Anti-Inflammasome Effect of Impressic Acid on Diesel Exhaust Particulate Matter-Induced NLRP1 Inflammasome via the Keap1/p62/Nrf2-Signaling Pathway in Keratinocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.3. Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Assay
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Real-Time PCR
2.6. Immunoprecipitation Assay
2.7. Intracellular ROS Production
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
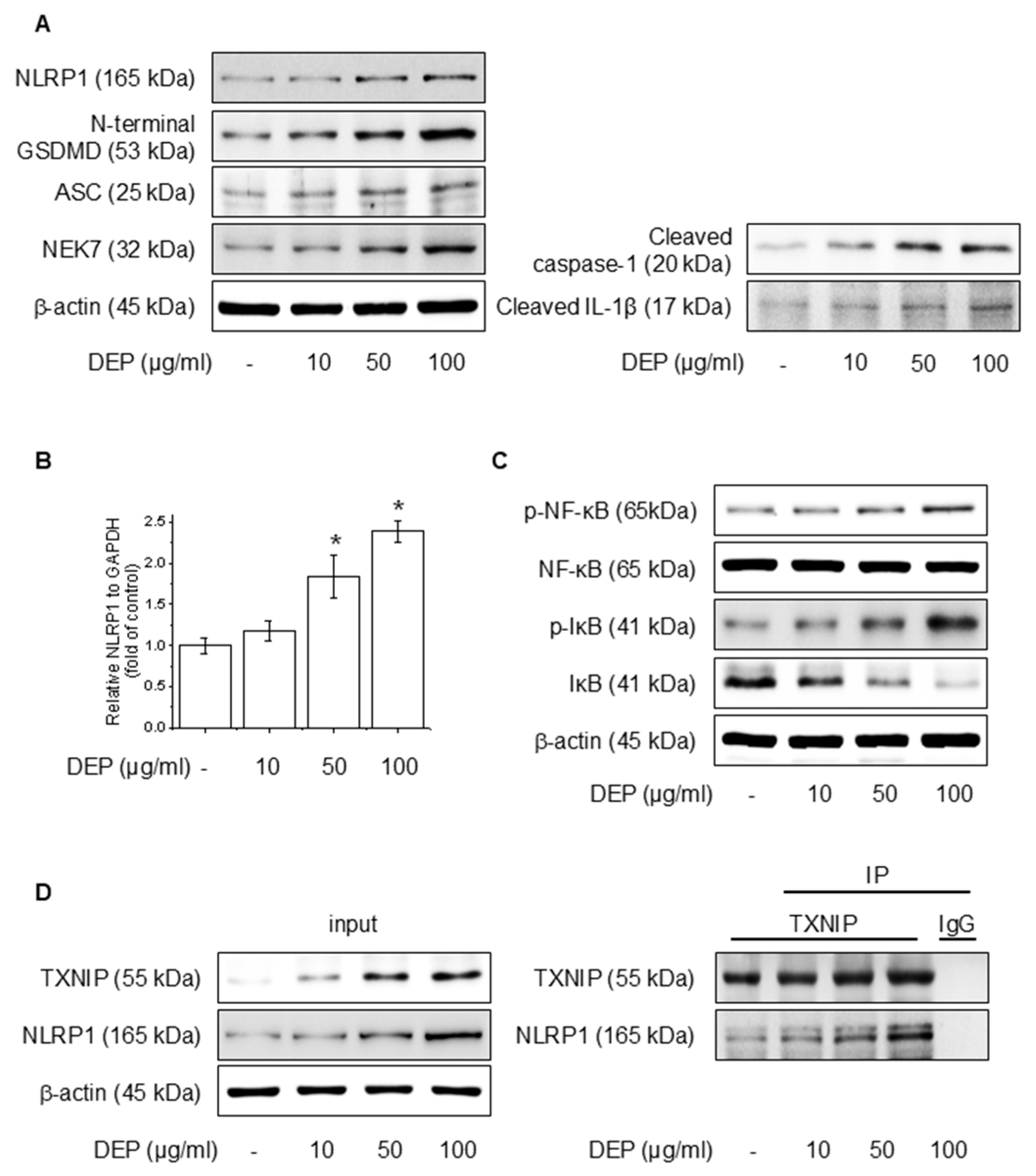
3.1. DEP Induces NLRP1 Inflammasome Complex in HaCaT Cells
3.2. IPA Attenuates DEP-Induced NLRP1 Inflammasome Complex in HaCaT Cells
3.3. IPA Increases Antioxidant Enzyme Gene Expression and Protein Levels
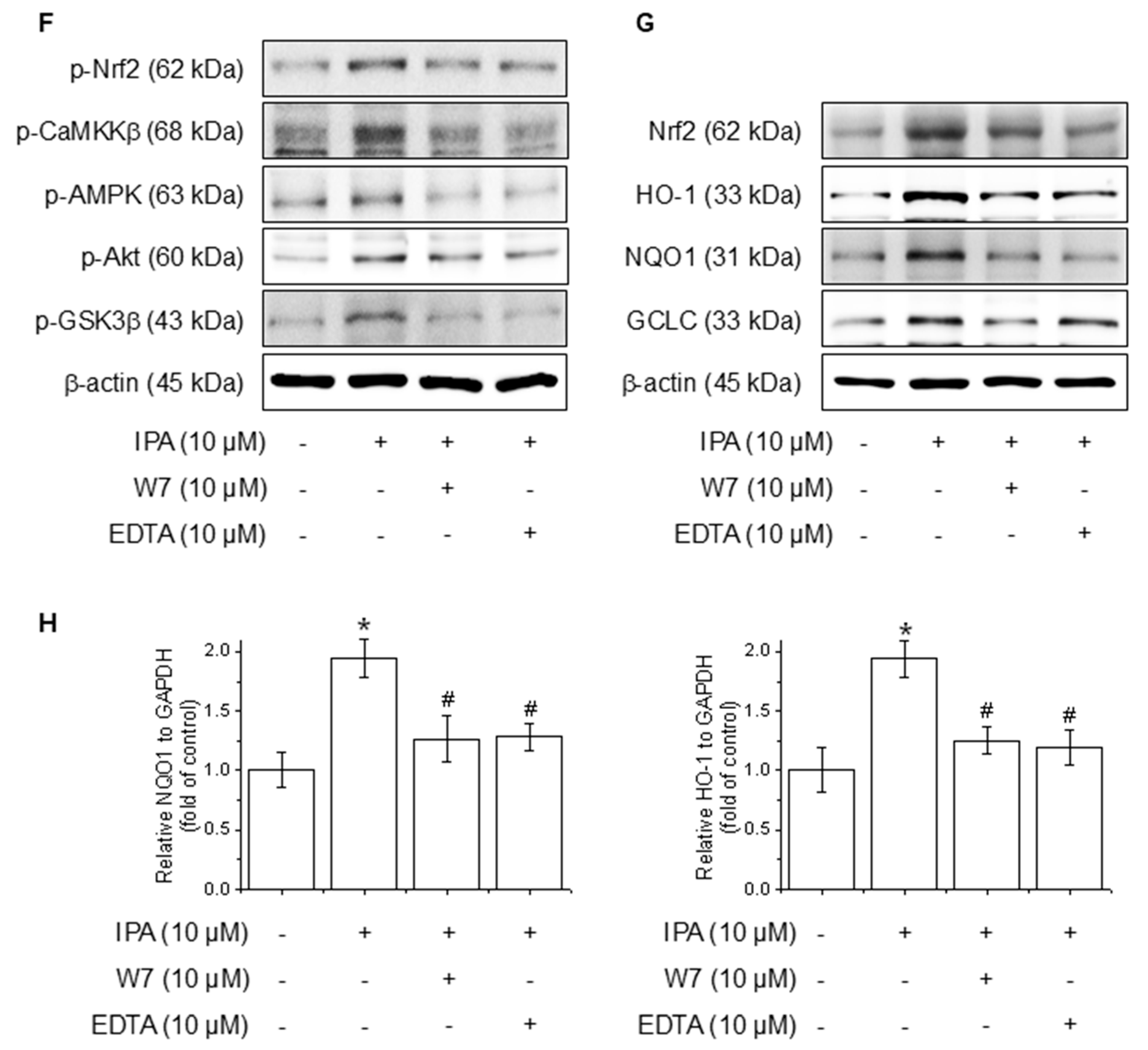
3.4. IPA Activates Calcium on Nrf2 Expression Through the Akt/AMPK/GSK3β-Signaling Pathway
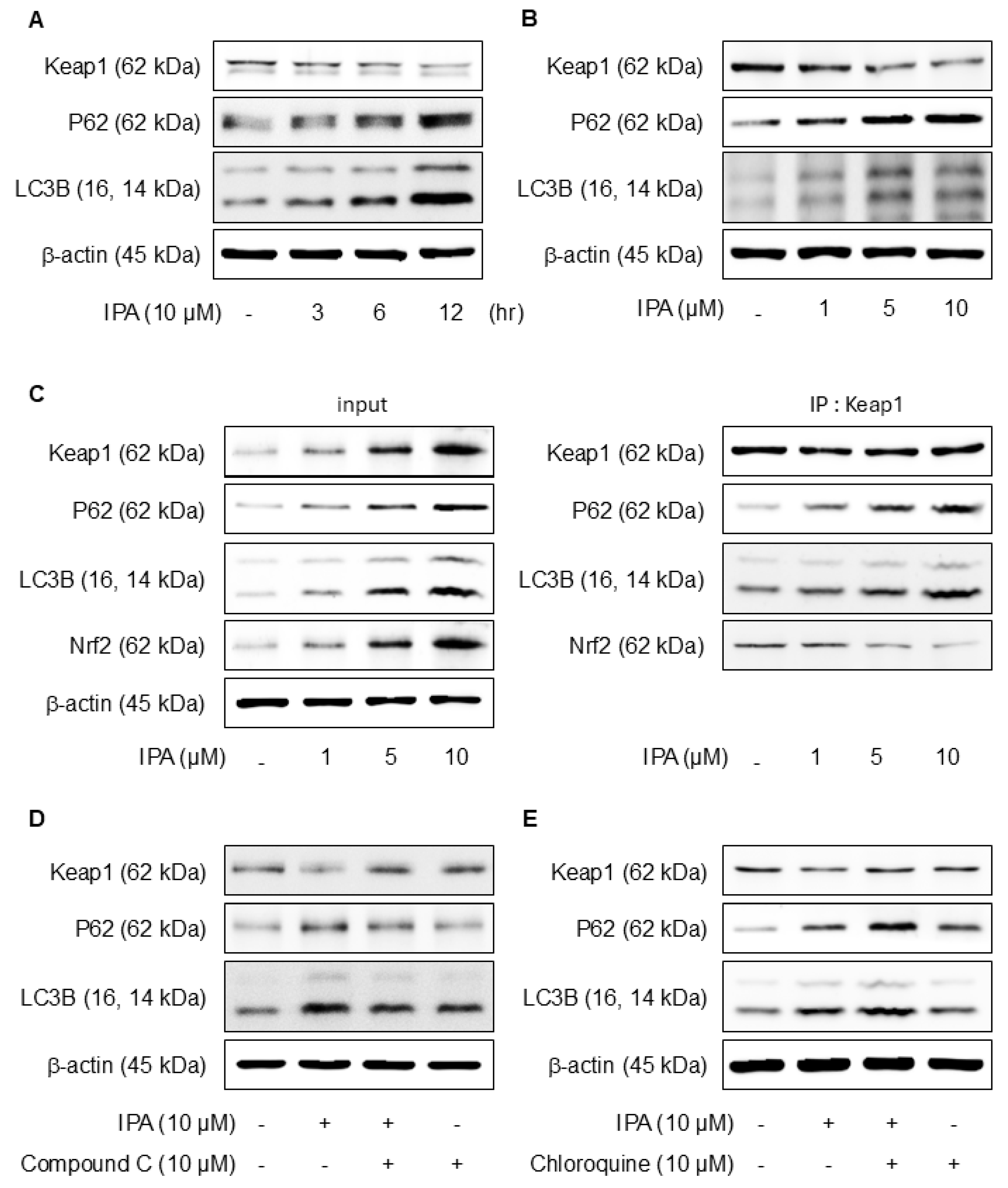
3.5. IPA Stimulates Nrf2 via an Autophagy-Mediated Pathway
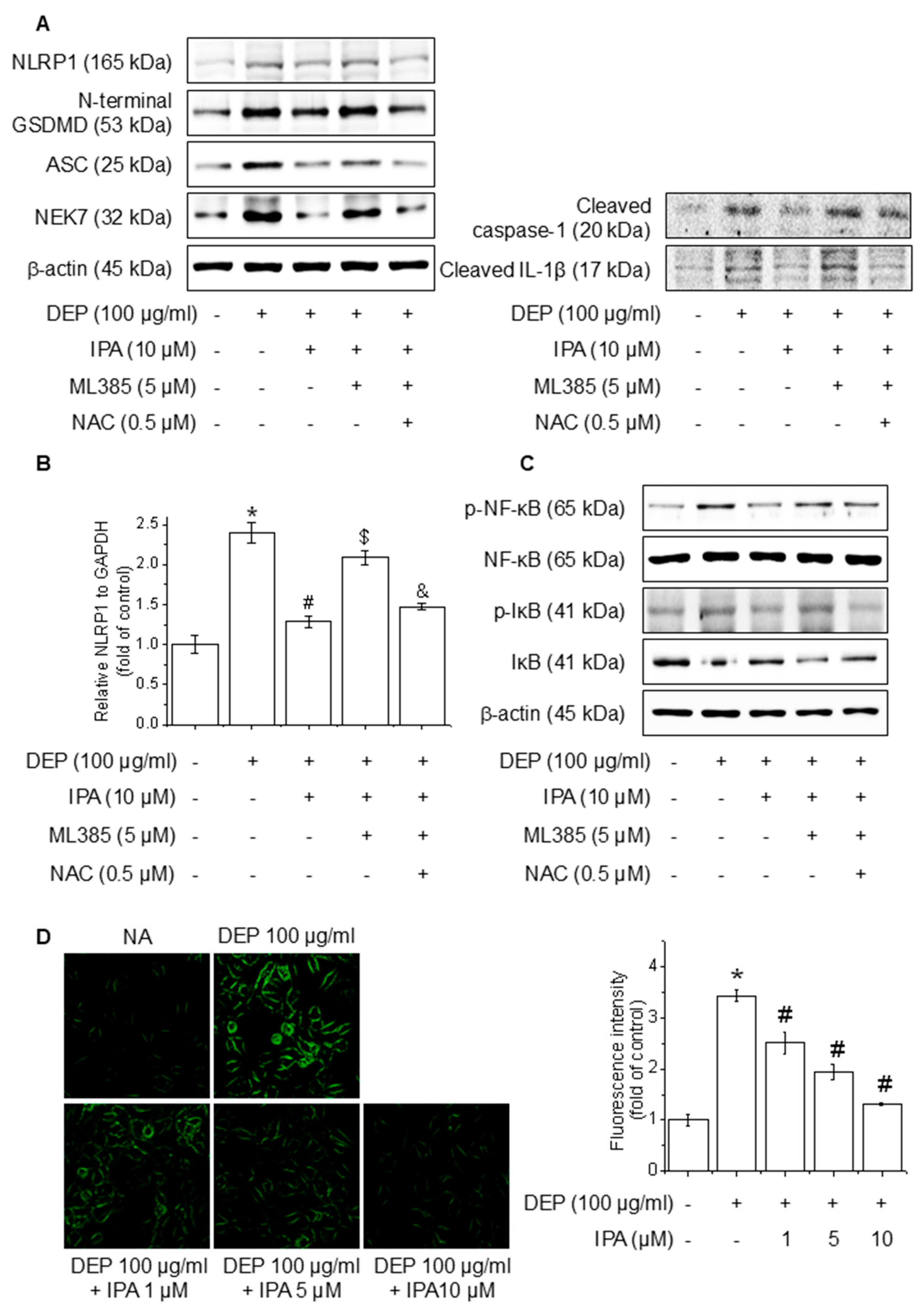
3.6. IPA Suppresses ROS Production on DEP-Induced NLRP1 Inflammasome Through the Nrf2-Signaling Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CARD | C-terminal caspase activation and recruitment domain |
| DEP | Diesel exhaust particulate matter |
| DMSO | Dimethylsulfoxide |
| GSDMD | Gasdermin D |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IPA | Impressic Acid |
| NLRP1 | NOD-like receptor protein1 |
| PM2.5 | Particulate matter |
| PYD | Pyrin domain |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
References
- Farahani, V.J.; Pirhadi, M.; Sioutas, C. Are standardized diesel exhaust particles (DEP) representative of ambient particles in air pollution toxicological studies? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, P.; Shen, D.; Shen, J.; Tang, Q.; Xi, M.; Li, Y.; Li, C. The roles of Nrf2 and autophagy in modulating inflammation mediated by TLR4-NFκB in A549 cell exposed to layer house particulate matter 2.5 (PM2.5). Chemosphere 2019, 235, 1134–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paarwater, B.A.; Mouton, J.M.; Sampson, S.L.; Malherbe, S.T.; Shaw, J.A.; Walzl, G.; Kotze, L.A.; du Plessis, N. Inhaled particulate matter affects immune responsiveness of human lung phagocytes to mycobacteria. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol 2021, 321, L566–L575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, G.; Verdin, A.; Grare, C.; Abbas, I.; Achour, D.; Ledoux, F.; Roumie, M.; Cazier, F.; Courcot, D.; Lo Guidice, J.M.; et al. Toxicological appraisal of the chemical fractions of ambient fine (PM2.5-0.3) and quasi-ultrafine (PM0.3) particles in human bronchial epithelial BEAS-2B cells. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Hu, R.; Yang, D.; Zhao, J.; Kan, H.; Tan, J.; Guan, M.; Kang, Z.; Xu, F. Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) upregulates expression of Inflammasome NLRP1 via ROS/NF-κB signaling in HaCaT Cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 2200–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.Y.; Ngoc, L.T.N.; Chae, M.; Tran, V.V.; Lee, Y.C. Effects of Microwave-Assisted Opuntia humifusa Extract in Inhibiting the Impacts of Particulate Matter on Human Keratinocyte Skin Cell. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrick, B.M.; Rodriguez, L.; Lakshmikanth, T.; Pou, C.; Henckel, E.; Arzoomand, A.; Olin, A.; Wang, J.; Mikes, J.; Tan, Z.; et al. Bifidobacteria-mediated immune system imprinting early in life. Cell 2021, 184, 3884–3898.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, E.K.; Yoon, H.K.; Jee, B.K.; Ko, H.J.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lim, Y. COX-2 expression and inflammatory effects by diesel exhaust particles in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 176, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Li, H.; Cai, J.; Wang, C.; Lin, Z.; Liu, C.; Niu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Li, W.; Kan, H. Fine Particulate Air Pollution and the Expression of microRNAs and Circulating Cytokines Relevant to Inflammation, Coagulation, and Vasoconstriction. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 017007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cai, J.; Chen, R.; Zhao, Z.; Ying, Z.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Hao, K.; Kinney, P.L.; Chen, H.; et al. Particulate Matter Exposure and Stress Hormone Levels: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Crossover Trial of Air Purification. Circulation 2017, 136, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niebler, M.; Qian, X.; Höfler, D.; Kogosov, V.; Kaewprag, J.; Kaufmann, A.M.; Ly, R.; Böhmer, G.; Zawatzky, R.; Rösl, F.; et al. Post-translational control of IL-1β via the human papillomavirus type 16 E6 oncoprotein: A novel mechanism of innate immune escape mediated by the E3-ubiquitin ligase E6-AP and p53. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Sarkar, M.K.; Okamura, K.; Harris, J.E.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Fitzgerald, K.A. Activation of the NLRP1 inflammasome in human keratinocytes by the dsDNA mimetic poly (dA:dT). Porc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2213777120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Callaway, J.B.; Ting, J.P. Inflammasomes: Mechanism of action, role in disease, and therapeutics. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, H.D.; Contassot, E.; French, L.E. The inflammasomes in autoinflammatory diseases with skin involvement. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1805–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Liwinski, T.; Elinav, E. Inflammasome activation and regulation: Toward a better understanding of complex mechanisms. Cell Discov 2020, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustin, B.; Lartigue, L.; Bruey, J.M.; Luciano, F.; Sergienko, E.; Bailly-Maitre, B.; Volkmann, N.; Hanein, D.; Rouiller, I.; Reed, J.C. Reconstituted NALP1 inflammasome reveals two-step mechanism of caspase-1 activation. Mol. Cell 2007, 25, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burian, M.; Yazdi, A.S. NLRP1 Is the Key Inflammasome in Primary Human Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 2507–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, B.S.; Latz, E.; Schmidt, F.I. The intra- and extracellular functions of ASC specks. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbrother, W.J.; Gordon, N.C.; Humke, E.W.; O’Rourke, K.M.; Starovasnik, M.A.; Yin, J.P.; Dixit, V.M. The PYRIN domain: A member of the death domain-fold superfamily. Protein Sci. 2001, 10, 1911–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinam, V.A.K.; Fitzgerald, K.A. Inflammasome Complexes: Emerging Mechanisms and Effector Functions. Cell 2016, 165, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, S.H.; Hengartner, M.O. Programmed cell death: Alive and well in the new millennium. Trends Cell Biol. 2001, 11, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenini, G.; Karakaya, T.; Hennig, P.; Filippo, M.D.; Beer, H.D. The NLRP1 Inflammasome in Human Skin and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciążyńska, M.; Bednarski, I.A.; Wódz, K.; Narbutt, J.; Lesiak, A. NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasomes as a new approach to skin carcinogenesis. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 1649–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.; Rüegg, A.; Werner, S.; Beer, H.D. Active caspase-1 is a regulator of unconventional protein secretion. Cell 2008, 132, 818–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aglietti, R.A.; Dueber, E.C. Recent Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Pyroptosis and Gasdermin Family Functions. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrowski, Y.; Peric, M.; Koglin, S.; Kammerbauer, C.; Göss, C.; Anz, D.; Simanski, M.; Gläser, R.; Harder, J.; Hornung, V.; et al. Cytosolic DNA triggers inflammasome activation in keratinocytes in psoriatic lesions. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 82ra38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ruan, J.; Pan, Y.; Magupalli, V.G.; Wu, H.; Lieberman, J. Inflammasome-activated gasdermin D causes pyroptosis by forming membrane pores. Nature 2016, 535, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 519–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.J.; Fernando, I.P.S.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, A.; Je, J.G.; Seo, M.J.; Jee, Y.H.; Jeon, Y.J.; Kim, S.Y.; et al. (-)-Loliolide Isolated from Sargassum horneri Suppressed Oxidative Stress and Inflammation by Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling in IFN-γ/TNF-α-Stimulated HaCaT Keratinocytes. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.A.; Yang, S.Y.; Koo, J.E.; Koh, Y.S.; Kim, Y.H. Lupane-type triterpenoids from the steamed leaves of Acanthopanax koreanum and their inhibitory effects on the LPS-stimulated pro-inflammatory cytokine production in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 6703–6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Lee, G.H.; Jin, S.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Hwang, Y.P.; Han, E.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Jeong, H.G. Impressic Acid Ameliorates Atopic Dermatitis-Like Skin Lesions by Inhibiting ERK1/2-Mediated Phosphorylation of NF-κB and STAT1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Jin, S.W.; Pham, T.H.; Park, J.S.; Kim, C.Y.; Choi, J.H.; Han, E.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Jeong, H.G. Impressic Acid Attenuates the Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response by Activating the AMPK/GSK3β/Nrf2 Axis in RAW264.7 Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Min, D.S.; Yun, H.E.; Kim, K.T.; Sun, Y.N.; Dat, L.D.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, H.P. Impressic acid from Acanthopanax koreanum, possesses matrix metalloproteinase-13 down-regulating capacity and protects cartilage destruction. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 209, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.A.; Yang, S.Y.; Song, S.B.; Kim, Y.H. Effects of impressic acid from Acanthopanax koreanum on NF-κB and PPARγ activities. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Standard Reference Material 2975: Diesel Particulate Matter (Industrial Forklift); U.S. Department of Commerce: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2021.
- Ye, X.; Zuo, D.; Yu, L.; Zhang, L.; Tang, J.; Cui, C.; Bao, L.; Zan, K.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; et al. ROS/TXNIP pathway contributes to thrombin induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell apoptosis in microglia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 485, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wei, M.; Lu, B.; Wang, Z.; Ji, L. Baicalein and baicalin alleviate acetaminophen-induced liver injury by activating Nrf2 antioxidative pathway: The involvement of ERK1/2 and PKC. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 150, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, S.; Inoue, Y.; Hori, Y.; Miyajima, C.; Morishita, D.; Ohoka, N.; Hida, S.; Makino, T.; Hayashi, H. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Kurarinone Involves Induction of HO-1 via the KEAP1/Nrf2 Pathway. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, M.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Tran, K.; Reddy, S.P.; Malik, A.B. Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1126–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, Y.L.; Gao, C.; Gu, Y.T.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.H.; Zhang, Z. Salvianolic Acid A Protects the Kidney against Oxidative Stress by Activating the Akt/GSK-3β/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway and Inhibiting the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in 5/6 Nephrectomized Rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 2853534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Su, D.; Li, L.; Cai, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhai, J.; Li, M.; Wu, X.; Hu, K. Anti-inflammatory effects of Aureusidin in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages via suppressing NF-κB and activating ROS- and MAPKs-dependent Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 387, 114846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, C.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Numazawa, S.; Tang, H.; Tang, X.; Han, X.; Li, J.; Yang, M.; Wang, Z.; et al. The crosstalk between Nrf2 and AMPK signal pathways is important for the anti-inflammatory effect of berberine in LPS-stimulated macrophages and endotoxin-shocked mice. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2014, 20, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, H.; Lv, H.; Cheng, G.; Ci, X. Nrf2-mediated liver protection by esculentoside A against acetaminophen toxicity through the AMPK/Akt/GSK3β pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 101, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Lao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gillespie, D.A. Akt: A double-edged sword in cell proliferation and genome stability. J. Oncol. 2012, 2012, 951724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, A.; Hatano, N.; Fujiwara, Y.; Sha’ri, A.; Takabatake, S.; Akano, H.; Kanayama, N.; Magari, M.; Nozaki, N.; Tokumitsu, H. AMP-activated protein kinase-mediated feedback phosphorylation controls the Ca2+/calmodulin (CaM) dependence of Ca2+/CaM-dependent protein kinase kinase β. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 19804–19813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Enaka, M.; Muragaki, Y. Activation of KEAP1/NRF2/P62 signaling alleviates high phosphate-induced calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells by suppressing reactive oxygen species production. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; Jeong, S.H.; Yi, K.; Chung, K.M.; Hong, C.J.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, E.K.; Yu, S.W. Phosphorylation of p62 by AMP-activated protein kinase mediates autophagic cell death in adult hippocampal neural stem cells. J. Biol. Chem 2017, 292, 13795–13808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, L.; Fiocco, Z.; Mellett, M.; Aoki, R.; Rubegni, P.; French, L.E.; Satoh, T.K. Role of the NLRP1 inflammasome in skin cancer and inflammatory skin diseases. Br. J. Dermatol. 2024, 190, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Guo, J.; Nong, Y.; Mo, W.; Fang, H.; Mi, J.; Qi, Q.; Yang, M. 18β-Glycyrrhetinic acid induces human HaCaT keratinocytes apoptosis through ROS-mediated PI3K-Akt signaling pathway and ameliorates IMQ-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in mice. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 21, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan, A.; Mioc, A.; Prodea, A.; Mioc, M.; Buzatu, R.; Ghiulai, R.; Racoviceanu, R.; Caruntu, F.; Socia, C. The Optimized Delivery of Triterpenes by Liposomal Nanoformulations: Overcoming the Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanov, S.R.; Andonova, V.Y. Lipid Nanoparticulate Drug Delivery Systems: Recent Advances in the Treatment of Skin Disorders. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wen, J.; Sharma, M. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Topical Drug Delivery: Mechanisms, Dosage Form Perspectives, and Translational Status. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 3203–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.Y.; Lee, G.H.; Maeng, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Yun, H.-Y.; Jeong, G.-S.; Jeong, H.G. Anti-Inflammasome Effect of Impressic Acid on Diesel Exhaust Particulate Matter-Induced NLRP1 Inflammasome via the Keap1/p62/Nrf2-Signaling Pathway in Keratinocytes. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050610
Lee SY, Lee GH, Maeng J, Kim SY, Yun H-Y, Jeong G-S, Jeong HG. Anti-Inflammasome Effect of Impressic Acid on Diesel Exhaust Particulate Matter-Induced NLRP1 Inflammasome via the Keap1/p62/Nrf2-Signaling Pathway in Keratinocytes. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(5):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050610
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seung Yeon, Gi Ho Lee, Jeonghwan Maeng, Su Yeon Kim, Hwi-Yeol Yun, Gil-Saeng Jeong, and Hye Gwang Jeong. 2025. "Anti-Inflammasome Effect of Impressic Acid on Diesel Exhaust Particulate Matter-Induced NLRP1 Inflammasome via the Keap1/p62/Nrf2-Signaling Pathway in Keratinocytes" Antioxidants 14, no. 5: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050610
APA StyleLee, S. Y., Lee, G. H., Maeng, J., Kim, S. Y., Yun, H.-Y., Jeong, G.-S., & Jeong, H. G. (2025). Anti-Inflammasome Effect of Impressic Acid on Diesel Exhaust Particulate Matter-Induced NLRP1 Inflammasome via the Keap1/p62/Nrf2-Signaling Pathway in Keratinocytes. Antioxidants, 14(5), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050610





