Measurement of the Energy Intensity of Human Well-Being and Spatial Econometric Analysis of Its Influencing Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methodology
2.1. The Measurement of EIWB
2.2. Spatial Characteristics of EIWB
2.3. Spatial Econometric Analysis
2.3.1. Variable Selection of Influencing Factors
2.3.2. Model Setting
2.4. Decomposition of Spatial Effects
2.5. Data Collection
3. Results and Discussion
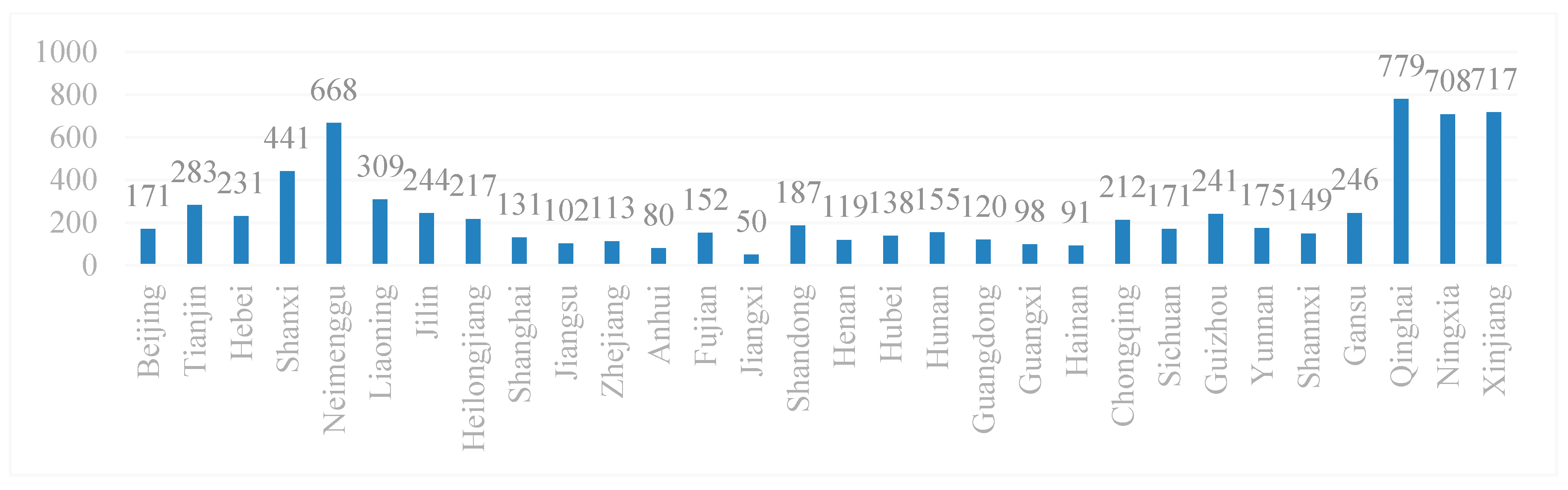
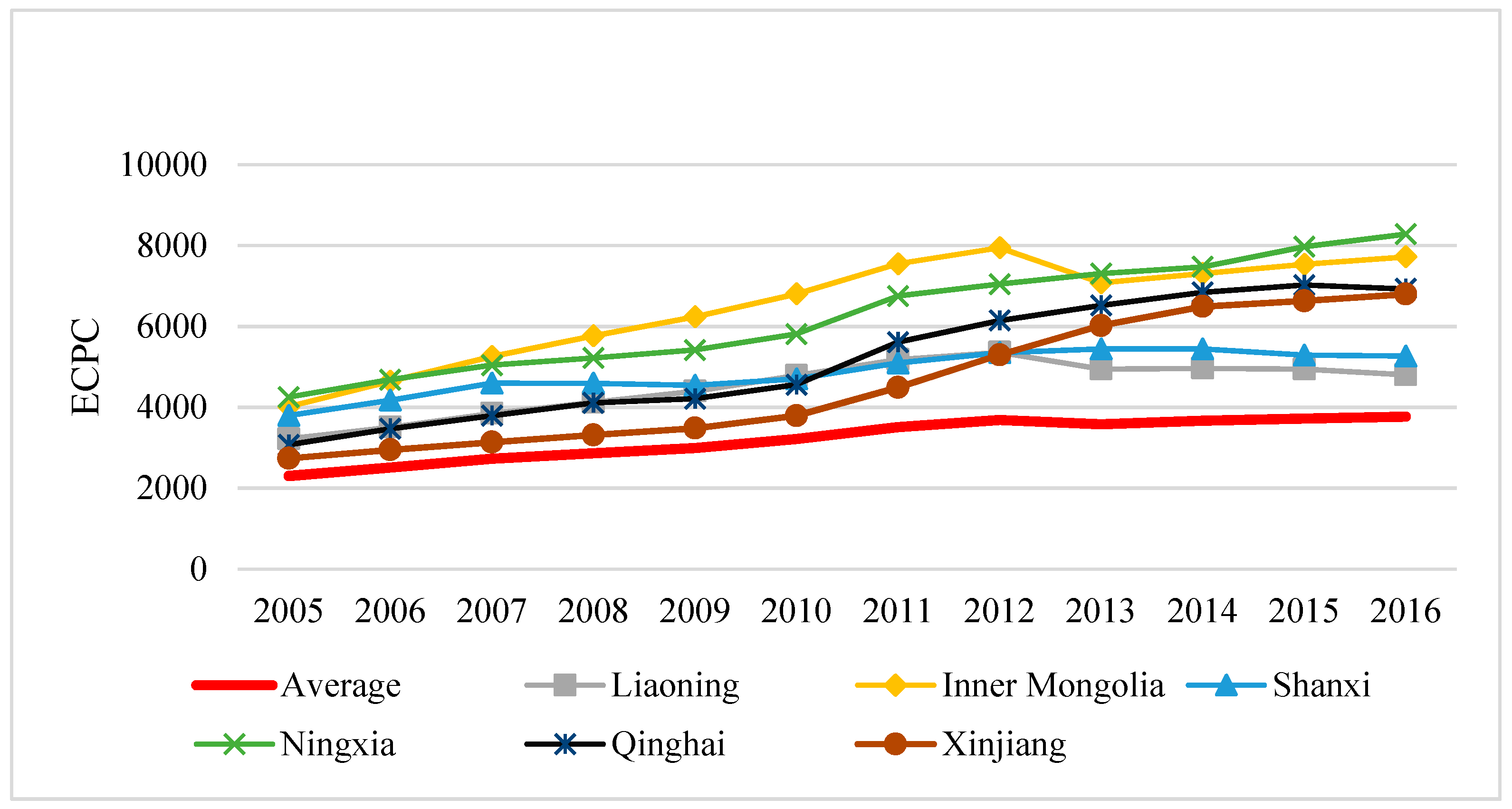
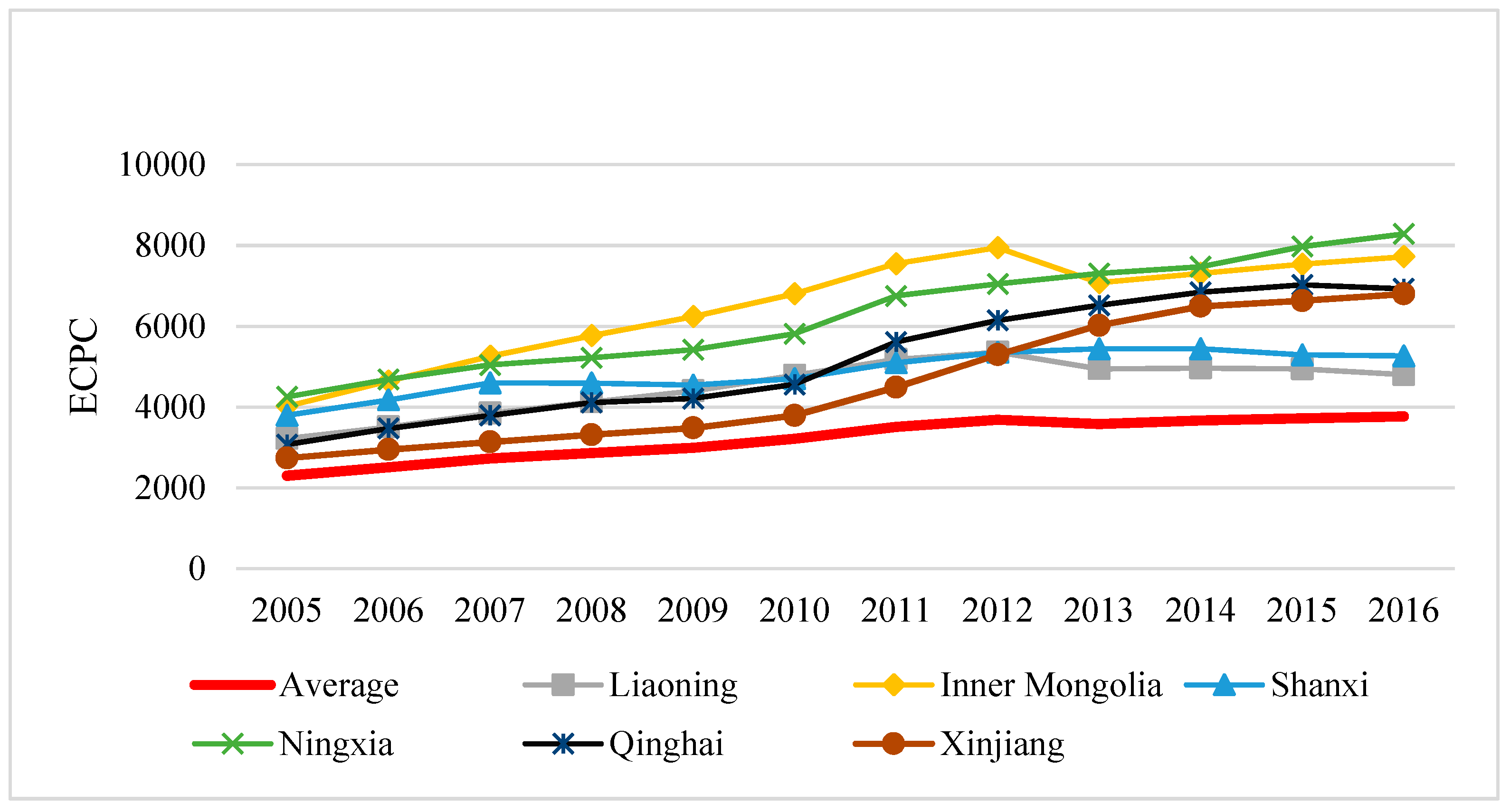
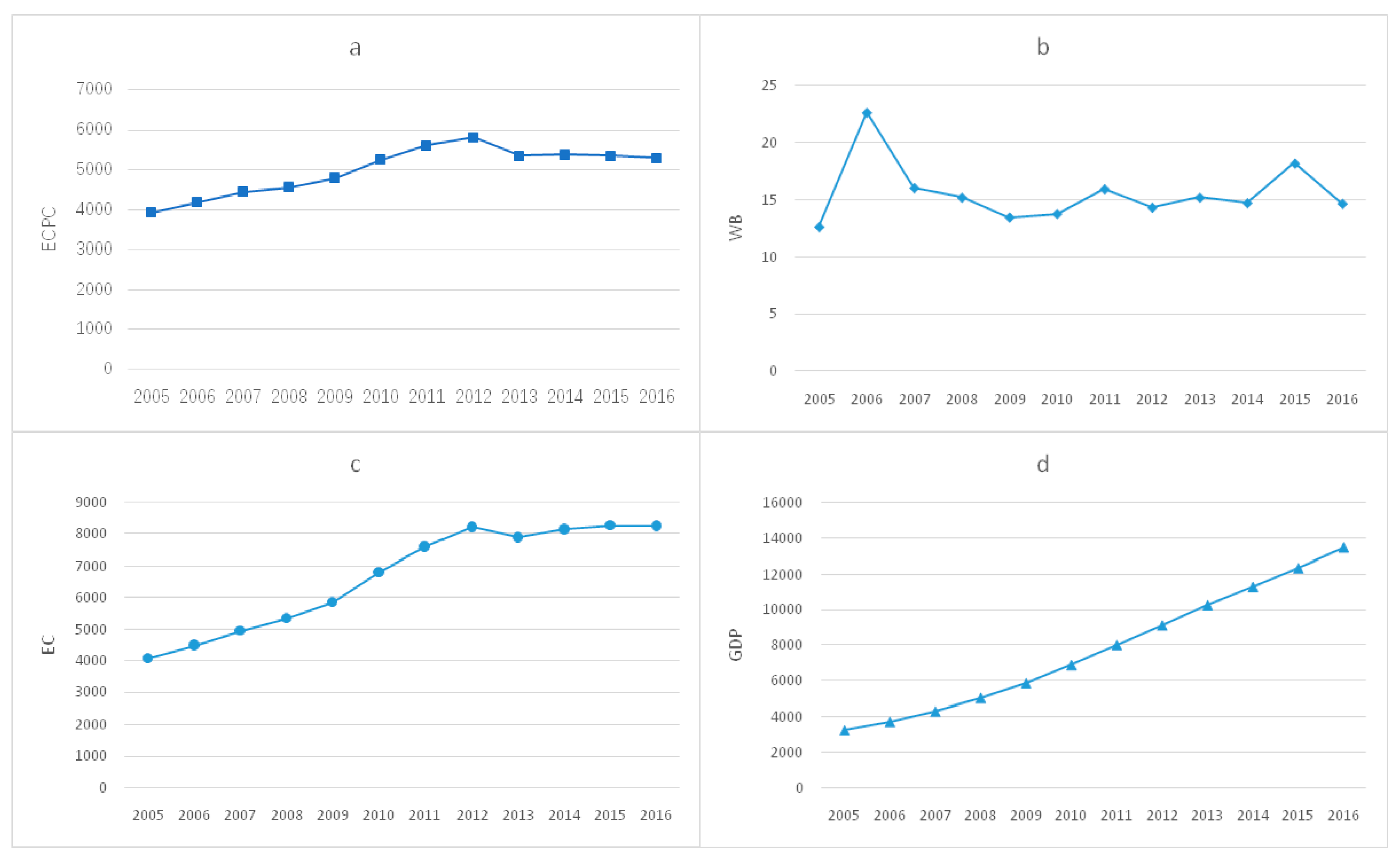
3.1. Values of EIWB and Its Distribution
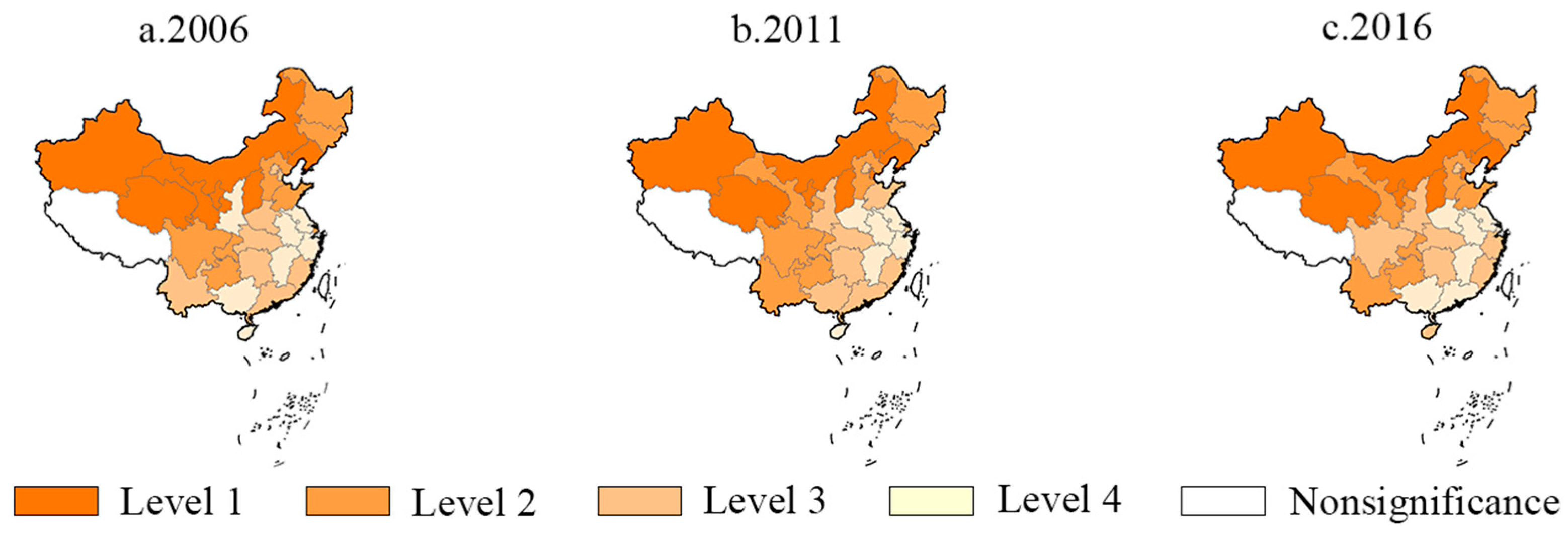
3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation of EIWB
3.3. Spatial Econometric Analysis of the Influencing Factors of EIWB
4. Conclusions and Policy Implications
4.1. Conclusions
4.2. Policy Implications
5. Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, W.X.; Tian, Y.Z.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhao, B.X.; Liu, Y.C.; Zhang, X.Q. Understanding the spatial-temporal patterns and influential factors on air quality index: The case of north China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.J.; Kou, X.J.; Geng, H.; Xie, J.F.; Yang, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.X.; Cai, Z.W.; Dong, C. Effect of ambient PM2.5 on lung mitochondrial damage and fusion/fission gene expression in rats. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehlman, M.A. Causal relationship from exposure to chemicals in oil refining and chemical industries and malignant melanoma. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1076, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trasande, L.; Schechter, C.B.; Haynes, K.A.; Landrigan, P.J. Mental retardation and prenatal methylmercury toxicity. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2006, 49, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.C. Energy intensity, target level of energy intensity, and room for improvement in energy intensity: An application to the study of regions in the EU. Energy Policy 2014, 67, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shao, S.; Yang, L.; Miao, Z. Improvement pathway of energy consumption structure in China’s industrial sector: From the perspective of directed technical change. Energy Econ. 2018, 72, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, G.; Palma, A. Technology invention and adoption in residential energy consumption. Energy Econ. 2017, 66, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lin, B. The improvement gap in energy intensity: Analysis of China’s thirty provincial regions using the improved DEA (data envelopment analysis) model. Energy 2015, 84, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Du, D.; Hao, Y. The driving forces of the change in China’s energy intensity: An empirical research using DEA-Malmquist and spatial panel estimations. Econ. Model. 2017, 65, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, F. Energy and Society: The Relation between Energy, Social Change, and Economic Development; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, R.A.; Mattos, C.R.; Balestieri, J.A. The limits of human development and the use of energy and natural resources. Energy Policy 2006, 34, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, D.M.; Ebenhack, B.W. Understanding the role of energy consumption in human development through the use of saturation phenomena. Energy Policy 2008, 36, 1430–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, T.; Rosa, E.A.; York, R. Environmentally efficient well-being: Is there a Kuznets curve? Appl. Geogr. 2012, 32, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgenson, A.K.; Alekseyko, A.; Giedraitis, V. Energy consumption, human well-being and economic development in central and eastern European nations: A cautionary tale of sustainability. Energy Policy 2014, 66, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.S.; Kamran, S.M.; Fan, H.Z. Real estate investment and energy efficiency: Evidence from China’s policy experiment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, W.L.; Hu, J.L.; Hsiao, C.; Chang, M.C. Energy efficiency of the Baltic Sea countries: An application of stochastic frontier analysis. Energies 2019, 12, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Sun, L.Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Liu, T.T.; Fang, K. Does industrial transfer within urban agglomerations promote dual control of total energy consumption and energy intensity? J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 204, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumbri, I.A.; Ikeda, S.; Jimichi, M.; Saka, C.; Managi, S. Inequality of health stock and the relation to national wealth. Int. J. Equity Health 2019, 18, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.L.; Wang, S.C. Total-factor energy efficiency of regions in China. Energy Policy 2006, 34, 3206–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueyoshi, T.; Goto, M.; Wang, D. Malmquist index measurement for sustainability enhancement in Chinese municipalities and provinces. Energy Econ. 2017, 67, 554–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apergis, N.; Aye, G.C.; Barros, C.P.; Gupta, R.; Wanke, P. Energy efficiency of selected OECD countries: A slacks based model with undesirable outputs. Energy Econ. 2015, 51, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Wang, X. An empirical study of energy efficiency in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region considering the haze effect. J. Arid Land Res. Environ. 2015, 10, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Li, G.; Su, Y.; Liu, J. Regional differences and convergence analysis of energy efficiency in China: On stochastic frontier analysis and panel unit root. Chin. J. Manag. Sci. 2013, 21, 175–184. [Google Scholar]
- Long, X.; Oh, K.; Cheng, G. Are stronger environmental regulations effective in practice? The case of China’s accession to the WTO. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 39, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.H.; Wang, D.; Du, T.Y.; Zhang, A.L.; Zhou, Y.X. Total-factor energy efficiency in China’s agricultural sector: Trends, disparities and potentials. Energies 2018, 11, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.C.; Xiang, Y.W.; Jia, H.Y.; Chen, L. Analysis of total factor energy efficiency and its influencing factors on key energy-intensive industries in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Sustainability 2018, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartney, G.; Popham, F.; McMaster, R.; Cumbers, A. Defining health and health inequalities. Public Health 2019, 172, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogundari, K.; Awokuse, T. Human capital contribution to economic growth in Sub-Saharan Africa: Does health status matter more than education? Econ. Anal. Policy 2018, 58, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liang, W.; Zhang, L.; Guo, X. Risk assessment for long-distance gas pipelines in coal mine gobs based on structure entropy weight method and multi-step backward cloud transformation algorithm based on sampling with replacement. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A. Democratic institutions and the energy intensity of well-being: A cross-national study. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2017, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweidan, O.D.; Alwaked, A.A. Economic development and the energy intensity of human well-being: Evidence from the GCC countries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Cheng, J.H.; Shen, J. Spatial effects of air pollution on public health in China. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2019, 73, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.S.; Ray, B.K. Decomposition of energy consumption and energy intensity in Indian manufacturing industries. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2010, 14, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adom, P.K. Determinants of energy intensity in South Africa: Testing for structural effects in parameters. Energy 2015, 89, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guang, F.; He, Y.; Wen, L.; Sharp, B. Energy intensity and its differences across China’s regions: Combining econometric and decomposition analysis. Energy 2019, 180, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, R.; Mercado, J. Energy intensity: A decomposition and counterfactual exercise for Latin American countries. Energy Econ. 2014, 42, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, L.; Padilla, E. Energy intensity in road freight transport of heavy goods vehicles in Spain. Energy Policy 2015, 85, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H. Provincial energy intensity in China: The role of urbanization. Energy Policy 2015, 86, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Exploring the relationship between urbanization and energy consumption in China using ARDL (autoregressive distributed lag) and FDM (factor decomposition model). Energy 2009, 34, 1846–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y. The relationship between energy consumption structure, economic structure and energy intensity in China. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 5475–5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Anshasy, A.A.; Katsaiti, M.S. Energy intensity and the energy mix: What works for the environment? J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 136, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xiao, B.; Song, L. What cause the decline of energy intensity in China’s cities? A comprehensive panel-data analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 1298–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübler, M.; Keller, A. Energy savings via FDI? Empirical evidence from developing countries. Environ. Dev. Econ. 2010, 15, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, C.; Wang, S.; Li, S. Impacts of energy consumption structure, energy intensity, economic growth, urbanization on PM2.5 concentrations in countries globally. Appl. Energy 2018, 230, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, P.; Filipović, S.; Radovanović, M. Underlying causal factors of the European Union energy intensity: Econometric evidence. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 89, 216–227. [Google Scholar]
- Ikefuji, M.; Horii, R. Wealth heterogeneity and escape from the poverty—Environment trap. J. Public Econ. Theory. 2007, 9, 1041–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.; Wen, X.; Lu, Y.; Yu, K. Economic growth and cardiorespiratory fitness of children and adolescents in urban areas: A panel data analysis of 27 provinces in China, 1985–2014. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisa, R.; Clemente, J.; Pueyo, F. The influence of (public) health expenditure on longevity. Int. J. Public Health 2014, 59, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.; Nandakumar, A.K.; Wallack, S.; Hodgkin, D.; Gaumer, G.; Erbil, C. Health expenditures, health outcomes and the role of good governance. Int. J. Health Care Financ. Econ. 2013, 13, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Stern, D.I. China’s changing energy intensity trend: A decomposition analysis. Energy Econ. 2008, 30, 1037–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Du, D.; Tao, Q. An analysis of technological factors and energy intensity in China. Energy Policy 2017, 109, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.L.; Chen, W.; Cheng, J.Q. Effects of environmental regulation and FDI on urban innovation in China: A spatial Durbin econometric analysis. Energy Policy 2019, 235, 210–224. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, C.; Wilson, C.; Anable, J. The diffusion of domestic energy efficiency policies: A spatial perspective. Energy Policy 2018, 114, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhorst, J.P. Applied spatial econometrics: Raising the bar. Spat. Econ. Anal. 2010, 5, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeSage, J.P. Introduction to Spatial Econometrics; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.; Kong, Y.; Ren, X.; Shi, Y.; Chiang, S. The determinants of urban sustainability in Chinese resource-based cities: A panel quantile regression approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, L.; Li, S. Natural resource abundance, natural resource-oriented industry dependence, and economic growth: Evidence from the provincial level in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 139, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wu, M.; Sun, Y.; Shi, X.; Sun, A.; Zhang, P. Resource abundance, industrial structure, and regional carbon emissions efficiency in China. Resour. Policy 2019, 60, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.G.; Lu, F. Spatial distribution characteristics and convergence of China’s regional energy intensity: An industrial transfer perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 903–917. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, S.G.; Lin, H.C. Competitive dominance of emission trading over Pigouvian taxation in a globalized economy. Econ. Lett. 2018, 163, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Feng, C. Impacts of oriented technologies and economic factors on China’s industrial climate mitigation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; See, K.F.; Chi, J. Water resources and water pollution emissions in China’s industrial sector: A green-biased technological progress analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 1412–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, P.; Guo, X. Energy consumption associated with urbanization in China: Efficient- and inefficient-use. Energy 2018, 165, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, S.; Bi, F.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Xue, W. Provincial analysis and zoning of atmospheric pollution in China from the atmospheric transmission and the trade transfer perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, I.; Kim, B.H.S. Regional disparity of medical resources and its effect on age-standardized mortality rates in Korea. Ann. Reg. Sci. 2019, 62, 305–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Industrial structure, technical progress and carbon intensity in China’s provinces. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2935–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zheng, M.; Chen, J. The effects of environmental regulation and technical progress on CO2 Kuznets curve: An evidence from China. Energy Policy 2015, 77, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Author | Input and Output Variables | Method |
|---|---|---|
| Sueyoshi et al. [20] | GPR, CO2, SO2, dust, waste water, ammonia nitrogen, energy, labor, capital | DEA, Malmquist productivity index |
| Apergis et al. [21] | productive capital stock, labor, renewable energy, non-renewable energy | SBM |
| Feng et al. [22] | energy, labor, capital stock, number of patent authorizations, GDP | SBM, Tobit model |
| Zhao et al. [23] | energy, labor, capital stock, GDP | SFA |
| Long et al. [24] | GRP, SO2, capital, labor, coal | Directional distance function |
| Yang et al. [25] | labor, capital stock, energy consumption | DEA, Tobit model |
| Li et al. [26] | capital, labor, industrial energy consumption, industrial output, CO2 | DEA |
| Test | Statistics | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Wald spatial error | 31.95 *** | <0.001 |
| Wald spatial lag | 34.90 *** | <0.001 |
| LR spatial error | 250.27 *** | <0.001 |
| LR spatial lag | 198.04 *** | <0.001 |
| Hausman | 17.80 ** | 0.013 |
| Year | Moran’s I | E(I) | Sd(I) | z | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 0.408 *** | −0.034 | 0.119 | 3.726 | <0.001 |
| 2006 | 0.394 *** | −0.034 | 0.119 | 3.607 | <0.001 |
| 2007 | 0.375 *** | −0.034 | 0.118 | 3.462 | <0.001 |
| 2008 | 0.385 *** | −0.034 | 0.120 | 3.504 | <0.001 |
| 2009 | 0.354 *** | −0.034 | 0.117 | 3.336 | <0.001 |
| 2010 | 0.396 *** | −0.034 | 0.116 | 3.703 | <0.001 |
| 2011 | 0.381 *** | −0.034 | 0.118 | 3.535 | <0.001 |
| 2012 | 0.367 *** | −0.034 | 0.117 | 3.416 | <0.001 |
| 2013 | 0.409 *** | −0.034 | 0.115 | 3.861 | <0.001 |
| 2014 | 0.405 *** | −0.034 | 0.116 | 3.797 | <0.001 |
| 2015 | 0.358 *** | −0.034 | 0.115 | 3.406 | <0.001 |
| 2016 | 0.355 *** | −0.034 | 0.115 | 3.376 | <0.001 |
| Year | H-H | L-H | L-L | H-L |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | Hebei, Shanxi, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, Xinjiang | Jilin, Heilongjiang, Sichuan, Shannxi | Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, Fujian, Jiangxi, Shandong, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Chongqing, Yunnan | Guizhou |
| 2011 | Shanxi, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning, Jilin, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, Xinjiang | Beijing, Hebei, Heilongjiang, Sichuan, Shannxi | Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, Fujian, Jiangxi, Shandong, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Chongqing, Guizhou, Yunnan | Tianjin |
| 2016 | Shanxi, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning, Qinghai, Ningxia, Xinjiang | Beijing, Hebei, Jilin, Heilongjiang, Sichuan, Shannxi, Gansu | Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, Fujian, Jiangxi, Shandong, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Chongqing, Guizhou, Yunnan | Tianjin |
| Variable | W1 | W2 | W3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | Coefficient | p-Value | |
| lnis | 0.590 *** | <0.001 | 0.532 *** | <0.001 | 0.964 *** | <0.001 |
| lnul | 1.152 *** | <0.001 | 1.190 *** | <0.001 | 1.920 *** | <0.001 |
| lnes | 0.424 *** | <0.001 | 0.426 *** | <0.001 | 0.161 * | 0.093 |
| lnfdi | −0.080 *** | 0.002 | −0.159 *** | <0.001 | −0.306 *** | <0.001 |
| lnpcdi | 0.835 *** | <0.001 | 0.378 * | 0.080 | −0.138 | 0.445 |
| lnhe | −0.198 *** | 0.009 | −0.029 | 0.772 | 0.131 | 0.231 |
| lnt | −0.146 *** | <0.001 | −0.089 ** | 0.038 | −0.264 *** | <0.001 |
| W*lnis | 0.841 *** | 0.001 | −0.393 | 0.276 | 0.743 * | 0.074 |
| W*lnul | −0.088 | 0.808 | 0.750 | 0.108 | 1.522 *** | 0.008 |
| W*lnes | −0.336 ** | 0.021 | 0.832 *** | 0.001 | −0.459 ** | 0.013 |
| W*lnfdi | −0.266 *** | <0.001 | −0.404 *** | <0.001 | −0.116 | 0.142 |
| W*lnpcdi | −0.292 | 0.333 | 0.537 | 0.284 | 0.464 | 0.305 |
| W*lnhe | −0.717 *** | <0.001 | 0.436 | 0.114 | −0.623 * | 0.010 |
| W*lnt | −0.369 *** | <0.001 | −0.222 * | 0.070 | 0.628 *** | <0.001 |
| ρ | 0.599 ** | 0.042 | 0.184 ** | 0.047 | 0.064 ** | 0.047 |
| Sigma2_e | 0.110 *** | <0.001 | 0.165 *** | <0.001 | 0.203 *** | <0.001 |
| Variable | EIWB | ECPC | WB | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Effects | Indirect Effects | Total Effects | Direct Effects | Indirect Effects | Total Effects | Direct Effects | Indirect Effects | Total Effects | |
| IS | 0.607 *** (5.67) | 0.924 *** (3.28) | 1.531 *** (4.53) | 0.385 *** (4.55) | 0.131 (0.51) | 0.516 * (1.66) | −0.070 ** (−2.18) | −0.174 ** (−1.99) | −0.243 ** (−2.35) |
| UL | 1.142 *** (6.16) | 0.006 (0.02) | 1.147 *** (3.81) | 0.788 *** (10.86) | −0.339 (−0.18) | 0.449 ** (2.45) | 0.231 *** (7.79) | −0.180 (−0.27) | 0.051 (0.83) |
| ES | 0.425 *** (6.20) | −0.331 ** (−2.24) | 0.094 (0.70) | 1.351 *** (8.12) | −0.992 ** (−2.20) | 0.358 (0.78) | −0.026 (−0.38) | 0.364 ** (2.28) | 0.338 ** (2.16) |
| FDI | −0.083 *** (−3.32) | −0.287 *** (−4.97) | −0.370 *** (−5.53) | 0.181 *** (8.74) | 0.132 *** (4.80) | 0.313 *** (7.09) | 0.269 *** (2.70) | 0.503 ** (2.18) | 0.772 ** (2.35) |
| PCDI | 0.845 *** (5.17) | −0.260 (−0.82) | 0.585 ** (2.21) | 0.176 *** (2.69) | 0.062 ** (2.36) | 0.238 *** (3.13) | 0.101 *** (3.93) | −0.012 (−1.32) | 0.089 *** (3.55) |
| HE | −0.189 *** (−2.61) | −0.739 *** (−4.00) | −0.928 *** (−2.60) | 0.558 (1.50) | 0.075 (0.94) | 0.131 (1.20) | 1.090 *** (4.40) | 0.098 (1.06) | 1.188 *** (3.20) |
| T | −0.152 *** (−4.36) | −0.394 *** (−5.68) | −0.546 *** (−7.37) | 0.360 *** (4.77) | 0.620 *** (4.12) | 0.980 *** (5.34) | 0.463 ** (2.36) | 1.034 ** (2.36) | 1.497 *** (2.77) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Long, R.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; Wu, M.; Li, Q. Measurement of the Energy Intensity of Human Well-Being and Spatial Econometric Analysis of Its Influencing Factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010357
Long R, Zhang Q, Chen H, Wu M, Li Q. Measurement of the Energy Intensity of Human Well-Being and Spatial Econometric Analysis of Its Influencing Factors. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(1):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010357
Chicago/Turabian StyleLong, Ruyin, Qin Zhang, Hong Chen, Meifen Wu, and Qianwen Li. 2020. "Measurement of the Energy Intensity of Human Well-Being and Spatial Econometric Analysis of Its Influencing Factors" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 1: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010357
APA StyleLong, R., Zhang, Q., Chen, H., Wu, M., & Li, Q. (2020). Measurement of the Energy Intensity of Human Well-Being and Spatial Econometric Analysis of Its Influencing Factors. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(1), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010357





