Rainfall Runoff Simulation for Climate-Resilient Watershed Management: A Case Study of the Mangla Watershed, Pakistan †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
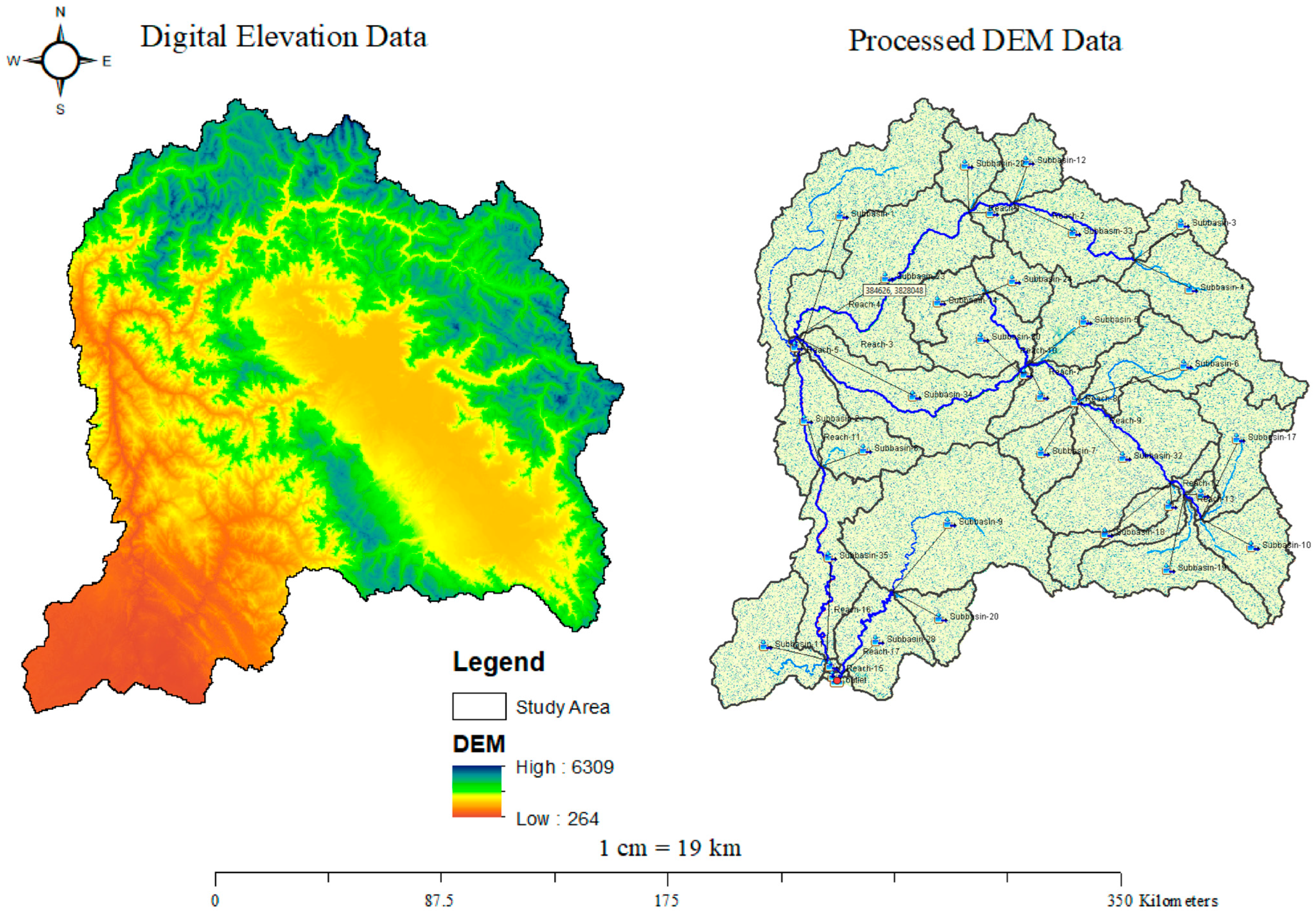
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Used
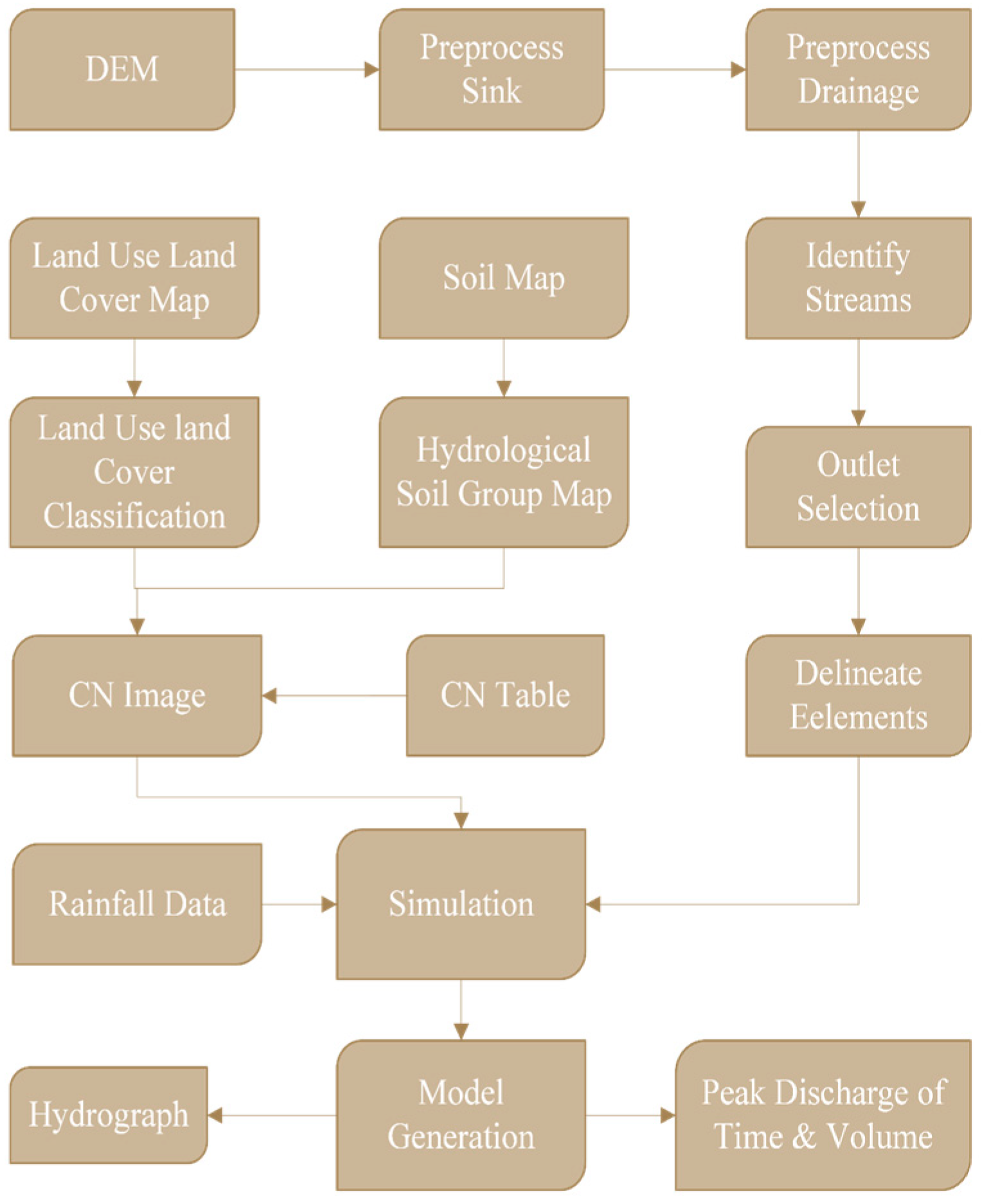
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. Parameter Estimation
2.4.1. Loss Estimation
2.4.2. Transform Method
2.4.3. Baseflow
2.4.4. Routing
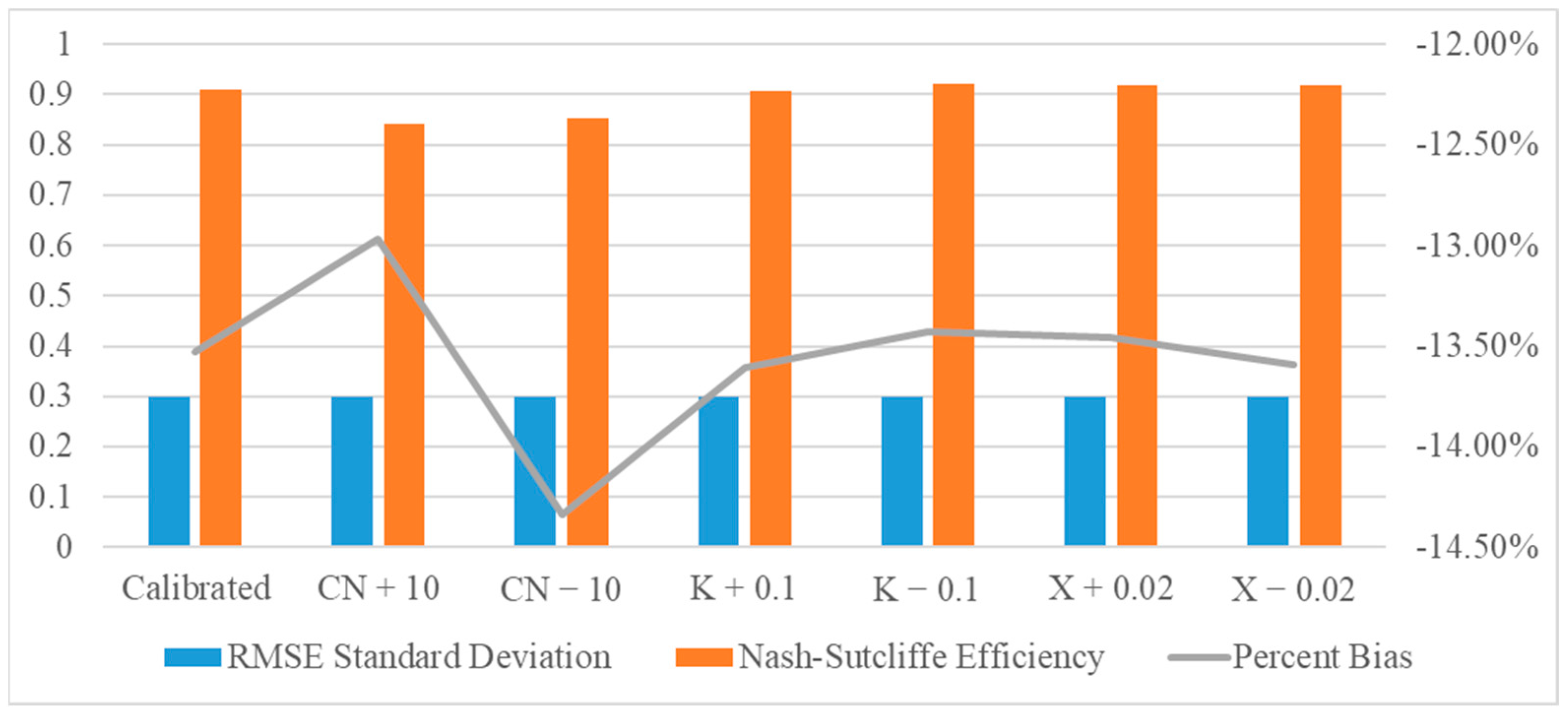
2.5. Sensitivity Analysis
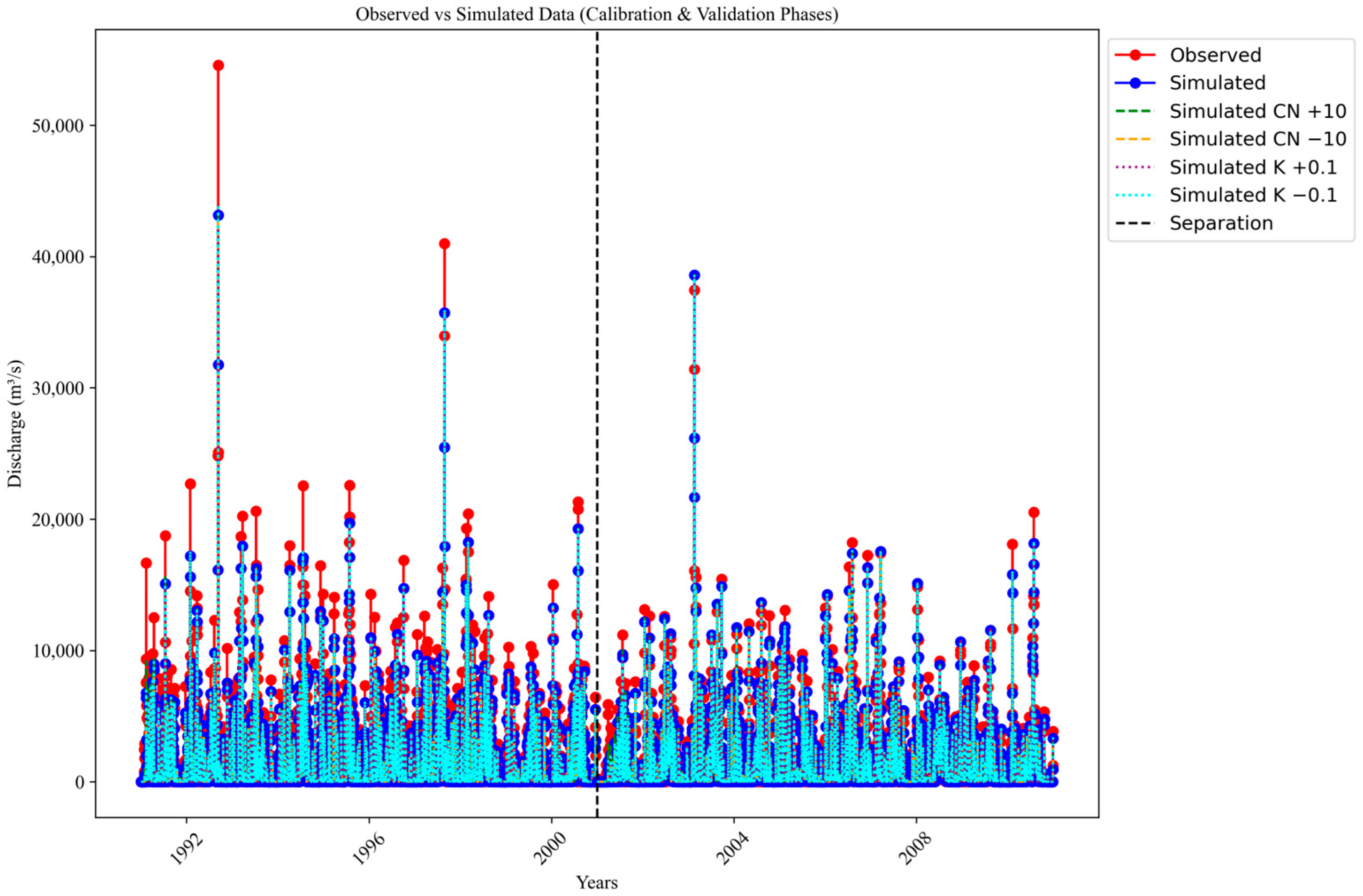
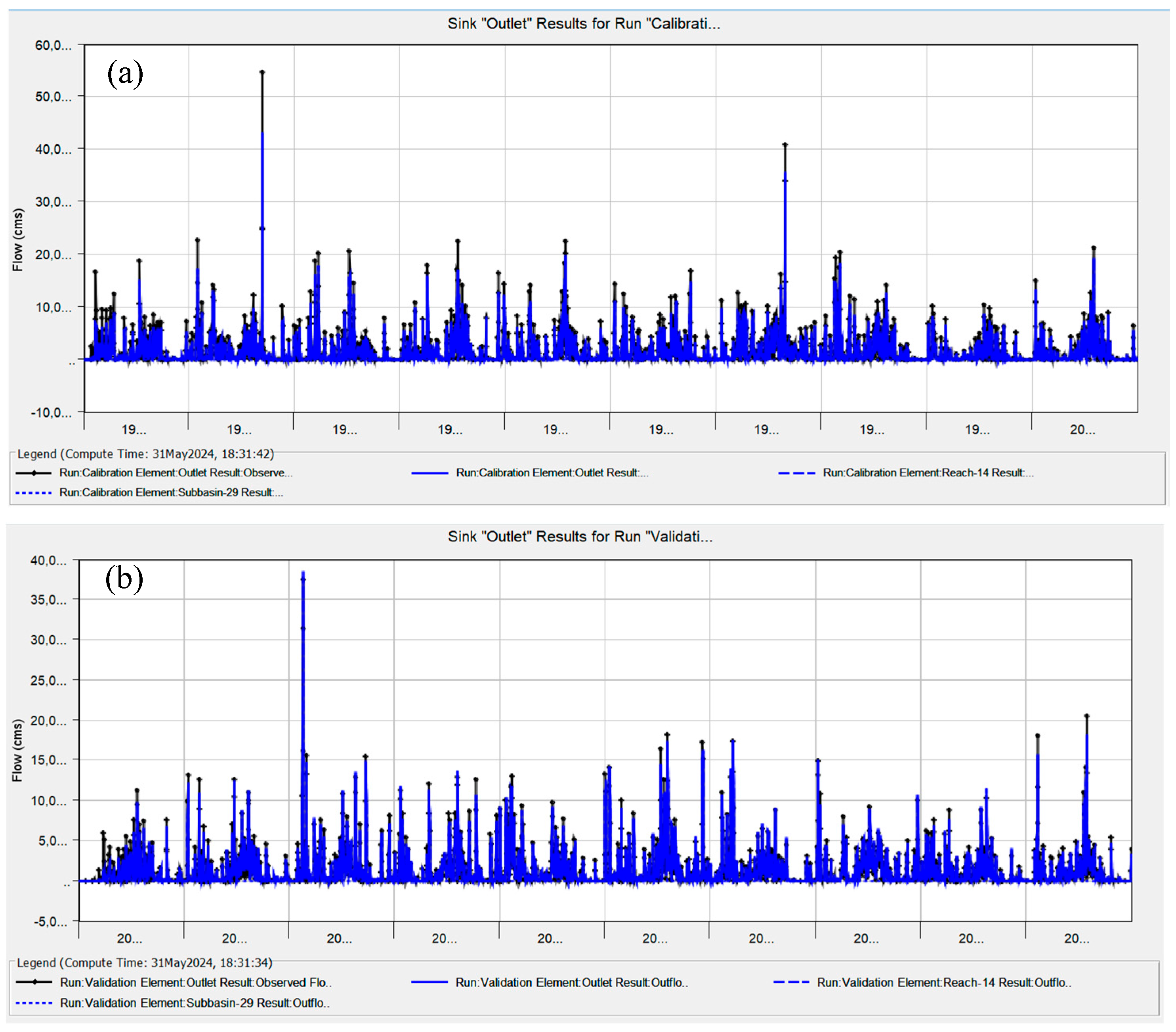
2.6. Model Calibration and Validation
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macalam, F.J.; Wang, K.; Onodera, S.-I.; Saito, M.; Nagano, Y.; Yamazaki, M.; Nang, Y.W. Hydrological Modeling of the Chikugo River Basin Using SWAT: Insights into Water Balance and Seasonal Variability. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vairavamoorthy, K.; Gorantiwar, S.D.; Pathirana, A. Managing urban water supplies in developing countries–Climate change and water scarcity scenarios. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2008, 33, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, L.; Baddoo, T.D. Hydrological Modeling in A Semi-Arid Region Using HEC-HMS. J. Water Resour. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 5, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, S.U.; Khan, N.M.; Israr, M.; Nabi, H.; Khan, M. Runoff Modelling Using HEC HMS for Rural Watershed. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Dev. 2019, 6, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, L.-C. Sustainable Water Management in the Baltic Sea Basin: 1. The Waterscape; Baltic University Press: Uppsala, Sweden, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gosain, A.K.; Mani, A.; Dwivedi, C. Hydrological modelling-literature review. Adv. Fluid Mech. 2009, 339, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Devia, G.K.; Ganasri, B.P.; Dwarakish, G.S. A Review on Hydrological Models. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, M.; Waseem, M.; Latif, Y.; Azam, M.I.; Ahmad, I.; Abbas, S.; Sarwar, M.K.; Nabi, G. Statistical downscaling and hydrological modeling-based runoff simulation in trans-boundary mangla watershed Pakistan. Water 2020, 12, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halwatura, D.; Najim, M.M.M. Application of the HEC-HMS model for runoff simulation in a tropical catchment. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 46, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleyiblo, J.O.; Li, Z. Application of HEC-HMS for flood forecasting in Misai and Wan’an catchments in China. Water Sci. Eng. 2010, 3, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Skhakhfa, I.D.; Ouerdachi, L. Hydrological modelling of Wadi ressoul watershed, Algeria, by HEC-HMS model. J. Water Land Dev. 2016, 31, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.P.; Chakrabarty, A. Flash flood risk assessment for upper Teesta river basin: Using the hydrological modeling system (HEC-HMS) software. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusop, Z.; Chan, C.H.; Katimon, A. Runoff characteristics and application of HEC-HMS for modelling stormflow hydrograph in an oil palm catchment. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 56, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibangayuka, N.; Mulungu, D.M.M.; Izdori, F. Evaluating the performance of HBV, HEC-HMS and ANN models in simulating streamflow for a data scarce high-humid tropical catchment in Tanzania. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2022, 67, 2191–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekar, P.R. Rainfall-Runoff Modelling of a River Basin Using HEC HMS: A Review Study. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2021, 9, 506–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, H.; Zaman, M.; Liu, S.; Saifullah, M.; Usman, M.; Chauhdary, J.N.; Anjum, M.N.; Waseem, M. Appraisal of Climate Change and Its Impact on Water Resources of Pakistan: A Case Study of Mangla Watershed. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, A.N.A.; Almuktar, S.; Scholz, M. Rainfall-runoff modeling using the HEC-HMS model for the al-adhaim river catchment, northern Iraq. Hydrology 2021, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, N.; Kurian, C.; Sudheer, K. Development of a flood forecasting model using HEC-HMS. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Water Resources and Flood Management with Special Reference to Flood Modelling, Surat, India, 14–15 October 2016; Sardar Vallabhbhai National Institute of Technology: Surat, India, 2016; pp. 14–15. [Google Scholar]


| Data Type | Source | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| Topography | USGS Shuttle Radar Topography Mission | 30 × 30 m2 |
| Land use data | European Space Agency (ESA) Global Land Cover map | 300 × 300 m2 |
| Soil data | FAO World Soil Database V 1.2 | 1 km |
| Climate data | Pakistan Meteorological Department (PMD) and Water and Power | Daily |
| Hydrological data | Water and Power Development Authority (WAPDA) | Daily |
| Indices | Satisfactory Range | Calibration Period | Validation Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE Standard Deviation | 0 < RMSE Std. Dev. < 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency | 0.5 < NSE ≤ 1 | 0.91 | 0.945 |
| Percent Bias | −25% < PBIAS < +25% | −13.53% | −2.91% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rehman, S.U.; Chang, T.; Zaman, M.; Jaweed, A.B. Rainfall Runoff Simulation for Climate-Resilient Watershed Management: A Case Study of the Mangla Watershed, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. Proc. 2025, 36, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025036007
Rehman SU, Chang T, Zaman M, Jaweed AB. Rainfall Runoff Simulation for Climate-Resilient Watershed Management: A Case Study of the Mangla Watershed, Pakistan. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings. 2025; 36(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025036007
Chicago/Turabian StyleRehman, Saffi Ur, Tingting Chang, Muhammad Zaman, and Abdullah Bin Jaweed. 2025. "Rainfall Runoff Simulation for Climate-Resilient Watershed Management: A Case Study of the Mangla Watershed, Pakistan" Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings 36, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025036007
APA StyleRehman, S. U., Chang, T., Zaman, M., & Jaweed, A. B. (2025). Rainfall Runoff Simulation for Climate-Resilient Watershed Management: A Case Study of the Mangla Watershed, Pakistan. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings, 36(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025036007









