Validating TIR-Derived Total Column Water Vapor Using Sun Photometers and GPS Measurements †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. TCWV Retrieval Using Landsat 8/9 TIR Channels
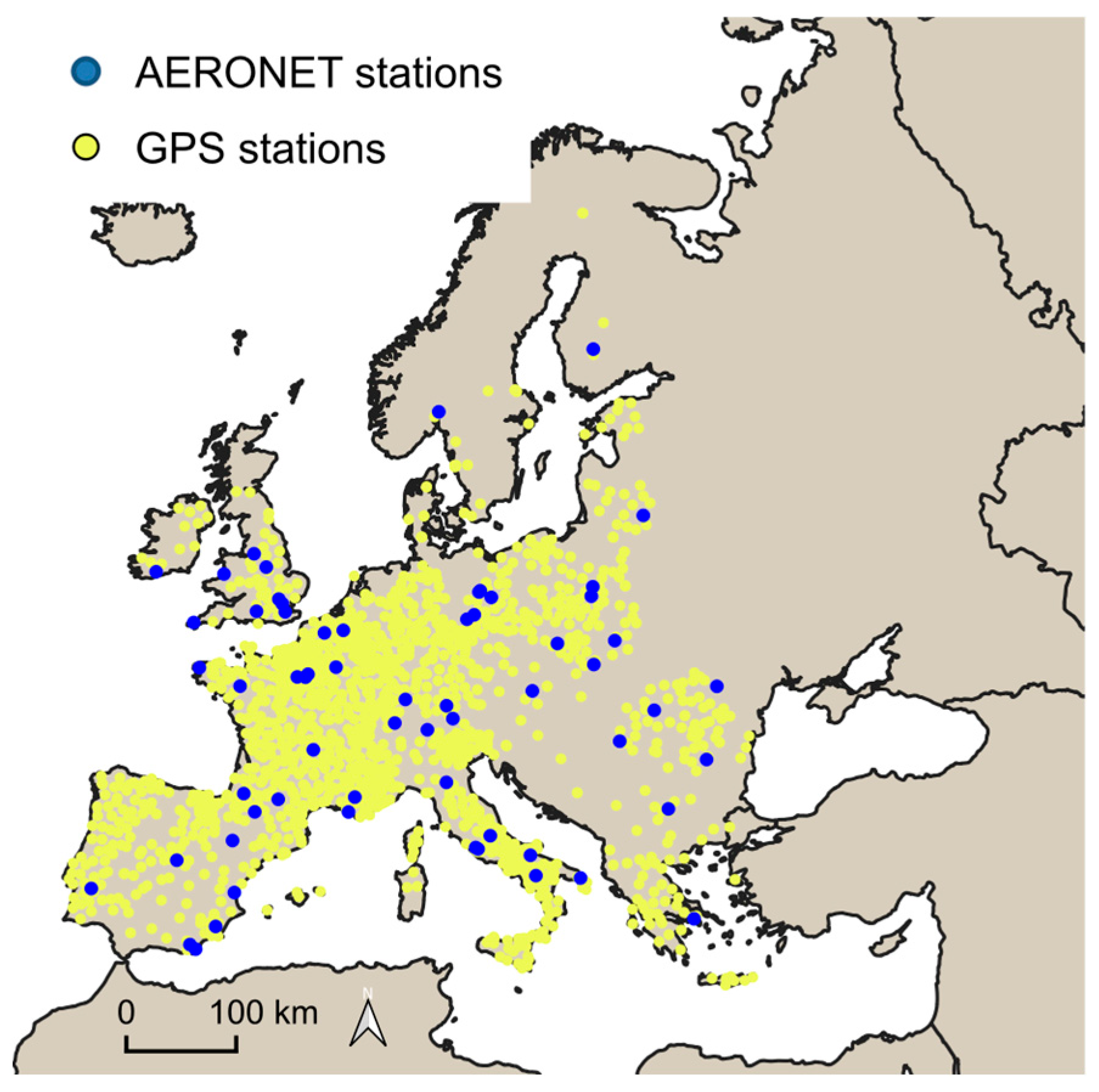
2.2. Validation Datasets
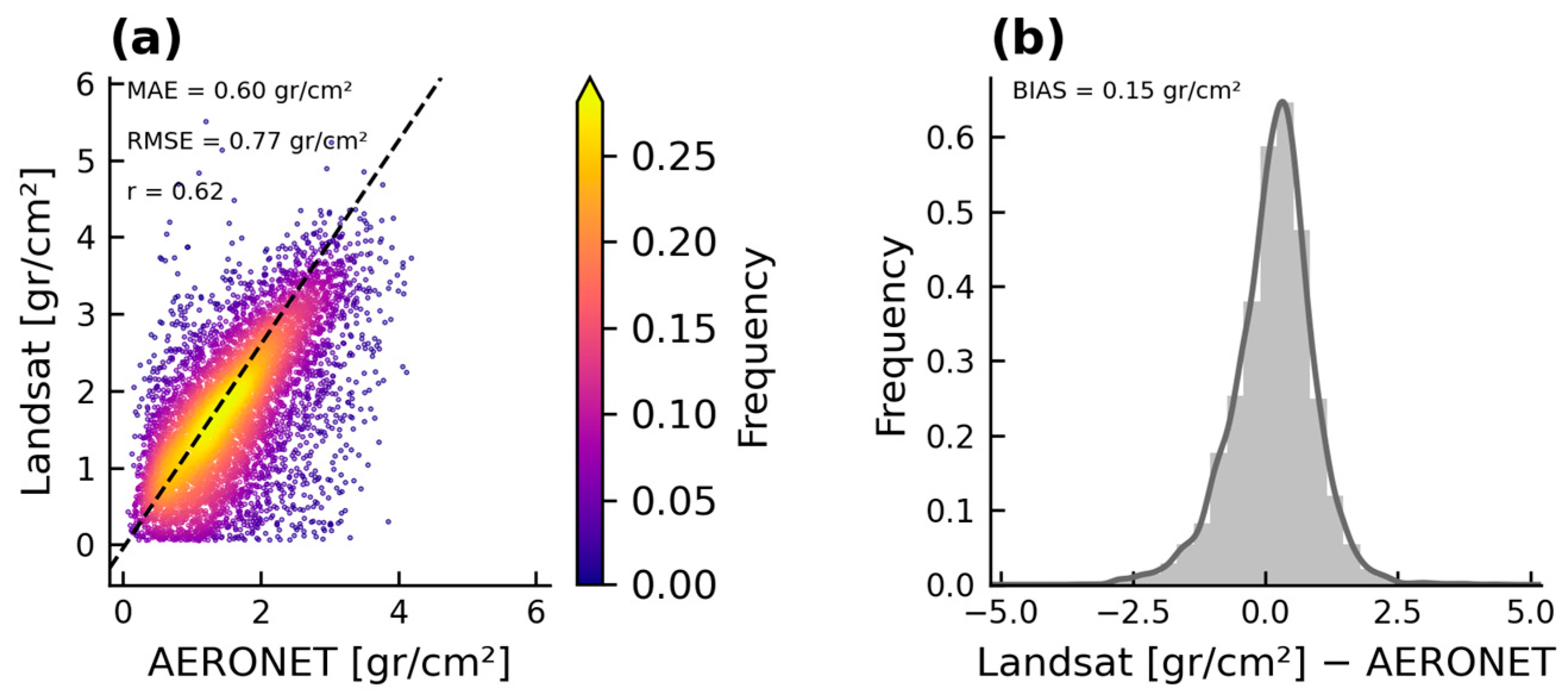
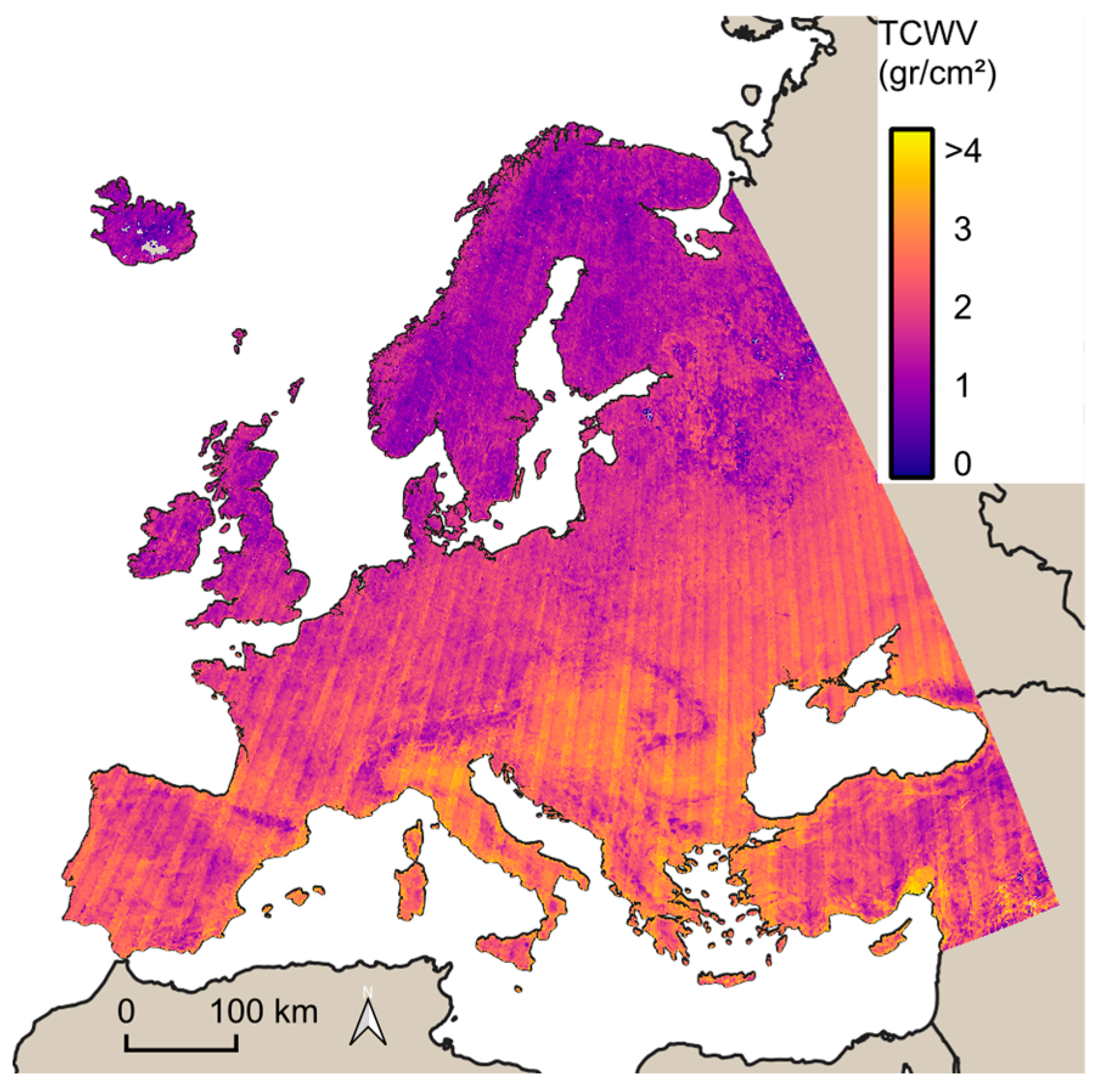
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bojinski, S.; Verstraete, M.; Peterson, T.C.; Richter, C.; Simmons, A.; Zemp, M. The Concept of Essential Climate Variables in Support of Climate Research, Applications, and Policy. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 1431–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, S.; Roca, R.; Weckwerth, T.; Andronova, N. Tropospheric Water Vapor, Convection, and Climate. Rev. Geophys. 2010, 48, RG2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessler, A.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, P. Water-Vapor Climate Feedback Inferred from Climate Fluctuations, 2003–2008. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L20704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Tang, B.-H.; Wu, H.; Ren, H.; Yan, G.; Wan, Z.; Trigo, I.F.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite-Derived Land Surface Temperature: Current Status and Perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulley, G.; Ghent, D. Taking the Temperature of the Earth: Steps Towards Integrated Understanding of Variability and Change; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Ramírez, D.; Whiteman, D.N.; Smirnov, A.; Lyamani, H.; Holben, B.N.; Pinker, R.; Andrade, M.; Alados-Arboledas, L. Evaluation of AERONET Precipitable Water Vapor versus Microwave Radiometry, GPS, and Radiosondes at ARM Sites. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 9596–9613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanelli, M.; Mascitelli, A.; Sanò, P.; Diémoz, H.; Estellés, V.; Federico, S.; Iannarelli, A.M.; Fratarcangeli, F.; Mazzoni, A.; Realini, E.; et al. Precipitable Water Vapour Content from ESR/SKYNET Sun–Sky Radiometers: Validation against GNSS/GPS and AERONET over Three Different Sites in Europe. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Blewitt, G.; Kreemer, C.; Hammond, W.C.; Argus, D.; Yin, X.; Van Malderen, R.; Mayer, M.; Jiang, W.; Awange, J.; et al. An Enhanced Integrated Water Vapour Dataset from More than 10 000 Global Ground-Based GPS Stations in 2020. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 723–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursinski, E.; Hajj, G.; Schofield, J.; Linfield, R.; Hardy, K.R. Observing Earth’s Atmosphere with Radio Occultation Measurements Using the Global Positioning System. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 23429–23465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.; Lyapustin, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T. AERONET Processing Algorithms Refinement. In Proceedings of the AERONET Workshop, El Arenosillo, Spain, 12–15 October 2004; pp. 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Borger, C.; Beirle, S.; Wagner, T. A 16-Year Global Climate Data Record of Total Column Water Vapour Generated from OMI Observations in the Visible Blue Spectral Range. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 3023–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, M.; Valks, P.; Loyola, D.; Aberle, B.; Slijkhuis, S.; Wagner, T.; Beirle, S.; Lang, R. Total Column Water Vapour Measurements from GOME-2 MetOp-A and MetOp-B. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 1111–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Borsdorff, T.; Aemisegger, F.; Feist, D.G.; Kivi, R.; Hase, F.; Schneider, M.; Landgraf, J. First Data Set of H 2 O/HDO Columns from the Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI). Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Du, C.; Liu, R.; Qin, Q.; Yan, G.; Li, Z.-L.; Meng, J. Atmospheric Water Vapor Retrieval from Landsat 8 Thermal Infrared Images. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 1723–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, P.W. Retrieval of Temperature and Moisture Profiles from AMSU-A and AMSU-B Measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 39, 2429–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Li, Z.-L.; Stoll, M.P.; Becker, F. Improvements in the Split-Window Technique for Land Surface Temperature Determination. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Jia, L.; Su, Z.; Wan, Z.; Zhang, R. A New Approach for Retrieving Precipitable Water from ATSR2 Split-Window Channel Data over Land Area. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 5095–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; He, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, G.; Long, T. NDVI-Based Split-Window Algorithm for Precipitable Water Vapour Retrieval from Landsat-8 TIRS Data over Land Area. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 6, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Xu, Y.; Yeh, T.-K.; Xu, T.; Wang, Y.; Su, W. Improving the Capability of Water Vapor Retrieval from Landsat 8 Using Ensemble Machine Learning. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 122, 103407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-Scale Geospatial Analysis for Everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippopoulos, K.; Pantavou, K.; Cartalis, C.; Agathangelidis, I.; Mavrakou, T.; Polydoros, A.; Nikolopoulos, G. A Novel Artificial Neural Network Methodology to Produce High-Resolution Bioclimatic Maps Using Earth Observation Data: A Case Study for Cyprus. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| AERONET Stations | GPS Stations | |
|---|---|---|
| MAE (gr/cm2) | 0.60 | 0.59 |
| RMSE (gr/cm2) | 0.77 | 0.79 |
| BIAS (gr/cm2) | 0.15 | 0.13 |
| r | 0.62 | 0.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agathangelidis, I.; Ban, Y.; Cartalis, C.; Philippopoulos, K. Validating TIR-Derived Total Column Water Vapor Using Sun Photometers and GPS Measurements. Environ. Earth Sci. Proc. 2025, 35, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025035006
Agathangelidis I, Ban Y, Cartalis C, Philippopoulos K. Validating TIR-Derived Total Column Water Vapor Using Sun Photometers and GPS Measurements. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings. 2025; 35(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025035006
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgathangelidis, Ilias, Yifang Ban, Constantinos Cartalis, and Konstantinos Philippopoulos. 2025. "Validating TIR-Derived Total Column Water Vapor Using Sun Photometers and GPS Measurements" Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings 35, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025035006
APA StyleAgathangelidis, I., Ban, Y., Cartalis, C., & Philippopoulos, K. (2025). Validating TIR-Derived Total Column Water Vapor Using Sun Photometers and GPS Measurements. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings, 35(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025035006








