Early Exercise Affects Mitochondrial Transcription Factors Expression after Cerebral Ischemia in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Neurological Status
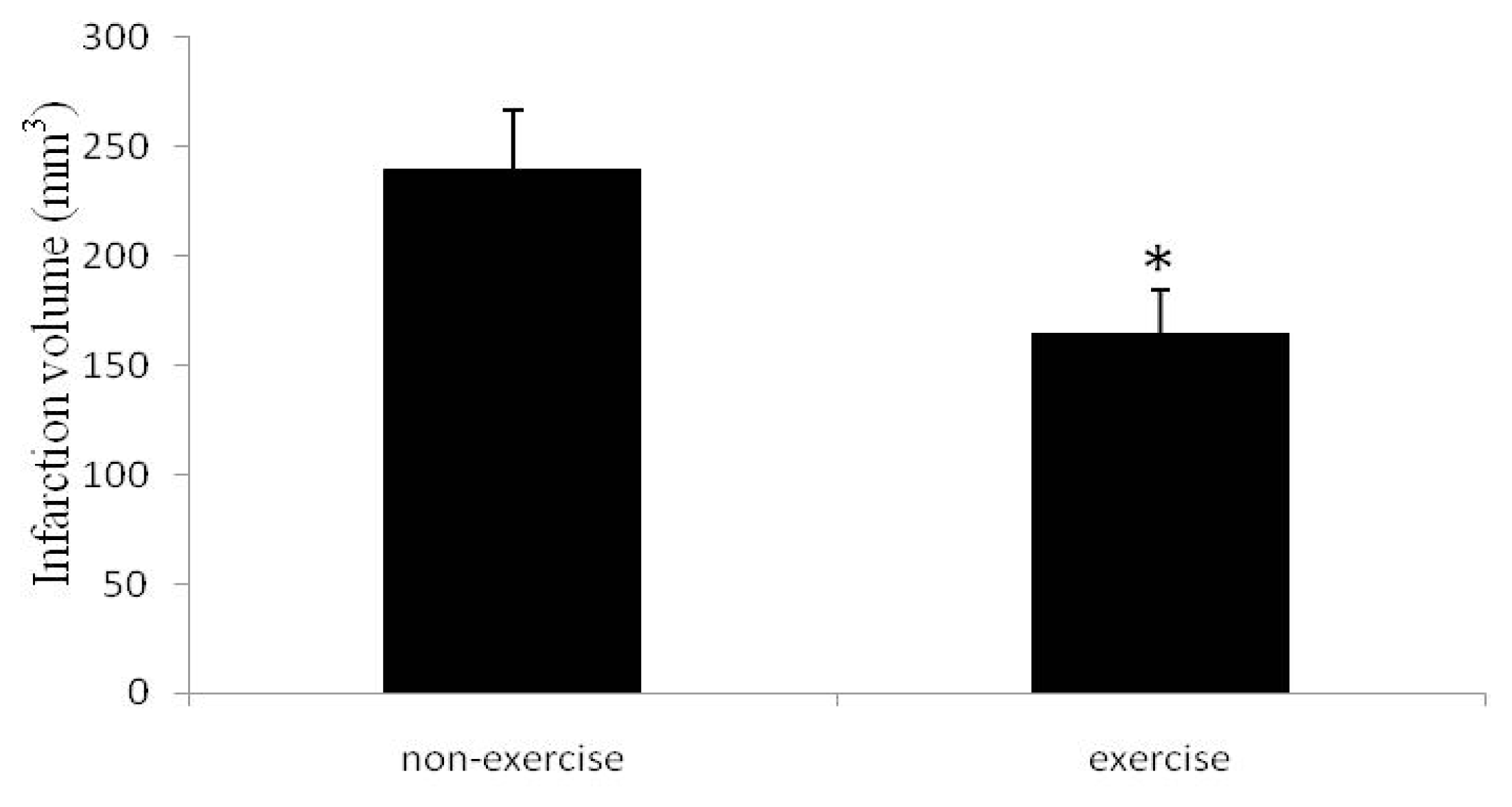
2.2. Cerebral Infarct Volume
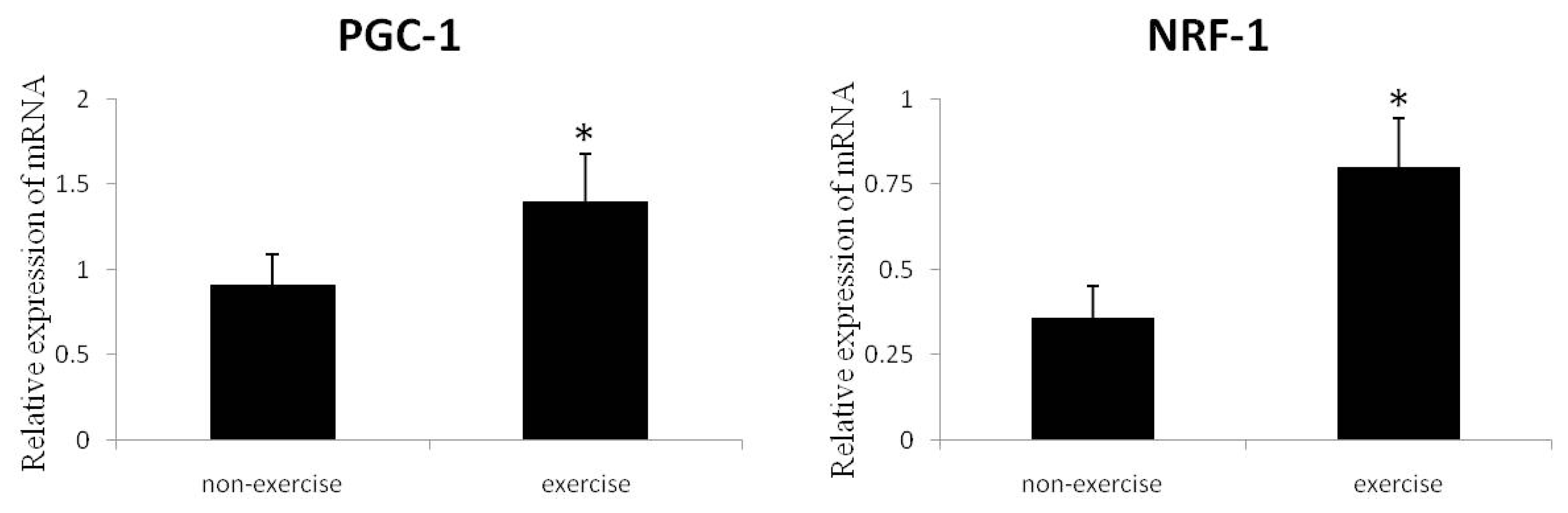
2.3. Expression of Mitochondrial-Specific Transcription Factors
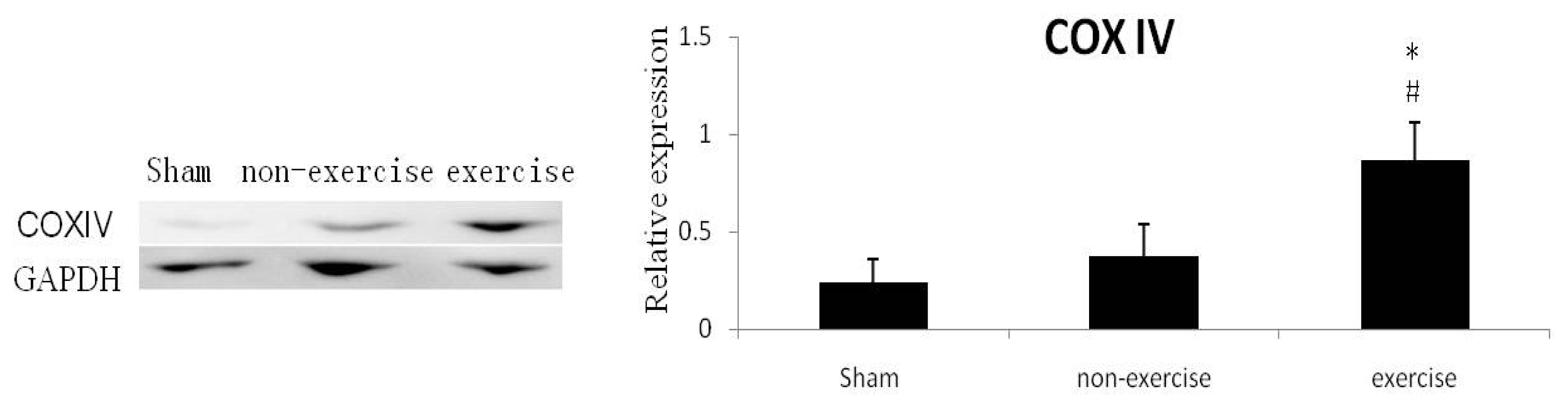
2.4. Expression of Mitochondrial Protein
2.5. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Animals and Experimental Groups
3.2. Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion (MCAO)
3.3. Evaluation of Neurological Status
3.4. Measurement of Cerebral Infarction Volume
3.5. RNA Isolation and RT-PCR
3.6. Western Blotting
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Chung, J.Y.; Kim, M.W.; Bang, M.S.; Kim, M. The effect of exercise on trkA in the contralateral hemisphere of the ischemic rat brain. Brain Res 2010, 1353, 187–193. [Google Scholar]
- DeBow, S.B.; Davies, M.A.; Clarke, H.L.; Colbourne, F. Constraint-induced movement therapy and rehabilitation exercises lessen motor deficits and volume of brain injury after striatal hemorrhagic stroke in rats. Stroke 2003, 34, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Marin, R.; Williams, A.; Hale, S.; Burge, B.; Mense, M.; Bauman, R.; Tortella, F. The effect of voluntary exercise exposure on histological and neurobehavioral outcomes after ischemic brain injury in the rat. Physiol. Behav 2003, 80, 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.R.; Wang, R.Y.; Wang, P.S.; Yu, S.M. Treadmill training effects on neurological outcome after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Can. J. Neurol. Sci 2003, 30, 252–258. [Google Scholar]
- Burnett, M.G.; Shimazu, T.; Szabados, T.; Muramatsu, H.; Detre, J.A.; Greenberg, J.H. Electrical forepaw stimulation during reversible forebrain ischemia decreases infarct volume. Stroke 2006, 37, 1327–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Hood, D.A.; Saleem, A. Exercise-induced mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis 2007, 17, 332–337. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, D.C.; Han, D.H.; Garcia-Roves, P.M.; Geiger, P.C.; Jones, T.E.; Holloszy, J.O. Exercise-induced mitochondrial biogenesis begins before the increase in muscle PGC-1alpha expression. J. Biol. Chem 2007, 282, 194–199. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, J.L.; Murphy, E.A.; McClellan, J.L.; Carmichael, M.D.; Davis, J.M. Exercise training increases mitochondrial biogenesis in the brain. J. Appl. Physiol 2011, 111, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Bayod, S.; del Valle, J.; Canudas, A.M.; Lalanza, J.F.; Sanchez-Roigé, S.; Camins, A.; Escorihuela, R.M.; Pallas, M. Long-term treadmill exercise induces neuroprotective molecular changes in rat brain. J. Appl. Physiol 2011, 111, 1380–1390. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.; Signore, A.P.; Iwai, M.; Cao, G.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J. Rapidly increased neuronal mitochondrial biogenesis after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Stroke 2008, 39, 3057–3063. [Google Scholar]
- Valerio, A.; Bertolotti, P.; Delbarba, A.; Perego, C.; Dossena, M.; Ragni, M.; Spano, P.; Carruba, M.O.; de Simoni, M.G.; Nisoli, E. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition reduces ischemic cerebral damage, restores impaired mitochondrial biogenesis and prevents ROS production. J. Neurochem 2011, 116, 1148–1159. [Google Scholar]
- Pyoria, O.; Talvitie, U.; Nyrkko, H.; Kautiainen, H.; Pohjolainen, T.; Kasper, V. The effect of two physiotherapy approaches on physical and cognitive functions and independent coping at home in stroke rehabilitation. A preliminary follow-up study. Disabil. Rehabil. 2007, 29, 503–511. [Google Scholar]
- Langhammer, B.; Lindmark, B.; Stanghelle, J.K. Stroke patients and long-term training: Is it worthwhile? A randomized comparison of two different training strategies after rehabilitation. Clin. Rehabil 2007, 21, 495–510. [Google Scholar]
- Gertz, K.; Priller, J.; Kronenberg, G.; Fink, K.B.; Winter, B.; Schröck, H.; Ji, S.; Milosevic, M.; Harms, C.; Böhm, M.; Dirnagl, U.; Laufs, U.; Endres, M. Physical activity improves long-term stroke outcome via endothelial nitric oxide synthase-dependent augmentation of neovascularization and cerebral blood flow. Circ. Res 2006, 99, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Moseley, A.M.; Stark, A.; Cameron, I.D.; Pollock, A. Treadmill training and body weight support for walking after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev 2005, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlsson, A.L.; Johansson, B.B. The environment influences functional outcome of cerebral infarction in rats. Stroke 1995, 26, 644–649. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.R.; Wang, R.Y.; Wang, P.S. Early and late treadmill training after focal brain ischemia in rats. Neurosci. Lett 2003, 339, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Risedal, A.; Zeng, J.; Johansson, B.B. Early training may exacerbate brain damage after focal brain ischemia in the rat. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab 1999, 19, 997–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Lanza, I.R.; Sreekumaran Nair, K. Regulation of skeletal muscle mitochondrial function: Genes to proteins. Acta Physiol 2010, 199, 529–547. [Google Scholar]
- Ljubicic, V.; Joseph, A.M.; Saleem, A.; Uguccioni, G.; Collu-Marchese, M.; Lai, R.Y.; Nguyen, L.M.; Hood, D.A. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle: Effects of exercise and aging. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1800, 223–234. [Google Scholar]
- McLeod, C.; Pagel, I.; Sack, M. The mitochondrial biogenesis regulatory program in cardiac adaptation to ischemia—A putative target for therapeutic intervention. Trends Cardiovasc 2005, 15, 118–123. [Google Scholar]
- Onyango, I.G.; Lu, J.; Rodova, M.; Lezi, E.; Crafter, A.B.; Swerdlow, R.H. Regulation of neuron mitochondrial biogenesis and relevance to brain health. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 228–234. [Google Scholar]
- Viña, J.; Gomez-Cabrera, M.C.; Borras, C.; Froio, T.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Martinez-Bello, V.E.; Pallardo, F.V. Mitochondrial biogenesis in exercise and in ageing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev 2009, 61, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Hood, D.A. Mechanisms of exercise-induced mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab 2009, 34, 465–472. [Google Scholar]
- Longa, E.Z.; Weinstein, P.R.; Carlson, S.; Cummins, R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 1989, 20, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, D.C.; Campbell, C.A.; Stretton, J.L.; Mackay, K.B. Correlation between motor impairment and infarct volume after permanent and transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Stroke 1997, 28, 2060–2066. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Hu, Y.S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, G.; Yu, H.X.; Zheng, Q.P.; Zhu, D.N.; Xia, C.M.; Cao, Z.J. Pre-ischemic treadmill training affects glutamate and gamma aminobutyric acid levels in the striatal dialysate of a rat model of cerebral ischemia. Life Sci 2009, 84, 505–511. [Google Scholar]
- DiFiglia, M.; Sapp, E.; Chase, K.; Schwarz, C.; Meloni, A.; Young, C.; Martin, E.; Vonsattel, J.P.; Carraway, R.; Reeves, S.A. Huntingtin is a cytoplasmic protein associated with vesicles in human and rat brain neurons. Neuron 1995, 14, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar]
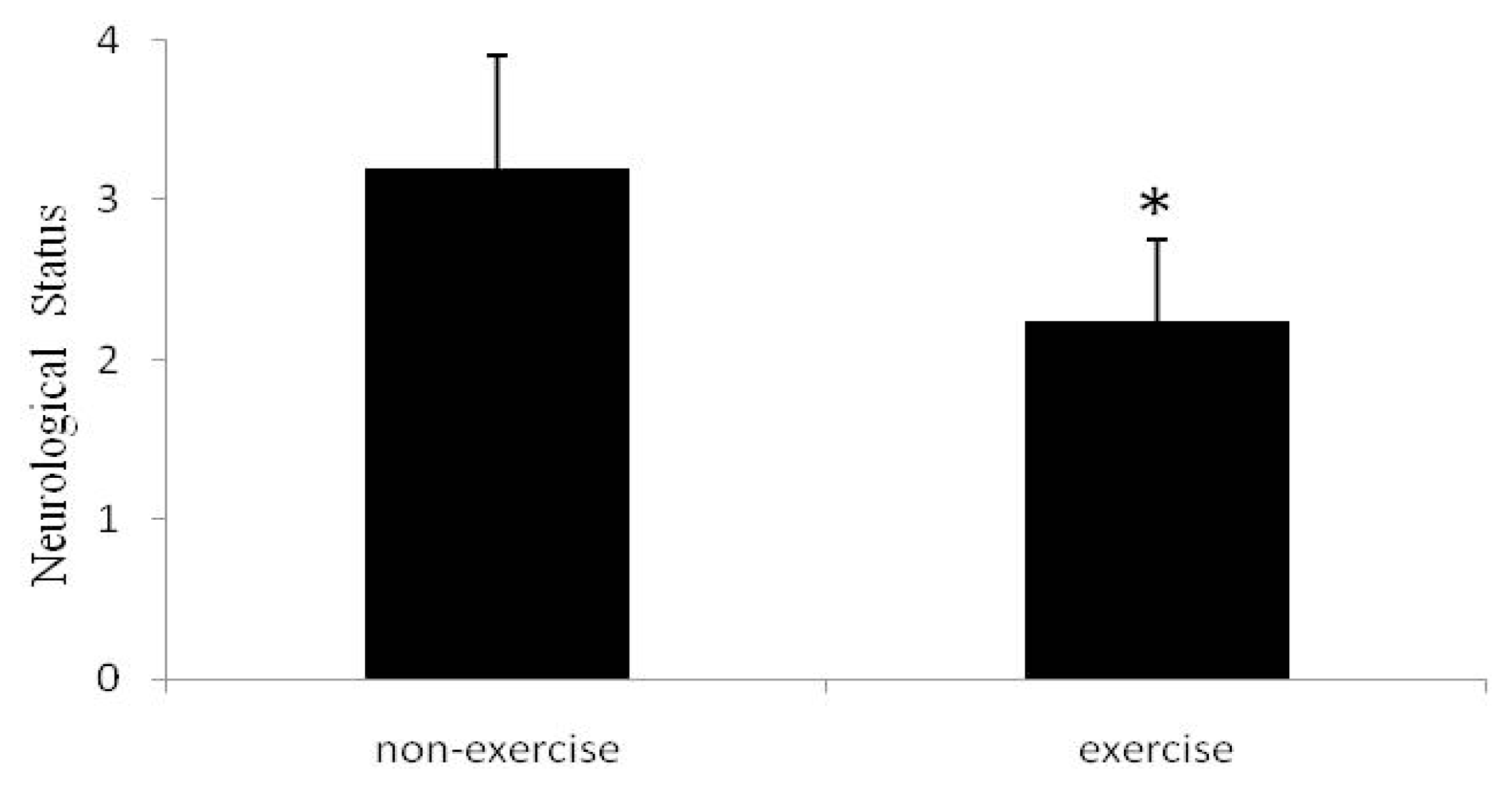
| Gene | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| PGC-1 | GTGCAGCCAAGACTCTGTATGG | GTCCAGGTCATTCACATCAAGTTC |
| NRF-1 | TTACTCTGCTGTGGCTGATGG | CCTCTGATGCTTGCGTCGTCT |
| GAPDH | GGGTCAGAAGGATTCCTATG | GGTCTCAAACATGATCTGGG |
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Sha, H.; Zhang, P.; Jia, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, J. Early Exercise Affects Mitochondrial Transcription Factors Expression after Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 1670-1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13021670
Zhang Q, Wu Y, Sha H, Zhang P, Jia J, Hu Y, Zhu J. Early Exercise Affects Mitochondrial Transcription Factors Expression after Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(2):1670-1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13021670
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qi, Yi Wu, Hongying Sha, Pengyue Zhang, Jie Jia, Yongshan Hu, and Jianhong Zhu. 2012. "Early Exercise Affects Mitochondrial Transcription Factors Expression after Cerebral Ischemia in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 2: 1670-1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13021670
APA StyleZhang, Q., Wu, Y., Sha, H., Zhang, P., Jia, J., Hu, Y., & Zhu, J. (2012). Early Exercise Affects Mitochondrial Transcription Factors Expression after Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(2), 1670-1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13021670




