Abstract
Miocene tuffs preserved in argillaceous sediment interbedded with lacustrine successions are commonly encountered throughout the Dinarides Lake System (DLS) in south-eastern Europe. In this contribution the volcanic glass degradation and co-genetic Mn-Fe precipitation were studied in a 14.68 Ma felsic tuff from DLS Livno-Tomislavgrad Basin. Microbial activity has been involved in both reactions thus adding the interest of revealing effects of biotic and abiotic processes taking place during tuff eogenesis. X-ray diffraction and electron microbeam analysis with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy revealed the pitting or granular structures developed at glass rims along with smectite flakes protruding from a degrading glass. Mn-Fe mineralization emerges in the form of Mn-Fe coatings, an initial step to micronodule formation, where traces of biogenetic influence included a high content of phases rich in structural Mn (IV) (i.e., ranciéite and jacobsite) and presence of microbial microfossils. Co-genetic ties between glass degradation and Mn-Fe precipitation were established through the report of dioctahedral smectite formed out of altered glass; which then served as nuclei of the ongoing biotic and abiotic Mn-Fe mineralization. These processes manifest on a continuous involvement of microbial life in the course of eogenesis of pyroclastic material in lacustrine environments.
1. Introduction
In marine and lacustrine environments pyroclastic deposits may be preserved across wide lateral extents (Figure 1) [1,2]. Composed of amorphous vitric particles these deposits undergo diagenetic alterations on a much shorter timescale than more crystalline rocks [3,4,5]. Numerous research reported on glass high reactivity in geological record which eventually led to the formation of the clay minerals and zeolites [3,6,7,8]. Contrary to the wealth of knowledge on the subject of abiotic conditions involved in volcanic glass diagenesis [9,10,11] in recent decades a growing body of evidence has started to emphasize an increasingly important role of microbial activity in the process of volcanic glass degradation and diagenesis [12,13,14]. Such inferences were largely based on conspicuous glass morphologies like pitting and tubular structures or bacterial biofilms present at the surface of volcanic material recovered from the deep sea and freshwater settings [15,16,17,18]. It is believed that various organisms exploit the inherent instability of volcanic glass in aqueous setting by manipulating the local redox conditions in order to extract available bio-essential nutrients, thus, corroding the surface of the affected material [19,20,21]. Adding to the distinguishing weathering features the impacts of microbial metabolism and biological excretions may also result in the formation of clay minerals of low-crystallinity [3,12,22,23]. The metabolically mediated processes of glass alteration may take place at exceedingly high rates despite the biological activity that operates at reduced timescale compared to abiotic mechanisms [13]. This explains the fact that 70% to 80% of volcanic glass present at the uppermost oceanic crust is altered due to microbial activity [14].
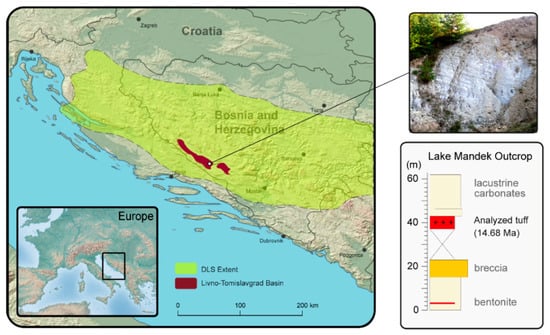
Figure 1.
The map of the Dinarides Lake System probable extent with the location and analyzed stratigraphic column from the Livno-Tomislavgrad basin, lake Mandek locality (modified after De Leeuw et al. (2011) and Mandic et al. (2019) [24,25].
The study of microbial-mineral interaction has also been proven to be vital in our understanding of the precipitation of various ferromanganese minerals typically found in the soil, deep-sea and lacustrine Mn-Fe nodules [26,27,28,29,30]. The oxidation of Fe and Mn at surface conditions is normally held responsible for inorganic precipitation of their oxy-hydroxides [30,31]. On the other hand, an increasingly accepted pathway of concentration of Mn phases in the marine and lacustrine sediments assumes the Mn(II) oxidation and Mn(III/IV) reduction by diverse bacteria and fungi, and to a lesser extent by the phototrophic green algae, diatoms, and cyanobacteria [26,27,30,32,33,34,35]. Presence of the organisms directly involved in the Mn-Fe mineral formation is attested through the identification of (a) the potential biominerals such as δMnO2, todorokite, birnessite, jacobsite and ranciéite [26] or (b) the characteristic bacterial microfossils featured by Mn encrustations [26,27,28].
This study has a focus on Miocene tuff from the Dinarides Lake System (Livno-Tomislavgrad Paleolake, Figure 1) where penecontemporaneous processes of glass degradation and Mn-Fe precipitation have been reported. The aim of this investigation was to find morphological, geochemical, and mineralogical clues as to how bacterial activity facilitated the alteration of felsic glass having led to smectite neoformation and subsequent Mn-Fe precipitation, which is yet another process driven by microorganisms. To address these goals, we formulated the following research questions. Do the altered volcanic glass and alteration-prone minerals show evidences of microbial activity? Is it possible to claim the same for Mn-Fe mineralization? Assuming both processes to be bacterially facilitated is it possible to establish a causative and genetic link between the two?
2. Geological Setting
The Dinarides, as a constituent of the Alpine-Himalayan orogeny, experienced their major orogenic stage from the middle Eocene to early Oligocene [36,37]. During their late Oligocene post-orogenic stage, the Dinaric mountains were affected by onset of extension and/or extensional tectonics, which resulted in development of a vast number of intramountain basins [37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. Following the commencement of favorable climatic conditions during the Miocene Climatic Optimum [44,45], these intramountain depression started to host a vast network of alpine lakes, known as the Dinarides Lake System (DLS) [43]. Spanning across vast areas of modern Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Montenegro, the area of the DLS comprised an area larger than 50,000 km2, with more than 150 freshwater lakes [40,46,47].
The largest and probably the longest lasting member of the DLS was the Livno-Tomislavgrad Paleolake. Existing from 17 to ~5 Ma, this paleolake accumulated more than 2.6 km of lacustrine deposits in two distinct phases of lake formation, chiefly defined by limestone and clay, occasional coal beds and numerous intervals of tuffs [24]. In its earliest stage the lake was defined by swampy conditions, eventually superseded by progressive flooding and deepening of the basin. The sampled tuff layer was recovered at the lake Mandek locality, showing a thickness of 6 m (Figure 1). Its stratigraphic position corresponds to the late phase of the first depositional cycle in the basin [48]. 40Ar/39Ar dating of the Mandek ash provided an age of 14.68 ± 0.16 Ma corresponding to the early middle Miocene [48]. The volcanic ash was found to be weakly lithified and of white color. Covered by dense vegetation, the lithology at its base remains somewhat unknown; with a broad breccia horizon found 14 m below the ash horizon, while at its upper boundary it is overlain by shallow water carbonates.
3. Materials and Methods
A single tuff sample was obtained from the lake Mandek locality near the city of Livno in southern Bosnia and Herzegovina (E 17.02255, N 43.73045; Figure 1). Laboratory work was carried out at Texas Tech University’s Department of Geosciences and the Microscopy Center of the College of Arts and Sciences. Petrographic analyses were completed using a Leica dm750p polarizing microscope in order to determine morphological and textural changes of the tuff, with a focus on the assessment of glass alteration and extent of Mn-Fe mineralization. A glass lab spatula was utilized to hand-pick the areas of representative tuff affected by visible Mn-Fe mineralization (Figure 2a). The separate was thereupon analyzed X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) measurements. The powder separate was first X-rayed using a Bruker D8-Advanced diffractometer. The size of the divergent slit was 0.2 mm whilst the receiving slit was 1 mm wide. Measurement parameters comprised a step scan in the Bragg–Brentano geometry using CuKα radiation (40 kV and 40 mA) with a counting time of 5 s per 0.02° from 3 to 60 °2θ. Diffractograms were analyzed in the Bruker EVA diffraction suite supported by PDF4 crystallographic database. SEM analyses were carried out by means of a Zeiss Crossbeam 540 apparatus equipped with the energy-dispersive spectrometer (EDS) (Table 1). Carbon-coated thin sections and powder separates were used for this investigation. The measurements were performed at high vacuum, 15 kV and ~1 nA, with two silicon drift energy dispersive X-ray detectors from Oxford instruments. High-resolution back-scatter electron images have been acquired using a 4-quadrant-backscatter detector. EDS analyses were performed on spots with a diameter of at least 100 nm, with acquisition live time of 20 s. The Zeiss AZtec software (Oxford Instruments, Oxford, UK) was used for EDS spectra quantification in a standardless mode. Chemical data were used as oxide percentages and were normalized to 100%. The NIST DTSA-II software package (NIST, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) [49] was used to quantify EDS spectra from literature when no chemical data was provided [50,51].
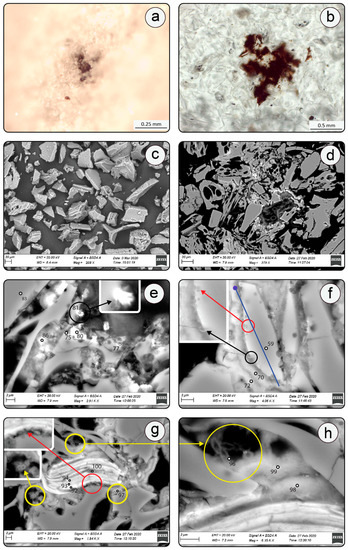
Figure 2.
Optical (a,b) and BSE images (c–h) of the analyzed sample: (a) Mn-Fe mineralization at the surface of the sample, (b) fresh volcanic glass coated with brown Mn-Fe coatings, (c) glass shards and pumice grains in the loose material powdered sample, (d) BSE image of an area depicted in (a), (e) BSE image of shards coated by todorokite-like mineralization. Spectra acquisition points are marked and correspond to Table 1. Dendritic todorokite is shown in the inset (analysis 81), (f) Glass shards featuring pitting textures surrounded by Mn-Fe mineralization. Red and black circles correspond to pitting texture and neoformed smectite, respectively, are shown in inset. Blue line corresponds to EDS compositional profile provided in Figure 5a where the dot represents the onset of measurement, (g) altered biotite grain featuring pitting texture (red circle) and surrounded by Mn-Fe mineralization and bacteria microfossils (yellow circle), (h) Mn-Fe mineralization and bacterial microfossils in the proximity of altered biotite (yellow circle).

Table 1.
Representative EDS analyses of fresh and altered volcanic glass, biotite, Mn-Fe micronodules, smectite and microbial microfossils. Analysis numbers correspond to acquisition spots depicted in Figure 2 and Figure 4
4. Results
4.1. Description and Eogenetic Evolution of Volcanic Tuff
The analyzed tuff largely consists of fresh pumice and shards (Figure 2a–f), while mineral phases, such as plagioclase, quartz and biotite account for ~1 to 2 vol.% each (Figure 2g). Brownish, and occasionally opaque, aggregates emerge upon closer inspection as coatings of glass and mineral particles (Figure 2a,b). XRD mineralogy of hand-picked glass coatings consists of amorphous matter (bulging from ~15 to 35 °2θ), quartz, trydimite, cristobalite, plagioclase (labradorite), and K-feldspar (sanidine) (Figure 3, Table 2). Smectite from dioctahedral beidellite-montmorillonite series and possibly Mn oxide (i.e., jacobsite and ranciéite) were also detected.
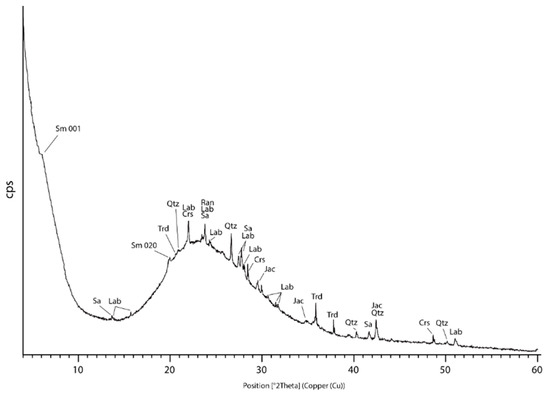

Table 2.
Values for d-spacing (d/Å) and diffraction angles (°2θ) of the highest intensity reflections for identified phases present in the analyzed separate.
Presence of the former is suggested by a poorly-defined 001 diffraction peak at d = 14.65 Å and relatively strong peak centered at d = 4.48 Å (Table 2), which likely corresponds to the asymmetric 02l (020) peak system [52]. The peaks at d = 3.74 Å and d = 2.49 Å as well as d = 2.58 Å and 3.02 Å conform to ranciéite and jacobsite diffraction data, respectively (Figure 3) [53,54]. Various minor and diffuse X-ray reflections likely belong to the other low-crystallinity Mn oxides and hydroxides such as todorokite which is commonly associated to ranciéite [53]. The SEM-EDS analyses revealed glass shards to be highly vesicular exhibiting the cuspate-wall shapes, sensu Fisher and Schminke (1984) [7] (Figure 2c,d). Such morphological characteristics conform well with the high SiO2 (~75–80 wt.%) and low MgO/FeO (~0.04–0.13) geochemistry of tuffs (Table 1, analyses 78, 79, 83), which is consistent with the tuff origin from very viscous felsic magmas that normally accompany highly explosive Plinian eruptions [7,55,56]. Glass shards appear rather fresh (Figure 2a–c) but early stages of alteration were nevertheless observed in the form of sub-micron smectite-like laths protruding from the surface of individual shards (Figure 2f and Figure 4a–c) [57]. Characteristic honeycomb morphology of smectite (Figure 4b,c) as well as the clear increase in the concentrations of Al2O3 and MgO (from ~13 to 18 wt.% and ~0.1 to 3 wt.%, respectively; Table 1, analyses 40, 44, 78, 79, 33p) relative to the glassy substrate are both in favor of beidellite to montmorillonite composition [58]. Both Al2O3 and MgO were likely concentrated from the dissolved glass. An additional line of evidence indicating the mobilization and depletion in SiO2 (17%), Al2O3 (2%) and alkalis (30–50%) toward glass rims may be inferred from the shards’ compositional line profile (Figure 2f and Figure 5a), which suggests the incorporation of those elements in neoformed smectite. Compositional profiles made through the glass separate concur with the established pattern clearly showing the spikes of Al as a result of its concentration in the Al-rich dioctahedral smectite (Figure 4a,c, and Figure 5b,c). Finally, a typical microbial etching developed in the form of pitting textures was commonly found along the rims of altered shards (Figure 2f,g) [15,17,59].
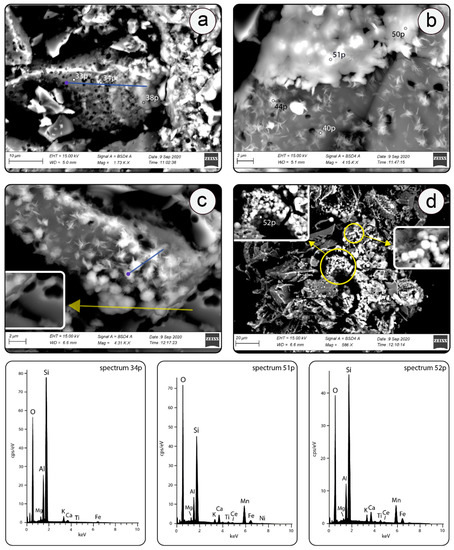
Figure 4.
BSE images of loose powder rich in Mn-Fe mineralization. (a) Extensively smectitized pumice affected by Mn-Fe coating. Blue marks the EDS compositional profile shown in Figure 5b. (b) Ferromanganese coating in close relationship with smectitized shard. (c) Shard showing a gradual transition from smectitized surface towards Mn-Fe coatings (i.e., micronodule). Blue line marks the EDS compositional profile shown in Figure 5c. Inset shows the fragment of fresh glass. (d) Shard and pumice aggregates featured by Mn-Fe coatings which exhibit cocci-like morphologies (yellow circle left) and Streptococcus genus bead-like cell division pattern (yellow circle right). Spectra acquisition points are marked and correspond to Table 1. Representative EDS spectra correspond to smectite (spectrum 34p) and Mn-Fe coatings (spectra 51p and 52p).
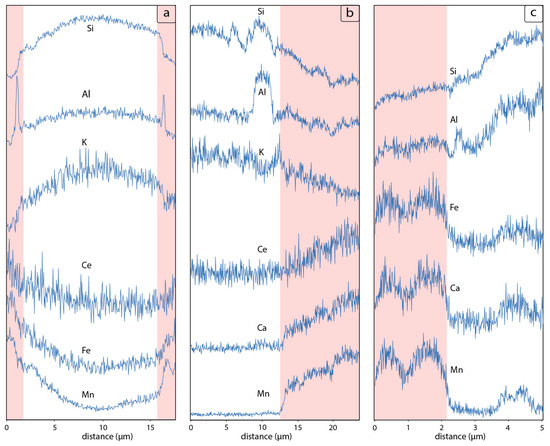
When present, smectite flakes are found in a direct contact or proximity to Mn-Fe mineralization (Figure 2f and Figure 4a–c). In thin sections, the Mn-Fe mineralization emerges in band-like forms encircling glass shards (Figure 2d–f). On the other hand, in powder samples it is manifested in the form of distinctly granular Mn-Fe coatings, henceforth referred to as micronodules (Figure 4a–d). Altered biotite is typically found in a close spatial relationship with the optically inactive Mn-Fe mineralizations (Figure 2g,h). Biotite phenocrysts underwent an extensive exfoliation and distortion (Figure 2g) with a substantial loss of K2O, FeO, MgO and TiO2 towards mineral rims (Table 1, analyses 92, 93, 94). Conversely, the concentrations of MnO show an inverse relationship with respect to the trend outlined by other major oxides with values abruptly increasing from 10 to 16 wt.% towards grain edges (Table 1). Similarly, to altered shards, biotite also retains morphological clues indicative of microbial activity. This is primarily demonstrated by pitting textures present at the outer edges of exfoliated layers, and also by numerous MnO and CeO2 rich oval morphologies which are alike to the spherical shapes suggested as one of the typical Mn-rich alteration textures indicative of microbial alteration in deep-sea basalts (Figure 2g,h) [50,60].
4.2. SEM-EDS Mineralogy and Morphology of Mn-Fe Micronodules
The investigated Mn-Fe mineralization developed in the form of nodular coatings (i.e., micronodules) which may attain up to ~2 μm in thickness (Figure 2d–h and Figure 4a–d) and are found surrounding individual shards and/or biotite. The chemistry of micronodules is provided in Table 1, while representative EDS spectra are given in Figure 4. The Mn-Fe micronodules show a wide range of SiO2 and FeO concentrations (19 to 50. wt.% and 2 to 16 wt.%, respectively), and virtually a bimodal distribution of MnO (30 or ~50 wt.%). The contents of Al2O3 and CeO2 are rather uniform of ~9 and 3 wt. %, respectively (Table 1, analyses 70, 72, 80, 81, 86, 38p, 50p, 51p, 52p). Taking into account the size of Mn-Fe micronodules (~2 μm), which is equivalent to the size of interaction volume at given acceleration voltage of 20 kV [61] the analyses of Mn-Fe mineralization were likely impacted by the Si-rich substrate (i.e., glass or smectite; Figure 2e–g, Figure 4a–c and Figure 5a–c). Detailed SEM investigation also showed that Mn-Fe micronodules grew over smectite displaying the characteristic honeycomb texture [62] (Figure 2f, and Figure 4b,c). Although the morphology of the Mn micronodules is similar, there are significant compositional differences between Mn-Fe micronodules formed around biotite and those around shards (Table 1, analyses 70, 72, 98 and 99, Figure 2f,h). The former exhibit higher silica content while the latter contain comparatively lower concentrations of FeO, MgO and K2O. Conversely, MnO abundances within individual micronodules observed as Mn-Fe bands in thin sections are consistent at ~30 wt.% (Table 1).
Albeit smaller in size the morphology and chemistry of analyzed Mn-Fe mineralization shows a correlation with the Mn nodules described in literature [63,64,65,66,67]. Based on granular morphology, minuscule size, and layered chemistry of studied coatings these may be described as juvenile Mn-micronodules [68,69,70], which are characterized by variable chemistry [69,71] and XRD mineralogy that regularly demonstrates presence of Mn-oxides (i.e., burserite, todorokite, δMnO2, jacobsite, and ranciéite), Fe-oxyhydroxides and detrital aluminosilicates [72,73,74]. Knowing that Mn-Fe mineralization generally occurs in the form of poorly crystalline nano to microscale aggregates of variable water content the SEM-EDS identification of individual Mn phases may be somewhat challenging [60,61,62]. However, the chemistry of analyzed micronodules (Table. 1, analyses 70, 72, 98, 99, 38p, 50p, 51p,52p) and their band-like morphology in thin-section fit well to the compositional characteristics of various Mn-Fe concretions [75,76]. This is primarily inferred through the comparison of MnO/FeO values which are virtually unaffected by mixed analyses with the Si-rich host material on top of which Mn-Fe mineralization developed. The MnO/FeO in the studied micronodules is on average 4 ± 2 (Table 1) which fits the range shown by Mn-nodules (MnO/FeO = ~3–6, Table 1, analyses 70, 72, 96, 97, 50p, 51p, 52p) recovered from the ocean floor [77]. Moreover, the exceedingly high MnO/FeO reported in the dendritic outgrowths (Figure 2e), spanning from ~14 to 23 (Table 1, analyses 80,81,86), is comparable with the nodules of analogue morphology documented offshore Peru (MnO/FeO ~15.6 to 21) [75,76].
The composition of low-MnO and high-SiO2 portions of micronodules corresponds well to the mixture of smectite/glass substrate, Mn-oxides and Fe-oxyhydroxides, while the high-MnO areas as well as elevated Ba and Ca are consistent with todorokite, which is a typical product of biologically oxidized Mn (Table 1, analyses 80, 86) [72,74,78]. The rare-earth elements content of the bands also supports their make-up of various Mn-oxides and Fe oxy-hydroxides as both Ce and Eu due to their variable oxidation states show preferential fractionation towards these compounds [79,80]. Accordingly, the measured concentrations of Ce were remarkably high in the studied Mn-Fe mineralization (Figure 2f,g, Figure 4b,d, and Figure 5a,b; Table 1. analyses 70, 72, 98, 99, 51p, 52p) which favors an oxidizing environment conducive to both the oxidation of Ce3+ and Fe oxy-hydroxide precipitation [79,80,81]. Indeed, the stratigraphic position of the analyzed tuff interlayered by shallow water carbonates and breccias, is in favor of an open type alpine lake with oxic conditions [24].
5. Discussion
5.1. Microbially Mediated Glass Transformations
Felsic tuffs are known to be more refractory to alteration when compared to mafic ones which typically undergo a relatively quick degradation in the marine or freshwater depositional environments [7,82,83]. The difference between the two stems from a lower extent of SiO2 polymerization, and a higher abundance of highly soluble cations (i.e., Ca2+ and Mg2+) as in mafic glass [5,7,83]. Recent textural and mineralogical studies on glass alterations suggest that microbial activity may weather a layer of up to 1 µm per annum [13,14,20,84,85]. Similarly, to glass shards from deep-ocean sediments, volcanic material recovered from Pleistocene and Holocene terrestrial deposits commonly exhibits numerous alteration features attributed to microbial corrosion [16,17]. With some caution, the presence of irregular pitting, granular or tubular structures at the surface of volcanic glass may serve as evidence of microbial etching [15,86]. Taking into account that many chemical or biological indicators such as presence of C or live microbes remain vulnerable to obliteration or profound alteration by abiotic diagenetic changes [16,87], it follows that the most immediate evidences of bacterial activity in ancient tuffs is the pitting or tubular morphologies developed along the rims of receptive phases. In the studied tuff such morphological features were found along shard and biotite edges (Figure 2f,g), which are both diagenetically unstable solids [5]. The abundance of easily oxidized cations released through glass degradation, such as Mg and Fe, likely provided a favorable substrate for microbial etching [17,28].
Although the high susceptibility of volcanic glass to bacterial corrosion is well documented [13,15,20,84], recent work also demonstrates that various clay minerals can both enhance, or be generated through, microbial interaction with volcanic material [12,13,23]. Experiments undertaken by Cuadros et al. (2013) [12] show microorganisms rapidly coating fragments of rhyolitic glass in waters of diverse salinity, producing dioctahedral and trioctahedral smectite. Similar results were observed from recently deposited volcanic ash (<2 ka) where various bacterial species were found coated by fibers and/or flakes of smectite [88]. Moreover, the high surface area and the abundance of bio-essential nutrients (i.e., Ca2+, Mg2+ and K+) adsorbed or interlayered in smectite may foster an overall biological activity in such microenvironments thus promoting bacterial surface adhesion and biofilm generation [89,90,91]. One may therefore infer that the origin of smectite-like laths proximal to the glass pitting structures (Figure 2f) may be genetically related to the processes involving glass corrosion, biofilm formation, and/or bacterial adhesion to the surface of the glass [89,90].
5.2. Bacterial Textures in Mn-Fe Miconodules
The role of microbes in the formation of Mn-Fe micro(nodules) has long been suggested [92,93]. Recent work, based on bacterial culturing experiments, as well as DNA extraction, identified a multitude of metal-oxidizing microbes in Mn-Fe nodules [29,30]. Although the relationship between the oxidation of Mn(II) and cellular function in microorganisms is still not fully understood [26,27,28] laboratory experiments have demonstrated that bacteria commonly found in freshwater environments, such as Bacillus sp. and Pseudomonas putida, regularly produce bio-oxides with a high proportion of structural Mn(IV), high specific surface areas and low crystallinity, typically akin to highly disordered birnessite i.e., δMnO2 [26].
Biogenically generated δMnO2 likely undergoes an abiotic transformation towards more crystalline oxides of Mn (i.e., todorokite, birnessite, bursierite and jacobsite) which are typically reported in Mn-Fe encrustations [26,28,94]. Precipitation of these Mn compounds may fully adhere to the processes of abiotic crystallization especially in the environments rich in dissolved Mn(II) (i.e., hydrothermal vents and acid mine drainages) [95]. It is however believed that the formation of the mentioned Mn phases proceeds from biogenic δMnO2 in those settings deprived in Mn(II), such as the oxic water columns of open lakes [95]. Thus, the occurrence of microbial microfossils [26,27,28,71,96] encrusted by minerals containing high proportion of structural Mn(IV) relative to Mn(II) (i.e., δMnO2, todorokite, birnessite, jacobsite, ranciéite) may be utilized in identification of biogenic influences involved in the genesis of the studied Mn-Fe micronodules.
The BSE images of the thin section in the areas next to altered biotite (Figure 2g,h, Table 1, analyses 96, 97, 102) show evidences of numerous ~1 to 1.8 µm long Mn-rich oval forms (MnO = 25.7–33 wt.%, Table 1, analyses 96,97,102) found in a direct contact with Mn-Fe coatings. The high content of SiO2 and reported elliptical shapes are characteristic for various types of Si-secreting species (i.e., pennate diatoms); however, the size of the forms reported herein did not exceed 2 µm which makes the attribution of these forms to lacustrine microfossils highly unlikely [97]. Moreover, the siliceous microfossil assemblages described from contemporaneous basins of the DLS bioprovince are significantly coarser and of contrasting morphologies [98]. Conversely, described forms are strikingly similar to the cross-sections of hollow encrustations described as fossilized bacterial cells, which are normally referred to as cocci stemming as precipitates of distinct Mn-rich alteration products at the surface of freshly dredged deep sea basaltic glass [50]. The inference on their biogenetic signatures can be drawn from an elevated content of C suggesting an ongoing microbial activity at the time of sample retrieval which gave rise to the substantial Mn enrichment (MnO = ~20 wt.%) relative to the Mn-lacking glassy substrate [50]. While about 15 Ma of deposition of analyzed tuff and thin-section carbon coating must have compromised the original content of C the rest of measured elements are all in favor of biogenically generated Mn-oxides; namely the high abundances of MnO, BaO (~1.1 wt.%), CeO (~0.8 wt.%), and CaO (6.6 wt.%) (Table 1, analyses 96, 97, 98, 102) are consistent with the composition of biogenically-formed δMnO2 and more crystalline Mn-oxides identified by X-ray diffraction (i.e., jacobsite and ranicéite; Figure 3) [54]. Another set of evidences of microbially generated Mn-Fe mineralization is their MnO/FeO ratio (Table 1). Wang et al. (2012) [51] have shown that the portion of Mn-Fe micronodules consistent with bacterial morphologies (i.e., fossilized cocci) is marked by a strong increase in MnO/FeO relative to the rest of micronodules devoid of typical bacterial forms (i.e., banding). Furthermore, the microbial encrustations described here display a 3-fold decrease in FeO relative to the banding (~15 to 5 wt.%, Table 1.) and an abrupt increase in MnO/FeO, rising from ~2.1 to 5.2 (Figure 2g,h; Table 1, analyses 98,99,102). Lastly, the biogenicity of observed encrustations is also supported by the fact that almost identical morphologies are described in laboratory experiments where the microbial spores of Bacillus sp. were found to become rapidly coated with poorly crystalline δMnO2 in Mn2+ enriched solutions [27,99,100,101].
A different set of clues pointing to microbial origin of Mn-Fe nodules was identified through SEM-EDS investigation of tuff powder separates rich in the visible Mn-Fe mineralization (Figure 2a). Numerous Mn-rich spherical forms (MnO = 15.1–33.8 wt. %, MnO/FeO = 2.7–8.9, Table 1, analyses 50p, 51p, 52p) are documented ranging in size from ~1.1 to 2.5 µm. They developed on top of agglomerated laths of smectite grown at the surface of glass shards (Figure 4a–d, Table 1). Morphologically, and to a limited extent compositionally (MnO = ~15 wt%, MnO/FeO = 1.38), the comparable assemblages of Mn-rich spheres (1–2 µm) emerging from the clayey substrate have been reported in the close association with aforementioned hollow cocci-like morphologies found at the surface of altered basaltic glass in the deep sea setting [50]. Considering the comparable shapes and sizes, as well as the proximity to the hollow cocci spheres, Thorseth et al. (2003) [50] hypothesized that the observed spheres originated from fossilized cocci whose subsequent burial and infilling by inorganic precipitation obliterated their original organic content. The aggregations of 1 to 3 µm sized cocci spheres have become increasingly important in the identification of Mn-Fe mineralization present across the vastly different depositional environments, such as Mn nodules from the Clarion-Clipperton Fracture Zone (CCFZ) of the Eastern Pacific, as well as desert varnishes from the Gangdese region in Tibet, PRC [51,68,102]. In the former, the micronodules are characterized by the surfaces accommodating numerous cocci whose relatively high C content is taken as a proof of their biogenicity. The contents of the rest of diagnostic elements (SiO2 = ~49 wt.%., MnO = ~30 wt.%, MnO/FeO = ~4) of cocci-like micronodule surfaces from the CCFZ are in agreement with the values obtained from Mn-Fe mineralization reported here (Table 1, analyses 70, 72, 96, 97). Finally, a thorough SEM study of the CCFZ micronodule cocci aggregations revealed the conspicuous bead-like chain arrangements analogue to the ones observed in Figure 4d. This is interpreted as a typical cell division pattern of the Streptococcus genus [68,103].
The presence of numerous cell encrustations rich in insoluble Mn(IV), marked by the high specific surface area, likely supplied an energetically favorable substrate which served as a nucleus in the ensuing precipitation of inorganic Mn-Fe mineralization [51,68]. This may explain the relatively uniform Mn-Fe coatings with the peculiar intermittent spherical outgrowths (Figure 4a,b). While these spherical outgrowths represent fossilized cocci the ensuing Mn-Fe mineralization is linked to the widespread inorganic coating. This is further substantiated by the consistent overall chemistry and significantly higher MnO/FeO of individual cocci and spherical outgrowths compared to the surrounding Mn-Fe coatings (Figure 4b,c and Figure 5b,c; Table 1, analyses 98, 98, 102, 38p, 50p, 51p, 52p).
5.3. Glass Smectitization as a Trigger of Mn-Fe Precipitation
The close spatial relationship of Mn-Fe micronodules and altered shards/biotite (Figure 2e–g, Figure 4a–c) indicates co-genetic ties between the onset of Mn-Fe mineralization and eogenesis of volcanic glass. In BSE images is this relationship aptly demonstrated through a gradual outgrowth of Mn-Fe micronodules on aggregates of smectite flakes developed at shard surfaces (Figure 4a–c). The role of smectite facilitating the Mn-Fe mineralization is ascertained by (a) the lack of Mn-Fe compounds at those shards devoid of smectite flakes (Figure 4a–c) and (b) the chemistry of micronodules whose EDS chemistry, as a result of a ~2 µm-interaction-volume at given acceleration voltage [61], unveil the smectite substrate (Figure 4b; Al2O3/SiO2 = 0.25, K2O = 1.5, CaO = 5.2, Table 1, analyses 56, 40p, 44p) at which micronodules grew (Figure 4b).
The genesis of studied micronodules thus likely commenced by crystallization of beidellite-montmorillonite at shard surfaces through the interaction with water and where the microbial corrosion has operated the most efficiently (Figure 2f and Figure 6a) [13,15,87,88]. Smectite eventually developed its characteristic honey-comb or aggregated textures (Figure 2f, Figure 4a–c) with high specific surface areas and availability of bio-essential cations from its interlayer space and/or charged surfaces (i.e., Ca, K, Mg) [104] thus facilitating the adhesion and flourishing of Fe and Mn metabolizing organisms. The numerous Mn-rich cocci and spheroid morphologies developed at the studied shards (Figure 2g,h and Figure 4d) are evidence of the dwelling presence of such organisms [51,68], whose encrustations then served as nucleating seeds, sensu Wang et al., 2009 [68] (Figure 4a–d and Figure 6b), for further micronodule formation. This final step operated through the accretion of abiotic and/or biotic Mn-phases such as todorokite, ranciéite and jacobsite over smectite flakes and individual cocci leading to the appearance of globular micron-sized micronodules (Figure 3, Figure 4b–d and Figure 6c, Table 2). Deeper investigation on the role of smectite in Mn-Fe precipitation may enhance our understanding on why Mn-Fe nodules readily form on a pyroclastic substrate [105]. Finally, taking into account that the processes of glass degradation and Mn-Fe precipitation are both marked by textural and/or mineralogical markers of biogenic activity one can assume that the (co)evolution of glass alteration followed by smectite crystallization and Mn-Fe precipitation testify to a continuous involvement of microbial life in the course of diagenesis of the felsic tuff investigated here.
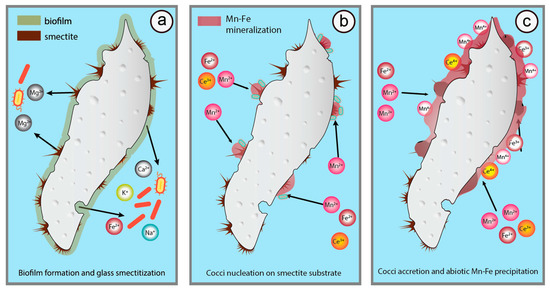
Figure 6.
Proposed three-step model of glass degradation and Mn-Fe micronodule generation. (a) shard smectitization, microbial corrosion and pitting texture formation, biofilm generation and extraction of bio-essential nutrients from glass (Fe2+, K, Na, Ca) and smectite flakes (Fe3+, Mg); (b) nucleation of Mn-oxide encrusted cocci on smectite substrate; (c) accretion of individual mineralized cocci and ensuing abiotic precipitation of various Mn-Fe oxy-hydroxides marking an early stage of micronodule formation.
6. Conclusions
(1) Felsic tuff from Miocene strata of the Livno-Tomislavgrad paleolake situated at the south of the Dinarides Lake System shows incipient glass eogenesis which gave birth to the peculiar Mn-Fe coatings of glass shards.
(2) Smectite of beidellite-montmorillonite composition was found as a main product of glass eogenesis regularly emerging in a close spatial relationship with Mn-Fe mineralization. From their textural context it follows that crystallization of smectite preceded the formation of Mn-Fe mineralization. Mn precipitates have the characteristic globular forms (i.e., Mn-Fe micronodules).
(3) Various bacterial textures present at glass surfaces and within Mn-Fe micronodules are related to the presence of smectite who is known to promote microorganism activity.
(4) High morphological and compositional resemblance of analyzed and deep-ocean Mn-Fe micronodules is in favor of shard degradation and Mn-Fe micronodule formation which take place irrespectively of the type of depositional environment (terrestrial, lacustrine, deep sea).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.Š. and L.B.; data curation, L.B. and G.Z.; formal analysis, L.B. and G.Z.; funding acquisition, B.Š. and L.B.; supervision, B.Š. and O.M.; writing—original draft, L.B. and B.Š.; writing—review and editing, B.Š. and O.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Texas Tech University Virginia Clair Fund Scholarship awarded to L.B.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Tvrtko Ćubela (Livno) for his kind help during the field work in the Livno-Tomislavgrad Basin. Further gratitude is extended to Vecteezy.com for providing the art used in Figure 6. The constructive reviews by two anonymous reviewers as well as the editorial handling, criticism and suggestions by Javier Cuadros contributed significantly to the manuscript quality.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Smith, D.G.; Fisher, T.G. Glacial Lake Agassiz: The northwestern outlet and paleoflood. Geology 1993, 21, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, R.A.; Sims, K.W.W. Bending as a mechanism for triggering off-axis volcanism on the East Pacific Rise. Geology 2005, 33, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsaglia, K.M.; Tazaki, K. Diagenetic trends in Leg 126 sandstones. Proc. Ocean Drill. Prog. Sci. Results 1992, 126, 125–138. [Google Scholar]
- Bohor, B.F.; Triplehorn, D.M. Tonsteins: Altered Volcanic Ash Layers in Coal-Bearing Sequences; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1993; Volume 285, ISBN 0813722853. [Google Scholar]
- Gifkins, C.C.; Herrmann, W.; Large, R.R. Altered Volcanic Rocks: A Guide to Description and Interpretation; Centre for Ore Deposit Research, University of Tasmania: Hobart, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lipman, P.W. Chemical comparison of glassy and crystalline volcanic rocks. Bull. U.S. Geol. Soc. 1965, 1201, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R.V.; Schmincke, H.U. Pyroclastic Rocks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984; ISBN 3540127569. [Google Scholar]
- Casey, W.H.; Bunker, B. Leaching of mineral and glass surfaces during dissolution. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 1990, 23, 397–426. [Google Scholar]
- Reich, V.; Von Rad, U. Eocene porcellanites and early Cretaceous cherts from the western North Atlantic basin. Initial Rep. Deep Sea Drill. Proj. 1979, 43, 437–448. [Google Scholar]
- Aoyagi, K.; Kazama, T. Transformational changes of clay minerals, zeolites and silica minerals during diagenesis. Sedimentology 1980, 27, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broxton, D.E.; Bish, D.L.; Warren, R.G. Distribution and chemistry of diagenetic minerals at Yucca Mountain, Nye County, Nevada. Clays Clay Miner. 1987, 35, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadros, J.; Afsin, B.; Jadubansa, P.; Ardakani, M.; Ascaso, C.; Wierzchos, J.; Adams, J. Pathways of volcanic glass alteration in laboratory experiments through inorganic and microbially-mediated processes. Clay Miner. 2013, 48, 423–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadros, J. Clay minerals interaction with microorganisms: A review. Clay Miner. 2017, 52, 235–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudigel, H.; Furnes, H.; McLoughlin, N.; Banerjee, N.R.; Connell, L.B.; Templeton, A. 3.5 billion years of glass bioalteration: Volcanic rocks as a basis for microbial life? Earth Sci. Rev. 2008, 89, 156–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockell, C.S.; Herrera, A. Why are some microorganisms boring? Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cockell, C.S.; Olsson-Francis, K.; Herrera, A.; Meunier, A. Alteration textures in terrestrial volcanic glass and the associated bacterial community. Geobiology 2009, 7, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, A.; Cockell, C.S.; Self, S.; Blaxter, M.; Reitner, J.; Arp, G.; Dröse, W.; Thorsteinsson, T.; Tindle, A. Bacterial colonization and weathering of terrestrial obsidian in Iceland. Geomicrobiol. J. 2008, 25, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLoughlin, N.; Furnes, H.; Banerjee, N.R.; Staudigel, H.; Muehlenbachs, K.; De Wit, M.; Van Kranendonk, M.J. Micro-bioerosion in volcanic glass: Extending the ichnofossil record to Archaean basaltic crust. In Current Developments in Bioerosion; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 371–396. [Google Scholar]
- Staudigel, H.; Chastain, R.A.; Yayanos, A.; Bourcier, W. Biologically mediated dissolution of glass. Chem. Geol. 1995, 126, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorseth, I.H.; Furnes, H.; Tumyr, O. Textural and chemical effects of bacterial activity on basaltic glass: An experimental approach. Chem. Geol. 1995, 119, 139–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisk, M.R.; Giovannoni, S.J.; Thorseth, I.H. Alteration of oceanic volcanic glass: Textural evidence of microbial activity. Science 1998, 281, 978–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Navas, A.; Martín Algarra, A.; Nieto, F. Bacterially-Mediated Authigenesis of clays in Phosphate Stromatolites. Sedimentology 1998, 45, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konhauser, K.O.; Urrutia, M.M. Bacterial clay authigenesis: A common biogeochemical process. Chem. Geol. 1999, 161, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leeuw, A.; Mandic, O.; Krijgsman, W.; Kuiper, K.; Hrvatović, H. A chronostratigraphy for the Dinaride Lake System deposits of the Livno-Tomislavgrad Basin: The rise and fall of a long-lived lacustrine environment. Stratigraphy 2011, 8, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandic, O.; Sant, K.; Kallanxhi, M.-E.; Ćorić, S.; Theobalt, D.; Grunert, P.; de Leeuw, A.; Krijgsman, W. Integrated bio-magnetostratigraphy of the Badenian reference section Ugljevik in southern Pannonian Basin-implications for the Paratethys history (middle Miocene, Central Europe). Glob. Planet. Chang. 2019, 172, 374–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebo, B.M.; Bargar, J.R.; Clement, B.G.; Dick, G.J.; Murray, K.J.; Parker, D.; Verity, R.; Webb, S.M. Biogenic manganese oxides: Properties and mechanisms of formation. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2004, 32, 287–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebo, B.M.; Johnson, H.A.; McCarthy, J.K.; Templeton, A.S. Geomicrobiology of manganese(II) oxidation. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, H.L.; Newman, D.K.; Kappler, A. Ehrlich’s Geomicrobiology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; ISBN 1466592419. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, L.Y.; La Duc, M.T.; Grund, T.J.; Nealson, K.H. Bacterial and archaeal populations associated with freshwater ferromanganous micronodules and sediments. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 3, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommers, M.G.; Dollhopf, M.E.; Douglas, S. Freshwater ferromanganese stromatolites from lake vermilion, Minnesota: Microbial culturing and environmental scanning electron microscopy investigations. Geomicrobiol. J. 2002, 19, 407–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, R.B.; Renaut, R.W.; Williams, T.M. Characteristics and origins of laminated ferromanganese nodules from Lake Malawi, Central Africa. In Limnology, Climatology and Paleoclimatology of the East African Lakes; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2019; pp. 461–474. [Google Scholar]
- Gillette, N.J. Oneida Lake pancakes. N. Y. State Conserv. 1961, 18, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Saratovsky, I.; Gurr, S.J.; Hayward, M.A. The structure of manganese oxide formed by the fungus Acremonium sp. strain KR21-2. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 3291–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiro, T.G.; Bargar, J.R.; Sposito, G.; Tebo, B.M. Bacteriogenic manganese oxides. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer-Chaput, B.; Horwitz, M.A.; de Pedro Beato, E.; Melchiorre, P. Photochemical generation of radicals from alkyl electrophiles using a nucleophilic organic catalyst. Nat. Chem. 2019, 11, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tari, V. Evolution of the northern and western Dinarides: A tectonostratigraphic approach. In Continental Collision and the Tectono-Sedimentary Evolution of Forelands; Copernicus: Göttingen, Germany, 2002; ISBN 3936586004. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, S.M.; Bernoulli, D.; Fügenschuh, B.; Matenco, L.; Schefer, S.; Schuster, R.; Tischler, M.; Ustaszewski, K. The Alpine-Carpathian-Dinaridic orogenic system: Correlation and evolution of tectonic units. Swiss J. Geosci. 2008, 101, 139–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tari, V.; Pamić, J. Geodynamic evolution of the northern Dinarides and the southern part of the Pannonian Basin. Tectonophysics 1998, 297, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbar, T. Orogenic evolution of the External Dinarides in the NE Adriatic region: A model constrained by tectonostratigraphy of Upper Cretaceous to Paleogene carbonates. Earth Sci. Rev. 2009, 96, 296–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leeuw, A.; Mandic, O.; Krijgsman, W.; Kuiper, K.; Hrvatović, H. Paleomagnetic and geochronologic constraints on the geodynamic evolution of the Central Dinarides. Tectonophysics 2012, 530, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Unen, M.; Matenco, L.; Nader, F.H.; Darnault, R.; Mandic, O.; Demir, V. Kinematics of foreland-vergent crustal accretion: Inferences from the Dinarides evolution. Tectonics 2019, 38, 49–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Unen, M.; Matenco, L.; Demir, V.; Nader, F.H.; Darnault, R.; Mandic, O. Transfer of deformation during indentation: Inferences from the post-middle Miocene evolution of the Dinarides. Glob. Planet. Change 2019, 182, 103027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrić, N.; Sant, K.; Matenco, L.; Mandic, O.; Tomljenović, B.; Pavelić, D.; Hrvatović, H.; Demir, V.; Ooms, J. The link between tectonics and sedimentation in asymmetric extensional basins: Inferences from the study of the Sarajevo-Zenica Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2017, 83, 305–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachos, J.; Pagani, M.; Sloan, L.; Thomas, E.; Billups, K. Trends, rhythms, and aberrations in global climate 65 Ma to present. Science 2001, 292, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Moreno, G.; Mandic, O.; Harzhauser, M.; Pavelić, D.; Vranjković, A. Vegetation and climate dynamics during the early middle Miocene from Lake Sinj (Dinaride Lake system, SE Croatia). Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2008, 152, 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Krstić, N.; Dumurdzanov, N.; Jankonić-Golubović, J.; Vujnović, L.; Olujić, J. Interbedded tuff and bentonite in the Neogene lacustrine sediments of the Balkan Peninsula. A review. J. Natl. Volcan. Group Italy 2001, 13, 1000–1009. [Google Scholar]
- Hrvatović, H. Geological Guidebook Through Bosnia and Herzegovina; Geological Survey of Bosnia and Herzegovina: Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- De Leeuw, J.H.W.M. Paleomagnetic and geochronologic constraints on the Miocene evolution of semi-isolated basins in southeastern Europe. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, N.W.M. Getting Started with NIST DTSA-II. Micros. Today 2011, 19, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorseth, I.H.; Pedersen, R.B.; Christie, D.M. Microbial alteration of 0-30-Ma seafloor and sub-seafloor basaltic glasses from the Australian Antarctic Discordance. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 215, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gan, L.; Wiens, M.; Schloßmacher, U.; Schröder, H.C.; Müller, W.E.G. Distribution of Microfossils Within Polymetallic Nodules: Biogenic Clusters Within Manganese Layers. Mar. Biotechnol. 2012, 14, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, G. Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals and Their X-ray Identification; The Mineralogical Society of Great Britain and Ireland: Twickenham, UK, 1982; Volume 5, ISBN 0903056089. [Google Scholar]
- Bardossy, G.; Brindley, G.W. Rancieite associated with a karstic bauxite deposit. Am. Mineral. 1978, 63, 762–767. [Google Scholar]
- Sileo, E.E.; Alvarez, M.; Rueda, E.H. Structural studies on the manganese for iron substitution in the synthetic goethite—Jacobsite system. Int. J. Inorg. Mater. 2001, 3, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiken, G.; Wohletz, K. Volcanic Ash; University Presses of California, Chicago, Harvard & MIT: Oakland, CA, USA, 1985; ISBN 0520052412. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, G.P.L. Plinian eruptions and their products. Bull. Volcanol. 1981, 44, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, N. Smectites. Reviews in Mineralogy. In Hydrous Phyllosilicates; Bailey, S.W., Ed.; Mineralogical Society of America: Washington, DC, USA, 1988; Volume 19, pp. 497–559. [Google Scholar]
- Ddani, M.; Meunier, A.; Zahraoui, M.; Beaufort, D.; El Wartiti, M.; Fontaine, C.; Boukili, B.; El Mahi, B. Clay mineralogy and chemical composition of bentonites from the Gourougou volcanic massif (northeast Morocco). Clays Clay Miner. 2005, 53, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannoni, S.J.; Fisk, M.R.; Mullins, T.D.; Furnes, H. Genetic Evidence for Endolithic Microbial Life Colonizing Basaltic Glass/Seawater Interfaces. Proc. Ocean Drill. Prog. Sci. Results 1996, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furnes, H.; Staudigel, H.; Thorseth, I.H.; Torsvik, T.; Muehlenbachs, K.; Tumyr, O. Bioalteration of basaltic glass in the oceanic crust. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2001, 2, 2000GC000150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, D.C. Monte Carlo Modeling for Electron Microscopy and Microanalysis; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1995; ISBN 0195358465. [Google Scholar]
- Fesharaki, O.; García-Romero, E.; Cuevas-González, J.; López-Martínez, N. Clay mineral genesis and chemical evolution in the Miocene sediments of Somosaguas, Madrid Basin, Spain. Clay Miner. 2007, 42, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepkay, P.E. Kinetics of microbial manganese oxidation and trace metal binding in sediments: Results from an in situ dialysis technique. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1985, 30, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparatos, D.; Massas, I.; Godelitsas, A. Fe-Mn concretions and nodules formation in redoximorphic soils and their role on soil phosphorus dynamics: Current knowledge and gaps. Catena 2019, 182, 104106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, H.; Singh, R.P.; Prasad, J. Chemical and mineralogical composition of Fe-Mn concretions and calcretes occurring in sodic soils of Eastern Uttar Pradesh, India. Soil Res. 2001, 39, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šegvić, B.; Girardclos, S.; Zanoni, G.; Gonzalez, C.A.; Steimer-Herbet, T.; Besse, M. Origin and paleoenvironmental significance of Fe–Mn nodules in the Holocene perialpine sediments of Geneva Basin, western Switzerland. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 160, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinin, A.V.; Sval’nov, V.N.; Berezhnaya, E.D.; Rimskaya-Korsakova, M.N.; Demidova, T.P. Geochemistry of trace and minor elements in sediments and manganese micronodules from the Angola Basin. Lithol. Miner. Resour. 2013, 48, 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Schloßmacher, U.; Wiens, M.; Schröder, H.C.; Müller, W.E.G. Biogenic origin of polymetallic nodules from the Clarion-Clipperton Zone in the Eastern Pacific Ocean: Electron microscopic and EDX evidence. Mar. Biotechnol. 2009, 11, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattan, J.N. Manganese micronodules: A possible indicator of sedimentary environments. Mar. Geol. 1993, 113, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothe, J.; Kneedler, E.M.; Pecher, K.; Tonner, B.P.; Nealson, K.H.; Grundl, T.; Meyer-Ilse, W.; Warwick, T. Spectromicroscopy of Mn distributions in micronodules produced by biomineralization. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 1999, 6, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandernack, K.W.; Post, J.; Tebo, B.M. Manganese mineral formation by bacterial spores of the marine Bacillus, strain SG-1: Evidence for the direct oxidation of Mn(II) to Mn(IV). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 4393–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, R.M.; Rossman, G.R. Mineralogy of manganese dendrites and coatings. Am. Miner. 1979, 64, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar]
- McKeown, D.A.; Post, J.E. Characterization of manganese oxide mineralogy in rock varnish and dendrites using X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 2001, 86, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugović, B.; Šegvić, B.; Šegvić, T. Mn-crust todorokite mineralization on SW backshore Cretaceous limestones from the island of Dugi Otok (Central Adriatic, Croatia). Acta Adriat. 2008, 49, 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- von Stackelberg, U. Manganese nodules of the Peru Basin. Handb. Mar. Miner. Depos. 2000, 197–238. [Google Scholar]
- Marchig, V.; Von Stackelberg, U.; Hufnagel, H.; Durn, G. Compositional changes of surface sediments and variability of manganese nodules in the Peru Basin. Deep. Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2001, 48, 3523–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronan, D.S. Manganese Nodules, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128130810. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.H.; Zhu, M.; Ginder-Vogel, M.; Ni, C.; Parikh, S.J.; Sparks, D.L. Formation of nano-crystalline todorokite from biogenic Mn oxides. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 3232–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacRae, N.D.; Nesbitt, H.W.; Kronberg, B.I. Development of a positive Eu anomaly during diagenesis. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1992, 109, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leybourne, M.I.; Johannesson, K.H. Rare earth elements (REE) and yttrium in stream waters, stream sediments, and Fe-Mn oxyhydroxides: Fractionation, speciation, and controls over REE + Y patterns in the surface environment. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 5962–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, C.R.; Elderfield, H. Rare earth elements in Saanich Inlet, British Columbia, a seasonally anoxic basin. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 2561–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, D.B.; Roy, R. Experimental hydrothermal studies on rock alteration and clay mineral formation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1963, 27, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff-Boenisch, D.; Gislason, S.R.; Oelkers, E.H.; Putnis, C. V The dissolution rates of natural glasses as a function of their composition at pH 4 and 10.6, and temperatures from 25 to 74 C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 4843–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, A.W. Microtubules in basalt glass from Hawaii Scientific Driling Project #2 phase 1 core and Hilina slope, Hawaii: Evidence of the occurrence and behavior of endolithic microorganisms. Geobiology 2008, 6, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménez, B.; Pasini, V.; Brunelli, D. Life in the hydrated suboceanic mantle. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furnes, H.; McLoughlin, N.; Muehlenbachs, K.; Banerjee, N.; Staudigel, H.; Dilek, Y.; De Wit, M.; Van Kranendonk, M.; Schiffman, P. Oceanic Pillow Lavas and Hyaloclastites as Habitats for Microbial Life Through Time—A Review. In Links Between Geological Processes, Microbial Activities & Evolution of Life: Microbes and Geology; Dilek, Y., Furnes, H., Muehlenbachs, K., Eds.; Modern Approaches in Solid Earth Sciences; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 1–68. ISBN 978-1-4020-8306-8. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, L.C.; Cockell, C.S.; Piceno, Y.M.; Andersen, G.L.; Thorsteinsson, T.; Marteinsson, V. Bacterial diversity of weathered terrestrial Icelandic volcanic glasses. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 60, 740–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, M.; Tomita, K. Microbial biomineralization in weathered volcanic ash deposit and formation of biogenic minerals by experimental incubation. Am. Mineral. 2001, 86, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimova, A.; Katz, A.; Steiner, N.; Rudolph, E.; Wei, H.; Steiner, J.C.; Gottlieb, P. Bacteria-clay interaction: Structural changes in smectite induced during biofilm formation. Clays Clay Miner. 2009, 57, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimova, A.; Roberts, M.; Katz, A.; Rudolph, E.; Steiner, J.C.; Alfano, R.R.; Gottlieb, P. Effects of smectite clay on biofilm formation by microorganisms. Biofilms 2006, 3, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.J.; Pacheco, A.P.; Pinho, I.A.; Melo, L.F. The effect of clay particles on the activity of suspended autotrophic nitrifying bacteria and on the performance of an air-lift reactor. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauskopf, K.B. Separation of manganese from iron in sedimentary processes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1957, 12, 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapffe, C. Deposition of manganese. Econ. Geol. 1931, 26, 799–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, J.C.; Polgári, M.; Gyollai, I.; Fintor, K.; Kovács, I.; Fekete, J.; Mojzsis, S.J. Biogenesis of the Neoproterozoic kremydilite manganese ores from Urucum (Brazil)—A new manganese ore type. Precambrian Res. 2020, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargar, J.R.; Tebo, B.M.; Bergmann, U.; Webb, S.M.; Glatzel, P.; Chiu, V.Q.; Villalobos, M. Biotic and abiotic products of Mn (II) oxidation by spores of the marine Bacillus sp. strain SG-1. Am. Mineral. 2005, 90, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, B.; Das, S.K.; Munda, P. Biogenic signature and ultra microfossils in ferromanganese nodules of the Central Indian Ocean Basin. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 73, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasle, G.R.; Syvertsen, E.E.; Steidinger, K.A.; Tangen, K.; Tomas, C.R. Identifying Marine Diatoms and Dinoflagellates; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; ISBN 0080534414. [Google Scholar]
- Pisera, A.; Siver, P.A.; Mandic, O. Miocene siliceous microfossils from the open cast coal mine Gračanica (Bugojno paleolake, Bosnia and Herzegovina) and their significance: A preliminary report. Paleobiodivers. Paleoenviron. 2020, 100, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, A.; Knowles, E. Microbial transformations of minerals and metals: Recent advances in geomicrobiology derived from synchrotron-based X-ray spectroscopy and X-ray microscopy. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2009, 37, 367–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nealson, K.H.; Tebo, B. Structural features of manganese precipitating bacteria. Orig. Life 1980, 10, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Waasbergen, L.G.; Hildebrand, M.; Tebo, B.M. Identification and characterization of a gene cluster involved in manganese oxidation by spores of the marine Bacillus sp. strain SG-1. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 3517–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, L.; Wiens, M.; Schloßmacher, U.; Jochum, K.P.; Schröder, H.C.; Müller, W.E.G. Evidence for a biogenic, microorganismal origin of rock varnish from the Gangdese Belt of Tibet. Micron 2011, 42, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.J.; Ray, C.G. Medical Microbiology; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2004; p. 370. [Google Scholar]
- Perdrial, J.N.; Warr, L.N.; Perdrial, N.; Lett, M.-C.; Elsass, F. Interaction between smectite and bacteria: Implications for bentonite as backfill material in the disposal of nuclear waste. Chem. Geol. 2009, 264, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S.D.; Sudhakar, M. Coexistence of pumice and manganese nodule fields—Evidence for submarine silicic volcanism in the Central Indian Basin. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1993, 40, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).