Cotton Textile with Antimicrobial Activity and Enhanced Durability Produced by L-Cysteine-Capped Silver Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Silver Nanoparticle Synthesis and Cotton Fabric Preparation
2.2. Analytical Characterization of the Cys-AgNPs, Bio-AgNPs Solutions, and the Cotton Fabric Covered in Cys-AgNPs and Bio-AgNPs
2.3. Characterization of the Cotton Fabric Covered in Cys-AgNPs and Bio-AgNPs
2.4. Antibacterial Activity of the Cotton Fabric Covered in L-Cys-AgNPs, bio-AgNPs, and AgNO3
3. Results and Discussions
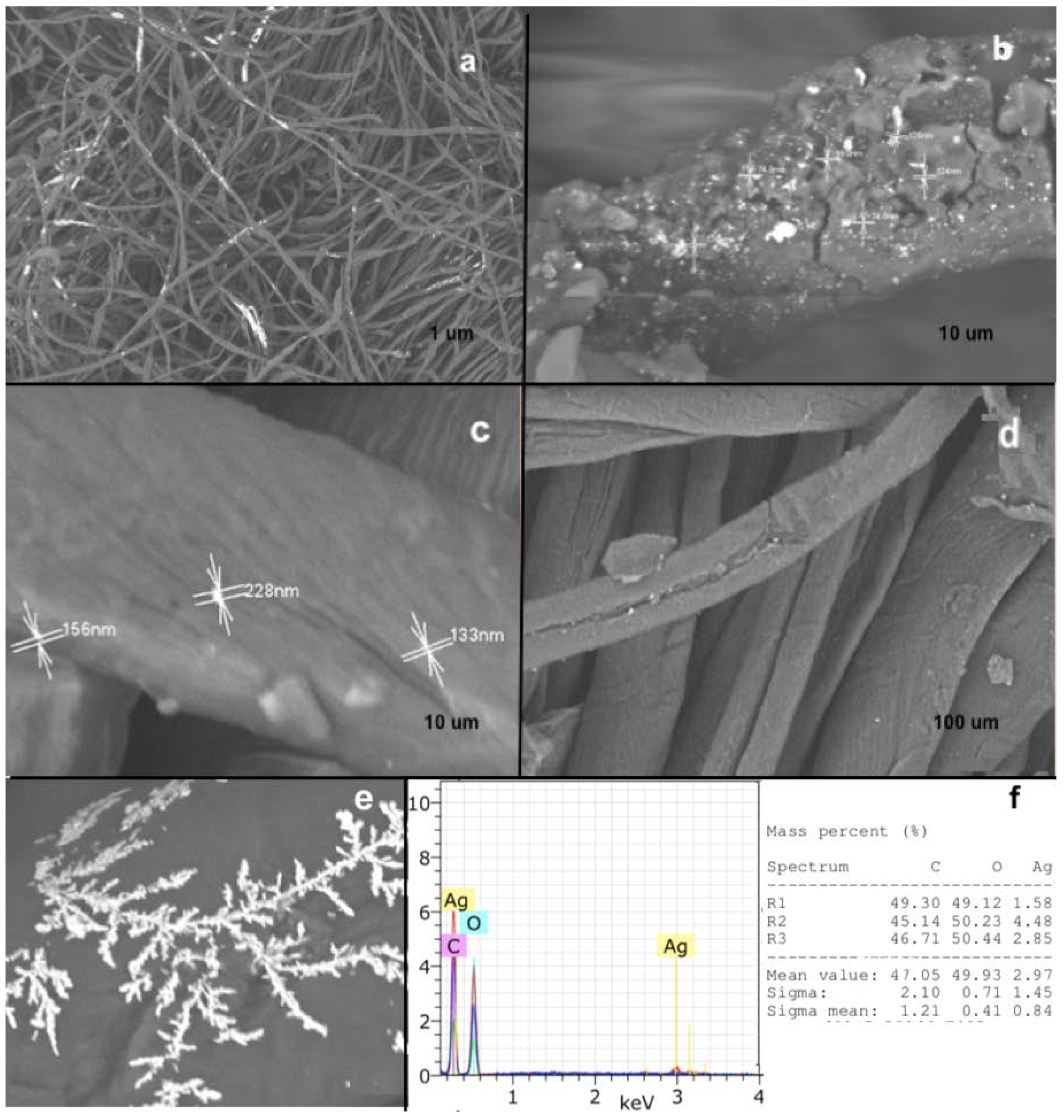
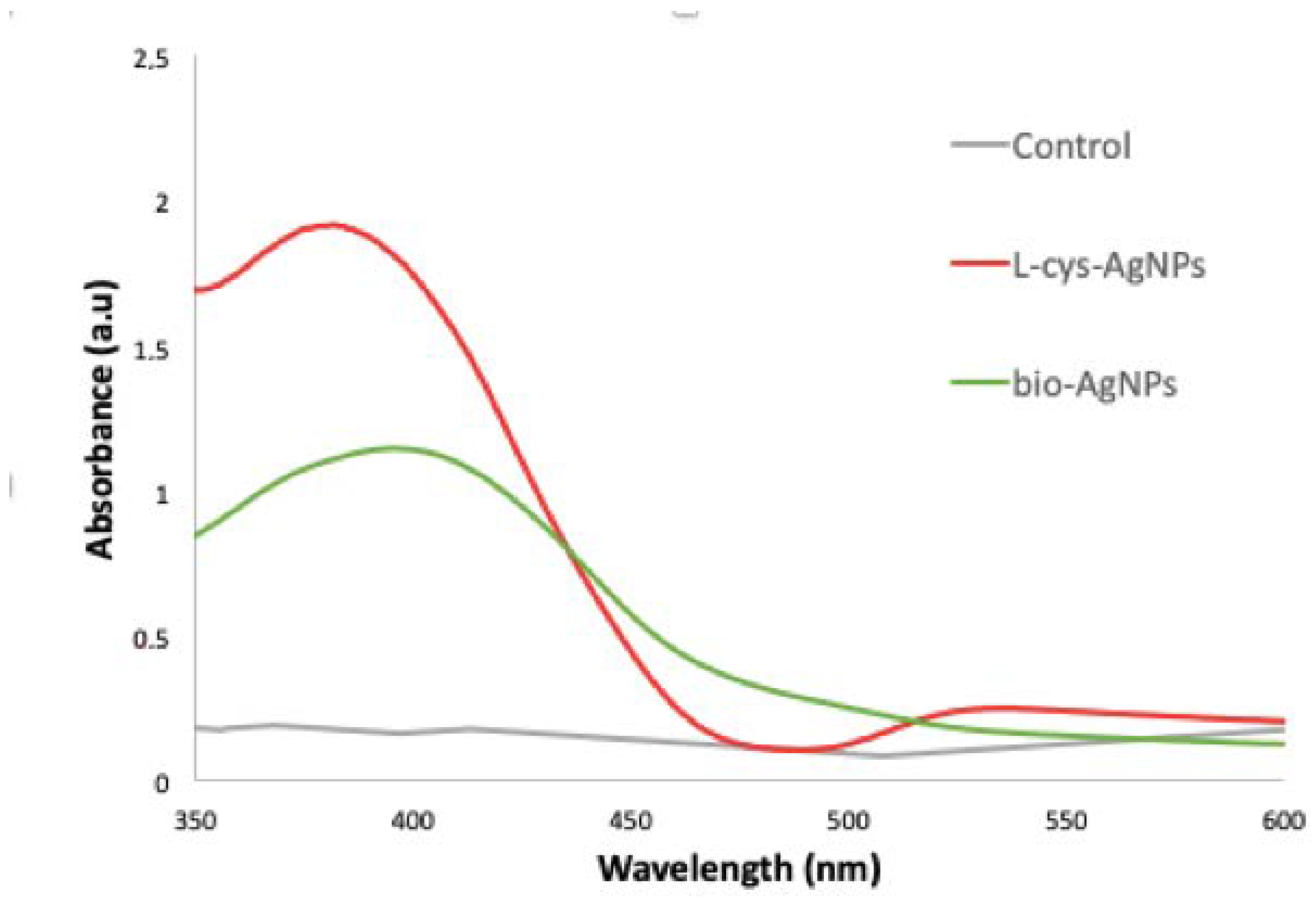
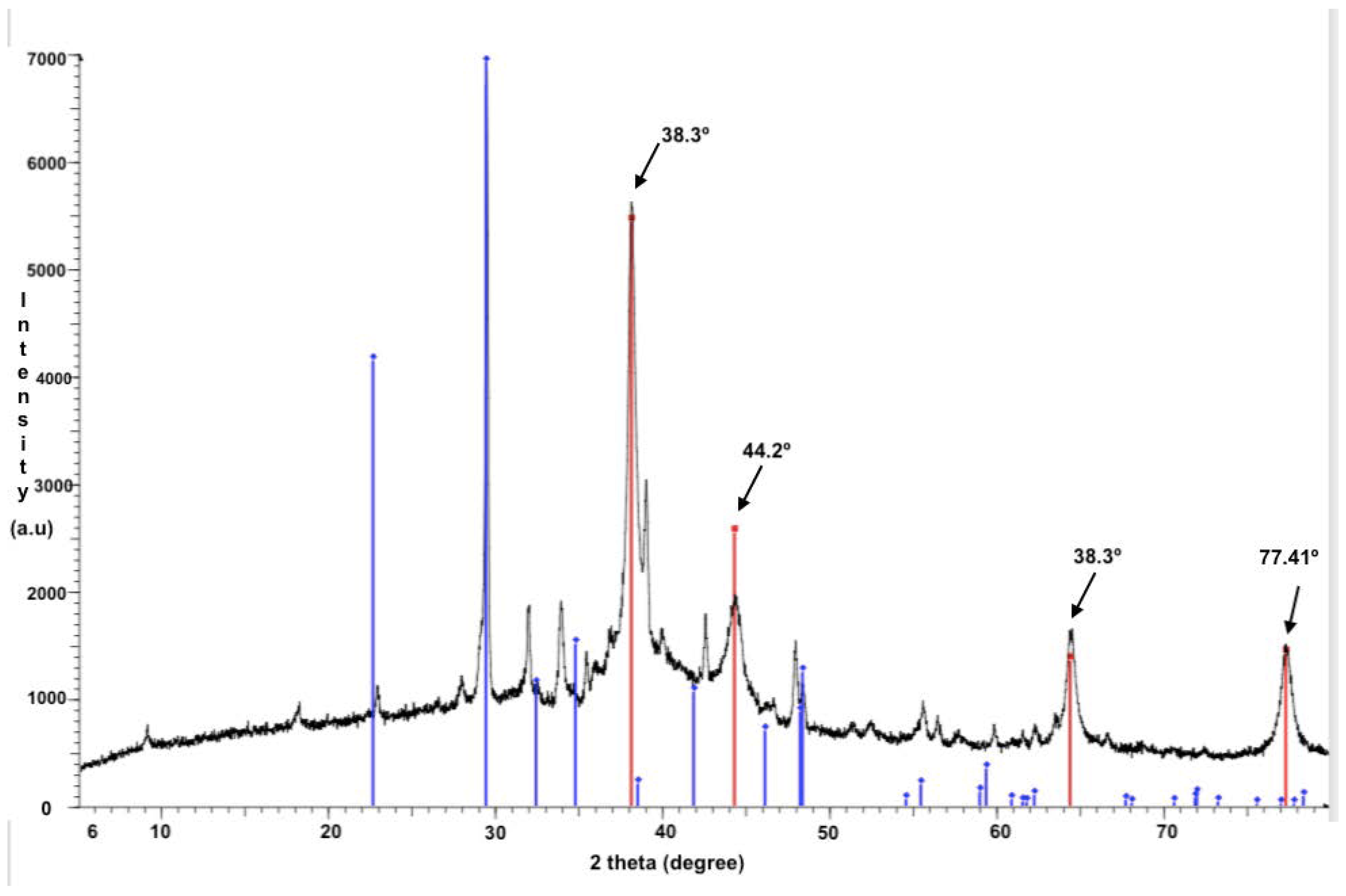
3.1. Characterization of the L-Cys-AgNPs and the Bio-AgNPs Previous Stabilization onto the Cotton Fabric
3.2. Characterization of the Cotton Fabric Covered in L-Cys-AgNPs, Bio-AgNPs, and AgNO3
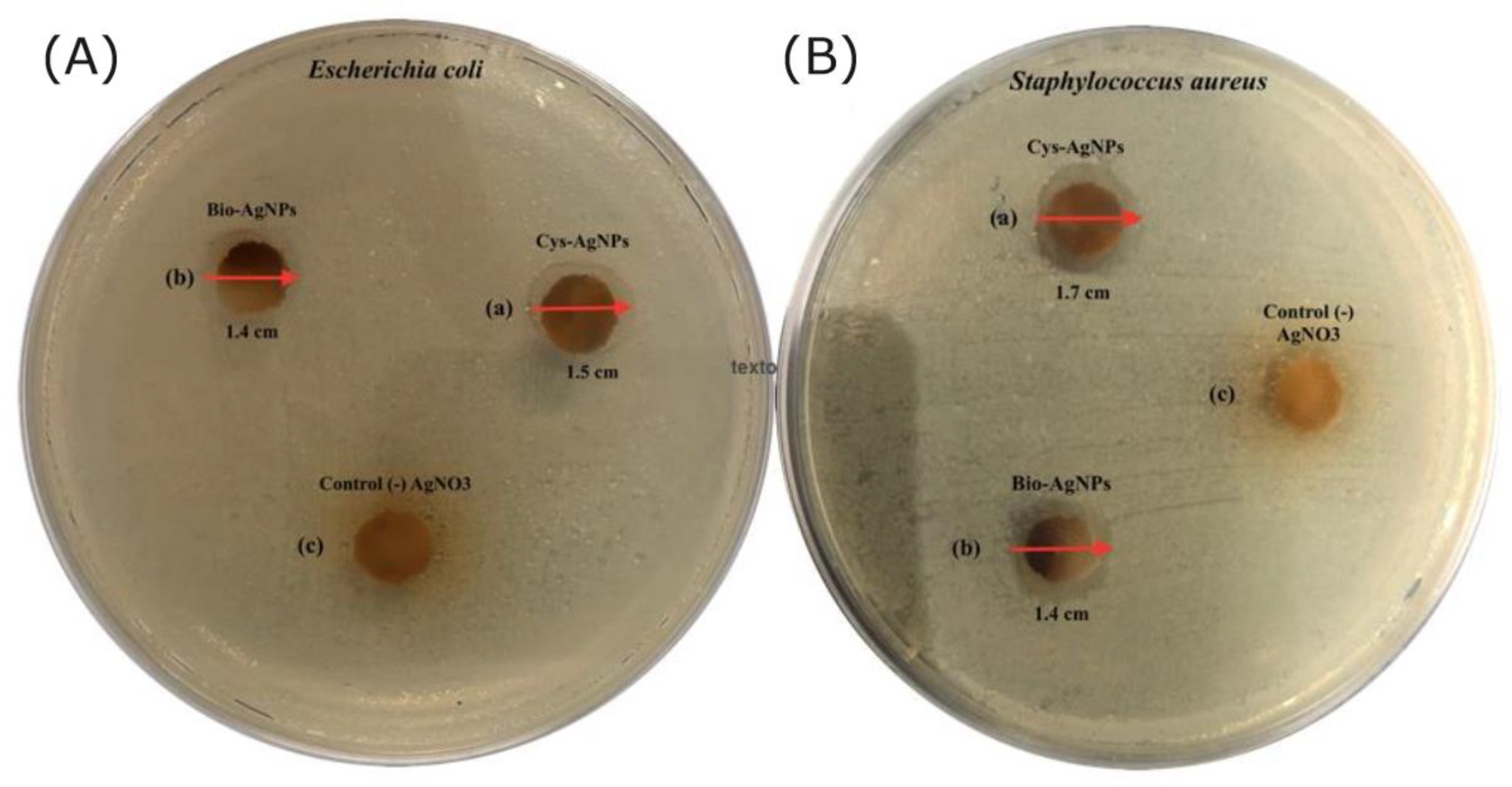
3.3. Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of the Optimized L-Cys-AgNPs and the Bio-AgNPs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahluwalia, V.; Elumalai, S.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Sangwan, R. Nanosilver particle synthesis using Swertia paniculata herbal extract and its antimicrobial activity. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 114, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.; Vizuete, K.S.; Sharma, V.; Debut, A.; Cumbal, L. Ecofriendly synthesis of monodispersed silver nanoparticles using Andean Mortiño berry as reductant and its photocatalytic activity. Vacuum 2019, 160, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, B.H.; Nazir, M.; Muhammad, W.; Hashmi, S.S.; Rahman, L.; Hano, C. A Comparative Evaluation of the Antiproliferative Activity against HepG2 Liver Carcinoma Cells of Plant-Derived Silver Nanoparticles from Basil Extracts with Contrasting Anthocyanin Contents. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saravanan, M.; Arokiyaraj, S.; Lakshmi, T.; Pugazhendhi, A. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Phenerochaete chrysosporium (MTCC-787) and their antibacterial activity against human pathogenic bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 117, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.L.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Shaheen, T.I.; Hassabo, A.G. Laminating of chemically modified silan based nanosols for advanced functionalization of cotton textiles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 95, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Lin, X.; Zou, F.; Fan, Y.; Li, D.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X. In situ synthesis of gold nanoparticles on cotton fabric for multifunctional applications. Cellulose 2017, 24, 4547–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, N.K.; Zille, A.; Oliveira, F.R.; Carneiro, N.; Souto, A.P. Effect of Particle Size on Silver Nanoparticle Deposition onto Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) Plasma Functionalized Polyamide Fabric. Plasma Processes Polym. 2013, 10, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rashidi, A.; Shahidi, S.; Ghoranneviss, M.; Dalalsharifi, S.; Wiener, J. Effect of Plasma on the Zeta Potential of Cotton Fabrics. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2013, 15, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuranova, T.; Rincon, A.G.; Bozzi, A.; Parra, S.; Pulgarin, C.; Albers, P.; Kiwi, J. Antibacterial textiles prepared by RF-plasma and vacuum-UV mediated deposition of silver. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2003, 161, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahltig, B.; Haufe, H.; Böttcher, H. Functionalisation of textiles by inorganic sol–gel coatings. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 4385–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Hernandez, G.; Di Girolamo, M.; Sarret, G.; Bureau, S.; Fernandez-Martinez, A.; Lelong, C.; Eymard Vernain, E. In situ formation of silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) onto textile fibers. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 1316–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, G.; Chakraborty, J.N. Antimicrobial performance of cotton finished with triclosan, silver and chitosan. Fash. Text. 2015, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, K.H. Preparation and properties of multifunctional cotton fabrics treated by phenolic acids. Cellulose 2014, 21, 2111–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burden, M.; Cervantes, L.; Weed, D.; Keniston, A.; Price, C.S.; Albert, R.K. Newly cleaned physician uniforms and infrequently washed white coats have similar rates of bacterial contamination after an 8 h workday: A randomized controlled trial. J. Hops. Med. 2011, 6, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.Y.; Hui, S.; Jun, H.C. Hydrogen-Bond-Mediated in Situ Fabrication of AgNPs/Agar/PAN Electrospun Nanofibers as Reproducible SERS Substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 1586–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisternas, C.; Tortella, G.; Seabra, A.B.; Pieretti, J.C.; Araya-Castro, K.; Hermosilla, E.; Cristina Diez, M.; Rubilar, O. Development of a new biomimetic method for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles based on fungal metabolites: Optimization and antibacterial activity. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.; Kalathil, S.; Lee, J.T.; Cho, M.H. Synthesis of L-Cysteine Capped Silver Nanoparticles by Electrochemically Active Biofilm and their Antibacterial Activities. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc 2012, 33, 2592–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manosalva, N.; Tortella, G.; Diez, M.C.; Schalchli, H.; Seabra, A.B.; Durán, N.; Rubilar, O. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Effect of synthesis reaction parameters on antimicrobial activity. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalishwaralal, K.; Deepak, V.; Ramkumarpandian, S.; Nellaiah, H.; Sangiliyandi, G. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by the culture supernatant of Bacillus licheniformis. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 4411–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaviya, S.; Santhanalakshmi, J. Biosynthesis of silver nano-flakes by Crossandra infundibuliformis leaf extract. Mater. Lett. 2012, 79, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansell, M.P.; Limwaikambo, L. The structure of cotton and other plant fibers. In Handbook of Fibers and Other Textiles; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 63–64. [Google Scholar]
- Shakirullah, M.; Ahmad, W.; Ahmad, I.; Ishaq, M.; Khan, M.I. Desulphurization of liquid fuels by selective adsorption through mineral clays as adsorbents. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2012, 57, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, C.; Lee, M.; Choe, E.K. Characterization of cotton fabric scouring by FT-IR ATR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 58, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Duan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, F.; Liu, X. Double Protect Copper Nanoparticles Loaded on L-cysteine Modified Cotton Fabric with Durable Antibacterial Properties. Fibers Polym. 2018, 19, 2324–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Susceptibility Testing of Mycobacteria, Nocardia, and Other Aerobic Actinomycetes; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Paredes, D.; Ortiz, C.; Torres, R. Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of antibacterial effect of Ag nanoparticles against Escherichia coli O157:H7 and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 1717–1729. [Google Scholar]
- Raffi, M.; Hussain, F.; Bhatti, T.M.; Akhter, J.I.; Hameed, A.; Hasan, M.M. Antibacterial characterization of silver nanoparticles against E. coli ATCC-15224. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2008, 24, 192–196. [Google Scholar]
- Ivask, A.; ElBadawy, A.; Kaweeteerawat, C. Toxicity mechanisms in Escherichia coli vary for silver nanoparticles and differ from ionic silver. ACS Nano 2013, 8, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.S.; Cha, J.-R.; Gong, M.-S. Investigation of the antimicrobial and wound healing properties of silver nanoparticle-loaded cotton prepared using silver carbamate. Text. Res. J. 2017, 88, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Size (nm) | Z-Potential (mV) | PDI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| L-Cys-AgNPs | 89 | −27 | 0.151 |
| Bio-AgNPs | 109 | −24 | 0.12 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Novoa, C.C.; Tortella, G.; Seabra, A.B.; Diez, M.C.; Rubilar, O. Cotton Textile with Antimicrobial Activity and Enhanced Durability Produced by L-Cysteine-Capped Silver Nanoparticles. Processes 2022, 10, 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10050958
Novoa CC, Tortella G, Seabra AB, Diez MC, Rubilar O. Cotton Textile with Antimicrobial Activity and Enhanced Durability Produced by L-Cysteine-Capped Silver Nanoparticles. Processes. 2022; 10(5):958. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10050958
Chicago/Turabian StyleNovoa, Carla Cisternas, Gonzalo Tortella, Amedea B. Seabra, María Cristina Diez, and Olga Rubilar. 2022. "Cotton Textile with Antimicrobial Activity and Enhanced Durability Produced by L-Cysteine-Capped Silver Nanoparticles" Processes 10, no. 5: 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10050958
APA StyleNovoa, C. C., Tortella, G., Seabra, A. B., Diez, M. C., & Rubilar, O. (2022). Cotton Textile with Antimicrobial Activity and Enhanced Durability Produced by L-Cysteine-Capped Silver Nanoparticles. Processes, 10(5), 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10050958









