- Article
Energy Integration and Valorization of Surplus Electricity Through Alkaline Water Electrolysis Within a Self-Generation Scheme Using Gas Turbogenerators
- Juan Cadavid,
- David Patiño-Ruiz and
- Alejandro Martínez-Amariz
- + 3 authors
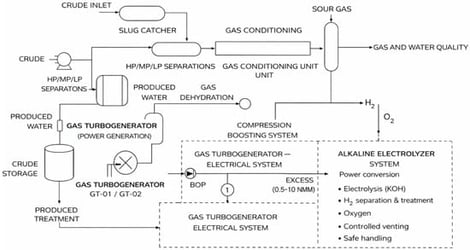
This study assesses the technical, operational, environmental, and economic feasibility of integrating alkaline water electrolysis (AEL) using on-site measured surplus electricity from two 20 MW natural-gas turbogenerators installed at a Central Processing Facility (CPF) in a Colombian oilfield. Unlike approaches based on modeled profiles, the analysis relies on more than 31,000 experimental records of gas consumption and active power, enabling an accurate characterization of the structural availability of energy surpluses under real operating conditions. A specialized industrial water treatment and purification company was consulted and provided with the physicochemical characterization results obtained from process water samples analyzed by an accredited laboratory. Based on these parameters, the technical supplier confirmed the feasibility of designing a multistage treatment train, including equalization, filtration, clarification, activated carbon, ultrafiltration, and reverse osmosis, capable of achieving final conductivities at or below 5 µS/cm. This water quality level is compatible with typical industrial alkaline electrolysis requirements and in line with technical specifications commonly aligned with ASTM and ISO standards for pressurized AEL systems. A strategic comparison between PEM and AEL technologies, supported by IFE/EFE matrices and sensitivity analyses, identified alkaline electrolysis as the optimal alternative under a stable electrical profile and capital expenditure constraints. Energy sizing for scenarios between 1.5 and 10 MW, assuming continuous 24 h operation and an average specific consumption of 50 kWh/kg H2, yields productions between 0.5 and 3.5 t H2/day, with electrical efficiencies above 70%. A 20-year financial analysis indicates a techno-economic threshold near 3 MW (NPV > 0; IRR > WACC), with optimal performance in the 6.5–10 MW range and payback periods between 2 and 4 years under internal valorization of the surplus electricity. From an environmental perspective, the produced hydrogen is classified as low-carbon rather than “green” due to its thermal origin; however, the integration improves the turbines’ operating regime and valorizes surplus electrical exergy that was previously unused, providing a replicable strategy for industrial assets with self-generation and treatable water availability.
10 March 2026