Abstract
The removal of salicylic acid (SA) and ibuprofen (IB) by sorption onto HDTMA-modified montmorillonite (HM) and zeolite (HZ) was investigated at pH 7. The single sorption data were fitted well by the Freundlich, Langmuir, Dubinin−Radushkevich (DR), and Polanyi−Dubinin−Manes (PDM) models (R2 > 0.94). The sorption affinity of Freundlich and the maximum sorption capacity of Langmuir and PDM models of pharmaceuticals onto HM were consistently higher than that of HZ mainly owing to the higher organic carbon content. In addition, the KF, qmL, and qm values were in the order of IB > SA owing to higher hydrophobicity and molar volume. Since the predominant speciation of SA and IB is anionic at pH 7 (>pKa), sorption onto HM occurs mainly by the two-dimensional surface adsorption onto the pseudo-organic medium in the HM, whereas the interaction of anionic pharmaceuticals with the positively charged “head” of HDTMA is responsible for HZ. Sorption isotherms were fitted well by the PDM model, which indicated that pore-filling was one of the dominating sorption mechanisms. The extended Langmuir model, modified Langmuir competitive model, and ideal adsorbed solution theory employed with Freundlich and Langmuir sorption models were applied to predict binary sorption. The effect of competition between the solutes was clearly evident in the characteristic curves; the maximum sorbed volume (qv.m) was reduced, and the sorbed volume (qv) had a wider distribution toward the sorption potential density.
1. Introduction
The nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) constitute a class of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and have been widely used medications across the world [1]. NSAIDs can be classified as anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic [2]. Aspirin (known as acetylsalicylic acid, ASA) and ibuprofen (IB) are commonly used in clinical medicine as pain relieving, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory drugs [3,4,5]. Aspirin is a widely sold “over the counter” drug and metabolized to salicylic acid (SA) [5]. A few NSAIDs including ibuprofen, naproxen, propyphenazone, and salicylic acid have been detected up to ppb levels in surface water over the countries [6]. SA, a phytohormone, has been also used in the growth and development of the whole plant [7]. Recently, most of the pharmaceuticals have no regulatory standards yet, but have received attention due to the potential negative effects of these compounds on ecosystems and public health. SA and IB are frequently found in significant quantities in the effluents from wastewater treatment plants in Europe and North America [2]. ASA and IB are frequently detected in Korean rivers [8].
Pharmaceutical pollutants in aquatic systems have been treated by physical, biochemical, and chemical processes. Although technologies based on membranes, reverse osmosis, ozonation, and oxidation are highly efficient, the operational costs are high. To remove pharmaceuticals from aquatic environment, sorption is one of the main physical processes [9]. Sorbent materials (e.g., activated carbon [10,11], clay [12], and organoclay [12,13]) have been typically used to remove pharmaceuticals via sorption. An alternative is to use surfactant-modified clay minerals, namely organoclays. Natural clays (e.g., montmorillonite and bentonite) are inherently hydrophilic owing to the hydration of inorganic cations that exist in the interlayers of clay. The permanent negative charges in the natural clays can be modified by cationic surfactants. This surfactant-modified clay mineral enhances the removal of organic pollutants. Organoclays are prepared by simply exchanging inorganic cations on the clay surface by organic cations with long hydrocarbon chains such as the hexadecyltrimethylammonium (HDTMA) cation [14]. HDTMA modification of zeolites effectively sorbed hydrophobic organic contaminants such as benzene, phenol, and toluene [15]. Recently, several studies have suggested the potential application of organoclays for removing pharmaceuticals from water; amoxicillin, sulfamethoxazole, and trimethoprim [12], diclofenac sodium [13], and β-lactam [16]. Once the HDTMA cation is bound to the montmorillonite and zeolite, HDTMA is not leaching and thus not harmful for wildlife. Clay-bound HDTMA is significantly less toxic to bacteria than free HDTMA [17]. Li et al. [18] have also shown that HDTMA, when bound to the zeolite surface, was not toxic to microorganisms. HDTMA bound to the zeolite surface did not inhibit microbial growth [19].
Typically, the traditional Freundlich and Langmuir isotherm models have been used to predict pharmaceutical sorption on organoclays. Recently a few studies have reported on the use of the Dubinin–Radushkevich (DR) model to explain sorption mechanisms (physical versus chemical sorption) for ionizable organic compounds such as 4-chlorophenol [20] and herbicides [21] on tetrabutylammonium (DEDMAM)-montmorillonite. Fuller et al. [22] have applied the DR model for the sorption of nonionic organic solutes (benzene, CCl4, TCE, and 1,2-DCB) on tetraalkylammonium bentonites. The Polanyi theory has been developed to explain sorption of contaminants by volume filling in micropores [23]. The “characteristic curve” of the Polanyi theory can describe the mechanistic sorption mechanisms. However, the applicability of Polanyi theory to evaluate pharmaceutical sorption onto organoclays has not been fully investigated yet. So far, a few studies have reported on the sorption of a single pharmaceutical onto organoclays [12,13,16]. However, only a few studies have investigated binary sorption of pharmaceuticals [24,25]. Anggraini et al. [24] analyzed the binary sorption of amoxicillin and ampicillin onto myristyltrimethylammonium (MTA)-montmorillonite sorption by a modified extended-Langmuir isotherm model. Ghemit et al. [25] also reported single and binary sorption mechanism of diclofenac and ibuprofen onto HDTMA-bentonite by Langmuir and Freundlich models.
In this work, the single and binary sorption behaviors of SA and IB on HM and HZ were investigated at pH 7. The single sorption data were predicted by Freundlich, Langmuir, DR, and Polanyi−Dubinin−Manes (PDM) models. The physicochemical properties of HM and HZ were correlated with the single-sorption model parameters to investigate the sorption mechanisms. The binary sorption of SA and IB was predicted by an extended Langmuir model (ELM), modified Langmuir competitive model (MLCM), and ideal adsorbed solution theory (IAST).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The physicochemical properties of salicylic acid and ibuprofen are summarized in Table 1. 14C-radiolabeled salicylic acid (SA) with a specific activity of 0.1 mCi/mL and ibuprofen (IB) with a specific activity of 0.1 mCi/mL were obtained from ARC chemicals (Saint Louis, MO, USA) and used as radiotracers. To prepare stock solutions of unlabeled pharmaceuticals, SA (≥99%, Sigma-Aldrich, Munich, Germany) dissolved in HPLC-grade methanol (99.9%, Merck, Munich, Germany) and IB (≥98%, Fluka, Buchs, Switzerland) dissolved in ultrapure water (Nex Power 1000, Human Corporation, Seoul, Korea) with high concentrations. Electrolyte solution used in experiments was prepared in distilled and deionized water (DDI, MilliporeSigma™ Synergy™, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) containing 10 mM of KNO3 (99%, Daejung Chemical Co., Siheung, Korea) with 1% of NaN3 (99%, Duksan Chemical Co., Ansan, Korea) as a bacterial inhibitor. The solution pH was adjusted to 7 using a 10-mM phosphate buffer (4.3 mM NaH2PO4 (98.0–102.0%, Duksan, Ansan, Korea) + 5.7 mM Na2HPO4 (min. 98.0%, Duksan, Ansan, Korea), respectively.

Table 1.
Physicochemical properties of salicylic acid (SA) and ibuprofen sodium (IB).
2.2. Sorbents Preparation and Characterization
To prepare HM and HZ, the impurities in the montmorillonite-KSF (Aldrich Chemical Co., Munich, Germany) and zeolite (Wangpyo Chemical Co., Pohang, Korea) were removed by washing them several times with DDI water at 60 °C [26]. A cationic surfactant, hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride (HDTMA chloride solution, 25 wt %, Aldrich Chemical Co., Munich, Germany), was used as an organic modifier. HM and HZ were prepared by the cation-exchange adsorption of HDTMA onto the washed montmorillonite and zeolite to the extent of 100% cation-exchange capacity (CEC) [26]. For preparing HM and HZ, 31 g of washed montmorillonite and zeolite was added into 1 L of a 5000 mg/L (for HM) and 1400 mg/L (for HZ) HDTMA solution in a 2-L glass beaker. The suspension was thoroughly mixed with a mechanical stirrer for 24 h at 250 rpm. Then, HM and HZ were washed again with ultrapure water to remove remaining free surfactant. The collected HM and HZ were dried in an oven for 1 d at 60 °C, sieved through a US standard No. 200 sieve (75 µm) and kept in an amber bottle until use.
Organic carbon content (foc) in the HM and HZ was determined by an elemental analyzer (Flash 2000, Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA). Specific surface area (ABET) was calculated by N2 adsorption/desorption data fitted to the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) model (Autosorb-iQ and Quadrasorb Si, Quantachrome, Boynton Beach, FL, USA). The sodium acetate method (US EPA method 9081) was used to measure the CEC [28]. The pH of point of zero charge (pHPZC) of the sorbents was determined by the method by Appel et al. [29]. The X-ray diffraction (XRD, X’pert PRO MRD, Malvern PANalytical, Malvern, Almelo, The Netherlands) with a Cu Kα source (40 kW, 25 mA) in range of 1–25°, a time per step of 1 s and analyzed by the Bragg equation (nλ = 2dsinθ) was used to determine d-spacing.
2.3. Sorption Isotherm of Pharmaceuticals onto HM and HZ
A subsample of the stock solution was diluted with an electrolyte solution to prepare a solution for sorption. The radiolabeled SA and IB were injected into an aqueous solution containing unlabeled pharmaceuticals to yield 2000 cpm/mL. Single-sorption experiments were conducted using 40-mL amber vials with Teflon-faced silicon septa (Kimble Chase, Vineland, NJ, USA) at 25 °C. At first, 0.5 g of HM or HZ was added into the vial and then filled with six different initial concentrations of SA (0.072–0.724 mmol/L) and IB (0.044–0.438 mmol/L) solution without headspace. The vials were shaken at 150 rpm for 2 d at 25 °C and centrifuged for 40 min at 1500 rpm to separate the aqueous solution. A total of 1 mL of the supernatant was mixed with 8 mL of an Ecolite+ liquid scintillation cocktail (MP Biochemicals, LLC., Irvine, CA, USA), and radioactivity (as a tracer of chemical concentration) in the aqueous phase was measured by a liquid scintillation counter (LSC, Tri-Carb 2900TR, Perkin-Elmer Co., Waltham, MA, USA).
For binary (SA/IB) sorption, binary solution was prepared with mixing SA and IB at an equal molar ratio. To measure each solute concentration, SA/IB mixture solution was prepared by i) injecting radiolabeled SA (14C-SA) into unlabeled SA/IB and ii) injecting radiolabeled IB (14C-IB) into unlabeled SA/IB, respectively. After sorption, the equilibrium concentrations of the binary solutions were determined by LSC. All experiments were performed in triplicate.
The sorption isotherm models were estimated by the single sorption models (Freundlich, Langmuir, DR, and PDM model) and the bisolute sorption models (ELM, MLCM, and IAST) as listed in Table 2. The sorption model parameters were estimated by non-linear regression using a commercial software, TableCurve 2D® (Version 5.01, SYSTAT Software, Inc.). The ELM and MLCM parameters were determined using a Matlab® curve-fitting toolbox (Version R2019a, The MathWorks, Inc.).

Table 2.
Sorption isotherm models.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Sorbents
The physicochemical properties of the sorbents, such as the foc, pore size, ABET, CEC, and pHPZC, are given in Table 3. Both foc and ABET of HM (foc = 7.71%; ABET = 25.39 m2/g) were higher than those of HZ (foc = 2.03%; ABET = 24.17 m2/g), whereas the pore size of HZ (124.2 Å) was higher than that of HM (97.31 Å). The ABET and pore size of HM and HZ affects the sorption properties [40]. The CEC of HZ (61.5 meq/100 g) was three times higher than that of HM (23.3 meq/100 g). The pHPZC indicates that net charge of HM and HZ was negative when pH was higher than pHPZC. The pHPZC of HM and HZ was 1.9 and 6.2, respectively. At pH 7, anionic speciation was the dominant form for both IB (anionic speciation = 98.4%, pKa = 4.91) and SA (anionic speciation = 99.9%, pKa = 2.97) because the working solution pH 7 was greater than pKa, as shown in Figure S1. The working pH (7.0) of the aqueous solution was also higher than the pHPZC of HM and HZ; thus, HM and HZ were negatively charged. Therefore the electrostatic attraction between the predominant SA and IB anions and the negatively charged HM and SA were less likely to occur.

Table 3.
Physicochemical properties of the sorbents used.
The XRD patterns of the washed montmorillonite and zeolite and HM and HZ are shown in Figure S2. The patterns of montmorillonite and HM at 2θ < 10° was different indicating changes in interlayer size caused by the surfactant modification. The diffraction peak at 5.94° for the raw montmorillonite shifted to a lower angle at 4.9° after modification and the interlayer spacing of HM (18.0 Å) increased more than that of raw montmorillonite (14.8 Å). As the surfactant was inserted into the interlayer space, the interlayer spacing was expanded owing to surfactant modification [41]. HDTMA molecules appeared to combine to form an aggregate (or a pseudo-organic phase medium) in the lamellar spacing, which reduced the BET surface area (ABET) [42]. Zeolite is a crystalline aluminosilicate with different cavity structures. The structure of HZ did not exhibit changes compared to that of zeolite (e.g., new peaks) due to the unchanged crystalline nature that remained after the HDTMA modification [43]. After the HDTMA modification, the BET surface area, ABET, of sorbents (HM: 25.39 m2/g, HZ: 24.17 m2/g) decreased (montmorillonite: 125.7 m2/g, zeolite: 53.69 m2/g). The cation-exchange capacity (CEC) of washed montmorillonite and zeolite were 75.3 meq/100 g montmorillonite and 132.5 meq/100g zeolite (Table S1). After the HDTMA modification, the CEC of HM (23.3 meq/100 g) and HZ (61.5 meq/100 g) were less than those of washed montmorillonite and zeolite owing to the cation exchange with HDTMA.
The ABET, BJH pore volume, and size analysis can explain the textural characterization of HM and HZ (Table 3). In Figure 1, the N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms at 293 K of HM and HZ belongs to the type IV isotherm defined by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) [44]. The isotherm exhibited a steep hysteresis loop of type H1 at a relatively high pressure (P/P0 = 0.4–1.0), indicating that HM and HZ were mesoporous. The pore size distribution was uniform in the range of 1.0–15 nm and the average pore size of HM and HZ were 9.7 nm and 12.4 nm, respectively (Figure 1). The molecular size of SA (=0.86 nm) and IB (=0.67 nm) were less than the pore size of HM and HM, thus these molecules could be adsorbed by pore-filling. As shown in Figure S3, the DFT procedure revealed that the micropore size distribution in the HM and HZ had a unimodal distribution with the majority of pore size of 1−15 nm. The determined ABET of HM (25.39 m2/g) was slightly greater than that of HZ (24.17 m2/g), whereas the pore volume of HM (0.095 cm3/g) was slightly smaller than that of HZ (0.103 cm3/g; Table 3).
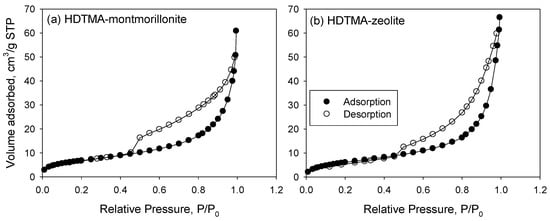
Figure 1.
N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms of sorbents: (a) HDTMA-montmorillonite (HM) and (b) HDTMA-zeolite (HZ).
3.2. Single Sorption
The single sorption of SA and IB onto HM and HZ was conducted at pH 7. At pH 7 (>pKa), anionic speciation was predominant (>99%) for both SA and IB (Figure S2). The sorption of SA and IB onto HM and HZ is shown in Figure 2; the Freundlich, Langmuir, DR, and PDM model parameters are summarized in Table 4. The sorption data were fitted well by all single-sorption models (R2 > 0.94; Table 4). The IB had higher KF values than SA in both sorbents indicating the sorption affinity. The HM had consistently higher KF than HZ mainly owing to the higher organic carbon content (foc). The NF values of the two sorbents at equilibrium were in the range of 0.49–0.77, which showed that sorption was highly nonlinear and favorable [45]. The qmLs of HM were higher than those of HZ for both SA and IB, which was attributed to the higher organic carbon content (foc) but not to CEC, ABET, and pores size. The maximum sorption capacity (qmL) of the Langmuir model in HM (SA: 42.4 mmol/kg, IB: 59.3 mmol/kg) was higher than that of HZ (SA: 23.8 mmol/kg, IB: 59.4 mmol/kg) for both SA and IB, corresponding to increase in foc (HM: 7.71 > HZ: 2.03; Table 4). The qmL of IB in HM and HZ was approximately the same. A separation factor (SF [= 1 / (1 + bLC0)]) was determined the fundamental characteristic of the Langmuir model [46]. The value of SF describes that the isotherm types can be irreversible (SF = 0), unfavorable (SF > 1), linear (SF = 1), or favorable (0 < SF < 1). All SF values were between 0.49 and 0.78 (Table 4 and Figure S4), which indicated that the sorption of SA and IB onto sorbents was favorable [46].
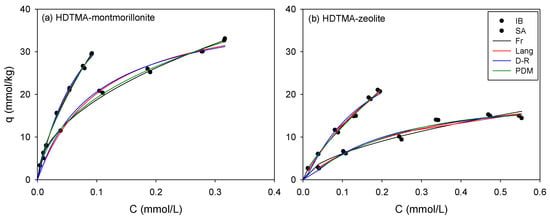
Figure 2.
Single sorption of SA and ibuprofen (IB) onto (a) HM and (b) HZ at pH 7. Lines indicate single-sorption model fitting.

Table 4.
Model parameters for single sorption of Pharmaceuticals onto HM and HZ at pH 7.
The sorption of SA and IB is attributed to interactions between the negatively charged SA and IB and the positively charged HDTMA bilayer [47]. The octanol/water partition coefficient (log Kow) of IB (=3.5) was higher than SA (=2.3), which was consistent with an increase in the KF of the Freundlich model and qm of the Langmuir model. The octanol:water distribution ratio (log Dow) for ionizable organic compounds (IOCs) has been used to express the hydrophobicity of the organic partition coefficient in environmental studies [48]. The log Dow was also in the order of IB (2.8) > SA (−1.1; Table 1). The DR model parameters are summarized in Table 4. The qmD values exhibited the same tendency as KF of Freundlich and qmL of Langmuir models. The qmD of IB was higher than SA in both sorbents; HM had consistently higher qmD than HZ for both SA and IB. The qmD was consistently lower than qmL of the Langmuir model for both HM and HZ owing to the difference in the sorption mechanisms. The E values in the DR model can be used to predict whether the sorption mechanism occurs through ion-exchange or physical sorption. In this study, the estimated mean free energy, E in Equation (4) were less than 8 KJ/mol indicating that SA and IB were sorbing all sorbents mainly via physical sorption [49].
The sorption in HM occurs by the surface adsorption of SA and IB onto the two-dimensional surface of the pseudo-organic medium because the dominant speciation of SA and IB is anionic at pH 7 (>pKa) [50,51]. HDTMA modified aluminosilicate minerals (i.e., zeolite) can significantly enhance the sorption of IOCs, such as SA and IB used in this study, from aqueous solutions [42]. The hydrophobic benzene ring(s) in the SA and IB can be oriented to the inside of the HDTMA bilayers and stabilized by the hydrophobic interaction between the benzene ring(s) and the C16 tails of HDTMA cations [52]. For HZ, the interaction between anionic pharmaceuticals and HDTMA with a positively charged “head” on both inner and outer layers is a part of the sorption mechanism [47,52,53,54]. Dong et al. [52] reported that sorption of anionic speciation of bisphenol A onto HZ occurs by interaction with the positively charged HDTMA. Xie et al. [53] also explained that anion species of bisphenol A, p-chlorophenol, and phenol sorption onto HZ is attributed to Coulombic interaction. Sun et al. [47] and Krajišnik et al. [55] showed the net attractive interactions between anionic diclofenac and the positively charged HDTMA bilayer at the HZ surface.
The PDM model was proposed to normalize the aqueous concentration to the water solubility of the compounds from the Polanyi theory. In this study, PDM was also attempted because solubility (S) and molar volume (Vm) are included as model parameters, considering that the solubility and molar volume of SA and IB are considerably different. The Polanyi theory has been used to describe the sorption process of organic compounds in highly meso- and microporous sorbents, which indicates that sorption occurs by the pore-filling mechanism [22]. In the PDM model (Equation (5)), the exponent b = 2 corresponds to a log-normal distribution of sorption energies [32]. The PDM model fitted well to the SA and IB sorption data (R2 > 0.963), as shown in Figure 2. The PDM model parameters are summarized in Table 4. It was observed that the maximum sorption capacity (qm) of SA was less than IB and the qm of HM (SA: 63.97 mmol/kg, IB: 412.08 mmol/kg) was higher than that of HZ (SA: 31.44 mmol/kg, IB: 307.55 mmol/kg).
The correlation or the “characteristic” curve, the plot of sorbed volume (qv) against the Polanyi potential normalized by molar volume (εsw/Vm), is shown in Figure 3, together with model fitting. Although the pore size of HM (97.3 Å) was less than that of HZ (124.2 Å; Table 3), the maximum sorbed volume (qv,m) of HM was higher than that of HZ for both SA and IB (Table 5). The maximum sorbed volume (qv,m) was also affected by the hydrophobicity of pharmaceuticals (log Kow) and foc of HM and HZ organoclays. This indicates that pore-filling as well as two-dimensional surface sorption (HM) and hydrophobic attraction (HZ) are involved in the sorption process.
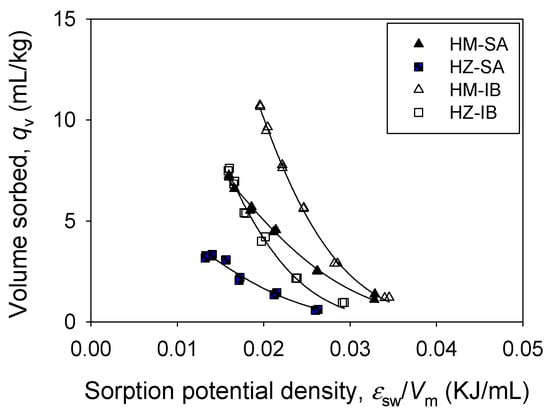
Figure 3.
Characteristic curves of SA and IB sorption onto HM and HZ.

Table 5.
Summary of characteristic curves of single and binary sorption of SA and IB onto HM and HZ at pH 7.
This “characteristic” curve can be used to identify whether the Polanyi theory mechanistically captures the sorption mechanism of pharmaceuticals by sorbents based on two assumptions. One assumption is that there is no molecular sieving effect. As mentioned before, this is true because the pore size of HM (124.2 Å) and HZ (97.31 Å; Table 3) was greater than the molecular size of SA (8.6 Å) and IB (6.7 Å; Table 1). The second assumption is that the molar volume of sorbates affects the sorption [55]. Figure 3 clearly shows the separation of the correlation curve of two pharmaceuticals (SA and IB). Several literature reported similar results for sorbents such as carbon sorbents [31], natural soil [27], polymers [23], and organoclays [20,21]. PDM was useful to describe the individual sorption isotherm data because Vm is the constant used in the regression analysis.
The characteristic curves at different temperatures were on the same curve for HM and HZ, respectively, and in accordance with the sorbent structure [23]. Long et al. [23] also have shown that the characteristic curves of naphthalene on polymer sorbents at different temperatures fall onto a single curve. The characteristic curve of the sorption of pharmaceuticals onto HM and HZ at 293, 303, and 313 K is shown in Figure 4. According to the Polanyi theory, all curves were essentially a single curve and had the high coefficient of determination (R2) of the PDM model (0.94 < R2 < 0.98). Thus, to describe pharmaceutical sorption on HM and HZ, the Polanyi theory is mechanistically useful to indicate that pore-filling is also one of the dominating sorption mechanisms. The cause of differences in sorption affinity is the steric hindrance owing to the size and shape of solute molecules.
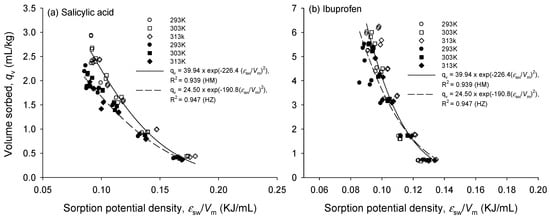
Figure 4.
Effect of temperature on the characteristic curves of (a) SA and (b) IB sorption onto HM and HZ, respectively. Empty and filled symbols represent HM and HZ, respectively.
In summary, the sorption mechanisms are attributed to the (i) two-dimensional surface of the pseudo-organic medium sorption for HM and the interaction between anionic pharmaceuticals and the positively charged “head” of HDTMA for HZ and the (ii) pore-filling mechanism, which can be described by the PDM model, is also possible.
3.3. Binary Sorption
As expected, the sorbed amount in binary sorption was less than that in single sorption. The ELM (Equation (6)), MLCM (Equation (7)), and the IAST (Equation (8))-single-sorption models (Freundlich and Langmuir) were fitted to the binary sorption data of SA/IB on HM and HZ (Figure 5). The coefficient of determination (R2), sum of square errors (SSE), and root mean square error (RMSE) values are listed in Table 6. The ELM (0.72 < R2 < 0.95), MLCM (0.93 < R2 < 0.99), and IAST (0.86 < R2 < 0.99) models positively predicted the binary sorption data in SA/IB systems. The interaction coefficients, η, of MLCM explain the suppression in sorption owing to competition. In the MLCM, the higher the interaction coefficient (η), the smaller is the inhibitory effect of pharmaceuticals on the sorption of other species [56]. The interaction coefficient (η) of SA (1) was consistently higher than that of IB (2) for both HM (η1: 0.871, η2: 0.532) and HZ (η1: 0.341, η2: 0.277), which explains that SA (1) was more affected than IB (2) in binary sorption (Table 6). The selectivity of IB (=Kd,SA/Kd,IB at Cinitial = 0.05 mM) was less than SA for both HM and HZ (Table S2) in the binary sorption system.
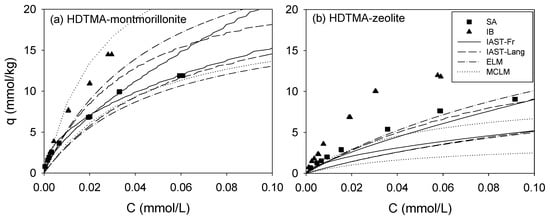
Figure 5.
Binary sorption of SA/IB onto (a) HM and (b) HZ at pH 7. Lines indicate binary sorption model fitting.

Table 6.
Model parameters for the binary sorption of SA(1) and IB(2) onto HM and HZ at pH 7 (solutes: SA/IB).
In addition, the Polanyi theory was analyzed for the SA/IB competition system. The correlation curve of qv versus ɛsw/Vm for the SA/IB competition system is shown in Figure 6. Compared to single sorption (Figure 6), a binary sorption curve (Figure 6) exhibited a wider distribution than a single-sorption curve owing to the competition for pore-filling. The qv,m of HM was higher than that of HZ for both SA and IB (Table 5) and the same as qv,m patterns in single sorption. In binary sorption, the qv,m of pharmaceuticals on HM (SA: 3.67 mL/kg, IB: 69.9 mL/kg) and HZ (SA: 3.29 mL/kg, IB: 32.3 mL/kg) were lower than those in single sorption on HM (SA: 6.12 mL/kg, IB: 91.3 mL/kg) and HZ (SA: 3.01 mL/kg, IB: 68.2 mL/kg), respectively.
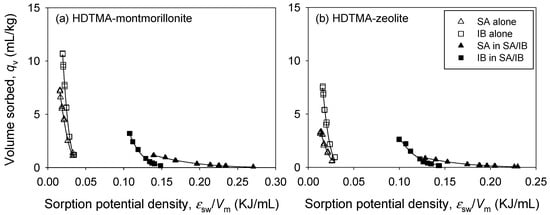
Figure 6.
Comparison of the characteristic curves of single and binary sorption of SA/IB onto (a) HM and (b) HZ.
4. Conclusions
The sorption of SA and IB onto HDTMA-modified montmorillonite and zeolite was conducted at pH 7. This study investigated sorption behaviors of SA and IB on the HM and HZ. The single-sorption data were fitted well by the Freundlich, Langmuir, DR, and PDM models. The sorption of IB was higher than that of SA owing to its higher hydrophobicity (log Kow or log Dow). The Freundlich constant (KF) and the maximum sorption capacity (qmL) of SA and IB on HM were slightly higher than those of pharmaceuticals on HZ, mainly owing to the higher organic carbon content (foc). The sorption capacity (qmL) of SA (42.4 mmol/kg) and IB (59.3 mmol/kg) in HM was higher than that of SA (23.8 mmol/kg) and IB (59.4 mmol/kg) in HZ, respectively. At working solution pH 7, the anionic speciation of SA and IB are dominant. Therefore, the sorption mechanism of anionic pharmaceuticals was explained by the two-dimensional surface of the pseudo-organic medium adsorption for HM and by the interaction of anionic pharmaceuticals with the positively charged “head” of HDTMA for HZ. According to the Polanyi theory, the characteristic curves of pharmaceuticals onto HM and HZ at 293, 303, and 313 K fell on a single curve. The good fits of the PDM model in single solute sorption implicated that the sorption of pharmaceuticals onto HM and HZ also occurred by pore-filling. In the binary sorption, ELM, MLCM, and IAST coupled with single-sorption models fitted positively to the data (0.66 < R2 < 0.99). Compared to single sorption, the qv,m of pharmaceuticals were reduced, and the characteristic curve exhibited a wide distribution owing to the competition in pore-filling. Therefore the pore-filling mechanism would be also responsible for the sorption of phenolic compounds in HM and HZ.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2075-163X/10/10/898/s1, Figure S1: Distribution of speciation of SA and IB as a function of pH, Figure S2: XRD patterns of montmorillonite and HM; zeolite and HZ, Figure S3: DFT pore size distribution of organoclays, Figure S4: SF as a function of initial concentration, Table S1: Physicochemical properties of raw clays.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C. and W.S.S.; methodology, J.C. and W.S.S.; software, W.S.S.; validation, W.S.S.; investigation, J.C.; data curation, J.C. and W.S.S.; writing—original draft preparation, J.C.; review and editing, W.S.S.; supervision, W.S.S.; project administration, W.S.S.; funding acquisition, W.S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Korea Environment Industry and Technology Institute (KEITI) through The Chemical Accident Prevention Technology Development Project, funded by Korea Ministry of Environment (MOE) (2019001960002).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Nomenclature
| a ((mL)b+1(mol·Jb)−1) | fitting parameters |
| A | interfacial area between the solution and solid sorbent |
| b (−) | fitting parameters |
| bL (L/mmol) | site energy factor |
| βD (mol2/J2) | Dubinin–Radushkevich constant |
| E (kJ/mol) | mean free energy |
| ε (J/mol) | sorption potential (=RT ln(1 + 1/C)) |
| εsw (J/mol) | effective sorption potential, Polanyi potential (=RT ln(Sw/C)) |
| KF ((mmol/kg)/(mmol/L)) | Freundlich sorption coefficient (sorption affinity) |
| NF | linearity coefficient |
| ηi | constant interaction factor |
| qm (mL/kg) | maximum sorption capacity |
| qmD (mg/kg) | the theoretical saturation capacity |
| qmL (mmol/kg) | maximum sorption capacity |
| qmL,i(mmol/kg) and bL,i (L/mmol) | Langmuir model parameters obtained from single sorption |
| R (J/mol·K) | ideal gas constant |
| Sw (mmol/L) | solute solubility in water |
| T (K) | absolute temperature |
| Vm (mL/mol) | molar volume of solute |
| π | spreading pressure |
References
- Dionísio, R.; Daniel, D.; Arenas, F.; Campos, J.C.; Costa, P.C.; Nunes, B.; Correia, A.T. Effect of pH on salicylic acid toxicity in terms of biomarkers determined in the marine gastropod Gibbula umbilicalis. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 158, 104995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.; Coimbra, R.N.; Escapa, C.; Figueiredo, S.A.; Freitas, O.M.; Otero, M. Green microalgae Scenedesmus Obliquus utilization for the adsorptive removal of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) from water samples. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-M.; Wei, C.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.-S.; Liu, Y.-N. Investigation of competitive binding of ibuprofen and salicylic acid with serum albumin by affinity capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. 2011, B879, 1934–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, V.; Giraldo, L.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C. Thermodynamic analysis of acetaminophen and salicylic acid adsorption onto granular activated carbon: Importance of chemical surface and effect of ionic strength. Thermochim. Acta 2020, 683, 178467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essandoh, M.; Kunwat, B.; Pittman Charles, U., Jr.; Mohan, D.; Mlsna, T. Sorptive removal of salicylic acid and ibuprofen from aqueous solutions using pine wood fast pyrolysis biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 265, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J. Pharmaceuticals in the Environment and Management Approaches in Korea; Korea Environment Institute (KEI): Seoul, Korea, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Raskin, I. Role of salicylic acid in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1992, 43, 439–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakdong River Water Environment Research Institute. A Survey on the Monitoring of Potentially Hazardous Compounds and Contamination Routes in Tributary of the Nakdong River System; 3rd year report; National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER): Daegu, Korea, 2015.
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) from wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 620–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailler, R.; Gasperi, J.; Conquet, Y.; Deshayes, S.; Zedek, S.; Cren-Olivé, C.; Cartiser, N.; Eudes, V.; Bressy, A.; Caupos, E.; et al. Study of a large scale powdered activated carbon pilot: Removals of a wide range of emerging and priority micropollutants from wastewater treatment plant effluents. Water Res. 2015, 72, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.; Campinas, M.; Acero, J.; Rosa, M.J. Investigating PPCP removal from wastewater by powdered activated carbon/ultrafiltration. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.D.; Fernandez, E.; Fougère, L.; Destandau, E.; Boussafir, M.; Sohmiya, M.; Sugahara, Y.; Guégan, R. Competitive association of antibiotics with a clay mineral and organoclay derivatives as a control of their lifetimes in the environment. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 15332–15342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, G.S.; de Andrade, J.R.; da Silva, M.G.C.; Vieira, M.G.A. Adsorption of diclofenac sodium onto commercial organoclay: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. Powder Technol. 2019, 345, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Boyd, S.A. Cationic surfactant adsorption by swelling and non-swelling layer silicates. Langmuir 1995, 11, 2508–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, S.-M.; Dixon, J.B. Preparation and application of organo-minerals as sorbents of phenol, benzene, and toluene. Appl. Clay Sci. 2001, 18, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, T.; Shibayama, T. Removal and degradation of b-lactam antibiotics in water using didodecyldimethylammonium bromide-modified montmorillonite organoclay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocker, F.H.; Guerin, W.F.; Boyd, S.A. Bioavailability of naphthalene sorbed to cationic surfactant-modified smectite clay. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 2953–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bowman, R.S. Sorption of perchloroethylene by surfactant-modified zeolite as controlled by surfactant loading. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2278–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeve, P.J.; Fallowfield, H.J. Natural and surfactant modified zeolites: A review of their applications for water remediation with a focus on surfactant desorption and toxicity towards microorganisms. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 205, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçay, M. Characterization and adsorption properties of tetrabutylammonium montmorillonite (TBAM) clay: Thermodynamic and kinetic calculations. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2006, 296, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçay, G.; Akçay, M.; Yurdakoç, K. The characterization of prepared organomontmorillonite (DEDMAM) and sorption of phenoxyalkanoic acid herbicides from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2006, 296, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, M.; Smith, J.A.; Burns, S.E. Sorption of nonionic organic solutes from water to tetraalkylammonium bentonites: Mechanistic considerations and application of the Polanyi–Manes potential theory. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2007, 313, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Li, A.; Wu, H.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Q. Polanyi-based models for the adsorption of naphthalene from aqueous solutions onto nonpolar polymeric adsorbents. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2008, 319, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anggraini, M.; Kurniawan, A.; Ong, L.K.; Martin, M.A.; Liu, J.-C.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Indraswati, N.; Ismadji, S. Antibiotic detoxification from synthetic and real effluents using a novel MTAB surfactant-montmorillonite (organoclay) sorbent. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 16298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghemit, R.; Makhloufi, A.; Djebri, N.; Flilissa, A.; Zerroual, L.; Boutahala, M. Adsorptive removal of diclofenac and ibuprofen from aqueous solution by organobentonites: Study in single and binary systems, Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 8, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Shin, W.S.; Song, D.-I.; Choi, S.J. Multi-step competitive sorption and desorption of chlorophenols in surfactant modified montmorillonite. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2005, 166, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Ball, W.P. Adsorption-partitioning uptake of nine low-polarity organic chemicals on a natural sorbent. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Cation-Exchange Capacity of Soils (Sodium Acetate)–Test Methods for the Evaluation of Solid Waste: Laboratory Manual Physical Chemical Methods; US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/hw-sw846/sw-846-test-method-9081-cation-exchange-capacity-soils-sodium-acetate (accessed on 9 October 2020).
- Appel, C.; Ma, L.Q.; Rhue, R.D.; Kennelley, E. Point of zero charge determination in soils and minerals via traditional methods and detection of electroacoustic mobility. Geoderma 2003, 113, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen-King, R.M.; Grathwohl, P.; Ball, W.P. New modeling paradigms for the sorption of hydrophobic organic chemicals to heterogeneous carbonaceous matter in soils, sediments, and rocks. Adv. Water Resour. 2002, 25, 985–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Lu, J.D.; Li., A.; Hu, D.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Q. Adsorption of naphthalene onto the carbon adsorbent from waste ion exchange resin: Equilibrium and kinetic characteristics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleineidam, S.; Schüth, C.; Grathwohl, P. Solubility-normalized combined adsorption-partitioning sorption isotherms for organic pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 4689–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, K.K.H.; Porter, J.F.; McKay, G. Langmuir Isotherm Models Applied to the Multicomponent Sorption of Acid Dyes from Effluent onto Activated Carbon. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2000, 45, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellot, J.C.; Condoret, J.S. Modelling of liquid chromatography equilibrium. Process Biochem. 1993, 28, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, N.; Jajjati, S.; Mahmudi, Z.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Maity, A.; Gupta, V.K. Modeling of competitive ultrasonic assisted removal of the dyes—Methylene blue and Safranin-O using Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 268, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, C.J.; Prausnitz, J.M. Thermodynamics of multi-solute adsorption from dilute liquid solutions. AIChE J. 1972, 18, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.Y.; Singer, P.C. Competitive Adsorption of Phenols on Activated Carbon. J. Environ. Eng. 1984, 110, 976–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.S. Competitive sorption of anionic and cationic dyes onto cetylpyridinium-modified montmorillonite. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2008, 43, 1459–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.-I.; Choi, J.; Shin, W.S. The modified Song isotherm model: Application to multisolute sorption of phenols in organoclays using the ideal adsorbed solution theory. Environ. Technol. 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groisman, L.; Rav-Acha, C.; Gerstl, Z.; Mingelgrin, U. Sorption of organic compounds of varying hydrophobicities from water industrial wastewater by long- and short-chain organoclays. Appl. Clay Sci. 2004, 24, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Frost, R.L.; He, H.; Xi, Y. Changes in the surfaces of adsorbed para-nitrophenol on HDTMA organoclay-The XRD and TG study. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2007, 307, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.H.; Fan, C.; Chiang, P.N.; Wang, M.K.; Lin, K.C. p-nitrophenol, phenol and aniline sorption by organo-clays. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanos, A.G.; Katsou, E.; Malamis, S.; Psarras, K.; Pavaltou, E.A.; Haralambous, K.J. Evaluation of modified mineral performance for chromate sorption from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 211–212, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.V.; Gadipelli, S.; Wood, B.; Ramisetty, K.A.; Stewart, A.A.; Howard, C.A.; Brett, D.J.L.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F. Characterization of the adsorption site energies and heterogeneous surfaces of porous materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 10104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, A.S.; Sakaria, P.L.; Vasudevan, M.; Pawar, R.R.; Sudheesh, N.; Bajaj, H.C.; Mody, H.M. Adsorption of an anionic dye from aqueous medium by organoclays: Equilibrium modeling, kinetic and thermodynamic exploration. RCS Adv. 2012, 2, 8663–8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, G.; Al Duri, B. Prediction of multicomponent adsorption equilibrium data using empirical correlations. Chem. Eng. J. 1989, 41, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Shi, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. Sorption and retention of diclofenac on zeolite in the presence of cationic surfactant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septian, A.; Oh, S.; Shin, W.S. Sorption of antibiotics onto montmorillonite and kaolinite: Competition modelling. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 2940–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kamash, A.M. Evaluation of zeolite A for the sorptive removal of Cs+ and Sr2+ ions from aqueous solutions using batch and fixed bed column operations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, M.G.; Sparks, D.L.; Dentel, S.K. Sorption of pentachlorophenol to HDTMA-clay as a function of ionic strength and pH. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 2330–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Shin, W.S.; Song, D.-I.; Choi, S.J. Sequential competitive sorption and desorption of chlorophenols in organoclay. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2006, 23, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, X.; Lin, Y. Adsorption of bisphenol A from water by surfactant-modified zeolite. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2010, 348, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Meng, W.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, H. Removal of organic pollutants by surfactant modified zeolite: Comparison between ionizable phenolic compounds and non-ionizable organic compounds. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 231–232, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajišnik, D.; Kaković, A.; Milojević, M.; Malenović, A.; Kragović, M.; Bogdanović, D.B.; Dondur, V.; Milić, J. Properties of diclofenac sodium sorption onto natural zeolite modified cetylpyridinium chloride. Colloids Surf. B 2011, 83, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Zhu, L.; Xing, B. Adsorption of polycylic aromatic hydrocarbons by carbon nanomaterials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, F.; Jing, X.; Ling, P.; Li, A. Displacement mechanism of binary competitive adsorption for aqueous divalent metal ions onto a novel IDA-chelating resin: Isotherm and kinetic modeling. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).