Abstract
Background: Bariatric surgery is proven to change eating behavior and cause sustained weight loss, yet the exact mechanisms underlying these changes are not clearly understood. We explore this in a novel way by examining how bariatric surgery affects the brain–gut–microbiome (BGM) axis. Methods: Patient demographics, serum, stool, eating behavior questionnaires, and brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were collected before and 6 months after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG). Differences in eating behavior and brain morphology and resting-state functional connectivity in core reward regions were correlated with serum metabolite and 16S microbiome data. Results: LSG resulted in significant weight loss and improvement in maladaptive eating behaviors as measured by the Yale Food Addiction Scale (YFAS). Brain imaging showed a significant increase in brain volume of the putamen (p.adj < 0.05) and amygdala (p.adj < 0.05) after surgery. Resting-state connectivity between the precuneus and the putamen was significantly reduced after LSG (p.adj = 0.046). This change was associated with YFAS symptom count. Bacteroides, Ruminococcus, and Holdemanella were associated with reduced connectivity between these areas. Metabolomic profiles showed a positive correlation between this brain connection and a phosphatidylcholine metabolite. Conclusion: Bariatric surgery modulates brain networks that affect eating behavior, potentially through effects on the gut microbiota and its metabolites.
1. Introduction
Over the last decade, obesity and obesity-related comorbidities have become the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in the developed world [1]. It is expected that this trend will continue to rise along with the risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and other obesity-related diseases [1]. To date, dietary and lifestyle modifications remain one of the main treatments for obesity. Unfortunately, a large proportion of patients will continue to have difficulty maintaining a diet long enough to reach significant and sustainable weight loss. While a variety of pharmacological interventions have had minor successes, bariatric surgery remains one of the few proven methods that is able to accomplish significant and sustained weight loss over time [2]. The two most common surgical procedures for bariatric surgery include Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) and laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG). Both RYGB and LSG have similar effects on weight loss and have been shown to be associated with lower hunger scores and changes in food preference [3,4]. At baseline, resting-state functional brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies have shown that patients with obesity have alterations in the connections relating to metabolic sensing and reward processing [5,6]. After bariatric surgery, these connections and alterations in brain signaling often normalize [7,8,9]. However, the exact mechanism by which bariatric surgery can alter appetite, eating behaviors and brain signaling is still poorly understood.
One potential area that can connect bariatric surgery to changes in brain signaling and behavior is the brain–gut–microbiome (BGM) axis. The BGM axis is a tightly regulated bidirectional axis whose derailment is a feature of such diseases as irritable bowel syndrome, autism spectrum disorder, and even obesity [10]. Preclinical models have shown that the gut microbiome is involved in brain development, behavior, and neurotransmitter signaling [11,12,13], and that the brain can alter the gut microbiome via changes in mucus production, motility, and immune signaling [14]. In regards to obesity, alterations in the gut microbiome have been associated with changes in eating behavior, development of metabolic syndrome, and alterations in gastrointestinal hormones such as glucagon-like peptide-1 [10,15,16,17]. Changes in eating behavior and gastrointestinal hormones have also been seen in patients who have undergone bariatric surgery. Several studies have shown that bariatric surgery, including LSG, can lead to sustained and significant changes in the gut microbiome, in eating behaviors, and in satiety signaling [18,19,20]. However, how these changes are connected to brain signaling is not entirely clear. In our study, by using an integrated systems biology approach, we applied morphological and functional resting state brain imaging, microbial analysis, and serum metabolomics to investigate the role of bariatric surgery induced changes on the brain–gut–microbiome axis in regulating eating behaviors.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection and Study Design
Patients were recruited from the University of California, Los Angeles Bariatric Surgery Program. Only patients undergoing LSG were included to negate any effect of different surgical procedures on brain and microbiome alterations. We further focused our selection to female patients as female patients have a higher prevalence of food addiction than males [21]. Inclusion criteria included adult patients who were considering bariatric surgery and met eligible criteria for surgery. Because brain morphology differs by handedness and advanced age, we limited the study to include right-handed patients age 18 to 55 years old undergoing laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) following the Guidelines for Clinical Application of Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery by of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) [22,23]. Exclusion criteria includes a prior history of major gastrointestinal surgery including weight loss surgery, use of medications known to affect hunger, satiety or intestinal motility, any contraindication to undergo MRI, current or past alcohol or drug abuse, pregnancy, current use of insulin or insulin dependent diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, use of probiotics, or use of antibiotics within 1 month of enrollment. Patients were enrolled into the study before undergoing LSG. Subjects underwent a screening visit and 2 study visits occurring at baseline and at 6 months after surgery. Multimodal magnetic resonance brain imaging (MRI), demographic information, height, weight, measures of eating behavior, questionnaire for anxiety and depression, stool samples for 16S ribosomal RNA sequencing, and serum for metabolomics and inflammatory markers were collected at baseline and at 6 months. All subjects gave their informed consent for inclusion before they participated in the study. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the UCLA Institutional Review Board (IRB# 13-001552).
2.2. Anthropometrics and Body Composition
A certified nutritionist at the UCLA Clinical & Translational Research Center (CTRC) measured height, weight and Body Mass Index (BMI) using techniques and methods described in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III) at baseline and at 6 months after surgery. All measurements were taken in duplicate.
2.3. Patient Questionnaire
To assess for anxiety or depressions, patients were asked the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). A cutoff of 8 or above was considered as abnormal, similar to prior research [24]. To measure eating behaviors, both the Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire R21(TFEQ-R21) and the Yale Food Addiction Scale (YFAS) were used. The TFEQ-R21 is a 21-question survey that measures three categories of eating behavior: cognitive restraint (CR), uncontrolled eating (UE), and emotional eating (EE). A higher score in each subcategory represents higher restraint for eating, more uncontrolled eating, and a predisposition to emotional eating, respectively [25]. The YFAS is a 25-question survey developed to assess food addiction based on the substance dependence criteria, as found in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorder, 4th Edition (DSM-4) [26]. It measures withdrawal, dependence on food, tolerance, continued use despite problems, loss of control, time eating, an inability to cut down, and clinical significant impairment. Food addiction was defined as having a YFAS symptom count ≥3 with clinically significant impairment or distress [21].
2.4. 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene Sequencing and Analysis
Similar to prior published works, DNA was extracted using the ZymoBIOMICS DNA Microprep Kit (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, USA) per the manufacturer’s protocol. The V4 region of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene was amplified by PCR and underwent 250 × 2 paired-end sequencing on an Illumina HiSeq (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) [27,28]. The sequences were processed using the DADA2 pipeline in R which assigns taxonomy using the SILVA 132 database [29]. After pre-processing in R, the data were incorporated into QIIME 2 version 2019.10 [30]. Amplicon sequence variants were filtered if not present in at least 15% of all samples. Sequence depths ranged from 60,710 to 269,258 per sample.
2.5. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Acquisition
All neuroimaging was conducted at baseline and at 6-month follow-up on a 3T Siemens PRISMA at the UCLA Ahmanson-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center. T1 images were acquired using the Magnetization Prepared- Rapid Gradient Echo (MP-RAGE) sequence (TR: 2300 ms, TE: 2.98 ms, TI: 900ms, flip angle: 9°, field of view: 240 × 256, slice thickness: 1 mm, voxel resolution: 1 × 1 × 1 mm) to assess brain structure. A 10-min resting-state fMRI scan was acquired to assess resting-state functional connectivity (TR: 2000 ms, TE: 28 ms, flip angle: 77°, acquisition matrix: 64 × 64, slice thickness: 4mm, voxel resolution: 3.44 × 3.44 × 4 mm, 300 volumes).
2.6. Brain Regions of Interest
Regions of interest (ROIs) for the morphometry analysis included the bilateral hypothalamus, nucleus accumbens, amygdala, brainstem, putamen and anterior insula based on past literature [31,32,33,34,35]. The same ROIs were used as seeds for the resting-state functional connectivity analysis to the rest of the brain.
2.7. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Processing: Voxel-Based Morphometry
To determine differences in gray matter from baseline to 6 months, a voxel-based morphometry analysis was completed using FMRIB Software Library (FSL)-voxel-based morphometry (VBM), part of the FSL software package [36]. Brain extraction was first conducted using the robust version of the Brain Extraction Tool (BET), which calls the command multiple times, moving the center of gravity to the true center. All images were then checked manually to confirm the brain had been extracted adequately. All brain images were then segmented into gray matter (GM), white matter (WM) and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) using FMRIB’s Automated Segmentation Tool (FAST) in FSL [37]. A study specific GM template was then created using affine non-linear registration to the ICBM-152 template. Finally, all GM images were non-linearly registered—including a Jacobian modulation to account for differences in transformation—to the study-specific template [38,39] and smoothed with a 4 mm Gaussian kernel. This created a 4D smoothed image.
2.8. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Processing Resting-State Functional Pair-Wise Connections
Preprocessing for the structural and resting-state functional images were done in SPM12 [40]. The first two volumes were discarded to allow for stabilization of the magnetic field. Slice-timing correction was performed followed by six-degree motion correction alignment. The motion parameters were examined for excessive motion in each degree for motion less than 2 mm. Mean frame-wise displacement (FD) and root mean squared (RMS) realignment estimates were also calculated as robust measures of motion using publicly available MATLAB code from GitHub [41]. Each subject’s T1 images was segmented into gray matter, white matter and cerebrospinal fluid, then normalized into the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) space. Resting-state images were then co-registered with their respective anatomical T1 images, resulting in resting-state images normalized in MNI space.
The pre-processed, normalized functional images, along with their normalized T1 images and segmentations were then uploaded to the CONN fMRI toolbox [42]. The Schaefer 400 cortical atlas, Harvard-Oxford Subcortical atlas, and the Ascending Arousal Network brainstem atlas were used as ROI’s in MNI space for each subject. The functional images were then denoised using ordinary least squares regression of potential confounding effects and temporal band-pass filtering (0.008–0.09 Hz). The aCompCor method [43] was used and included noise components from white matter, cerebrospinal fluid, estimated subject-motion parameters, and session effects. Fisher transformed correlations were computed (Z) between the functional time series of all the parcellated regions to derive a 417 × 417 matrix for each participant. The bottom half of the undirected matrix was then concatenated into one vector of each subject representing each ROI pair.
2.9. Metabolomics
Serum was collected from patients while they were fasting and stored at −80 C until being sent to Metabolon Inc (Morrisville, NC, USA) for processing as a single batch. Serum samples were processed and analyzed using an integrated analytic platform that consists of automated sample preparation, Liquid Chromatography/Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (LC/GC/MS), peak identification and deconvolution, and chemical intelligence. Data are curated by mass spectrometry analysts using specialized software. Biochemicals are identified by comparison to library entries of purified standards. Chromatographic properties and mass spectra allow matching to the specific compound or an isobaric entity using proprietary visualization and interpretation software. Peaks are quantified using area under the curve. Library matches for each compound are verified for each sample. Based on prior published works on serum metabolites and bariatric surgery, we focused our analysis to short chain fatty acids, branched chain amino acids, para-Cresol, phenylacetylglutamine, phenol, indoles, tryptophan-related metabolites, N-acetyl-putrescine, glutamate, and phosphatidylcholine [44,45,46,47].
2.10. Statistical Analysis
Clinical continuous variables were associated to each other using linear regression model in R. Means were compared using a univariate analysis of variance in R. Normality of data was tested using the Shapiro–Wilk method by using the function shapiro.test in R. Homogeneity of variance was tested using the F-test by using the function var.test in R. Categorical data were compared using the Fisher’s exact test in R. All means are expressed along with their standard deviations.
Multilevel sparse partial least square linear discriminant analysis (sPLS-DA) was done to analyze microbiome data using the Mixomics package in R (http://www.R-project.org). sPLS-DA identifies amplicon sequence variants that discriminates subjects by categories by simultaneously performing feature selection and modeling using lasso penalization. sPLS-DA operates using a supervised framework to find linear combinations of a limited set of variables, here amplicon sequence variants, that predicts altered resting state pairwise signaling, similar to prior published works [48]. In summary, microbial data were transformed into relative abundances and analyzed similar to the pathway described on www.mixomics.org (case study: Koren diverse bodysites). Two components were retained after error analysis. Forty amplicon sequence variants were retained in the model. Performance of the model was evaluated using the perf function in Mixomics which employs a 5-fold cross-validation with 100 repeats. Accuracy of the model was assessed using auroc function of Mixomics which graphs the area under the receiver operating curve of the model. Alpha diversity was measured using the Shannon Index, which measures species evenness. Data were rarefied for alpha diversity measurements to a depth of 60,709 sequences. Alpha diversity was tested using analysis of variance in R (formula: shannon~brain connection of interest). Differential abundance testing of microbiome data was performed using DESEq2 in R, which employs a Bayesian approach to fit non-rarified count data to a negative binomial model [49]. p-values were converted to q-values to correct for multiple hypothesis testing and a q-value < 0.05 was deemed significant [50].
Brain voxel morphometry at 6 months compared to baseline was analyzed using a general linear model (GLM) with permutation-based testing at 5000 iterations to create clusters with the Threshold Free Cluster Enhancement (TFCE) method [51]. All significance testing was conducted at p < 0.05, corrected for multiple comparisons using the false discovery rate (FDR) method. Images of results were produced in Mango software (http://ric.uthscsa.edu/mango). Resting state pairwise connections at 6 months compared to baseline was analyzed using univariate analysis of variance adjusting for multiple hypothesis testing using the FDR method. Similar to above, normality of data was tested using the Shapiro–Wilk method by using the function shapiro.test in R. The homogeneity of variance was tested using the F-test by using the function var.test in R.
Correlations between metabolites and brain connectivity was assessed using linear regression adjusting for multiple hypothesis testing by using the FDR method. All statistical analysis was done using R.
3. Results
3.1. LSG Reduces Measures of Obesity and Maladaptive Eating Behavior
Eighteen subjects were enrolled in the study, of which, 14 underwent brain imaging. The average age of the participants were 37.4 years old + 9.7 (Table 1). The average weight and BMI before surgery was 119.4 + 19.8kg and 45.5 kg/m2 + 4.9, respectively. The demographic makeup of the participants is described in Table 1. LSG led to significant reductions in weight at 6 months (Figure 1). The average percentage of total body weight loss was 24.3% + 5.2 at 6 months after surgery.

Table 1.
Baseline patient characteristics.
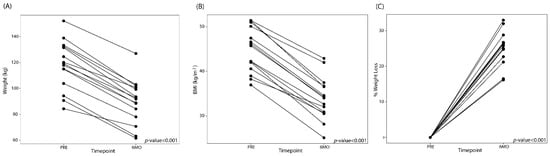
Figure 1.
Line plots showing the (A) weight change, (B) changes in BMI, and (C) total percent body weight loss after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG). PRE: Before LSG, 6M0: 6 months post-LSG.
There was a significant reduction in maladaptive eating behaviors as measured by YFAS symptom count (p-value < 0.001) and TFEQ_R21 as well as a reduction in anxiety and depression scores post bariatric surgery (Table 2). Three subjects reached criteria for food addiction diagnosis pre-surgery, but no patients fulfilled the criteria for food addiction after surgery (p = 0.22).

Table 2.
Patient questionnaire results.
3.2. LSG Induces Changes in Morphology and Brain Connectivity that Are Associated with Eating Behavior
By analyzing the functional and structural brain MRI of patients before and after surgery, we saw significant changes in important reward regions including the amygdala and the putamen.
Voxel-based morphometry analysis showed that subjects displayed a significantly higher gray matter volume in a cluster consisting of the putamen and amygdala after 6 months compared to baseline (t = 5.30, p(FDR) = 0.002, cluster size = 518 voxels, MNI: X = 18, Y = −10, Z = −8) (Figure 2). Changes in voxel-based morphometry was not associated with any changes in eating behaviors, anxiety, or depression.
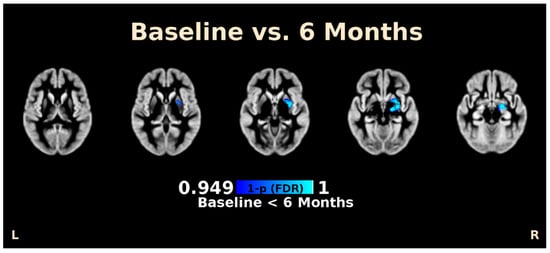
Figure 2.
Voxel-based morphometry (VBM) analysis of brain MRI imaging of patients at baseline and 6 months post laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Images above shows significant increases in brain volume in the amygdala and putamen after adjusting for false discovery rate (FDR). Inferior to superior cross-sectional images are presented from left to right.
By analyzing the resting state pairwise connectivity of the brain, we found that patients had lower connectivity between the precuneus and the putamen at 6 months after surgery compared to baseline (p.adj = 0.046). The connectivity between the precuneus to the putamen across both timepoints was positively correlated to the YFAS symptom count (p-Value = 0.013) (Figure 3). This change in brain connectivity was not significantly correlated with either scores for anxiety or depression or any of the subscales of the TFEQ-R21.
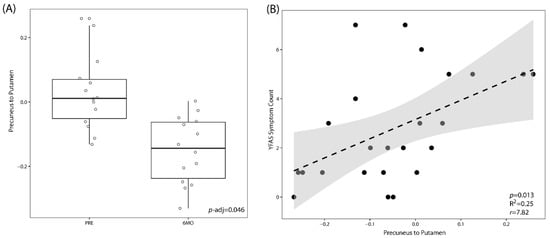
Figure 3.
LSG leads to a significant decrease in the resting-state connectivity between the precuneus and the putamen. (A) Box plot showing resting-state connectivity between the precuneus and the putamen at baseline (PRE) versus those at 6 months (6MO) post bariatric surgery. p-Values are adjusted for multiple hypothesis testing. (B) Linear correlation between resting state connectivity between the precuneus and the putamen to food addiction behavior as measured by the Yale Food Addiction Scale (YFAS).
3.3. LSG Induced Changes at the Reward Network Are Associated with Shifts in the Gut Microbiome and Circulating Metabolites
We then examined whether the brain connectivity between the putamen and precuneus was associated with any microbial or serum metabolite changes induced by surgery. By using the median value, resting state connectivity between the precuneus and the putamen were categorized as either high or low connectivity. There was no significant difference between subjects with a low versus a high connectivity in regard to alpha diversity. However, subjects with a higher connectivity between the precuneus and putamen did have a trend towards a lower alpha diversity than subjects with a lower level of connectivity (Figure 4A). Through the supervised learning model, sPLS-DA, subjects with low connectivity separated from subjects with high connectivity (Figure 4B) with an area under the receiver operating curve of 0.97. Thirty separate amplicon sequence variants contributed to the variation seen in the first component axis (Figure 4C). Of these 30 amplicon sequence variants, Bacteroides and Lachnospiraceae were associated the most to a low connectivity, while Anaerostipes was associated the most with a high connectivity. The taxonomic profiles are summarized in Figure 4D between patients with low or high connectivity. Differential abundance testing adjusting for time showed 28 different taxa associated with the connectivity between the precuneus and the putamen. An undefined species belonging to the family Ruminococcaceae and genus CAG-56 were associated with high connectivity while the other 26 taxa were associated with a low connectivity. Notable taxa belonging to those 26 associated with a low connectivity included 5 Bacteroides species, 2 Ruminococcus species, and Holdemanella, a microbe that was also associated with low connectivity, as determined by sPLS-DA (Figure 4E). Only one serum metabolite was significantly correlated with the connectivity between the precuneus and the putamen after adjusting for multiple hypothesis testing: 1-palmitoyl-2-palmitoleoyl, a phosphatidylcholine-related metabolite, was positively associated with the connectivity between the precuneus and the putamen (p.adj = 0.038, r = 0.63). There was no relationship between 1-palmitoyl-2-palmitoleoyl with any patient questionnaire data.
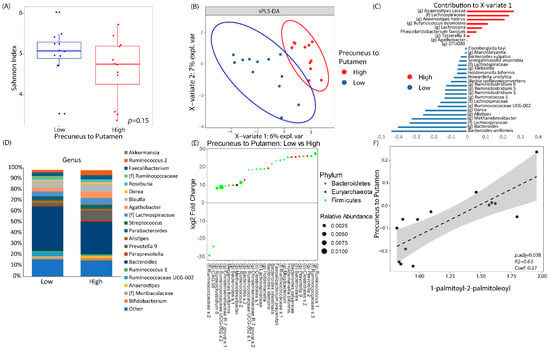
Figure 4.
Brain connectivity was associated with significant changes in the fecal microbiome and serum metabolomics. Resting-state connectivity between the precuneus and the putamen were dichotomized as either high vs low based on its median value. (A) Alpha diversity between low vs high brain connectivity as measured by Shannon Index (a metric of species evenness). (B) Sparse partial least square discriminant analysis (sPLS-DA) plot showing how the gut microbiome can discriminate between patients with low or high connectivity. (C) The amplicon sequence variants that contributed to X-variate 1 of the sPLS-DA plot. (D) Taxonomic plots by genus of microbial communities between patients with low vs high connectivity between the precuneus and the putamen. Genera are only listed if they had a relative abundance of at least 1%. (E) Differential abundance testing as performed by DESEq2 adjusting for time showing log2 fold change in microbes of patients with low connectivity versus those with high connectivity. (F) Linear correlation between resting state connectivity between the precuneus and the putamen to 1-palmitoyl-2-palmitoleoyl, a phosphatidylcholine metabolite.
3.4. Associations Between Eating Behaviors with Shifts in the Gut Microbiome and Circulating Metabolites
We then performed differential abundance testing with DESEq2 to see which microbes were associated with YFAS symptom count and levels of 1-palmitoyl-2-palmitoleoyl. Similar to above, we dichotomized the YFAS symptom count as either high or low by using a cutoff of three and we dichotomized the levels of 1-palmitoyl-2-palmitoleoyl as high or low by using the median value. The microbes that were associated with YFAS and 1-palmitoyl-2-palmitoleoyl are summarized in Figure 5. There were eight taxa that were positively associated with YFAS and seven taxa that were negatively associated. The two most abundant taxa belonged to the genus Prevotella and were both positively associated with YFAS. The most abundant taxa that was negatively associated belonged to the family Ruminococcaceae. Nine taxa were positively associated with 1-palmitoyl-2-palmitoleoyl and 11 taxa were negatively associated. Of the 20 taxa, the one with the greatest relative abundance was one belonging to the genus Ruminococcus and it was negatively associated with 1-palmitoyl-2-palmitoleoyl.
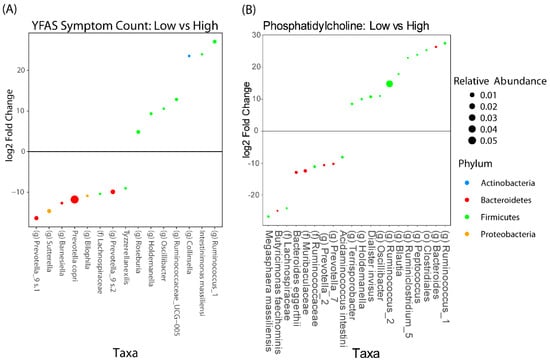
Figure 5.
DESEq2 analysis adjusted for timepoints, showing the taxa that are associated with (A) YFAS symptom count and (B) phosphatidylcholine metabolite and 1-palmitoyl-2-palmitoleoyl. Taxa that have a positive fold change are those that are associated with a lower YFAS symptom count or 1-palmitoyl-2-palmitoleoyl level, respectively.
A summary figure of the previously mentioned analysis representing all of the key associations between the brain, microbes, metabolites, and eating behavior is shown in Figure 6.
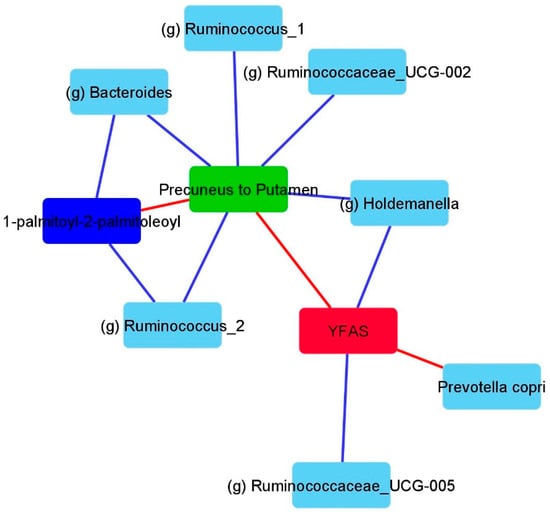
Figure 6.
Summary figure depicting a subset of the associations across brain imaging, microbiome, metabolite, and eating behavior. This figure was solely created based on analysis, as previously mentioned above. Blue lines depict negative associations and red lines depict positive associations. YFAS: Yale Food Addiction Score.
4. Discussion
This is one of the first studies to examine the interconnections between bariatric surgery and eating behavior through the brain–gut–microbiome axis. Despite the small sample size, this study showed a significant association between improvement in eating behaviors induced by bariatric surgery with changes in brain function at the putamen, a core reward region, and with shifts in gut microbiome composition.
In our study, we show that LSG decreased anxiety and depression scores as well as improved eating behavior as measured by the Yale Food Addiction Scale and the Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire. There is ample evidence that easy access to energy-dense and highly palatable foods play a major factor in the development of the current obesity epidemic [52]. Hedonic overeating is defined as eating beyond metabolic requirements from the expectation of or from the actual pleasure derived from consuming highly palatable foods. In obesity, the neuronal mechanisms that modulate the motivation to consume food are disrupted, resulting in impaired control and overconsumption of highly hedonic foods [53]. In prior published studies, bariatric surgery often leads to changes in food preference, meal frequency and meal size [54,55]. The exact reason for this change is likely multifactorial and includes alterations in appetite regulating gastrointestinal hormones, patient motivation, and changes in central nervous signaling [54,56]. Similar to other studies, we found, among our study subjects, a high incidence of addiction-like behaviors to food which were improved after surgery [57]. We also found that the proportion of subjects that fulfill the criteria for food addiction as defined by the YFAS decreased from 16.7% to 0% after surgery. Although the term food addiction is controversial, it is true that in obesity there is a disruption in the function of the brain’s reward network which is characterized by heightened response to food cues in core reward regions, a finding that is very similar to those seen in drug addiction [53,58]. Interestingly, bariatric surgery, mainly RYGB and LSG, are able to modify obesity-related alterations in brain function within the reward centers [20,56].
In line with these findings, we saw changes in both brain morphometric and connectivity within the reward network in our subjects after surgery. LSG led to an increase in amygdala and putamen volumes. Moreover, in this study, LSG induced a decrease in the connectivity between the precuneus and the putamen, which was linearly related to eating behaviors, as measured by the YFAS score. The putamen is located at the dorsal striatum, which is part of the extended reward network of the brain. In imaging studies, the putamen and the amygdala display higher reactivity to high-calorie food cues among obese subjects than among lean subjects [59,60]. The putamen is also preferentially activated during the consumption of drinks with a high sugar content [61]. The precuneus is involved in a variety of functions which include perception, cue reactivity, and salience. Studies in addiction have shown that connections to the precuneus were positively associated with nicotine dependence [62]. Our group found that, in healthy volunteers, anatomical connectivity between the putamen and the precuneus were key regions contributing to the discrimination in overweight/obese individuals from normal weight individuals [33]. Altered connectivity between the putamen and the precuneus has also been observed in obese women with food addiction behaviors [63]. Therefore, the reduction in connectivity seen in the present study between the precuneus and the putamen post bariatric surgery is in line with previous published data and suggests a possible central mechanism behind bariatric surgery induced changes in eating behavior, leading to weight loss.
In previous clinical trials, anxiety and depression metrics would often decrease after bariatric surgery [64,65]. The cause for this improvement is often attributed to a better self-image, an improvement in self-reported physical health, and a subjective increase in more positive social interactions [65]. A large body of evidence indicates that certain negative emotions such as depression, loneliness, and anxiety, leads to a tendency to overeat in obese individuals compared to normal-weight individuals [66]. To what extent changes in mood improve eating behaviors after bariatric surgery or whether surgically induced weigh loss improves mood cannot be answered in this study. There is, however, a body of evidence linking the gut microbiome to anxiety-related behaviors [67]. Thus the possible effect of bariatric surgery on the gut microbiome and its effect on anxiety/depression is a field that requires further exploration.
Because there is a direct effect of bariatric surgery on the gut microbiome, we wanted to further explore the connection between this altered morphometry and connectivity in the brain to changes in the gut microbiome. This study showed that the reduced connectivity between the precuneus and the putamen was associated with significant changes in the gut microbiome. By using sPLS-DA, we found that the gut microbiome can be used to discriminate among subjects with low or high connectivity between the precuneus and the putamen. The microbiome that distinguished those patients with low connectivity comprised of several species belonging to Bacteroides, Ruminococcus, and Holdemanella. The sPLS-DA model was further confirmed when we did an unbiased differential abundance testing with DESEq2. With a DESEq2 analysis adjusting for time, we showed that the associations between Bacteroides, Ruminococcus, and Holdemanella and the brain connectivity were independent of the effect of bariatric surgery. Similarly, we found associations between the gut microbiome, specifically Holdemanella and Ruminococcus, and YFAS symptom score. Human and mouse studies have shown that Bacteroides is associated with a lower BMI and leaner weight [68]. Prior studies of bariatric surgery patients have shown that those with the most significant weight loss were those that had higher levels of Bacteroides in stools [18]. Similarly, in a prospective trial, Bacteroides richness was higher in those individuals that were able to achieve sustained weight loss compared to overweight individuals [69]. Similarly, Ruminococcus has been associated with a lean body mass and a diet that is higher in fiber [70]. In another study of 98 participants, researchers found a significant reduction in Ruminococcus in patients who were obese or overweight compared to healthy controls [71]. While the data on Holdemanella is not as robust as Ruminococcus and Bacteroides, one study examining the role of avocado in weight loss did see a rise in Holdemanella with weight loss and avocado supplementation [72]. Therefore, the microbial associates we ascribed to food addiction and the connectivity of the precuneus and putamen are in line with the available data that associate the gut microbiome to obesity.
In addition to microbiome changes, bariatric surgery is also known to produce significant changes in serum metabolites. In our data, we see that a phosphatidylcholine metabolite, 1-palmitoyl-2-palmitoleoyl, was positively associated with the connection between the precuneus and the putamen. We also show that 1-palmitoyl-2-palmitoleoyl was also negatively associated with microbes belonging to the genus Bacteroides and Ruminoccocus, the same microbes that were negatively associated with the brain connections between the precuneus and the putamen. Phosphatidylcholines are major components in cell membrane and are involved in a variety of pathways including lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity [73]. In several studies of bariatric surgery patients, the levels of phosphatidylcholine significantly decrease alongside weight loss and the level of phosphatidylcholine was positively associated with increased cholesterol transportation [44,74]. In addition to being related to obesity, studies have also shown phosphatidylcholine to be an integral compound in such neurological processes as dementia and acetylcholine synthesis [75,76]. Therefore, by showing a strong relationship between phosphatidylcholine and the connections related to the putamen, our data, alongside prior published works, suggests that decreases in phosphatidylcholine may play a critical role in the changes in the brain function seen after surgery, and these changes may be potentially linked to the gut microbiome, although the mechanism behind the latter link is not clear. Gut microbiome participates in the metabolism of dietary phosphatidylcholine, and its byproducts have been linked to atherosclerosis. However, to what extent the decrease in this metabolite in the host serum is due to changes in diet and/or gut microbiome–host metabolic interactions needs to be further explored.
We would like to acknowledge four important limitations of the current study. First, the main limitation to this study is its small sample size. Despite this, we were able to show significant changes relating bariatric surgery to the brain–gut–microbiome axis. Moreover, the longitudinal design of the study partially compensates for this shortcoming and gives a sense of the directionality of the associations. Second, we assessed eating behaviors and more specifically addictive-like eating behavior with the YFAS symptom score, which has a limited range (0–7) and may not be as sensitive to detect changes in other eating behaviors including impulsive eating behaviors. In addition, because of the small sample size, we could not control for the effect of changes in mood (anxiety, depression) or in appetite/gut peptide levels on the YFAS score after surgery. Third, because of the design and small sample size, we were not able to assess for the effect of dietary changes on the gut microbiome and metabolites. Furthermore, sPLS-DA modeling of the microbiome does tend to overfit data with small sample sizes. We have tried to overcome this limitation by also performing unbiased differential abundance testing with DESEq2 to confirm the findings from the sPLS-DA model. However, future larger studies should be performed to validate the findings found in our model. Fourth, our population comprises a relatively small number of women aged 18 to 55, without major comorbidities, and therefore our findings cannot be extrapolated to other obese populations. The strengths of our study include a well-characterized population, followed closely for 6 months. Data and samples were prospectively collected in a standard manner. This data included eating behavior questionnaires, anthropometrics, high-resolution fMRI of the brain, stool samples for high-depth sequencing using up to date analysis techniques that provide better taxonomic resolution, and well-characterized serum metabolite data.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this is one of the few studies to date to examine the effects of bariatric surgery on eating behavior using a multi-omics approach. We believe that our study builds on prior published works to show how bariatric surgery can affect eating behavior through alterations in the gut microbiome, serum metabolites, and brain morphometry and connectivity. While these results may shed new light on novel pathways to aid patients with weight loss, they should be validated in a larger cohort of patients that includes both men and women. Future studies will also be required to further investigate the mechanisms behind these BGM interactions following bariatric surgery.
Author Contributions
C.S., E.A.M. and E.D. conceived, designed and supervised the project, secured funding, provided expertise and feedback, and contributed to the data interpretation and manuscript writing. T.S.D., A.G., J.P.J. participated in the data analyses, interpretation and manuscript writing.; J.S., A.B., Y.C., E.D. and C.S., recruited, handled the patients and collected data and specimens; J.S., A.G., E.G., R.R.B., P.V. and V.O., conducted the imaging experiments and imaging analysis; and T.S.D., J.P.J., V.L., performed the laboratory analyses. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health DDRC P30 DK 41301 (C.S.), UL1TR000124 (C.S.), T32 DK 718044 (T.D.), R01 DK048351 (E.A.M.), K23 106528 (AG); and VA IK2CX001717 (J.P.J.).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kim, R.; Lee, D.H.; Subramanian, S.V. Understanding the obesity epidemic. BMJ 2019, 366, l4409. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sjostrom, L.; Peltonen, M.; Jacobson, P.; Sjostrom, C.D.; Karason, K.; Wedel, H.; Ahlin, S.; Anveden, A.; Bengtsson, C.; Bergmark, G. Bariatric surgery and long-term cardiovascular events. JAMA 2012, 307, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Shin, A.C.; Lenard, N.R.; Townsend, R.L.; Patterson, L.M.; Sigalet, D.L.; Berthoud, H.-R. Meal patterns, satiety, and food choice in a rat model of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2009, 297, R1273–R1282. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zakeri, R.; Batterham, R.L. Potential mechanisms underlying the effect of bariatric surgery on eating behaviour. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2018, 25, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kullmann, S.; Heni, M.; Linder, K.; Zipfel, S.; Haring, H.U.; Veit, R.; Fritsche, A.; Preissl, H. Resting-state functional connectivity of the human hypothalamus. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014, 35, 6088–6096. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Garcia, I.; Jurado, M.A.; Garolera, M.; Segura, B.; Sala-Llonch, R.; Marques-Iturria, I.; Pueyo, R.; Sender-Palacios, M.J.; Vernet-Vernet, M.; Narberhaus, A.; et al. Alterations of the salience network in obesity: A resting-state fMRI study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 34, 2786–2797. [Google Scholar]
- Hankir, M.K.; Seyfried, F.; Hintschich, C.A.; Diep, T.A.; Kleberg, K.; Kranz, M.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Tellez, L.A.; Rullmann, M.; Patt, M.; et al. Gastric Bypass Surgery Recruits a Gut PPAR-alpha-Striatal D1R Pathway to Reduce Fat Appetite in Obese Rats. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 335–344. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Ji, G.; Hu, Y.; Xu, M.; Jin, Q.; Liu, L.; von Deneen, K.M.; Zhao, J.; Chen, A.; Cui, G.; et al. Bariatric surgery in obese patients reduced resting connectivity of brain regions involved with self-referential processing. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 4755–4765. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, H.K.; Tuulari, J.J.; Tuominen, L.; Hirvonen, J.; Honka, H.; Parkkola, R.; Helin, S.; Salminen, P.; Nuutila, P.; Nummenmaa, L. Bariatric surgery normalizes brain opioid receptors. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 989. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, C.R.; Osadchiy, V.; Kalani, A.; Mayer, E.A. The Brain-Gut-Microbiome Axis. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 133–148. [Google Scholar]
- Bercik, P.; Denou, E.; Collins, J.; Jackson, W.; Lu, J.; Jury, J.; Deng, Y.; Blennerhassett, P.; Macri, J.; McCoy, K.D.; et al. The intestinal microbiota affect central levels of brain-derived neurotropic factor and behavior in mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 599–609.e3. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz Heijtz, R.; Wang, S.; Anuar, F.; Qian, Y.; Bjorkholm, B.; Samuelsson, A.; Hibberd, M.L.; Forssberg, H.; Pettersson, S. Normal gut microbiota modulates brain development and behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3047–3052. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Neufeld, K.M.; Kang, N.; Bienenstock, J.; Foster, J.A. Reduced anxiety-like behavior and central neurochemical change in germ-free mice. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 255–264.e199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tolhurst, G.; Heffron, H.; Lam, Y.S.; Parker, H.E.; Habib, A.M.; Diakogiannaki, E.; Cameron, J.; Grosse, J.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M. Short-chain fatty acids stimulate glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion via the G-protein-coupled receptor FFAR2. Diabetes 2012, 61, 364–371. [Google Scholar]
- Everard, A.; Lazarevic, V.; Derrien, M.; Girard, M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Muccioli, G.M.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Possemiers, S.; Van Holle, A.; de Vos, W.M.; et al. Responses of gut microbiota and glucose and lipid metabolism to prebiotics in genetic obese and diet-induced leptin-resistant mice. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2775–2786. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vijay-Kumar, M.; Aitken, J.D.; Carvalho, F.A.; Cullender, T.C.; Mwangi, S.; Srinivasan, S.; Sitaraman, S.V.; Knight, R.; Ley, R.E.; Gewirtz, A.T. Metabolic syndrome and altered gut microbiota in mice lacking Toll-like receptor 5. Science 2010, 328, 228–231. [Google Scholar]
- Furet, J.-P.; Kong, L.-C.; Tap, J.; Poitou, C.; Basdevant, A.; Bouillot, J.-L.; Mariat, D.; Corthier, G.; Doré, J.; Henegar, C.; et al. Differential adaptation of human gut microbiota to bariatric surgery-induced weight loss: Links with metabolic and low-grade inflammation markers. Diabetes 2010, 59, 3049–3057. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.V.; Ashrafian, H.; Bueter, M.; Kinross, J.; Sands, C.; le Roux, C.W.; Bloom, S.R.; Darzi, A.; Athanasiou, T.; Marchesi, J.; et al. Metabolic surgery profoundly influences gut microbial-host metabolic cross-talk. Gut 2011, 60, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholtz, S.; Miras, A.D.; Chhina, N.; Prechtl, C.G.; Sleeth, M.L.; Daud, N.M.; Ismail, N.A.; Durighel, G.; Ahmed, A.R.; Olbers, T.; et al. Obese patients after gastric bypass surgery have lower brain-hedonic responses to food than after gastric banding. Gut 2014, 63, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, E.L.; Ariel-Donges, A.H.; Bauman, V.; Merlo, L.J. What Is the Evidence for “Food Addiction?” A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, K.I.; Park, K.M. Are there differences in brain morphology according to handedness? Brain Behav. 2017, 7, e00730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Matloff, W.; Ning, K.; Kim, H.; Dinov, I.D.; Toga, A.W. Age-Related Differences in Brain Morphology and the Modifiers in Middle-Aged and Older Adults. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 4169–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjelland, I.; Dahl, A.A.; Haug, T.T.; Neckelmann, D. The validity of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. An updated literature review. J. Psychosom. Res. 2002, 52, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelleri, J.C.; Bushmakin, A.G.; Gerber, R.A.; Leidy, N.K.; Sexton, C.C.; Lowe, M.R.; Karlsson, J. Psychometric analysis of the Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire-R21: Results from a large diverse sample of obese and non-obese participants. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gearhardt, A.N.; Corbin, W.R.; Brownell, K.D. Preliminary validation of the Yale Food Addiction Scale. Appetite 2009, 52, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Jacobs, J.P.; McHardy, I.H.; Braun, J. Sampling of intestinal microbiota and targeted amplification of bacterial 16S rRNA genes for microbial ecologic analysis. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2014, 107, 7–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.P.; Dong, T.S.; Agopian, V.; Lagishetty, V.; Sundaram, V.; Noureddin, M.; Ayoub, W.S.; Durazo, F.; Benhammou, J.; Enayati, P.; et al. Microbiome and bile acid profiles in duodenal aspirates from patients with liver cirrhosis: The Microbiome, Microbial Markers and Liver Disease Study. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 48, 1108–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Mayer, E.A.; Hamadani, K.; Bhatt, R.; Fling, C.; Alaverdyan, M.; Torgerson, C.; Ashe-McNalley, C.; Van Horn, J.D.; Naliboff, B.; et al. Sex differences in the influence of body mass index on anatomical architecture of brain networks. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Coveleskie, K.; Gupta, A.; Kilpatrick, L.A.; Mayer, E.D.; Ashe-McNalley, C.; Stains, J.; Labus, J.S.; Mayer, E.A. Altered functional connectivity within the central reward network in overweight and obese women. Nutr. Diabetes 2015, 5, e148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Mayer, E.A.; Sanmiguel, C.P.; Van Horn, J.D.; Woodworth, D.; Ellingson, B.M.; Fling, C.; Love, A.; Tillisch, K.; Labus, J.S. Patterns of brain structural connectivity differentiate normal weight from overweight subjects. NeuroImage Clin. 2015, 7, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cedernaes, J.; Bass, J. Decoding obesity in the brainstem. Elife 2016, 5, e16393. [Google Scholar]
- Val-Laillet, D.; Aarts, E.; Weber, B.; Ferrari, M.; Quaresima, V.; Stoeckel, L.E.; Alonso-Alonso, M.; Audette, M.; Malbert, C.H.; Stice, E. Neuroimaging and neuromodulation approaches to study eating behavior and prevent and treat eating disorders and obesity. NeuroImage Clin. 2015, 8, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.M.; Jenkinson, M.; Woolrich, M.W.; Beckmann, C.F.; Behrens, T.E.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Bannister, P.R.; De Luca, M.; Drobnjak, I. Advances in functional structural MR image analysis implementation as, F.S.L. Neuroimage 2004, 23 (Suppl. 1), S208–S219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Brady, M.; Smith, S. Segmentation of brain MR images through a hidden Markov random field model and the expectation-maximization algorithm. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2001, 20, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Good, C.D.; Johnsrude, I.S.; Ashburner, J.; Henson, R.N.; Friston, K.J.; Frackowiak, R.S. A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. Neuroimage 2001, 14, 21–36. [Google Scholar]
- Douaud, G.; Smith, S.; Jenkinson, M.; Behrens, T.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Vickers, J.; James, S.; Voets, N.; Watkins, K.; Matthews, P.M.; et al. Anatomically related grey and white matter abnormalities in adolescent-onset schizophrenia. Brain 2007, 130, 2375–2386. [Google Scholar]
- Friston, K.; Ashburner, J.; Kiebel, S.; Nichols, T.; Penny, W. (Eds.) Statistical Parametric Mapping. In Statistical Parametric Mapping; Academic Press: London, UK, 2007; p. vii. [Google Scholar]
- Power, J.D.; Mitra, A.; Laumann, T.O.; Snyder, A.Z.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Petersen, S.E. Methods to detect, characterize, and remove motion artifact in resting state fMRI. Neuroimage 2014, 84, 320–341. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto-Castanon, A. Handbook of Functional Connectivity Magnetic Resonance Imaging Methods in CONN; Hilbert Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Behzadi, Y.; Restom, K.; Liau, J.; Liu, T.T. A component based noise correction method (CompCor) for BOLD and perfusion based fMRI. Neuroimage 2007, 37, 90–101. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson, E.R.; Allin, K.H.; Madsbad, S.; Fenger, M. Phosphatidylcholine and its relation to apolipoproteins A-1 and B changes after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: A cohort study. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Samczuk, P.; Ciborowski, M.; Kretowski, A. Application of Metabolomics to Study Effects of Bariatric Surgery. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 6270875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, N.; Caixas, A.; Ahlers, M.; Patel, K.; Gao, Z.; Dutia, R.; Blaser, M.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Laferrere, B. Longitudinal changes of microbiome composition and microbial metabolomics after surgical weight loss in individuals with obesity. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2019, 15, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar]
- Narath, S.H.; Mautner, S.I.; Svehlikova, E.; Schultes, B.; Pieber, T.R.; Sinner, F.M.; Gander, E.; Libiseller, G.; Schimek, M.G.; Sourij, H.; et al. An Untargeted Metabolomics Approach to Characterize Short-Term and Long-Term Metabolic Changes after Bariatric Surgery. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161425. [Google Scholar]
- Sanmiguel, C.P.; Jacobs, J.; Gupta, A.; Ju, T.; Stains, J.; Coveleskie, K.; Lagishetty, V.; Balioukova, A.; Chen, Y.; Dutson, E.; et al. Surgically Induced Changes in Gut Microbiome and Hedonic Eating as Related to Weight Loss: Preliminary Findings in Obese Women Undergoing Bariatric Surgery. Psychosom. Med. 2017, 79, 880–887. [Google Scholar]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar]
- Storey, J.D.; Tibshirani, R. Statistical significance for genomewide studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9440–9445. [Google Scholar]
- Winkler, A.M.; Ridgway, G.R.; Webster, M.A.; Smith, S.M.; Nichols, T.E. Permutation inference for the general linear model. Neuroimage 2014, 92, 381–397. [Google Scholar]
- Swinburn, B.A.; Sacks, G.; Hall, K.D.; McPherson, K.; Finegood, D.T.; Moodie, M.L.; Gortmaker, S.L. The global obesity pandemic: Shaped by global drivers and local environments. Lancet 2011, 378, 804–814. [Google Scholar]
- Volkow, N.D.; Wang, G.J.; Tomasi, D.; Baler, R.D. Obesity and addiction: Neurobiological overlaps. Obes. Rev. 2013, 14, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Najim, W.; Docherty, N.G.; le Roux, C.W. Food Intake and Eating Behavior after Bariatric Surgery. Physiol Rev. 2018, 98, 1113–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurenius, A.; Larsson, I.; Bueter, M.; Melanson, K.J.; Bosaeus, I.; Forslund, H.B.; Lonroth, H.; Fandriks, L.; Olbers, T. Changes in eating behaviour and meal pattern following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochner, C.N.; Stice, E.; Hutchins, E.; Afifi, L.; Geliebter, A.; Hirsch, J.; Teixeira, J. Relation between changes in neural responsivity and reductions in desire to eat high-calorie foods following gastric bypass surgery. Neuroscience 2012, 209, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepino, M.Y.; Stein, R.I.; Eagon, J.C.; Klein, S. Bariatric surgery-induced weight loss causes remission of food addiction in extreme obesity. Obesity 2014, 22, 1792–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gearhardt, A.N.; Yokum, S.; Orr, P.T.; Stice, E.; Corbin, W.R.; Brownell, K.D. Neural correlates of food addiction. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoeckel, L.E.; Weller, R.E.; Cook, E.W., 3rd; Twieg, D.B.; Knowlton, R.C.; Cox, J.E. Widespread reward-system activation in obese women in response to pictures of high-calorie foods. Neuroimage 2008, 41, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothemund, Y.; Preuschhof, C.; Bohner, G.; Bauknecht, H.C.; Klingebiel, R.; Flor, H.; Klapp, B.F. Differential activation of the dorsal striatum by high-calorie visual food stimuli in obese individuals. Neuroimage 2007, 37, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stice, E.; Burger, K.S.; Yokum, S. Relative ability of fat and sugar tastes to activate reward, gustatory, and somatosensory regions. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; King, J.A.; Ursprung, W.W.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, N.; Kennedy, D.N.; Ziedonis, D.; DiFranza, J.R. The development and expression of physical nicotine dependence corresponds to structural and functional alterations in the anterior cingulate-precuneus pathway. Brain Behav. 2014, 4, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.S.; Wang, P.W.; Ko, C.H.; Hsieh, T.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Yen, J.Y. Altered brain correlates of response inhibition and error processing in females with obesity and sweet food addiction: A functional magnetic imaging study. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 11, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Osterhues, A.; von Lengerke, T.; Mall, J.W.; de Zwaan, M.; Muller, A. Health-Related Quality of Life, Anxiety, and Depression in Bariatric Surgery Candidates Compared to Patients from a Psychosomatic Inpatient Hospital. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 2378–2387. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, J.R.; Aasprang, A.; Bergsholm, P.; Sletteskog, N.; Vage, V.; Natvig, G.K. Anxiety and depression in association with morbid obesity: Changes with improved physical health after duodenal switch. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2010, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ganley, R.M. Emotion and eating in obesity: A review of the literature. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1989, 8, 343–361. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, E.A.; Knight, R.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Cryan, J.F.; Tillisch, K. Gut microbes and the brain: Paradigm shift in neuroscience. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 15490–15496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remely, M.; Hippe, B.; Zanner, J.; Aumueller, E.; Brath, H.; Haslberger, A.G. Gut Microbiota of Obese, Type 2 Diabetic Individuals is Enriched in Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Akkermansia muciniphila and Peptostreptococcus anaerobius after Weight Loss. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2016, 16, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, S.F.; Murphy, E.F.; Nilaweera, K.; Ross, P.R.; Shanahan, F.; O’Toole, P.W.; Cotter, P.D. The gut microbiota and its relationship to diet and obesity: New insights. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 186–202. [Google Scholar]
- Schwiertz, A.; Taras, D.; Schafer, K.; Beijer, S.; Bos, N.A.; Donus, C.; Hardt, P.D. Microbiota and SCFA in lean and overweight healthy subjects. Obesity 2010, 18, 190–195. [Google Scholar]
- Henning, S.M.; Yang, J.; Woo, S.L.; Lee, R.P.; Huang, J.; Rasmusen, A.; Carpenter, C.L.; Thames, G.; Gilbuena, I.; Tseng, C.-H.; et al. Hass Avocado Inclusion in a Weight-Loss Diet Supported Weight Loss and Altered Gut Microbiota: A 12-Week Randomized, Parallel-Controlled Trial. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2019, 3, nzz068. [Google Scholar]
- van der Veen, J.N.; Kennelly, J.P.; Wan, S.; Vance, J.E.; Vance, D.E.; Jacobs, R.L. The critical role of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine metabolism in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 1558–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graessler, J.; Bornstein, T.D.; Goel, D.; Bhalla, V.P.; Lohmann, T.; Wolf, T.; Koch, M.; Qin, Y.; Licinio, J.; Wong, M.-L.; et al. Lipidomic profiling before and after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in obese patients with diabetes. Pharm. J. 2014, 14, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, B.N.; Kim, M.; Chuang, Y.F.; Beason-Held, L.; Kitner-Triolo, M.; Kraut, M.; Lirette, S.T.; Windham, B.G.; Griswold, M.E.; Legido-Quigley, C.; et al. Blood metabolite markers of cognitive performance and brain function in aging. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 1212–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.Y.; Moriyama, T.; Uezu, E.; Uezu, K.; Hirata, R.; Yohena, N.; Masuda, Y.; Kokubu, T.; Yamamoto, S. Administration of phosphatidylcholine increases brain acetylcholine concentration and improves memory in mice with dementia. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 1484–1489. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).