Unraveling the Resistance of IGF-Pathway Inhibition in Ewing Sarcoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
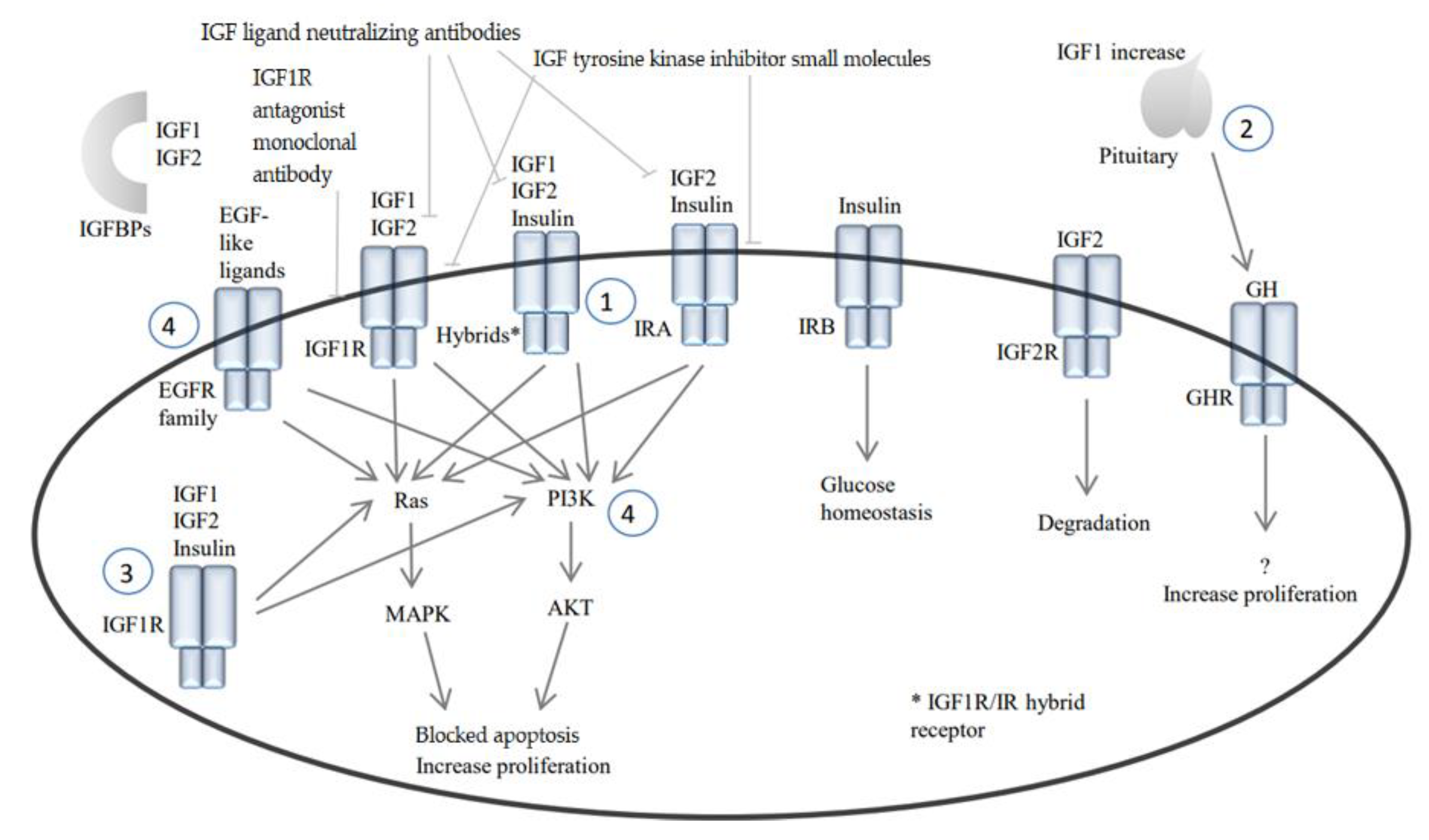
2. IGF1/Insulin Pathway and Cancer
2.1. Insulin Receptor and Insulin
2.2. IGF2R and IGF Binding Proteins
3. IGF1R Pathway Inhibitors and Resistance
3.1. IGF1R Antagonist Monoclonal Antibodies
3.2. IGF1R Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Small Molecules
3.3. IGF Ligand Neutralizing Antibodies
4. Strategies to Overcome Resistance Mechanisms of IGF1R-Inhibitors
4.1. Activation of IRA and/or Hybrid Receptors
4.2. Disruption of Negative Feedback
4.3. Autocrine Loops in the Tumor
4.4. Activation or Mutation of Other Pathways
4.5. Use of Biomarkers
4.6. Ewing Sarcoma vs. Other Solid Tumors
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Hormones, T.E. Breast Cancer Collaborative Group; Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1), IGF binding protein 3 (IGFBP3), and breast cancer risk: Pooled individual data analysis of 17 prospective studies. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, C.; Wang, C.-Y.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Xiao, L.; Smith, A.W.; Reding, K.W.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Baumgartner, K.B.; Bernstein, L.; Ballard-Barbash, R.; et al. Associations of insulin-like growth factor and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 with mortality in women with breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, P.J.; Bs, C.L.M.; Gorlick, R.; Kolb, E.A.; Keir, S.T.; Reynolds, C.P.; Kang, M.H.; Maris, J.M.; Wu, J.; Smith, M.A. Initial testing of a monoclonal antibody (IMC-A12) against IGF-1R by the pediatric preclinical testing program. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 54, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehman, C.E.; Khalil, A.A.; Axelrod, M.J.; Dougherty, M.I.; Schoeff, S.S.; Taniguchi, L.E.; Mendez, R.E.; David, A.P.; Mcgarey, P.O.; Hubbard, M.A.; et al. Antitumor effect of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor inhibition in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 1470–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Echeverría, C.; A Pearson, M.; Marti, A.; Meyer, T.; Mestan, J.; Zimmermann, J.; Gao, J.; Brueggen, J.; Capraro, H.-G.; Cozens, R.; et al. In vivo antitumor activity of NVP-AEW541—A novel, potent, and selective inhibitor of the IGF-IR kinase. Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.-S.; Mulvihill, M.J.; Rosenfeld-Franklin, M.; Cooke, A.; Feng, L.; Mak, G.; O’Connor, M.J.; Yao, Y.; Pirritt, C.; Buck, E.; et al. A novel, potent, and selective insulin-like growth factor-I receptor kinase inhibitor blocks insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in vitro and inhibits insulin-like growth factor-I receptor dependent tumor growth in vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 2158–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iams, W.T.; Lovly, C.M. Molecular Pathways: Clinical Applications and Future Direction of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Receptor Pathway Blockade. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4270–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haluska, P.; Shaw, H.M.; Batzel, G.N.; Yin, N.; Molina, J.R.; Molife, L.R.; A Yap, T.; Roberts, M.L.; Sharma, A.; Gualberto, A.; et al. Phase I Dose Escalation Study of the Anti Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Receptor Monoclonal Antibody CP-751,871 in Patients with Refractory Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 5834–5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolcher, A.W.; Sarantopoulos, J.; Patnaik, A.; Papadopoulos, K.; Lin, C.-C.; Rodon, J.; Murphy, B.; Roth, B.; McCaffery, I.; Gorski, K.S.; et al. Phase I, Pharmacokinetic, and Pharmacodynamic Study of AMG 479, a Fully Human Monoclonal Antibody to Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor 1. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5800–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmos, D.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Molife, L.R.; Okuno, S.H.; Schuetze, S.M.; Paccagnella, M.L.; Batzel, G.N.; Yin, D.; Pritchard-Jones, K.; Judson, I.; et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and preliminary activity of the anti-IGF-1R antibody figitumumab (CP-751,871) in patients with sarcoma and Ewing’s sarcoma: A phase 1 expansion cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzrock, R.; Patnaik, A.; Aisner, J.; Warren, T.; Leong, S.; Benjamin, R.; Eckhardt, S.G.; Eid, J.E.; Greig, G.; Habben, K.; et al. A Phase I Study of Weekly R1507, A Human Monoclonal Antibody Insulin-like Growth Factor-I Receptor Antagonist, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 2458–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juergens, H.; Daw, N.C.; Geoerger, B.; Ferrari, S.; Villarroel, M.; Aerts, I.; Whelan, J.; Dirksen, U.; Hixon, M.L.; Yin, D.; et al. Preliminary Efficacy of the Anti-Insulin–Like Growth Factor Type 1 Receptor Antibody Figitumumab in Patients With Refractory Ewing Sarcoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4534–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malempati, S.; Weigel, B.; Ingle, A.M.; Ahern, C.H.; Carroll, J.M.; Roberts, C.T.; Reid, J.M.; Schmechel, S.; Voss, S.D.; Cho, S.Y.; et al. Phase I/II Trial and Pharmacokinetic Study of Cixutumumab in Pediatric Patients With Refractory Solid Tumors and Ewing Sarcoma: A Report From the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, H.; Doi, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Watanabe, J.; Boku, N.; Fuse, N.; Yoshino, T.; Ohtsu, A.; Otani, S.; Shibayama, K.; et al. Phase 1 study of ganitumab (AMG 479), a fully human monoclonal antibody against the insulin-like growth factor receptor type I (IGF1R), in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 70, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tap, W.D.; Demetri, G.; Barnette, P.; Desai, J.; Kavan, P.; Tozer, R.; Benedetto, P.W.; Friberg, G.; Deng, H.; McCaffery, I.; et al. Phase II Study of Ganitumab, a Fully Human Anti–Type-1 Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor Antibody, in Patients With Metastatic Ewing Family Tumors or Desmoplastic Small Round Cell Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1849–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöffski, P.; Adkins, D.; Blay, J.-Y.; Gil, T.; Elias, A.; Rutkowski, P.; Pennock, G.; Youssoufian, H.; Gelderblom, H.; Willey, R.; et al. An open-label, phase 2 study evaluating the efficacy and safety of the anti-IGF-1R antibody cixutumumab in patients with previously treated advanced or metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma or Ewing family of tumours. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappo, A.S.; Vassal, G.; Crowley, J.J.; Bolejack, V.; Hogendoorn, P.C.W.; Chugh, R.; Ladanyi, M.; Grippo, J.F.; Dall, G.; Staddon, A.P.; et al. A phase 2 trial of R1507, a monoclonal antibody to the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R), in patients with recurrent or refractory rhabdomyosarcoma, osteosarcoma, synovial sarcoma, and other soft tissue sarcomas: Results of a Sarcoma Alliance. Cancer 2014, 120, 2448–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Capanu, M.; O’Reilly, E.M.; Ma, J.; Chou, J.F.; Gansukh, B.; Shia, J.; Kalin, M.; Katz, S.; Abad, L.; et al. A phase II study of cixutumumab (IMC-A12, NSC742460) in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzanov, I.; Lindsay, C.R.; Goff, L.; Sosman, J.; Gilbert, J.; Berlin, J.; Poondru, S.; Simantov, R.; Gedrich, R.; Stephens, A.; et al. A Phase I Study of Continuous Oral Dosing of OSI-906, a Dual Inhibitor of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 and Insulin Receptors, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 21, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.L.; Kim, E.S.; Nava-Parada, P.; Alam, S.; Johnson, F.M.; Stephens, A.W.; Simantov, R.; Poondru, S.; Gedrich, R.; Lippman, S.M.; et al. Phase I Study of Intermittent Oral Dosing of the Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 and Insulin Receptors Inhibitor OSI-906 in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 21, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassnacht, M.; Berruti, A.; Baudin, E.; Demeure, M.J.; Gilbert, J.; Haak, H.; Kroiss, M.; I Quinn, D.; Hesseltine, E.; Ronchi, C.L.; et al. Linsitinib (OSI-906) versus placebo for patients with locally advanced or metastatic adrenocortical carcinoma: A double-blind, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, P.C.; Cooney, M.; Tyler, A.; Wright, J.; Dreicer, R.; Garcia, J.A. A phase 2 study of OSI-906 (linsitinib, an insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 inhibitor) in patients with asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic (non-opioid requiring) metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Investig. New Drugs 2018, 36, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiappori, A.A.; Otterson, G.A.; Dowlati, A.; Traynor, A.M.; Horn, L.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Ross, H.J.; Hann, C.L.; Abu Hejleh, T.; Nieva, J.; et al. A Randomized Phase II Study of Linsitinib (OSI-906) Versus Topotecan in Patients With Relapsed Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Oncologist 2016, 21, 1163–1164e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haluska, P.; Menefee, M.; Plimack, E.R.; Rosenberg, J.; Northfelt, D.; Lavallee, T.; Shi, L.; Yu, X.-Q.; Burke, P.; Huang, J.; et al. Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of MEDI-573, a Bispecific, Antiligand Monoclonal Antibody against IGFI and IGFII, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4747–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iguchi, H.; Nishina, T.; Nogami, N.; Kozuki, T.; Yamagiwa, Y.; Yagawa, K. Phase I dose-escalation study evaluating safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of MEDI-573, a dual IGF-I/II neutralizing antibody, in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumours. Investig. New Drugs 2014, 33, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bono, J.; Lin, C.-C.; Chen, L.-T.; Corral, J.; Michalarea, V.; Rihawi, K.; Ong, M.; Lee, J.-H.; Hsu, C.-H.; Yang, J.C.-H.; et al. Two first-in-human studies of xentuzumab, a humanised insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-neutralising antibody, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frappaz, D.; Federico, S.M.; Pearson, A.D.; Gore, L.; Macy, M.E.; Dubois, S.G.; Aerts, I.; Iannone, R.; Geschwindt, R.; Van Schanke, A.; et al. Phase 1 study of dalotuzumab monotherapy and ridaforolimus–dalotuzumab combination therapy in paediatric patients with advanced solid tumours. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 62, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Wu, Z.; Dong, W.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Pang, Z.; Ma, W.; Du, J. Update of IGF-1 receptor inhibitor (ganitumab, dalotuzumab, cixutumumab, teprotumumab and figitumumab) effects on cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 29501–29518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baserga, R. The decline and fall of the IGF-I receptor. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 228, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.M.; Bielack, S.S.; Gorlick, R.G.; Skubitz, K.; Daw, N.C.; Herzog, C.E.; Monge, O.R.; Lassaletta, A.; Boldrini, E.; Pápai, Z.; et al. A phase II study of clinical activity of SCH 717454 (robatumumab) in patients with relapsed osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotlandi, K.; Benini, S.; Sarti, M.; Serra, M.; Lollini, P.L.; Maurici, D.; Picci, P.; Manara, M.C.; Baldini, N. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor-mediated circuit in Ewing’s sarcoma/peripheral neuroectodermal tumor: A possible therapeutic target. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 4570–4574. [Google Scholar]
- Garofalo, C.; Manara, M.C.; Nicoletti, G.; Marino, M.T.; Lollini, P.-L.; Astolfi, A.; Pandini, G.; A López-Guerrero, J.; Schaefer, K.-L.; Belfiore, A.; et al. Efficacy of and resistance to anti-IGF-1R therapies in Ewing’s sarcoma is dependent on insulin receptor signaling. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2730–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulanet, D.B.; Ludwig, D.L.; Kahn, C.R.; Hanahan, D. Insulin receptor functionally enhances multistage tumor progression and conveys intrinsic resistance to IGF-1R targeted therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 10791–10798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Dimitrov, D.S. Antibody-based therapeutics against components of the IGF system. OncoImmunology 2012, 1, 1390–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zapf, J.; Hauri, C.; Waldvogel, M.; Futo, E.; Hasler, H.; Binz, K.; Guler, H.P.; Schmid, C.; Froesch, E.R. Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I induces its own specific carrier protein in hypophysectomized and diabetic rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 3813–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualberto, A.; Pollak, M. Emerging role of insulin-like growth factor receptor inhibitors in oncology: Early clinical trial results and future directions. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3009–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Steller, M.; Delgado, C.H.; Bartels, C.J.; Woodworth, C.D.; Zou, Z. Overexpression of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and autocrine stimulation in human cervical cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 1761–1765. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, M.; Buck, E.; Mulvihill, M.J. Modulation of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and its signaling network for the treatment of cancer: Current status and future perspectives. Oncol. Rev. 2013, 7, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, H.; Jiang, Z.; You, L.; Liao, Y. Crosstalk between IGF-1R and other tumor promoting pathways. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 2912–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, A.; Petnga, W.; Macaulay, V.M.; Weyer-Czernilofsky, U.; Bogenrieder, T. Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) Pathway Targeting in Cancer: Role of the IGF Axis and Opportunities for Future Combination Studies. Target. Oncol. 2017, 12, 571–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Qi, X.; Chen, Y.; Sun, B.; Dai, Y.; Gu, Y. PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK1/2 signaling pathways are involved in IGF-1-induced VEGF-C upregulation in breast cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 137, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djiogue, S.; Kamdje, A.H.N.; Vecchio, L.; Kipanyula, M.J.; Farahna, M.; Aldebasi, Y.; Etet, P.F.S. Insulin resistance and cancer: The role of insulin and IGFs. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2012, 20, R1–R17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, A.; Morcavallo, A.; Pandini, G.; Vigneri, R.; Belfiore, A. Differential Signaling Activation by Insulin and Insulin-Like Growth Factors I and II upon Binding to Insulin Receptor Isoform A. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 3594–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Belfiore, A.; Malaguarnera, R.; Vella, V.; Lawrence, M.C.; Sciacca, L.; Frasca, F.; Morrione, A.; Vigneri, R. Insulin Receptor Isoforms in Physiology and Disease: An Updated View. Endocr. Rev. 2017, 38, 379–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groot, S.; on behalf of the Dutch Breast Cancer Research Group; Charehbili, A.; Van Laarhoven, H.W.M.; Mooyaart, A.L.; Dekker-Ensink, N.G.; Van De Ven, S.; Janssen, L.G.M.; Swen, J.J.; Smit, V.T.H.B.M.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor expression and IGF1R 3129G > T polymorphism are associated with response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients: Results from the NEOZOTAC trial (BOOG 2010-01). Breast Cancer Res. 2016, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renehan, A.G.; Zwahlen, M.; Minder, C.; O’Dwyer, S.T.; Shalet, S.M.; Egger, M. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, and cancer risk: Systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, S.; Gelderblom, H.; Fiocco, M.; Bovée, J.V.; Van Der Hoeven, J.J.; Pijl, H.; Kroep, J.R. Serum levels of IGF-1 and IGF-BP3 are associated with event-free survival in adult Ewing sarcoma patients treated with chemotherapy. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 2963–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cohn, A.; Tabernero, J.; Maurel, J.; Nowara, E.; Sastre, J.; Chuah, B.Y.S.; Kopp, M.V.; Sakaeva, D.D.; Mitchell, E.P.; Dubey, S.; et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 study of ganitumab or conatumumab in combination with FOLFIRI for second-line treatment of mutant KRAS metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsantis, I.; Economopoulou, P.; Psyrri, A.; Maratou, E.; Pectasides, D.; Gogas, H.; Kentepozidis, N.; Mountzios, G.; Dimitriadis, G.; Giannouli, S. Prognostic Significance of IGF-1 Signalling Pathway in Patients With Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2019, 39, 4185–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, V.; Milluzzo, A.; Scalisi, N.M.; Vigneri, P.; Sciacca, L. Insulin Receptor Isoforms in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminska, D.; Hämäläinen, M.; Cederberg, H.; Käkelä, P.; Venesmaa, S.; Miettinen, P.; Ilves, I.; Herzig, K.-H.; Kolehmainen, M.; Karhunen, L.; et al. Adipose tissue INSR splicing in humans associates with fasting insulin level and is regulated by weight loss. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciacca, L.; Vigneri, R.; Tumminia, A.; Frasca, F.; Squatrito, S.; Frittitta, L.; Vigneri, P. Clinical and molecular mechanisms favoring cancer initiation and progression in diabetic patients. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 23, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Lu, J.; Wu, S.; Bi, Y.; Mu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Chen, L.; Shi, L.; Li, Q.; et al. Association of insulin resistance with breast, ovarian, endometrial and cervical cancers in non-diabetic women. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 2334–2344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.; Jones, E.Y.; Forbes, B.E. Keeping IGF-II under control: Lessons from the IGF-II–IGF2R crystal structure. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2009, 34, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röttgering, B.T.; Szuhai, K. Insulin-Like Growth Factor 2 in Physiology, Cancer, and Cancer Treatment. OBM Genet. 2019, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemmons, D.R. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and their role in controlling IGF actions. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1997, 8, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, J.B.; Duan, C. IGF-Binding Proteins: Why Do They Exist and Why Are There So Many? Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toretsky, J.A.; Steinberg, S.M.; Thakar, M.; Counts, D.; Pironis, B.; Parente, C.; Eskenazi, A.; Helman, L.; Wexler, L.H. Insulin-like growth factor type 1 (IGF-1) and IGF binding protein-3 in patients with Ewing sarcoma family of tumors. Cancer 2001, 92, 2941–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, R.C. IGF binding proteins in cancer: Mechanistic and clinical insights. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, H.; Aleksic, T.; Haluska, P.; Macaulay, V.M. Can we unlock the potential of IGF-1R inhibition in cancer therapy? Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 1096–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, S.; Kaminsky-Forrett, M.-C.; Henry, S.; Zanetta, S.; Geoffrois, L.; Bompas, E.; Moxhon, A.; Mignion, L.; Guigay, J.; Knoops, L.; et al. Phase II study of figitumumab in patients with recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: Clinical activity and molecular response (GORTEC 2008-02). Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 2153–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendell, J.C.; Jones, S.F.; Hart, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Lane, C.M.; Earwood, C.; Infante, J.R.; Barton, J.; Burris, H.A. A phase Ib study of linsitinib (OSI-906), a dual inhibitor of IGF-1R and IR tyrosine kinase, in combination with everolimus as treatment for patients with refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2014, 33, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haluska, P.H.; Dudek, A.Z.; Bono, P.; Sleight, B.; Joensuu, H.; Juergens, H.; Pollak, M. Phase I study of figitumumab and pegvisomant in patients with advanced 2solid tumors. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2012, 22, S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, E.; Gokhale, P.C.; Koujak, S.; Brown, E.; Eyzaguirre, A.; Tao, N.; Rosenfeld-Franklin, M.; Lerner, L.; Chiu, M.I.; Wild, R.; et al. Compensatory Insulin Receptor (IR) Activation on Inhibition of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Receptor (IGF-1R): Rationale for Cotargeting IGF-1R and IR in Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 2652–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikram, A.; Jena, G. S961, an insulin receptor antagonist causes hyperinsulinemia, insulin-resistance and depletion of energy stores in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 398, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchikawa, E.; Choi, E.; Shang, G.; Yu, H.; Bai, X.-C. Activation mechanism of the insulin receptor revealed by cryo-EM structure of the fully liganded receptor-ligand complex. eLife 2019, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thissen, J.-P.; Ketelslegers, J.-M.; Underwood, L.E. Nutritional Regulation of the Insulin-Like Growth Factors*. Endocr. Rev. 1994, 15, 80–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, S.; Dutch Breast Cancer Research Group (BOOG); Lugtenberg, R.T.; Cohen, D.; Welters, M.J.P.; Ehsan, I.; Vreeswijk, M.P.G.; Smit, V.T.H.B.M.; De Graaf, H.; Heijns, J.B.; et al. Fasting mimicking diet as an adjunct to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer in the multicentre randomized phase 2 DIRECT trial. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nencioni, A.; Caffa, I.; Cortellino, S.; Longo, V.D. Fasting and cancer: Molecular mechanisms and clinical application. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, S.; Pijl, H.; Van Der Hoeven, J.J.M.; Kroep, J.R. Effects of short-term fasting on cancer treatment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, D. Insulin-like Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors: Baby or the Bathwater? J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2012, 104, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatelli, M.C.; Minoia, M.; Molè, D.; Cason, V.; Tagliati, F.; Margutti, A.; Bondanelli, M.; Ambrosio, M.R.; Degli Uberti, E. Growth Hormone Excess Promotes Breast Cancer Chemoresistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 3931–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; You, C.; Liu, L.; Rao, Z.; Sima, X.; Zhou, L.; Xu, J.-G. Craniopharyngioma cell growth is promoted by growth hormone (GH) and is inhibited by tamoxifen: Involvement of growth hormone receptor (GHR) and IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1R). J. Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 20, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felice, D.L.; El-Shennawy, L.; Zhao, S.; Lantvit, D.L.; Shen, Q.; Unterman, T.G.; Swanson, S.M.; Frasor, J. Growth hormone potentiates 17β-estradiol-dependent breast cancer cell proliferation independently of IGF-I receptor signaling. Endocrinol. 2013, 154, 3219–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Van Garderen, E.; A Schalken, J. Morphogenic and tumorigenic potentials of the mammary growth hormone/growth hormone receptor system. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2002, 197, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wan, M.; Li, G.; Xu, Z.; Chen, C.; Liu, F.; Li, J. Growth hormone receptor overexpression predicts response of rectal cancers to pre-operative radiotherapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2006, 42, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, K.; Wan, Y.; Qian, P.-X.; Perry, J.K.; Chiesa, J.; Mertani, H.C.; Zhu, T.; Lobie, P.E. Tumor Expression of Human Growth Hormone and Human Prolactin Predict a Worse Survival Outcome in Patients with Mammary or Endometrial Carcinoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E1619–E1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebre-Medhin, M.; Kindblom, L.-G.; Wennbo, H.; Törnell, J.; Meis-Kindblom, J.M. Growth Hormone Receptor Is Expressed in Human Breast Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoia, M.; Gentilin, E.; Molè, D.; Rossi, M.; Filieri, C.; Tagliati, F.; Baroni, A.; Ambrosio, M.R.; Degli Uberti, E.; Zatelli, M.C. Growth Hormone Receptor Blockade Inhibits Growth Hormone-Induced Chemoresistance by Restoring Cytotoxic-Induced Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cells Independently of Estrogen Receptor Expression. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E907–E916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renehan, A.G.; Brennan, B.M. Acromegaly, growth hormone and cancer risk. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 22, 639–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, P. Cancer in Acromegaly. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 9, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steuerman, R.; Shevah, O.; Laron, Z. Congenital IGF1 deficiency tends to confer protection against post-natal development of malignancies. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 164, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guevara-Aguirre, J.; Balasubramanian, P.; Guevara-Aguirre, M.; Wei, M.; Madia, F.; Cheng, C.-W.; Hwang, D.; Martin-Montalvo, A.; Saavedra, J.; Ingles, S.; et al. Growth Hormone Receptor Deficiency Is Associated with a Major Reduction in Pro-Aging Signaling, Cancer, and Diabetes in Humans. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 70ra13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arteaga, C.L.; Osborne, C.K. Growth inhibition of human breast cancer cells in vitro with an antibody against the type I somatomedin receptor. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 6237–6241. [Google Scholar]
- Leporati, P.; Fonte, R.; De Martinis, L.; Zambelli, A.; Magri, F.; Pavesi, L.; Rotondi, M.; Chiovato, L. A male patient with acromegaly and breast cancer: Treating acromegaly to control tumor progression. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pollak, M. The insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptor family in neoplasia: An update. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladenstein, R.; Pötschger, U.; Le Deley, M.C.; Whelan, J.; Paulussen, M.; Oberlin, O.; Berg, H.V.D.; Dirksen, U.; Hjorth, L.; Michon, J.; et al. Primary Disseminated Multifocal Ewing Sarcoma: Results of the Euro-EWING 99 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3284–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieur, A.; Tirode, F.; Cohen, P.; Delattre, O. EWS/FLI-1 Silencing and Gene Profiling of Ewing Cells Reveal Downstream Oncogenic Pathways and a Crucial Role for Repression of Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 3. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 7275–7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janknecht, R. EWS–ETS oncoproteins: The linchpins of Ewing tumors. Gene 2005, 363, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Board WCoTE. Soft Tissue and Bone Tumours: WHO Classification of Tumours, 5th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, J.I.; Clemmons, D.R. Insulin-Like Growth Factors and Their Binding Proteins: Biological Actions*. Endocr. Rev. 1995, 16, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.E.; Rotwein, P. Growth, differentiation, and survival: Multiple physiological functions for insulin-like growth factors. Physiol. Rev. 1996, 76, 1005–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotlandi, K.; Manara, M.C.; Serra, M.; Marino, M.T.; Ventura, S.; Garofalo, C.; Alberghini, M.; Magagnoli, G.; Ferrari, S.; Llombart-Bosch, A.; et al. Expression of insulin-like growth factor system components in Ewing’s sarcoma and their association with survival. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotlandi, K.; Manara, M.C.; Nicoletti, G.; Lollini, P.-L.; Lukas, S.; Benini, S.; Croci, S.; Perdichizzi, S.; Zambelli, D.; Serra, M.; et al. Antitumor Activity of the Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Receptor Kinase Inhibitor NVP-AEW541 in Musculoskeletal Tumors. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 3868–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotlandi, K.; Benini, S.; Nanni, P.; Lollini, P.L.; Nicoletti, G.; Landuzzi, L.; Serra, M.; Manara, M.C.; Picci, P.; Baldini, N. Blockage of insulin-like growth factor-I receptor inhibits the growth of Ewing’s sarcoma in athymic mice. Cancer Res 1998, 58, 4127–4131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amin, H.M.; Morani, A.C.; Daw, N.C.; Lamhamedi-Cherradi, S.-E.; Subbiah, V.; Menegaz, B.A.; Vishwamitra, D.; Eskandari, G.; George, B.; Benjamin, R.S.; et al. IGF-1R/mTOR Targeted Therapy for Ewing Sarcoma: A Meta-Analysis of Five IGF-1R-Related Trials Matched to Proteomic and Radiologic Predictive Biomarkers. Cancers 2020, 12, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, C.; Mancarella, C.; Grilli, A.; Manara, M.C.; Astolfi, A.; Marino, M.T.; Conte, A.; Sigismund, S.; Carè, A.; Belfiore, A.; et al. Identification of Common and Distinctive Mechanisms of Resistance to Different Anti-IGF-IR Agents in Ewing’s Sarcoma. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancarella, C.; Pasello, M.; Manara, M.C.; Toracchio, L.; Sciandra, E.F.; Picci, P.; Scotlandi, K. Insulin-Like Growth Factor 2 mRNA-Binding Protein 3 Influences Sensitivity to Anti-IGF System Agents Through the Translational Regulation of IGF1R. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasanisi, P.; Bruno, E.; Venturelli, E.; Morelli, D.; Oliverio, A.; Baldassari, I.; Rovera, F.; Iula, G.; Taborelli, M.; Peissel, B.; et al. A Dietary Intervention to Lower Serum Levels of IGF-I in BRCA Mutation Carriers. Cancers 2018, 10, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drs, A.M.V.M.; Bovée, J.V.M.G.; Peterse, E.F.; Hogendoorn, P.C.W.; Gelderblom, H. Ewing sarcoma: The clinical relevance of the insulin-like growth factor 1 and the poly-ADP-ribose-polymerase pathway. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 53, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sand, L.G.; Szuhai, K.; Hogendoorn, P.C.W. Sequencing Overview of Ewing Sarcoma: A Journey across Genomic, Epigenomic and Transcriptomic Landscapes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 16176–16215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Velden, D.L.; Hoes, L.R.; Van Der Wijngaart, H.; Henegouwen, J.M.V.B.; Van Werkhoven, E.; Roepman, P.; Schilsky, R.L.; De Leng, W.W.J.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Nuijen, B.; et al. The Drug Rediscovery protocol facilitates the expanded use of existing anticancer drugs. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 574, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Trial | Patients | Compound | Endocrine Side Effects and Biomarkers | Clinical Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGF1R Antagonist Monoclonal Antibodies | |||||
| Haluska et al., 2007, [7] | Phase I | 24 patients with distinct solid tumors or sarcoma | Figitumumab (CP-751, 871) | -Hyperglycemia, increase of insulin, GH and IGF-1 | 7/12 SD, 1 long responder |
| Tolcher et al., 2009, [8] | Phase I | 53 patients with distinct tumors and sarcoma | Ganitumab (AMG 479) | -5 patients with hyperglycemia -IGF1 levels increase during treatment -patients with complete response possess IGF1R in metastases | 1 CR, 2 PR |
| Olmos et al., 2010, [9] | Phase I | 29 patients with distinct sarcoma (16 Ewing sarcoma) | Figitumumab (CP-751, 871) | -5 patients with hyperglycemia | 1 CR, 1 PR (both Ewing sarcoma), 8 SD |
| Kurzrock et al., 2010, [10] | Phase I | 35 patients with distinct solid tumors or sarcoma (9 Ewing) | Teprotumumab (R1507, RO4858696) | -2 patients with hyperglycemia -IGF1 serum levels increase during treatment | 2/33 PR, 14/33 SD |
| Juergens et al., 2011, [11]] | Phase I/II | 31 (phase 1) and 107 (phase 2) patients with distinct sarcoma (16 and 107 Ewing, respectively) | Figitumumab (CP-751, 871) | -3 patients with grade 3 hyperglycemia -IGF1 baseline levels were prognostic for survival, higher levels were associated with better survival -Highest IGF1 level showed a reduced clinical benefit -Increase of serum levels of IGF1, GH and insulin during treatment | 15/106 PR, 25/106 SD |
| Malempati et al., 2012, [12] | Phase I/II | 47 patients with distinct solid tumors or sarcoma (35 Ewing) | Cixutumumab (IMC-A12) | -14/44 patients hyperglycemia -Increase in serum levels IGF-I and IGFBP-3 -No change in serum levels IGF-II and IGFBP-2 | 3/25 PR, 5/25 SD (Ewing sarcoma), 2/13 SD (Other) |
| Murakami et al., 2012, [13] | Phase I | 19 patients with distinct solid tumors | Ganitumab (AMG 479) | -IGF1 and IGFBP3 increased after administration, GH not -IGF1 and IGFBP3 were not predictive or prognostic for a response of treatment | 7/19 SD |
| Tap et al., 2012, [14] | Phase II | 38 patients with distinct sarcoma (22 Ewing sarcoma) | Ganitumab (AMG 479) | -5/38 hyperglycemia (2 pts grade III) -IGF1 serum level increased | 2/35 PR, 21/35 SD |
| Schöffski et al., 2013, [15] | Phase II | 113 patients with distinct sarcoma (18 Ewing sarcoma) | Cixutumumab (IMC-A12) | -22/111 hyperglycemia (6 patients, grade III) | 2/111 PR, 44/111 SD |
| Pappo et al., 2014, [16] | Phase II | 163 patients with distinct sarcoma | R1507 | -15/163 hyperglycemia (4 patients, grade III) | 4/163 PR, 42/163 SD |
| Abou-Alfa et al., 2014, [17] | Phase II | 24 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma | Cixutumumab (IMC-A12) | -24/24 hyperglycemia (11 patients, grade III) | 7/24 SD |
| Frappaz et al., 2016, [26] | Phase II | 20 patients with distinct sarcoma (6 Ewing sarcoma) | Dalotuzumab(Mk-0646) | - 3/20 hyperglycemia | 1 PR |
| IGF1R/IR Dual Inhibitors | |||||
| Puzanov et al., 2014, [18] | Phase I | 95 patients with distinct solid tumors and sarcoma | Linsitinib (OSI-906) | -4 patients with hyperglycemia -Efficacy independent of KRAS mutation -Increase of IGF1 serum levels | 30/95 SD |
| Jones et al., 2015, [19] | Phase I | 97 patients with distinct solid tumors and sarcoma | Linsitinib (OSI-906) | - 37% hyperglycemia -Increase of IGF1 serum levels | 2/66 PR, 27/66 SD |
| Fassnacht et al., 2015, [20] | Phase III | 90 patients with adrenocortical carcinoma | Linsitinib (OSI-906) | -2 patients with grade III hyperglycemia -IGF1 serum levels increase | 3/90 PR |
| Barata et al., 2018, [21] | Phase II | 17 patients with metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer | Linsitinib (OSI-906) | -8 patients with hyperglycemia | 1/17 PR, 8/17 SD |
| Chiappori et al., 2016, [22] | Phase II | 29 patients with small cell lung cancer | Linsitinib (OSI-906) | -7/29 hyperglycemia (1 patient grade III) | 1/29 SD |
| IGF1/2 Neutralizing Antibody | |||||
| Haluska et al., 2014, [23] | Phase I | 43 patients with distinct solid tumors (1 Ewing) | Medi-573 | -1 Patient with hyperglycemia -No elevation of insulin or GH -IGF1 and IGF2 suppressed | 13/39 SD |
| Iguchi et al., 2015, [24] | Phase I | 10 patients with distinct solid tumors | Medi-573 | -1 patient with hyperglycemia -IGF1/2 decreased | 4/10 SD |
| De Bono et al., 2020, [25] | Phase I | 125 patients with distinct solid tumors and sarcoma | Xentuzumab | -2 patients with grade III hyperglycemia -IGF bioactivity decreased, total levels did not decrease -No effects on IGF2 | 2/125 PR, 55 SD |
| Resistance Mechanism | Example | Proposed Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Activation of the pathway trough IRA or hybrid receptors | IGF1R is inhibited, but IRA and hybrids receptors still activate the downstream pathway | Add an IRA inhibitor |
| Short-term fasting | ||
| Abrogation of negative feedback | High levels of IGF1 still activate the receptor due to a competitive affinity | Increase dose of IGF1-inhibitor |
| Decrease IGF1 levels by adding GH antagonist [35,79] | ||
| High levels of insulin activate IRA and hybrid receptors | Add an IRA inhibitor | |
| Short-term fasting | ||
| High levels of glucose | Short-term fasting | |
| High levels of GH activate the GHR and causes an increase in IGF1 serum levels | Adding GH antagonist | |
| Autocrine loops in the tumor | Expression of the receptor and ligand by the tumor | IGF1 inhibitors not effective, biomarker studies necessary to select patient who does not benefit from treatment |
| Expression of the receptor by the tumor and the ligands by stroma | ||
| Other pathways mutated | Other drivers likeEGFR) or secondary mutations (PI3K or PTEN) | Combination therapy [39] |
| IGF1 inhibitors not effective, biomarker studies necessary to select patient who does not benefit from treatment |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Groot, S.; Röttgering, B.; Gelderblom, H.; Pijl, H.; Szuhai, K.; Kroep, J.R. Unraveling the Resistance of IGF-Pathway Inhibition in Ewing Sarcoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123568
de Groot S, Röttgering B, Gelderblom H, Pijl H, Szuhai K, Kroep JR. Unraveling the Resistance of IGF-Pathway Inhibition in Ewing Sarcoma. Cancers. 2020; 12(12):3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123568
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Groot, Stefanie, Bas Röttgering, Hans Gelderblom, Hanno Pijl, Karoly Szuhai, and Judith R. Kroep. 2020. "Unraveling the Resistance of IGF-Pathway Inhibition in Ewing Sarcoma" Cancers 12, no. 12: 3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123568
APA Stylede Groot, S., Röttgering, B., Gelderblom, H., Pijl, H., Szuhai, K., & Kroep, J. R. (2020). Unraveling the Resistance of IGF-Pathway Inhibition in Ewing Sarcoma. Cancers, 12(12), 3568. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123568







