Nutraceutical Compounds Targeting Inflammasomes in Human Diseases
Abstract
1. Background
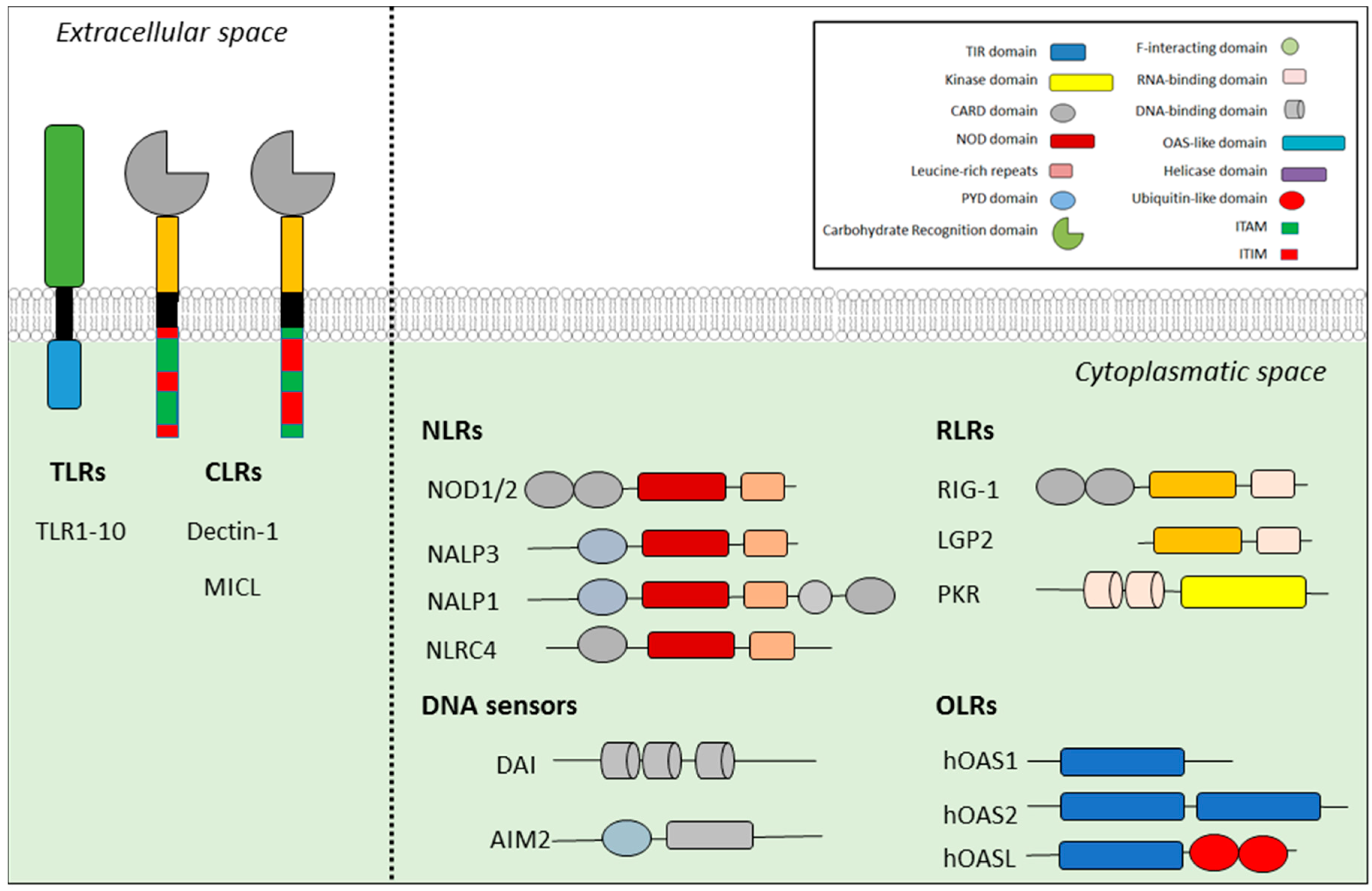
2. Inflammasomes
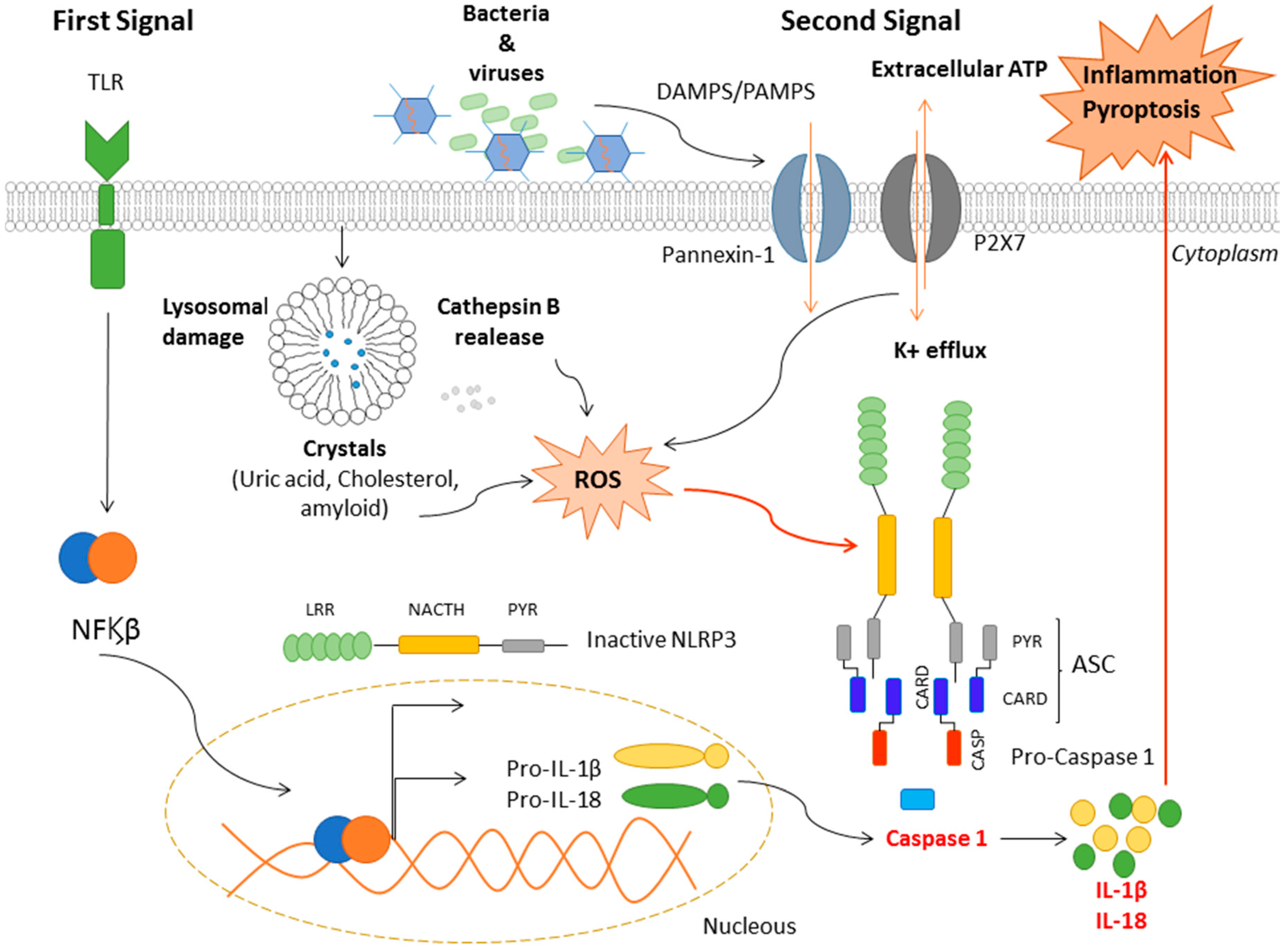
3. Mechanisms of NLRP3 Activation
4. Nutraceutical Compounds
5. Nutraceutical Compounds, the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Cardiovascular Diseases
6. Nutraceutical Compounds, the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Type 2 Diabetes
7. Nutraceutical Compounds, the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Neurological Diseases
8. Nutraceutical Compounds, the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Cancer
9. Conclusion and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IS | immune system |
| ASC | apoptosis-associated speck-like protein |
| PAMPs | pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| DAMPs | damage-associated molecular patterns |
| PRRs | pattern recognition receptors |
| TLRs | toll-like receptors |
| CLRs | c-type lectin receptors |
| RLRs | retinoic acid inducible gene-I (RIG1)-like receptors |
| OLRs | olygoadenylate synthetase-like receptors |
| CARD | caspase recruitment |
| PYR | pyrin domains |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| CVDs | cardiovascular diseases |
| PUFAs | polyunsaturated fatty acids |
References
- Schroder, K.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasomes. Cell 2010, 140, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, J.; Boche, D.; Rakic, S. What do we know about the inflammasome in humans? Brain Pathol. 2017, 27, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abderrazak, A.; Syrovets, T.; Couchie, D.; El Hadri, K.; Friguet, B.; Simmet, T.; Rouis, M. NLRP3 inflammasome: From a danger signal sensor to a regulatory node of oxidative stress and inflammatory diseases. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamkanfi, M.; Dixit, V.M. Inflammasomes and Their Roles in Health and Disease. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 28, 137–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, J.C.; Barton, G.M. Emerging principles governing signal transduction by pattern-recognition receptors. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 7, a016253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogensen, T.H. Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 240–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzman, A. Molecular biology of the cell. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2003, 31, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zoete, M.R.; Palm, N.W.; Zhu, S.; Flavell, R.A. Inflammasomes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Mohammadi, M.T.; Rezaee, R.; Sahebkar, A. Fenofibrate improves renal function by amelioration of NOX-4, IL-18, and p53 expression in an experimental model of diabetic nephropathy. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 7458–7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Chang, Y.J.; Pichavant, M.; Shore, S.A.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Iwakura, Y.; Israel, E.; Bolger, K.; Faul, J.; et al. Interleukin-17-producing innate lymphoid cells and the NLRP3 inflammasome facilitate obesity-associated airway hyperreactivity. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebe, A.; Hoss, F.; Latz, E. NLRP3 inflammasome and the IL-1 pathway in atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1722–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoseini, Z.; Sepahvand, F.; Rashidi, B.; Sahebkar, A.; Masoudifar, A.; Mirzaei, H. NLRP3 inflammasome: Its regulation and involvement in atherosclerosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 2116–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ference, B.A.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Graham, I.; Ray, K.K.; Packard, C.J.; Bruckert, E.; Hegele, R.A.; Krauss, R.M.; Raal, F.J.; Schunkert, H.; et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic, and clinical studies. A consensus statement fromthe European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2459–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Xing, S.; Gong, Z.; Xing, Q. NLRP3 inflammasomes show high expression in Aorta of patients with atherosclerosis. Heart Lung Circ. 2013, 22, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ising, C.; Venegas, C.; Zhang, S.; Scheiblich, H.; Schmidt, S.V.; Vieira-Saecker, A.; Schwartz, S.; Albasset, S.; McManus, R.M.; Tejera, D.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation drives tau pathology. Nature 2019, 575, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Kummer, M.P.; Stutz, A.; Delekate, A.; Schwartz, S.; Vieira-Saecker, A.; Griep, A.; Axt, D.; Remus, A.; Tzeng, T.C.; et al. NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer’s disease and contributes to pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Nature 2013, 493, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yuan, Y.H.; Chen, N.H.; Wang, H.B. The mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome/pyroptosis activation and their role in Parkinson’s disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 67, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moossavi, M.; Parsamanesh, N.; Bahrami, A.; Atkin, S.L.; Sahebkar, A. Role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Dong, Y.; Ye, M.; Jin, S.; Yang, J.; Joosse, M.E.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lazarev, M.; Brant, S.R.; et al. The Pathogenic Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases of Both Mice and Humans. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2017, 11, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangan, M.S.J.; Olhava, E.J.; Roush, W.R.; Seidel, H.M.; Glick, G.D.; Latz, E. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Torre-Minguela, C.; del Castillo, P.M.; Pelegrín, P. The NLRP3 and pyrin inflammasomes: Implications in the pathophysiology of autoinflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Li, W.-W.; Stary, C.; Clark, J.D.; Xu, S.; Xiong, X. The inflammasome as a target for pain therapy. Br. J. Anaesth. 2016, 117, 693–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Callaway, J.B.; Ting, J.P.-Y. Inflammasomes: Mechanism of action, role in disease, and therapeutics. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBusk, R. Diet-Related Disease, Nutritional Genomics, and Food and Nutrition Professionals. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2009, 109, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín Ortega, A.M.; Segura Campos, M.R. Bioactive Compounds as Therapeutic Alternatives. In Bioactive Compounds: Health Benefits and Potential Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 247–264. ISBN 9780128147757. [Google Scholar]
- Madalena, D.A.; Pereira, R.N.; Vicente, A.A.; Ramos, Ó.L. New insights on bio-based micro-and nanosystems in food. In Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 708–714. ISBN 9780128140451. [Google Scholar]
- Mahfoudhi, N.; Ksouri, R.; Hamdi, S. Nanoemulsions as potential delivery systems for bioactive compounds in food systems: Preparation, characterization, and applications in food industry. In Emulsions; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 365–403. [Google Scholar]
- Gul, K.; Singh, A.K.; Jabeen, R. Nutraceuticals and Functional Foods: The Foods for the Future World. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2617–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavillard, L.E.; Marín-Aguilar, F.; Bullon, P.; Cordero, M.D. Cardiovascular diseases, NLRP3 inflammasome, and western dietary patterns. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 131, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Min, D.S.; Park, H.; Kim, H.P. Flavonoids interfere with NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 355, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Li, S.; Huang, W.; Xiang, L.; Liu, D.; Hu, Y.; Wang, P.; Lu, X.; et al. Coptisine from Coptis chinensis blocks NLRP3 inflammasome activation by inhibiting caspase-1. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 147, 104348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Zhang, L.; Ling, S.; Duan, J.; Qian, F.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.-W. Scropolioside B inhibits IL-1β and cytokines expression through NF-κB and inflammasome NLRP3 pathways. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 819053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Jiang, W.; Spinetti, T.; Tardivel, A.; Castillo, R.; Bourquin, C.; Guarda, G.; Tian, Z.; Tschopp, J.; Zhou, R. Omega-3 Fatty Acids Prevent Inflammation and Metabolic Disorder through Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Immunity 2013, 38, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, X.; Zheng, G.; Fan, S.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, D.; Shan, Q.; Hu, B.; Zheng, Y. Protective effect of different flavonoids against endothelial senescence via NLRP3 inflammasome. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 26, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajdukovic, J. The Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Cardiovascular Diseases. J. Clin. Exp. Cardiolog. 2015, 6, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Gurley, E.C.; Zhou, H. Flavonoid Apigenin Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response through Multiple Mechanisms in Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Franco, O.; Hernández-Vargas, P.; Ortiz-Muñoz, G.; Sanjuán, G.; Suzuki, Y.; Ortega, L.; Blanco, J.; Egido, J.; Gómez-Guerrero, C. Parthenolide Modulates the NF-κB–Mediated Inflammatory Responses in Experimental Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 1864–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, M.; Robles, M.; West, J.E.; Ortiz De Montellano, B.R.; Rodriguez, E. Ethnopharmacology of Mexican asteraceae (compositae). Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1998, 38, 539–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Gao, X.; Wu, X.; Wu, Z.; Cheng, L.; Zhu, L.; Shen, D.; Tong, X. Parthenolide inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory cytokines through the toll-like receptor 4 signal pathway in THP-1 cells. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2015, 47, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juliana, C.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Wu, J.; Datta, P.; Solorzano, L.; Yu, J.-W.; Meng, R.; Quong, A.A.; Latz, E.; Scott, C.P.; et al. Anti-inflammatory compounds parthenolide and Bay 11-7082 are direct inhibitors of the inflammasome. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 9792–9802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Ahn, H.; Han, B.-C.; Lee, S.-H.; Cho, Y.-W.; Kim, C.H.; Hong, E.-J.; An, B.-S.; Jeung, E.-B.; Lee, G.-S. Korean red ginseng extracts inhibit NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasome activation. Immunol. Lett. 2014, 158, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domiciano, T.P.; Wakita, D.; Jones, H.D.; Crother, T.R.; Verri, W.A.; Arditi, M.; Shimada, K. Quercetin Inhibits Inflammasome Activation by Interfering with ASC Oligomerization and Prevents Interleukin-1 Mediated Mouse Vasculitis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.X.; Du, C.T.; Chen, W.; Lei, Q.Q.; Li, N.; Qi, S.; Zhang, X.J.; Hu, G.Q.; Deng, X.M.; Han, W.Y.; et al. Genipin inhibits NLRP3 and NLRC4 inflammasome activation via autophagy suppression. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Zong, B.; Yuan, H.; Wang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; et al. Gypenosides improve diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting ROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 4437–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, M.; Xu, L.; Lv, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; He, W.F. Morroniside alleviates coxsackievirus B3-induced myocardial damage apoptosis via restraining NLRP3 inflammasome activation. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 1222–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Lee, G.S. Isorhamnetin and hyperoside derived from water dropwort inhibits inflammasome activation. Phytomedicine 2017, 24, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalons, P.; Amor, S.; Courtaut, F.; Cantos-Villar, E.; Richard, T.; Auger, C.; Chabert, P.; Schni-Kerth, V.; Aires, V.; Delmas, D. Study of potential anti-inflammatory effects of red wine extract and resveratrol through a modulation of interleukin-1-beta in macrophages. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.Y.; Hu, M.M.; Xin, Y.F.; Gang, C. Resveratrol alleviates vascular inflammatory injury by inhibiting inflammasome activation in rats with hypercholesterolemia and vitamin D2 treatment. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 64, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Yang, R.; Yang, J.; Yang, J.; Ding, J.; Wu, H.; Zhang, J. Resveratrol pretreatment protects rat hearts from ischemia/reperfusion injury partly via a NALP3 inflammasome pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 8731–8741. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, F.; Ye, B.; Cao, J.; Cai, X.; Lin, L.; Huang, S.; Huang, W.; Huang, Z. Curcumin Represses NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and P2X7R Signaling in PMA-Induced Macrophages. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wu, A.; Kwan Law, B.Y.; Liu, C.; Zeng, W.; Ling Qiu, A.C.; Han, Y.; He, Y.; Wai Wong, V.K. The active components derived from Penthorum chinense Pursh protect against oxidative-stress-induced vascular injury via autophagy induction. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 146, 160–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Liu, W.; Lan, T.; Pan, W.; Chen, X.; Wu, H.; Xu, D. Salvianolate reduces atrial fibrillation through suppressing atrial interstitial fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad2/3 and TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathways in post-MI rats. Phytomedicine 2018, 51, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, M.-H.; Wang, Q.; Qin, M.-J.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X.-Q.; Liu, B.-L.; Wen, X.-D. Ilexgenin A inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress and ameliorates endothelial dysfunction via suppression of TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation in an AMPK dependent manner. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 99, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S., II; Jeong, S., II; Kim, K.J.; Kim, H.J.; Yu, H.H.; Park, R.; Kim, H.M.; You, Y.O. Tanshinone IIA from Salvia miltiorrhiza Inhibits Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression and Production of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in Activated RAW 264.7 Cells. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 1057–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Wei, B.; Wei, L.; Hua, K.; Yu, X.; Li, H.; Ji, H. Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate ameliorates ischemia-induced myocardial inflammation and lipid accumulation in Beagle dogs through NLRP3 inflammasome. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 196, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Yi, L.; Zhou, X.; Mi, M. Dihydromyricetin inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway in vascular endothelial cells. BioFactors 2018, 44, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.C.; Li, Z.; Xu, W.; Xiang, C.H.; Ma, Y.F. Luteolin alleviates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and directs macrophage polarization in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 265–273. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, G.J.; Robertson, S.; Barraclough, J.; Xia, Q.; Mallat, Z.; Bursill, C.; Celermajer, D.S.; Patel, S. Colchicine Acutely Suppresses Local Cardiac Production of Inflammatory Cytokines in Patients With an Acute Coronary Syndrome. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e002128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Lu, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, F.; Shen, H.; Yao, D.; Gong, K.; Zhang, Z. Triptolide attenuates pressure overload-induced myocardial remodeling in mice via the inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 485, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Cheng, X.; Tang, L.; Jiang, M. The cardioprotective effect of total flavonoids on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion in rats. BioMed Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Fan, Z.; Xiang, D.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Gao, L.; Feng, C. The protective effect of umbelliferone ameliorates myocardial injury following ischemia-reperfusion in the rat through suppression NLRP3 inflammasome and upregulating the PPAR-γ. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 3404–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viljoen, A.; Mncwangi, N.; Vermaak, I. Anti-Inflammatory Iridoids of Botanical Origin. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 2104–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badorff, C.; Fichtlscherer, B.; Rhoads, R.E.; Zeiher, A.M.; Muelsch, A.; Dimmeler, S.; Knowlton, K.U. Nitric oxide inhibits dystrophin proteolysis by coxsackieviral protease 2A through S-nitrosylation: A protective mechanism against enteroviral cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2000, 102, 2276–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairweather, D.L.; Rose, N.R. Coxsackievirus-induced myocarditis in mice: A model of autoimmune disease for studying immunotoxicity. Methods 2007, 41, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, M.; Takahashi, M.; Hata, T.; Kashima, Y.; Usui, F.; Morimoto, H.; Izawa, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Masumoto, J.; Koyama, J.; et al. Inflammasome Activation of Cardiac Fibroblasts Is Essential for Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Circulation 2011, 123, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, G.X.; Li, J.M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, S.P. Anti-inflammatory and immune suppressive effects of Conus officinalis glucosides in rats. Chin. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2007, 27, 316–320. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, Y.-H.; Chang, H.-K.; Kim, S.-E.; Kim, Y.-M.; Seo, J.-H.; Shin, M.-C.; Shin, M.-S.; Yi, J.-W.; Shin, D.-H.; Kim, H.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Effects of the Aqueous Extract of Corni Fructus in Murine RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells. J. Med. Food 2009, 12, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, D.; Block, R.; Mousa, S.A. Omega-3 Fatty Acids EPA and DHA: Health Benefits Throughout Life. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Fan, S.; Wang, X.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, D.; Shan, Q.; Zheng, Y. Purple sweet potato color inhibits endothelial premature senescence by blocking the NLRP3 inflammasome. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calgarotto, A.K.; Maso, V.; Junior, G.C.F.; Nowill, A.E.; Filho, P.L.; Vassallo, J.; Saad, S.T.O. Antitumor activities of Quercetin and Green Tea in xenografts of human leukemia HL60 cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Wang, F.-M.; Kong, L.-D. Quercetin and Allopurinol Ameliorate Kidney Injury in STZ-Treated Rats with Regulation of Renal NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Lipid Accumulation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; De Ferranti, S.; Després, J.P.; Fullerton, H.J.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2016 update a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 133, e38–e48. [Google Scholar]
- Shishodia, S. Molecular mechanisms of curcumin action: Gene expression. BioFactors 2013, 39, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.-M.; Zhang, G.-L. Novel Neolignan from Penthorum chinense. J. Integr. Plant. Biol. 2007, 49, 1611–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, H.L.; Chen, X.Q.; Wu, X.; Zhang, D.Y. A new flavanone from the aerial parts of Penthorum chinense. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirii, H.; Niwa, T.; Yamada, Y.; Wada, H.; Saito, K.; Iwakura, Y.; Asano, M.; Moriwaki, H.; Seishima, M. Lack of Interleukin-1β Decreases the Severity of Atherosclerosis in ApoE-Deficient Mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razani, B.; Feng, C.; Coleman, T.; Emanuel, R.; Wen, H.; Hwang, S.; Ting, J.P.; Virgin, H.W.; Kastan, M.B.; Semenkovich, C.F. Autophagy links inflammasomes to atherosclerotic progression. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, N.; Zu, G.; Li, Z.; Zhou, J.; Gao, D.; Lv, L.; Tian, X.; et al. New insights into salvianolic acid A action: Regulation of the TXNIP/NLRP3 and TXNIP/ChREBP pathways ameliorates HFD-induced NAFLD in rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.P.; Zhang, H.; Xie, Y.M.; Zeng, X.B.; Hu, J.; Zhuang, Y. Analysis of salvianolate injection combined with usual drugs in treatment of coronary heart disease in real world. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi 2013, 38, 3186–3189. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Buriner, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; De Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension|European Heart Journal|Oxford Academic. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Cheng, T.H.; Shih, N.L.; Liu, J.C.; Chen, J.J.; Hong, H.J.; Chan, P. Tanshinone IIA Induces Heme Oxygenase 1 Expression and Inhibits Cyclic Strain-Induced Interleukin 8 Expression in Vascular Endothelial Cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2016, 44, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.C.; Yu, Y.B.; Lee, J.H. Isolation of steroids and flavonoids from the herb of Oenanthe javanica Dc. Korean J. Pharmacogn. 1993, 24, 244–246. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, G.; Yao, X.; Zang, Z.; Huang, Z. Antiarrhythmic effect of Oenanthe javanica (Bl.) DC. injection. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 1990, 15, 429–431. [Google Scholar]
- Xin-Bo, Y.; Zheng-Ming, H.; Wen-Bin, C.; Ming, Z.; Hong-Yan, C.; Jing-Zhen, Z. Antidiabetic effect of Oenanthe javanica flavone. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2000, 21, 239–242. [Google Scholar]
- Ku, S.K.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.M.; Bae, J.S. Antithrombotic and profibrinolytic activities of isorhamnetin-3-O-galactoside and hyperoside. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.M.; Soleas, G.J.; Levesque, M. Moderate alcohol consumption: The gentle face of janus. Clin. Biochem. 1999, 32, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, P.M.; Forrest, L.L.; Spouge, J.L.; Hajibabaei, M.; Ratnasingham, S.; van der Bank, M.; Chase, M.W.; Cowan, R.S.; Erickson, D.L.; Fazekas, A.J.; et al. A DNA barcode for land plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12794–12797. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnefont-Rousselot, D. Resveratrol and cardiovascular diseases. Nutrients 2016, 8, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.X.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.Q.; Mao, Q.; Wei, X.L.; Wen, X.D.; Wang, Q. Triterpenoid-rich fraction from ilex hainanensis merr. attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by high fat diet in rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2013, 41, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Tang, L. Roles of the NLRP3 inflammasome in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 114, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.-Q.; Wu, W.-Y.; Jiao, R.-Q.; Gu, T.-T.; Xu, Q.; Pan, Y.; Kong, L.-D. Curcumin and allopurinol ameliorate fructose-induced hepatic inflammation in rats via miR-200a-mediated TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 137, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Luo, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, X.; Li, A.; Li, J.; Liu, K.; Liu, B. Ginsenoside Rb1 and compound K improve insulin signaling and inhibit ER stress-associated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in adipose tissue. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 40, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, H.; Ahad, A.; Iqbal, J.; Siddiqui, W.A. Pharmacological potential of tocotrienols: A review. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samra, Y.A.; Said, H.S.; Elsherbiny, N.M.; Liou, G.I.; El-Shishtawy, M.M.; Eissa, L.A. Cepharanthine and Piperine ameliorate diabetic nephropathy in rats: Role of NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome. Life Sci. 2016, 157, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Yin, N.; Liu, W.; Cui, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, E. Curcumin Ameliorates Diabetic Nephropathy by Suppressing NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abderrazak, A.; El Hadri, K.; Bosc, E.; Blondeau, B.; Slimane, M.-N.; Buchele, B.; Simmet, T.; Couchie, D.; Rouis, M. Inhibition of the Inflammasome NLRP3 by Arglabin Attenuates Inflammation, Protects Pancreatic β-Cells from Apoptosis, and Prevents Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Development in ApoE2Ki Mice on a Chronic High-Fat Diet. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 357, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Liu, K.; Huang, F.; Liu, B. Metformin and resveratrol inhibit Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission and prevent ER stress-associated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the adipose tissue of diabetic mice. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 434, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Lu, Q.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Zheng, Z. Vitamin D 3 Protects against Diabetic Retinopathy by Inhibiting High-Glucose-Induced Activation of the ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Song, J.; Hou, F.; Ma, X.; Liu, B.; Huang, F. Mangiferin suppresses endoplasmic reticulum stress in perivascular adipose tissue and prevents insulin resistance in the endothelium. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Yang, Q.; Chen, J.; Yu, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, W.; Chen, M. Salvianolic Acid A Ameliorates Early-Stage Atherosclerosis Development by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats. Molecules 2020, 25, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalitha, N.; Sadashivaiah, B.; Ramaprasad, T.R.; Singh, S.A. Anti-hyperglycemic activity of myricetin, through inhibition of DPP-4 and enhanced GLP-1 levels, is attenuated by co-ingestion with lectin-rich protein. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.-J.; Kang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Liang, X.; García, M.P.G.; Rodgers, D.; Kagel, D.R.; Du, M. Red raspberries suppress NLRP3 inflammasome and attenuate metabolic abnormalities in diet-induced obese mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 53, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Yang, H.; Deng, J.; Fan, D. Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg5 against kidney injury via inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and the MAPK signaling pathway in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 155, 104746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eo, H.; Lee, H.-J.; Lim, Y. Ameliorative effect of dietary genistein on diabetes induced hyper-inflammation and oxidative stress during early stage of wound healing in alloxan induced diabetic mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Ding, X.-Q.; Pan, Y.; Gu, T.-T.; Wang, M.-X.; Liu, Y.-L.; Wang, F.-M.; Wang, S.-J.; Kong, L.-D. Quercetin and allopurinol reduce liver thioredoxin-interacting protein to alleviate inflammation and lipid accumulation in diabetic rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 1352–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbis, A.; Perdreau, S.; Vincent-Baudry, S.; Charbonnier, M.; Bernard, M.-C.; Raccah, D.; Senft, M.; Lorec, A.-M.; Defoort, C.; Portugal, H.; et al. Glycemic and insulinemic meal responses modulate postprandial hepatic and intestinal lipoprotein accumulation in obese, insulin-resistant subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Shah, G.; Singh, S.; Gohil, P.; Chauhan, K.; Shah, K.; Chorawala, M. Effect of piperine in the regulation of obesity-induced dyslipidemia in high-fat diet rats. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2011, 43, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Su, M.; Zhou, F. Mangiferin inhibits hippocampal NLRP3 inflammasome and exerts antidepressant effects in a chronic mild stress mice model. Behav. Pharmacol. 2017, 28, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcocer-Gómez, E.; Casas-Barquero, N.; Williams, M.R.; Romero-Guillena, S.L.; Cañadas-Lozano, D.; Bullón, P.; Sánchez-Alcazar, J.A.; Navarro-Pando, J.M.; Cordero, M.D. Antidepressants induce autophagy dependent-NLRP3-inflammasome inhibition in Major depressive disorder. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 121, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, X.; Qin, T.; Qu, R.; Ma, S. Apigenin ameliorates chronic mild stress-induced depressive behavior by inhibiting interleukin-1β production and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the rat brain. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 296, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, D.; Xie, Q.; Yi, W.; Gupta, S.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Deng, X. Resveratrol Protects against Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy and Inhibits the NLRP3/IL-1 β Axis in Microglia. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, R.; Wang, X.; Fu, Q.; Ma, S. Umbelliferone ameliorates cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury via upregulating the PPAR gamma expression and suppressing TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 600, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; He, Q.; Zheng, J.; Li, L.Y.; Hou, Y.H.; Song, F.Z. Sulforaphane improves outcomes and slows cerebral ischemic/reperfusion injury via inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 45, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, Z.; Wei, X.; Han, H.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W.; Li, F.; Xin, T.; Pang, Q.; et al. NLRP3 deficiency ameliorates neurovascular damage in experimental ischemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, H.; Fang, F.; Deng, X.; Ma, S. Astragaloside IV attenuates cognitive impairments induced by transient cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in mice via anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 639, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Jiang, N.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Yin, M.; Ma, X.; Zhou, K.; Qi, J.; Yu, B.; et al. Ruscogenin attenuates cerebral ischemia-induced blood-brain barrier dysfunction by suppressing TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation and the MAPK pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Cai, Q.; Lu, D.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, T.; Chen, H. The neuroprotection of Sinomenine against ischemic stroke in mice by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome via AMPK signaling. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 40, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jiang, L.; Che, F.; Lu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wang, H. Arctigenin attenuates ischemic stroke via SIRT1-dependent inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Li, L.; Zhao, J. Resveratrol alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation through Sirt1-dependent autophagy induction. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 50, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Fu, Q.; Ma, S. Curcumin attenuates glutamate neurotoxicity in the hippocampus by suppression of ER stress-associated TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation in a manner dependent on AMPK. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 286, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Xue, J.; Yu, J.; Kang, N.; Wang, X. Chrysophanol Inhibits NALP3 Inflammasome Activation and Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion in Mice. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhang, B.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, D.; Huang, R.; Li, W.; Li, W. Ginsenoside Rg1 protects against neuronal degeneration induced by chronic dexamethasone treatment by inhibiting NLRP-1 inflammasomes in mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, T.; Wang, D.; Yang, L.; Xu, J.; Yanagita, T.; Xue, C.; Chang, Y.; Wang, Y. Effects of Astaxanthin and Docosahexaenoic-Acid-Acylated Astaxanthin on Alzheimer’s Disease in APP/PS1 Double-Transgenic Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 4948–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, V.G.; das Graças Carvalho, M.; Caramelli, P.; de Sousa, L.P.; Gomes, K.B. Resolution of inflammation, n-3 fatty acid supplementation and Alzheimer disease: A narrative review. J. Neuroimmunol. 2017, 310, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, M.T.; Sceneay, J.; Paget, C.; Wong, C.S.F.; Duret, H.; Tschopp, J.; Moller, A.; Smyth, M.J. NLRP3 Suppresses NK Cell-Mediated Responses to Carcinogen-Induced Tumors and Metastases. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 5721–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cătană, C.-S.; Atanasov, A.G.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Natural products with anti-aging potential: Affected targets and molecular mechanisms. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1649–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhang, J.-J.; Lin, J.-H.; Yen, G.-C. Beneficial Properties of Phytochemicals on NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Gout and Complication. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, L.Z.; Liu, W.; Luo, Y.; Okamoto, M.; Qu, D.; Dunn, J.H.; Fujita, M. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses melanoma growth by inhibiting inflammasome and IL-1β secretion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 414, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.-Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Jeong, H.-J.; Kim, S.-Y.; Shin, T.-Y.; Um, J.-Y.; Hong, S.-H.; Kim, H.-M. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Inhibits Secretion of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-8 through the Attenuation of ERK and NF-κB in HMC-1 Cells. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2007, 142, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.-Y.; Ka, S.-M.; Chang, J.-M.; Chen, H.-C.; Shui, H.-A.; Li, C.-Y.; Hua, K.-F.; Chang, W.-L.; Huang, J.-J.; Yang, S.-S.; et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate prevents lupus nephritis development in mice via enhancing the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway and inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, D.; Yano, S.; Yamada, K.; Tachibana, H. Green Tea Polyphenol Epigallocatechin-3-gallate Signaling Pathway through 67-kDa Laminin Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 3050–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, D.; Li, M.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, W.; Shan, Q. Luteoloside Suppresses Proliferation and Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, T.; Chen, K.; Xia, Y.; Dai, W.; Xu, S.; Xu, L.; Wang, F.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; et al. Isorhamnetin: A hepatoprotective flavonoid inhibits apoptosis and autophagy via P38/PPAR-α pathway in mice. BioMed Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M.; Thompson, J.K.; MacPherson, M.B.; Beuschel, S.L.; Westbom, C.M.; Sayan, M.; Shukla, A. Curcumin: A Double Hit on Malignant Mesothelioma. Cancer Prev. Res. 2014, 7, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, M.; Fan, X.; Yuan, B.; Takagi, N.; Liu, S.; Han, X.; Ren, J.; Liu, J. Berberine inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome pathway in human triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cell. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, J.-F.; Mei, Q.-B.; Zhou, X.-G.; Tang, Y.; Xiong, R.; Qiu, W.-Q.; Pan, R.; Law, B.Y.-K.; Wong, V.K.-W.; Yu, C.-L.; et al. Polyphyllin VI Induces Caspase-1-Mediated Pyroptosis via the Induction of ROS/NF-κB/NLRP3/GSDMD Signal Axis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhuan, B.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, Z. Huaier extract suppresses non-small cell lung cancer progression through activating NLRP3-dependent pyroptosis. Anat. Rec. 2019, ar.24307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, E.; Tuguzbaeva, G.; Chen, X.; Qin, Y.; Li, A.; Sun, X.; Dong, C.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zahra, S.M.; et al. Anthocyanin is involved in the activation of pyroptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Phytomedicine 2019, 56, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, A.; de Rosny, C.; Kieu, T.-L.-V.; Perrey, S.; Berger, H.; Fluckiger, A.; Muller, T.; Pais de Barros, J.-P.; Pichon, L.; Hichami, A.; et al. Docosahexaenoic acid inhibits both NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and JNK-mediated mature IL-1β secretion in 5-fluorouracil-treated MDSC: Implication in cancer treatment. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuldashev, M.P. Cynaroside content of the plants Ferula varia and F. foetida. Chem. Nat. Compd. 1997, 33, 597–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Kitts, D.D. Luteolin and luteolin-7-O-glucoside from dandelion flower suppress iNOS and COX-2 in RAW264.7 cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 265, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Sun, G.; Wang, M.; Xiao, J.; Sun, X. Protective effects of cynaroside against H2O2-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyoblasts. J. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 112, 2019–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Li, S.; Wang, W.; Hong, Y.; Tang, K.; Luo, Q. Screening and identification of the antibacterial bioactive compounds from Lonicera japonica Thunb. leaves. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Nutraceutical Compound | Classification/Source | Overall Role in Inflammasomes | Experimental Model | Molecular Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apigenin | Flavonoid/Citrus fruits, vegetables | NLRP3, AIM2 inhibitor | -Human THP1 cells -Mouse J774A.1 macrophage -HEK-293 cells | 1. Syk/Pyk2 pathway interruption 2. Inhibits ERK1/2 and NFϏβ activation in macrophages 3. Inhibits oligomerization of ASC and interferes with its assembly in the cytoplasm 4. No activation of caspase 1 | [30,36] |
| Parthenolide | Sesquiterpene lactone/Tanacetum parthenium (L.) Sch. Bip. | NLRP3, NALP1, NLRC4 inhibitor | -LPS-induced inflammation in NG5 cell line mouse bone marrow cells | 1. Inhibits NFϏβ 2. Inhibits oligomerization and ASC recruitments 3. Inhibits NLRP3 and caspase 1 | [40] |
| Scropoloside B | Iridoids glycosides/Scrophularia dentata Royle ex Benth. | NLRP3 inhibitor | -HEK293 cells -Human THP1 cells | 1. Inhibits NFϏβ 2. Decreases the expression of NLRP3 and Il-1β | [32] |
| Catapol | Iridoids glycosides/Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) Libosch. ex Fisch. & C.A. Mey | NLRP3 inhibitor | -HEK293 cells -Human THP1 cells | 1.Decreases the expression of NLRP3 | [32] |
| Rh1 and Rg3 | Ginsenoside/Panax ginseng C.A.Mey. | NLRP3, AIM2 inhibitor | -LPS-induced inflammation in bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) and THP-1 cells -LPS-induced inflammation in Male C57BL/6 mice (8-week-old) | 1.Inhibits the NLRP3 and AIM2 expression 2.Inhibits ASC pyroptosome formation 3.Inhibits caspase 1 activation and the secretion of IL-1 | [41] |
| DHA | ω-3FAs/Fish, Crustaceans, Molluscs, Eggs | NLRP3, NLRPb1 inhibitor | -Mouse model -Human THP1 cells | 1. Decreases the expression of genes involved in the inflammatory pathways of NFϏβ 2. Inhibits the activation of caspase 1 and the release of IL-1β | [33] |
| PSPC | Flavonoid/Fruits, vegetables, leaves and grains | NLRP3 inhibitor | -Male ICR mice -HUVECs | 1. Suppress ROS level 2. Downregulation of pro-caspase1 | [34] |
| Quercetin | Flavonoids/Fruits, vegetables, leaves, and grains | NLRP3, AIM2 inhibitor | -Vasculitis model in C57BL/6 mice | 1. Impaired expression of caspase-1 and IL-1β 2. Prevention of ASC oligomerization | [42] |
| Puerarin and Troxerutin | Isoflavone/Root of Pueraria lobata (Willd.) Ohwi Flavonoid/Sophora japonica L. | NLRP3 inhibitor | -HUVECs cells | 1. Decreases NLPR3, Il-1B and casapase-1 levels | [34] |
| Genipin | Iridoids glycosides/Gardenia jasminoides J.Ellis | NLRP3, NLRC4 inhibitor | -Mouse model -BMDMs cells | 1. Inhibits NLRP3 and NLRC4 inflammasomes 2. Decreases Il-1β, caspase-1 and ASC protein levels | [43] |
| Gypenoside | Triterpenoid saponin/Gynostemma pentaphylla (Thunb.) Makino | NLRP3 inhibitor | -H9C2 cells -SD rats | 1. Inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome 2. Decreases Il-1β and IL-18 protein levels | [44] |
| Morroniside | Iridoid glycoside/Cornus officinalis Siebold & Zucc. | NLRP3 inhibitor | -SD rats | 1. Inhibits NLRP3 2. Downregulation of ASC, caspase-3, Il-1β and IL-18 | [45] |
| Isorhamnetin and Hyperoside | Flavonoids/Water dropwort Oenanthe javanica (Blume) DC. | NLPR3, AIM-2 inhibitor | -Bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) form C57BL/6 mice -THP1 cells | 1.Decreases the of Il-1β, IL-18 and caspase-1 secretion | [46] |
| Resveratrol | Stilbene (flavonoid)/Skin of grapes, blueberries, raspberries, cmulberries and red wine | NLRP3 inhibitor | -J774A.1 cells -Raw 264.7 cells -Sprague–Dawley rat | 1. Decreases the secretion of Il-1β 2. Decreases the ACS and NLRP3 proteins 1. Suppresses NFϏβ and inhibits NLRP3 1.Supresses IL-1β and IL-18 2.Decreases NLRP3 and caspase-1 expression | [47] [48] [49] |
| Curcumin | Polyphenol/Curcuma longa L. roots | NLRP3 inhibitor | -THP1 cells -PMA-induced macrophages | 1. Decreases NLRP3 expression and Il-1β and caspase 1 secretion through the inhibition of TLR4/MyD88/ NFϏβ signalling and P2X7R expression | [50] |
| Thonningianin A | Polyphenol/Penthorum chinense Pursh | NLRP3 inhibitor | -ApoE-KO mice | 1. Decreases NLRP3 and Il-1β expression | [51] |
| Salvianolato | Polyphenol/Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge | NLRP3 inhibitor | -SPF Sprague-Dawley rats | 1. Decreases NLRP3, pro-caspase1, caspase-1, Il-1β, IL-18 and TXNIP expression | [52] |
| Ilexgenin A | Triterpenoid/Ilex hainanensis Merr. | NLRP3 inhibitor | -EA.hy-926 cells -Primary rat vascular endothelial cells (VECs) | 1. Decreases the TXNIP/NLRP3 activation under ER stress condition | [53] |
| Tanshinone IIA and sodium tanshinone IIA | Diterpenoid/Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge | NLRP3 inhibitor | -RAW264.7 macrophages -Beagle dogs | 1. Decreases IL-1β levels 1. Inhibits the generation of ROS and TXNIP 2. Decreases the NLRP3 activation and the secretion of IL1-β and IL-18 | [54] [55] |
| Dihydromyricetin | Flavonoid/Ampelopsis grossedentata (Hand.-Mazz.) W.T.Wang | NLRP3 inhibitor | -HUVECs | 1. Attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome | [56] |
| Luteolin | Flavonoid/Reseda luteola L. | NLRP3 inhibitor | -RAW264.7 cells | 1. Inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome 2. Decreases TNF-α and IL-6 levels | [57] |
| Colchicine | Alkaloid/Colchicum autumnale L. | NLRP3 inhibitor | -ACS patients | 1. Suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome 2. Decreases Il-1β, IL-6 and IL-18 levels | [58] |
| Triptolide | Diterpenoid/Tripterygiumwilfordii Hook F. | NLRP3 inhibitor | -C57/BL6 mice | 1. Inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome 2. Inhibits IL-1β, IL-18, MCP-1 and VCAM-1 release | [59] |
| Total flavones | Flavonoids/Abelmoschus manihot (L.) Medic | NLRP3 inhibitor | -I/R Rats | 1. Inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome 2. Decreases the IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α levels | [60] |
| Umbelliferone | Phenolic coumarin/Rutaceae and Umbelliferae | NLRP3 inhibitor | -Sprague-Dawley rats | 1. Inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome and IL-6 and TNF-α levels | [61] |
| Nutraceutical Compound | Classification/Source | Overall Role in Inflammasomes | Experimental Model | Molecular Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ginsenoside Rb1 and Ginsenoside CK | Triterpene saponins/Panax ginseng C.A.Mey. root | NLRP3 inhibitor | -3T3-L1 adipocyte cells -Mouse model | 1. Inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome 2. Attenuation of TXNIP expression 3. Reduction in IL-1β expression 4. Reduction in IRS-1 phosphorylation and PI3K and AKT activation | [92] |
| γ-Tocotrienol | Isomers unsaturated Vitamin E/Fruits, vegetables, nuts, meats, cooking oils and some grains | NLRP3 inhibitor | -Mouse model of type 2 diabetes | 1. Inhibits NFϏβ 2. Inhibits NLRP3 activation | [93] |
| DHA | Omega 3 Fatty acids (ω-3FAs)/Animal and plant origin | NLRP3, NLRP1b inhibitor | -Human THP1 cells -Mouse model | 1. Decreases the expression of genes involved in the NFϏβ inflammatory pathways 2. Inhibits caspase1 activation and thus inhibits IL-1β release | [33] |
| PiperineCepharanthine | Alkaloid/Black pepper/Stephania cepharantha “Hayata” | NLRP3 inhibitor | -Diabetic nephropathy model in adult male (SD rats) | 1. Decreases the levels of oxidative stress and activation of NFKβ 2. Decreases levels of TXNIP and NLRP3 mRNA and proteins in kidney tissues 3. Increase insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-1) | [94] |
| Curcumin | Flavonoid/Curcuma longa L. | NLRP3 inhibitor | -C57BL/KsJ db/db (diabetic) mice model HK-2 cells | 1. Decreases the NLRP3 i, capase1 and IL-1B expression | [95] |
| Arglabin | Sesquiterpene lactone/Artemisia glabella Kar. & Kir. | NLRP3 inhibitor | -INS-1 cells -ApoE2Ki mice | 1. Degrading NLRP3 and pro-IL-1β, pro-caspase 1 and ASC | [96] |
| Resveratrol | Stilbene/Skin of grapes, blueberries, raspberries and mulberries | NLRP3 inhibitor | -3T3-L1 adipocytes -Streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice (ICR male mice) | 1. Decreases TXNIP levels and inhibits cleavage caspase-1 induction 2. Reduced release of IL-1β | [97] |
| Vitamin D3 | Cholecalciferol/Fish, beef, cheese, egg yolk | NLRP3 inhibitor | -HRMECs -Streptozotocin-induced SD rats | 1. Decreases the TXNIP levels 2. Decreases NLRP3 activation | [98] |
| Mangiferin | Naturally occurring glucosylxanthone/Mango | NLRP3 inhibitor | -Perivascular adipose tissue isolated from male SD rats and from high-fat diet feeding in mice | 1. Decreased levels of TXNIP and inhibition of cleaved caspase-1induction 2. Reduced release of IL-1β | [99] |
| Salvianolic acid A | Propanoic acid/Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge | NLRP3 inhibitor | -Male Zucker diabetic fatty rats | 1. Inhibits NFϏβ 2. Inhibits NLRP3 activation | [100] |
| Myricetin | Flavonoid/Horsegram seed coat (Macrotyloma uniflorum (Lam.) Verdc.) | NLRP3 inhibitor | -Streptozotocin-induced diabetic male Wistar rats | 1. Decreases the expression of NLRP3, ASC and Caspase-1 | [101] |
| Polyphenols | Polyphenol/Freeze-dried red raspberry | NLRP3 inhibitor | -High-fat diet feeding C57BL/6 mice | 1. Decreases NLRP3 and caspase-1 levels 2. Decreases IL-1β and IL-18 production | [102] |
| Ginsenoside Rg5 | Ginsenoside/Panax ginseng C.A.Mey. | NLRP3 inhibitor | -High-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice (C57BL/6 mice) | 1. Decreases the expression of NLRP3, ASC and Caspase-1 2. Decreases the expression of IL-1β and IL-18 3. Decreases of NFϏβ and P38 MAPK phosphorylation | [103] |
| Genistein | Isoflavone/Legumes | NLRP3 activator | -Alloxan-induced diabetic ICR mice | 1. Restored expression levels of NLRP3, ASC and Caspase-1 2. Improves the levels of NF-Ϗβ, NFϏβ, TNFα COX2 and iNOS | [104] |
| Curcumin+Allopurinol | Flavonoid/Curcuma longa L. | NLRP3 inhibitor | -BRL-3A cells and -Human HepG2 cells exposed to high fructose -Fructose-fed rat (Male SD rats) | 1. Decreases overexpression of TXNIP via up-regulating miR-200a | [91] |
| Quercetin+Allopurinol | Flavonoid/Found in many fruits, vegetables, leaves and grains | NLRP3 inhibitor | -BRL-3A and -Human HepG2 exposed to high glucose -Streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats (Male SD rats) | 1. Decreases overexpression of TXNIP 2. Reduces expression of IL-1β 3. Modulates the expression of proteins involved in lipid metabolism | [105] |
| Nutraceutical Compound | Classification/Source | Overall Role in Inflammasomes | Experimental Model | Molecular Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magniferin | Poliphenol of C-glucosylxanthone/Mangifera indica L. (Mango tree) | NLRP3 inhibitor | -CMS in mice | 1. Inhibits hippocampal NLRP3 inflammasome 2. Inhibits caspase-1/Il-1β axis 3. Decreases the ASC expression 4. Decreases the Il-18 production | [108] |
| Apigenin | Flavone/Citrus fruits, vegetables | NLRP3 inhibitor | -Rat model of chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) | 1. Increases the expression levels of PPARγ 2. Decreases the NLPR3, Il-1B and casapase-1 levels | [110] |
| Resveratrol | Stilbene/Skin of grapes, blueberries, raspberries and mulberries | NLRP3 inhibitor | -C57BL/6 mouse model -Mouse BV2 cells -MCAO-injury rats | 1. Decreases the NLRP3 generation via activation of SIRT1 2. Downregulates the level of IL-1β and IL-18 3. Decreases the NFϏβ levels | [111] |
| Umbelliferone | 7-hydroxycoumarin/Plants: Rutaceae and Apiaceae families Carrot, coriander, garden angelica | NLRP3 inhibitor | -Rat model of ischemic reperfusion (SD rats) | 1. Decreases the TXNIP expression 2. Increases the PPARγ levels 3. Inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome | [112] |
| Sulphoraphane | Isothiocyanate/Broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbages | NLRP3 inhibitor | -Brain ischemia/reperfusion injury model in adult male (SD rats) | 1. Suppresses I/R-induced NLRP3 inflammasome expression 2. Downregulation of cleaved caspase-1 3. Reducing IL-1β and IL-18 expression | [113] |
| Curcumin | Pigment from tumeric/Curcuma longa L. | NLRP3 inhibitor | -INS-1 cells -ApoE2Ki mice | 1. Inhibits hippocampal NLRP3 inflammasome 2. Downregulates TXNIP/NLRP3 with the regulation of AMPK activity | [120] |
| Rg1 | Ginsenoside/Panax ginseng C.A. Mey Panax japonicus (T.Nees) C.A. Mey. | NLRP1 inhibitor | -ICR mice | 1. Reduces expression levels of NLRP1, caspase 1 and 5, ASC and IL-1β and IL-18 2. Increases expression of the glucocorticoid receptors | [122] |
| Astragaloside-IV | Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge | NLRP3 inhibitor | -ICR mice | 1. Attenuates NLRP3 2. Decreases IL-1β and TNF-α levels 3. Decreases NFϏβ translation | [115] |
| Ruscogenin | Steroidal sapognin/Ophiopogon japonicus (Thunb.) Ker Gawl | NLRP3 inhibitor | -bEnd.3 cells-C57BL/6J mice | 1. Inhibits NLRP3, IL-1β, caspase-1 and TXNIP expression | [116] |
| Sinomenine | Alkaloid/Sinomenium acutum (Thunb.) Rehder & E.H.Wilson | NLRP3 inhibitor | -MCAO mice model -OGD cell model (Primary mixed glial cells) | 1. Inhibits the NLRP3 via AMPK pathway 2. Inhibits ASC and caspase-1 | [117] |
| Arctigenin | Lignan/Arctium lappa L. | NLRP3 inhibitor | -MCAO-injury rats -OGD-injury EX527 cells | 1. Decreases the NLRP3 generation via activation of SIRT1 2. Downregulates the level of IL-1β and IL-18 | [118] |
| Asthaxantin | Carotenoid/marine organisms, such as crab, salmon, shrimp, krill and microalgae | NLRP3 inhibitor | -PSEN1(APP/PS1) double-transgenic mice | 1. Decreases the ASC expression 2. Reduces the IL-1β and TNF-α levels | [123] |
| Chrysophano | Anthraquinone/Rheum genus | NLRP3 inhibitor | -MCAO Male CD1 mice | 1. Decreases the NLRP3 and ASC expression 2. Reduces the IL-1β and caspase 1 expression | [121] |
| Nutraceutical Compound | Classification/Source | Overall Role in Inflammasomes | Experimental Model | Molecular Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECGC | Phenol/Green tea | NLRP3 inhibitor | -HMC | 1. Inhibitory effect on proliferation 2. Suppresses NFϏβ activity 3. Decreases IL-1β secretion 4. Decreases caspase-1 activation | [128] |
| Luteoloside | Taraxacum officinale (L.) Weber ex F.H.Wigg. and Cynara scolymus L. | NLRP3 inhibitor | -HCC | 1. Inhibition of cell migration and invasion 2. Suppresses proliferation and metastasis 3. Downregulates the expression level of caspase 1 and IL-1β | [132] |
| Isorhamnetin | Flavonoid/Hippophae rhamnoides L. | NLRP3, AIM2 inhibitor | -BMDMs | 1. Downregulates the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines 2. Attenuates the secretion of IL-1β resulting from NLRP3, NLRC4, and AIM2 inflammasome activation | [133] |
| Curcumin | Polyphenol/Curcuma longa L. | NLRP3 activator | -Malignant mesothelioma cells | 1. Activates NLRP3 inflammasome 2. Activates the expression of caspase-1 3. Attenuates the expression of NFϏβ, TLR and IL-1β | [134] |
| Berberine | Alkaloid/Chinese herbs | NLRP3 | -Triple-negative breast MDA-MB-231 cancer cells | 1. Reduces pro-caspase-1, caspase-1, IL-1β, P2X7 and ASC expression | [135] |
| Polyphyllin VI | Saponin/Trillium tschonoskii Maxim. | NLRP3 activator | -Non-Small-Cell Lung A549 and H1299 cancer cells | 1. Activation of caspase-1 via the induction of the ROS/NFϏβ /NLRP3/GSDMD signal axis 2. Upregulates NLRP3 inflammasome | [136] |
| Huaier extract | A kind of fungus/Trametes robiniophila Murr. | NLRP3 activator | -Non-Small-Cell Lung H520 -H358 cancer cells | 1. Upregulates NLRP3 2. Activation of caspase-1, IL-1β, and IL-18 | [137] |
| Anthocyanins | Natural pigment widely found in colored plants | NLRP3 activator | -Oral squamous HaCaT, Tca8113 -SCC15 cancer cells | 1. Upregulates NLRP3 2. Activation of caspase-1 and IL-1β | [138] |
| DHA | ω-3FAs/Fish, Crustaceans, Molluscs, Eggs | NLRP3 | -Myeloid-derived suppressor cells | 1. Reduction in IL-1β secretion, inhibition of JNK pathway through β-arrestin-2 activation | [139] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castejón-Vega, B.; Giampieri, F.; Alvarez-Suarez, J.M. Nutraceutical Compounds Targeting Inflammasomes in Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4829. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144829
Castejón-Vega B, Giampieri F, Alvarez-Suarez JM. Nutraceutical Compounds Targeting Inflammasomes in Human Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(14):4829. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144829
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastejón-Vega, Beatriz, Francesca Giampieri, and José M. Alvarez-Suarez. 2020. "Nutraceutical Compounds Targeting Inflammasomes in Human Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 14: 4829. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144829
APA StyleCastejón-Vega, B., Giampieri, F., & Alvarez-Suarez, J. M. (2020). Nutraceutical Compounds Targeting Inflammasomes in Human Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(14), 4829. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21144829






