Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensor for Electrochemical Detection of Cortisol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Discussion
3.1. Cortisol Antibody
3.2. Aptamer
4. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer
4.1. Bulk Imprinting
4.1.1. Thermal Polymerization
4.1.2. Photopolymerization
4.1.3. Radical Polymerization
4.1.4. Free Radical Polymerization
4.2. Surface Imprinting
5. MIP Optimization and Electrochemical Detection of Cortisol
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. COVID-19 Pandemic Triggers 25% Increase in Prevalence of Anxiety and Depression Worldwide; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Salari, N.; Hosseinian-Far, A.; Jalali, R.; Vaisi-Raygani, A.; Rasoulpoor, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Rasoulpoor, S.; Khaledi-Paveh, B. Prevalence of Stress, Anxiety, Depression among the General Population during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Glob. Health 2020, 16, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parlak, O.; Keene, S.T.; Marais, A.; Curto, V.F.; Salleo, A. Molecularly Selective Nanoporous Membrane-Based Wearable Organic Electrochemical Device for Noninvasive Cortisol Sensing. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeasmin, S.; Wu, B.; Liu, Y.; Ullah, A.; Cheng, L.J. Nano Gold-Doped Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor for Rapid and Ultrasensitive Cortisol Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 206, 114142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, E.; Göktug, Ö.; İnam, R.; Doyduk, D. Development and Characterization of Iron (III) Phthalocyanine Modified Carbon Nanotube Paste Electrodes and Application for Determination of Fluometuron Herbicide as an Electrochemical Sensor. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 895, 115389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavičius, S.; Morkvėnaitė-Vilkončienė, I.; Samukaitė-Bubnienė, U.; Ratautaitė, V.; Plikusienė, I.; Viter, R.; Ramanavičius, A. Electrochemically Deposited Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors. Sensors 2022, 22, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugo, S.M.; Alberkant, J. Flexible Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor for Cortisol Monitoring in Sweat. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 1825–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapnell, R.D.; Dempsey-Hibbert, N.C.; Peeters, M.; Tridente, A.; Banks, C.E. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Electrochemical Biosensors: Overcoming the Challenges of Detecting Vital Biomarkers and Speeding up Diagnosis. Talanta Open 2020, 2, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, E.; Mustafa, Y.L.; Herdes, C.; Leese, H.S. Optimization of Cortisol-Selective Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Enabled by Molecular Dynamics Simulations. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 7243–7253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, C. Chronic Heart Failure: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment. Nurs. Older People 2014, 26, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, B.; Reeder, J.T.; Seo, S.H.; Lee, S.U.; Hourlier-Fargette, A.; Shin, J.; Sekine, Y.; Jeong, H.; Oh, Y.S.; et al. Soft, Skin-Interfaced Microfluidic Systems with Integrated Immunoassays, Fluorometric Sensors, and Impedance Measurement Capabilities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States Am. 2020, 117, 27906–27915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomello, G.; Scholten, A.; Parr, M.K. Current Methods for Stress Marker Detection in Saliva. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 191, 113604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Shi, W.; Tian, L.; Su, M.; Jiang, M.; Li, J.; Gu, H.; Yu, C. Preparation of Nanostructured PDMS Film as Flexible Immunosensor for Cortisol Analysis in Human Sweat. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1184, 339010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, A.; Vasudev, A.; Arya, S.K.; Pasha, S.K.; Bhansali, S. Recent Advances in Cortisol Sensing Technologies for Point-of-Care Application. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zea, M.; Bellagambi, F.G.; Ben Halima, H.; Zine, N.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Villa, R.; Gabriel, G.; Errachid, A. Electrochemical Sensors for Cortisol Detections: Almost There. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 132, 116058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearlmutter, P.; DeRose, G.; Samson, C.; Linehan, N.; Cen, Y.; Begdache, L.; Won, D.; Koh, A. Sweat and Saliva Cortisol Response to Stress and Nutrition Factors; Nature Publishing Group UK: London, UK, 2020; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, E.; Koren, G.; Rieder, M.; Van Uum, S.H.M. The Detection of Cortisol in Human Sweat: Implications for Measurement of Cortisol in Hair. Ther. Drug Monit. 2014, 36, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogeser, M.; Jacob, K. Improved HPLC Method for the Determination of Cortisol and Cortisone in Urine. J. Lab. Med. 2000, 24, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Xie, Q.; Jin, J.; Qiao, T.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Deng Huihua, H.; Lu, Z. HPLC-FLU Detection of Cortisol Distribution in Human Hair. Clin. Biochem. 2010, 43, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharef, O.; Feely, J.; Kavanagh, P.; Scott, K.; Sharma, S. An HPLC Method for the Determination of Cortisol/Cortisone Ratio in Human Urine. Biomed. Chromatogr. BMC 2007, 21, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, S.E.; Haegele, A.D. Differential Measurement of Cortisol and Cortisone in Human Saliva by HPLC with Uv Detection. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 1991, 14, 1813–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosicka, K.; Siemiątkowska, A.; Szpera-Goździewicz, A.; Krzyścin, M.; Bręborowicz, G.; Główka, F. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Methods for the Analysis of Endogenous Cortisol and Cortisone in Human Urine: Comparison of Mass Spectrometry and Fluorescence Detection. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 56, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lim, H.-S.; Shin, H.-J.; Kim, S.-A.; Park, J.; Kim, H.-C.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.-T.; Lee, K.-R.; et al. Simultaneous Determination of Cortisol and Cortisone from Human Serum by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2014, 2014, 787483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakusic, J.; De Nys, S.; Creta, M.; Godderis, L.; Duca, R.C. Study of Temporal Variability of Salivary Cortisol and Cortisone by LC-MS/MS Using a New Atmospheric Pressure Ionization Source. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spano, G.; Cavalera, S.; Di Nardo, F.; Giovannoli, C.; Anfossi, L.; Baggiani, C. Development of a Biomimetic Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Based on a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for the Detection of Cortisol in Human Saliva. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 2320–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Jiang, Y.; White, T.; Spassova, D. Validation of Nonradioactive Chemiluminescent Immunoassay Methods for the Analysis of Thyroxine and Cortisol in Blood Samples Obtained from Dogs, Cats, and Horses. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1997, 9, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohen, F.; Pazzagli, M.; Kim, J.B.; Lindner, H.R. An Immunoassay for Plasma Cortisol Based on Chemiluminescence. Steroids 1980, 36, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogan, S.F. Neural Stimulation and Recording Electrodes. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 10, 275–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rycke, E.; Foubert, A.; Dubruel, P.; Bol’hakov, O.I.; De Saeger, S.; Beloglazova, N. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Monitoring of Zearalenone in Diverse Matrices. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 129342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourya, A.; Mazumdar, B.; Sinha, S.K. Determination and Quantification of Heavy Metal Ion by Electrochemical Method. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, R.; Williams, T.; Schvaneveldt, M.; Rappleye, D. A Comparison of Square-Wave Voltammetry Models to Determine the Number of Electrons Exchanged in Metal Deposition. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 414, 140220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, M.; Pandiaraj, M.; Bhansali, S.; Ponpandian, N.; Viswanathan, C. Carbon Fiber Based Electrochemical Sensor for Sweat Cortisol Measurement. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhu, S.; Anthuuvan, A.J.; Ramasamy, S.; Manickam, P.; Bhansali, S.; Nagamony, P.; Chinnuswamy, V. ZnO Nanorod Integrated Flexible Carbon Fibers for Sweat Cortisol Detection. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2020, 2, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Tu, J.; Yang, Y.; Min, J.; Wang, M.; Song, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xu, C.; Ye, C.; IsHak, W.W.; et al. Investigation of Cortisol Dynamics in Human Sweat Using a Graphene-Based Wireless MHealth System. Matter 2020, 2, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.B.; Meeseepong, M.; Trung, T.Q.; Kim, B.Y.; Lee, N.E. A Wearable Lab-on-a-Patch Platform with Stretchable Nanostructured Biosensor for Non-Invasive Immunodetection of Biomarker in Sweat. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 156, 112133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Kannan, P.; Natarajan, B.; Maiyalagan, T.; Subramanian, P.; Jiang, Z.; Mao, S. MnO2 Cacti-like Nanostructured Platform Powers the Enhanced Electrochemical Immunobiosensing of Cortisol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 317, 128134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nah, J.S.; Barman, S.C.; Zahed, M.A.; Sharifuzzaman, M.; Yoon, H.; Park, C.; Yoon, S.; Zhang, S.; Park, J.Y. A Wearable Microfluidics-Integrated Impedimetric Immunosensor Based on Ti3C2Tx MXene Incorporated Laser-Burned Graphene for Noninvasive Sweat Cortisol Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munje, R.D.; Muthukumar, S.; Panneer Selvam, A.; Prasad, S. Flexible Nanoporous Tunable Electrical Double Layer Biosensors for Sweat Diagnostics. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnamon, D.; Ghanta, R.; Lin, K.C.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. Portable Biosensor for Monitoring Cortisol in Low-Volume Perspired Human Sweat. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, P.; Upasham, S.; Jagannath, B.; Manuel, R.; Pali, M.; Prasad, S. CortiWatch: Watch-Based Cortisol Tracker. Future Sci. OA 2019, 5, FSO416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Li, X.; Xu, G.; Lu, Y.; Low, S.S.; Liu, G.; Zhu, L.; Li, C.; Liu, Q. Battery-Free, Wireless, and Flexible Electrochemical Patch for in Situ Analysis of Sweat Cortisol via near Field Communication. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 172, 112782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pali, M.; Jagannath, B.; Lin, K.-C.; Upasham, S.; Sankhalab, D.; Upashama, S.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. CATCH (Cortisol Apta WATCH): ‘Bio-Mimic Alarm’ to Track Anxiety, Stress, Immunity in Human Sweat. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 390, 138834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmi, N.; Baradaran, B.; Hejazi, M.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Mosafer, J.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; de la Guardia, M. Recent Advances on Aptamer-Based Biosensors to Detection of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 113, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanghavi, B.J.; Moore, J.A.; Chávez, J.L.; Hagen, J.A.; Kelley-Loughnane, N.; Chou, C.F.; Swami, N.S. Aptamer-Functionalized Nanoparticles for Surface Immobilization-Free Electrochemical Detection of Cortisol in a Microfluidic Device. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 78, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Lee, W.; Park, J.; Kim, W.; Kim, W.; Lee, G.; Lee, H.-J.; Hong, J.; Park, J. Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Aptasensor for the Highly Sensitive Direct Detection of Cortisol in Human Saliva. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 304, 127424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churcher, N.K.M.; Greyling, C.; Upasham, S.; Lin, K.-C.; Rice, P.; Pali, M.; Spiro, J.; Prasad, S. AptaStrensor (Aptamer-Based Sensor for Stress Monitoring): The Interrelationship between NPY and Cortisol towards Chronic Disease Monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2022, 10, 100145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Chen, H.; Ye, H.; Chen, Z.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Guo, Z. An Ultrasensitive Aptamer-Antibody Sandwich Cortisol Sensor for the Noninvasive Monitoring of Stress State. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 190, 113451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, L.; Ding, Y.; Liu, H.; Cui, H. Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on Functionalized Graphene and Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Trace Cortisol Assay. Analyst 2022, 147, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppaiah, G.; Velayutham, J.; Hansda, S.; Narayana, N.; Bhansali, S.; Manickam, P. Towards the Development of Reagent-Free and Reusable Electrochemical Aptamer-Based Cortisol Sensor. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 145, 108098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantelli, L.; Paschoalino, W.J.; Kogikosky, S.; Pessanha, T.M.; Kubota, L.T. DNA Super-Lattice-Based Aptasensor for Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Cortisol. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2022, 12, 100228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belbruno, J.J. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pešić, M.P.; Todorov, M.D.; Becskereki, G.; Horvai, G.; Verbić, T.; Tóth, B. A Novel Method of Molecular Imprinting Applied to the Template Cholesterol. Talanta 2020, 217, 121075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantha-Iyengar, G.; Shanmugasundaram, K.; Nallal, M.; Lee, K.P.; Whitcombe, M.J.; Lakshmi, D.; Sai-Anand, G. Functionalized Conjugated Polymers for Sensing and Molecular Imprinting Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 88, 1–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertuğrul Uygun, H.D.; Uygun, Z.O.; Canbay, E.; Girgin Sağın, F.; Sezer, E. Non-Invasive Cortisol Detection in Saliva by Using Molecularly Cortisol Imprinted Fullerene-Acrylamide Modified Screen Printed Electrodes. Talanta 2020, 206, 120225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klangphukhiew, S.; Srichana, R.; Patramanon, R. Cortisol Stress Biosensor Based on Molecular Imprinted Polymer. Multidiscip. Digit. Publ. Inst. Proc. 2017, 1, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diliën, H.; Peeters, M.; Royakkers, J.; Harings, J.; Cornelis, P.; Wagner, P.; Steen Redeker, E.; Banks, C.E.; Eersels, K.; Van Grinsven, B.; et al. Label-Free Detection of Small Organic Molecules by Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Functionalized Thermocouples: Toward in Vivo Applications. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, N.; Sunayama, H.; Kitayama, Y.; Kamon, Y.; Takeuchi, T. Oriented, Molecularly Imprinted Cavities with Dual Binding Sites for Highly Sensitive and Selective Recognition of Cortisol. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempe, H.; Kempe, M. Ouzo Polymerization: A Bottom-up Green Synthesis of Polymer Nanoparticles by Free-Radical Polymerization of Monomers Spontaneously Nucleated by the Ouzo Effect; Application to Molecular Imprinting. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 616, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, N.; Taniguchi, S.I.; Takano, E.; Kitayama, Y.; Takeuchi, T. A Molecularly Imprinted Nanocavity-Based Fluorescence Polarization Assay Platform for Cortisol Sensing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 1770–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, J.E.L.; Khan, S.; Neres, L.C.S.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T. Preparation of a Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Noninvasive Determination of Cortisol. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gestring, I.; Mewes, D. Degassing of Molten Polymers. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2002, 57, 3415–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, J.; Urbani, C.; Whittaker, M.R.; Monteiro, M.J. Effect of Degassing on Surfactant-Free Emulsion Polymerizations of Styrene Mediated with RAFT. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 904–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, F. Talanta Molecularly Imprinted Monolithic Column-Based SERS Sensor for Selective Detection of Cortisol in Dog Saliva. Talanta 2022, 249, 123609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, C.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Molecularly Imprinted Thin Film Surfaces in Sensing: Chances and Challenges. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 161, 104855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, E.; Khalafi-Nezhad, A.; Mohammadi, A.; Abdouss, M.; Salami-Kalajahi, M. Synthesis of New Molecularly Imprinted Polymer via Reversible Addition Fragmentation Transfer Polymerization as a Drug Delivery System. Polymer 2018, 143, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrier, S. 50th Anniversary Perspective: RAFT Polymerization—A User Guide. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 7433–7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, O.; Josse, T.; Abbasi, M.; De Winter, J.; Trouillet, V.; Gerbaux, P.; Wilhelm, M.; Barner-Kowollik, C. ATRP-Based Polymers with Modular Ligation Points under Thermal and Thermomechanical Stress. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 2854–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Z. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for Atrazine Detection by Electropolymerization of o-Phenylenediamine. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 56534–56540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usha, S.P.; Shrivastav, A.M.; Gupta, B.D. A Contemporary Approach for Design and Characterization of Fiber-Optic-Cortisol Sensor Tailoring LMR and ZnO/PPY Molecularly Imprinted Film. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manickam, P.; Pasha, S.K.; Snipes, S.A.; Bhansali, S. A Reusable Electrochemical Biosensor for Monitoring of Small Molecules (Cortisol) Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, B54–B59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillan, L.; Jansson, E. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer on Roll-to-Roll Printed Electrodes as a Single Use Sensor for Monitoring of Cortisol in Sweat. Flex. Print. Electron. 2022, 7, 025014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Yin, L.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Moon, J.M.; Teymourian, H.; Wang, J. Touch-Based Stressless Cortisol Sensing. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2008465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykstra, G.; Reynolds, B.; Smith, R.; Zhou, K.; Liu, Y. Electropolymerized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Synthesis Guided by an Integrated Data-Driven Framework for Cortisol Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 25972–25983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, D.; Lu, H.; Li, L.; Ding, Y.; Ma, G. A Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensors Based on Bamboo-like Carbon Nanotubes Loaded with Nickel Nanoclusters for Highly Selective Detection of Cortisol. Microchem. J. 2022, 175, 107231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu-Scheers, E.; Bouden, S.; Grillot, C.; Nicolle, J.; Warmont, F.; Bertagna, V.; Cagnon, B.; Vautrin-Ul, C. Trace Anthracene Electrochemical Detection Based on Electropolymerized-Molecularly Imprinted Polypyrrole Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 848, 113253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Thomas, J.L.; Liu, W.C.; Zhang, Z.X.; Liu, B.D.; Yang, C.H.; Lin, H.Y. A Multichannel System Integrating Molecularly Imprinted Conductive Polymers for Ultrasensitive Voltammetric Determination of Four Steroid Hormones in Urine. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, F.W.; Zhang, X.; Yarman, A.; Wollenberger, U.; Gyurcsányi, R.E. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Biopolymers. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 14, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilă, A.M.; Stoica, E.B.; Iordache, T.V.; Sârbu, A. Modern and Dedicated Methods for Producing Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Layers in Sensing Applications. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.J.; Yuan, L.P.; Shen, Y.D.; Liu, Y.X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, S.W.; Xie, Z.X.; Lei, H.T.; Sun, Y.M.; Xu, Z.L. A Full-Automated Magnetic Particle-Based Chemiluminescence Immunoassay for Rapid Detection of Cortisol in Milk. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1035, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotta, E.; Di Giulio, T.; Malitesta, C. Electrochemical Sensing of Macromolecules Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Challenges, Successful Strategies, and Opportunities. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 5165–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cetó, X.; del Valle, M. A Novel Electronic Tongue Using Electropolymerized Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for the Simultaneous Determination of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 198, 113807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
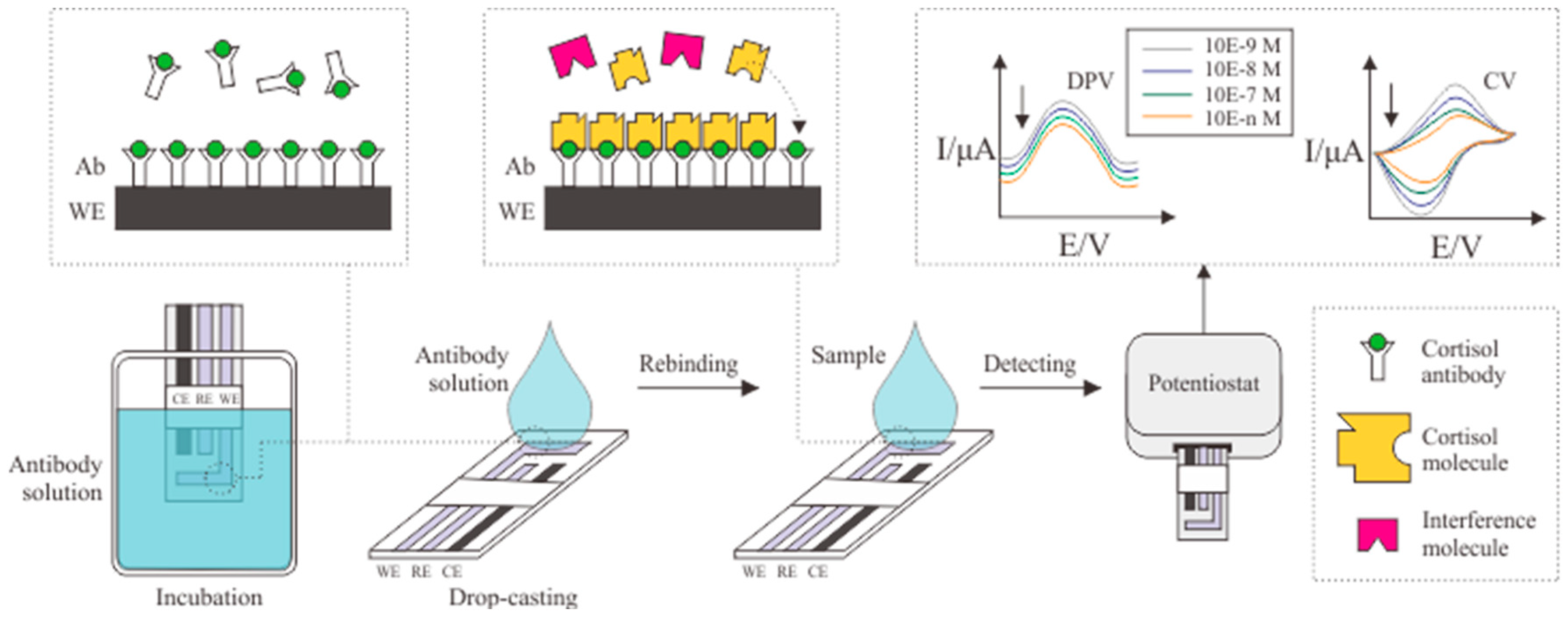
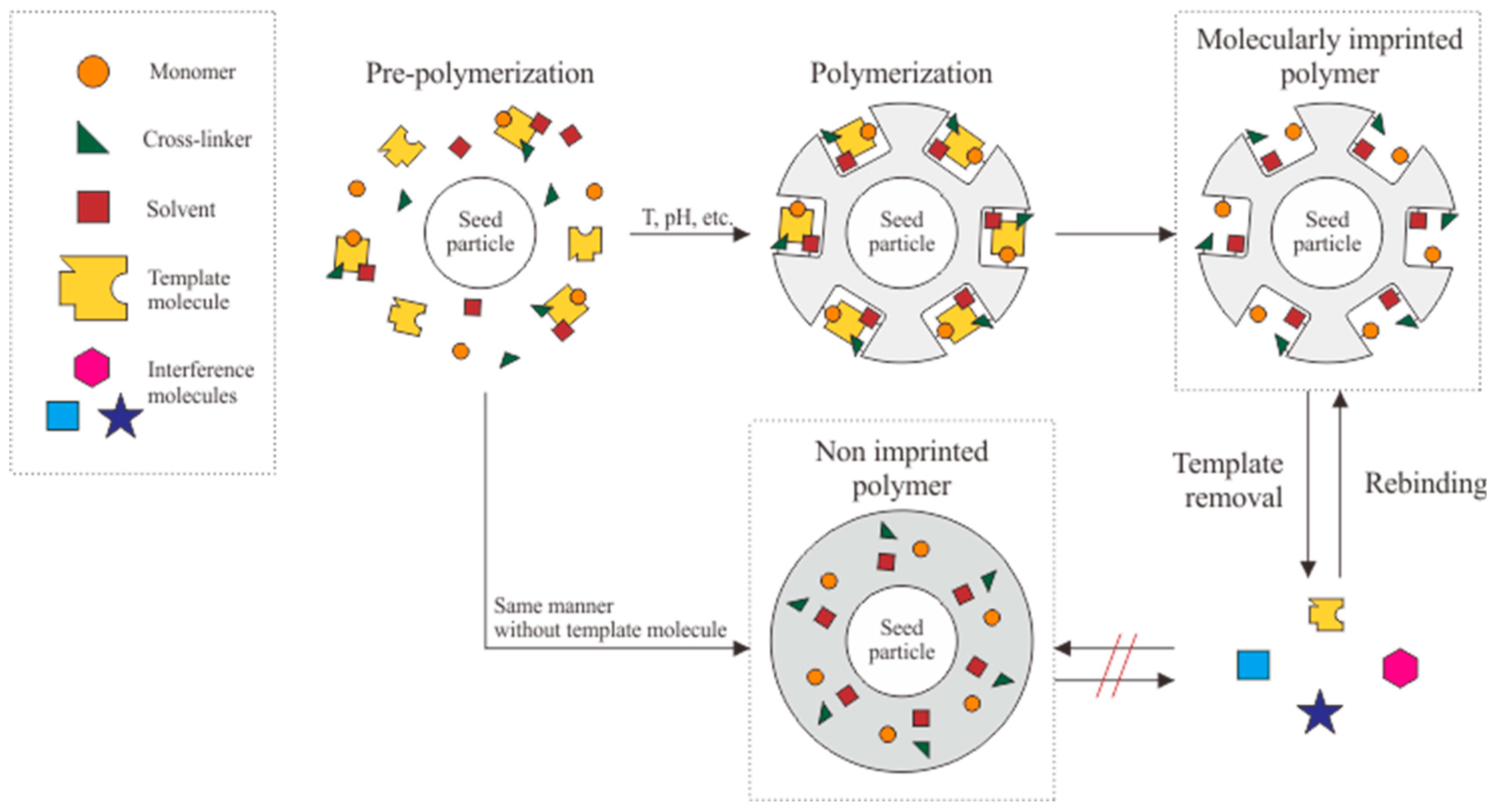

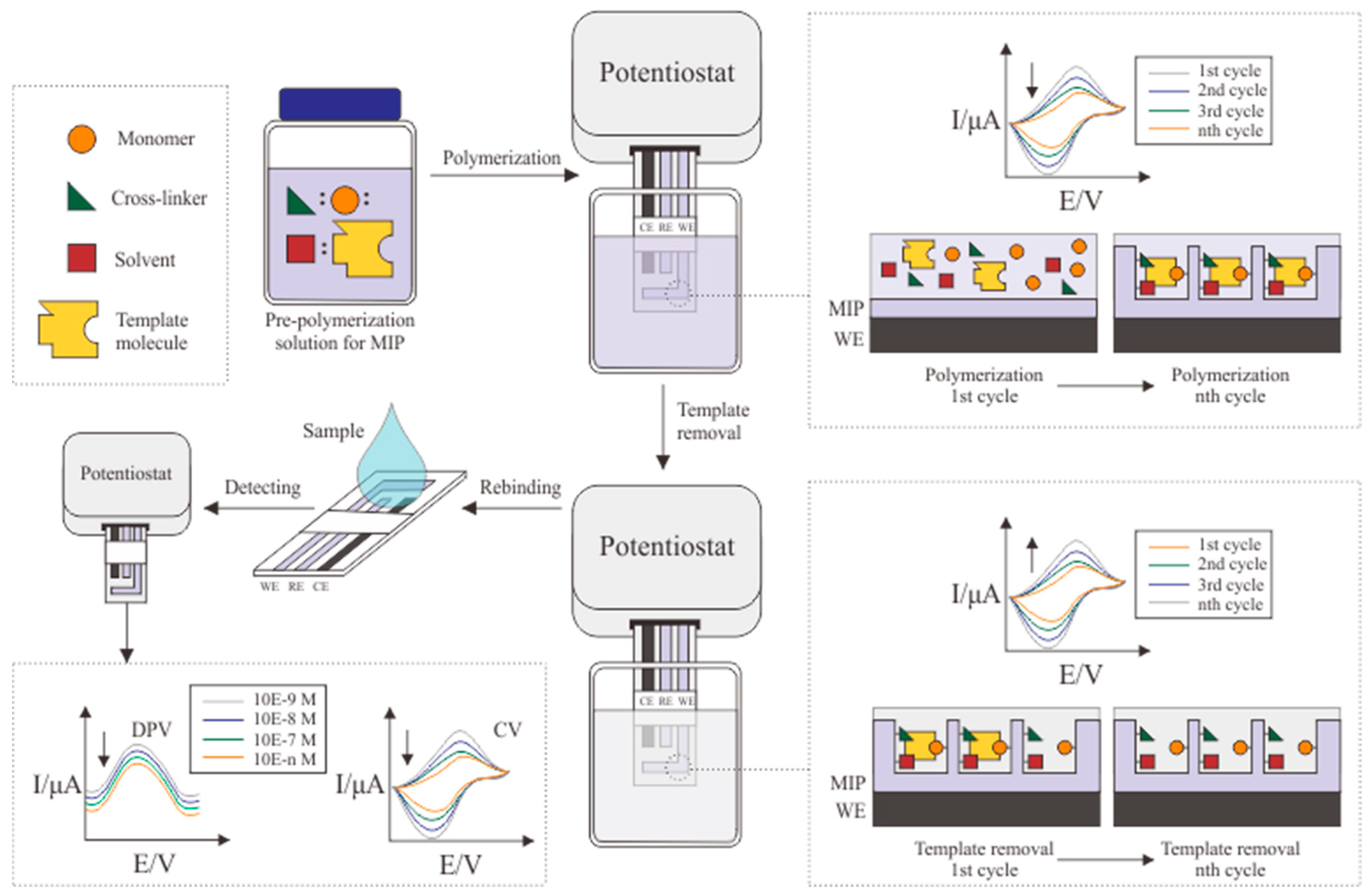
| Electrode | Immobilization Method | Detection Method | Bioreceptor | Linear Range (g/mL) | LOD (g/mL) | Matrix | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AuNPs–MWCNTs–PDMS | Physical adsorption | CV | Cortisol monoclonal antibody | 1 × 10−15 to 1 × 10−6 | 0.3 × 10−15 | Sweat | [13] |
| Carbon yarn | Physical adsorption | DPV, CV | Cortisol monoclonal antibody | 1 × 10−15 to 1 × 10−6 | 5 × 10−18 | Sweat | [32] |
| ZnO nanorod yarn based | Physical adsorption | DPV, CV | Cortisol monoclonal antibody | 1 × 10−15 to 1 × 10−6 | 0.45 × 10−15 CV and 0.098 × 10−15 DPV | Sweat | [33] |
| Graphene | Physical adsorption | DPV | Cortisol monoclonal antibody | 0.43 to 50.2 × 10−9 | 0.08 × 10−9 | Sweat | [34] |
| Au | Physical adsorption | CV, EIS | Cortisol antibody | 1 × 10−12 to 1 × 10−6 | 1 × 10−12 | Sweat | [35] |
| MnO2 | Physical adsorption | EIS | Cortisol antibody | 0.1 to 1500 × 10−12 | 0.023 × 10−12 | Sweat | [36] |
| Laser-burned graphene | Physical adsorption | EIS | Cortisol antibody | 0.01 to 100 × 10−9 | 3.88 × 10−12 | Sweat | [37] |
| ZnO | Cross-linking (DSP) | EIS | Cortisol antibody | 10 to 200 × 10−9 | 1 × 10−9 | Sweat | [38] |
| Pd/MoS2 | Cross-linking (DSP) | EIS | Cortisol antibody | 1 to 500 × 10−9 | 1 × 10−9 | Sweat | [39] |
| Au | Cross-linking (DSP) | CV | Cortisol antibody | 1 × 10−12 to 100 × 10−9 | - | Sweat | [40] |
| Carbon-AuNPs | Physical adsorption | DPV | Cortisol antibody | 22 to 386 × 10−12 | 7.47 × 10−12 | Sweat | [41] |
| Electrode | Immobilization Method | Detection Method | Bioreceptor | Linear Range (g/mL) | LOD (g/mL) | Matrix | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO | Physical adsorption | EIS | Cortisol aptamer | 1 to 256 × 10−9 | 1 × 10−9 | Sweat | [42] |
| AuNPs | Physical adsorption | SWV | Cortisol aptamer | 30 × 10−12 to 10 × 10−6 | 10 × 10−12 | Serum and Saliva | [44] |
| AuNPs | Physical adsorption | LSPR | Cortisol aptamer | 0.03 to 362 × 10−9 | 0.03 × 10−9 | Saliva | [45] |
| Au | Physical adsorption | nF-EIS | Cortisol aptamer | 1 to 256 × 10−9 | - | Sweat | [46] |
| GCE– MWCNTs/CMK-3/AgNPs | Physical adsorption | DPV | Cortisol aptamer | 0.1 × 10−12 to 10 × 10−9 | 0.09 × 10−12 | Saliva | [47] |
| GCE–FG–N-CQDs | Physical adsorption | CV, DPV | Cortisol aptamer | 0.3 × 10−12 to 0.03 × 10−9 | 0.1 × 10−12 | Saliva | [48] |
| Au | Physical adsorption | SWV | Cortisol aptamer | 0.05 to 100 × 10−9 | 0.05 × 10−9 | Serum | [49] |
| AuNPs | Cross-linking (DNA-based superlattice) | EIS | Cortisol aptamer | 181 to 3600 × 10−12 | 47.12 × 10−12 | Saliva | [50] |
| Electrode | Detection Method | Polymer | Solvent | Polymerization Technique | Linear Range (g/mL) | LOD (g/mL) | Matrix | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEDOT/PSS | CV | MAA–EDMA | DCM | Thermal polymerization | 0.03 to 3.6 × 10−6 | - | Sweat | [3] |
| CNC/CNT | CV | MAA-co-EGDMA | Acetonitrile–water | Thermal polymerization | 6 to 60 × 10−9 | 2.0 × 10−9 g/mL ± 0.4 × 10−9 | Sweat | [7] |
| - | UV Analysis | MAA–EGDMA | DCM | Photo polymerization | 0.03 to 0.36 × 10−6 | - | Sweat | [9] |
| - | - | MISA–Acrylamide | Chloroform | Photo-polymerization | 2.5 to 20 × 10−9 | 1.02 × 10−9 | Saliva | [25] |
| SPCE | CV | MAA–Acrylamide | Toluene | Multi-step swelling and polymerization | 0.46 to 7.25 × 10−9 | 0.43 × 10−9 | - | [55] |
| PLLA | DPV | MAA | Chloroform | Bulk polymerization | 3.6 to 29 × 10−6 | 3.6 × 10−6 | - | [56] |
| Gold-coated glass | - | MPC–MBAAm–dimethyl sulfoxide | DCM | SI-AGET ATRP | - | 1.74 × 10−12 | Sweat | [57] |
| - | UV Analysis | PETRA | Ethanol–water | Free radical polymerization | - | 0.69 × 10−6 | - | [58] |
| NPs | - | Itaconic acid–styrene–DVB | THF | Radical polymerization | - | 29 × 10−9 | - | [59] |
| Fe3O4 | UV Analysis | Fe3O4@SiO2-C=C/EGDMA/AIBN | Acetonitrile | Magnetic polymerization | 0.01 to 0.1 × 10−6 | 0.004 × 10−6 | Sweat | [60] |
| Ag | Raman Spectroscopy | MAA–AIBN–EGDMA | Methanol–toluene–dodecanol | Photo polymerization | 0.03 × 10−6 to 0.36 × 10−3 | 0.03 × 10−6 | Sweat | [63] |
| ZnO | UV Analysis | Py | Ethanol | Radical polymerization | 1 × 10−12 to 0.1 × 10−6 | 25.9 × 10−15 | Saliva | [69] |
| Electrode | Detection Method | Polymer | Solvent | Linear Range (g/mL) | LOD (g/mL) | Matrix | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au@GCE | CV, SWV, EIS | o-PD | Acetate buffer solution | 0.36 × 10−12 to 181 × 10−9 | 72.5 × 10−15 | Sweat | [4] |
| SPCE | EIS | Fullerene–acrylamide | PBS | 0.18 to 23 × 10−9 | 0.05 × 10−9 | Sweat | [54] |
| SPCE | CV | Py | PBS | 0.36 × 10−12 to 3.6 × 10−6 | 0.36 × 10−12 | Sweat | [70] |
| SPCE | CV | Py-PB | PBS | 0.1 × 10−9 to 10 × 10−6 | 0.06 × 10−9 | Sweat | [71] |
| Ag/AgCl | CV | Py-PB | PBS | - | 0.207 × 10−9 | Sweat | [72] |
| SPCE | DPV | Py | PBS–KCl | - | 3.6 × 10−12 | - | [73] |
| GCE/NiNC-N-CNTs | DPV | o-PD | PBS | 0.36 to 3 × 10−9 | 0.86 × 10−15 | Sweat | [74] |
| SPCE | CV | ANI-co-metanilic acid | Water | 1 to 1000 × 10−18 | 2 × 10−18 | Urine | [76] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yulianti, E.S.; Rahman, S.F.; Whulanza, Y. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensor for Electrochemical Detection of Cortisol. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121090
Yulianti ES, Rahman SF, Whulanza Y. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensor for Electrochemical Detection of Cortisol. Biosensors. 2022; 12(12):1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121090
Chicago/Turabian StyleYulianti, Elly Septia, Siti Fauziyah Rahman, and Yudan Whulanza. 2022. "Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensor for Electrochemical Detection of Cortisol" Biosensors 12, no. 12: 1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121090
APA StyleYulianti, E. S., Rahman, S. F., & Whulanza, Y. (2022). Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensor for Electrochemical Detection of Cortisol. Biosensors, 12(12), 1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121090






