Tectorigenin, a Flavonoid-Based Compound of Leopard Lily Rhizome, Attenuates UV-B-Induced Apoptosis and Collagen Degradation by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress in Human Keratinocytes
Abstract
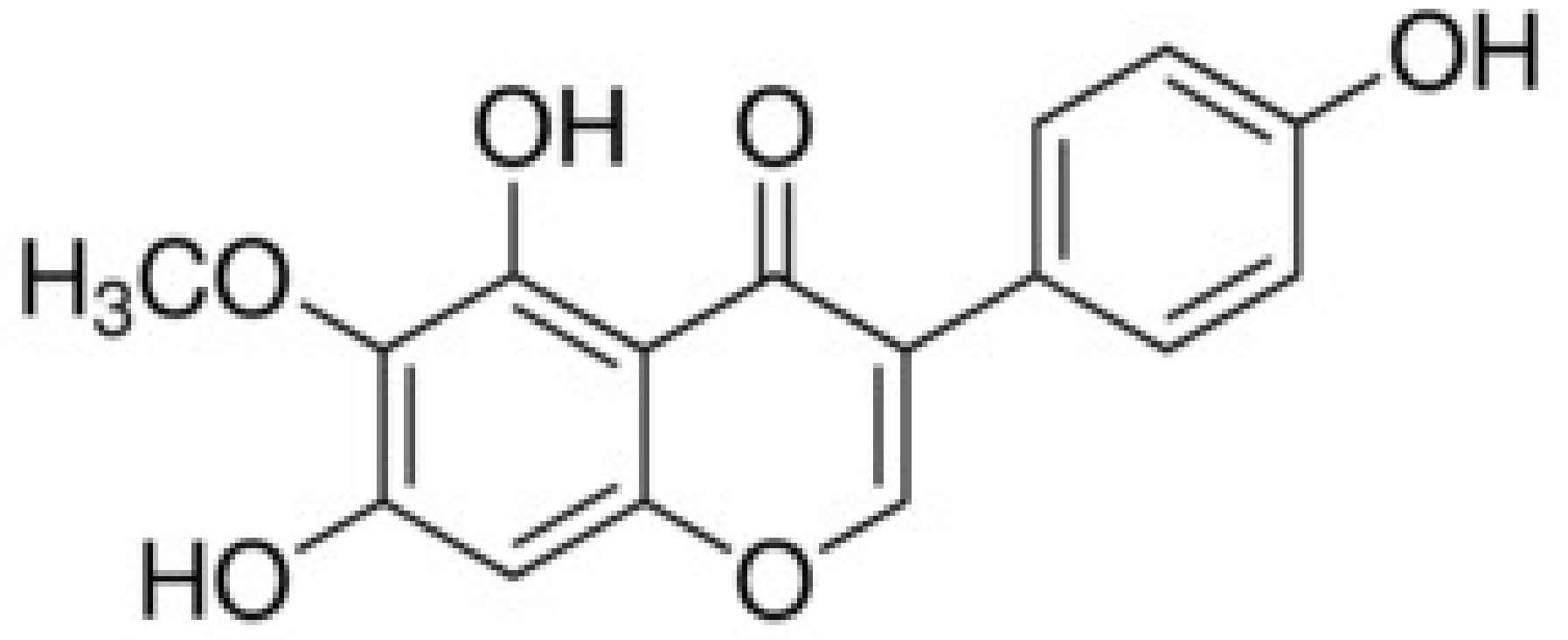
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Measurement of Cell Viability
2.4. Measurement of Intracellular ROS
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Measurement of MMP-1 Levels
2.7. Measurement of GSH Levels
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
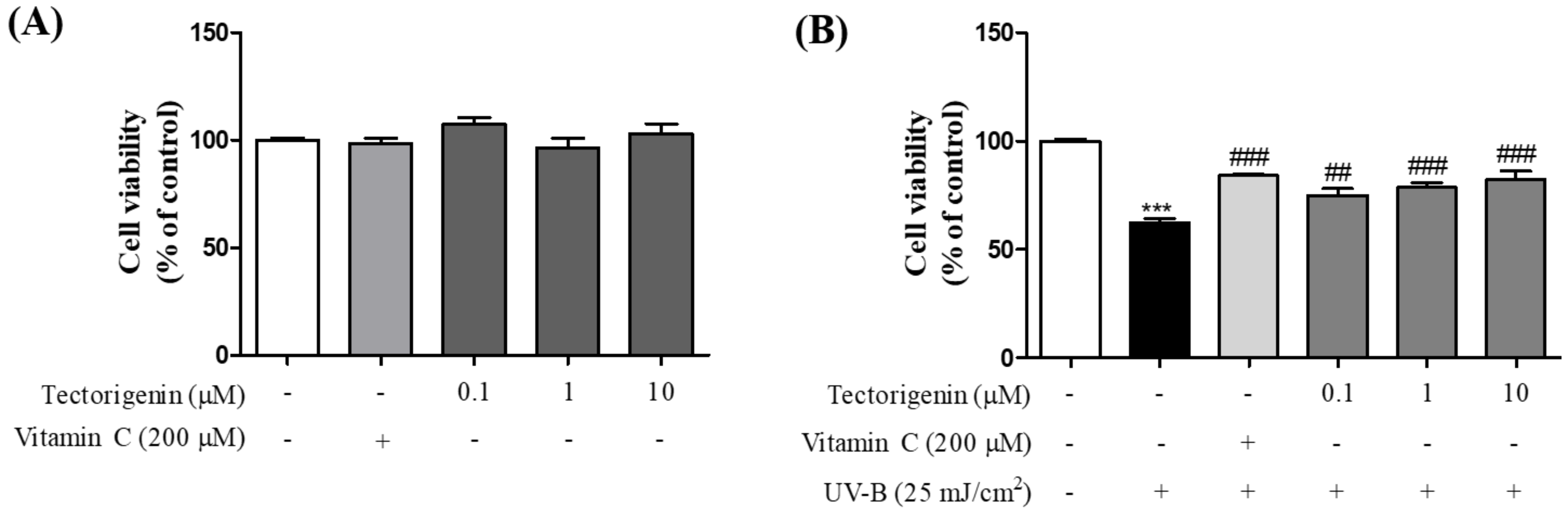
3.1. Tectorigenin Protects Keratinocytes against UV-B-Induced Damage
3.2. Tectorigenin Inhibits UV-B-Induced ROS Generation in Keratinocytes
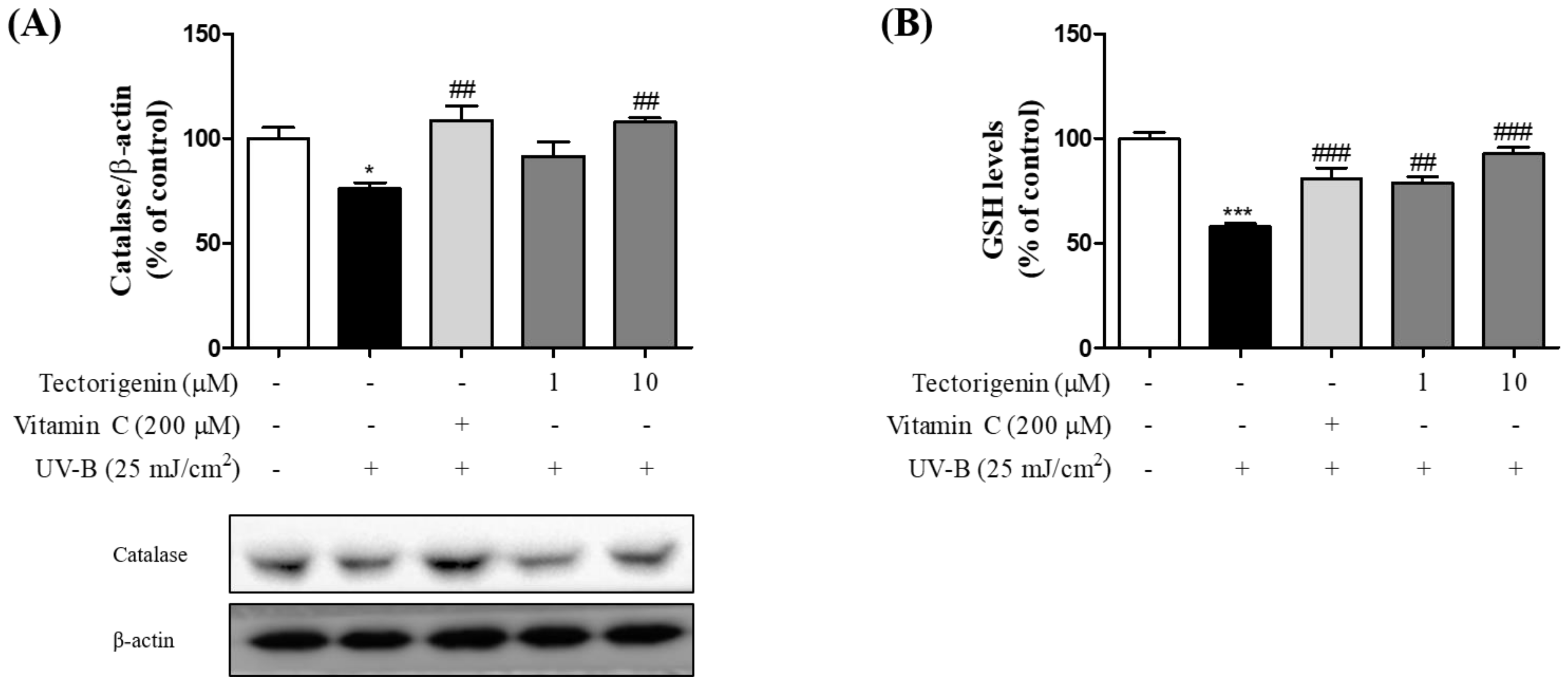
3.3. Tectorigenin Stimulates the Release of Anti-Oxidative Enzymes Effective against UV-B-Induced Damage
3.4. Tectorigenin Protects Keratinocytes against the UV-B-Induced Expression of Apoptosis-Related Proteins
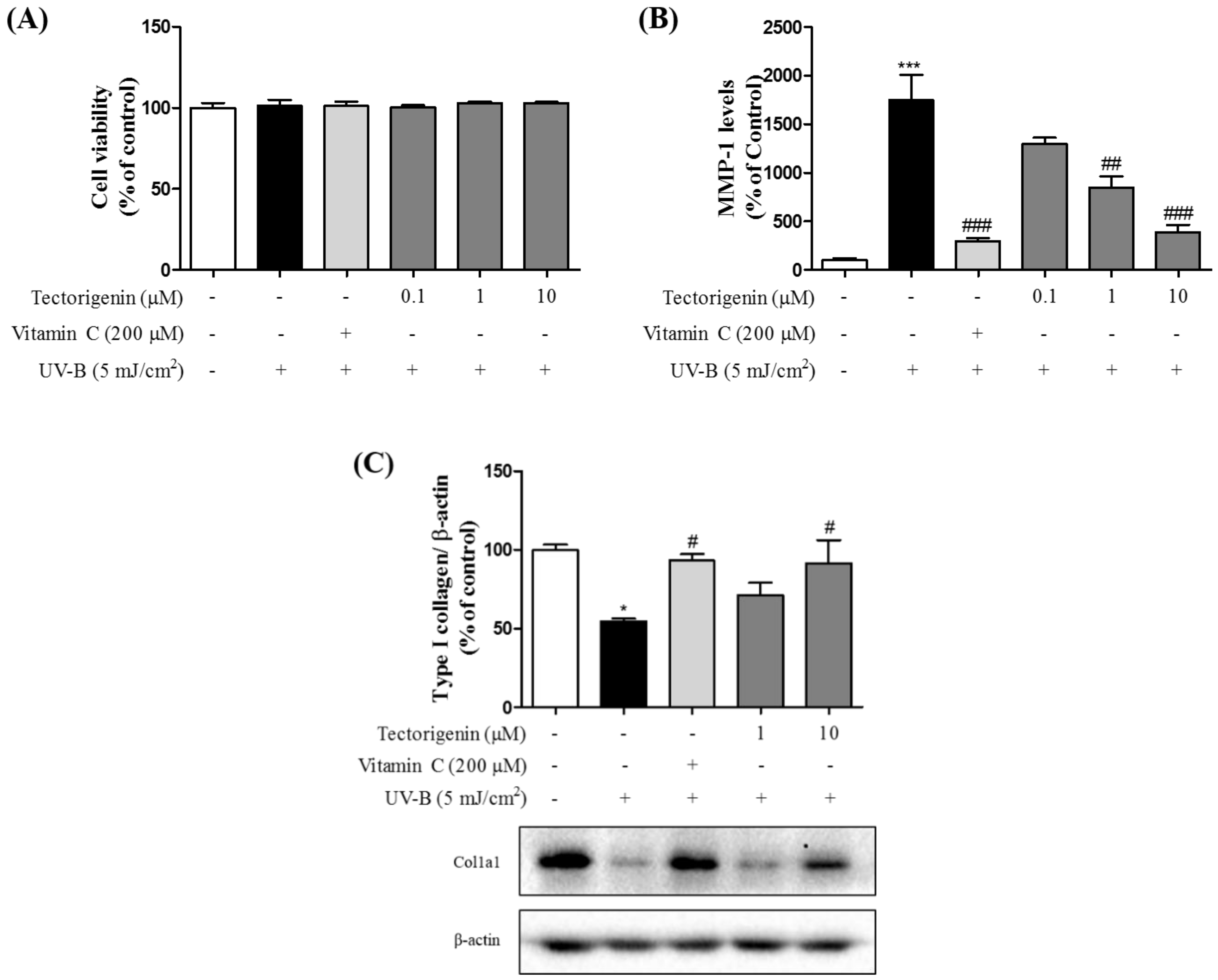
3.5. Tectorigenin Attenuates UV-B-Induced Collagen Degradation in Keratinocytes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bergfeld, W.F. The aging skin. Int. J. Fertil. Womens Med. 1997, 42, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poon, F.; Kang, S.; Chien, A.L. Mechanisms and treatments of photoaging. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2015, 31, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.; Elwood, J.; English, D. Prevention of Skin Cancer. Cancer Prevention—Cancer Causes; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Vierkotter, A.; Krutmann, J. Environmental influences on skin aging and ethnic-specific manifestations. Dermato-Endocrinology 2012, 4, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulms, D.; Schwarz, T. Molecular mechanisms of UV-induced apoptosis. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2000, 16, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inomata, S.; Matsunaga, Y.; Amano, S.; Takada, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Tsunenaga, M.; Nishiyama, T.; Kohno, Y.; Fukuda, M. Possible involvement of gelatinases in basement membrane damage and wrinkle formation in chronically ultraviolet B-exposed hairless mouse. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilcher, B.K.; Sudbeck, B.D.; Dumin, J.A.; Welgus, H.G.; Parks, W.C. Collagenase-1 and collagen in epidermal repair. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1998, 290, S37–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svobodova, A.; Vostalova, J. Solar radiation induced skin damage: Review of protective and preventive options. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2010, 86, 999–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonesi, M.; Loizzo, M.R.; Provenzano, E.; Menichini, F.; Tundis, R. Anti-Psoriasis Agents from Natural Plant Sources. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 1250–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z.; Thu, H.E.; Shuid, A.N.; Kesharwani, P.; Khan, S.; Hussain, F. Phytotherapeutic potential of natural herbal medicines for the treatment of mild-to-severe atopic dermatitis: A review of human clinical studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicentini, F.T.; He, T.; Shao, Y.; Fonseca, M.J.; Verri, W.A., Jr.; Fisher, G.J.; Xu, Y. Quercetin inhibits UV irradiation-induced inflammatory cytokine production in primary human keratinocytes by suppressing NF-kappaB pathway. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2011, 61, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittie, L.; Fisher, G.J. Natural and sun-induced aging of human skin. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a015370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.X.; Shi, D.H.; Chen, Y.X.; Cui, J.T.; Wang, Y.R.; Jiang, C.P.; Wu, J.H. The therapeutic effects of tectorigenin on chemically induced liver fibrosis in rats and an associated metabonomic investigation. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 1479–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.T.; Ben, K.L. Use of MTT Assay for the Determination of Cell Viability and Proliferation. Immunol. J. 1992, 8, 266–269. [Google Scholar]
- Berneburg, M.; Plettenberg, H.; Krutmann, J. Photoaging of human skin. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2000, 16, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, C.; Bernstein, H.; Payne, C.M.; Garewal, H. DNA repair/pro-apoptotic dual-role proteins in five major DNA repair pathways: Fail-safe protection against carcinogenesis. Mutat. Res. 2002, 511, 145–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelikani, P.; Fita, I.; Loewen, P.C. Diversity of structures and properties among catalases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, H.R.; Mazurier, F.; Cario-Andre, M.; Pain, C.; Ged, C.; Taieb, A.; De Verneuil, H. Protective effects of catalase overexpression on UVB-induced apoptosis in normal human keratinocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 17999–18007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.H.; Lee, S.R.; Kim, M.K.; Shin, C.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Chung, J.H. Activation of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha Improves Aged and UV-Irradiated Skin by Catalase Induction. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenk, J.; Schuller, J.; Hinrichs, C.; Syrovets, T.; Azoitei, N.; Podda, M.; Wlaschek, M.; Brenneisen, P.; Schneider, L.A.; Sabiwalsky, A.; et al. Overexpression of phospholipid-hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase in human dermal fibroblasts abrogates UVA irradiation-induced expression of interstitial collagenase/matrix metalloproteinase-1 by suppression of phosphatidylcholine hydroperoxide-mediated NFkappaB activation and interleukin-6 release. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 45634–45642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weschawalit, S.; Thongthip, S.; Phutrakool, P.; Asawanonda, P. Glutathione and its antiaging and antimelanogenic effects. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 10, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Ming, M.; He, Y.Y. Caffeine promotes ultraviolet B-induced apoptosis in human keratinocytes without complete DNA repair. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 22825–22832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gruijl, F.R. Photocarcinogenesis: UVA vs. UVB radiation. Skin Pharmacol. Appl. Skin Physiol. 2002, 15, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jans, J.; Schul, W.; Sert, Y.G.; Rijksen, Y.; Rebel, H.; Eker, A.P.; Nakajima, S.; Van Steeg, H.; De Gruijl, F.R.; Yasui, A.; et al. Powerful skin cancer protection by a CPD-photolyase transgene. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. p53 function and dysfunction. Cell 1992, 70, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, I.; Beissert, S.; Kulms, D. Anti-apoptotic NF-kappaB and “gain of function” mutp53 in concert act pro-apoptotic in response to UVB+IL-1 via enhanced TNF production. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jung, E.; Lee, J.; Huh, S.; Hwang, C.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, E.J.; Cheon, J.M.; Hyun, C.G.; Kim, Y.S.; et al. Emodin inhibits TNF alpha-induced MMP-1 expression through suppression of activator protein-1 (AP-1). Life Sci. 2006, 79, 2480–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, K.E.; Tagliaferro, A.R.; Bobilya, D.J. Flavonoid antioxidants: Chemistry, metabolism and structure-activity relationships. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2002, 13, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promden, W.; Monthakantirat, O.; Umehara, K.; Noguchi, H.; De-Eknamkul, W. Structure and antioxidant activity relationships of isoflavonoids from Dalbergia parviflora. Molecules 2014, 19, 2226–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.C.; Hsu, B.Y.; Wu, N.L.; Tsui, W.H.; Lin, T.J.; Su, C.C.; Hung, C.F. Anti-photoaging effects of soy isoflavone extract (aglycone and acetylglucoside form) from soybean cake. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 4782–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noh, D.; Choi, J.G.; Huh, E.; Oh, M.S. Tectorigenin, a Flavonoid-Based Compound of Leopard Lily Rhizome, Attenuates UV-B-Induced Apoptosis and Collagen Degradation by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress in Human Keratinocytes. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121998
Noh D, Choi JG, Huh E, Oh MS. Tectorigenin, a Flavonoid-Based Compound of Leopard Lily Rhizome, Attenuates UV-B-Induced Apoptosis and Collagen Degradation by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress in Human Keratinocytes. Nutrients. 2018; 10(12):1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121998
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoh, Dongjin, Jin Gyu Choi, Eugene Huh, and Myung Sook Oh. 2018. "Tectorigenin, a Flavonoid-Based Compound of Leopard Lily Rhizome, Attenuates UV-B-Induced Apoptosis and Collagen Degradation by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress in Human Keratinocytes" Nutrients 10, no. 12: 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121998
APA StyleNoh, D., Choi, J. G., Huh, E., & Oh, M. S. (2018). Tectorigenin, a Flavonoid-Based Compound of Leopard Lily Rhizome, Attenuates UV-B-Induced Apoptosis and Collagen Degradation by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress in Human Keratinocytes. Nutrients, 10(12), 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121998





