Pathological Insight into 5-HT2B Receptor Activation in Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
1.2. Systemic Sclerosis
1.3. Rheumatoid Arthritis
1.4. Current Therapeutic Strategies
2. The Serotonergic Pathways in Tissue Repair and Fibrosis
5-HT Synthesis and Signaling
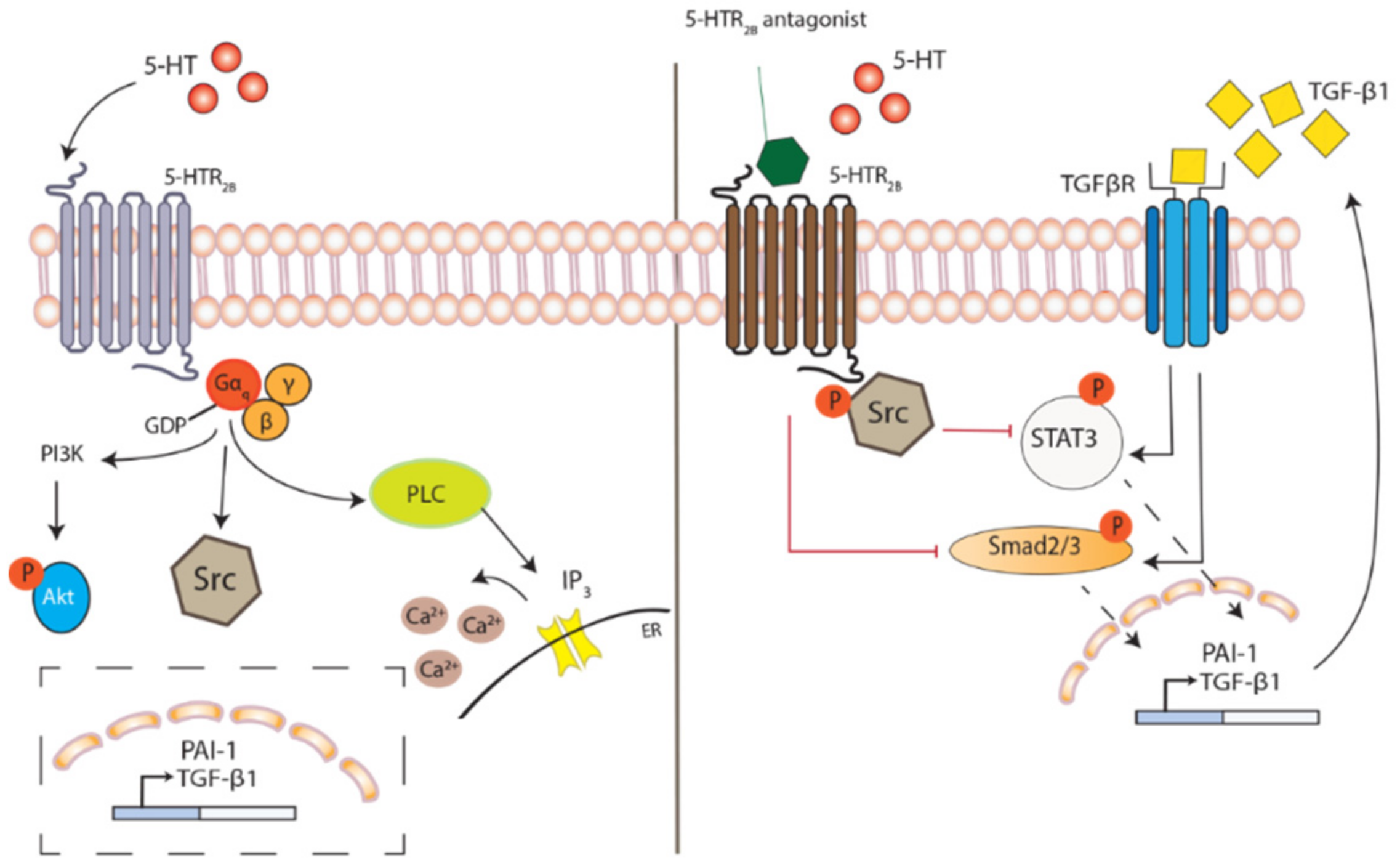
3. TGF-β—A Potential Second Messenger to 5-HT
3.1. A Piece of PAI?
3.2. Impacts of 5-HT2 Receptor Activation on Downstream Signaling
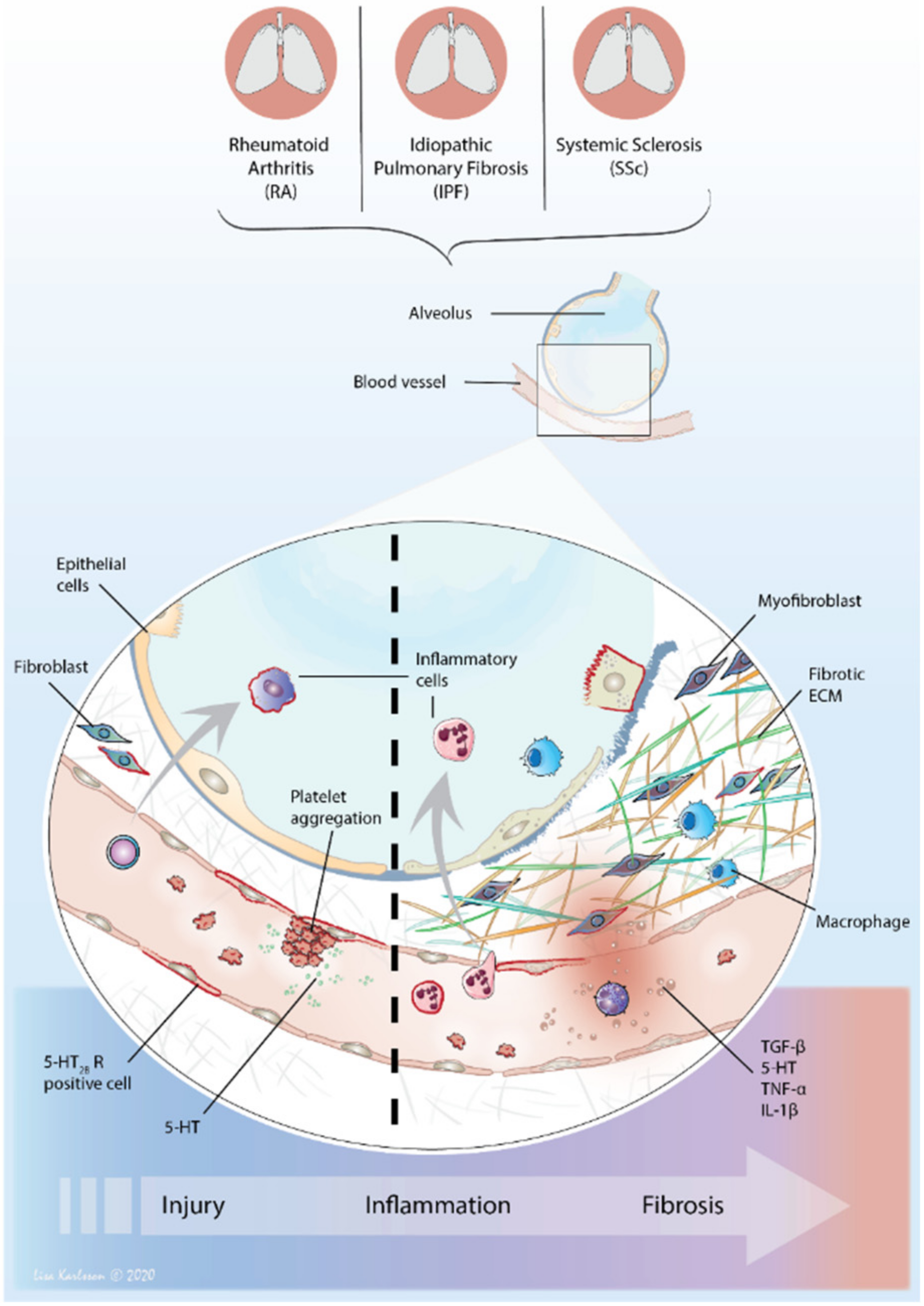
4. Vascular Impact in ILD—A Local Delivery System for 5-HT
5. The Immune Modulating Impact of 5-HT
6. The Perfect Interstitial Storm—Vascular System, Inflammation and Fibrosis
6.1. 5-HT—From Circulation to Local Tissue Delivery
6.2. The Distribution of 5-HT2 Receptors—Tuning Inflammation and Fibrosis
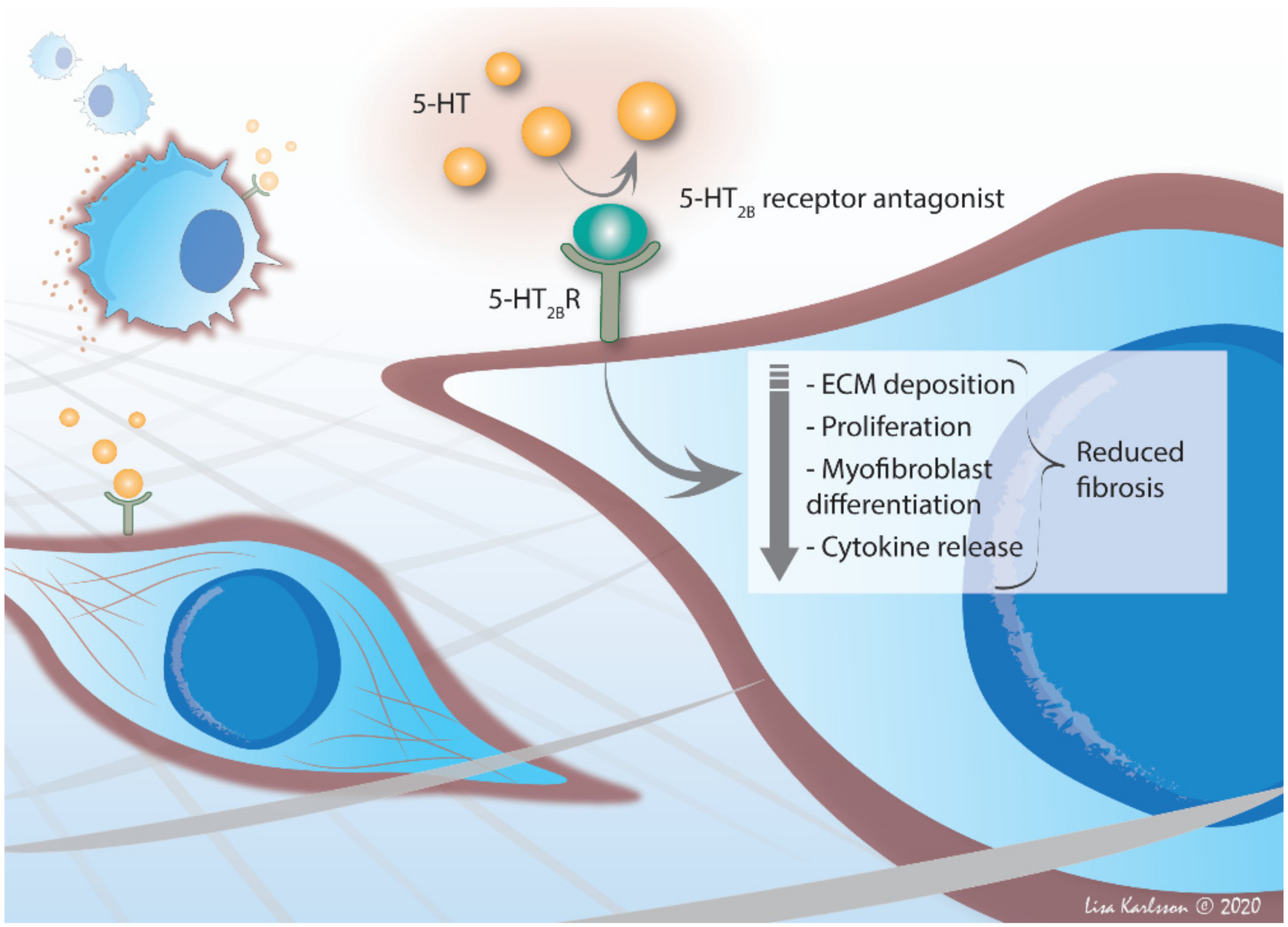
6.3. 5-HT2B Receptor—An Important Player in Fibrosis
7. Therapeutic Potential in 5-HT2B Receptor Antagonism
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ILD | Interstitial lung disease |
| PF | Progressive fibrosing |
| IPF | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| 5-HT | Serotonin, 5-hydroxytryptamine |
| SSc | Systemic sclerosis |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| UIP | Usual interstitial pneumonia |
| HRCT | High-resolution computed tomography |
| FVC | Forced vital capacity |
| NSIP | Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia |
| lcSSc | Limited cutaneous SSc |
| dcSSc | Diffuse cutaneous SSc |
| ACPA | Anti-citrullinated protein antibody |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| TGF-β1 | Transforming growth factor |
| TPH | Tryptophan hydroxylase |
| IDO | Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase |
| TDO | Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase |
| SERT | Serotonin re-uptake transporter |
| GPCR | G-protein coupled receptors |
| PLC | Phospholipase C |
| IP3 | Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PAI-1 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| α-SMA | Alpha-smooth muscle actin |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| PDGF | Platelet-derived growth factor |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| IL | Interleukin |
| PAH | Pulmonary arterial hypertension |
| vWF | von Willebrand factor |
| Tsk-1 | Tight skin 1 |
| αvβ6 | alphaVbeta6 |
References
- Cottin, V.; Hirani, N.A.; Hotchkin, D.L.; Nambiar, A.M.; Ogura, T.; Otaola, M.; Skowasch, D.; Park, J.S.; Poonyagariyagorn, H.K.; Wuyts, W.; et al. Presentation, diagnosis and clinical course of the spectrum of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 180076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottin, V.; Wollin, L.; Fischer, A.; Quaresma, M.; Stowasser, S.; Harari, S. Fibrosing interstitial lung diseases: Knowns and unknowns. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2019, 28, 180100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Myers, J.; Richeldi, L.; Ryerson, C.J.; Lederer, D.J.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Danoff, S.K.; Morell, F.; et al. Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, e44–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, J.P.; Fogarty, A.W.; Hubbard, R.B.; McKeever, T.M. Global incidence and mortality of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A systematic review. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.-F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Statement: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Evidence-based Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestro, E.; Calabrese, F.; Turato, G.; Lunardi, F.; Bazzan, E.; Marulli, G.; Biondini, D.; Rossi, E.; Sanduzzi, A.; Rea, F.; et al. Immune Inflammation and Disease Progression in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropski, J.A.; Blackwell, T.S. Progress in Understanding and Treating Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2019, 70, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.J.; Collard, H.R.; Pardo, A.; Raghu, G.; Richeldi, L.; Selman, M.; Swigris, J.; Taniguchi, H.; Wells, A.U. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, Y.H.; Ng, Y.; Barnes, H.; Goh, N.S.; McDonald, C.F.; E Holland, A. Prognosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis without anti-fibrotic therapy: A systematic review. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2020, 29, 190158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Collard, H.R. Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Pulm. Funct. Test. 2018, 194, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, J.; Marangoni, R.G. Systemic sclerosis in 2016: Dermal white adipose tissue implicated in SSc pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirsaeidi, M.; Barletta, P.; Glassberg, M.K. Systemic Sclerosis Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: New Directions in Disease Management. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royle, J.G.; Lanyon, P.C.; Grainge, M.J.; Abhishek, A.; A Pearce, F. The incidence, prevalence, and survival of systemic sclerosis in the UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhai, M.; Avouac, J.; Walker, U.A.; Cerinic, M.M.; Riemekasten, G.; Airó, P.; Hachulla, E.; Valentini, G.; E Carreira, P.; Cozzi, F.; et al. A gender gap in primary and secondary heart dysfunctions in systemic sclerosis: A EUSTAR prospective study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 75, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhai, M.; Meune, C.; Boubaya, M.; Avouac, J.; Hachulla, E.; Balbir-Gurman, A.; Riemekasten, G.; Airó, P.; Joven, B.; Vettori, S.; et al. Mapping and predicting mortality from systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distler, O.; Assassi, S.; Cottin, V.; Cutolo, M.; Danoff, S.K.; Denton, C.P.; Distler, J.H.; Hoffmann-Vold, A.-M.; Johnson, S.R.; Ladner, U.M.; et al. Predictors of progression in systemic sclerosis patients with interstitial lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1902026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, E.J.; Jaafar, S.; Assassi, S.; Domsic, R.T.; Frech, T.M.; Gordon, J.K.; Broderick, R.J.; Hant, F.N.; Hinchcliff, M.E.; Shah, A.A.; et al. Performance Characteristics of Pulmonary Function Tests for the Detection of Interstitial Lung Disease in Adults With Early Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 1892–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacchi, C.; Sebastiani, M.; Cassone, G.; Cerri, S.; Della Casa, G.; Salvarani, C.; Manfredi, A. Therapeutic Options for the Treatment of Interstitial Lung Disease Related to Connective Tissue Diseases. A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, U.A.; Tyndall, A.; Czirjak, L.; Denton, C.; Farge-Bancel, D.; Kowal-Bielecka, O.; Muller-Ladner, U.; Bocelli-Tyndall, C.; Matucci-Cerinic, M. Clinical risk assessment of organ manifestations in systemic sclerosis: A report from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials And Research group database. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluett, J.; Jani, M.; Symmons, D.P.M. Practical Management of Respiratory Comorbidities in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatol. Ther. 2017, 4, 309–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisset, J.; Lee, J.S. New trajectories in the treatment of interstitial lung disease: Treat the disease or treat the underlying pattern? Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2019, 25, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimundo, K.; Solomon, J.J.; Olson, A.L.; Kong, A.M.; Cole, A.L.; Fischer, A.; Swigris, J.J. Rheumatoid Arthritis–Interstitial Lung Disease in the United States: Prevalence, Incidence, and Healthcare Costs and Mortality. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 46, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, E.K.; Ambrosini, R.D.; Kottmann, R.M.; Ritchlin, C.T.; Schwarz, E.M.; Rahimi, H. Reinterpreting Evidence of Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease to Understand Etiology. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2019, 15, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, A.J.; Chu, S.G.; Madan, R.; Doyle, T.J.; Dellaripa, P.F. Thoracic Manifestations of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Chest Med. 2019, 40, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparks, J.A.; A Fletcher, E.; Huang, J.; Ba, E.A.F.; Bs, A.Z.; Ba, H.M.F.; Gill, R.R.; Hatabu, H.; Nishino, M.; Murphy, D.J.; et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Activity Predicting Incident Clinically Apparent Rheumatoid Arthritis–Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: A Prospective Cohort Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Clinical Research Network. Prednisone, azathioprine, and N-acetylcysteine for pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1968–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, G.; Steele, R.; Baron, M.; Hudson, M. Corticosteroids and the risk of scleroderma renal crisis: A systematic review. Rheumatol. Int. 2010, 32, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somogyi, V.; Chaudhuri, N.; Torrisi, S.E.; Kahn, N.; Müller, V.; Kreuter, M. The therapy of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: What is next? Eur. Respir. Rev. 2019, 28, 190021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, D.; Ramage, J.; Srirajaskanthan, R. Update on Pathophysiology, Treatment, and Complications of Carcinoid Syndrome. J. Oncol. 2020, 2020, 8341426-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothman, R.B.; Baumann, M.H.; Savage, J.E.; Rauser, L.; McBride, A.; Hufeisen, S.J.; Roth, B.L. Evidence for Possible Involvement of 5-HT 2B Receptors in the Cardiac Valvulopathy Associated With Fenfluramine and Other Serotonergic Medications. Circulation 2000, 102, 2836–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothman, R.B.; Baumann, M.H. Serotonergic drugs and valvular heart disease. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2009, 8, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutcheson, J.D.; Setola, V.; Roth, B.L.; Merryman, W.D. Serotonin receptors and heart valve disease—It was meant 2B. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 132, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löfdahl, A.; Rydell-Törmänen, K.; Müller, C.; Holst, C.M.; Thiman, L.; Ekström, G.; Wenglén, C.; Larsson-Callerfelt, A.; Westergren-Thorsson, G. 5-HT2B receptor antagonists attenuate myofibroblast differentiation and subsequent fibrotic responses in vitro and in vivo. Physiol. Rep. 2016, 4, e12873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaidy, S.M.; Essawy, S.S. The antifibrotic effects of alveolar macrophages 5-HT2C receptors blockade on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Pharmacol. Rep. 2016, 68, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, A.; Marchal-Sommé, J.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Quesnel, C.; Borie, R.; Dehoux, M.; Ruffie, C.; Callebert, J.; Launay, J.M.; Henin, D.; et al. Modulation of bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis by serotonin receptor antagonists in mice. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 32, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, M.K.; Makary, S. 5-HT7 receptor antagonism (SB-269970) attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats via downregulating oxidative burden and inflammatory cascades and ameliorating collagen deposition: Comparison to terguride. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 814, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dees, C.; Akhmetshina, A.; Zerr, P.; Reich, N.; Palumbo, K.; Horn, A.; Jüngel, A.; Beyer, C.; Krönke, G.; Zwerina, J.; et al. Platelet-derived serotonin links vascular disease and tissue fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Königshoff, M.; Dumitrascu, R.; Udalov, S.; Amarie, O.V.; Reiter, R.; Grimminger, F.; Seeger, W.; Schermuly, R.T.; Eickelberg, O. Increased expression of 5-hydroxytryptamine2A/B receptors in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A rationale for therapeutic intervention. Thorax 2010, 65, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimkhani, M.R.; Oakley, F.; Murphy, L.B.; Mann, J.; Moles, A.; Perugorria, M.J.; Ellis, E.L.; Lakey, A.F.; Burt, A.D.; Douglass, A.; et al. Stimulating healthy tissue regeneration by targeting the 5-HT2B receptor in chronic liver disease. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1668–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolivo, D.M.; Larson, S.A.; Dominko, T. Tryptophan metabolites kynurenine and serotonin regulate fibroblast activation and fibrosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 3663–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Copland, I.; Post, M.; Yeger, H.; Cutz, E. Mechanical stretch-induced serotonin release from pulmonary neuroendocrine cells: Implications for lung development. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2006, 290, L185–L193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushnir-Sukhov, N.M.; Brown, J.M.; Wu, Y.; Kirshenbaum, A.; Metcalfe, D.D. Human mast cells are capable of serotonin synthesis and release. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, 498–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, J.B.E.; Hamon, M.; Darmon, M. Serotonergic signaling: Multiple effectors and pleiotropic effects. WIREs Membr. Transp. Signal. 2012, 1, 685–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, J.; Pasche, B. Transforming growth factor beta as a therapeutic target in systemic sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2009, 5, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, T.; Ihn, H.; Xu, W.; Smith, E.; LeRoy, C.; Trojanowaska, M. Increased expression of TGF-beta receptors by scleroderma fibroblasts: Evidence for contribution of autocrine TGF-beta signaling to scleroderma phenotype. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1998, 110, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, M.; Margetts, P.J.; Sime, J.; Gauldie, J. Proteoglycans decorin and biglycan differentially modulate TGF-beta-mediated fibrotic responses in the lung. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2001, 280, L1327–L1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufvesson, E.; Westergren-Thorsson, G. Biglycan and decorin induce morphological and cytoskeletal changes involving signalling by the small GTPases RhoA and Rac1 resulting in lung fibroblast migration. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 4857–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfdahl, A.; Wenglén, C.; Rydell-Törmänen, K.; Westergren-Thorsson, G.; Larsson-Callerfelt, A.-K. Effects of 5-Hydroxytryptamine Class 2 Receptor Antagonists on Bronchoconstriction and Pulmonary Remodeling Processes. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenglén, C.; Arozenius, H.; Pettersson, L.; Ekstrom, G. An orally available, highly selective 5-hydroxytryptamine 2B (5-HT2B) receptor antagonist ameliorating pulmonary and dermal fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54 (Suppl. 63), PA2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenglén, C.; Pettersson, A.H.; Ekström, L.; An, G. Orally Available Highly Selective 5-Hydroxytryptamine 2B Receptor Antagonist Ameliorating Pulmonary and Dermal Fibrosis in Preclinical Models of Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70 (Suppl 10). [Google Scholar]
- Sonnylal, S.; Denton, C.P.; Zheng, B.; Keene, D.R.; He, R.; Adams, H.P.; VanPelt, C.S.; Geng, Y.J.; Deng, J.M.; Behringer, R.R.; et al. Postnatal induction of transforming growth factor beta signaling in fibroblasts of mice recapitulates clinical, histologic, and biochemical features of scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Vaughan, E.D. PAI-1 in tissue fibrosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marudamuthu, A.S.; Shetty, S.K.; Bhandary, Y.P.; Karandashova, S.; Thompson, M.; Sathish, V.; Florova, G.; Hogan, T.B.; Pabelick, C.M.; Prakash, Y.S.; et al. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Suppresses Profibrotic Responses in Fibroblasts from Fibrotic Lungs. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 9428–9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-P.; Wang, W.-L.; Liu, J.; Li, W.-B.; Bai, L.-L.; Yuan, Y.-D.; Song, S.-X. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 promotes the proliferation and inhibits the apoptosis of pulmonary fibroblasts by Ca2+ signaling. Thromb. Res. 2013, 131, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.Y.; Wu, H.; Island, E.R.; Chong, S.S.; Warburton, D.; Anderson, K.D.; Tuan, T.-L. Differential expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in early and late gestational mouse skin and skin wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 2002, 10, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, R.; Burwell, T.; Sun, H.; Delaney, T.; Bakken, J.; Cheng, L.; Rebelatto, M.C.; Czapiga, M.; De-Mendez, I.; Coyle, A.J.; et al. Resolution of Skin Fibrosis by Neutralization of the Antifibrinolytic Function of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandary, Y.P.; Shetty, S.K.; Marudamuthu, A.S.; Gyetko, M.R.; Idell, S.; Gharaee-Kermani, M.; Shetty, R.S.; Starcher, B.C.; Shetty, S. Regulation of alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis and pulmonary fibrosis by coordinate expression of components of the fibrinolytic system. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2012, 302, L463–L473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camelo, A.; Dunmore, R.; Sleeman, M.A.; Clarke, D.L. The epithelium in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Breaking the barrier. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 4, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, T.J.; Hunninghake, G.W. Medical progress: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, K. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis May Be a Disease of Recurrent, Tractional Injury to the Periphery of the Aging Lung: A Unifying Hypothesis Regarding Etiology and Pathogenesis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2012, 136, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang-Tsai, S.; Sisson, T.H.; Hattori, N.; Tsai, C.G.; Subbotina, N.M.; Hanson, K.E.; Simon, R.H. Reduction in Fibrotic Tissue Formation in Mice Genetically Deficient in Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Misra, D.P.; Prasad, N.; Rastogi, K.; Singh, H.; Agarwal, M.K.R. 5-HT2 and 5-HT2B antagonists attenuate pro-fibrotic phenotype in human adult dermal fibroblasts by blocking TGF-beta1 induced non-canonical signaling pathways including STAT3: Implications for fibrotic diseases like scleroderma. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 2128–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Tanbouly, D.M.; Wadie, W.; Sayed, R.H. Modulation of TGF-beta/Smad and ERK signaling pathways mediates the anti-fibrotic effect of mirtazapine in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 329, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutcheson, J.D.; Ryzhova, L.M.; Setola, V.; Merryman, W.D. 5-HT(2B) antagonism arrests non-canonical TGF-beta1-induced valvular myofibroblast differentiation. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012, 53, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, D.; Šumová, B.; Mallano, T.; Chen, C.-W.; Distler, A.; Bergmann, C.; Ludolph, I.; Horch, R.E.; Gelse, K.; Ramming, A.; et al. Activation of STAT3 integrates common profibrotic pathways to promote fibroblast activation and tissue fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, F.; Xian, J.; Demer, L.L.; Tintut, Y. Serotonin receptor type 2B activation augments TNF-α-induced matrix mineralization in murine valvular interstitial cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Vilchez, I.; Diaz-Ricart, M.; White, J.G.; Escolar, G.; Galan, A.M. Serotonin enhances platelet procoagulant properties and their activation induced during platelet tissue factor uptake. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 84, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanags, D.M.; Rodgers, S.E.; Duncan, E.M.; Lloyd, J.V.; Bochner, F. Potentiation of ADP-induced aggregation in human platelet-rich plasma by 5-hydroxytryptamine and adrenaline. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 106, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crovetti, G.; Martinelli, G.; Issi, M.; Barone, M.; Guizzardi, M.; Campanati, B.; Moroni, M.; Carabelli, A. Platelet gel for healing cutaneous chronic wounds. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2004, 30, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthar, M.; Gupta, S.; Bukhari, S.; Ponemone, V. Treatment of chronic non-healing ulcers using autologous platelet rich plasma: A case series. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindemann, S.; Tolley, N.D.; Dixon, D.A.; Mclntyre, T.M.; Prescott, S.M.; Zimmerman, G.A.; Weyrich, A.S. Activated platelets mediate inflammatory signaling by regulated interleukin 1beta synthesis. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 154, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Ohba, M.; Nakamura, M.; Sasano, T.; Ono, M.; Sugawara, S.; Endo, Y. Dynamics of platelet mobilisation into lungs in response to 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) in mice. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 102, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefrançais, E.; Ortiz-Muñoz, G.; Caudrillier, A.; Mallavia, B.; Liu, F.; Sayah, D.M.; Thornton, E.E.; Headley, M.B.; David, T.; Coughlin, T.D.S.R.; et al. The lung is a site of platelet biogenesis and a reservoir for haematopoietic progenitors. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 544, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dygai, A.M.; Skurikhin, E.; Pershina, O.V.; Stepanova, I.E.; Khmelevskaya, E.S.; Ermakova, N.; Reztsova, A.M.; Krupin, V.A.; Reikhart, D.V.; Goldberg, V.E. Response of Hemopoietic, Progenitor, and Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells to Administration of Ketanserin during Pulmonary Fibrosis. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 158, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Probst, C.K.; Montesi, S.B.; Medoff, B.D.; Shea, B.S.; Knipe, R.S. Vascular permeability in the fibrotic lung. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 1900100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielli, A.; Avvedimento, E.V.; Krieg, T. Scleroderma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1989–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntelis, K.; Bogdanos, D.; Dimitroulas, T.; Sakkas, L.; Daoussis, D. Platelets in Systemic Sclerosis: The Missing Link Connecting Vasculopathy, Autoimmunity, and Fibrosis? Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2019, 21, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottin, V.; Brown, K.K. Interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc-ILD). Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, M.; Collins, B.F.; Ho, L.A.; Raghu, G. Rheumatoid arthritis-associated lung disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2015, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabbi-Achengli, Y.; Coman, T.; Collet, C.; Callebert, J.; Corcelli, M.; Lin, H.; Rignault, R.; Dy, M.; De Vernejoul, M.-C.; Côté, F. Serotonin Is Involved in Autoimmune Arthritis through Th17 Immunity and Bone Resorption. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boilard, E.; Blanco, P.; A Nigrovic, P. Platelets: Active players in the pathogenesis of arthritis and SLE. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagermeier, J.; Dauber, J.; Yousem, S.; Gibson, K.; Kaminski, N. Abnormal Vascular Phenotypes in Patients With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Secondary Pulmonary Hypertension. Chest 2005, 128, 601S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner-Warwick, M. Precapillary Systemic-pulmonary Anastomoses. Thorax 2008, 18, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, S.; Millar, A. Vascular remodelling in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. QJM 2014, 107, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farber, H.W.; Loscalzo, J. Pulmonary arterial hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behr, J.; Ryu, J.H. Pulmonary hypertension in interstitial lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 31, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddahibi, S. 055 Cross-talk between endothelial and smooth muscle cells in pulmonary hypertension: Critical role for serotonin-induced smooth muscle hyperplasia. Rev. Mal. Respir. 2006, 23, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aiello, R.J.; Bourassa, P.-A.; Zhang, Q.; Dubins, J.; Goldberg, D.R.; De Lombaert, S.; Humbert, M.; Guignabert, C.; Cavasin, M.A.; McKinsey, T.A.; et al. Tryptophan hydroxylase 1 Inhibition Impacts Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling in Two Rat Models of Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 360, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.; Carrier, E.J.; Bloodworth, N.C.; Schroer, A.K.; Chen, P.; Ryzhova, L.M.; Gladson, S.; Shay, S.; Hutcheson, J.D.; Merryman, W.D. Serotonin 2B Receptor Antagonism Prevents Heritable Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launay, J.-M.; Herve, P.; Peoch, K.; Tournois, C.; Callebert, J.; Nebigil, C.G.; Etienne, N.; Drouet, L.; Humbert, M.; Simonneau, G.; et al. Function of the serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine 2B receptor in pulmonary hypertension. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, M.; Ding, L.; Wang, D.; Han, J.; Gao, P. Serotonin: A Potent Immune Cell Modulator in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shajib, M.S.; Khan, W.I. The role of serotonin and its receptors in activation of immune responses and inflammation. Acta Physiol. 2015, 213, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Las Casas-Engel, M.; Corbi, A.L. Serotonin modulation of macrophage polarization: Inflammation and beyond. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 824, 89–115. [Google Scholar]
- Dürk, T.; Panther, E.; Müller, T.; Sorichter, S.; Ferrari, D.; Pizzirani, C.; Di Virgilio, F.; Myrtek, D.; Norgauer, J.; Idzko, M. 5-Hydroxytryptamine modulates cytokine and chemokine production in LPS-primed human monocytes via stimulation of different 5-HTR subtypes. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cui, R.; Feng, Y.; Gao, W.; Bi, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, C. Serotonin Exhibits Accelerated Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis through TPH1 Knockout Mouse Experiments. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmqvist, N.; Siller, M.; Klint, C.; Sjödin, A. A human and animal model-based approach to investigating the anti-inflammatory profile and potential of the 5-HT2B receptor antagonist AM1030. J. Inflamm. 2016, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Becnel, J.; Zerfaoui, M.; Rohatgi, R.; Boulares, A.H.; Nichols, C.D. Serotonin 5-Hydroxytryptamine2A Receptor Activation Suppresses Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Induced Inflammation with Extraordinary Potency. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 327, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson-Callerfelt, A.-K.; Dahlén, S.-E.; Kühl, A.-R.; Lex, D.; Uhlig, S.; Martin, C. Modulation of antigen-induced responses by serotonin and prostaglandin E2 via EP1 and EP4 receptors in the peripheral rat lung. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 699, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubera, M.; Maes, M.; Kenis, G.; Kim, Y.-K.; Lasoń, W. Effects of serotonin and serotonergic agonists and antagonists on the production of tumor necrosis factor α and interleukin-6. Psychiatry Res. 2005, 134, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kling, A.; Seddighzadeh, M.; Arlestig, L.; Alfredsson, L.; Rantapaa-Dahlqvist, S.; Padyukov, L. Genetic variations in the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor gene (HTR2A) are associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 1111–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, S.; Alstergren, P. Blood serotonin and joint pain in seropositive versus seronegative rheumatoid arthritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2002, 11, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tominaga, K.; Alstergren, P.; Kurita, H.; Kopp, S. Serotonin in an antigen-induced arthritis of the rabbit temporomandibular joint. Arch. Oral Biol. 1999, 44, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhfouri, G.; Rahimian, R.; Ghia, J.-E.; Khan, W.I.; Rashidian, A. Impact of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists on peripheral and central diseases. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloutier, N.; Paré, A.; Farndale, R.W.; Schumacher, H.R.; Nigrovic, P.A.; Lacroix, S.; Boilard, E. Platelets can enhance vascular permeability. Blood 2012, 120, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alstergren, P.; Kopp, S. Pain and synovial fluid concentration of serotonin in arthritic temporomandibular joints. Pain 1997, 72, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mitchell, J.; Sharma, M.; Gabriel, A.; Moriyama, K.; Palmer, P.P. Leukotrienes mediate 5-hydroxytryptamine-induced plasma extravasation in the rat knee joint via CysLT-type receptors. Inflamm. Res. 2004, 53, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloez-Tayarani, I.; Changeux, J.P. Nicotine and serotonin in immune regulation and inflammatory processes: A perspective. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, M.F.; Fiebich, B.L.; Ulrich-Merzenich, G.; Candelario-Jalil, E.; Koch, F.-W.; Vetter, H. Serotonin mediates PGE2 overexpression through 5-HT2A and 5-HT3 receptor subtypes in serum-free tissue culture of macrophage-like synovial cells. Rheumatol. Int. 2008, 28, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, J.; Weissbarth, E.; Baruth, B.; Mielke, H.; Deicher, H. Serotonin content of platelets in inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1983, 26, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirigoyen, D.; Burgos, P.I.; Mezzano, V.; Durán, J.; Barrientos, M.; Sáez, C.G.; Panes, O.; Mezzano, D.; Iruretagoyena, M. Inhibition of angiogenesis by platelets in systemic sclerosis patients. Arthritis Res. 2015, 17, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulin, F.; Doyle, T.J.; Fletcher, E.A.; Ascherman, D.P.; Rosas, I.O. Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Shared Mechanistic and Phenotypic Traits Suggest Overlapping Disease Mechanisms. Rev. Invest. Clin. 2015, 67, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Solomon, J.J.; Olson, A.L.; Fischer, A.; Bull, T.; Brown, K.K.; Raghu, G. Scleroderma lung disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2013, 22, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shochet, G.E.; Brook, E.; Israeli-Shani, L.; Edelstein, E.; Shitrit, D. Fibroblast paracrine TNF-α signaling elevates integrin A5 expression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smadja, D.M.; Mauge, L.; Nunes, H.; D’Audigier, C.; Juvin, K.; Borie, R.; Carton, Z.; Bertil, S.; Blanchard, A.; Crestani, B.; et al. Imbalance of circulating endothelial cells and progenitors in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Angiogenesis 2012, 16, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacha, N.C.; Blandinieres, A.; Rossi, E.; Gendron, N.; Nevo, N.; Lecourt, S.; Guerin, C.L.; Renard, J.M.; Gaussem, P.; Angles-Cano, E.; et al. Endothelial Microparticles are Associated to Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2018, 14, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, M.L.; Marasini, B.; Bianchi, E.; Agostoni, A. Plasma free and intraplatelet serotonin in patients with Raynaud’s phenomenon. Int. J. Cardiol. 1988, 19, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtierotti, R.; Ingegnoli, F.; Griffini, S.; Grovetti, E.; Borghi, M.O.; Bucciarelli, P.; Luigi, M.P.; Cugno, M. Detection of early endothelial damage in patients with Raynaud’s phenomenon. Microvasc. Res. 2017, 113, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welford, R.W.; Vercauteren, M.; Trébaul, A.; Cattaneo, C.; Eckert, D.; Garzotti, M.; Sieber, P.; Segrestaa, J.; Studer, R.; Groenen, P.M.A.; et al. Serotonin biosynthesis as a predictive marker of serotonin pharmacodynamics and disease-induced dysregulation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, A.C.R.; Clara, R.O.; Coimbra, J.B.; Júlio, A.R.; Albuquerque, R.C.; De Oliveira, E.M.; Campa, A.; Maria-Engler, S. The expanding roles of 1-methyl-tryptophan (1-MT): In addition to inhibiting kynurenine production, 1-MT activates the synthesis of melatonin in skin cells. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 4782–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, R.K.; Pant, N.; Saksena, S.; Singla, A.; Nazir, T.M.; Vohwinkel, L.; Turner, J.R.; Goldstein, J.; Alrefai, W.A.; Dudeja, P.K. Function, expression, and characterization of the serotonin transporter in the native human intestine. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G254–G262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Iwamoto, N.; Distler, O. Molecular targets for therapy in systemic sclerosis. Fibrogenes. Tissue Repair 2012, 5 (Suppl. 1), S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artlett, C.M. Animal models of systemic sclerosis: Their utility and limitations. Open Access Rheumatol. Res. Rev. 2014, 6, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, C.; Schett, G.; Distler, O.; Distler, J.H.W. Animal models of systemic sclerosis: Prospects and limitations. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2831–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujino, K.; Sheppard, D. Critical Appraisal of the Utility and Limitations of Animal Models of Scleroderma. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2016, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.J.; Chisholm, A.; Collard, H.R.; Flaherty, K.R.; Myers, J.; Raghu, G.; Walsh, S.L.F.; White, E.S.; Richeldi, L. The diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Current and future approaches. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; Baldi, F.; Pasciuto, G.; Macagno, F.; Panico, L. Current and Future Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Therapy. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 357, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann-Vold, A.-M.; Weigt, S.S.; Saggar, R.; Palchevskiy, V.; Volkmann, E.R.; Liang, L.L.; Ross, D.; Ardehali, A.; Lynch, J.P.; Belperio, J.A. Endotype–phenotyping may predict a treatment response in progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease. EBioMedicine 2019, 50, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Ma, T.; Lian, X.; Gao, J.; Wang, W.; Weng, W.; Lu, X.; Sun, W.; Cheng, Y.; Fu, Y.W.; et al. Clopidogrel Reduces Fibronectin Accumulation and Improves Diabetes-Induced Renal Fibrosis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.-X.; Qi, G.-M.; Liu, O.; Li, T.-T.; Yang, M.; Cui, W.; Zhang, W.-M.; Qi, Y.-F.; Du, J. Inhibition of Platelet Activation by Clopidogrel Prevents Hypertension-Induced Cardiac Inflammation and Fibrosis. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2013, 27, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefayene, M.; Mouded, M.; Stebbins, C.; Zhao, G.; Song, G.; Christmann, R.; Violette, S.; Gallagher, D. Phase 2B dose selection of BG00011 for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Mech. Lung Inj. Repair 2018, 52, PA596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annes, J.P.; Chen, Y.; Munger, J.S.; Rifkin, D.B.; et al. Integrin alphaVbeta6-mediated activation of latent TGF-beta requires the latent TGF-beta binding protein-1. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 165, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblanc, R.; Houssin, A.; Peyruchaud, O. Platelets, autotaxin and lysophosphatidic acid signalling: Win-win factors for cancer metastasis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 3100–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; van den Blink, B.; Hamblin, M.J.; Brown, A.W.; Golden, J.A.; Ho, L.A.; Wijsenbeek, M.S.; Vasakova, M.; Pesci, A.; Antin-Ozerkis, D.E.; et al. Long-term treatment with recombinant human pentraxin 2 protein in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An open-label extension study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, N.; Barron, L.; Gomez, I.G.; Johnson, B.G.; Roach, A.; Kameoka, S.; Jack, R.M.; Lupher, M.L.; Gharib, S.A.; Duffield, J.S. Pentraxin-2 suppresses c-Jun/AP-1 signaling to inhibit progressive fibrotic disease. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e87446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, D.; Denton, C.P.; Jahreis, A.; Van Laar, J.M.; Frech, T.M.; E Anderson, M.; Baron, M.; Chung, L.; Fierlbeck, G.; Lakshminarayanan, S.; et al. Safety and efficacy of subcutaneous tocilizumab in adults with systemic sclerosis (faSScinate): A phase 2, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 2630–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distler, O.; Highland, K.B.; Gahlemann, M.; Azuma, A.; Fischer, A.; Mayes, M.D.; Raghu, G.; Sauter, W.; Girard, M.; Alves, M.; et al. Nintedanib for Systemic Sclerosis–Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2518–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Maier, C.; Zhang, Y.; Soare, A.; Dees, C.; Beyer, C.; Harre, U.; Chen, C.W.; Distler, O.; Schett, G.; et al. Nintedanib inhibits macrophage activation and ameliorates vascular and fibrotic manifestations in the Fra2 mouse model of systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1941–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley, J.M.; Brancato, S.K.; Thomay, A.A.; Reichner, J.S.; Albina, J.E. The phenotype of murine wound macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 87, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendin, L.E.; Löfdahl, A.; Åhrman, E.; Müller, C.; Notermans, T.; Michaliková, B.; Rosmark, O.; Zhou, X.-H.; Dellgren, G.; Silverborn, M.; et al. Matrisome Properties of Scaffolds Direct Fibroblasts in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, K.R.; Wells, A.U.; Cottin, V.; Devaraj, A.; Walsh, S.L.; Inoue, Y.; Richeldi, L.; Kolb, M.; Tetzlaff, K.; Stowasser, S.; et al. Nintedanib in Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Löfdahl, A.; Tornling, G.; Wigén, J.; Larsson-Callerfelt, A.-K.; Wenglén, C.; Westergren-Thorsson, G. Pathological Insight into 5-HT2B Receptor Activation in Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010225
Löfdahl A, Tornling G, Wigén J, Larsson-Callerfelt A-K, Wenglén C, Westergren-Thorsson G. Pathological Insight into 5-HT2B Receptor Activation in Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(1):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010225
Chicago/Turabian StyleLöfdahl, Anna, Göran Tornling, Jenny Wigén, Anna-Karin Larsson-Callerfelt, Christina Wenglén, and Gunilla Westergren-Thorsson. 2021. "Pathological Insight into 5-HT2B Receptor Activation in Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 1: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010225
APA StyleLöfdahl, A., Tornling, G., Wigén, J., Larsson-Callerfelt, A.-K., Wenglén, C., & Westergren-Thorsson, G. (2021). Pathological Insight into 5-HT2B Receptor Activation in Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(1), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010225




