Soil Moisture Mapping Using Sentinel-1 SAR Data and Cloud-Based Regression Modeling on Google Earth Engine †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
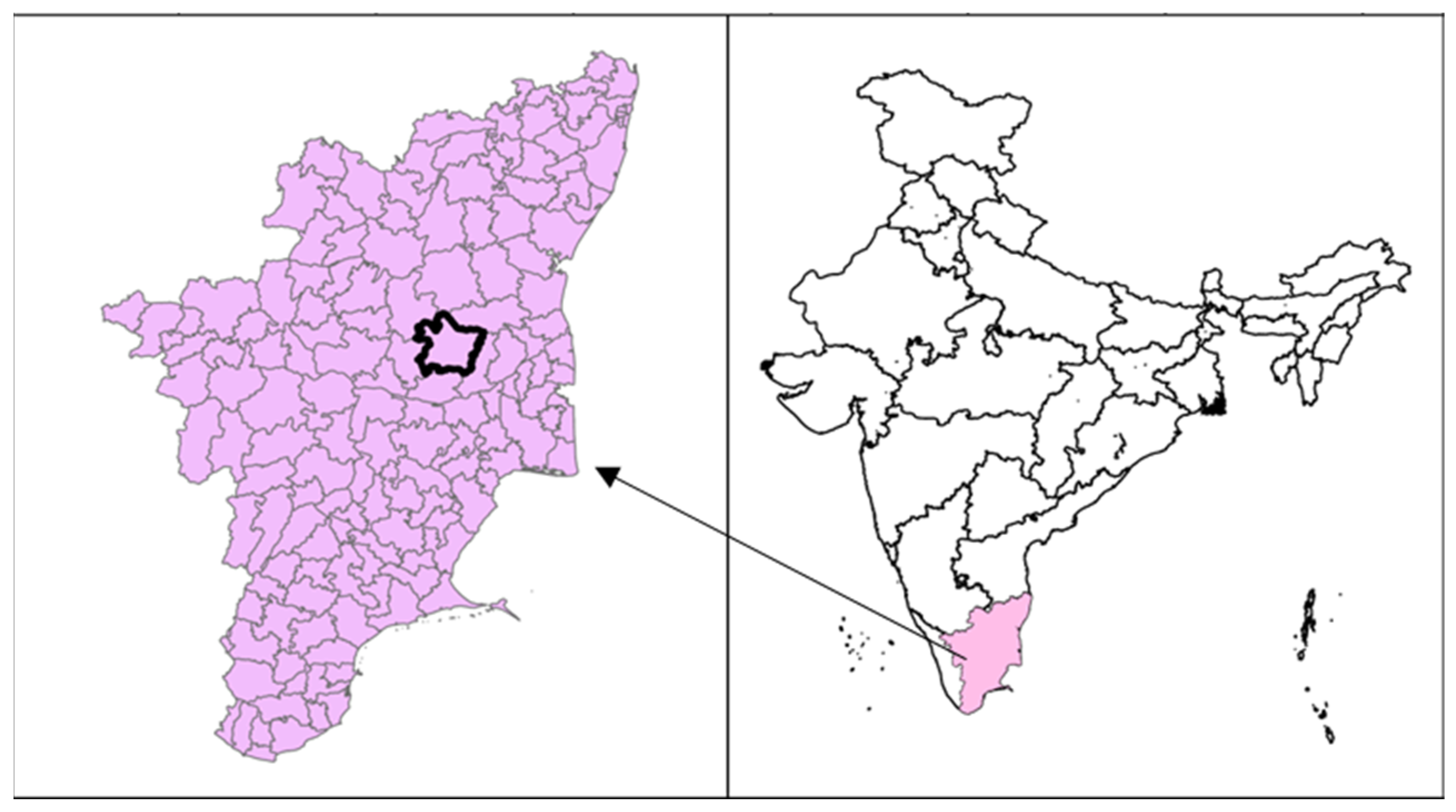
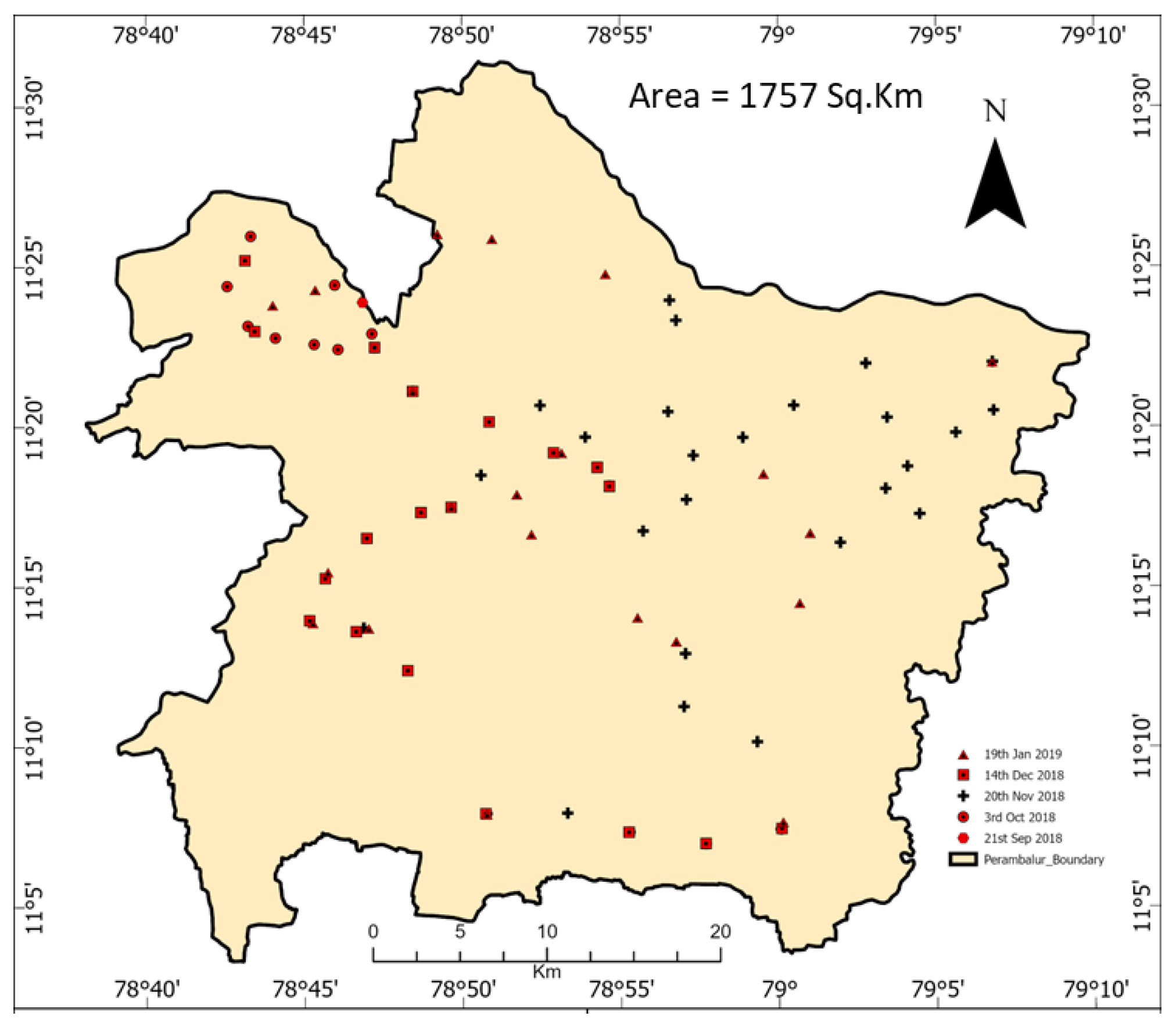
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition: In Situ and Satellite
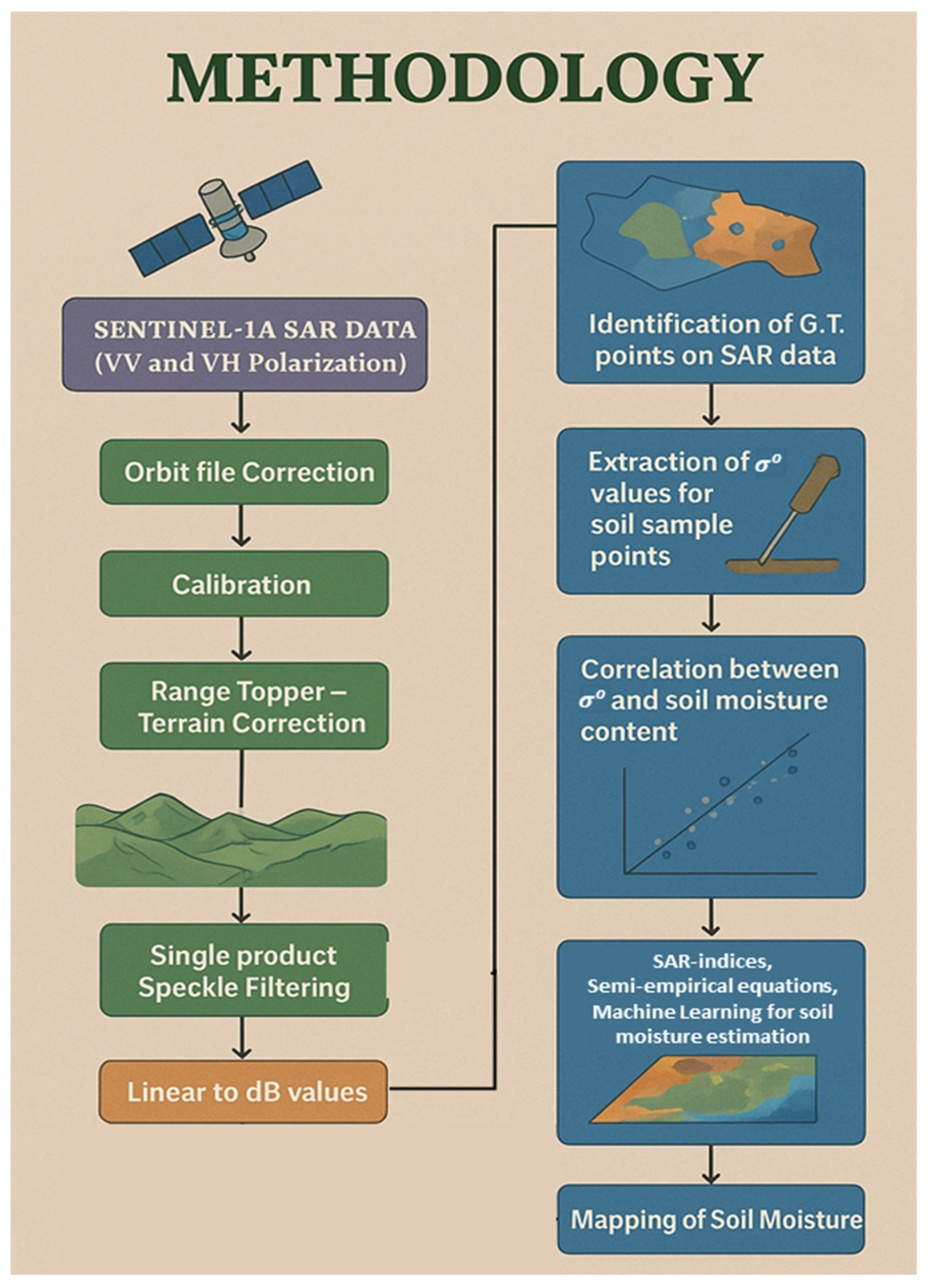
2.3. Preprocessing of SAR
2.4. Estimating Soil Moisture
2.4.1. Feature Engineering
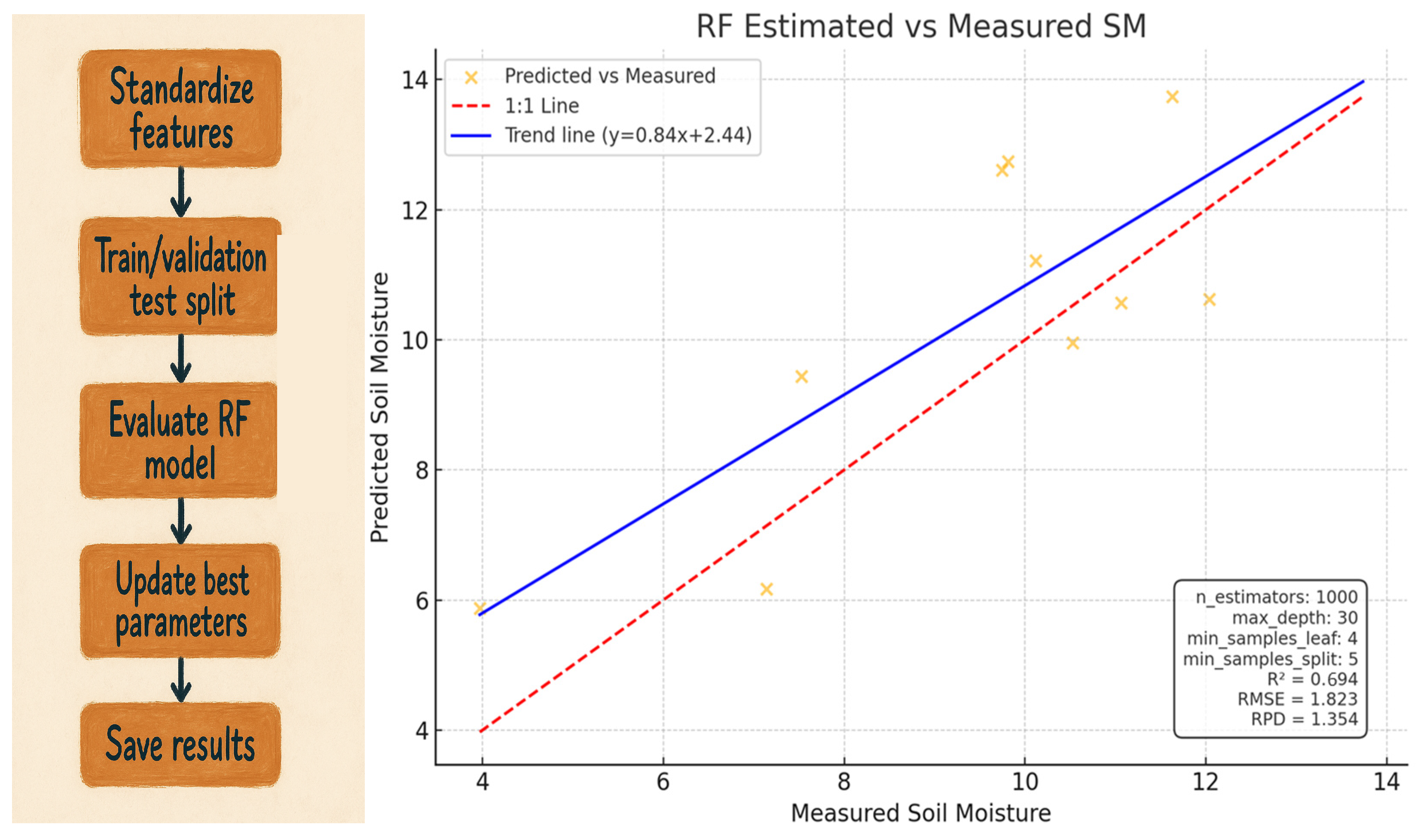
2.4.2. Random Forest (RF) Regression
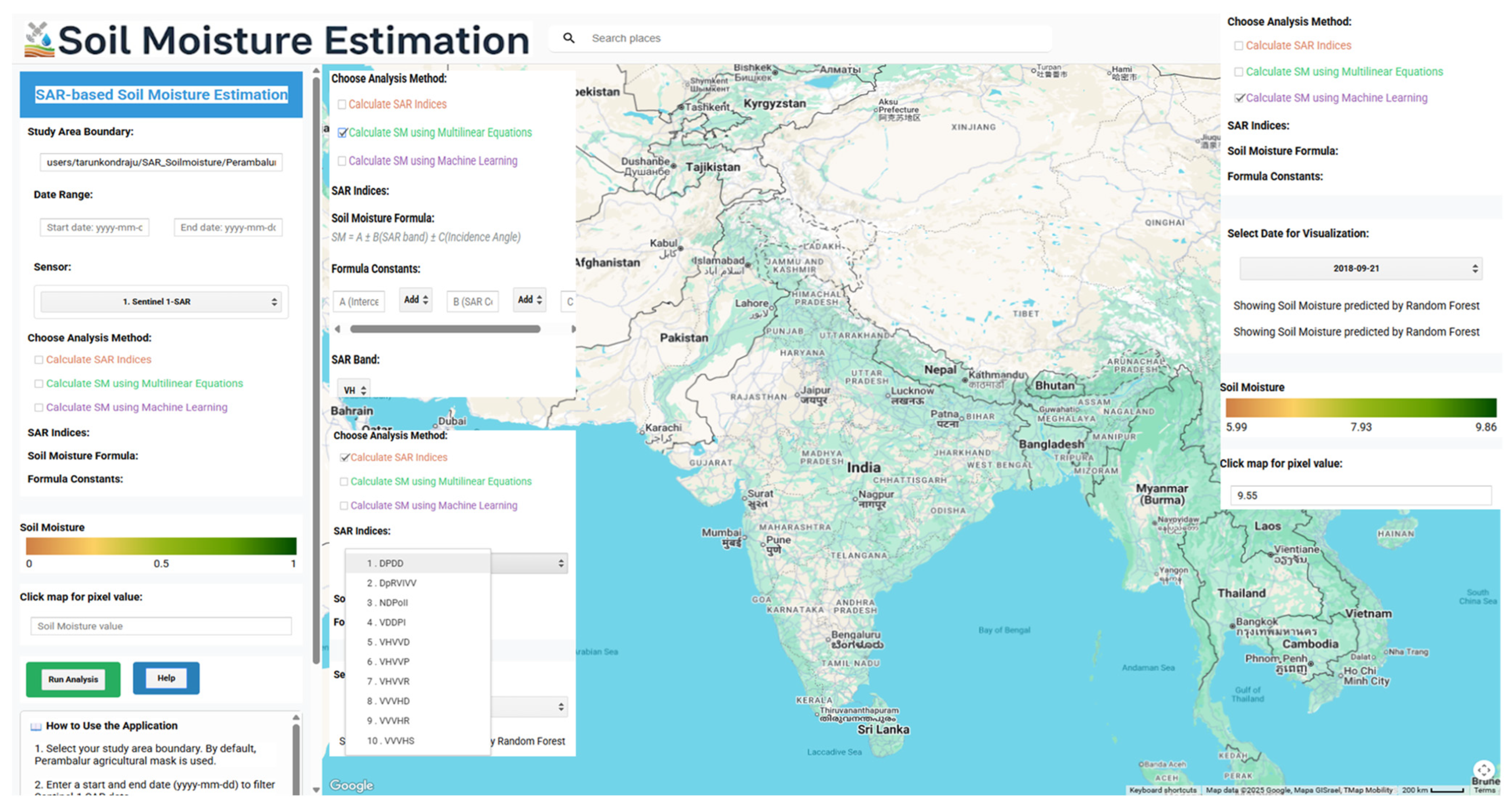
2.5. Google Earth Engine (GEE) Tool Development
3. Results
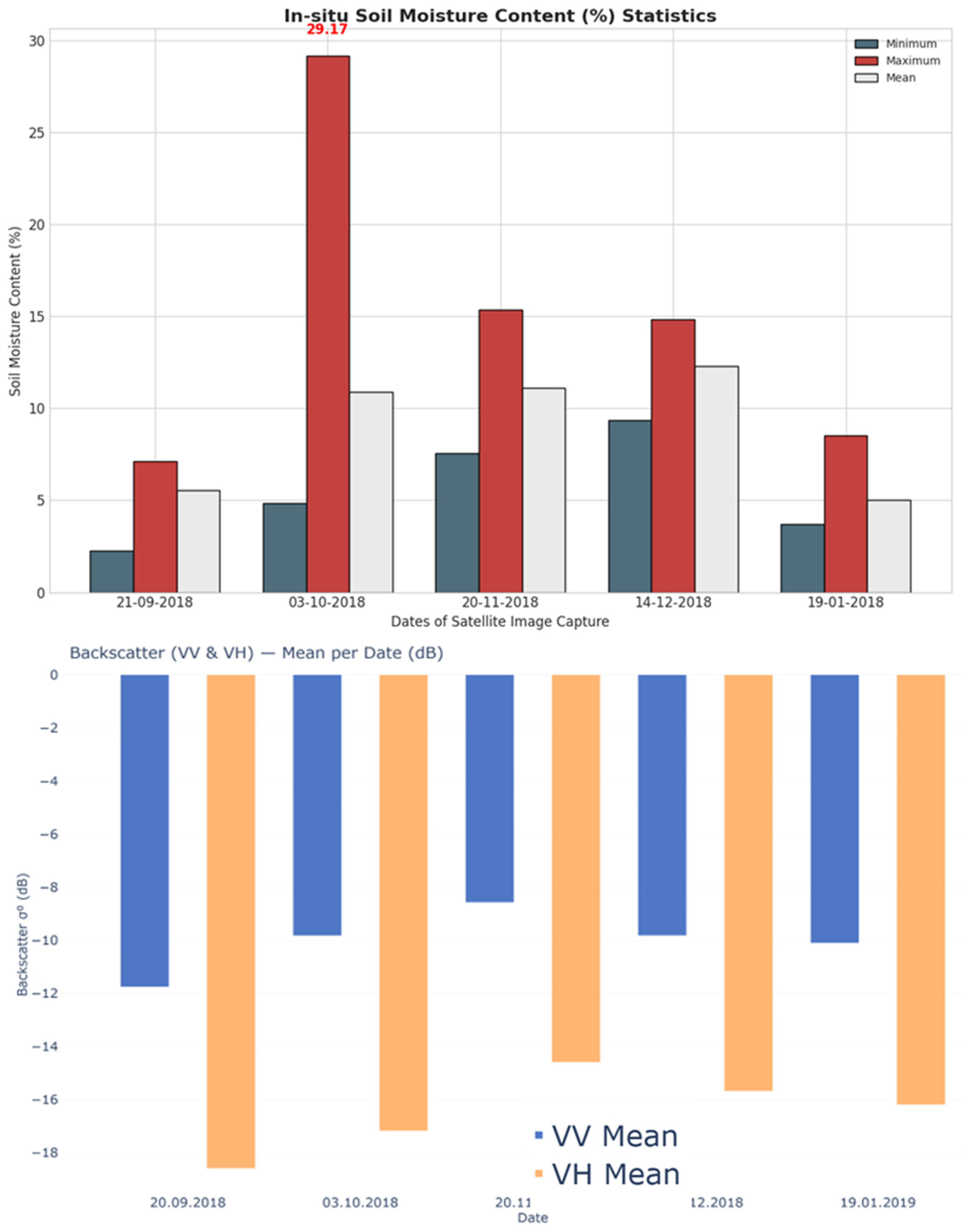
3.1. In Situ Soil Moisture and SAR Backscatter Dynamics
3.2. Random Forest (RF) Model Performance
3.3. Model Evaluation
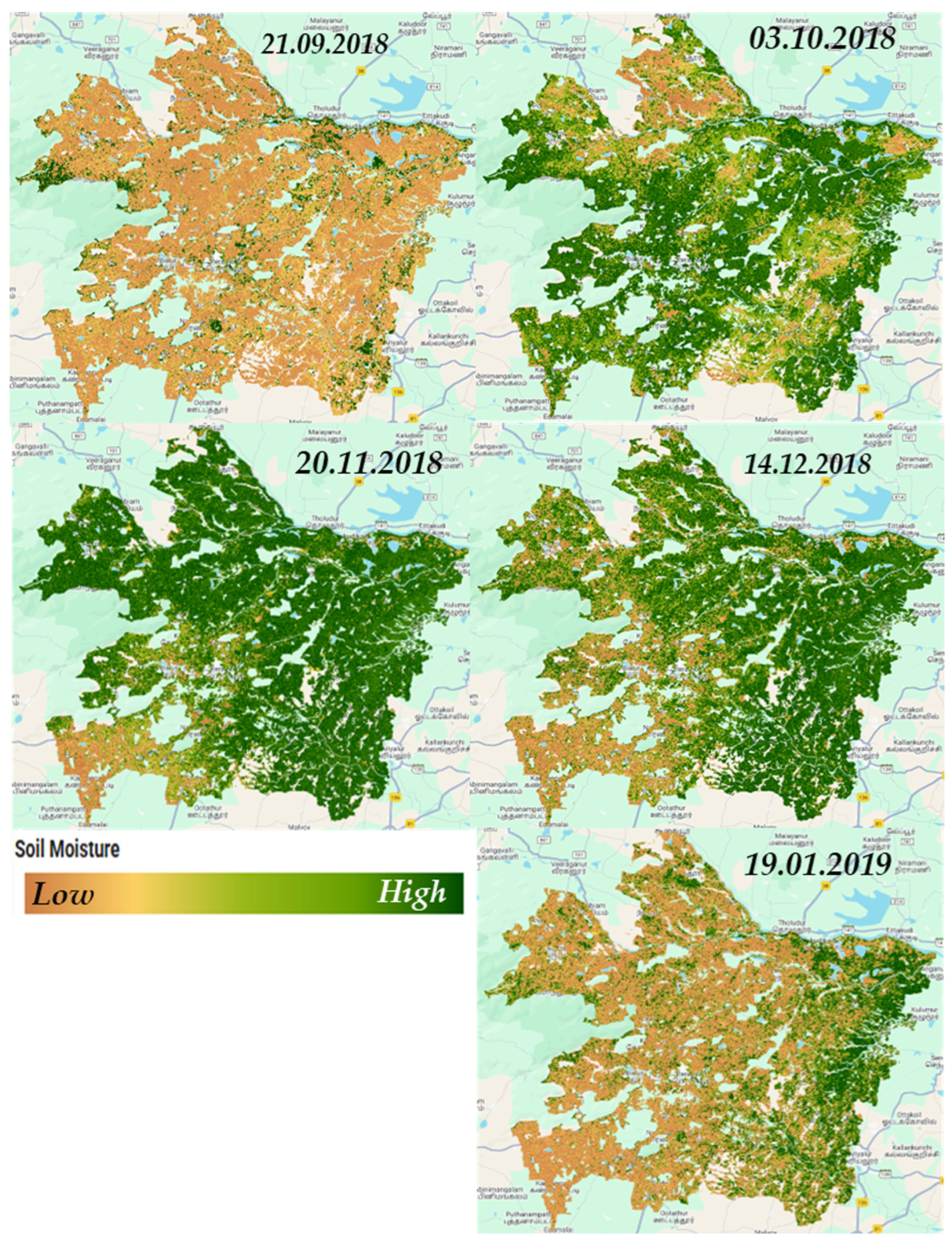
3.4. Spatial Soil Moisture Mapping and GEE Application
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Corti, T.; Davin, E.L.; Hirschi, M.; Jaeger, E.B.; Lehner, I.; Orlowsky, B.; Teuling, A.J. Investigating soil moisture–climate interactions in a changing climate: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 125–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobriyal, P.; Qureshi, A.; Badola, R.; Hussain, S.A. A review of the methods for monitoring soil moisture. J. Hydrol. 2012, 458, 180–189. [Google Scholar]
- Vereecken, H.; Huisman, J.A.; Bogena, H.; Vanderborght, J.; Vrugt, J.A.; Hopmans, J.W. On the value of soil moisture meas-urements in vadose zone hydrology: A review. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W00D06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robock, A.; Vinnikov, K.Y.; Schlosser, C.A.; Speranskaya, N.A.; Entin, J.K. The global soil moisture data bank. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 1281–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Blöschl, G.; Pampaloni, P.; Calvet, J.C.; Bizzarri, B.; Wigneron, J.P.; Kerr, Y. Operational readiness of microwave remote sensing of soil moisture. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Topp, G.C.; Davis, J.L.; Annan, A.P. Electromagnetic determination of soil water content: Measurements in coaxial trans-mission lines. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 16, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Western, A.W.; Grayson, R.B.; Blöschl, G. Scaling of soil moisture: A hydrologic perspective. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2002, 30, 149–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoku, E.G.; Jackson, T.J.; Lakshmi, V.; Chan, T.K.; Nghiem, S.V. Soil moisture retrieval from AMSR-E. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing: Active and Passive, Vol. 2: Radar Remote Sensing and Surface Scattering and Emission Theory; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, R.; Snoeij, P.; Geudtner, D.; Bibby, D.; Davidson, M.; Attema, E.; Potin, P.; Rommen, B.; Floury, N.; Brown, M.; et al. GMES Sentinel-1 mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, N.; Zribi, M.; Paloscia, S.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; Lievens, H.; Van Der Velde, R.; Panciera, R.; Bouvet, A.; De Lannoy, G. An overview of the soil moisture products from the Sentinel-1 mission. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 596. [Google Scholar]
- Hajnsek, I.; Pottier, E.; Cloude, S.R. Inversion of surface parameters from polarimetric SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 727–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zribi, M.; Baghdadi, N.; Holah, N.; Fafin, O. New methodology for soil surface moisture estimation from C-band radar data. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, W08410. [Google Scholar]
- Attema, E.P.W.; Ulaby, F.T. Vegetation modeled as a water cloud. Radio Sci. 1978, 13, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; He, B.; Li, X.; Zeng, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. First assessment of Sentinel-1A data for soil moisture retrieval using a coupled water cloud model and advanced integral equation model over the central Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 714. [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowska-Zielinska, K.; Musial, J.; Malinska, A.; Budzynska, M.; Gurdak, R.; Kiryla, W.; Bartold, M.; Grzybowski, P. Soil moisture in wetlands—Estimation by a combination of the C-band Sentinel-1 and optical data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Paloscia, S.; Pettinato, S.; Santi, E.; Notarnicola, C.; Pasolli, L.; Reppucci, A. Soil moisture mapping using Sentinel-1 images: Algorithm and preliminary validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 134, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.; Le, N.; Ha, N.; Nguyen, L.; Tran, D.; Nguyen, C.; Bui, D.T. A new approach for soil moisture estimation using Sentinel-1 SAR data and a Random Forest algorithm. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3338. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Han, D.; Ramirez, M.R.; Islam, T. Machine learning techniques for downscaling SMOS satellite soil moisture using MODIS land surface temperature for hydrological application. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 3127–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.S.; Alonso, L.; Moreno, J.F.; Mateo, M.P. A multi-resolution, multi-temporal approach for estimating fractional vegetation cover with remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 345–355. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountrakis, G.; Im, J.; Ogole, C. Support vector machines in remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, A.; De Lannoy, G.; Albergel, C.; Vreugdenhil, M.; Wagner, W.; Dorigo, W. Validation of the ESA CCI soil moisture product in the U.S. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 194, 141–153. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Zribi, M.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Baghdadi, N.; Seguin, B. Determination of soil moisture from C-band radar data. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 32, 130–139. [Google Scholar]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, M.; Ghorbanian, A.; Ahmadi, S.A.; Kakooei, M.; Moghimi, A.; Mirmazloumi, S.M.; Moghaddam, S.H.A.; Mahdavi, S.; Ghahremanloo, M.; Parsian, S.; et al. Google Earth Engine Cloud Computing Platform for Remote Sensing Big Data Appli-cations: A Comprehensive Review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5326–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimple, U.; Sitole, A.; Patel, A.; Simon, B. Google Earth Engine based analysis for agricultural drought monitoring in Bun-delkhand region, India. Geomat. Nat. Haz. Risk 2021, 12, 166–184. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, T.; Jagdhuber, T.; Piles, M.; Kainulainen, J.; Karbou, F.; Ikonen, J. Towards a global soil moisture product from Sen-tinel-1: A deep learning approach. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 219. [Google Scholar]
- Steele-Dunne, S.C.; McNairn, H.; Monsivais-Huertero, A.; Judge, J.; Liu, P.W.; Papathanassiou, K. Radar remote sensing of agricultural canopies: A review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 2249–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amazirh, A.; Merlin, O.; Er-Raki, S.; Gao, Q.; Rivalland, V.; Malbeteau, Y.; Khabba, S.; Escorihuela, M.J. An operational soil moisture mapping algorithm at high resolution over agricultural areas using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1811. [Google Scholar]
- Ramalingam, S.; Ramasamy, J.; Ramalingam, K.; Sivakumar, K.; Sellaperumal, P.; Deepagaran, G. Estimation of soil moisture from Sentinel-1A synthetic aperture radar (SAR) in Perambalur district of Tamil Nadu. Pharma Innov. J. 2019, 8, 360–362. [Google Scholar]
| Index Name | Formula | Purpose/Description |
|---|---|---|
| DPDD (Differential Power Detection Difference) | Highlights total scattering power differences related to dielectric variation. | |
| NDPoII (Normalized Difference Polarization Index) | Normalizes VV and VH to reduce topographic and geometric effects. | |
| VHVVR/VVVHR (Polarization Ratios) | , | Sensitive to surface moisture and scattering mechanisms. |
| VHVVD/VVVHD (Polarization Differences) | , | Indicates volumetric scattering due to vegetation or soil roughness. |
| VHVVP/VVVHS (Polarization Product and Sum) | , | Capture combined surface–volume scattering effects. |
| VDDPI (Volume-Dominant Difference Polarization Index) | Quantifies relative volumetric scattering in vegetated surfaces. |
| Model Type | Best Input Variables | R2 | RMSE (%) | MAE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forest (RF) | VV, VH, VV × VH, VH/VV, VH–VV | 0.65 | 3.40 | 2.36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kondraju, T.T.; Ramalingam, S.; Rejith, R.G.; Bhandari, A.; Sahoo, R.N.; Ranjan, R. Soil Moisture Mapping Using Sentinel-1 SAR Data and Cloud-Based Regression Modeling on Google Earth Engine. Environ. Earth Sci. Proc. 2025, 36, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025036009
Kondraju TT, Ramalingam S, Rejith RG, Bhandari A, Sahoo RN, Ranjan R. Soil Moisture Mapping Using Sentinel-1 SAR Data and Cloud-Based Regression Modeling on Google Earth Engine. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings. 2025; 36(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025036009
Chicago/Turabian StyleKondraju, Tarun Teja, Selvaprakash Ramalingam, Rajan G. Rejith, Amrita Bhandari, Rabi N. Sahoo, and Rajeev Ranjan. 2025. "Soil Moisture Mapping Using Sentinel-1 SAR Data and Cloud-Based Regression Modeling on Google Earth Engine" Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings 36, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025036009
APA StyleKondraju, T. T., Ramalingam, S., Rejith, R. G., Bhandari, A., Sahoo, R. N., & Ranjan, R. (2025). Soil Moisture Mapping Using Sentinel-1 SAR Data and Cloud-Based Regression Modeling on Google Earth Engine. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings, 36(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025036009






