Abstract
Taurochenodeoxycholic acid (TCDCA) as a primary bioactive substance of animal bile has been shown to exert good anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory functions in adjuvant arthritis in rats. The anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties of TCDCA have exhibited interesting similarities with the effects of glucocorticoids (GCs). To investigate the potential mechanisms of TCDCA in anti-inflammation and immunomodulation, we used a luciferase reporter assay to evaluate the activation of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) stimulated by TCDCA. Our results showed that GR was activated by TCDCA in a concentration-dependent manner. Moreover, the elevated expressions of c-Fos and phosphorylated c-Jun induced by interleukin-1β (IL-1β) were reversed by TCDCA. The inhibition of TCDCA on the transactivation of activator protein-1 (AP-1) was observed as well. However, the suppression of TCDCA on the phosphorylation of c-Jun was blocked incompletely by GR inhibitor RU486. These results have indicated that the anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory functions of TCDCA involve multiple pathways, with contributions from GR and its related AP-1 signaling pathway.
1. Introduction
Taurochenodeoxycholic acid (TCDCA, Figure 1), as a kind of primary bioactive substance of animal bile, is synthesized with taurine (Tau) and chenodeoxychlolic acid (CDCA) in the liver [1]. It is well documented that bile acids (BAs) are crucial in facilitating digestion, absorption, and excretion of dietary lipids, while an increasing number of biological functions of BAs have been discovered in the past few decades. It was found that BAs, as a kind of signal molecule, were involved in numerous cellular signaling pathways, including activating apoptotic, inflammatory and carcinogenic signaling pathways [2,3,4,5,6]. BAs have also been demonstrated to have anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects [4,7,8,9,10,11,12], which mainly operate by activating intracellular ligand-activated nuclear receptors (NRs), such as the farnesoid X receptor (FXR, NR1H4), glucocorticoid receptor (GR) [13,14,15,16], and membrane-type receptors, specifically the G protein-coupled BA receptor (TGR5 or GPBAR-1) [17]. In our previous study, we found that TCDCA could be used to combat adjuvant arthritis by inhibiting the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and induce apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) [7,8,18], which suggested that TCDCA may be a potential therapeutic agent for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or other inflammatory diseases.
Figure 1.
The chemical structure of taurochenodeoxycholic acid.
Activator protein-1 (AP-1) as a transcription factor is composed of homo- and/or heterodimers of Jun and Fos proteins [19], with c-Jun-c-Fos heterodimer being the principal form of AP-1. A previous study found that AP-1 played an essential role in the pathogenesis of RA, including synovial hyperplasia and abnormal immune responses [20]. AP-1-regulated IL-1β is the most important cytokine responsible for cartilage breakdown and osteoclastogenesis in RA [21]. IL-1β and AP-1 influence each other’s expression, activity and cross-talk involved in RA joint destruction [21]. Thus, suppression of AP-1 may result in decreasing synovial overgrowth and joint destruction [22]. Therefore, we thought suppression of AP-1 might play a critical role in combatting adjuvant arthritis using TCDCA. In the current study, we observed the influence of TCDCA on AP-1 activation and its mechanisms involved in the anti-inflammatory effects of TCDCA.
2. Results
2.1. Cell Viability
To determine the cytotoxicity of TCDCA, an MTT assay was performed. FLS was treated with TCDCA (0.01 μM–100 μM), and cytotoxicity was not observed (Figure 2).
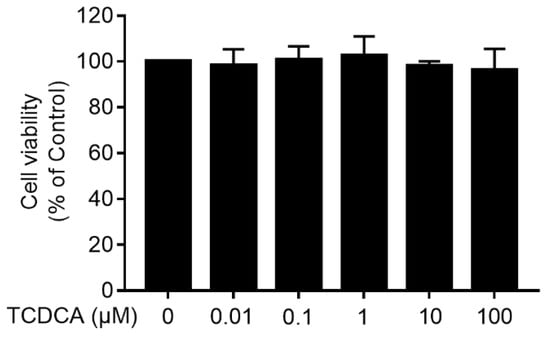
Figure 2.
The cytotoxicity of TCDCA on fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS). Untreated FLS were used as a negative control. Results were representative of three independent experiments.
2.2. Taurochenodeoxycholic Acid Induced the Transcriptional Activation of Glucocorticoid Receptor
To determine the role of TCDCA on the transcriptional activation of GR, a luciferase report assay was used. The results showed that GR was activated significantly by incubating with TCDCA (10 and 100 μM) for 24 h in a concentration-dependent manner compared to the control (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). As shown in Figure 3, the maximum fold on the activation of GR by TCDCA (100 μM) was 10.88-fold, and the positive control dexamethasone (Dex, 500 nM) activated GR by a fold of 61.37.
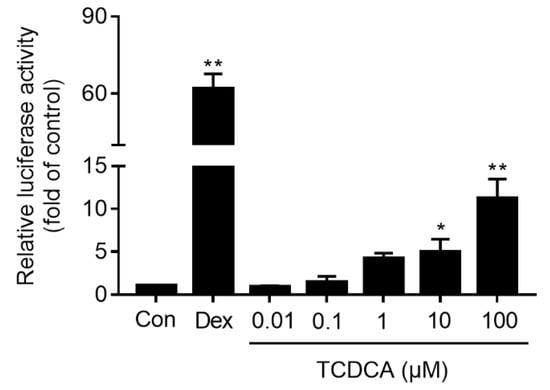
Figure 3.
Activation of GR stimulated by TCDCA. Untreated HEK 293t cells were used as the negative control, and Dex (500 nM) was used as the positive control. Results were representative of three independent experiments. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 vs. control.
2.3. Effects of TCDCA on c-Jun, c-Fos Expression and c-Jun (Ser63) Phosphorylation
Western blot was used to determine the effects of TCDCA on the phosphorylation of c-Jun (Ser63) and expression of c-Fos. As shown in Figure 4A, the phosphorylation of c-Jun (Ser63) and the expression of c-Fos were increased remarkably by IL-1β (10 ng/mL) stimulation compared to the control (P < 0.01). TCDCA (100 μM) inhibited the increased phosphorylation of c-Jun (Ser63) and expression of c-Fos induced by IL-1β (P < 0.01). Meanwhile, Dex (500 nM), the positive control, also reduced c-Jun (Ser63) phosphorylation and c-Fos expression stimulated by IL-1β (P < 0.01), and such repression was much stronger than TCDCA. Furthermore, the diminished expression of c-Fos and phosphorylation of c-Jun (Ser63) by Dex (500 nM) were absolutely reversed by GR inhibitor RU486 (10 μM, Figure 4B). However, RU486 only partially reversed inhibition of phosphorylated c-Jun induced by TCDCA (100 μM). These results indicated that TCDCA could suppress the expression of c-Fos and the phosphorylation of c-Jun (Ser63) and the repression was, at least in part, related to TCDCA-induced activation of GR.
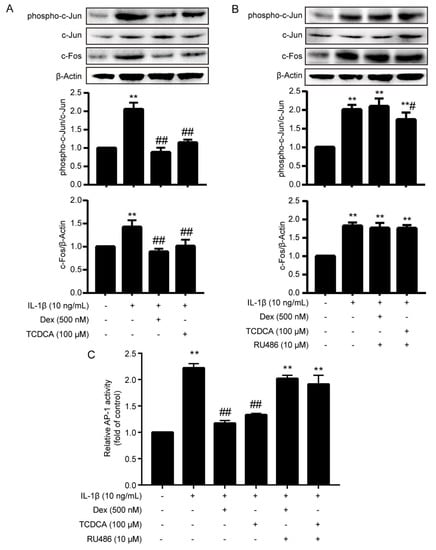
Figure 4.
TCDCA inhibited the activation of AP-1. (A) Inhibition of c-Jun, phosphorylated c-Jun (Ser63) and c-Fos are detected by immunoblotting using specific antibodies, β-actin was used as a loading control. Untreated FLS was used as a negative control, and Dex was used as a positive control. (B) RU486 blocked the suppression of phosphorylation of c-Jun (Ser63) and expression of c-Fos induced by TCDCA. (C) TCDCA inhibited AP-1 activity. Results were representative of three independent experiments. ** P < 0.01 vs. control, # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01 vs. IL-1β.
2.4. TCDCA Inhibited the Transactivation of AP-1
DNA-binding activity of the AP-1 c-Jun subunit was evaluated by a sensitive multi-well colorimetric assay. After IL-1β stimulation, the DNA-binding capacity of c-Jun in FLS was enhanced noticeably compared to the control (P < 0.01, Figure 4C). Dex (500 nM) and TCDCA (100 μM) repressed the enhancement elicited by IL-1β (P < 0.01), and the repression was blocked by RU486 (Figure 4C). These observations suggested that TCDCA inhibited the transactivation of AP-1 by activating GR, and indicated that the AP-1 pathway played an essential role in the anti-inflammatory effects of TCDCA.
3. Discussion
Glucocorticoids (GCs), as an agonist of the GR, is currently the principle therapeutic agent for RA treatment. The classical GR mediated signaling pathway was the primary mechanism of GCs anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory actions. The inactive GR resides in the cytoplasm, complexed with the chaperones molecular hsp90 and several immunophilins [23,24,25]. Binding to ligand induces a conformational change in GR and releases GR from the complexed chaperone proteins leading to the exposure of nuclear localization signals and facilitating nuclear translocation. After nuclear translocation, GR may dimerize and the homodimeric GR complex can stimulate or suppress transcriptional responses by binding to glucocorticoid response elements (GRE) or negative glucocorticoid response elements (nGRE). Meanwhile, another pathway is involved in anti-inflammatory effects of GR. Ligand-activated GR can bind to pro-inflammatory transcriptional factors including AP-1 and NF-κB and the protein-protein interactions can repress AP-1 and NF-κB regulated gene transcription [26]. The cross-talk between AP-1 or NF-κB and GR is an essential mechanism for anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory drugs. Thus, GR is considered to be a critical pharmacological target for anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory medicine.
Animal bile, as a traditional Chinese medicine, has been widely used for the treatment of inflammatory disease (such as acute tracheitis, winter cough, pneumonia and whooping cough) because of its advantageous anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory functions. In light of animal bile’s pharmacological effects, it was found that the major bioactive substances of animal bile were BAs, including CDCA, ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), TCDCA etc. Our previous study demonstrated that TCDCA showed remarkable inhibition of both acute and chronic inflammation. It especially favorably ameliorated the progressive development and bone destruction of adjuvant arthritis in rats [7]. Moreover, it was found that the anti-inflammatory action of TCDCA was mediated by inhibiting the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6, and suppressing the activity of NF-κB [18], which was also inhibited when GR was activated [27]. Considering the interesting similarity between the anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects and the chemical structures between TCDCA and GCs, we predicted that TCDCA may exert its anti-inflammatory effect by stimulating GR related signal pathways. In the present study, the luciferase reporter assay was used to evaluate TCDCA-induced GR transcriptional activation, and we found GR were activated by incubation with TCDCA (10, 100 μM) for 24 h (Figure 2). IL-1β is the predominant pro-inflammatory cytokine associated with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) [28], which has been widely used as a stimulator in RA related studies in vitro [29,30,31,32]. The strategy uses IL-1β to stimulate FLS in anti-arthritis drug discovery, which was used as well in this study. The results showed TCDCA could inhibit the increased expression of c-Fos and phosphorylation of c-Jun in FLS induced by IL-1β (Figure 4A). Furthermore, the transcriptional activity of AP-1 induced by IL-1β was suppressed when FLS was incubated with TCDCA (Figure 4C). These results suggested that the mechanism of TCDCA on anti-inflammation was possibly mediated via inhibiting transcriptional activity of AP-1, which was similar to UDCA [16,33,34,35].
However, the suppression of TCDCA on the phosphorylation of c-Jun (Figure 4B) can be blocked incompletely by RU486. Moreover, the capability of TCDCA in stimulating GR was much weaker compared to Dex (Figure 2). Surprisingly, for all other experiments the difference between Dex and TCDCA was not reflected. These data indicated that there were some other potential mechanisms involved in the anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties of TCDCA. FXR and TGR5, as two principal receptors of bile acids, played a pivotal role in anti-inflammation [36]. Previous studies demonstrated that activated TGR5 could inhibit LPS-induced NF-κB activation but not AP-1 activation [37]. However, activation of FXR resulted in elevating the suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3)-an inducible protein, which suppresses the transcriptional activity of AP-1 [38]. Therefore, the inhibition of TCDCA on AP-1 transcriptional activity may be mediated via TCDCA-activated FXR as well, which requires further investigation.
In summary, we found that TCDCA exhibited its anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties by inhibiting transcription and expression of AP-1 with GR partially contributing to this process.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
TCDCA was dissociated and depurated from chicken bile as described in our previous study [7,8], with the purity being> 99.5%. RU486 and recombinant IL-1β were purchased from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). Freund′s complete adjuvant (FCA) was purchased from the Shanghai Institute of Biological Products (Shanghai, China). The Nuclear Extract Kit and TransAM® c-Jun activation kit were purchased from Active Motif (Carlsbad, CA, USA). Phenol red-free Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) was purchased from Life Technologies (Waltham, MA, USA). pGL4.35 [luc2P/9 × GAL4UAS/Hygro], pBIND-GR and Bright-Glo™ the luciferase assay system were purchased from Promega (Madison, WI, USA).
4.2. Animals and Induction of Adjuvant Arthritis in Rats
The study was approved by the Animal Ethical Committee of Anhui Science and Technology University (No.007, Approval date: 25 February 2019) and conformed to national guidelines on the care and use of laboratory animals. Adjuvant arthritis models were preformed according to our previously reported method [7,8]. Briefly, thirty male wistar rats (11–13 weeks, 170 ± 10 g) were obtained from the experimental animal center of the Academy of Military Medical Sciences in China. All animals were maintained at a controlled temperature (22 ± 2 °C), and a regular light/dark cycle (7:00–19:00, light), and all animals had free access to food and water. Adjuvant arthritis rats were induced as previously described [39,40]. Briefly, rats were immunized on day 0 by intradermal injection of FCA into the foot pad, containing 10 mg heat-inactive Bacillus Calmette-Guerin in 1 mL paraffin oil, into the left hind paw with 0.1 mL for each rat.
4.3. Isolation and Culture of Adjuvant Arthritis FLS
Adjuvant arthritis FLS were isolated as previously described with modification [40]. Briefly, fresh synovial tissues were obtained from three adjuvant arthritis rats under sterile conditions each time. All the synovium tissues were minced with fine scissors, incubated in a plastic flask (Corning, New York, NY, USA) and maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle′s medium (DMEM, Gibco, Waltham, MA, USA) supplemented with 10 mM 4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-1-ethanesulfonic acid (HEPES, pH 7.2, Promega, Madison, WI, USA), 15% fetal calf serum (FCS, TBD, Tianjin, China), 100 U/mL penicillin and streptomycin (Gibco, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) 50 mM mercaptoethanol in a humidified 5% CO2-containing atmosphere at 37 °C for 7 days. After removal of the synovial pieces, the adherent cells were cultured in the same medium. At 70–80% confluence nonadherent cells were removed and adherent cells were trypsinized, split at a 1:3 ratio and recultured in the same medium. The synoviocytes were used in experiments from passages 3. After three passages, most of the cultured synoviocytes comprised a homogeneous population of FLS.
4.4. MTT Assay
FLS were seeded into 96-well plates at a cell density of 5 × 10 3 in 200 μL/well and incubated for 24 h till 80% confluence. Then, cells were incubated with or without TCDCA for another 24 h. At the end of the incubation period, 20 μL 5 mg/mL MTT was added in the medium for a further 4 h incubation, then the medium was removed and 150 μL DMSO was added to dissolve the formazan in the surviving cells. The 96-well plates were gently swirled for 5 min at room temperature. The absorbance was measured at 570 nm with 630 nm as a reference. Cell viability was calculated as the percentage of the control.
4.5. Luciferase Assay
HEK 293t cells were seeded at 1 × 104 cells/well in solid white 96-well plates (Nunc, Waltham, MA, USA) in phenol red-free DMEM with 5% bovine calf serum (80 μL/well), under a 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37 °C. 50 ng each of pGL4.35[luc2P/9×GAL4UAS/Hygro] vector and pBIND-GR vector in 10 μL lipofectamine® 2000-mediated transfection master mix was transiently introduced into HEK 293t cells. The plates were covered and placed in a tissue culture incubator at 37 °C overnight. 10 μL of 10× induction solutions was added to wells to be induced or control solution to non-induced wells and incubated for 24 h. Luciferase activity was analyzed by using the Bright-Glo™ luciferase assay system. Fold induction was calculated with the luminescence information as follows:
Fold induction = Average relative light units of induced cells/Average relative light units of control cells
4.6. Protein Extraction
FLS were seeded into flasks. After 4 h-attachment, cells were incubated with or without TCDCA alone or TCDCA and RU486 (10 μM) for 44 h and then stimulated by IL-1β (10 ng/mL) for another 4 h. After treatments, cells were collected and isolated by using the Nuclear Extract Kit according to the manufacturer′s instructions. The protein concentration was detected with a BCA kit.
4.7. Western Blotting
Protein extracts were separated by 12% denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred onto polyvinylidene fluoride membranes. After blocking in blocking buffer (Beyotime Biotechnology, Shanghai, China), the membranes were exposed to specific primary antibodies at a concentration of 1:1000 for anti-phospho-c-Jun(Ser63), -c-Jun and -c-Fos (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA) and 1:3000 for anti-β-actin (Proteintech group, Wuhan, China). Membranes were then washed and exposed to HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:1 000 dilution, KPL, Milford, MA, USA) for 1–2 h, at room temperature, followed by incubation with BeyoECL Plus (Beyotime Biotechnology, Shanghai, China).
4.8. Transactivation of AP-1 Assay
After treatment with TCDCA for 48 h, FLS were collected by scraping and centrifugation. Nuclear protein extracts were obtained from FLS by using the Nuclear Extract Kit according to the manufacturer′s instructions. Nuclear protein was stored at −80 °C. The activation of AP-1 was measured using the TransAM® c-Jun activation ELISA kit according to the manufacturer′s instruction. Briefly, 5 μg of nuclear protein samples were incubated for 1 h in a 96-well plate immobilized with an oligonucleotide containing a TRE (5′-TGA GTC A-3′), to which phosphorylated c-Jun contained in nuclear extracts specifically binded. After washing, phospho-c-Jun antibody (1:500 dilutions) was added to these wells and incubated for 1 h. Following incubation for 1 h with a secondary HRP-conjugated antibody (1:1000 dilution), specific binding was detected by spectrophotometry using a plate reader (Synergy 4, Bio-tek, Winooski, VT, USA) at 450 nm with a reference wavelength of 655 nm.
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (S.D.). Significance of the differences between controls and experimental groups was determined by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test. P < 0.05 was considered significant.
Author Contributions
Experimental Design, L.L., C.L. and P.L.; investigation, L.L., C.L., W.M.; writing—Original draft, L.L. and B.T.; writing—Review and editing, L.L., B.T., C.L. and P.L.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31160518, 31272605, 31802242), Young Talents Visiting and Training Program for Foreign Country of Anhui Education Department (gxgwfx2019047), Natural Science Key Foundation of Anhui Education Department (KJ2017A503, KJ2017A504), Talent Project of Anhui Science and Technology University (ZRC2014447), and Leading Academic Discipline Project of Anhui Science and Technology University (AKZDXK2015A04).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Nicholas Shorten, Institute of Biological, Environmental and Rural Sciences, Aberystwyth University, UK, for language editing and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hofmann, A.F. Chemistry and enterohepatic circulation of bile acids. Hepatology 1984, 4, 4S–14S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouscarel, B.; Kroll, S.D.; Fromm, H. Signal transduction and hepatocellular bile acid transport: Cross talk between bile acids and second messengers. Gastroenterology 1999, 117, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, A.; Bouscarel, B. Bile acids and signal transduction: Role in glucose homeostasis. Cell. Signal. 2008, 20, 2180–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Long, A.; Gilmer, J.F. Advances in bile acid medicinal chemistry. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 4029–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadaleta, R.M.; Oldenburg, B.; Willemsen, E.C.; Spit, M.; Murzilli, S.; Salvatore, L.; Klomp, L.W.; Siersema, P.D.; van Erpecum, K.J.; van Mil, S.W. Activation of bile salt nuclear receptor FXR is repressed by pro-inflammatory cytokines activating NF-kappaB signaling in the intestine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1812, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, W.K.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.J.; Jo, M.J.; Kumar, H.; Han, I.B.; Sohn, S. Anti-inflammatory effects of ursodeoxycholic acid by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 macrophages. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e180673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Mao, W.; Guan, H.; Li, L.; Wei, B.; Li, P. Effects of taurochenodeoxycholic acid on adjuvant arthritis in rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 2150–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, C.; Liu, M.; Shi, L.; Liu, Q.; Guan, H.; Li, P. taurochenodeoxycholic acid induces apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 706, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, L.; Guan, H.; Tong, S.; Liu, M.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Du, C.; Li, P. Effects of taurocholic acid on immunoregulation in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 15, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanguas-Casas, N.; Barreda-Manso, M.A.; Nieto-Sampedro, M.; Romero-Ramirez, L. TUDCA: An Agonist of the Bile Acid Receptor GPBAR1/TGR5 with Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Microglial Cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2017, 232, 2231–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comeglio, P.; Morelli, A.; Adorini, L.; Maggi, M.; Vignozzi, L. Beneficial effects of bile acid receptor agonists in pulmonary disease models. Expert Opin. Invest. Drugs 2017, 26, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, J.; Lajczak, N.K.; Kelly, O.B.; O’Dwyer, A.M.; Giddam, A.K.; Ni, G.J.; Franco, P.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Jefferies, C.A.; Keely, S.; et al. Ursodeoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid exert anti-inflammatory actions in the colon. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G550–G558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makishima, M.; Okamoto, A.Y.; Repa, J.J.; Tu, H.; Learned, R.M.; Luk, A.; Hull, M.V.; Lustig, K.D.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Shan, B. Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids. Science 1999, 284, 1362–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.J.; Blanchard, S.G.; Bledsoe, R.K.; Chandra, G.; Consler, T.G.; Kliewer, S.A.; Stimmel, J.B.; Willson, T.M.; Zavacki, A.M.; Moore, D.D.; et al. Bile acids: Natural ligands for an orphan nuclear receptor. Science 1999, 284, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Hollister, K.; Sowers, L.C.; Forman, B.M. Endogenous bile acids are ligands for the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR. Mol. Cell 1999, 3, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Prichard, D.; Majer, F.; Byrne, A.M.; Kelleher, D.; Long, A.; Gilmer, J.F. Ursodeoxycholic acid amides as novel glucocorticoid receptor modulators. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Miyamoto, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Tamai, Y.; Okada, H.; Sugiyama, E.; Nakamura, T.; Itadani, H.; Tanaka, K. Identification of membrane-type receptor for bile acids (M-BAR). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 298, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Liu, M.; Guan, H.; Liu, B.; Wang, C.; He, X.; Cao, J.; Li, P. Taurochenodeoxycholic acid suppresses NF-κB activation and related cytokines expression in peritoneal macrophages from adjuvant arthritis rat. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2018, 12, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, P.; Imagawa, M.; Chiu, R.; Stein, B.; Imbra, R.J.; Rahmsdorf, H.J.; Jonat, C.; Herrlich, P.; Karin, M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell 1987, 49, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asahara, H.; Fujisawa, K.; Kobata, T.; Hasunuma, T.; Maeda, T.; Asanuma, M.; Ogawa, N.; Inoue, H.; Sumida, T.; Nishioka, K. Direct evidence of high DNA binding activity of transcription factor AP-1 in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozawa, S.; Tsumiyama, K. Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and c-Fos/AP-1. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 1539–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Rossignol, S.; Ketheesan, N.; Haleagrahara, N. Redox-sensitive transcription factors play a significant role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 37, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmar, K.D.; Demady, D.R.; Stancato, L.F.; Krishna, P.; Pratt, W.B. Folding of the glucocorticoid receptor by the heat shock protein (hsp) 90-based chaperone machinery. The role of p23 is to stabilize receptor. hsp90 heterocomplexes formed by hsp90 p60 hsp70. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 21213–21220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmar, K.D.; Banach, M.; Galigniana, M.D.; Pratt, W.B. The role of DnaJ-like proteins in glucocorticoid receptor. hsp90 heterocomplex assembly by the reconstituted hsp90 p60 hsp70 foldosome complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 7358–7366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahn, C.; Lowenberg, M.; Hommes, D.W.; Buttgereit, F. Molecular mechanisms of glucocorticoid action and selective glucocorticoid receptor agonists. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2007, 275, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoak, K.A.; Cidlowski, J.A. Mechanisms of glucocorticoid receptor signaling during inflammation. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2004, 125, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekhbat, M.; Rowson, S.A.; Neigh, G.N. Checks and balances: The glucocorticoid receptor and NFkB in good times and bad. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2017, 46, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, J.; Calabrese, L. The role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2004, 43, i2–i9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, S.; Islam, V.I.; Thirugnanasambantham, K.; Pazhanivel, N.; Raghuraman, N.; Paulraj, M.G.; Ignacimuthu, S. Swertiamarin ameliorates inflammation and osteoclastogenesis intermediates in IL-1beta induced rat fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, M.S.; Lee, E.G.; Jeon, H.S.; Chae, H.J.; Park, S.J.; Lee, Y.C.; Yoo, W.H. Quercetin inhibits IL-1beta-induced proliferation and production of MMPs, COX-2, and PGE2 by rheumatoid synovial fibroblast. Inflammation 2012, 35, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Tong, B.; Wei, Z.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Dai, Y. Scopoletin suppresses IL-6 production from fibroblast-like synoviocytes of adjuvant arthritis rats induced by IL-1beta stimulation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 17, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Cai, Q.; Li, C.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, W. Therapeutic effects of matrine derivate MASM in mice with collagen-induced arthritis and on fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Makino, I. Ursodeoxycholic acid-dependent activation of the glucocorticoid receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992, 188, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Makino, Y.; Miura, T.; Hirano, F.; Okamoto, K.; Komura, K.; Sato, Y.; Makino, I. Ligand-independent activation of the glucocorticoid receptor by ursodeoxycholic acid. Repression of IFN-gamma-induced MHC class II gene expression via a glucocorticoid receptor-dependent pathway. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weitzel, C.; Stark, D.; Kullmann, F.; Scholmerich, J.; Holstege, A.; Falk, W. Ursodeoxycholic acid induced activation of the glucocorticoid receptor in primary rat hepatocytes. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 17, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Huang, W. Bile acid nuclear receptor FXR and digestive system diseases. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2015, 5, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pols, T.W.; Nomura, M.; Harach, T.; Lo, S.G.; Oosterveer, M.H.; Thomas, C.; Rizzo, G.; Gioiello, A.; Adorini, L.; Pellicciari, R.; et al. TGR5 activation inhibits atherosclerosis by reducing macrophage inflammation and lipid loading. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Huang, G.; Gong, W.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Gao, M.; Pan, Z.; He, F. FXR ligands protect against hepatocellular inflammation via SOCS3 induction. Cell Signal. 2012, 24, 1658–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Kim, C.H.; Moon, S.H.; Kang, S.G.; Park, Y.G. Protective and anti-arthritic effects of deer antler aqua-acupuncture (DAA), inhibiting dihydroorotate dehydrogenase, on phosphate ions-mediated chondrocyte apoptosis and rat collagen-induced arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2004, 4, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Y.; Chen, F.H.; Li, J.; Xia, L.J.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhang, X.M.; Yuan, F.L. Mechanism of fibroblast-like synoviocyte apoptosis induced by recombinant human endostatin in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Anat. Rec. 2008, 291, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds TCDCA is available from the authors. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).