Incidence of Post-Sedation Emesis in Cynomolgus (Macaca fascicularis) and Rhesus (Macaca mulatta) Macaques, and Evaluation of Prophylactic Antiemetic Efficacy
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
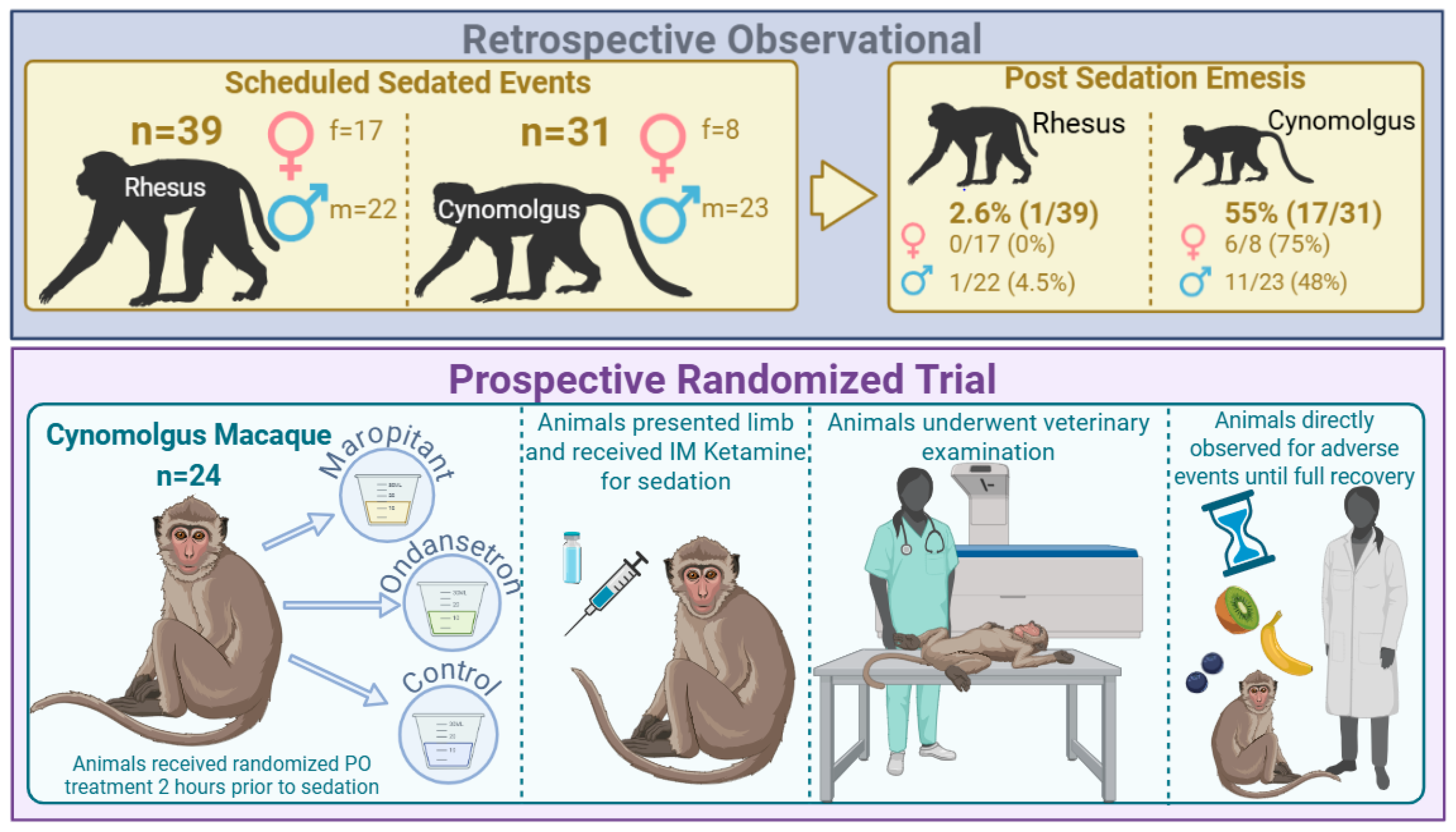
2.1. Animal Subjects
2.2. Retrospective Observational Study
2.3. Prospective Randomized Trial
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Retrospective Observational Study
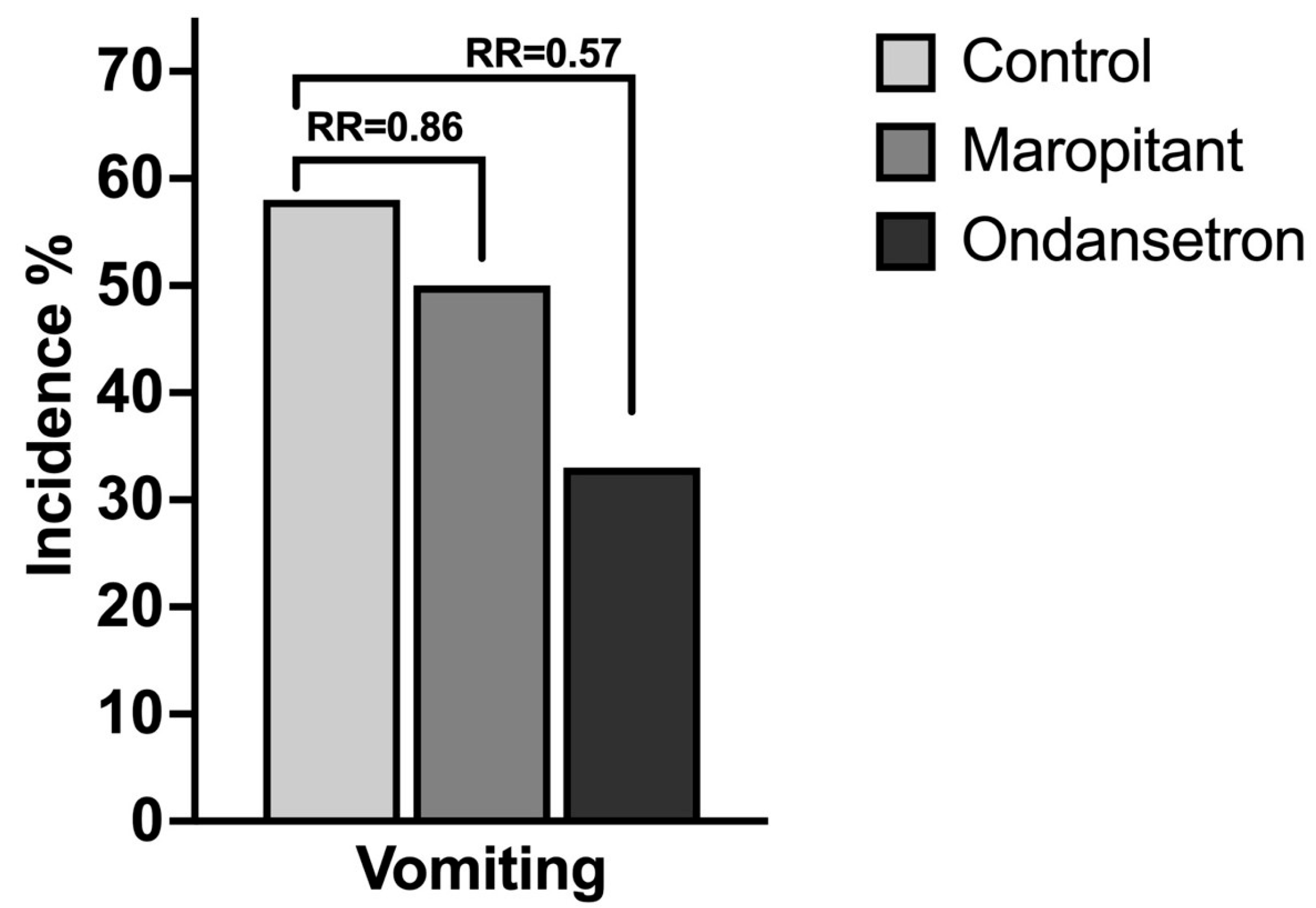
3.2. Prospective Randomized Trial
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NHP | Nonhuman Primate |
| TB | Tuberculosis |
| DEXA | Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry |
| MAC | Minimum alveolar concentration |
| PO | Per os |
References
- Oppler, S.H.; Palmer, S.D.; Phu, S.N.; Graham, M.L. The Role of Behavioral Management in Enhancing Clinical Care and Efficiency, Minimizing Social Disruption, and Promoting Welfare in Captive Primates. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, R.; Nahata, M. Ketamine for conscious sedation in pediatric emergency care. Pharmacotherapy 2005, 25, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorp, A.W.; Brown, L.; Green, S.M. Ketamine-associated vomiting: Is it dose-related? Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2009, 25, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesiyun, A.A.; Tatini, S.R. Incidence of ketamine-induced emesis in cynomologus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) used for staphylococcal enterotoxin bioassay. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1982, 63, 330–335. [Google Scholar]
- Springer, D.A.; Baker, K.C. Effect of ketamine anesthesia on daily food intake in Macaca mulatta and Cercopithecus aethiops. Am. J. Primatol. 2007, 69, 1080–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovbey, D.H.; Wilson, D.V.; Bednarski, R.M.; Hauptman, J.G.; Stanley, B.J.; Radlinsky, M.G.; Larenza, M.P.; Pypendop, B.H.; Rezende, M.L. Prevalence and risk factors for canine post-anesthetic aspiration pneumonia (1999–2009): A multicenter study. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2014, 41, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogan, D.A.; Johnson, L.R.; Sturges, B.K.; Jandrey, K.E.; Pollard, R.E. Etiology and clinical outcome in dogs with aspiration pneumonia: 88 cases (2004–2006). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2008, 233, 1748–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langston, W.T.; Wathen, J.E.; Roback, M.G.; Bajaj, L. Effect of ondansetron on the incidence of vomiting associated with ketamine sedation in children: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2008, 52, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, L.; Hall, D. BET 2: Antiemetic use in paediatric sedation with ketamine. Emerg. Med. J. 2018, 35, 524–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, M.; Johnson, D.W.; Chan, J.; Taljaard, M.; Barrowman, N.; Farion, K.J.; Ali, S.; Beno, S.; Dixon, A.; McTimoney, C.M.; et al. Risk Factors for Adverse Events in Emergency Department Procedural Sedation for Children. JAMA. Pediatr. 2017, 171, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Division on Earth and Life Studies; Health and Medicine Division; Institute for Laboratory Animal Research; Board on Health Sciences Policy; Committee on the State of the Science and Future Needs for Nonhuman Primate Model Systems. Nonhuman Primate Models in Biomedical Research: State of the Science and Future Needs; Yost, O.C., Downey, A., Ramos, K.S., Eds.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2023; Appendix E, Nonhuman Primate Investigator Survey and Responses. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK593149/ (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- Magden, E.; Mansfield, K.; Simmons, J.; Abee, C.R. Chapter 17—Nonhuman Primates. In Laboratory Animal Medicine, 3rd ed.; Fox, J.G., Anderson, L.C., Otto, G.M., Pritchett-Corning, K., Whary, M.T., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA; Cambridge, MA, USA; Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 771–930. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, G.; Zhang, G.; Fang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Ling, F.; Cooper, D.N.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; van Gool, A.J.; et al. Genome sequencing and comparison of two nonhuman primate animal models, the cynomolgus and Chinese rhesus macaques. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, J.R.; MacGuire, J.; Chang, S.; Dierks, E.; Roble, G.S. Assessment of pre-operative maropitant citrate use in macaque (Macaca fascicularis & Macaca mulatta) neurosurgical procedures. J. Med. Primatol. 2018, 47, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burke, J.E.; Hess, R.S.; Silverstein, D.C. Effectiveness of orally administered maropitant and ondansetron in preventing preoperative emesis and nausea in healthy dogs premedicated with a combination of hydromorphone, acepromazine, and glycopyrrolate. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2021, 260, S40–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Puente-Redondo, V.A.; Siedek, E.M.; Benchaoui, H.A.; Tilt, N.; Rowan, T.G.; Clemence, R.G. The anti-emetic efficacy of maropitant (Cerenia™) in the treatment of ongoing emesis caused by a wide range of underlying clinical aetiologies in canine patients in Europe. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2007, 48, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlacek, H.S.; Ramsey, D.S.; Boucher, J.F.; Eagleson, J.S.; Conder, G.A.; Clemence, R.G. Comparative efficacy of maropitant and selected drugs in preventing emesis induced by centrally or peripherally acting emetogens in dogs. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 31, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, M.A.; Cox, S.R.; Mahabir, S.; Miskell, C.; Lin, J.; Bunger, A.; McCall, R.B. Safety, pharmacokinetics and use of the novel NK-1 receptor antagonist maropitant (Cerenia™) for the prevention of emesis and motion sickness in cats. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 31, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Flores, M.; Sakai, D.M.; Learn, M.M.; Mastrocco, A.; Campoy, L.; Boesch, J.M.; Gleed, R.D. Effects of maropitant in cats receiving dexmedetomidine and morphine. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2016, 248, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchaoui, H.A.; Cox, S.R.; Schneider, R.P.; Boucher, J.F.; Clemence, R.G. The pharmacokinetics of maropitant, a novel neurokinin type-1 receptor antagonist, in dogs. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 30, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenward, H.; Elliott, J.; Lee, T.; Pelligand, L. Anti-nausea effects and pharmacokinetics of ondansetron, maropitant and metoclopramide in a low-dose cisplatin model of nausea and vomiting in the dog: A blinded crossover study. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 244. [Google Scholar]
- Foth, S.; Meller, S.; Kenward, H.; Elliott, J.; Pelligand, L.; Volk, H.A. The use of ondansetron for the treatment of nausea in dogs with vestibular syndrome. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henze, L.; Foth, S.; Meller, S.; Twele, F.; Charalambous, M.; Kenward, H.; Elliott, J.; Pelligand, L.; Volk, H. Ondansetron in dogs with nausea associated with vestibular disease: A double-blinded, randomized placebo-controlled crossover study. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2022, 36, 1726–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budde, J.; McClusky, D. Ondansetron. In Plumb’s Veterinary Drugs Handbook, 10th ed.; Educational Concepts: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sharun, K.; Jambagi, K.; Arya, M.; Aakanksha; Chaithra, S.N.; Patel, P.K.; Dixit, S.K.; Dhama, K. Clinical Applications of Substance P (Neurokinin-1 Receptor) Antagonist in Canine Medicine. Arch. Razi Inst. 2021, 76, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, D.M.; Pickel, V.M.; Joh, T.H.; Reis, D.J.; Miller, R.J. Immunocytochemical localization of catecholamine synthesizing enzymes and neuropeptides in area postrema and medical nucleus tractus solitarius of rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 1981, 196, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzi, D.; Pellegrini, B.; Tonelli, F.; Surrenti, C.; Calabro, A. Substance P (neurokinin-1) and neurokinin A (neurokinin-2) receptor gene and protein expression in the healthy and inflamed human intestine. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Recio, S.; Gascón, P. Biological and Pharmacological Aspects of the NK1-Receptor. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 495704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, M.; Berry, K.; McCort, H.; Reuter, J.D. Brain Abscess in a Rhesus Macaque (Macaca mulatta) with a Cephalic Implant. Comp. Med. 2013, 63, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lemoy, M.J.; Schouten, A.C.; Canfield, D.R. Granuloma Due to Oxidized Regenerated Cellulose in an Aged Rhesus Macaque (Macaca mulatta). Comp. Med. 2016, 66, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lucot, J.B. Pharmacology of motion sickness. J. Vestib. Res. 1998, 8, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grélot, L.; Miller, A.D. Neural control of respiratory muscle activation during vomiting. In Neural Control of the Respiratory Muscles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 239–248. [Google Scholar]
- De Waele, C.; Vibert, N.; Baudrimont, M.; Vidal, P. NMDA receptors contribute to the resting discharge of vestibular neurons in the normal and hemilabyrinthectomized guinea pig. Exp. Brain Res. 1990, 81, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thawley, V.J.; Drobatz, K.J. Assessment of dexmedetomidine and other agents for emesis induction in cats: 43 cases (2009–2014). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2015, 247, 1415–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thies, M.; Bracker, K.; Sinnott, V. Retrospective evaluation of the effectiveness of xylazine for inducing emesis in cats: 48 cats (2011–2015). J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2017, 27, 658–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyner, C.L.; Woody, B.J.; Reid, J.S.; Chafetz, E.P.; Lederer, H.A.; Norton, J.F.; Keefe, T.J.; Jöchle, W. Multicenter clinical comparison of sedative and analgesic effects of medetomidine and xylazine in dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1997, 211, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nystrom, M.R.; Odunayo, A.; Okafor, C.C. Assessment of hydromorphone and dexmedetomidine for emesis induction in cats. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2019, 29, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparasu, R.; McCoy, R.A.; Weber, C.; Mair, D.; Parasuraman, T.V. Opioid-induced emesis among hospitalized nonsurgical patients: Effect on pain and quality of life. J. Pain Symptom Manage. 1999, 18, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay Kraus, B.L. Effect of dosing interval on efficacy of maropitant for prevention of hydromorphone-induced vomiting and signs of nausea in dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2014, 245, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzutti, A.M.; Martín-Flores, M.; Litterio, N.J.; Himelfarb, M.A.; Invaldi, S.H.; Zarazaga, M.P. A comparison between maropitant and metoclopramide for the prevention of morphine-induced nausea and vomiting in dogs. Can. Vet. J. 2017, 58, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.H.; Ponnudurai, R.; Schaefer, R. Ondansetron: A selective 5-HT3 receptor antagonist and its applications in CNS-related disorders. CNS Drug Rev. 2001, 7, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, L.G.; Bird, S.T.; Sahin, L.; Tassinari, M.S.; Greene, P.; Reichman, M.E.; Andrade, S.E.; Haffenreffer, K.; Toh, S. Antiemetic use among pregnant women in the United States: The escalating use of ondansetron. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2017, 26, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egerton-Warburton, D.; Meek, R.; Mee, M.J.; Braitberg, G. Antiemetic use for nausea and vomiting in adult emergency department patients: Randomized controlled trial comparing ondansetron, metoclopramide, and placebo. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2014, 64, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeCamp, L.R.; Byerley, J.S.; Doshi, N.; Steiner, M.J. Use of antiemetic agents in acute gastroenteritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2008, 162, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, A.; Sorkin, E.M. Ondansetron: An update of its therapeutic use in chemotherapy-induced and postoperative nausea and vomiting. Drugs 1993, 45, 931–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute for Laboratory Animal Research. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Congress. Animal Welfare Act, 7 U.S.C. Chapter 54—Transportation, Sale, and Handling of Certain Animals. 2025. Available online: https://uscode.house.gov/view.xhtml?path=/prelim@title7/chapter54&edition=prelim (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS). Animal Welfare Act and Animal Welfare Regulations (Commonly known as the “Blue Book”). Issued July 2023. 2023. Available online: https://www.aphis.usda.gov/media/document/17164/file (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- Hermansson, G.; Sivertsson, R. Gender-related differences in gastric emptying rate of solid meals. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1996, 41, 1994–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, H.; Suzuki, H.; Matsuzaki, J.; Taniguchi, K.; Shimizu, T.; Yamane, T.; Masaoka, T.; Kanai, T. Gender difference of gastric emptying in healthy volunteers and patients with functional dyspepsia. Digestion 2017, 95, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M.; Iturrino, J.; Bharucha, A.E.; Burton, D.; Shin, A.; Jeong, I.D.; Zinsmeister, A.R. Performance characteristics of scintigraphic measurement of gastric emptying of solids in healthy participants. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 1076-e562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobel, G.; Tribukait, A.; Mekjavic, I.B.; Eiken, O. Effects of motion sickness on thermoregulatory responses in a thermoneutral air environment. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 1717–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngampramuan, S.; Cerri, M.; Del Vecchio, F.; Corrigan, J.J.; Kamphee, A.; Dragic, A.S.; Rudd, J.A.; Romanovsky, A.A.; Nalivaiko, E. Thermoregulatory correlates of nausea in rats and musk shrews. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumb, D.C. Maropitant. In Plumb’s Veterinary Drugs; PharmaVet: Stockholm, WI, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, M.L.; Mutch, L.A.; Kittredge, J.A.; Rieke, E.F.; Robinson, N.A.; Zolondek, E.K.; Faig, A.W.; DuFour, T.A.; Munson, J.W.; Schuurman, H.J. Management of adverse side-effects after chemotherapy in macaques as exemplified by streptozotocin: Case studies and recommendations. Lab. Anim. 2012, 46, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecoraro, H.L.; Haertel, A.J.; Cullin, C.; Prongay, K.; Lewis, A.D.; Ducore, R. Cerebral cysts of ependymal or ventricular origin in a juvenile rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta) with neurologic signs. J. Med. Primatol. 2019, 48, 378–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacVittie, T.J.; Farese, A.M.; Bennett, A.; Gelfond, D.; Shea-Donohue, T.; Tudor, G.; Booth, C.; McFarland, E.; Jackson, W. The acute gastrointestinal subsyndrome of the acute radiation syndrome: A rhesus macaque model. Health Phys. 2012, 103, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farese, A.M.; Hankey, K.G.; Cohen, M.V.; MacVittie, T.J. Lymphoid and myeloid recovery in rhesus macaques following total body X-irradiation. Health Phys. 2015, 109, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, M.; Bennett, A.; Farese, A.M.; Ward, A.; Taylor-Howell, C.; Cui, W.; Gibbs, A.; Lasio, G.; Jackson, W.; MacVittie, T.J. The delayed pulmonary syndrome following acute high-dose irradiation: A rhesus macaque model. Health Phys. 2014, 106, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoetis Inc. CERENIA—Maropitant Citrate Injectable Solution [US Freedom of Information Summary]; NADA 141-263; Zoetis Inc.: Charles City, IA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- ZyVet Animal Health Inc. Maropitant Citrate Tablets [US Freedom of Information Summary]; ANADA 200-747; ZyVet Animal Health Inc.: Pennington, NJ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chewy Pharmacy. Maropitant Citrate (Generic) Tablets. Available online: https://www.chewy.com/maropitant-citrate-generic-tablets/dp/1376478 (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Chewy Pharmacy. Ondansetron (Generic) Tablets. Available online: https://www.chewy.com/ondansetron-generic-tablets/dp/231829 (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- MERCK. Emend—Aprepitant [Package Insert]. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised November 2019. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm?event=overview.process&ApplNo=021549 (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Swallow, A.; Rioja, E.; Elmer, T.; Dugdale, A. The effect of maropitant on intraoperative isoflurane requirements and postoperative nausea and vomiting in dogs: A randomized clinical trial. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2017, 44, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niyom, S.; Boscan, P.; Twedt, D.C.; Monnet, E.; Eickhoff, J.C. Effect of maropitant, a neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist, on the minimum alveolar concentration of sevoflurane during stimulation of the ovarian ligament in cats. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2013, 40, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| All Animals | Cynomolgus | Rhesus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 18/70 (26%) | 17/31 (55%) | 1/39 (2.6%) |
| Male | 12/45 (27%) | 11/23 (48%) | 1/22 (4.5%) |
| Female | 6/25 (24%) | 6/8 (75%) | 0/17 (0%) |
| Control (n = 12) | Maropitant (n = 12) | Ondansetron (n = 12) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart Rate (beats per minute) | 137.3 ± 18.0 | 135.2 ± 24.41 | 143.0 ± 26.26 | NS |
| Respiratory Rate (breaths per minute) | 25.33 ± 5.21 | 25.67 ± 3.6 | 25.00 ± 4.22 | NS |
| Body Temperature (°F) | 98.94 ± 0.84 a | 100.3 ± 0.63 b | 99.96 ± 1.0 b | 0.0010 |
| Time to Recovery (minutes) | 198.7 ± 109.5 | 213.9 ± 106.2 | 162.0 ± 77.11 | NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coley, R.; Palmer, S.D.; Hubbard, J.; Graham, M.L. Incidence of Post-Sedation Emesis in Cynomolgus (Macaca fascicularis) and Rhesus (Macaca mulatta) Macaques, and Evaluation of Prophylactic Antiemetic Efficacy. Animals 2025, 15, 3292. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223292
Coley R, Palmer SD, Hubbard J, Graham ML. Incidence of Post-Sedation Emesis in Cynomolgus (Macaca fascicularis) and Rhesus (Macaca mulatta) Macaques, and Evaluation of Prophylactic Antiemetic Efficacy. Animals. 2025; 15(22):3292. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223292
Chicago/Turabian StyleColey, Rachel, Sierra D. Palmer, Jennifer Hubbard, and Melanie L. Graham. 2025. "Incidence of Post-Sedation Emesis in Cynomolgus (Macaca fascicularis) and Rhesus (Macaca mulatta) Macaques, and Evaluation of Prophylactic Antiemetic Efficacy" Animals 15, no. 22: 3292. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223292
APA StyleColey, R., Palmer, S. D., Hubbard, J., & Graham, M. L. (2025). Incidence of Post-Sedation Emesis in Cynomolgus (Macaca fascicularis) and Rhesus (Macaca mulatta) Macaques, and Evaluation of Prophylactic Antiemetic Efficacy. Animals, 15(22), 3292. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15223292







