Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoparticles to Overcome the Hydrophobicity of Ellagic Acid: An Antioxidant Hybrid Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Hydrotalcite Intercalated with EA
2.3. Aqueous Miscible Organic Solvent Treatment (AMOS-T) of the EA-LDH
2.4. Instrumental Characterization of the LDH
2.5. Determining the EA content of the EA-LDH
2.6. Antioxidant Activity of the Hybrid Materials
2.7. Release of EA from the Composites
3. Results and Discussion
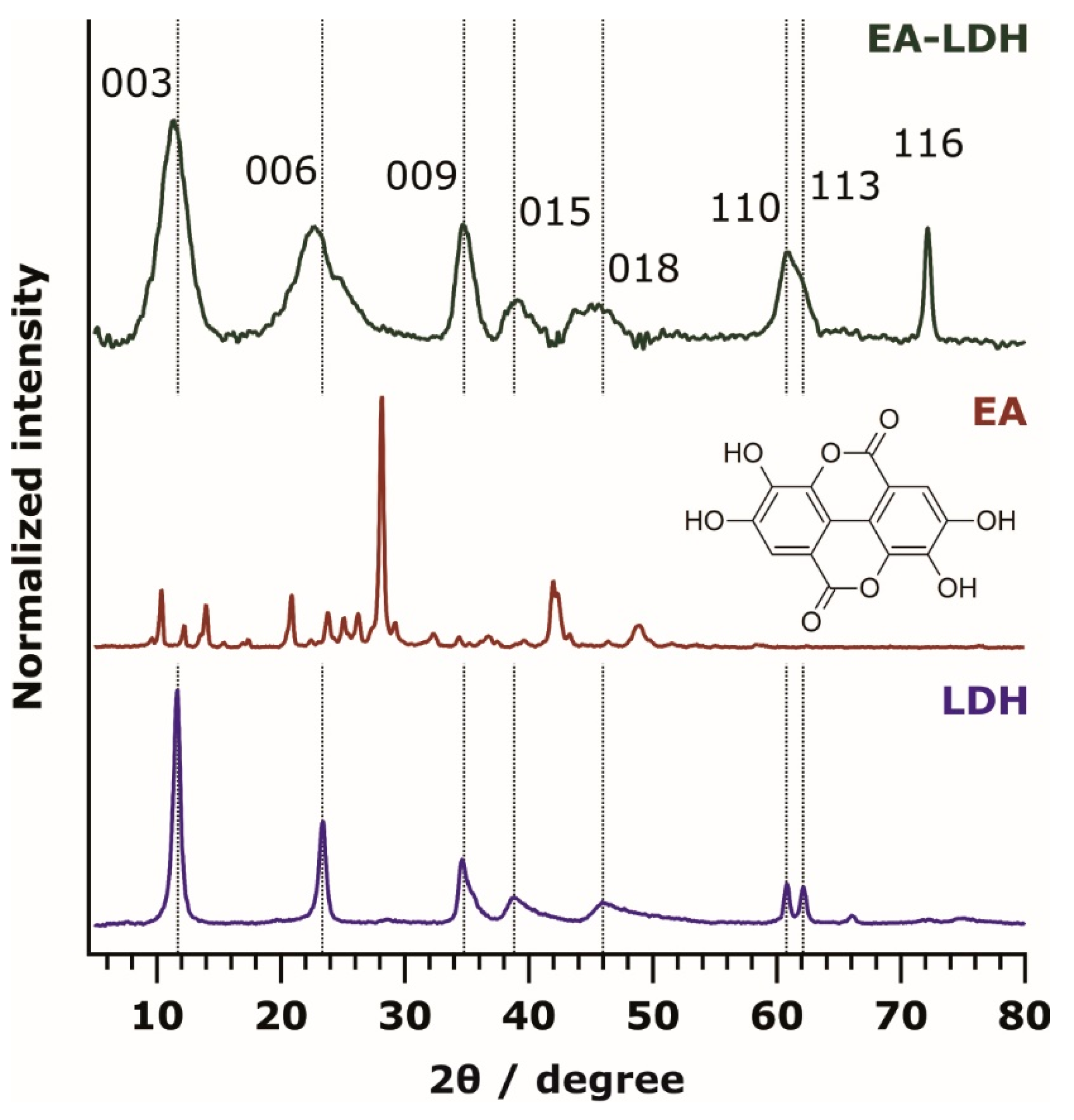
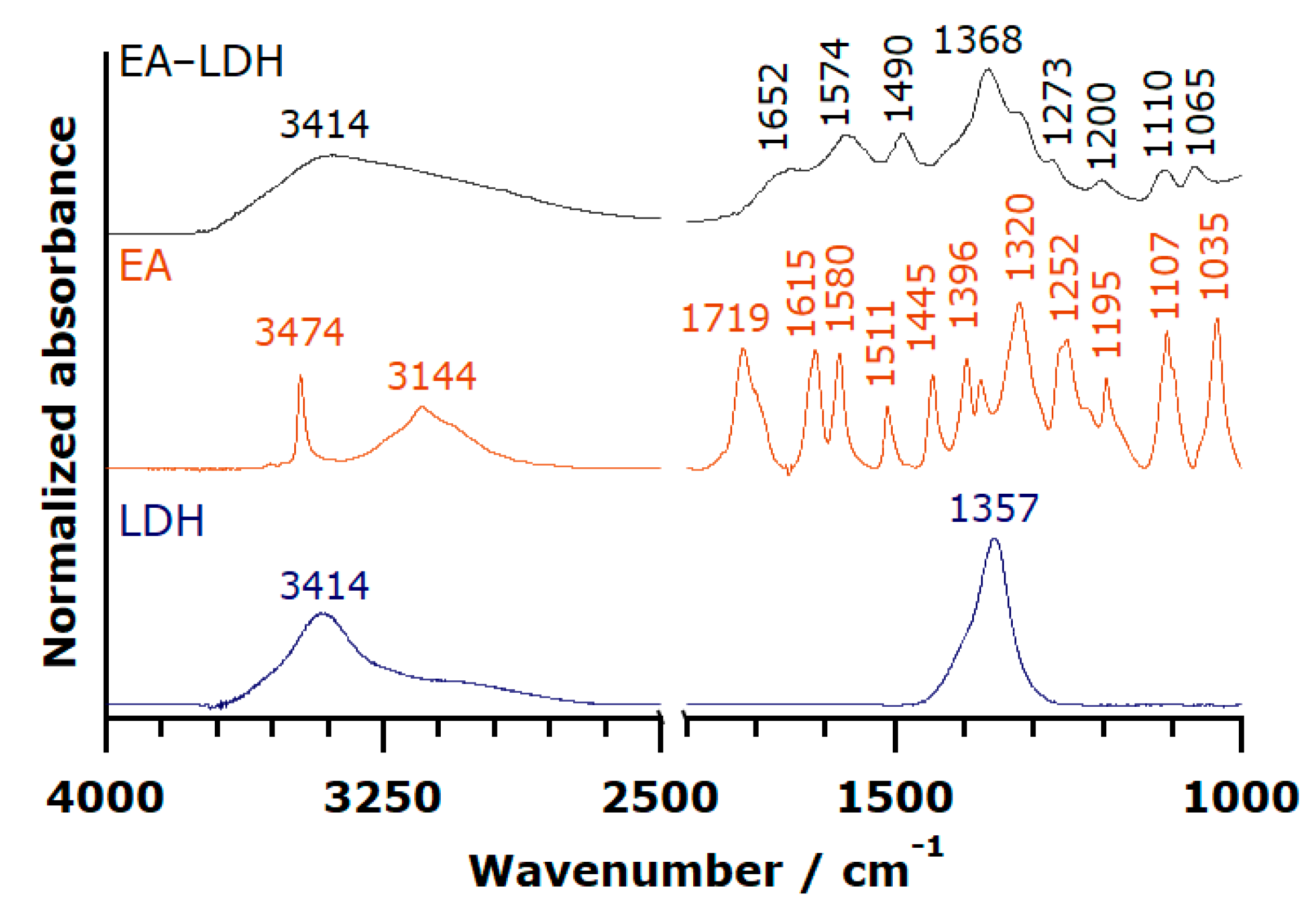
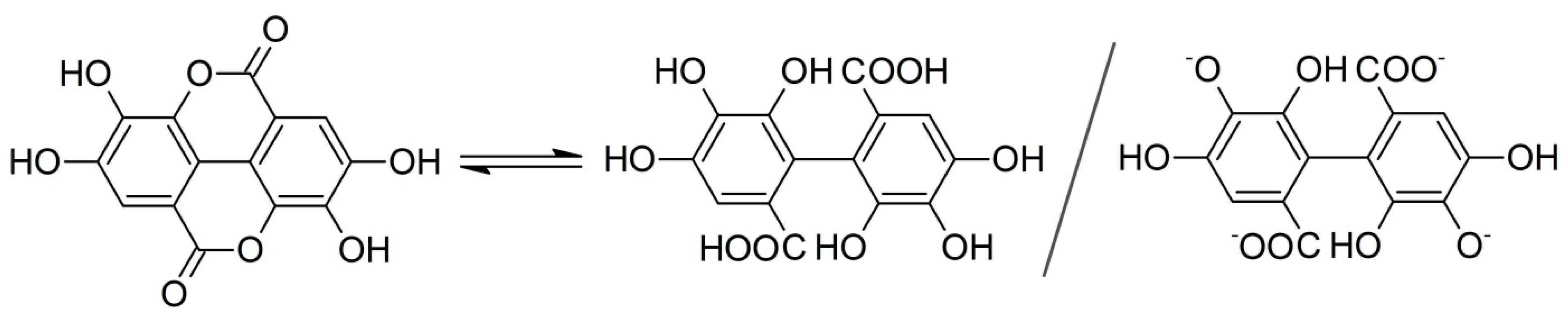
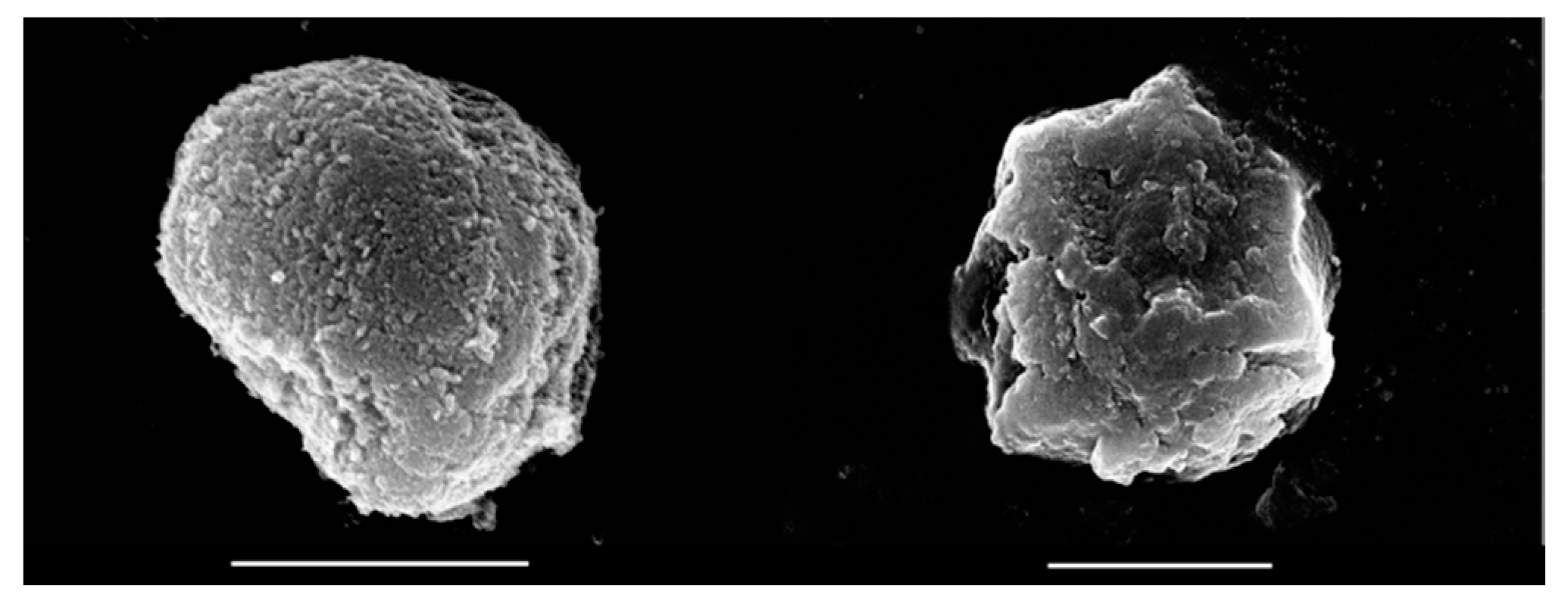
3.1. Structural Features
3.2. Determination of Antioxidant Content
3.3. Antioxidant Activity of EA-LDH and Leakage of EA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sideris, P.J.; Nielsen, U.G.; Gan, Z.H.; Grey, C.P. Mg/Al ordering in layered double hydroxides revealed by multinuclear NMR spectroscopy. Science 2008, 321, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.G.; Slade, R.C.T. Structural aspects of layered double hydroxides. In Layered Double Hydroxides; Duan, X., Evans, D.G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 119, pp. 1–87. [Google Scholar]
- Taviot-Gueho, C.; Prevot, V.; Forano, C.; Renaudin, G.; Mousty, C.; Leroux, F. Tailoring hybrid layered double hydroxides for the development of innovative applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1703868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Xu, Z.P.; Qiao, S.Z.; Liu, J.Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Y.F.; Zhang, J.; Qian, G.R. Triphosphate removal processes over ternary CaMgAl-layered double hydroxides. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 54, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahalagedara, M.N.; Samaraweera, M.; Dharmarathna, S.; Kuo, C.H.; Pahalagedara, L.R.; Gascon, J.A.; Suib, S.L. Removal of azo dyes: Intercalation into sonochemically synthesized NiAl layered double hydroxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 17801–17809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Zhang, K.L.; Wang, X.Q.; Zheng, F.L. Study on a novel binary ZnnEu layered double hydroxide with excellent fluorescence. J. Fluoresc. 2018, 28, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Wu, L.; Tang, A.T.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, B.; Zheng, Z.C.; Pan, F.S. A novel approach to fabricate protective layered double hydroxide films on the surface of anodized Mg-Al alloy. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1700163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.S.; Guo, Z.H.; Cao, Z.B.; Gao, Q.; Wang, D.; Boyer, C.; Kavallaris, M.; Sun, X.D.; Wang, X.M.; Zhao, L.Y.; et al. Manganese-based magnetic layered double hydroxide nanoparticle: A pH-sensitive and concurrently enhanced T-1/T-2-weighted dual-mode magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.D.; Li, J.H.; Wang, C.J.; Wang, Q.; Cader, M.Z.; Lu, J.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X.; O’Hare, D. Cellular uptake and gene delivery using layered double hydroxide nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Wang, Z.G.; Yan, L.; Chen, X.F.; Zhu, G.Y. Novel Pt-loaded layered double hydroxide nanoparticles for efficient and cancer-cell specific delivery of a cisplatin prodrug. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4868–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, R.; Balazs, M.; Dekany, I. Photooxidation of organic dye molecules on TiO2 and zinc-aluminum layered double hydroxide ultrathin multilayers. Colloid Surf. A 2005, 265, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Mori, K.; Mizugaki, T.; Ebitani, K.; Kaneda, K. Epoxidation of alpha,beta-unsaturated ketones using hydrogen peroxide in the presence of basic hydrotalcite catalysts. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 6897–6903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokudome, Y.; Morimoto, T.; Tarutani, N.; Vaz, P.D.; Nunes, C.D.; Prevot, V.; Stenning, G.B.G.; Takahashi, M. Layered double hydroxide nanoclusters: Aqueous, concentrated, stable, and catalytically active colloids toward green chemistry. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 5550–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Wang, Y.Y.; Xie, C.; Chen, C.; Liu, H.W.; Chen, R.; Huo, J.; Wang, S.Y. Acid-etched layered double hydroxides with rich defects for enhancing the oxygen evolution reaction. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 11778–11781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumboja, A.; Chen, J.W.; Zong, Y.; Lee, P.S.; Liu, Z.L. NiMn layered double hydroxides as efficient electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction and their application in rechargeable Zn-air batteries. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San Roman, M.S.; Holgado, M.J.; Salinas, B.; Rives, V. Characterisation of diclofenac, ketoprofen or chloramphenicol succinate encapsulated in layered double hydroxides with the hydrotalcite-type structure. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 55, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conterosito, E.; Van Beek, W.; Palin, L.; Croce, G.; Perioli, L.; Viterbo, D.; Gatti, G.; Milanesio, M. Development of a fast and clean intercalation method for organic molecules into layered double hydroxides. Cryst. Growth Des. 2013, 13, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.L.; Zhang, X.Q.; Li, S.P. A novel method to get methotrexatum/layered double hydroxides intercalation compounds and their release properties. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2013, 74, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Z.; Shao, R.F.; Li, L.; Xu, Z.P.; Gu, W.Y. Effective inhibition of colon cancer cell growth with MgAl-layered double hydroxide (LDH) loaded 5-FU and PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitor BEZ-235 through apoptotic pathways. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 3403–3411. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, X.; Xu, S.M.; Hu, T.Y.; Peng, L.Q.; Gao, R.; Liang, R.Z.; Wei, M.; Evans, D.; Duan, X. Layered double hydroxide monolayers for controlled loading and targeted delivery of anticancer drugs. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ay, A.N.; Akar, H.; Zaulet, A.; Vinas, C.; Teixidor, F.; Zumreoglu-Karan, B. Carborane-layered double hydroxide nanohybrids for potential targeted- and magnetically targeted-BNCT applications. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 3303–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenneisen, P.; Reichert, A.S. Nanotherapy and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cancer: A novel perspective. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratsinis, A.; Kelesidis, G.A.; Zuercher, S.; Krumeich, F.; Bolisetty, S.; Mezzenga, R.; Leroux, J.C.; Sotiriou, G.A. Enzyme-mimetic antioxidant luminescent nanoparticles for highly sensitive hydrogen peroxide biosensing. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 12210–12218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Liu, C.Q.; Pu, F.; Liu, Z.; Ren, J.S.; Qu, X.G. A GO-Se nanocomposite as an antioxidant nanozyme for cytoprotection. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 3082–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernekar, A.A.; Sinha, D.; Srivastava, S.; Paramasivam, P.U.; D’Silva, P.; Mugesh, G. An antioxidant nanozyme that uncovers the cytoprotective potential of vanadia nanowires. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, M.; Nafradi, M.; Rouster, P.; Murath, S.; Szilagyi, I. Highly stable enzyme-mimicking nanocomposite of antioxidant activity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 543, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, E.S.; Sim, W.Y.; Lee, S.K.; Jeong, J.S.; Kim, J.S.; Baek, I.H.; Choi, D.; Park, H.; Hwang, S.J.; Kim, M.S. Preparation and evaluation of resveratrol-loaded composite nanoparticles using a supercritical fluid technology for enhanced oral and skin delivery. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonkar, S.P.; Kutlu, B.; Leuteritz, A.; Heinrich, G. Nanohybrids of phenolic antioxidant intercalated into MgAl-layered double hydroxide clay. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 71, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Mendoza, N.; Vazquez-Velasco, M.; Gonzalez-Torres, L.; Benedi, J.; Sanchez-Muniz, F.J.; Morales-Gonzalez, J.A.; Jaramillo-Morales, O.A.; Valadez-Vega, C.; Bautista, M. Effect of extract and ellagic acid from Geranium schiedeanum on the antioxidant defense system in an induced-necrosis model. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkinen, S.; Heinonen, M.; Karenlampi, S.; Mykkanen, H.; Ruuskanen, J.; Torronen, R. Screening of selected flavonoids and phenolic acids in 19 berries. Food Res. Int. 1999, 32, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.I.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A.; Hess-Pierce, B.; Holcroft, D.M.; Kader, A.A. Antioxidant activity of pomegranate juice and its relationship with phenolic composition and processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 4581–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.V.; Tokumo, K.; Rigotty, J.; Zang, E.; Kelloff, G.; Reddy, B.S. Chemoprevention of colon carcinogenesis by dietary administration of piroxicam, alpha-difluoromethylornithine, 16-alpha-fluoro-5-androsten-17-one, and ellagic acid individually and in combination. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 4528–4534. [Google Scholar]
- Mertens-Talcott, S.U.; Percival, S.S. Ellagic acid and quercetin interact synergistically with resveratrol in the induction of apoptosis and cause transient cell cycle arrest in human leukemia cells. Cancer Lett. 2005, 218, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudarzi, M.; Mombeini, M.A.; Fatemi, I.; Aminzadeh, A.; Kalantari, H.; Nesari, A.; Najafzadehvarzi, H.; Mehrzadi, S. Neuroprotective effects of ellagic acid against acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Neurol. Res. 2019, 41, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przewloka, S.R.; Shearer, B.J. The further chemistry of ellagic acid II. Ellagic acid and water-soluble ellagates as metal precipitants. Holzforschung 2002, 56, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, D.G.; Nelson, P.F. Ellagic acid and the pulping of eucalypts. Part I. Some aspects of the chemistry of ellagic acid. Holzforschung 1965, 9, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, R.C.; Huang, M.T.; Chang, R.L.; Sayer, J.M.; Jerina, D.M.; Conney, A.H. Disposition of the naturally-occurring antimutagenic plant phenol, ellagic acid, and its synthetic derivatives, 3-o-decylellagic acid and 3,3’-di-o-methylallegic acid in mice. Carcinogenesis 1986, 7, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, M.Z.; Al Ali, S.H.; Zainal, Z.; Hakim, M.N. Development of antiproliferative nanohybrid compound with controlled release property using ellagic acid as the active agent. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaik, M.M.; Kowshik, M. Ellagic acid containing collagen-chitosan scaffolds as potential antioxidative bio-materials for tissue engineering applications. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomat. 2019, 68, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, S.; Turrini, F.; Catena, S.; Zunin, P.; Parodi, B.; Zuccari, G.; Pittaluga, A.M.; Boggia, R. Preparation of ellagic acid micro and nano formulations with amazingly increased water solubility by its entrapment in pectin or non-PAMAM dendrimers suitable for clinical applications. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 2438–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Choy, J.H. Layered double hydroxide nanoparticles as target-specific delivery carriers: Uptake mechanism and toxicity. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, M.; Terauchil, M.; Kikuchi, Y.; Nakao, A.; Okubo, J.; Yoshinaga, T.; Hiratsuka, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Hoshi, T. Deprotonation processes of ellagic acid in solution and solid states. Mon. Chem. 2003, 134, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.S.; McDermott, O.; Buffet, J.C.; O’Hare, D. Synthesis and characterisation of layered double hydroxide dispersions in organic solvents. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 51676–51682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, P.A.; Rana, S.; Verma, G. Making sense of Brownian motion: Colloid characterization by dynamic light scattering. Langmuir 2015, 31, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free-radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Food Sci. Technol. Lebensm. Wiss. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apak, R.; Guclu, K.; Ozyurek, M.; Karademir, S.E. Novel total antioxidant capacity index for dietary polyphenols and vitamins C and E, using their cupric ion reducing capability in the presence of neocuproine: CUPRAC method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 7970–7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, T.; Tsigdinos, G.A.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Pillaring of layered double hydroxides (LDHs) by polyoxometalate anions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 3653–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beres, A.; Palinko, I.; Kiricsi, I.; Nagy, J.B.; Yoshimichi, K.; Mizukami, F. Layered double hydroxides and their pillared derivatives-materials for solid base catalysis; synthesis and characterization. Appl. Catal. A 1999, 182, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznyak, S.K.; Tedim, J.; Rodrigues, L.M.; Salak, A.N.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Dick, L.F.P.; Ferreira, M.G.S. Novel inorganic host layered double hydroxides intercalated with guest organic inhibitors for anticorrosion applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 2353–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.H.; Wang, J.Q. A new route to prepare nanocomposites based on polyvinyl chloride and MgAl layered double hydroxide intercalated with laurylether phosphate. Express Polym. Lett. 2009, 3, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, S. Synthesis of hydrotalcite-like compounds and their structures and physicochemical properties 1. Systems Mg2+-Al3+-NO−3, Mg2+-Al3+-Cl−, Mg2+-Al3+-ClO−4, Ni2+-Al3+-Cl− and Zn2+-Al3+-Cl−. Clay Clay Min. 1975, 23, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijaikumar, S.; Dhakshinamoorthy, A.; Pitchumani, K. L-proline anchored hydrotalcite clays: An efficient catalyst for asymmetric Michael addition. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 340, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Zhang, W.H.; Shi, H.M.; He, J. An effective heterogeneous L-proline catalyst for the asymmetric aldol reaction using anionic clays as intercalated support. J. Catal. 2006, 241, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Thomas, A.C.; Xu, Z.P.; Campbell, J.H.; Lu, G.Q. In vitro sustained release of LMWH from MgAl-layered double hydroxide nanohybrids. Chem. Mat. 2008, 20, 3715–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Yu, J.Y.; Zhao, Z.J.; Fu, J.Y.; Zhao, M.L.; Wang, W.; Dai, J. Preparation and properties of a layered double hydroxide deicing additive for asphalt mixture. Cold Reg. Sci. Tech. 2015, 110, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, K.; Satpathy, M.; Mohapatra, L. Incorporation of Fe3+ into Mg/Al layered double hydroxide framework: Effects on textural properties and photocatalytic activity for H2 generation. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 7350–7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.L.; Sjastad, A.O.; Vistad, O.B.; Knudsen, K.D.; Roots, J.; Pedersen, J.S.; Norby, P. Characterization of exfoliated layered double hydroxide (LDH, Mg/Al=3) nanosheets at high concentrations in formamide. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murath, S.; Somosi, Z.; Toth, I.Y.; Tombacz, E.; Sipos, P.; Palinko, I. Delaminating and restacking MgAl-layered double hydroxide monitored and characterized by a range of instrumental methods. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1140, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.F.; Liu, J.J.; Clearfield, A.; Sims, J.E.; Speiegle, M.T.; Suib, S.L.; Sun, L.Y. Synthesis of layered double hydroxide single-layer nanosheets in formamide. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 12036–12041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, I.; Bhardwaj, V.; Hariharan, S.; Kumar, M. Analytical methods for assay of ellagic acid and its solubility studies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
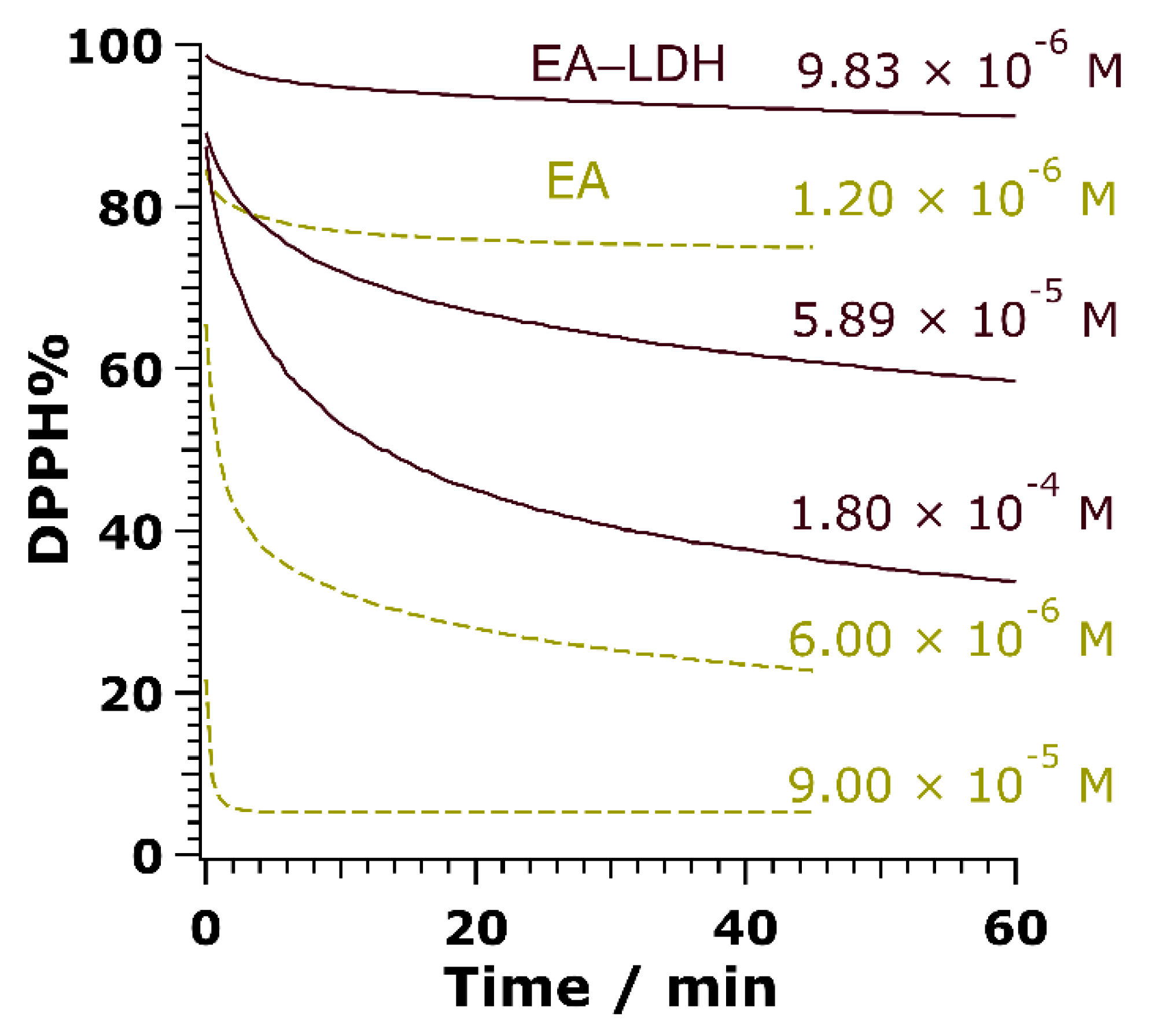
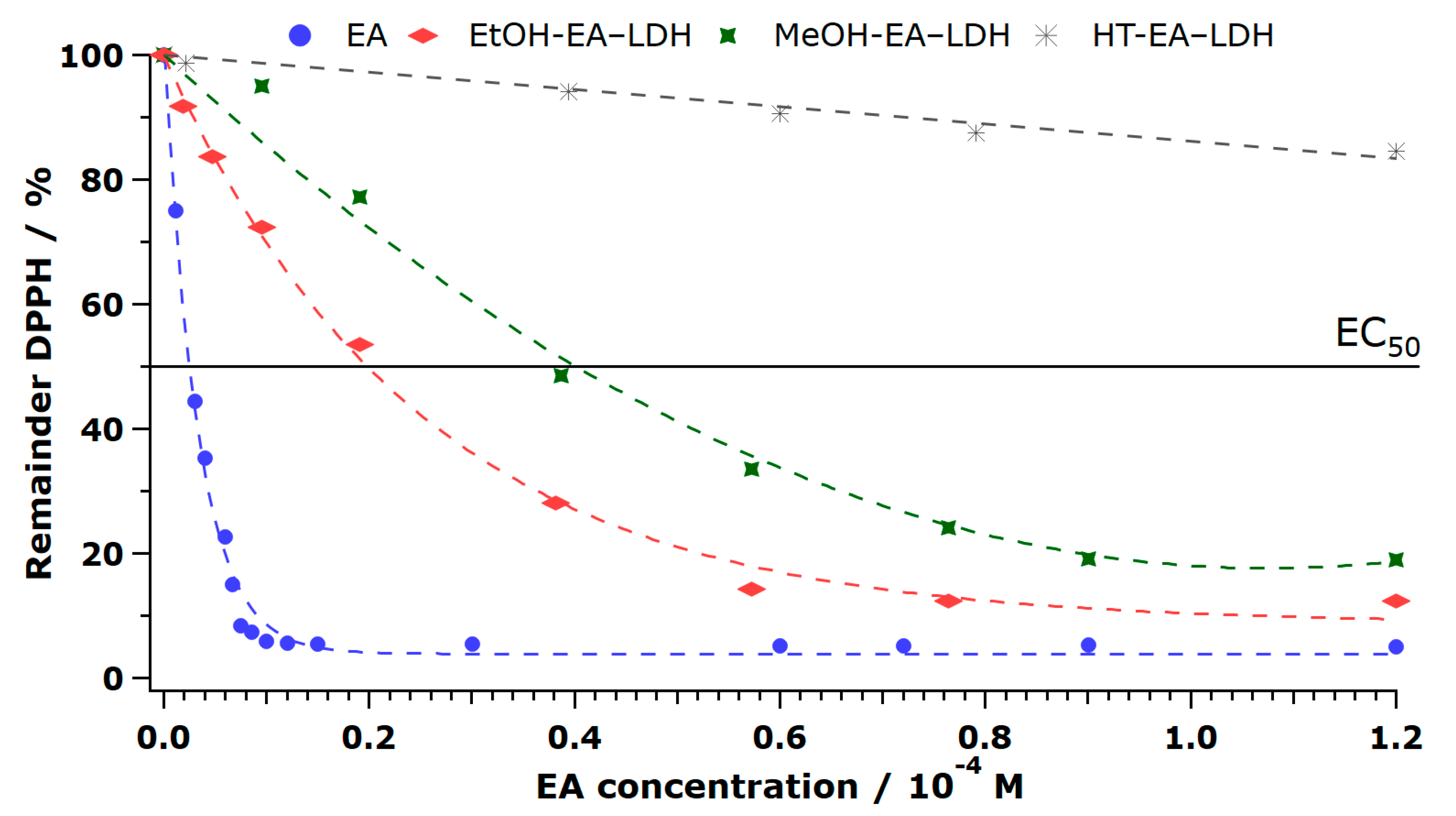

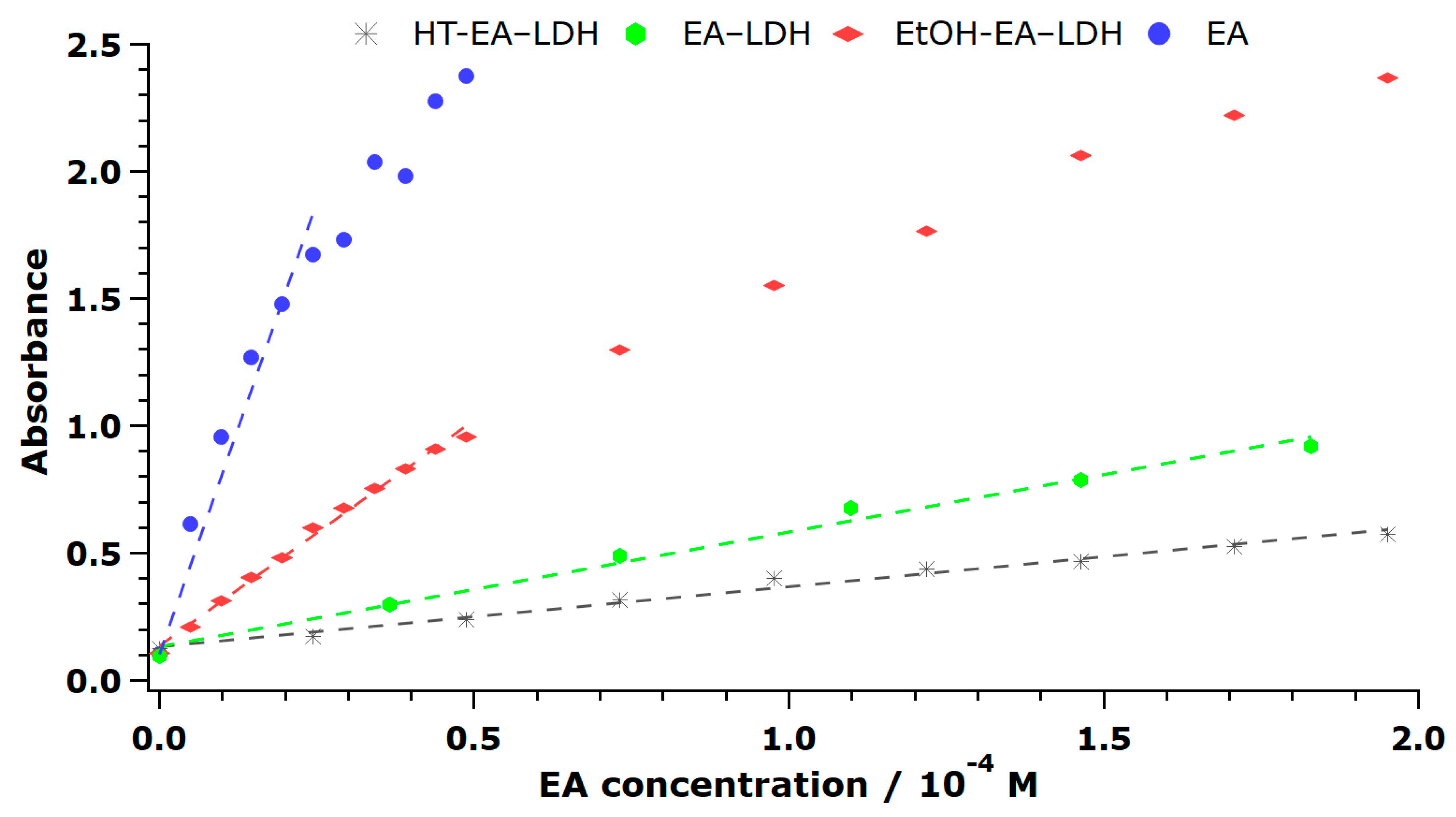
| Sample | EC50/10–5 Ma | NDPPHb | ε/103 M–1 cm–1c | TEACd |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EA | 0.25 | 11.78 | 71.0 | 4.61 |
| EA-LDH | 8.73 | 0.34 | 4.5 | 0.29 |
| HT-EA-LDHe | - | - | 2.4 | 0.15 |
| MeOH-EA-LDH | 4.19 | 0.70 | 14.7 | 0.96 |
| EtOH-EA-LDH | 1.98 | 1.48 | 17.7 | 1.15 |
| AC-EA-LDH | 2.17 | 1.35 | 17.8 | 1.16 |
| ACN-EA-LDH | 1.61 | 1.82 | 15.7 | 1.02 |
| FA-EA-LDHe | - | - | 1.5 | 0.10 |
| DMF-EA-LDH | 3.01 | 0.97 | 17.4 | 1.13 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muráth, S.; Szerlauth, A.; Sebők, D.; Szilágyi, I. Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoparticles to Overcome the Hydrophobicity of Ellagic Acid: An Antioxidant Hybrid Material. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9020153
Muráth S, Szerlauth A, Sebők D, Szilágyi I. Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoparticles to Overcome the Hydrophobicity of Ellagic Acid: An Antioxidant Hybrid Material. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(2):153. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9020153
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuráth, Szabolcs, Adél Szerlauth, Dániel Sebők, and István Szilágyi. 2020. "Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoparticles to Overcome the Hydrophobicity of Ellagic Acid: An Antioxidant Hybrid Material" Antioxidants 9, no. 2: 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9020153
APA StyleMuráth, S., Szerlauth, A., Sebők, D., & Szilágyi, I. (2020). Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoparticles to Overcome the Hydrophobicity of Ellagic Acid: An Antioxidant Hybrid Material. Antioxidants, 9(2), 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9020153







