A Catechol-Meter Based on Conventional Personal Glucose Meter for Portable Detection of Tyrosinase and Sodium Benzoate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Reagent Preparation
2.4. Detection of TYR Activity and SBA by the PGM-Based Method
2.5. Inhibition Kinetics Study and Validation of the PGM-Based Method
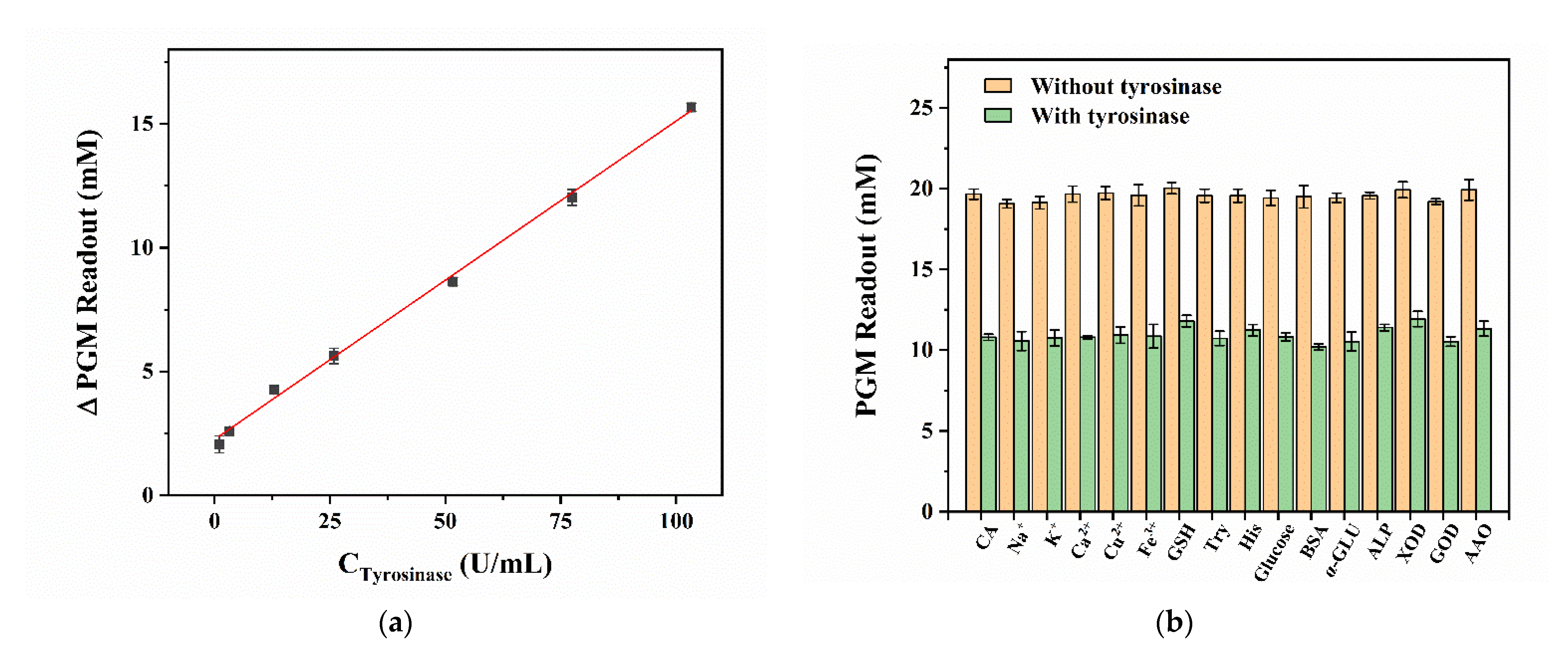
2.6. Selectivity and Interferences Studies
2.7. Real Sample Analysis
2.8. HPLC Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
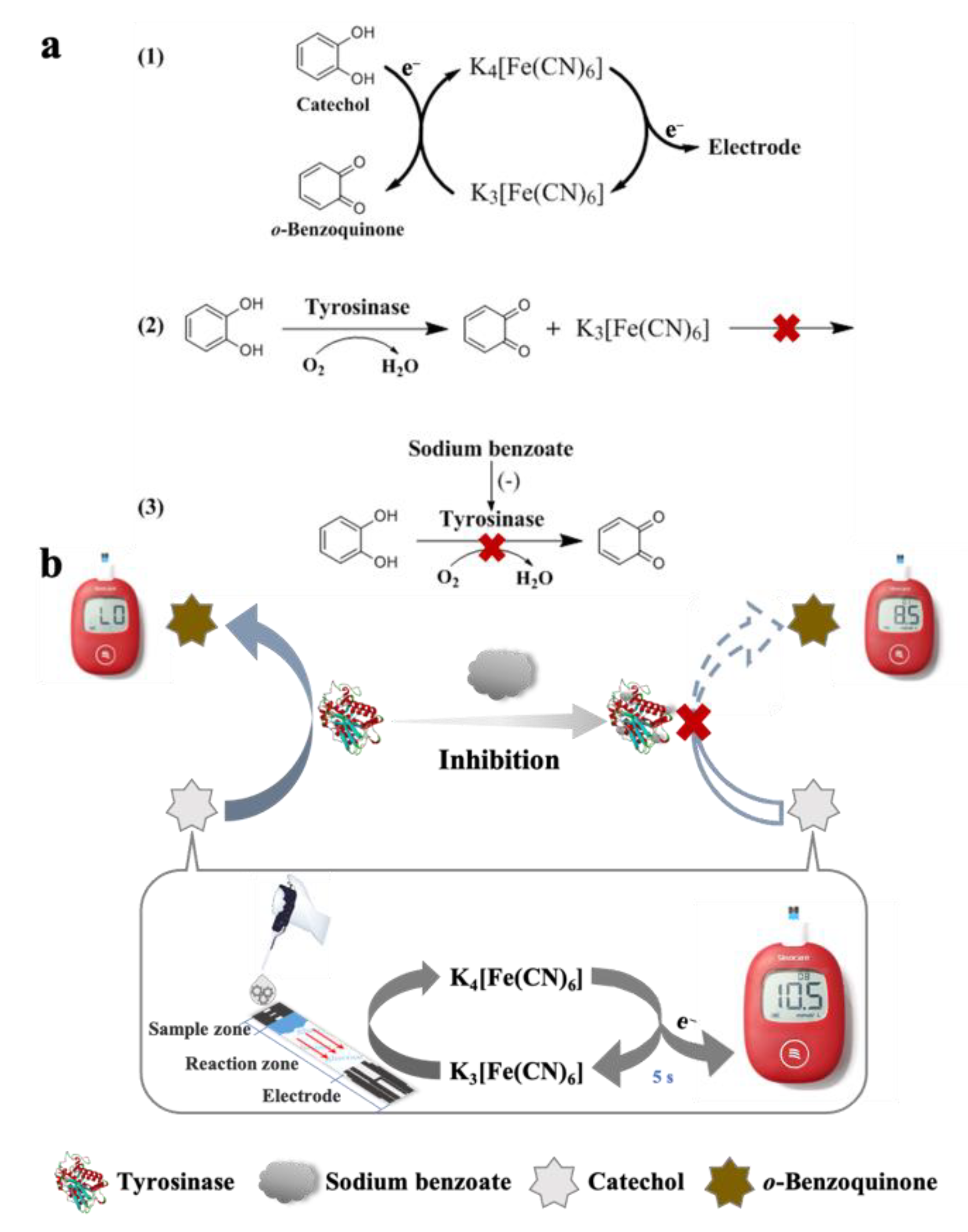
3.1. Principle of Portable Detection of TYR Activity and SBA
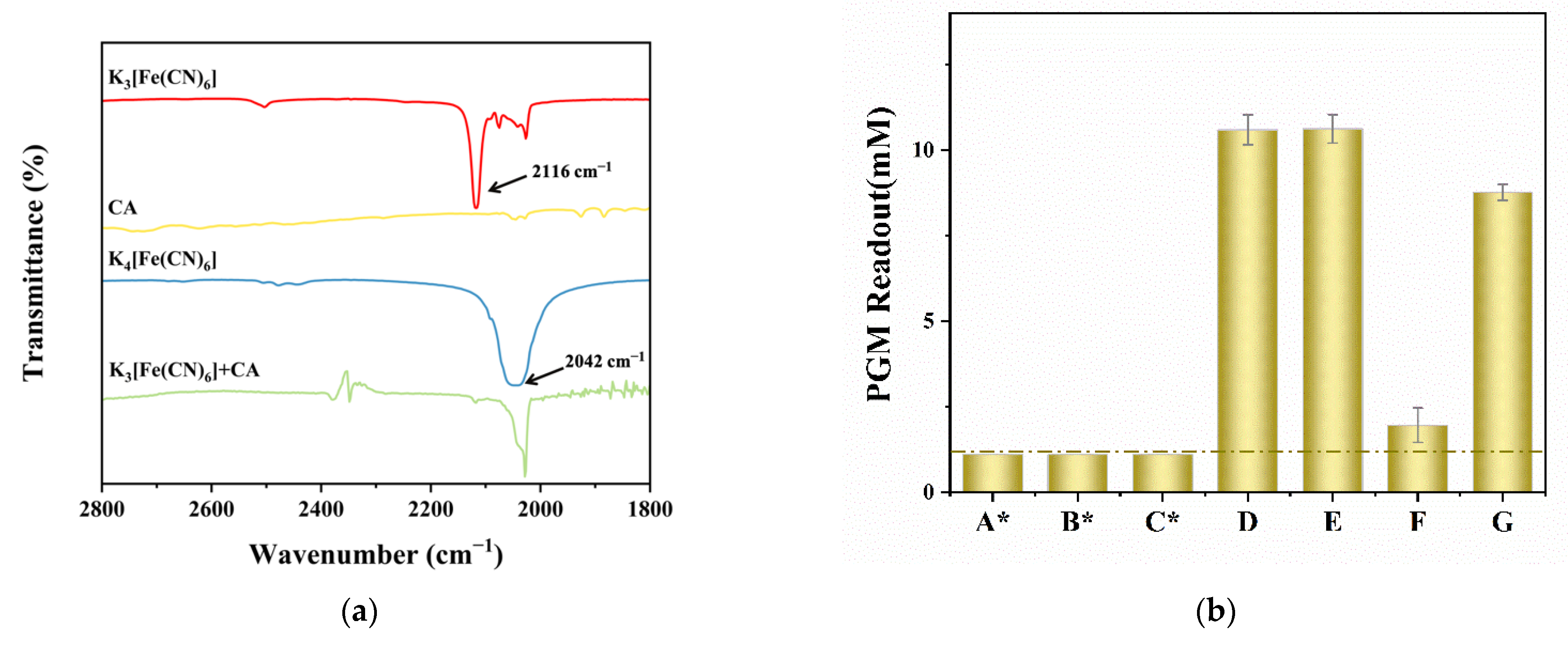
3.2. Optimization of the Experimental Conditions
3.3. Portable Detection of TYR Activity by the PGM-Based Method
3.4. Portable Detection of SBA by the PGM-Based Method
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Surekha, M.; Reddy, S.M. Preservatives|Classification and Properties. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Olmo, A.; Calzada, J.; Nunez, M. Benzoic acid and its derivatives as naturally occurring compounds in foods and as additives: Uses, exposure, and controversy. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3084–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Brashears, M.M.; Zhong, Q. Sodium benzoate and sodium bisulfate as preservatives in apple juice and alternative sanitizers for washing cherry tomatoes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 372, 109697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, B. Final report on the safety assessment of benzyl alcohol, benzoic acid, and sodium benzoate. Int. J. Toxicol. 2001, 20 (Suppl. S3), 23–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piper, J.D.; Piper, P.W. Benzoate and sorbate salts: A systematic review of the potential hazards of these invaluable preservatives and the expanding spectrum of clinical uses for sodium benzoate. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 868–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praphanphoj, V.; Boyadjiev, S.A.; Waber, L.J.; Brusilow, S.W.; Geraghty, M.T. Three cases of intravenous sodium benzoate and sodium phenylacetate toxicity occurring in the treatment of acute hyperammonaemia. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2000, 23, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Hong, H.; Liang, X.Y.; Liu, D.H. Assessment of benzoic acid levels in milk in China. Food Control. 2009, 20, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, S.L.; Quartey, N.K.A.; Ofosu, I.W. Sodium benzoate in non-alcoholic carbonated (soft) drinks: Exposure and health risks. Sci. Afr. 2020, 10, e00611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Xie, Y.; Qiao, X.; Bai, S. The China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA). In Approaching China’s Pharmaceutical Market; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 239–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Li, W.; Yang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, T. Online preconcentration in capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection for sensitive determination of sorbic and benzoic acids in soy sauce. Talanta 2011, 83, 1487–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.H.; Hu, C.C.; Chiu, T.C. Online dynamic pH junction-sweeping for the determination of benzoic and sorbic acids in food products by capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, B.; Bari, M.F.; Saleh, M.I.; Ahmad, K.; Talib, M.K. Simultaneous determination of preservatives (benzoic acid, sorbic acid, methylparaben and propylparaben) in foodstuffs using high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1073, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pylypiw, H.M.; Grether, M.T. Rapid high-performance liquid chromatography method for the analysis of sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate in foods. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 883, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goren, A.C.; Bilsel, G.; Simsek, A.; Bilsel, M.; Akcadag, F.; Topal, K.; Ozgen, H. HPLC and LC-MS/MS methods for determination of sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate in food and beverages: Performances of local accredited laboratories via proficiency tests in Turkey. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Üstün Özgür, M.; Kasapoğlu, M. Development and validation of a simple ultra fast liquid chromatographic method for the simultaneous determination of aspartame, acesulfame-k, caffeine and sodium benzoate in dietic soft drinks. J. Anal. Chem. 2019, 74, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, H.; Liu, P.; Qin, X.; Liu, G. Colorimetric quantification of sodium benzoate in food by using d-amino acid oxidase and 2D metal organic framework nanosheets mediated cascade enzyme reactions. Talanta 2022, 237, 122906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiyoshi, T.; Ikami, T.; Kikukawa, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Takai, R.; Kozaki, D.; Yamamoto, A. Direct quantitation of the preservatives benzoic and sorbic acid in processed foods using derivative spectrophotometry combined with micro dialysis. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Pi, F.; Sun, X. Sensitive techniques for POCT sensing on the residues of pesticides and veterinary drugs in food. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Wang, Y.N.; Fu, L.M.; Chen, K.L. Microfluidic paper-based chip platform for benzoic acid detection in food. Food Chem. 2018, 249, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.H.; Liu, C.C.; Chen, K.H.; Sheu, F.; Fu, L.M.; Chen, S.J. Microfluidic colorimetric analysis system for sodium benzoate detection in foods. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.; Prabhu, A.; Prasad, D.; Garlapati, V.K.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Mani, N.K.; Simal-Gandara, J. Paper-based microfluidic devices for food adulterants: Cost-effective technological monitoring systems. Food Chem. 2022, 390, 133173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musacchio, N.; Ciullo, I.; Scardapane, M.; Giancaterini, A.; Pessina, L.; Maino, S.; Gaiofatto, R.; Nicolucci, A.; Rossi, M.C.; Self-Care Study, G. Efficacy of self-monitoring blood glucose as a key component of a chronic care model versus usual care in type 2 diabetes patients treated with oral agents: Results of a randomized trial. Acta Diabetol. 2018, 55, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Yao, L.; Yan, C.; Xu, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, G.; Yao, B.; Chen, W. Recent progress of personal glucose meters integrated methods in food safety hazards detection. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 62, 7413–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Gong, J.; Rong, P.; Liu, C.; Chen, J. A portable and quantitative biosensor for cadmium detection using glucometer as the point-of-use device. Talanta 2019, 198, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, G.Y.; Qian, Z.M.; Li, W.J.; Li, C.H.; Hu, Y.J.; Yang, F.Q. A portable personal glucose meter method for enzyme activity detection and inhibitory activity evaluation based on alkaline phosphatase-mediated reaction. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 2457–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, F.Q. A simple and portable method for beta-Glucosidase activity assay and its inhibitor screening based on a personal glucose meter. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1142, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, D.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, D.; Tang, Y.; Hu, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Han, Z. A flexible assay strategy for non-glucose targets based on sulfhydryl-terminated liposomes combined with personal glucometer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 175, 112884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.K.; Ray, P.; Carlin, A.F.; Magallanes, C.; Morgan, S.C.; Laurent, L.C.; Aronoff-Spencer, E.S.; Hall, D.A. Hitting the diagnostic sweet spot: Point-of-care SARS-CoV-2 salivary antigen testing with an off-the-shelf glucometer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 180, 113111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Daglia, M.; Xiao, J.; Shi, J.; Zou, X. Bioinspired nanozyme enabling glucometer readout for portable monitoring of pesticide under resource-scarce environments. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, F.Q. Ascorbate oxidase enabling glucometer readout for portable detection of hydrogen peroxide. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2022, 160, 110096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gong, Z.M.; Li, Y.; Yang, F.Q. A simple and green method for direct determination of hydrogen peroxide and hypochlorite in household disinfectants based on personal glucose meter. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2022, 155, 109996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tief, K.; Hahne, M.; Schmidt, A.; Beermann, F. Tyrosinase, the key enzyme in melanin synthesis, is expressed in murine brain. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 241, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolff, M.; Schottenheim, J.; Decker, H.; Tuczek, F. Copper-O2 reactivity of tyrosinase models towards external monophenolic substrates: Molecular mechanism and comparison with the enzyme. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4077–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fartas, F.M.; Abdullah, J.; Yusof, N.A.; Sulaiman, Y.; Saiman, M.I. Biosensor based on tyrosinase immobilized on graphene-decorated gold nanoparticle/chitosan for phenolic detection in aqueous. Sensors 2017, 17, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancelliere, R.; Carbone, K.; Pagano, M.; Cacciotti, I.; Micheli, L. Biochar from brewers’ spent grain: A green and low-cost smart material to modify screen-printed electrodes. Biosensors 2019, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.S. An updated review of tyrosinase inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 2440–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paisan-Ruiz, C.; Houlden, H. Common pathogenic pathways in melanoma and Parkinson disease. Neurology 2010, 75, 1653–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.F.; Zhu, S.X.; Hou, F.B.; Zhao, D.F.; Pan, Q.S.; Xiang, Y.W.; Qian, X.K.; Ge, G.B.; Wang, P. Spectrophotometric assays for sensing tyrosinase activity and their applications. Biosensors 2021, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Gao, W.; Halawa, M.I.; Lan, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, G. Lucigenin fluorescent assay of tyrosinase activity and its inhibitor screening. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 280, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Xu, T.; Liang, K.; Li, J.; Fang, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Tang, Y.; et al. Self-assembled peptides-modified flexible field-effect transistors for tyrosinase detection. iScience 2022, 25, 103673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.; Zayats, M.; Willner, I. Dopamine-, L-DOPA-, adrenaline-, and noradrenaline-induced growth of Au nanoparticles: Assays for the detection of neurotransmitters and of tyrosinase activity. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooksey, C.J.; Garratt, P.J.; Land, E.J.; Ramsden, C.A.; Riley, P.A. Tyrosinase kinetics: Failure of the auto-activation mechanism of monohydric phenol oxidation by rapid formation of a quinomethane intermediate. Biochem. J. 1998, 333, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.; Fleck, R.W.; Yong, G.; Strothkamp, K.G. Benzoic acid inhibition of the α, β, and γ Isozymes of Agaricus bisporus tyrosinase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1990, 280, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Caër, S.; Vigneron, G.; Renault, J.P.; Pommeret, S. First coupling between a LINAC and FT-IR spectroscopy: The aqueous ferrocyanide system. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 426, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, D.; Xu, Q.; Hu, X. A promising voltammetric biosensor based on glutamate dehydrogenase/Fe3O4/graphene/chitosan nanobiocomposite for sensitive ammonium determination in PM2.5. Talanta 2019, 197, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Ferrer, Á.; Neptuno Rodríguez-López, J.; García-Cánovas, F.; García-Carmona, F. Tyrosinase: A comprehensive review of its mechanism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1995, 1247, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanes, J.; García-Cánovas, F.; Lozano, J.; García-Carmona, F. A kinetic study of the melanization pathway between L-tyrosine and dopachrome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 1987, 923, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.H.; Sun, Y.; Ma, P.Y.; Huang, Y.B.; Song, D.Q. Near-infrared fluorescent probe based on Ag&Mn:ZnInS QDs for tyrosinase activity detection and inhibitor screening. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.N.; Deng, B.; Yang, S.X.; Tian, H.Y.; Liu, Y.G.; Sun, B.G. A fluorescent probe for the visible colorimetric detection of tyrosinase. Chemistryselect 2021, 6, 9046–9051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, L.; Shi, W.; Gong, Q.; Ma, H. Near-infrared fluorescent probe with new recognition moiety for specific detection of tyrosinase activity: Design, synthesis, and application in living cells and zebrafish. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2016, 55, 14728–14732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhang, L.M.; Tian, Y. Electrochemical detection of tyrosinase in cell lysates at functionalized nanochannels via amplifying of ionic current response. Electroanalysis 2022, 34, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Xie, L.; Liu, J.; Zheng, J. Effective detection of tyrosinase by Keggin-type polyoxometalate-based electrochemical sensor. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2022, 26, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amore, T.; Di Taranto, A.; Berardi, G.; Vita, V.; Iammarino, M. Going green in food analysis: A rapid and accurate method for the determination of sorbic acid and benzoic acid in foods by capillary ion chromatography with conductivity detection. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 141, 110841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iammarino, M.; Taranto, A.D. Development and validation of an ion chromatography method for the simultaneous determination of seven food additives in cheeses. J. Anal. Sci. 2013, 3, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Chen, L.; Dong, J.; Cai, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with surface enhanced Raman scattering for the rapid detection of sodium benzoate. Talanta 2020, 208, 120360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamzah, H.H.; Yusof, N.A.; Salleh, A.B.; Bakar, F.A. An optical test strip for the detection of benzoic acid in food. Sensors 2011, 11, 7302–7313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Samples | Spiked (ppm) | PGM-Based Method | HPLC Method | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Found (ppm) | Recovery (%) | Found (ppm) | Recovery (%) | ||
| Cola | 0 | 0 a | - | 0 a | - |
| 50 | 46.2 ± 2.4 | 92.3 | 47.9 ± 2.1 | 95.9 | |
| 100 | 95.1 ± 2.9 | 95.1 | 98.4 ± 1.4 | 98.4 | |
| 200 | 213.5 ± 11.1 | 106.8 | 202.6 ± 8.4 | 101.3 | |
| Sprite | 0 | 151.5 ± 9.3 | - | 156.5 ± 5.1 | - |
| 50 | 52.2 ± 2.0 | 104.4 | 46.9 ± 0.2 | 93.7 | |
| 100 | 95.7 ± 8.7 | 95.7 | 98.5 ± 2.5 | 98.5 | |
| 200 | 183.3 ± 5.8 | 91.6 | 195.8 ± 1.4 | 97.9 | |
| Fanta | 0 | 179.5 ± 9.4 | - | 183.1 ± 0.3 | - |
| 50 | 47.3 ± 5.0 | 94.7 | 51.7 ± 0.4 | 103.4 | |
| 100 | 105.5 ± 9.4 | 105.5 | 100.0 ± 4.6 | 100.0 | |
| 200 | 212.4 ± 6.8 | 106.2 | 205.3 ± 2.2 | 102.7 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, T.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Zhou, H.-Y.; Peng, L.-J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, F.-Q. A Catechol-Meter Based on Conventional Personal Glucose Meter for Portable Detection of Tyrosinase and Sodium Benzoate. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121084
Tian T, Zhang W-Y, Zhou H-Y, Peng L-J, Zhou X, Zhang H, Yang F-Q. A Catechol-Meter Based on Conventional Personal Glucose Meter for Portable Detection of Tyrosinase and Sodium Benzoate. Biosensors. 2022; 12(12):1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121084
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Tao, Wei-Yi Zhang, Hang-Yu Zhou, Li-Jing Peng, Xi Zhou, Hao Zhang, and Feng-Qing Yang. 2022. "A Catechol-Meter Based on Conventional Personal Glucose Meter for Portable Detection of Tyrosinase and Sodium Benzoate" Biosensors 12, no. 12: 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121084
APA StyleTian, T., Zhang, W.-Y., Zhou, H.-Y., Peng, L.-J., Zhou, X., Zhang, H., & Yang, F.-Q. (2022). A Catechol-Meter Based on Conventional Personal Glucose Meter for Portable Detection of Tyrosinase and Sodium Benzoate. Biosensors, 12(12), 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12121084






