The Role of Ferroptosis in Osteoporosis and Advances in Chinese Herbal Interventions
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
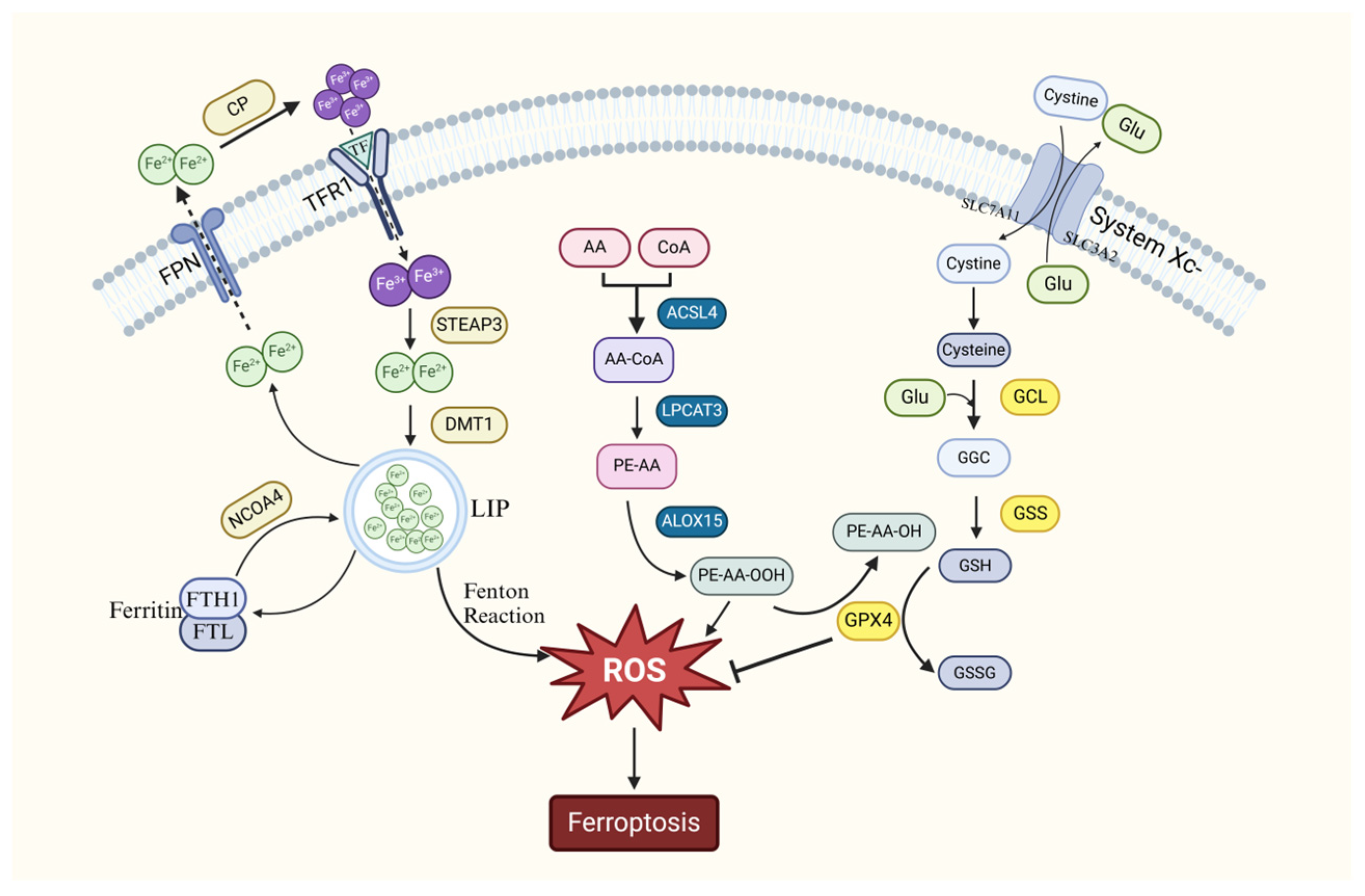
2. The Mechanism of Ferroptosis
2.1. Ferroptosis Caused by Abnormal Iron Metabolism
2.2. Ferroptosis Caused by Oxidative Stress in Cells
2.3. Ferroptosis Caused by Abnormal Lipid Peroxide Metabolism
2.4. Relationship Between Ferroptosis and Autophagy
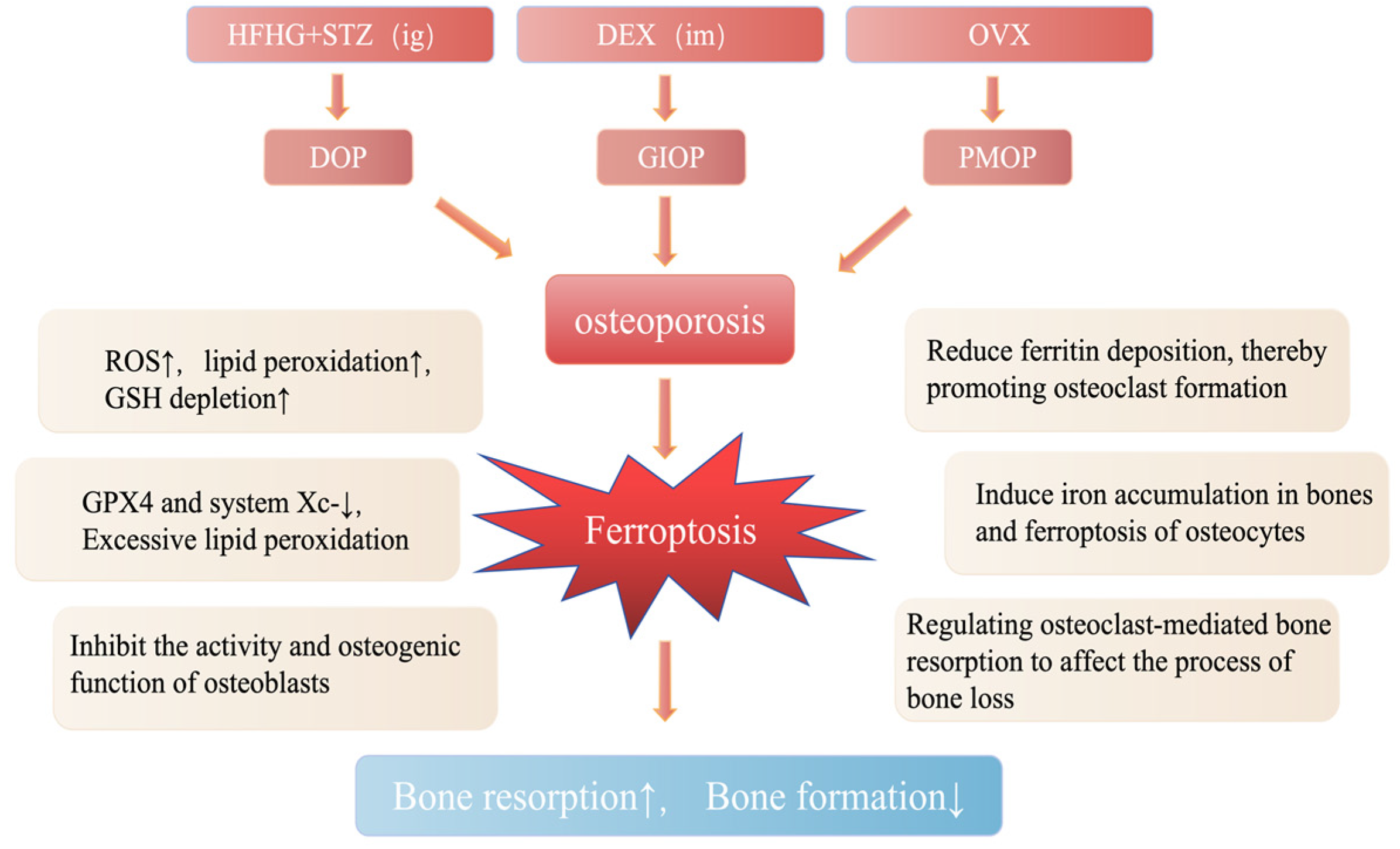
3. Relationship Between Ferroptosis and Osteoporosis
3.1. Diabetic Osteoporosis
3.2. Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
3.3. Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
4. Chinese Herbs Prevents Osteoporosis by Intervening Ferroptosis
4.1. Chinese Herbs
4.1.1. Eucommiae Cortex
4.1.2. Gastrodia Rhizoma
4.1.3. Epimedium Folium
4.1.4. Scutellariae Radix
4.1.5. Drynaria Rhizoma
4.2. Chinese Herbal Remedies
4.2.1. Erxian Decoction
4.2.2. Bugu Shengsui Capsule
4.2.3. Compound Lurong Jiangu Capsule
4.2.4. Xianling Gubao Capsule
4.2.5. Qing’e Pill
4.2.6. Zuogui Pill
4.3. Limitations and Challenges of Chinese Herbal Interventions in Treating OP via Ferroptosis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lyu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, D. Modulation of Bone Remodeling by the Gut Microbiota: A New Therapy for Osteoporosis. Bone Res. 2023, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolpho, L.F.; Gomes, M.P.O.; Freitas, G.P.; Bighetti-Trevisan, R.L.; Ramos, J.I.R.; Campeoti, G.H.; Zatta, G.C.; Almeida, A.L.G.; Tarone, A.G.; Marostica-Junior, M.R.; et al. Jaboticaba Peel Extract Attenuates Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss by Preserving Osteoblast Activity. Biology 2024, 13, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, R.; Aitken, J.M.; Anderson, L.B.; Hart, D.M.; Macdonald, E.B.; Clarke, A.C. Long-Term Prevention of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis by Œstrogen. Lancet 1976, 307, 1038–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xiao, Z.; Quarles, L.D.; Li, W. Osteoporosis: Mechanism, Molecular Target and Current Status on Drug Development. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 1489–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, C.M.; Alexander, D.D.; Boushey, C.J.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Lappe, J.M.; LeBoff, M.S.; Liu, S.; Looker, A.C.; Wallace, T.C.; Wang, D.D. Calcium plus Vitamin D Supplementation and Risk of Fractures: An Updated Meta-Analysis from the National Osteoporosis Foundation. Osteoporos. Int. 2016, 27, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, M.T.; Clarke, B.L.; Khosla, S. Bisphosphonates: Mechanism of Action and Role in Clinical Practice. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 1032–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpe, M.; Noble, S.; Spencer, C.M. Alendronate. Drugs 2001, 61, 999–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahle, J.L.; Long, G.G.; Sandusky, G.; Westmore, M.; Ma, Y.L.; Sato, M. Bone Neoplasms in F344 Rats Given Teriparatide [rhPTH(1-34)] Are Dependent on Duration of Treatment and Dose. Toxicol. Pathol. 2004, 32, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wang, Z.; You, X.; Zhou, H.; He, W.; Li, B.; Xia, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, G.; et al. Resveratrol Promotes Osteogenesis and Alleviates Osteoporosis by Inhibiting P53. Aging 2020, 12, 10359–10369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Yan, Y.; Zuo, D.; Zhuo, Z.; Sun, T.; Lin, H.; Han, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, H. Iron Metabolism and Ferroptosis in Diabetic Bone Loss: From Mechanism to Therapy. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1178573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; You, X.; Zhou, H.; He, W.; Li, Z.; Li, B.; Xia, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, G.; et al. MiR-16-5p Regulates Postmenopausal Osteoporosis by Directly Targeting VEGFA. Aging 2020, 12, 9500–9514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Shen, J.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Li, G.; Wang, Q.; Feng, X.; Qin, M.; et al. Mechanisms of Ferroptosis in Bone Disease: A New Target for Osteoporosis Treatment. Cell. Signal. 2025, 127, 111598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, E.D. Denosumab: A Review in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Drugs Aging 2018, 35, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Naguro, I.; Ichijo, H. Iron Homeostasis and Iron-Regulated ROS in Cell Death, Senescence and Human Diseases. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Swelm, R.P.L.; Wetzels, J.F.M.; Swinkels, D.W. The Multifaceted Role of Iron in Renal Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhou, L.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shen, J.; Ma, T.; Wang, Q.; et al. Advances in Exosome Modulation of Ferroptosis for the Treatment of Orthopedic Diseases. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2024, 257, 155312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D. Progress in the Study of Ferroptosis in Cancer Treatment: State-of-the-Art. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2023, 371, 110348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Lu, D. Ferroptotic Cell Death: New Regulatory Mechanisms for Metabolic Diseases. Endocrine, Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2021, 21, 785–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Liu, X. Ferroptosis—A New Target of Osteoporosis. Phytother. Res. 2022, 165, 111836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, G.; Yan, Y.; Lee, H.; Koppula, P.; Wu, S.; Zhuang, L.; Fang, B.; et al. DHODH-Mediated Ferroptosis Defence Is a Targetable Vulnerability in Cancer. Nature 2021, 593, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Aki, T.; Unuma, K.; Uemura, K. Chemically Induced Models of Parkinson’s Disease: History and Perspectives for the Involvement of Ferroptosis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 581191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Yan, Y.-L.; Liu, C.; Bo, L.; Li, G.-F.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.-J. Therapeutic Effect of Deferoxamine on Iron Overload-Induced Inhibition of Osteogenesis in a Zebrafish Model. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2014, 94, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, D.; Wu, J.; Xing, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xia, Y.; Zhou, P.; Xu, S. Iron Overload Threatens the Growth of Osteoblast Cells via Inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/FOXO3a/DUSP14 Signaling Pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 15668–15677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Yang, J.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L.; Peng, S.; Shang, P. The Effect of Abnormal Iron Metabolism on Osteoporosis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 195, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baschant, U.; Rauner, M.; Balaian, E.; Weidner, H.; Roetto, A.; Platzbecker, U.; Hofbauer, L.C. Wnt5a Is a Key Target for the Pro-Osteogenic Effects of Iron Chelation on Osteoblast Progenitors. Haematologica 2016, 101, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Wen, X.; Liu, W.; Hu, H.; Ye, B.; Zhou, Y. Comparison of the Effects of Deferasirox, Deferoxamine, and Combination of Deferasirox and Deferoxamine on an Aplastic Anemia Mouse Model Complicated with Iron Overload. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, T.; Gao, F. Mechanism and Application Prospect of Ferroptosis Inhibitors in Improving Osteoporosis. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1492610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, W. [Salvianolic Acid B Promotes the Proliferation, Migration and Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Gingival Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Activating the PI3K/AKT Pathway]. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi = Chin. J. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 37, 815–820. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, M. Effect of Desferrioxamine and Deferiprone (L1) on the Proliferation of MG-63 Bone Cells and on Phosphatase Alkaline Activity. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc.—Eur. Ren. Assoc. 1998, 13, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messa, E.; Carturan, S.; Maffe, C.; Pautasso, M.; Bracco, E.; Roetto, A.; Messa, F.; Arruga, F.; Defilippi, I.; Rosso, V.; et al. Deferasirox Is a Powerful NF-kappaB Inhibitor in Myelodysplastic Cells and in Leukemia Cell Lines Acting Independently from Cell Iron Deprivation by Chelation and Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging. Haematologica 2010, 95, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Cao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Duan, X.; Li, Y.; Kong, N.; Tian, R.; Wang, K.; et al. [Melatonin Promotes Osteogenesis of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Improving the Inflammatory State in Ovariectomized Rats]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi = Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi = Chin. J. Reparative Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 37, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, H.; Qi, G.; Jiang, C.; Chen, K.; Yan, Z. Iron Overload-induced Ferroptosis of Osteoblasts Inhibits Osteogenesis and Promotes Osteoporosis: An in Vitro and in Vivo Study. IUBMB Life 2022, 74, 1052–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Lin, B.; Deng, X.; Huang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, N. VDR Activation Attenuates Osteoblastic Ferroptosis and Senescence by Stimulating the Nrf2/GPX4 Pathway in Age-Related Osteoporosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 193, 720–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Yu, X.; Tu, J.; Zhang, Z. Ferroptosis: A New Regulatory Mechanism in Osteoporosis. Phytomedicine 2023, 2022, 2634431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Z.; E, M.; Qi, H.; et al. Therapeutic Application of Natural Products: NAD+ Metabolism as Potential Target. Phytomedicine 2023, 114, 154768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.-M.; Yoo, H.J.; Lee, K.-W. High Molecular Weight Fucoidan Restores Intestinal Integrity by Regulating Inflammation and Tight Junction Loss Induced by Methylglyoxal-Derived Hydroimidazolone-1. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Peng, Y.; Peng, X.; Zhuo, L.; Jiang, W. Natural Product Evodiamine-Inspired Medicinal Chemistry: Anticancer Activity, Structural Optimization and Structure-Activity Relationship. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 247, 115031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Monian, P.; Quadri, N.; Ramasamy, R.; Jiang, X. Glutaminolysis and Transferrin Regulate Ferroptosis. Mol. Cell 2015, 59, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Chen, X.; Kang, R.; Kroemer, G. Ferroptosis: Molecular Mechanisms and Health Implications. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theil, E.C. Ferritin: The Protein Nanocage and Iron Biomineral in Health and in Disease. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 12223–12233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Lv, H.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, L.; Wang, S.; Luo, J.; Liu, J.; Shang, P. Iron and Leukemia: New Insights for Future Treatments. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajoolabady, A.; Aslkhodapasandhokmabad, H.; Libby, P.; Tuomilehto, J.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Penninger, J.M.; Richardson, D.R.; Tang, D.; Zhou, H.; Wang, S.; et al. Ferritinophagy and Ferroptosis in the Management of Metabolic Diseases. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 32, 444–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Xie, Y.; Song, X.; Sun, X.; Lotze, M.T.; Zeh, H.J.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Autophagy Promotes Ferroptosis by Degradation of Ferritin. Autophagy 2016, 12, 1425–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Monian, P.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, W.; Xiang, J.; Jiang, X. Ferroptosis Is an Autophagic Cell Death Process. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, B.R.; Jiang, X.; Gu, W. Emerging Mechanisms and Disease Relevance of Ferroptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.W.; Amante, J.J.; Chhoy, P.; Elaimy, A.L.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.J.; Baer, C.E.; Dixon, S.J.; Mercurio, A.M. Prominin2 Drives Ferroptosis Resistance by Stimulating Iron Export. Dev. Cell 2019, 51, 575–586.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Song, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, Q.; Gao, Y.; Lu, G.; Luo, C. Ferroptosis Mediated by Lipid Reactive Oxygen Species: A Possible Causal Link of Neuroinflammation to Neurological Disorders. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5005136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yan, C.; He, L.; Xiang, S.; Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Inhibition of Ferroptosis through Regulating Neuronal Calcium Homeostasis: An Emerging Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer’s Disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 87, 101899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitalakumar, D.; Sharma, A.; Flora, S.J.S. Ferroptosis: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Biochem. Mol. Tox 2021, 35, e22830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Chen, Z.; Wu, D.; Chen, L. Ferritinophagy/Ferroptosis: Iron-related Newcomers in Human Diseases. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 9179–9190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Cao, W.; Jia, Y.; Lu, N. The Application of Ferroptosis in Diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, J.T.; Cahill, C.M. Iron-Responsive-like Elements and Neurodegenerative Ferroptosis. Learn. Mem. 2020, 27, 395–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, X.; Zeng, Y.; Mo, X.; Hong, S.; He, H.; Li, J.; Fatima, S.; Liu, Q. Oxidative Stress Induces Mitochondrial Iron Overload and Ferroptotic Cell Death. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-H.; Song, C.-C.; Pantopoulos, K.; Wei, X.-L.; Zheng, H.; Luo, Z. Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress Mediated Fe-Induced Ferroptosis via the NRF2-ARE Pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 180, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, B.R.; Friedmann Angeli, J.P.; Bayir, H.; Bush, A.I.; Conrad, M.; Dixon, S.J.; Fulda, S.; Gascón, S.; Hatzios, S.K.; Kagan, V.E.; et al. Ferroptosis: A Regulated Cell Death Nexus Linking Metabolism, Redox Biology, and Disease. Cell 2017, 171, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, S.; Wang, H. α-Lipoic Acid Alleviates Ferroptosis in the MPP+-induced PC12 Cells via Activating the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 Pathway. Cell Biol. Int. 2021, 45, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, M.; Ge, Y.; Chen, J.; Ma, J.; Wang, C.; Sun, M.; Wang, L.; Yao, S.; Yao, C. β-Amyloid Protein Induces Mitophagy-Dependent Ferroptosis through the CD36/PINK/PARKIN Pathway Leading to Blood–Brain Barrier Destruction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magtanong, L.; Ko, P.-J.; To, M.; Cao, J.Y.; Forcina, G.C.; Tarangelo, A.; Ward, C.C.; Cho, K.; Patti, G.J.; Nomura, D.K.; et al. Exogenous Monounsaturated Fatty Acids Promote a Ferroptosis-Resistant Cell State. Cell Chem. Biol. 2019, 26, 420–432.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Palte, M.J.; Deik, A.A.; Li, H.; Eaton, J.K.; Wang, W.; Tseng, Y.-Y.; Deasy, R.; Kost-Alimova, M.; Dančík, V.; et al. A GPX4-Dependent Cancer Cell State Underlies the Clear-Cell Morphology and Confers Sensitivity to Ferroptosis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, M.; Liu, Y.; Teng, X.; Gu, X. 4-Tert-Butylphenol Triggers Common Carp Hepatocytes Ferroptosis via Oxidative Stress, Iron Overload, SLC7A11/GSH/GPX4 Axis, and ATF4/HSPA5/GPX4 Axis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 242, 113944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland, A.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Lan, X.; Han, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, J. Ferroptosis and Its Role in Diverse Brain Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 4880–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zou, T.; Tuo, Q.; Xu, S.; Li, H.; Belaidi, A.A.; Lei, P. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms and Links with Diseases. Sig Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Wei, C.; Liu, G.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Cai, S.; Fang, L. Sorafenib Attenuates Liver Fibrosis by Triggering Hepatic Stellate Cell Ferroptosis via HIF-1α/SLC7A11 Pathway. Cell Prolif. 2022, 55, e13158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shen, Y.; Chen, C.; Sui, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J. The Crosstalk between Autophagy and Ferroptosis: What Can We Learn to Target Drug Resistance in Cancer? Cancer Biol. Med. 2019, 16, 630–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, A. Acid Sphingomyelinase Mediates Ferroptosis Induced by High Glucose via Autophagic Degradation of GPX4 in Type 2 Diabetic Osteoporosis. Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana-Codina, N.; Gikandi, A.; Mancias, J.D. The Role of NCOA4-Mediated Ferritinophagy in Ferroptosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1301, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Meng, L.; Han, L.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, H.; Kang, R.; Wang, X.; Tang, D.; Dai, E. Lipid Storage and Lipophagy Regulates Ferroptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 508, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Chen, P.; Liu, J.; Zhu, S.; Kroemer, G.; Klionsky, D.J.; Lotze, M.T.; Zeh, H.J.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Clockophagy Is a Novel Selective Autophagy Process Favoring Ferroptosis. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xu, W.; Zheng, H.; Zheng, X.; Li, B.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, S. Exosomes Derived from Vascular Endothelial Cells Antagonize Glucocorticoid-induced Osteoporosis by Inhibiting Ferritinophagy with Resultant Limited Ferroptosis of Osteoblasts. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 6691–6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostis, P.; Paschou, S.A.; Gkekas, N.N.; Artzouchaltzi, A.-M.; Christou, K.; Stogiannou, D.; Vryonidou, A.; Potoupnis, M.; Goulis, D.G. Efficacy of Anti-Osteoporotic Medications in Patients with Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review. Endocrine 2018, 60, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, J.N.; Drake, M.T.; Amin, S.; Melton, L.J.; McCready, L.K.; Khosla, S. In Vivo Assessment of Bone Quality in Postmenopausal Women With Type 2 Diabetes. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, S.; LeRoith, D. Diabetes and Fragility Fractures—A Burgeoning Epidemic? Bone 2008, 43, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napoli, N.; Chandran, M.; Pierroz, D.D.; Abrahamsen, B.; Schwartz, A.V.; Ferrari, S.L.; IOF Bone and Diabetes Working Group. Mechanisms of Diabetes Mellitus-Induced Bone Fragility. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eller-Vainicher, C.; Cairoli, E.; Grassi, G.; Grassi, F.; Catalano, A.; Merlotti, D.; Falchetti, A.; Gaudio, A.; Chiodini, I.; Gennari, L. Pathophysiology and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Bone Fragility. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 7608964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Zhao, W.; Sun, J.; Yang, M. Melatonin Suppresses Ferroptosis Induced by High Glucose via Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in Type 2 Diabetic Osteoporosis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 9067610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, M.; Yuan, K.; Wang, Q.; Mu, P.; Du, J.; Yu, Z.; Yang, S.; Huang, K.; et al. Targeting Ferroptosis Suppresses Osteocyte Glucolipotoxicity and Alleviates Diabetic Osteoporosis. Bone Res. 2022, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Ji, C.; Wang, Y.-N.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Xu, X.; Zhang, D. Maresin1 Suppresses High-Glucose-Induced Ferroptosis in Osteoblasts via NRF2 Activation in Type 2 Diabetic Osteoporosis. Cells 2022, 11, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krümmel, B.; von Hanstein, A.-S.; Plötz, T.; Lenzen, S.; Mehmeti, I. Differential Effects of Saturated and Unsaturated Free Fatty Acids on Ferroptosis in Rat β-Cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 106, 109013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Li, Z.; Xia, P.; Shi, A.; FuChen, X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, P. Ferroptosis and Ferritinophagy in Diabetes Complications. Mol. Metab. 2022, 60, 101470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Zhou, B.; Young, J.L.; Wintergerst, K.; Cai, L. Exposure to Low-Dose Cadmium Induces Testicular Ferroptosis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 234, 113373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Tan, K.; Yao, Z.; Lin, B.; Zhang, D.; Chen, W.-K.; Mao, S.; Zhang, W.; Chen, L.; Lin, Z.; et al. A Novel Anti-Osteoporosis Mechanism of VK2: Interfering with Ferroptosis via AMPK/SIRT1 Pathway in Type 2 Diabetic Osteoporosis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 2745–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.-Y.; Xu, C.; Xu, Y.-N.; Du, S.-Q.; Dai, Z.-H.; Jin, S.-Q.; Zheng, G.; Xie, C.-L.; Fang, W.-L. Poliumoside Protects against Type 2 Diabetes-Related Osteoporosis by Suppressing Ferroptosis via Activation of the Nrf2/GPX4 Pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 125, 155342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotiyarnwong, P.; McCloskey, E.V. Pathogenesis of Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis and Options for Treatment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandewalle, J.; Luypaert, A.; De Bosscher, K.; Libert, C. Therapeutic Mechanisms of Glucocorticoids. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunim, J.J. Studies on Metacortandralone and Metacortandracin in Rheumatoid Arthritis; Antirheumatic Potency, Metabolic Effects, and Hormonal Properties. JAMA 1955, 157, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttgereit, F. Views on Glucocorticoid Therapy in Rheumatology: The Age of Convergence. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzoli, R.; Biver, E. Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis: Who to Treat with What Agent? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compston, J. Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis: An Update. Endocrine 2018, 61, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Staa, T.P.; Leufkens, H.G.M.; Abenhaim, L.; Zhang, B.; Cooper, C. Use of Oral Corticosteroids and Risk of Fractures. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2000, 15, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersuker, K.; Hendricks, J.M.; Li, Z.; Magtanong, L.; Ford, B.; Tang, P.H.; Roberts, M.A.; Tong, B.; Maimone, T.J.; Zoncu, R.; et al. The CoQ Oxidoreductase FSP1 Acts Parallel to GPX4 to Inhibit Ferroptosis. Nature 2019, 575, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, X.; Fang, S. Extracellular Vesicles from Endothelial Progenitor Cells Prevent Steroid-Induced Osteoporosis by Suppressing the Ferroptotic Pathway in Mouse Osteoblasts Based on Bioinformatics Evidence. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Peng, H. Dexamethasone Induces Ferroptosis via P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 Pathway in Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 602, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.; He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, T.; Li, C. Ferroptosis Is Partially Responsible for Dexamethasone-Induced T Cell Ablation, but Not Osteoporosis in Larval Zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 242, 113872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, N.; Hao, L.; Zhou, W.; Li, L.; Liu, L.; Yang, F.; Xu, L.; Yao, G.; Zhu, C.; et al. Melatonin Inhibits the Ferroptosis Pathway in Rat Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Axis to Attenuate Steroid-Induced Osteoporosis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 8223737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amelio, P.; Cristofaro, M.A.; Tamone, C.; Morra, E.; Di Bella, S.; Isaia, G.; Grimaldi, A.; Gennero, L.; Gariboldi, A.; Ponzetto, A.; et al. Role of Iron Metabolism and Oxidative Damage in Postmenopausal Bone Loss. Bone 2008, 43, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okyay, E.; Ertugrul, C.; Acar, B.; Sisman, A.R.; Onvural, B.; Ozaksoy, D. Comparative Evaluation of Serum Levels of Main Minerals and Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Maturitas 2013, 76, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Zhang, H.; He, W.; Zhang, H. Iron Accumulation and Its Impact on Osteoporotic Fractures in Postmenopausal Women. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2023, 24, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.; Zhou, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, Y.; Chen, X.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Yan, S. Suppression of IRF9 Promotes Osteoclast Differentiation by Decreased Ferroptosis via STAT3 Activation. Inflammation 2024, 47, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Luo, H.; Wang, L.; Deng, Q.; Kui, W.; Da, W.; Chen, L.; Liu, S.; Xue, Y.; Yang, J.; et al. Aconine Attenuates Osteoclast-Mediated Bone Resorption and Ferroptosis to Improve Osteoporosis via Inhibiting NF-κB Signaling. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1234563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Qi, G.; He, X.; Yu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zou, W.; Yuan, H. Ferroptosis in Osteocytes as a Target for Protection Against Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2307388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, G.; Chen, B.; He, Q.; Mai, J.; Chen, W.; Pan, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; et al. Quercetin Protects against Iron Overload-Induced Osteoporosis through Activating the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Life Sci. 2023, 322, 121326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, X.; Li, L.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Hu, M. Structural Characterization and Anti-Osteoporosis Effects of Polysaccharide Purified from Eucommia Ulmoides Oliver Cortex Based on Its Modulation on Bone Metabolism. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 306, 120601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, M. Eucommia Ulmoides Oliver Polysaccharide Alleviates Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis by Stimulating Bone Formation via ERK/BMP-2/SMAD Signaling. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Sun, R.; Yang, H.; Gu, T.; Han, M.; Yu, C.; Chen, P.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, T.; Ding, Y.; et al. Aucubin Promotes BMSCs Proliferation and Differentiation of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Patients by Regulating Ferroptosis and BMP2 Signalling. J. Cell. Mol. Medi 2025, 29, e70288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Fang, T.; Yang, L.; Chen, Z.; Mu, S.; Fu, Q. Gastrodin Protects MC3T3-E1 Osteoblasts from Dexamethasone-Induced Cellular Dysfunction and Promotes Bone Formation via Induction of the NRF2 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 2059–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, L.; Yang, L.; Mu, S.; Fang, T.; Fu, Q. Gastrodin Alleviates Glucocorticoid Induced Osteoporosis in Rats via Activating the Nrf2 Signaling Pathways. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 11528–11540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Tang, Z.; Xu, H.; Su, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Tang, Z.; Xu, H.; et al. The Processing Methods, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Gastrodia Elata Bl.: A Comprehensive Review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 314, 116467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Zhao, L.; Tang, C.; Ling, L.; Xie, C.; Shi, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Cao, Y. Icariin Inhibits Osteoblast Ferroptosis via Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling and Enhances Healing of Osteoporotic Fractures. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 965, 176244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; Lu, Y.; Yin, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z. Baicalein Ameliorates Osteoporosis via AKT/FOXO1 Signaling. Aging 2021, 13, 17370–17379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; He, Q.; Zeng, J.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Chen, B.; Yang, J.; Xiao, J.; Zeng, C.; Luo, H.; et al. Naringenin Protects against Iron Overload-Induced Osteoarthritis by Suppressing Oxidative Stress. Phytomedicine 2022, 105, 154330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, J.L.; Bravenboer, N.; Luyten, F.P.; Verschueren, P.; Lems, W.F.; Klein-Nulend, J.; Bakker, A.D. Mechanical Loading Reduces Inflammation-Induced Human Osteocyte-to-Osteoclast Communication. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2015, 97, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Hu, J.; Song, C.; Li, P.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Y.; et al. Er-Xian Decoction Attenuates Ovariectomy-Induced Osteoporosis by Modulating Fatty Acid Metabolism and IGF1/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 301, 115835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Qi, B.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, N.; Fang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Dai, J.; Zhu, L. Quantitative Proteomics Revealed the Pharmacodynamic Network of Bugu Shengsui Decoction Promoting Osteoblast Proliferation. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 12, 833474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Qi, B.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, S.; Sun, C.; Li, Q.; Wei, X. Bu-Gu-Sheng-Sui Decoction Promotes Osteogenesis via Activating the ERK/Smad Signaling Pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 976121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Zhu, X.; Yao, F.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Luo, Z.; Zhao, D.; Li, X.; Leng, X.; Sun, L. Cytoprotective Effect of Fufang Lurong Jiangu Capsule against Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress in Bone Marrow Stromal Cell-Derived Osteoblasts through the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhang, X. Xianling Gubao Attenuates High Glucose-Induced Bone Metabolism Disorder in MG63 Osteoblast-like Cells. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Bei, J.; Li, Z.; Han, M.; Ma, B.; Ma, P.; Zhou, X. Qing’e Pill Inhibits Osteoblast Ferroptosis via ATM Serine/Threonine Kinase (ATM) and the PI3K/AKT Pathway in Primary Osteoporosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 902102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H.; Liu, H.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Ju, D. Effect of Zuogui Pill on Iron Overload in Osteoporosis Model Rats. Chin. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 59, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Lyu, Q.; Zheng, W.; Yang, Q.; Cao, G.; Huang, L.; Lyu, Q.; Zheng, W.; Yang, Q.; Cao, G.; et al. Traditional Application and Modern Pharmacological Research of Eucommia Ulmoides Oliv. Chin. Med. 2021, 16, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Hao, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; He, R.; Tao, R.; He, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Eucommia Ulmoides Oliv.: Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of an Important Traditional Chinese Medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, M.; Gao, W.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, B.; Kuang, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Advances in Eucommia Ulmoides Polysaccharides: Extraction, Purification, Structure, Bioactivities and Applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1421662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Qu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, X.; Duan, X.; Song, X.; Zhao, X.; Qu, Q.; et al. Research Progress of Eucommia Ulmoides Oliv and Predictive Analysis of Quality Markers Based on Network Pharmacology. CPB 2024, 25, 860–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Li, T.; Liu, Z.; Bao, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. A Review of “Plant Gold” Eucommia Ulmoides Oliv.: A Medicinal and Food Homologous Plant with Economic Value and Prospect. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Pan, D.; Zhang, M.; Leng, X.; Yao, B.; Guan, M.; Pan, D.; Zhang, M.; Leng, X.; Yao, B.; et al. The Aqueous Extract of Eucommia Leaves Promotes Proliferation, Differentiation, and Mineralization of Osteoblast-Like MC3T3-E1 Cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 3641317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Niu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, R.; Guo, X.; Mei, Q.; Pan, Y.; Niu, Y.; Li, C.; et al. Du-Zhong (Eucommia Ulmoides) Prevents Disuse-Induced Osteoporosis in Hind Limb Suspension Rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Fan, L.; Feng, S.; Ding, X.; An, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, M.; Zhai, X.; Li, Y. Network Pharmacology of Iridoid Glycosides from Eucommia Ulmoides Oliver against Osteoporosis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Z.G.; Li, C.; Hu, S.J.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.P.; Mei, Q.B. Du-Zhong (Eucommia ulmoides Oliv.) Cortex Extract Prevent OVX-Induced Osteoporosis in Rats. Bone 2009, 45, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Lai, F.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; He, Y.; Gong, M.; Lai, F.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; et al. Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, Applications, and Quality Control of Gastrodia Elata Blume: A Comprehensive Review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.-D.; Zhou, H.-Y.; Sui, Y.-P.; Du, X.-L.; Wang, W.; Dai, L.; Sui, F.; Huo, H.-R.; Jiang, T.-L.; Zhan, H.-D.; et al. The Rhizome of Gastrodia Elata Blume—An Ethnopharmacological Review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 189, 361–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, F. Mechanism and Prospect of Gastrodin in Osteoporosis, Bone Regeneration, and Osseointegration. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Wu, D.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Han, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, B.; Zhao, Y.; Qian, H.; et al. A Systematic Review of Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Toxicity of Epimedium Koreanum Nakai. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318, 116957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Lin, L.; Hao, F.; Shi, Z.; Gao, Y.; Yang, T.; Yang, C.; Wu, X.; Gao, R.; Ru, Y.; et al. Comprehensive Review of the Traditional Uses and the Potential Benefits of Epimedium Folium. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1415265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indran, I.R.; Liang, R.L.Z.; Min, T.E.; Yong, E.-L.; Indran, I.R.; Liang, R.L.Z.; Min, T.E.; Yong, E.-L. Preclinical Studies and Clinical Evaluation of Compounds from the Genus Epimedium for Osteoporosis and Bone Health. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 162, 188–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, Y.; Li, Y.; Gu, K.; Yin, H.; Ma, Y.; Si, Y.; Li, Y.; Gu, K.; Yin, H.; Ma, Y.; et al. Icariin Ameliorates Osteoporosis in Ovariectomized Rats by Targeting Cullin 3/Nrf2/OH Pathway for Osteoclast Inhibition. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 173, 116422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Yang, D.; Zhen, W.; Zhang, J.; Peng, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Yang, D.; Zhen, W.; et al. The Effect of Icariin on Bone Metabolism and Its Potential Clinical Application. Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, X.; Du, T.; Chen, K.; Guo, J.; Xiang, W.; Yao, X.; Sun, K.; Ye, Y.; Guo, F. Icariin Protects against Iron Overload-induced Bone Loss via Suppressing Oxidative Stress. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 10123–10137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, W.; Feng, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Kong, W.; Jiang, J. Iron Overload Induces G1 Phase Arrest and Autophagy in Murine Preosteoblast Cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6779–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Jing, X.; Guo, J.; Sun, K.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, F.; Ye, Y. Icariin Protects Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Against Iron Overload Induced Dysfunction Through Mitochondrial Fusion and Fission, PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK Pathways. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Tang, H.; Xie, L.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, Z.; Sun, Q.; Li, X.; Zhao, T.; Tang, H.; Xie, L.; et al. Scutellaria Baicalensis Georgi. (Lamiaceae): A Review of Its Traditional Uses, Botany, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Toxicology. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 1353–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, P.; Liu, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; He, C.; Xiao, P.; Shen, J.; Li, P.; et al. Traditional Uses, Ten-Years Research Progress on Phytochemistry and Pharmacology, and Clinical Studies of the Genus Scutellaria. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 265, 113198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Shang, Q.; Shen, G.; Li, B.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Chen, H.; Liu, H.; Xie, B.; et al. Restoring Bone-Fat Equilibrium: Baicalin’s Impact on P38 MAPK Pathway for Treating Diabetic Osteoporosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, T.; Fang, H.; Lu, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, T.; Fang, H.; et al. Drynaria Fortunei Improves Lipid Profiles of Elderly Patients with Postmenopausal Osteoporosis via Regulation of Notch1-NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Inflammation. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2022, 38, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-H.; Lin, W.-Y.; Li, C.-Y.; Dharini, K.K.; Chang, C.-Y.; Hong, J.-T.; Lin, M.-D.; Peng, C.-H.; Lin, W.-Y.; Li, C.-Y.; et al. Gu Sui Bu (Drynaria fortunei J. Sm.) Antagonizes Glucocorticoid-Induced Mineralization Reduction in Zebrafish Larvae by Modulating the Activity of Osteoblasts and Osteoclasts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 297, 115565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, Y. Research Progress on Drynaria Fortunei Naringin on Inflammation and Bone Activity. Zhongguo Gu Shang 2015, 28, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.W.; Cheung, H.P.; Tong, Y.; Lu, J.; Ng, T.B.; Zhang, Y.B.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Lee, K.F.; Lam, J.K.W.; Sze, S.C.W.; et al. Steroidogenic Effect of Erxian Decoction for Relieving Menopause via the P-Akt/PKB Pathway in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 195, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Xin, H.; Xu, P.; Yu, Z.; Shou, D.; Wang, N.; Xin, H.; Xu, P.; Yu, Z.; Shou, D.; et al. Erxian Decoction Attenuates TNF-α Induced Osteoblast Apoptosis by Modulating the Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Guo, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, S. Molecular Mechanism of Achyranthis Bidentatae Radix and Morindae Officinalis Radix in Osteoporosis Therapy: An Investigation Based on Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2023, 36, 101586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, Y.; Han, T.; Zhao, L.; Lv, L.; He, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xin, H. Metabolites of Curculigoside in Rats and Their Antiosteoporotic Activities in Osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 Cells. Fitoterapia 2017, 117, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Wang, J.; Ni, Y.; Yin, W.; Hou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, S.; Quan, R. Curculigoside Protects against Titanium Particle-Induced Osteolysis through the Enhancement of Osteoblast Differentiation and Reduction of Osteoclast Formation. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cai, Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, X.; Cao, S.; Huang, Y.; Wu, H.; Yang, H. Quality Evaluation of Angelica Sinensis Radix Dispensing Granules by Integrating Microvascular Activity and Chemical Analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.-L.; Zeng, R.; Gu, C.-M.; Qu, Y.; Huang, L.-F. Angelica Sinensis in China-A Review of Botanical Profile, Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry and Chemical Analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 190, 116–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-Y.; Jia, Y.-S.; Chai, L.-M.; Mu, X.-H.; Ma, S.; Xu, L.; Wei, X.; Li, J.-Y.; Jia, Y.-S.; Chai, L.-M.; et al. Effects of Chinese Herbal Formula Erxian Decoction for Treating Osteoporosis: A Systematic Review. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Fan, L.; Wang, K.; Chen, Y.; Liang, L.; Qin, X.; Lu, A.; Cao, P.; Yu, B.; Guan, D.; et al. Analysis of Molecular Mechanism of Erxian Decoction in Treating Osteoporosis Based on Formula Optimization Model. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6641838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.M.; Zhang, F.Z.; Zhou, W.Q. Clinical Study of Bugu Shengsui Capsule in Treating Primary Osteoporosis with Kidney-Yang Deficiency Syndrome. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi = Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 1997, 17, 526–530. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, J.; Cao, W.; Yu, A.; Li, P.; Liang, J.; Leng, X.; Jin, J.; Yu, P.; Liu, J. The Therapeutic Mechanism of Compound Lurong Jiangu Capsule for the Treatment of Cadmium-Induced Osteoporosis: Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1331488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zeng, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Luo, T.; Huang, H. Efficacy of Xianling Gubao Capsule in Treating Sarco-Osteopenia. Medicine 2019, 98, e15672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-R.; Cheng, L.-M.; Wang, K.-Z.; Yang, N.-P.; Yang, S.-H.; He, W.; Wang, Y.-S.; Wang, Z.-M.; Yang, P.; Liu, X.-Z.; et al. Herbal Fufang Xian Ling Gu Bao Prevents Corticosteroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head—A First Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Orthop. Transl. 2018, 12, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, G.; Mai, J.; He, Q.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Pan, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; et al. Bioinformatics Analysis Combined with Experimental Validation to Explore the Mechanism of XianLing GuBao Capsule against Osteoarthritis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 294, 115292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Wang, Z.; Guo, S.; Lin, Y. Effect of Qing’e Decoction on Leptin/Leptin Receptor and Bone Metabolism in Naturally Aging Rats. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 2532081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Cai, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Z. Elucidating the Estrogen-like Effects and Biocompatibility of the Herbal Components in the Qing’ E Formula. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 283, 114735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.-D.; Han, T.; Huang, B.-K.; Rahman, K.; Jiang, Y.-P.; Xu, H.-T.; Qin, L.-P.; Xin, H.-L.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Li, Y. Traditional Chinese Medicine Formulas for the Treatment of Osteoporosis: Implication for Antiosteoporotic Drug Discovery. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 189, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Han, D.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Z. Zuogui Pill Disrupt the Malignant Cycle in Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis through the Piezo1-Notch-1-GPX4 Pathway and Active Molecules Fishing. Phytomedicine 2024, 123, 155257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Chinese Herb | Source | Medicament Portions | Traditional Use | Experimental Model | Signaling Pathway | Mechanisms | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin | Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. | Bark | Tonifying liver and kidney, strong bones, tocolysis | MC3T3-E1 cells, Iron overload mice | Nrf2/HO-1 | ROS↓, ALP↑, Runx2↑, Osx↑, Caspase3↓, Bax↓, Nrf2↑ | [101] |
| Eucommia cortex polysaccharide | GIOP mice | ERK/JNK/Nrf2 | pERK↑, pJNK↓, Nrf2↑, NQO-1↑ | [102,103] | |||
| Aucubin | BMSCs cells, OVX rats | BMP2/SMADs | ROS↓, Fe2+↓, MDA↓, SOD↑, GPX4↑ | [104] | |||
| Gastrodine | Gastrodia elata Bl. | Tuber | Xifeng antispasmodic, calm the liver Yang, Qufeng Tongluo | MC3T3-E1 cells | Nrf2/KEAPl | ROS↓, Runx2↑, Osx↑, BMP2↓, OCN↓ | [105] |
| GIOP rats | Nrf2/KEAP1 | ROS↓, Nrf2↑ | [106] | ||||
| Icariin | Epimedium brevicornu Maxim. | Leaves | Tonify kidney yang, strong bones, dispel rheumatism | BMSCs cells | PI3K/AKT/mTOR,MAPK | ROS↓, Runx2↑, Osx↑, β-catenin↑, pPI3K↓, pAkT↓, pmTOR↓ | [107] |
| OVX rats | Nrf2/HO-1 | Nrf2↑, NQO-1↑, HO-1↑, Runx2↑, ALP↑, OPG↑, OCN↑, GPX4↑, BAX↓ | [108] | ||||
| Baicalein | Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi | Root | Clearing heat and drying dampness, purging fire detoxification, hemostasis, tocolysis | MC3T3-E1 cells | AKT/FoXO1 | AKT↓, FoXO1↑ | [109] |
| Naringenin | Drynaria fortune (Kunze) J.Sm. | Rhizome | Healing pain, tonifying kidney and strengthening bones | Iron overload mice | Nrf2/HO-1 | ROS↓, MDA↓, MMP3↓, MMP13↓, Bax↓, HO-1↑, Nrf2↑ | [110] |
| Chinese Herbal Remedy | Composition | Experimental Model | Signaling Pathway | Mechanisms | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erxian Decoction | Flavonoids (icariin, curculigoside), saponins (timosaponin, morin), alkaloids (berberine) and polysaccharides. | Human primary bone cells | RANKL/OPG | RANKL/OPG↓, Nrf2↑ | [111] |
| OVX rats | IGF1/PI3K/AKT | IGF1R↓, PI3K↓, AKT↓ | [112] | ||
| Bugu Shengsui Capsule | Flavonoids (icariin, psoralen), saponins (timosaponin, astragaloside), alkaloids (berberine) and polysaccharides (angelica polysaccharide). | OVX rats | Oxidative stress and iron accumulation | MDA↓, Ferritin↓, SOD↑, Hepcidin↑, | [113] |
| SAMP6 mice | ERK/Smad | ALP↑, RUNX2↑, ERK↑, Smad↑ | [114] | ||
| Compound Lurong Jiangu Capsule | Velvet antler polypeptide, eucommia ulmoides iridoid, angelica ferulic acid, notoginsenoside and tortoise shell mineral. | BMSCs cells | Nrf2/HO-1 | ROS↓, ALP↑, HO-1↑, Nrf2↑ | [115] |
| Xianling Gubao Capsule | Flavonoids (icariin), saponins (asperosaponin VI, timosaponin), coumarins (psoralen, isopsoralen), phenolic acids (salvianolic acid), diterpenoids (tanshinone), polysaccharides (rehmannia polysaccharide). | MG63 cells | OPG/OPGL, PI3K/Akt | OCN↑, OPN↑, RUNX2↑, OPG↑, OPGL↓, pAKT↓, p70S6K↓ | [116] |
| Qing’e Pill | Coumarins (psoralen, isopsoralen), iridoids (eucommia gum), polyunsaturated fatty acids (linoleic acid), organic sulfur (allicin). | OVX rats | ATM, PI3K/AKT | GPX4↑, Xct↑, pPI3K↓, pAKT↓, BMP2↓, MDA↓ | [117] |
| Zuogui Pill | Iridoids (catalpol, cornusoside), polysaccharides (yam polysaccharide), flavonoids (dodder flavonoids), saponins (dioscin), antler glue, tortoise shell glue. | OVX rats | OPG/RANKL | Ferric ion↓, Hepcidin↑, OPG↓, RANKL↑ | [118] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Xu, T.-Y.; Yu, A.-X.; Liang, J.-L.; Zhou, Y.-S.; Sun, H.-Z.; Dai, Y.-L.; Liu, J.; Yu, P. The Role of Ferroptosis in Osteoporosis and Advances in Chinese Herbal Interventions. Biology 2025, 14, 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040367
Li P, Xu T-Y, Yu A-X, Liang J-L, Zhou Y-S, Sun H-Z, Dai Y-L, Liu J, Yu P. The Role of Ferroptosis in Osteoporosis and Advances in Chinese Herbal Interventions. Biology. 2025; 14(4):367. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040367
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Pan, Tian-Yang Xu, Ao-Xue Yu, Jing-Ling Liang, Ya-Shuang Zhou, Huai-Zhu Sun, Yu-Lin Dai, Jia Liu, and Peng Yu. 2025. "The Role of Ferroptosis in Osteoporosis and Advances in Chinese Herbal Interventions" Biology 14, no. 4: 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040367
APA StyleLi, P., Xu, T.-Y., Yu, A.-X., Liang, J.-L., Zhou, Y.-S., Sun, H.-Z., Dai, Y.-L., Liu, J., & Yu, P. (2025). The Role of Ferroptosis in Osteoporosis and Advances in Chinese Herbal Interventions. Biology, 14(4), 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14040367






