Reactions of Plasmodium falciparum Ferredoxin:NADP+ Oxidoreductase with Redox Cycling Xenobiotics: A Mechanistic Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
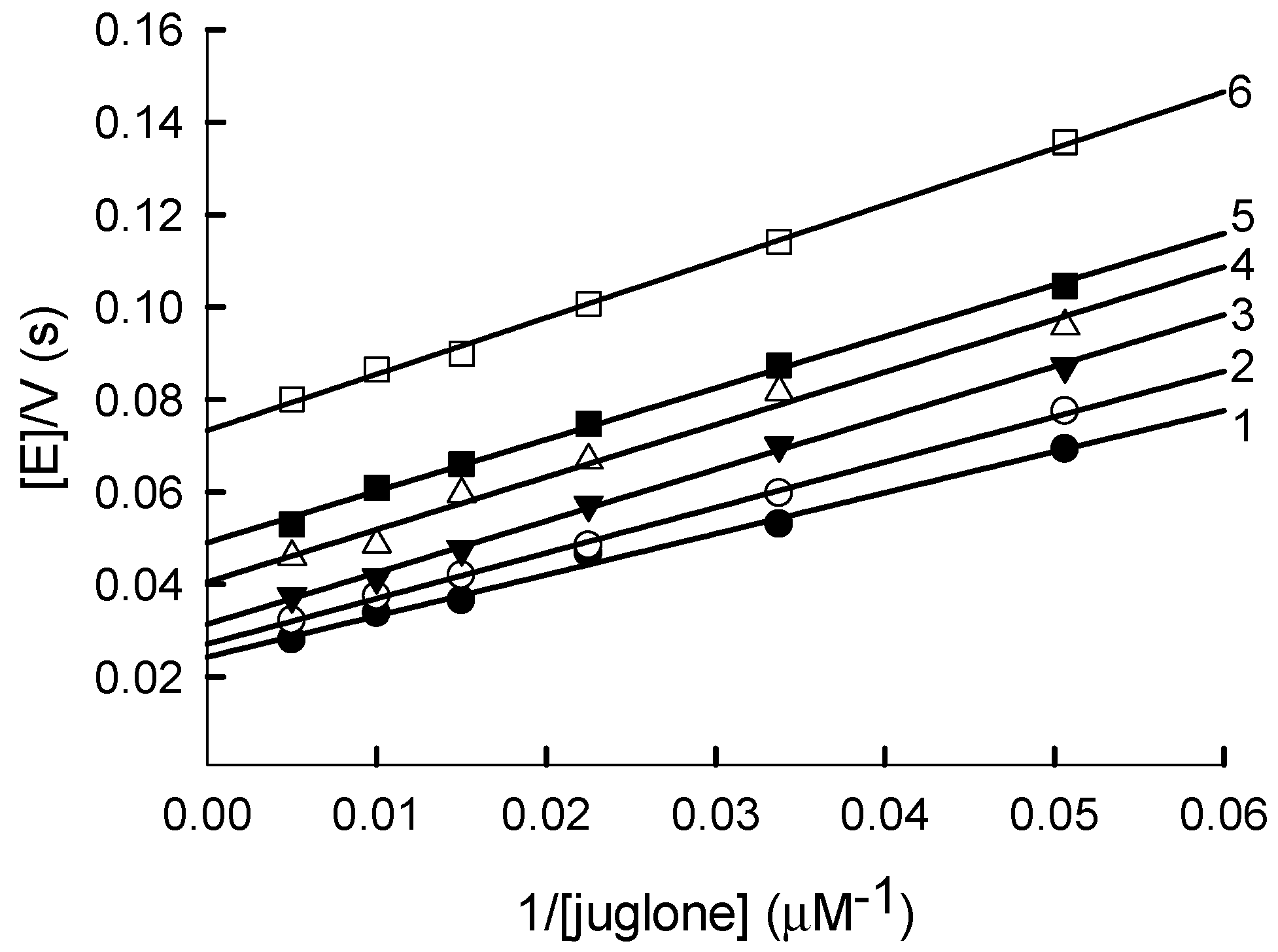
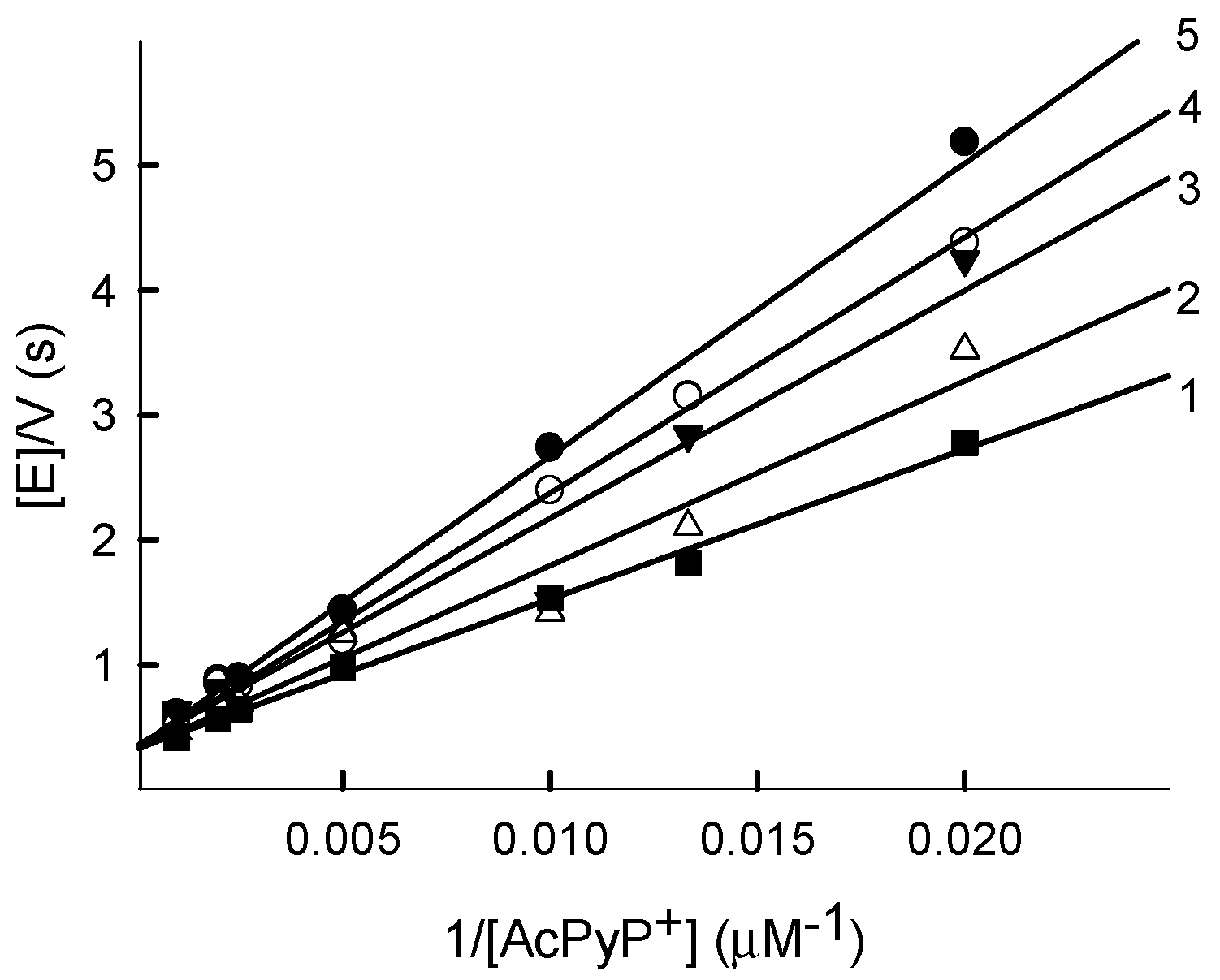
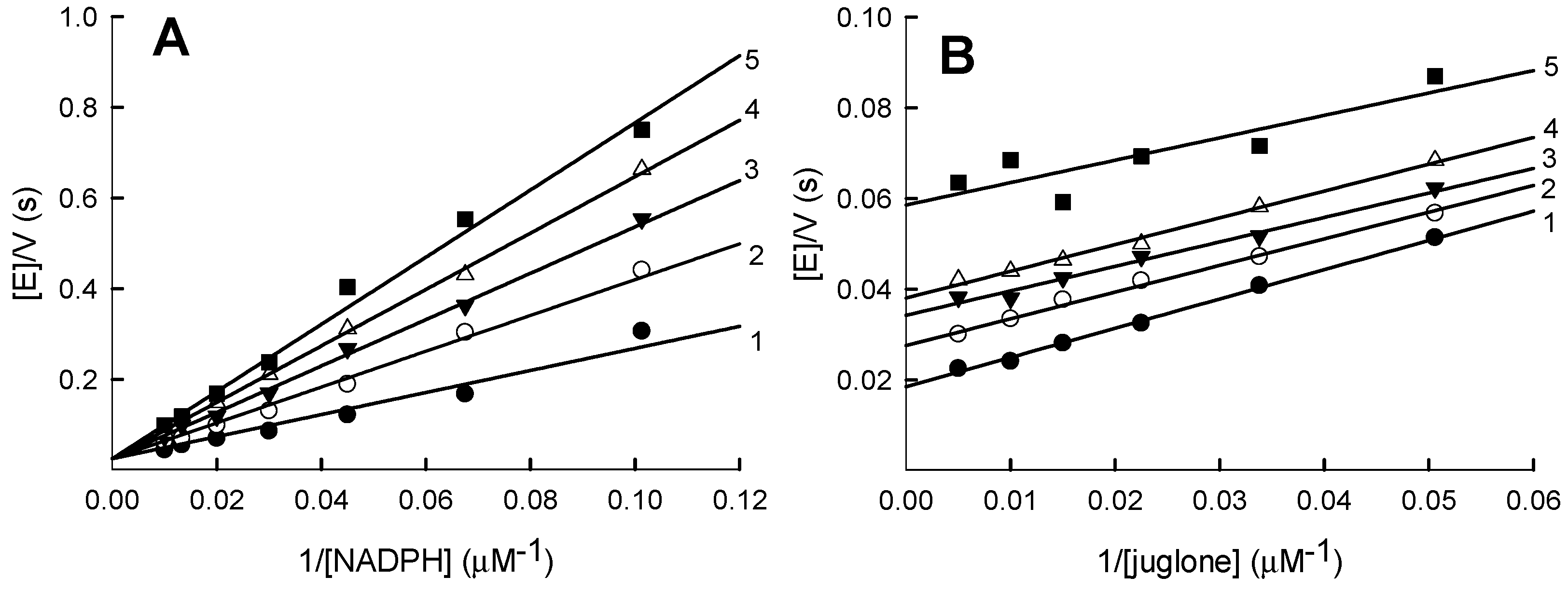
2.1. Steady-State Kinetics and Substrate Specificity Studies of PfFNR
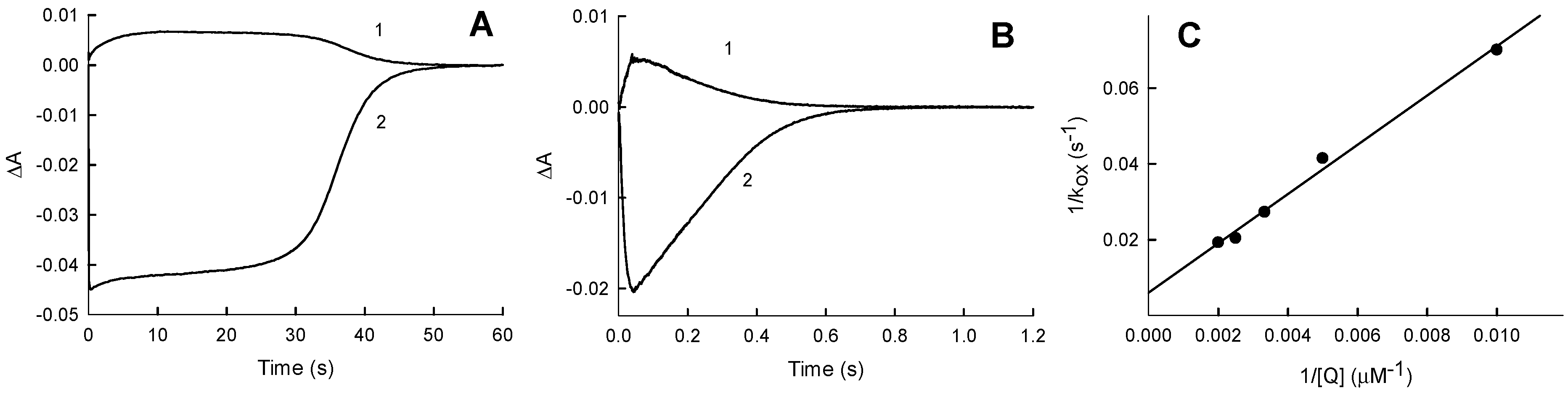
2.2. Kinetics of PfFNR Oxidation under Multiple Turnover Conditions
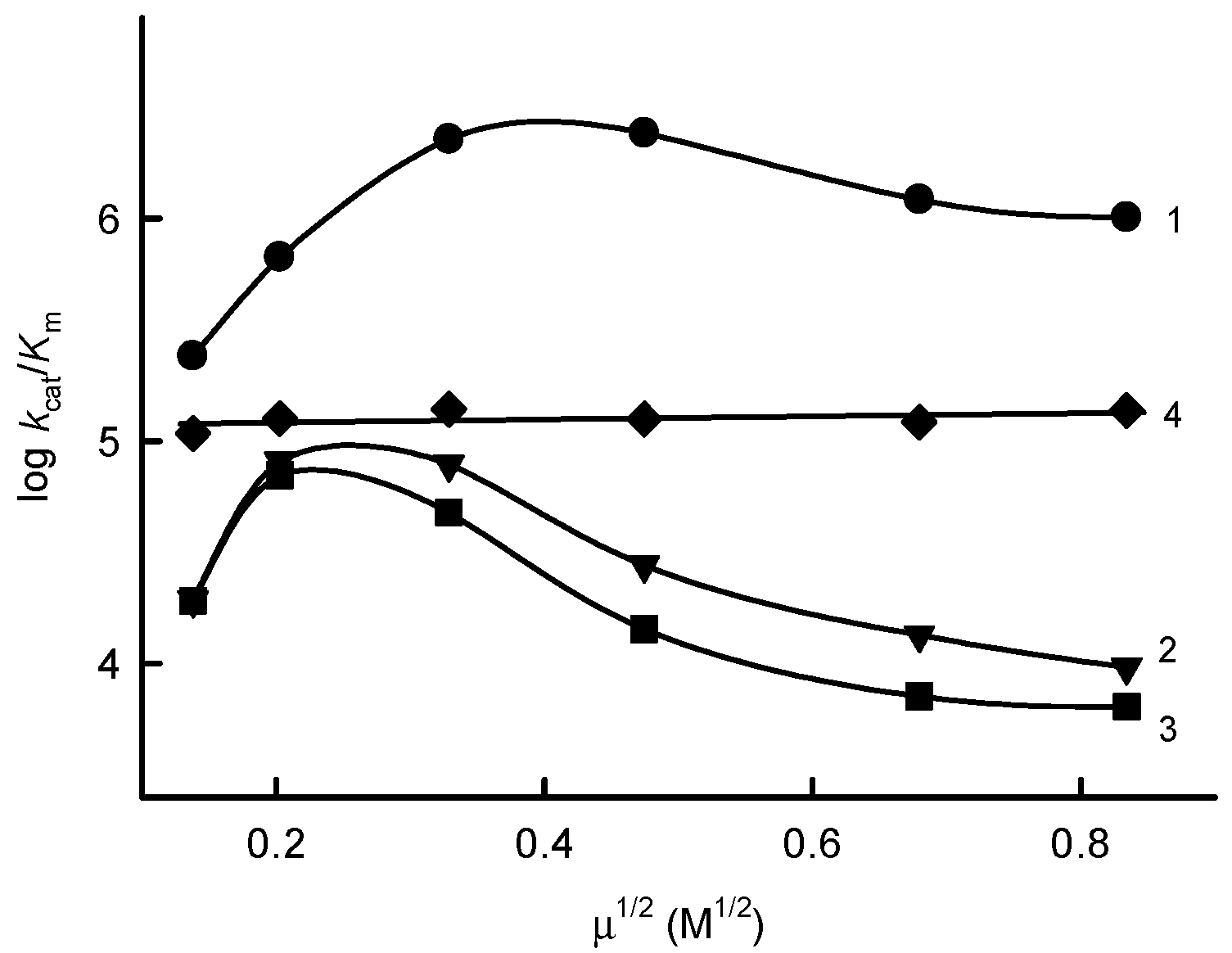
2.3. NADP+ Inhibition Studies
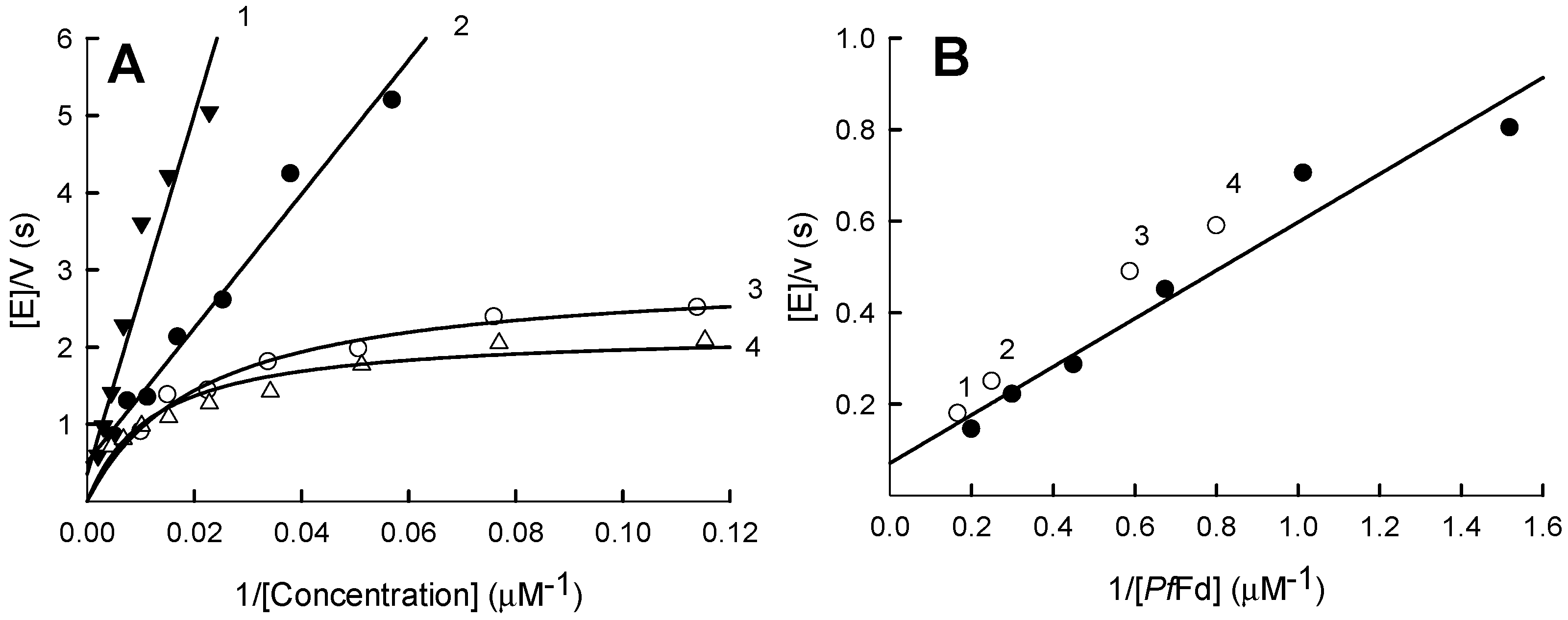
2.4. Stimulation of Quinone- and Nitroreductase Activity of PfFNR by Ferredoxin
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Enzymes and Reagents
4.2. Steady-State Kinetic Studies
4.3. Presteady-State Kinetic Studies
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AcPyP+ | 3-Acetylpyridineadenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| ArNO2 | aromatic nitrocompound |
| ArN→O | aromatic N-oxide |
| E17 | single-electron reduction midpoint potential at pH 7.0 |
| E07 | two-electron (standard) reduction midpoint potential at pH 7.0 |
| Fd | ferredoxin |
| FNR | ferredoxin:NADP+ oxidoreductase |
| kcat | catalytic constant |
| kcat/Km | bimolecular rate constant |
| Q | quinone |
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Bhatt, S.; Weiss, D.J.; Cameron, E.; Bisancia, D.; Mappin, B.; Dalrymple, U.; Battle, K.; Moyes, C.L.; Henry, A.; Eckhoff, P.A.; et al. The effect of malaria control on Plasmodium falciparum in Africa between 2000 and 2015. Nature 2015, 526, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, S. Redox and antioxidant systems of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 1291–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vennerstrom, L.J.; Eaton, J.W. Oxidants, oxidant drugs, and malaria. J. Med. Chem. 1988, 31, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grellier, P.; Šarlauskas, J.; Anusevičius, Ž.; Marozienė, A.; Houeee-Levin, C.; Schrevel, J.; Čėnas, N. Antiplasmodial activity of nitroaromatic and quinoidal compounds: Redox potential vs inhibition of erythrocyte glutathione reductase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 393, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, E.; Lima, L.M.; Bongard, E.; Charnaud, S.; Villar, R.; Solano, B.; Burguete, A.; Perez-Silanes, S.; Aldana, I.; Vivas, L.; et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of 3-phenylquinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxide derivatives as antimalarial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 1903–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grellier, P.; Marozienė, A.; Nivinskas, H.; Šarlauskas, J.; Aliverti, A.; Čėnas, N. Antiplasmodial activity of quinones: Roles of aziridinyl substituents and the inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum glutathione reductase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 494, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, C.; Bandyopadhyay, H. Redox active antiparasitic drugs. Antiox. Redox. Signal. 2012, 17, 555–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiliano, M.; Pabón, A.; Ramirez-Calderon, G.; Barea, C.; Deharo, E.; Galiano, S.; Aldana, I. New hydrazine and hydrazide quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxide derivatives: In silico ADMET, antiplasmodial and antileishmanial activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 1820–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, C.; Besset, T.; Moutet, J.C.; Fayolle, M.; Brückner, M.; Limosin, D.; Becker, K.; Davioud-Charvet, E. The aza-analogues of 1,4-naphthoquinones are potent substrates and inhibitors of plasmodial thioredoxin and glutathione reductases and of human erythrocyte glutathione reductase. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008, 6, 2731–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.K.; Patel, V.; Yang, J.C.; Dvorin, J.D.; Duraisingh, M.T.; Clardy, J.; Wirth, D.F. Type II NADH dehydrogenase of the respiratory chain of Plasmodium falciparum and its inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 972–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marozienė, A.; Lesanavičius, M.; Davioud-Charvet, E.; Aliverti, A.; Grellier, P.; Šarlauskas, J.; Čėnas, N. Antiplasmodial activity of nitroaromatic compounds: Correlation with their reduction potential and inhibitory action on Plasmodium falciparum glutathione reductase. Molecules 2019, 24, 4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čėnas, N.; Anusevičius, Ž.; Bironaitė, D.; Bachmanova, G.I.; Archakov, A.I.; Öllinger, K. The electron transfer reactions of NADPH:cytochrome P450 reductase with nonphysiological oxidants. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1994, 315, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anusevičius, Ž.; Martínez-Júlvez, M.; Genzor, C.G.; Nivinskas, H.; Gómez-Moreno, C.; Čėnas, N. Electron transfer reactions of Anabaena PCC 7119 ferredoxin:NADP+ reductase with nonphysiological oxidants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1997, 1320, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anusevičius, Ž.; Nivinskas, H.; Šarlauskas, J.; Sari, M.A.; Boucher, J.L.; Čėnas, N. Single-electron reduction of quinone and nitroaromatic xenobiotics by recombinant rat neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2013, 60, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermilion, J.L.; Ballou, D.P.; Massey, V.; Coon, M. Separate roles for FMN and FAD in catalysis by liver microsomal NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 266–277. [Google Scholar]
- Batie, C.J.; Kamin, H. Electron transfer by ferredoxin:NADP+ reductase. Rapid-reaction evidence for participation of a ternary complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 11976–11985. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda, H.; Kimura, S.; Iyanagi, T. One-electron reduction of quinones by the neuronal nitric oxide synthase reductase domain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1459, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimata-Ariga, Y.; Kurisu, G.; Kusunoki, M.; Aoki, S.; Sato, D.; Kobayashi, T.; Kita, K.; Horii, T.; Hase, T. Cloning and characterization of ferredoxin and ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase from human malaria parasite. J. Biochem. 2007, 141, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balconi, E.; Pennati, A.; Crobu, D.; Pandini, V.; Cerutti, R.; Zanetti, G.; Aliverti, A. The ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase/ferredoxin electron transfer system of Plasmodium falciparum. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 4249–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, M.; Balconi, E.; Aliverti, A.; Mastrangelo, E.; Seeber, F.; Bolognesi, M.; Zanetti, G. Ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase from Plasmodium falciparum undergoes NADP+-dependent dimerization and inactivation: Functional and crystallographic analysis. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 367, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimata-Ariga, Y.; Yuasa, S.; Saitoh, T.; Fukuyama, H.; Hase, T. Plasmodium-specific basic amino acid residues important for the interaction with ferredoxin on the surface of ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase. J. Biochem. 2018, 164, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardman, P. Reduction potentials of one-electron couples involving free radicals in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1989, 18, 1637–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, M.P.; Gamage, S.A.; Kovacs, M.S.; Pruijn, F.B.; Anderson, R.F.; Patterson, A.V.; Wilson, W.R.; Brown, J.M.; Denny, W.A. Structure-activity relationships of 1,2,4-benzotriazine 1,4-dioxides as hypoxia-selective analogues of tirapazamine. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.F.; Shinde, S.S.; Hay, M.P.; Denny, W.A. Potentiation of the cytotoxicity of the anticancer agent tirapazamine by benzotriazine N-oxides: The role of redox equilibria. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breccia, A.; Busi, F.; Gattavechia, E.; Tamba, M. Reactivity of nitro-thiophene derivatives with electron and oxygen radicals studied by pulse radiolysis and polarographic techniques. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 1990, 29, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, P.J. Molecular mechanisms of quinone cytotoxicity. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1991, 80, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chance, B. A simple relationship for a calculation of the “on” velocity constant in enzyme reactions. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1957, 71, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crobu, D.; Canevari, G.; Milani, M.; Pandini, V.; Vanoni, M.A.; Bolognesi, M.; Zanetti, G.; Aliverti, A. Plasmodium falciparum ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase His286 plays a dual role in NADP(H) binding and catalysis. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 9525–9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroni, S.; Pandini, V.; Vanoni, M.A.; Aliverti, A. A single tyrosine hydroxyl group almost entirely controls the NADPH specificity of Plasmodium falciparum ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase. Biochemistry 2011, 51, 3819–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anusevičius, Ž.; Misevičienė, L.; Medina, M.; Martinez-Julvez, M.; Gomez-Moreno, C.; Čėnas, N. FAD semiquinone stability regulates single- and two-electron reduction of quinones by Anabaena PCC7119 ferredoxin:NADP+ reductase and its Glu301Ala mutant. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 437, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiauga, B.; Williams, E.M.; Ackerley, D.F.; Čėnas, N. Reduction of quinones and nitroaromatic compounds by Escherichia coli nitroreductase A (NfsA): Characterization of kinetics and substrate specificity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 614, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, V.; Matthews, R.G.; Foust, G.P.; Howell, L.G.; Williams, C.H., Jr.; Zanetti, G.; Ronchi, S. A new intermediate in TPNH-linked flavoproteins. In Pyridine Nucleotide-Dependent Dehydrogenases; Sund, H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1970; pp. 393–411. [Google Scholar]
- Corrado, M.E.; Aliverti, A.; Zanetti, G.; Mayhew, S.G. Analysis of the oxidation-reduction potentials of recombinant ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase from spinach chloroplasts. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 239, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, M.; Martínez-Júlvez, M.; Hurley, J.K.; Tollin, G.; Gómez-Moreno, C. Involvement of glutamic acid 301 in the catalytic mechanism of ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase from Anabaena PCC 7119. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 2715–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, R.; Sutin, N. Electron transfers in chemistry and biology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1985, 811, 265–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardman, P.; Dennis, M.F.; Everett, S.A.; Patel, K.B.; Stratford, M.R.; Tracy, M. Radicals from one-electron reduction of nitro compounds, aromatic N-oxides and quinones: The kinetic basis for hypoxia-selectve, bioreductive drugs. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 1995, 61, 171–194. [Google Scholar]
- Nemeikaitė-Čėnienė, A.; Šarlauskas, J.; Jonušienė, V.; Marozienė, A.; Misevičienė, L.; Yantsevich, A.V.; Čėnas, N. Kinetics of flavoenzyme-catalyzed reduction of tirapazamine derivatives: Implications for their prooxidant cytotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauk, A.G.; Scott, R.A.; Gray, H.B. Distances of electron transfer to and from metalloprotein redox sites in reactions with inorganic complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 4360–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Roberts, D.L.; Paschke, R.; Shea, T.M.; Masters, B.S.S.; Kim, J.J.P. Three-dimensional structure of NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase: Prototype for FMN- and FAD-containing enzymes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 8411–8416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Misra, I.; Iyanagi, T.; Kim, J.J. Regulation of interdomain interactions by calmodulin in inducible nitric-oxide synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 30708–30717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.K.; Morales, R.; Martinez-Julvez, M.; Brodie, T.B.; Medina, M.; Gomez-Moreno, C.; Tollin, G. Structure-function relationships in Anabaena ferredoxin/ferredoxin:NADP+ reductase electron transfer: Insight from site-directed mutagenesis, transient absorption spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1554, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čėnas, N.K.; Marcinkevičienė, J.A.; Kulys, J.K.; Usanov, S.A. A negative cooperativity between NADPH and adrenodoxin on binding to NADPH:adrenodoxin reductase. FEBS Lett. 1990, 259, 338–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwito, H.; Jumina; Mustofa; Pudjiastuti, P.; Fanani, M.Z.; Kimata-Ariga, Y.; Katahira, R.; Kawakami, T.; Fujiwara, T.; Hase, T.; et al. Design and synthesis of chalcone derivatives as inhibitors of the ferredoxin – ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase interaction of Plasmodium falciparum: Pursuing new antimalarial agents. Molecules 2014, 19, 21473–21488. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pudjiastuti, P.; Puspaningsih, N.N.T.; Siswanto, I.; Fanani, M.Z.; Kimata-Ariga, Y.; Hase, T.; Sarker, S.D.; Nahar, L. Inhibitory activity and docking analysis of antimalarial agents from Stemona sp. toward ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase from malaria parasites. J. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 2018, 3469132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čėnas, N.; Nameikaitė-Čėnienė, A.; Sergedienė, E.; Nivinskas, H.; Anusevičius, Ž.; Šarlauskas, J. Quantitative structure-activity relationships in enzymatic single-electron reduction of nitroaromatic explosives: Implications for cytotoxicity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1528, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monge, A.; Martinez-Crespo, F.J.; Lopez de Cerain, A.; Palop, J.A.; Narro, S.; Senador, V.; Marin, A.; Sainz, Y.; Gonzalez, M. Hypoxia-selective agents derived from 2-quinoxalinecarbonitrile 1,4-di-N-oxides. 2. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 4488–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, M.; Hay, M.P.; Boyd, P.D.W. Complete 1H, 13C and 15N NMR assignment of tirapazamine and related 1,2,4-benzotriazine N-oxides. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2006, 44, 948–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, N.O.; Ciotti, M.M. Chemistry and properties of the 3-acetylpyridine analogue of diphosphopyridine nucleotide. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1956, 221, 823–832. [Google Scholar]
- Pladziewicz, J.R.; Carney, M.H. Reduction of ferricenium ion by horse heart ferricytochrome c. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 3544–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
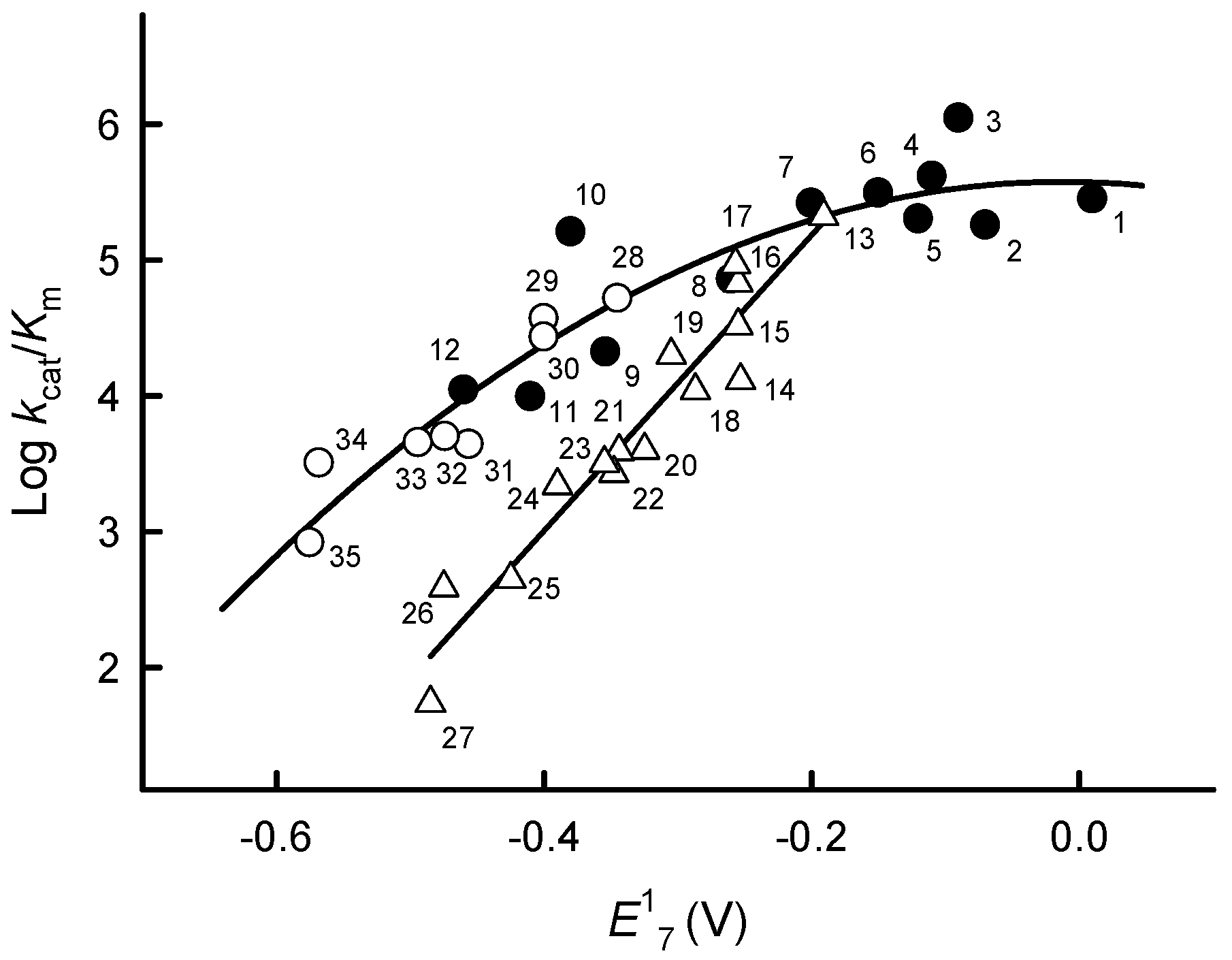
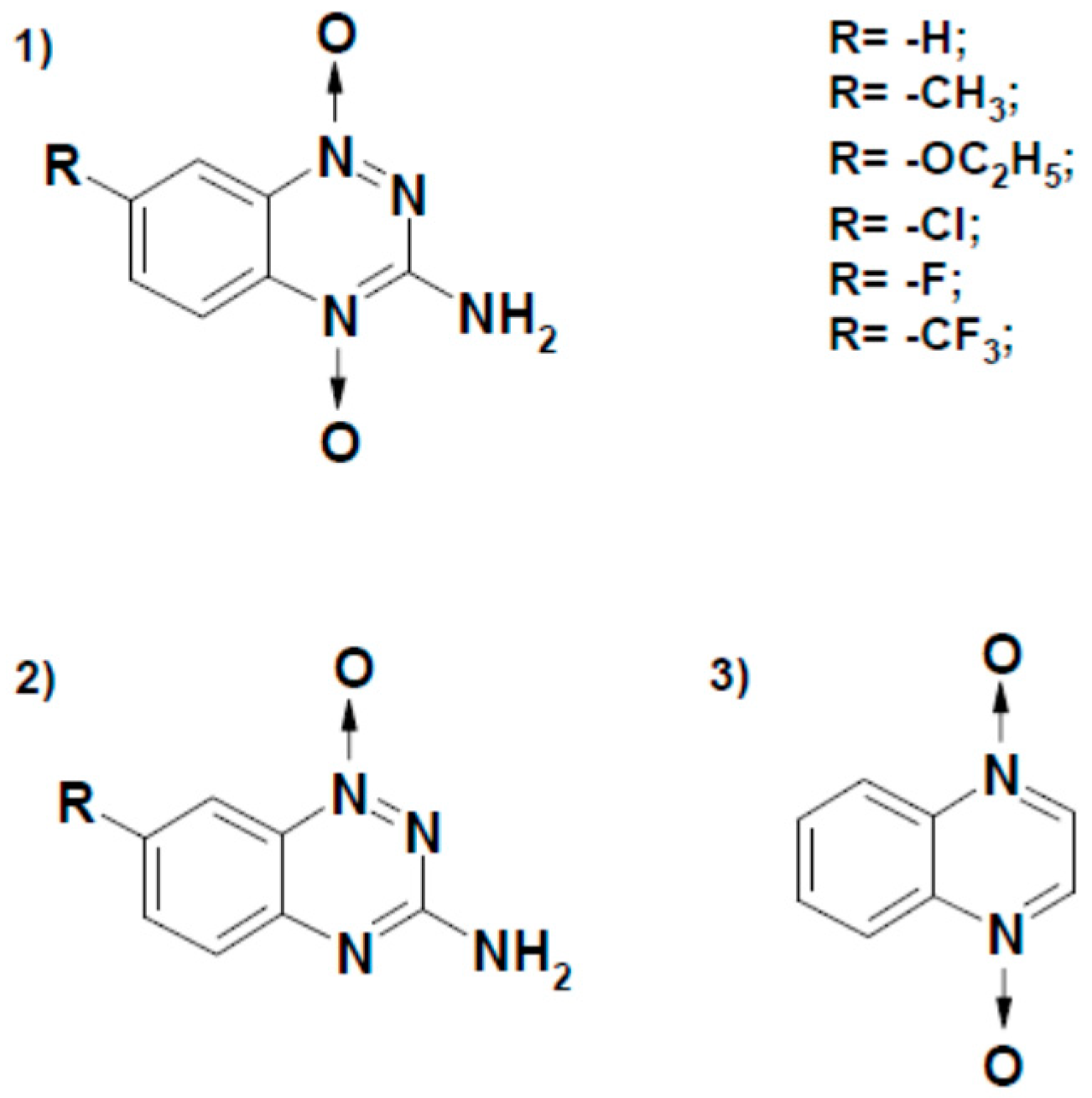
| No. | Compound | E17 (V) [22,23,24,25] | kcat(app) (s−1) | kcat/Km (M−1s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quinones | ||||
| 1 | 2-Methyl-1,4-benzoquinone | 0.01 | 32.4 ± 4.1 | 2.8 ± 0.2 × 105 |
| 2 | 2,5-Dimethyl-1,4-benzoquinone | −0.07 | 26.0 ± 2.3 | 1.8 ± 0.2 × 105 |
| 3 | 5-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone | −0.09 | 35.7 ± 5.1 | 1.1 ± 0.1 × 106 |
| 4 | 5,8-Dihydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone | −0.11 | 25.0 ± 3.8 | 4.1 ± 0.5 × 105 |
| 5 | 9,10-Phenanthrene quinone | −0.12 | 20.3 ± 3.3 | 2.0 ± 0.3 × 105 |
| 6 | 1,4-Naphthoquinone | −0.15 | 16.9 ± 2.1 | 3.1 ± 0.3 × 105 |
| 7 | 2-Methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone | −0.20 | 26.5 ± 3.2 | 2.6 ± 0.3 × 105 |
| 8 | Tetramethyl-1,4-benzoquinone | −0.26 | 33.1 ± 4.3 | 7.2 ± 0.8 × 104 |
| 9 | Benzylviologen | −0.354 | 4.8 ± 0.6 | 2.1 ± 0.1 × 104 |
| 10 | 9,10-Anthraquinone-2-sulphonate | −0.38 | 27.0 ± 3.2 | 1.6 ± 0.2 × 105 |
| 11 | 2-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone | −0.41 | 2.6 ± 0.3 | 9.8 ± 0.2 × 103 |
| 12 | 2-Methyl-3-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone | −0.46 | 14.0 ± 1.2 | 1.1 ± 0.1 × 104 |
| Nitroaromatic Compounds | ||||
| 13 | Tetryl | −0.191 | 40.0 ± 5.1 | 2.1 ± 0.4 × 105 |
| 14 | 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene a | −0.253 | 1.3 ± 0.3 × 104 | |
| 15 | Nifuroxime a | −0.255 | 3.3 ± 0.2 × 104 | |
| 16 | Nitrofurantoin a | −0.255 | 6.8 ± 0.5 × 104 | |
| 17 | 1,4-Dinitrobenzene | −0.257 | 9.1 ± 0.8 × 104 | |
| 18 | 1,2-Dinitrobenzene a | −0.287 | 1.1 ± 0.2 × 104 | |
| 19 | 5-Nitrothiophene-2-carbonic acid morpholide | −0.305 | 2.0 ± 0.2 × 104 | |
| 20 | 4-Nitrobenzaldehyde a | −0.325 | 4.0 ± 0.3 × 103 | |
| 21 | 3,5-Dinitrobenzoic acid a | −0.344 | 3.9 ± 0.5 × 103 | |
| 22 | 1,3-Dinitrobenzene a | −0.348 | 2.7 ± 0.2 × 103 | |
| 23 | 4-Nitroacetophenone a | −0.355 | 3.2 ± 0.4 × 103 | |
| 24 | 2-Nitrothiophene | −0.390 | 2.2 ± 0.2 × 103 | |
| 25 | 4-Nitrobenzoic acid a | −0.425 | 4.5 ± 0.4 × 102 | |
| 26 | 4-Nitrobenzyl alcohol | −0.475 | 3.9 ± 0.2 × 102 | |
| 27 | Nitrobenzene a | −0.485 | 5.5 ± 0.6 × 101 | |
| Aromatic N-Oxides | ||||
| 28 | 7-CF3-tirapazamine | −0.345 | 11.5 ± 2.0 | 5.2 ± 0.4 × 104 |
| 29 | 7-Cl-tirapazamine | −0.400 | 14.8 ± 1.3 | 3.7 ± 0.4 × 104 |
| 30 | 7-F-tirapazamine | −0.400 | 2.7 ± 0.2 × 104 | |
| 31 | 3-Amino-1,2,4-benzotriazine-1,4-dioxide (tirapazamine) | −0.456 | 4.4 ± 0.5 × 103 | |
| 32 | 7-CH3-tirapazamine | −0.474 | 5.0 ± 0.6 × 103 | |
| 33 | 7-C2H5O-tirapazamine | −0.494 | 4.5 ± 0.5 × 103 | |
| 34 | 3-Amino-1,2,4-benzotriazine-1-oxide | −0.568 | 3.2 ± 0.2 × 103 | |
| 35 | Quinoxaline-1,4-dioxide | −0.575 | 8.2 ± 0.9 × 102 | |
| Inorganic Complexes | ||||
| 36 | Ferricyanide b | 0.41 | 47.9 ± 4.0 | 3.0 ± 0.4 × 106 |
| 37 | Fe (EDTA)− | 0.12 | 4.3 ± 0.2 × 104 | |
| Flavoprotein | Reaction | Rp (Å) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q | ArNO2 | Fe (CN)3−6 | Fe (EDTA)− | ||
| P-450R, rat [12] | FMNH− − e− → FMNH., E17 = −0.270 V | 3.4 | 4.2 | 8.1 | 7.3 |
| n-NOS, rat [14] | FMNH− − e− → FMNH., E17 = −0.274 V | 4.7 | 3.9 | - | - |
| FNR, Anabaena PCC7118 a | FADH. − e− − H+ → FAD, E17 = −0.280 V | 5.0 | 4.4 | 9.2 | 10.4–11.4 |
| PfFNR, this work | FADH. − e− − H+ → FAD, E17 = −0.308 V b | 4.8 | 4.9 | 9.5 | 9.1 |
| FADH. − e− − H+ → FAD, E17 = −0.337 V c | 5.0 | 5.6 | 9.8 | 9.4 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lesanavičius, M.; Aliverti, A.; Šarlauskas, J.; Čėnas, N. Reactions of Plasmodium falciparum Ferredoxin:NADP+ Oxidoreductase with Redox Cycling Xenobiotics: A Mechanistic Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093234
Lesanavičius M, Aliverti A, Šarlauskas J, Čėnas N. Reactions of Plasmodium falciparum Ferredoxin:NADP+ Oxidoreductase with Redox Cycling Xenobiotics: A Mechanistic Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(9):3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093234
Chicago/Turabian StyleLesanavičius, Mindaugas, Alessandro Aliverti, Jonas Šarlauskas, and Narimantas Čėnas. 2020. "Reactions of Plasmodium falciparum Ferredoxin:NADP+ Oxidoreductase with Redox Cycling Xenobiotics: A Mechanistic Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 9: 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093234
APA StyleLesanavičius, M., Aliverti, A., Šarlauskas, J., & Čėnas, N. (2020). Reactions of Plasmodium falciparum Ferredoxin:NADP+ Oxidoreductase with Redox Cycling Xenobiotics: A Mechanistic Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(9), 3234. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21093234






