immunoassay. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ding, L.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Y. Tailoring noble metal nanoparticle designs to enable sensitive lateral flow immunoassay. Theranostics 2022, 12, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-González, M.; de la Escosura-Muñiz, A. Strip modification and alternative architectures for signal amplification in nanoparticle-based lateral flow assays. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 4111–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Tian, S.; Zhao, W.; Liu, K.; Ma, X.; Guo, J. Aptamer-based lateral flow assay on-site biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 186, 113279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taranova, N.A.; Byzova, N.A.; Pridvorova, S.M.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Comparative Assessment of Different Gold Nanoflowers as Labels for Lateral Flow Immunosensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 7098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranova, N.A.; Urusov, A.E.; Sadykhov, E.G.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Bifunctional gold nanoparticles as an agglomeration-enhancing tool for highly sensitive lateral flow tests: A case study with procalcitonin. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 4189–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panferov, V.G.; Safenkova, I.V.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Post-assay growth of gold nanoparticles as a tool for highly sensitive lateral flow immunoassay. Application to the detection of potato virus X. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musher, D.M.; Abers, M.S.; Corrales-Medina, V.F. Acute infection and myocardial infarction. NEJM 2019, 380, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannitsis, E.; Gopi, V. Biomarkers for infarct diagnosis and rapid rule-out/rule-in of acute myocardial infarction. Herz 2020, 45, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, R.V.; Devasiya, T.V.R.N.; Adigal, S.; Lukose, J.; Kartha, V.B.; Chidangil, S. Cardiovascular biomarkers in body fluids: Progress and prospects in optical sensors. Biophys. Rev. 2022, 14, 1023–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crapnell, R.D.; Dempsey, N.C.; Sigley, E.; Tridente, A.; Banks, C.E. Electroanalytical point-of-care detection of gold standard and emerging cardiac biomarkers for stratification and monitoring in intensive care medicine-a review. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, M.; Tu, D.; Tong, L.; Sarwar, M.; Bhimaraj, A.; Li, C.; Coté, G.L.; Di Carlo, D. A review of biosensor technologies for blood biomarkers toward monitoring cardiovascular diseases at the point-of-care. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.-D.; He, Y.; Wang, S.; Wong, G.T.; Irwin, M.G.; Xia, Z. Heart-type fatty acid binding protein (H-FABP) as a biomarker for acute myocardial injury and long-term post-ischemic prognosis. Acta Pharmacol. 2018, 39, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecollan, P.; Collet, J.-P.; Boon, G.; Tanguy, M.-L.; Fievet, M.-L.; Haas, R.; Bertho, N.; Siami, S.; Hubert, J.-C.; Coriat, P. Pre-hospital detection of acute myocardial infarction with ultra-rapid human fatty acid-binding protein (H-FABP) immunoassay. Int. J. Cardiol. 2007, 119, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byzova, N.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Vengerov, Y.Y.; Starovoitova, T.A.; Dzantiev, B.B. A triple immunochromatographic test for simultaneous determination of cardiac troponin I, fatty acid binding protein, and C-reactive protein biomarkers. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanson, G.T. Bioconjugate Techniques; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Taranova, N.A.; Slobodenuyk, V.D.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Network of gold conjugates for enhanced sensitive immunochromatographic assays of troponins. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 16445–16452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frens, G. Particle size and sol stability in metal colloids. Kolloid Z. Z. Polym. 1972, 250, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byzova, N.A.; Zvereva, E.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Eremin, S.A.; Dzantiev, B.B. Rapid pretreatment-free immunochromatographic assay of chloramphenicol in milk. Talanta 2010, 81, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byzova, N.A.; Zvereva, E.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Eremin, S.A.; Sveshnikov, P.G.; Dzantiev, B.B. Pretreatment-free immunochromatographic assay for the detection of streptomycin and its application to the control of milk and dairy products. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 701, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Gupta, V.B. Methods for the determination of limit of detection and limit of quantitation of the analytical methods. Chron. Young Sci. 2011, 2, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Xu, X.; Guo, L.; Xu, L.; Sun, M.; Hu, S.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C.; Li, A. An Overview for the Nanoparticles-Based Quantitative Lateral Flow Assay. Small Methods 2022, 6, 2101143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopac, T. Protein corona, understanding the nanoparticle–protein interactions and future perspectives: A critical review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 169, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.F.; Yan, Y.R.; Jiang, G.Q.; Adkins, J.; Shi, J.; Jiang, G.M.; Tian, S. Using a silver-enhanced microarray sandwich structure to improve SERS sensitivity for protein detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, M.O.; Covian, L.B.; Garcia, A.C.; Blanco-Lopez, M.C. Silver and gold enhancement methods for lateral flow immunoassays. Talanta 2016, 148, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhao, P.; Astruc, D. Anisotropic gold nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties, applications, and toxicity. Angew. Chem. Int. 2014, 53, 1756–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Li, N.; Astruc, D. State of the art in gold nanoparticle synthesis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 638–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharisov, B.I. A review for synthesis of nanoflowers. Recent Pat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 2, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shende, P.; Kasture, P.; Gaud, R. Nanoflowers: The future trend of nanotechnology for multi-applications. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlebtsov, N.G.; Trachuk, L.A.; Mel’nikov, A.G. The effect of the size, shape, and structure of metal nanoparticles on the dependence of their optical properties on the refractive index of a disperse medium. Opt. Spectrosc. 2005, 98, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Duan, H.; Chen, R.; Ma, T.; Zeng, L.; Leng, Y.; Xiong, Y. Effect of different-sized gold nanoflowers on the detection performance of immunochromatographic assay for human chorionic gonadotropin detection. Talanta 2019, 194, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borse, V.B.; Konwar, A.N.; Jayant, R.D.; Patil, P.O. Perspectives of characterization and bioconjugation of gold nanoparticles and their application in lateral flow immunosensing. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 878–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.-H.; Irudayaraj, J. In-situ immuno-gold nanoparticle network ELISA biosensors for pathogen detection. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 164, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yao, L.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, L.; Liu, G.; Ye, Y.; Chen, W. Gold nanoparticles based lateral flow immunoassay with largely amplified sensitivity for rapid melamine screening. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1989–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhou, T.; Yin, B.; He, P. Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric ELISA for quantification of ractopamine. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, C.R.; Kuang, H.; Hao, C.L.; Liu, L.Q.; Wang, L.B.; Xu, C.L. A silver enhanced and sensitive strip sensor for Cadmium detection. Food Agric. Immunol. 2014, 25, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, X.-B.; Liu, G.-W.; Zhang, B.-B.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, T.; Tang, J.-J.; Li, D.-N.; Wang, Z. A colloidal gold probe-based silver enhancement immunochromatographic assay for the rapid detection of abrin-a. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3710–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-Y.; Chen, M.-H.; Sheng, Z.-C.; Liu, D.-F.; Wu, S.-S.; Lai, W.-H. Development of colloidal gold immunochromatographic signal-amplifying system for ultrasensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in milk. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 62300–62305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovleva, E.A.; Andreeva, I.P.; Grigorenko, V.G.; Osipov, A.P. Immunochromatographic rapid analysis of human heart-type fatty acid-binding protein for acute myocardial infarction diagnosis. Mosc. Univ. Chem. Bull. 2011, 66, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Liu, X.; Ren, X.; Tan, L.; Fu, C.; Wu, Q.; Huang, Z.; Meng, X. Rapid and simultaneous detection of heart-type fatty acid binding protein and cardiac troponin using a lateral flow assay based on metal organic framework@ CdTe nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 7844–7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savin, M.; Mihailescu, C.-M.; Matei, I.; Stan, D.; Moldovan, C.A.; Ion, M.; Baciu, I. A quantum dot-based lateral flow immunoassay for the sensitive detection of human heart fatty acid binding protein (hFABP) in human serum. Talanta 2018, 178, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, C.; Jin, J.; Huang, L.; Yu, W.; Su, B.; Hu, J. Ratiometric Fluorescent Lateral Flow Immunoassay for Point-of-Care Testing of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 13152–13159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Wojnowski, W.; Tobiszewski, M. AGREE—Analytical GREEnness Metric Approach and Software. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10076–10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Biotinylated Protein | LOD, ng/mL | Cut off, ng/mL |
|---|---|---|
| Bovine serum albumin | 0.7 | 2.3 |
| Soybean trypsin inhibitor | 2 | 11.2 |
| Labels of the Formed Immune Complexes | LOD, ng/mL | Cut off, ng/mL |
|---|---|---|
| sGNP–IgG | 11.2 | 33 |
| GNF–IgG | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| sGNP–IgG–biotin—sGNP–Stp—sGNP–biotin | 0.7 | 2.3 |
| GNF–IgG–biotin—sGNP–Stp—GNF–biotin | 0.1 | 1 |
| GNF–IgG–biotin—sGNP–Stp—GNF–biotin + reduced gold salt | 0.05 | 0.4 |
| Marker | Detection Technique | LOD, ng/mL | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gold nanoparticles | Photometry | 3.8 | [26] |
| Gold nanoparticles | Photometry | 1.5 | [50] |
| ZrMOF@CdTe quantum dots | Fluorimetry | 1 | [51] |
| CdTe quantum dots | Fluorimetry | 0.221 | [52] |
| Fluorescence composite nanostructures | Fluorimetry | 0.21 | [53] |
| Combined gold markers with catalytic enhancement | Photometry | 0.05 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taranova, N.A.; Bulanaya, A.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Triple Enhancement for Sensitive Immunochromatographic Assay: A Case Study for Human Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121166
Taranova NA, Bulanaya AA, Zherdev AV, Dzantiev BB. Triple Enhancement for Sensitive Immunochromatographic Assay: A Case Study for Human Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Detection. Biosensors. 2022; 12(12):1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121166
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaranova, Nadezhda A., Alisa A. Bulanaya, Anatoly V. Zherdev, and Boris B. Dzantiev. 2022. "Triple Enhancement for Sensitive Immunochromatographic Assay: A Case Study for Human Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Detection" Biosensors 12, no. 12: 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121166
APA StyleTaranova, N. A., Bulanaya, A. A., Zherdev, A. V., & Dzantiev, B. B. (2022). Triple Enhancement for Sensitive Immunochromatographic Assay: A Case Study for Human Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Detection. Biosensors, 12(12), 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121166







