Birefringence of the Human Cornea: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Selection of Material for Review and Data Retrieval
3. What Is Birefringence?
4. What Causes Birefringence?
5. What Could Induce a Change in Corneal Birefringence?
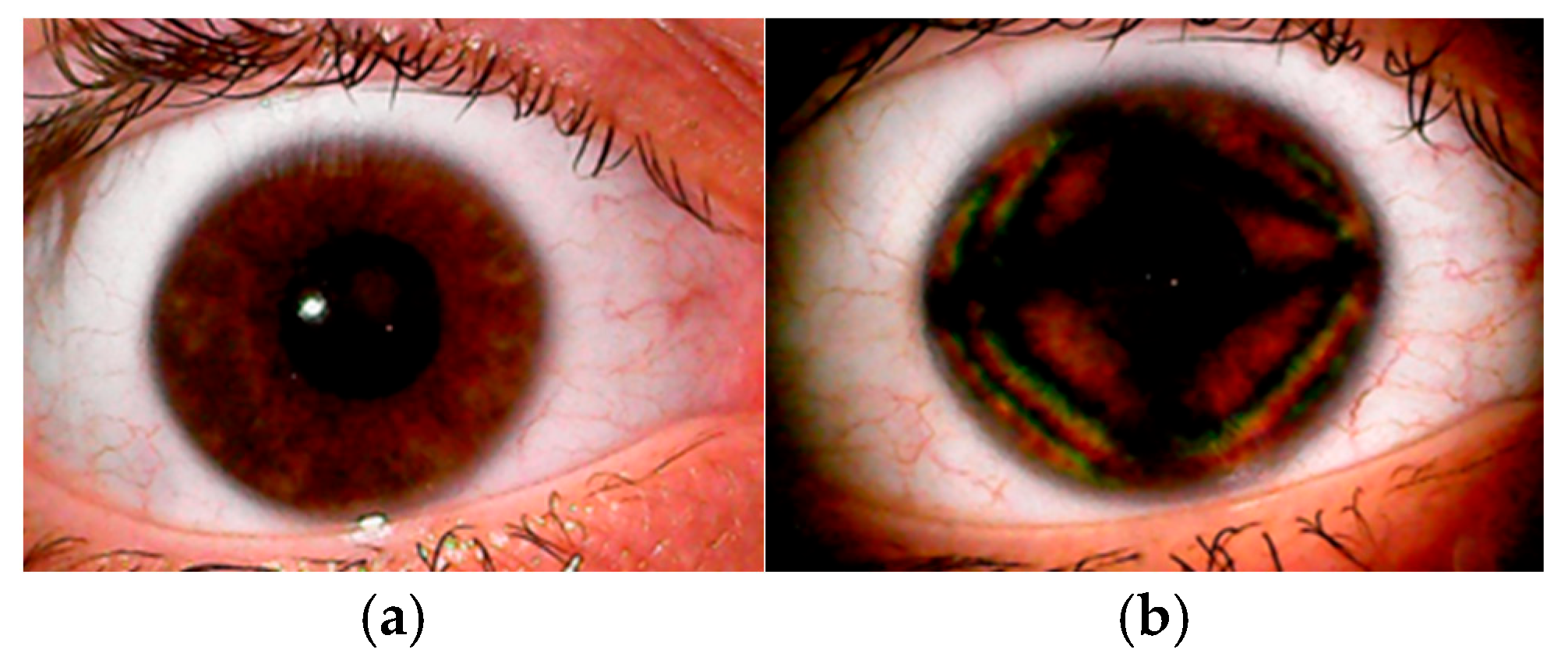
6. How Can the CBP Be Demonstrated and Observed in a Clinical Setting?
7. How Can Corneal Birefringence Be Categorized?
7.1. Does the Cornea Have Characteristics of a Uni- or Biaxial Crystal?
8. How Can Corneal Birefringence Be Quantified for Analysis and Statistical Purposes?
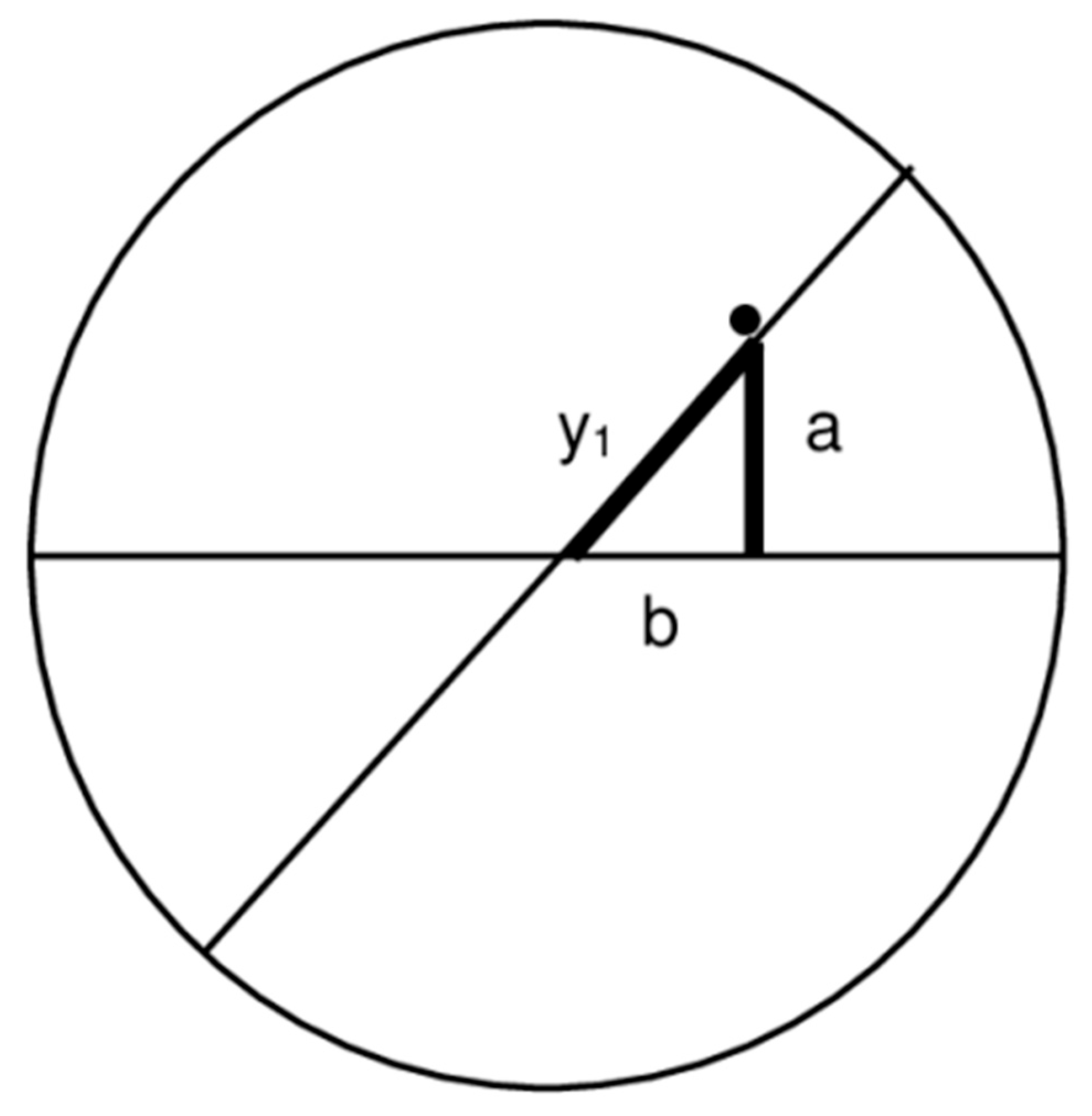
8.1. Orientation of the Slow Axis, Estimating Corneal Retardation and Differences in the Refractive Index (n1 − n2)
8.2. Matrix Analysis of Birefringent Patterns
9. Can the CBP Be Used to Model Corneal Structure?
- (i)
- Fresnel equations should predict the intensity distribution of the polarized light reflected off the ocular surface [80];
- (ii)
- Characteristics of the dark cross over the surface of a powered contact lens placed on the eye should differ in comparison with the dark cross over the ocular surface;
- (iii)
- The characteristics of the cross should be markedly different in cases of ectasia;
- (iv)
- The appearance of the cross should change in response to changes in the characteristics of the precorneal tear film during the interblink interval.
9.1. Modelling the Architecture of the Corneal Stroma
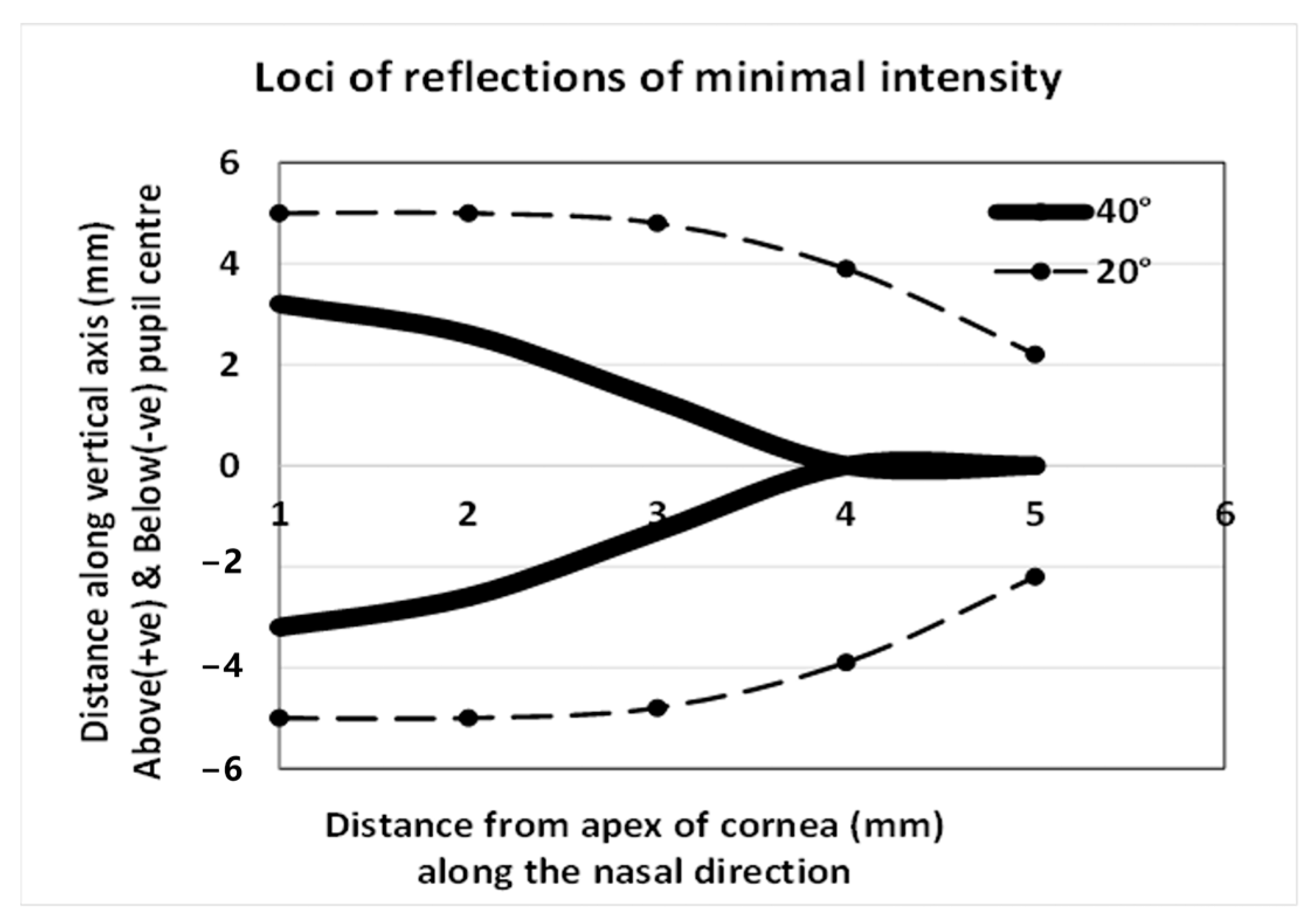
9.2. Is the CBP Representative of Corneal Thickness, Distribution, or Structure?
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CB | Corneal birefringence |
| CBP | Corneal birefringence pattern |
| SLP | Scanning laser polarimetry or Scanning laser polarimeter |
| OCT | Ocular coherence tomography or Ocular coherence tomographer |
| RNFL | Retinal nerve fiber layer |
| LASIK | Laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis |
| n1 − n2 | Difference in the refractive indices |
| t | Corneal thickness |
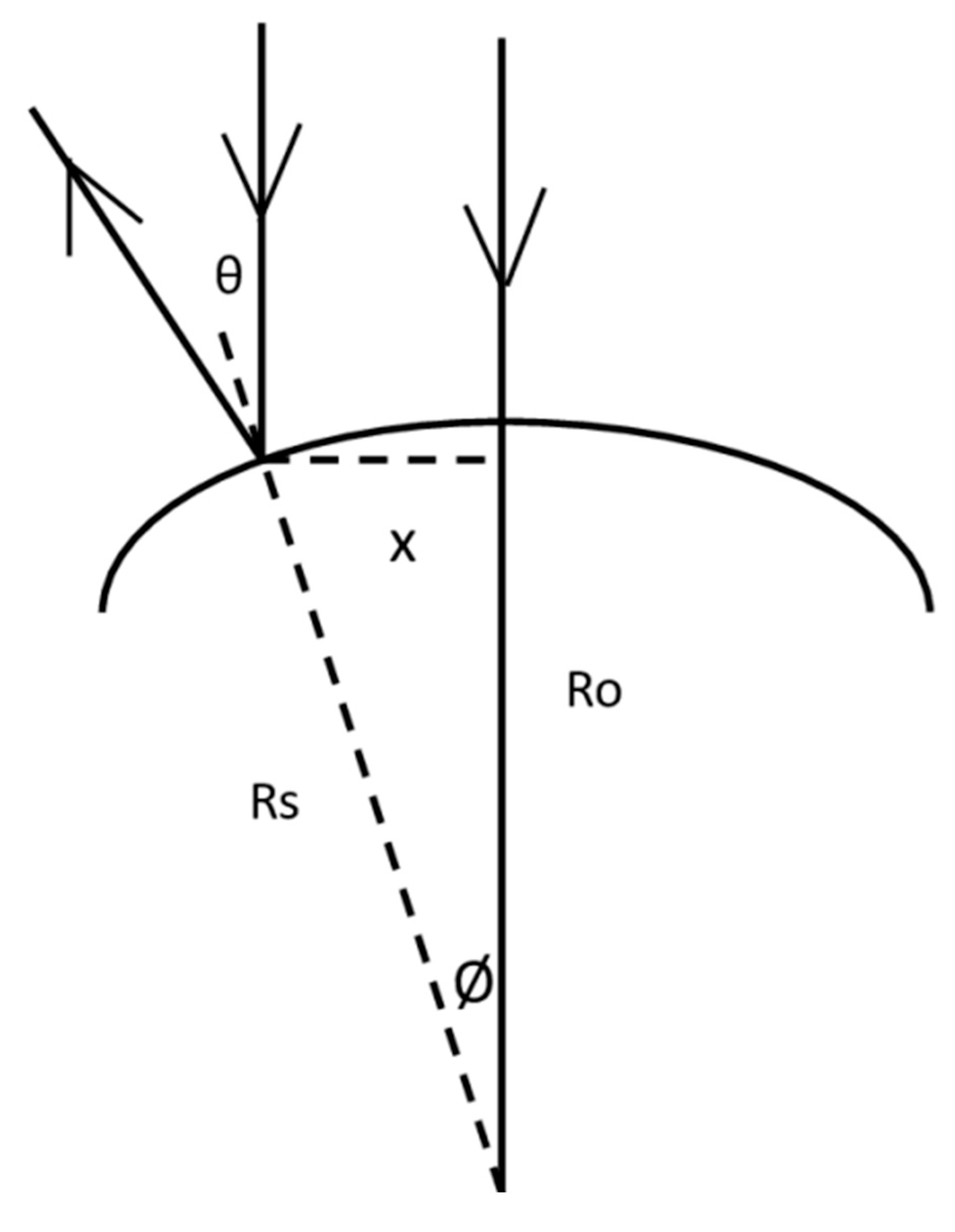
| Θ | Angle of incidence |
| Ψ | Angle of refraction |
| Ro | Radius at the apex of the cornea |
| Rs | Sagittal radius of the cornea at distance x from the apex |
Appendix A

References
- Choplin, N.T.; Schallhorn, S.C. The effect of excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy for myopia on nerve fiber layer thickness measurements as determined by scanning laser polarimetry. Ophthalmology 1999, 106, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collur, S.; Carroll, A.M.; Cameron, B.D. Human lens effect on in vivo scanning laser polarimetric measurements of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers 2000, 31, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gürses-Ozden, R.; Pons, M.E.; Barbieri, C.; Ishikawa, H.; Buxton, D.F.; Liebmann, J.M.; Ritch, R. Scanning laser polarimetry measurements after laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2000, 129, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenfield, D.S.; Knighton, R.W.; Huang, X.R. Effect of corneal polarization axis on assessment of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness by scanning laser polarimetry. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2000, 129, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogure, S.; Chiba, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Kowa, H.; Tsukahara, S. Effects of artefacts on scanning laser polarimetry of retinal nerve fibre layer thickness measurement. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2000, 84, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Knighton, R.W.; Huang, X.R.; Greenfield, D.S. Analytical model of scanning laser polarimetry for retinal nerve fiber layer assessment. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garway-Heath, D.F.; Greaney, M.J.; Caprioli, J. Correction for the erroneous compensation of anterior segment birefringence with the scanning laser polarimeter for glaucoma diagnosis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roberts, T.V.; Lawless, M.A.; Rogers, C.M.; Sutton, G.L.; Domniz, Y. The effect of laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis on retinal nerve fiber layer measurements obtained with scanning laser polarimetry. J. Glaucoma 2002, 11, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holló, G.; Nagy, Z.Z.; Vargha, P.; Süveges, I. Influence of post-LASIK corneal healing on scanning laser polarimetric measurement of the retinal nerve fibre layer thickness. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 86, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nevyas, J.Y.; Nevyas, H.J.; Nevyas-Wallace, A. Change in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness after laser in situ keratomileusis. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2002, 28, 2123–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choplin, N.T.; Zhou, Q.; Knighton, R.W. Effect of individualized compensation for anterior segment birefringence on retinal nerve fiber layer assessments as determined by scanning laser polarimetry. Ophthalmology 2003, 110, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holló, G.; Katsanos, A.; Kóthy, P.; Kerek, A.; Süveges, I. Influence of LASIK on scanning laser polarimetric measurement of the retinal nerve fibre layer with fixed angle and customised corneal polarization compensation. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2003, 87, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- McCarty, T.M.; Hardten, D.R.; Anderson, N.J.; Rosheim, K.; Samuelson, T.W. Evaluation of neuroprotective qualities of brimonidine during LASIK. Ophthalmology 2003, 110, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeles, R.; Abunto, T.; Bowd, C.; Zangwill, L.M.; Schanzlin, D.J.; Weinreb, R.N. Corneal changes after laser in situ keratomileusis: Measurement of corneal polarization magnitude and axis. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 137, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choplin, N.T.; Schallhorn, S.C.; Sinai, M.; Tanzer, D.; Tidwell, J.L.; Zhou, Q. Retinal nerve fiber layer measurements do not change after LASIK for high myopia as measured by scanning laser polarimetry with custom compensation. Ophthalmology 2005, 112, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagga, H.; Greenfield, D.S.; Feuer, W.J. Quantitative assessment of atypical birefringence images using scanning laser polarimetry with variable corneal compensation. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 139, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centofanti, M.; Oddone, F.; Parravano, M.; Gualdi, L.; Bucci, M.G.; Manni, G. Corneal birefringence changes after laser assisted in situ keratomileusis and their influence on retinal nerve fibre layer thickness measurement by means of scanning laser polarimetry. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 89, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tóth, M.; Holló, G. Enhanced corneal compensation for scanning laser polarimetry on eyes with atypical polarisation pattern. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 89, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shoji, T.; Takahashi, H.; Park, M.; Okazaki, K.; Tanito, M.; Chihara, E. Prospective evaluation of factors associated with post-LASIK corneal birefringence with scanning laser polarimetry. J. Glaucoma 2007, 16, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Götzinger, E.; Pircher, M.; Dejaco-Ruhswurm, I.; Kaminski, S.; Skorpik, C.; Hitzenberger, C.K. Imaging of birefringent properties of keratoconus corneas by polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 3551–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogure, S.; Kohwa, H.; Tsukahara, S. Effect of uncompensated corneal polarization on the detection of localized retinal nerve fiber layer defects. Ophthalmic Res. 2008, 40, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aristeidou, A.P.; Labiris, G.; Paschalis, E.I.; Foudoulakis, N.C.; Koukoula, S.C.; Kozobolis, V.P. Evaluation of the retinal nerve fiber layer measurements, after photorefractive keratectomy and laser in situ keratomileusis, using scanning laser polarimetry (GDX VCC). Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2010, 248, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iovieno, A.; Yeung, S.N.; Nahum, Y.; Teichman, J.; Lipari, E.; Busin, M.; Fontana, L. Polarimetric Interferometry for Assessment of Corneal Stromal Lamellae Orientation. Cornea 2016, 35, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, J.S.; Cameron, B.D.; Theru, S.; Coté, G.L. Effect of temperature, pH, and corneal birefringence on polarimetric glucose monitoring in the eye. J. Biomed. Opt. 2002, 7, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, B.H.; Coté, G.L. Modeling the corneal birefringence of the eye toward the development of a polarimetric glucose sensor. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 037012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pirnstill, C.W.; Malik, B.H.; Gresham, V.C.; Coté, G.L. In vivo glucose monitoring using dual-wavelength polarimetry to overcome corneal birefringence in the presence of motion. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2012, 14, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Westphal, P.; Kaltenbach, J.M.; Wicker, K. Corneal birefringence measured by spectrally resolved Mueller matrix ellipsometry and implications for non-invasive glucose monitoring. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 1160–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stanworth, A.; Naylor, E.J. Polarized light studies of the cornea I. The isolated cornea. J. Exp. Biol. 1953, 30, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanworth, A. Polarized light studies of the cornea II. The effect of intra-ocular pressure. J. Exp. Biol. 1953, 30, 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Yamanari, M.; Nagase, S.; Fukuda, S.; Ishii, K.; Tanaka, R.; Yasui, T.; Oshika, T.; Miura, M.; Yasuno, Y. Scleral birefringence as measured by polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography and ocular biometric parameters of human eyes in vivo. Biomed. Opt. Express 2014, 5, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Richhariya, A.; Verma, Y.; Rao, D.K.; Roberts, C.J.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Sangwan, V.S.; Punjabi, S.; Gupta, P.K. Effect of Intraocular Pressure and Anisotropy on the Optical Properties of the Cornea: A Study Using Polarization Sensitive Optical Coherence Tomography. Asia-Pacific J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 3, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, N.; Wu, Q.Y.S.; Leong, H.S.; Abdelaziem, A.; Mehta, J.S.; Liu, Y.-C. Corneal elastic property investigated by terahertz technology. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bartholin, E. Experiments with the Birefringent Icelandic Crystal, Which Led to the Discovery of a Wonderful and Extraordinary Refraction; Archibald, T., Translator; Introduction by Jed, Z. Buchwald and Kurt Moller Pedersen; Danish National Library of Science and Medicine: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1991; pp. 63–64. ISBN 87-7709-010-1. 160 DKK; Available online: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=F7RAAAAAcAAJ&pg=PP11&source=gbs_selected_pages&cad=3#v=onepage&q&f=false (accessed on 5 August 2023).
- Brewster, D. Experiments on the de-polarization of light as exhibited by various mineral, animal and vegetable bodies with a reference to the general principles of polarization. Phil Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1815, 105, 21–53. [Google Scholar]
- Valentin, G. Die Untersuchung der Pflanzen- und der Thiergewebe in Polarizirtem Lichte; Engelman: Leibzig, Germany, 1861. [Google Scholar]
- Koeppe, L. Die Ultra und Polarizationsmikroskopische Erforschung des Lebenden Auges und Ihre Ergebnisse; Ernst Bircher: Leibzig, Germany, 1921. [Google Scholar]
- Cogan, D.G. Some Ocular Phenomena Produced with Polarized Light. Arch. Ophthal. 1941, 25, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.M. Writing an Effective Review Article. J. Med. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 89–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhera, J. Narrative Reviews: Flexible, Rigorous, and Practical. J. Grad. Med. Educ. 2022, 14, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Douplik, A.; Saiko, I.G.; Schelkanova, I.; Tuchin, V.V. The response of tissue to laser light. In Lasers for Medical Applications: Diagnostics, Therapy and Surgery; Jelínková, H., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Electronic and Optical Materials: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 86–87. [Google Scholar]
- Longhurst, R.S. The propagation of light in crystals. In Geometrical and Physical Optics; Longhurst, R.S., Ed.; Longman Group: London, UK, 1967; pp. 483–511. ISBN 10: 0582443156/ISBN 13: 9780582443150. [Google Scholar]
- Born, M.; Wolf, E. Interference and diffraction with partially coherent light. In Principles of Optics; Born, M., Wolf, E., Eds.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1980; pp. 491–554. [Google Scholar]
- Daxer, A.; Fratzl, P. Collagen fibril orientation in the human corneal stroma and its implication in keratoconus. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1997, 38, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Meek, K.M.; Quantock, A.J. The use of x-ray scattering techniques to determine corneal ultrastructure. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2001, 20, 95–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bour, L.J. Polarized light and the eye. In Visual Optics and Instrumentation; Charman, W.N., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1991; pp. 310–325. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, B.F.; Logan, P.; Zajdenweber, M.E.; Santos, L.N.; Cheema, D.P.; Burnier, M.N., Jr. Histopathological study of 49 cases of keratoconus. Pathology 2008, 40, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykakis, E.; Carley, F.; Irion, L.; Denton, J.; Hillarby, M.C. An in depth analysis of histopathological characteristics found in keratoconus. Pathology 2012, 44, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournié, P.; Touboul, D.; Arné, J.L.; Colin, J.; Malecaze, F. Kératocône [Keratoconus]. J. Fr. Ophtalmol. 2013, 36, 618–626. (In French) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meek, K.M.; Tuft, S.J.; Huang, Y.; Gill, P.S.; Hayes, S.; Newton, R.H.; Bron, A.J. Changes in collagen orientation and distribution in keratoconus corneas. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 1948–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, R.; D’Souza, S.; Khamar, P.; Ghosh, A.; Nuijts, R.M.M.A.; Sethu, S. Biochemical Markers and Alterations in Keratoconus. Asia Pac. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 9, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.B.; Koh, S.; Sharma, N.; Woreta, F.A.; Hafezi, F.; Dua, H.S.; Jhanji, V. Keratoconus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2024, 10, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, R.N.; Bowd, C.; Greenfield, D.S.; Zangwill, L.M. Measurement of the magnitude and axis of corneal polarization with scanning laser polarimetry. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2002, 120, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, T.A.; Lemij, H.G. Longitudinal measurement variability of corneal birefringence and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in scanning laser polarimetry with variable corneal compensation. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2008, 126, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, M.; Asejczyk, M.; Kalinowski, K.; Pierścionek, B. Comparative analysis of the corneal birefringence pattern in healthy children and adults. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2021, 41, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knighton, R.W.; Huang, X.R. Linear birefringence of the central human cornea. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Misson, G.P. Circular polarization biomicroscopy: A method for determining human corneal stromal lamellar organization in vivo. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2007, 27, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipari, E.; Sborgia, A.; Nubile, M.; Mastropasqua, L.; Alessio, G. Polarimetric interferometry to objectively evaluate the optical properties of corneal stroma. J. Model. Ophthalmol. 2018, 2, 36–42. Available online: https://www.maio-journal.com/index.php/MAIO/article/view/69 (accessed on 5 August 2023). [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, M.; Owczarek, M.; Woźniak, W.A.; Kurzynowski, P. In vivo measurements of corneal birefringence properties using the one-way reflective Mueller polarimetry. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 15356–15365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knighton, R.W.; Huang, X.R.; Cavuoto, L.A. Corneal birefringence mapped by scanning laser polarimetry. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 13738–13751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pircher, M.; Hitzenberger, C.K.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U. Polarization sensitive optical coherence tomography in the human eye. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2011, 30, 431–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Patil, R.M.; Shetty, R.M.; Narasimhan, R.M.; Patel, Y.M.; Khamar, P.; Pircher, M.; Hitzenberger, C.K.; Nuijts, R.M.; Roy, A.S. Mapping of corneal birefringence in thin and asymmetric keratoconus corneas with ultrahigh-resolution polarization-sensitive OCT. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2022, 48, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misson, G.P. Birefringent Properties of the Human Cornea In Vivo: Towards a New Model of Corneal Structure. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Warwick, Warwick, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mastropasqua, R.; Nubile, M.; Salgari, N.; Lanzini, M.; Calienno, R.; Mattei, P.A.; Sborgia, A.; Agnifili, L. Interference figures of polarimetric interferometry analysis of the human corneal stroma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sobczak, M.; Asejczyk, M. Birefringent properties of the cornea measured by a Mueller type polarimeter in healthy adults and children. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 7872–7885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierscionek, B.K.; Weale, R.A. Is there a link between corneal structure and the ‘corneal cross’? Eye 1997, 11, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierscionek, B.K.; Weale, R.A. Investigation of the polarization optics of the living human cornea and lens with purkinje images. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 6845–6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, E. Polarisation. In Optics, 4th ed.; Hecht, E., Ed.; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1987; p. 337. ISBN 0-8053-8566-5. [Google Scholar]
- Stoiber, R.E.; Morse, S.A. Biaxial crystal optics. In Crystal Identification with the Polarizing Microscope; Stoiber, R.E., Morse, S.A., Eds.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1994; pp. 159–171. [Google Scholar]
- Misson, G.P. The theory and implications of the biaxial model of corneal birefringence. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2010, 30, 834–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaronski, J.W.; Kasprzak, H.T. Linear birefringence measurements of the in vitro human cornea. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2003, 23, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Blokland, G.J.; Verhelst, S.C. Corneal polarization in the living human eye explained with a biaxial model. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1987, 4, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donohue, D.J.; Stoyanov, B.J.; McCally, R.L.; Farrell, R.A. A numerical test of the normal incidence uniaxial model of corneal birefringence. Cornea 1996, 15, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanjul-Vélez, M.; Pircher, M.; Baumann, B.; Götzinger, E.; Arce-Diego, J.L.; Hitzenberger, C.K. Modelling human corneal polarization properties and comparison with PS-OCT measurements. In Ophthalmic Technologies XIX; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2009; Volume 7163, pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, M.; Jóźwik, A.; Kurzynowski, P. An integrated model of the human cornea as a linear biaxial birefringent medium. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Götzinger, E.; Pircher, M.; Sticker, M.; Fercher, A.F.; Hitzenberger, C.K. Measurement and imaging of birefringent properties of the human cornea with phase-resolved, polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2004, 9, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitzenberger, C.K.; Götzinger, E.; Pircher, M. Birefringence properties of the human cornea measured with polarization sensitive optical coherence tomography. Bull. Soc. Belg. Belge. Ophtalmol. 2006, 302, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greenfield, D.S.; Knighton, R.W. Stability of corneal polarization axis measurements for scanning laser polarimetry. Ophthalmology 2001, 108, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irsch, K.; Shah, A.A. Birefringence of the central cornea in children assessed with scanning laser polarimetry. J Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 086001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shurcliff, W.A. Overview of Mueller and Jones calculi. In Polarized Light; Shurcliff, W.A., Ed.; Harvard University Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1966; p. 122. Available online: https://pypolar.readthedocs.io/en/latest/jones-or-mueller.html (accessed on 5 August 2023).
- Lvovsky, A.I. Fresnel Equations. In Encyclopedia of Optical Engineering; Hoffman, C., Driggers, R., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, F.P. Uber die darstellung der hornhautoberflache und ihrer veranderungen im reflexbild. Arch. Augenheilkunde 1928, 98, 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, F.P. Bermerkungen zur.hartingers artukel uber Zeissischen cornealreflectographen und seine hornhautbilder. Ophthalmol. Optik. 1933, 21, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Tiffany, J.M. Refractive index of meibomian and other lipids. Curr. Eye Res. 1986, 5, 887–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, W.T.; Wolbarsht, M.L.; Yamanashi, B.S. The corneal polarization cross. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1978, 68, 1139–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanworth, A.; Naylor, E.J. The polarization optics of the isolated cornea. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1950, 34, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, J.M.; Jaronski, J. Spatially resolved polarization properties for in vitro corneas. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2001, 21, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atchison, D.A.; Smith, G. Passage of light into the eye. In Optics of the Human Eye; Atchison, D.A., Smith, G., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2000; p. 114. [Google Scholar]
- Bueno, J.M.; Berrio, E.; Artal, P. Corneal polarimetry after LASIK refractive surgery. J. Biomed. Opt. 2006, 11, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, J.M.; Vargas-Martín, F. Measurements of the corneal birefringence with a liquid-crystal imaging polarizcope. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, J.M. Measurement of parameters of polarization in the living human eye using imaging polarimetry. Vis. Res. 2000, 40, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobczak, M.; Asejczyk, M.; Wilczyński, M. The effect of pupil size on the measurement of corneal birefringence properties: Preliminary study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Deshmukh, R.; Mohan, R.M.; Madonadi Kuniyil, V.; Vaddavalli, P.K. Porcine Collagen Implants in Advanced Keratoconus: Outcomes at 1 Year. J. Refract. Surg. 2025, 41, e272–e279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, T.Y. Ray tracing through non-spherical surfaces. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1943, 55, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Authors | Year | Technique | Angle of Slow (Polarization) Axis (°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Greenfield et al. [4] | 2000 | Slit lamp/4th Purkinje Image | Mostly 10 to 20 (−54 to 90), n = 112 |
| Greenfield and Knighton [77] | 2001 | Slit lamp/4th Purkinje Image | 24 ± 18 (−13 to 67), n = 71. One year later, 21 ± 15 (−14 to 59) |
| Weinreb et al. [52] | 2002 | GDx™ with NFL analyser | 24.5 ± 17.4 (−13 to 73), R = 40 ± 15.7 nm (7–90), n = 55 * |
| Knighton and Huang [55] | 2002 | Slit lamp/4th Purkinje Image | (10 to 40), R = (40–140) nm, n = 73 |
| Angeles et al. [14] | 2004 | GDx-VCC™ | 31.5 (CI 27.7 to 37.3), R = 41.6 nm (CI 36.6 to 46.5), n = 37 |
| Knighton et al. [59] | 2008 | GDx-VCC™ | 10 to 40, n = 21 |
| Irsch and Shah [78] | 2012 | GDx-VCC™ | 23 ± 17 (−11 to 71), R = 39 nm ± 16 (10 to 77) 1 10 ± 13 (−6 to 51), R = 39 nm ± 17 (7 to 78) 2 |
| Characteristic Feature | Supportive Publications |
|---|---|
| Corneal architecture influences the CBP | [45,55,56,62,70,88,91] |
| The cornea is akin to a biaxial crystal | [69,70,71,72,73,74] |
| CBP may not be affected by intra-ocular pressure | [52,53,54] |
| CBP can be used to model the structure of the central cornea in vivo | [56,62,88,89] |
| CBP is altered in the abnormal corneas | [1,3,8,9,10,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,56,75,90] |
| CBP is affected by corneal refractive procedures | [1,3,8,9,10,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,22,89] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patel, S.; Tutchenko, L.; Dmytruk, I. Birefringence of the Human Cornea: A Review. Vision 2025, 9, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9040090
Patel S, Tutchenko L, Dmytruk I. Birefringence of the Human Cornea: A Review. Vision. 2025; 9(4):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9040090
Chicago/Turabian StylePatel, Sudi, Larysa Tutchenko, and Igor Dmytruk. 2025. "Birefringence of the Human Cornea: A Review" Vision 9, no. 4: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9040090
APA StylePatel, S., Tutchenko, L., & Dmytruk, I. (2025). Birefringence of the Human Cornea: A Review. Vision, 9(4), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/vision9040090






