Orographic Effect’s Correlation with Convection During a Low-Pressure System Passage over Greece in September 2023 †
Abstract
1. Introduction
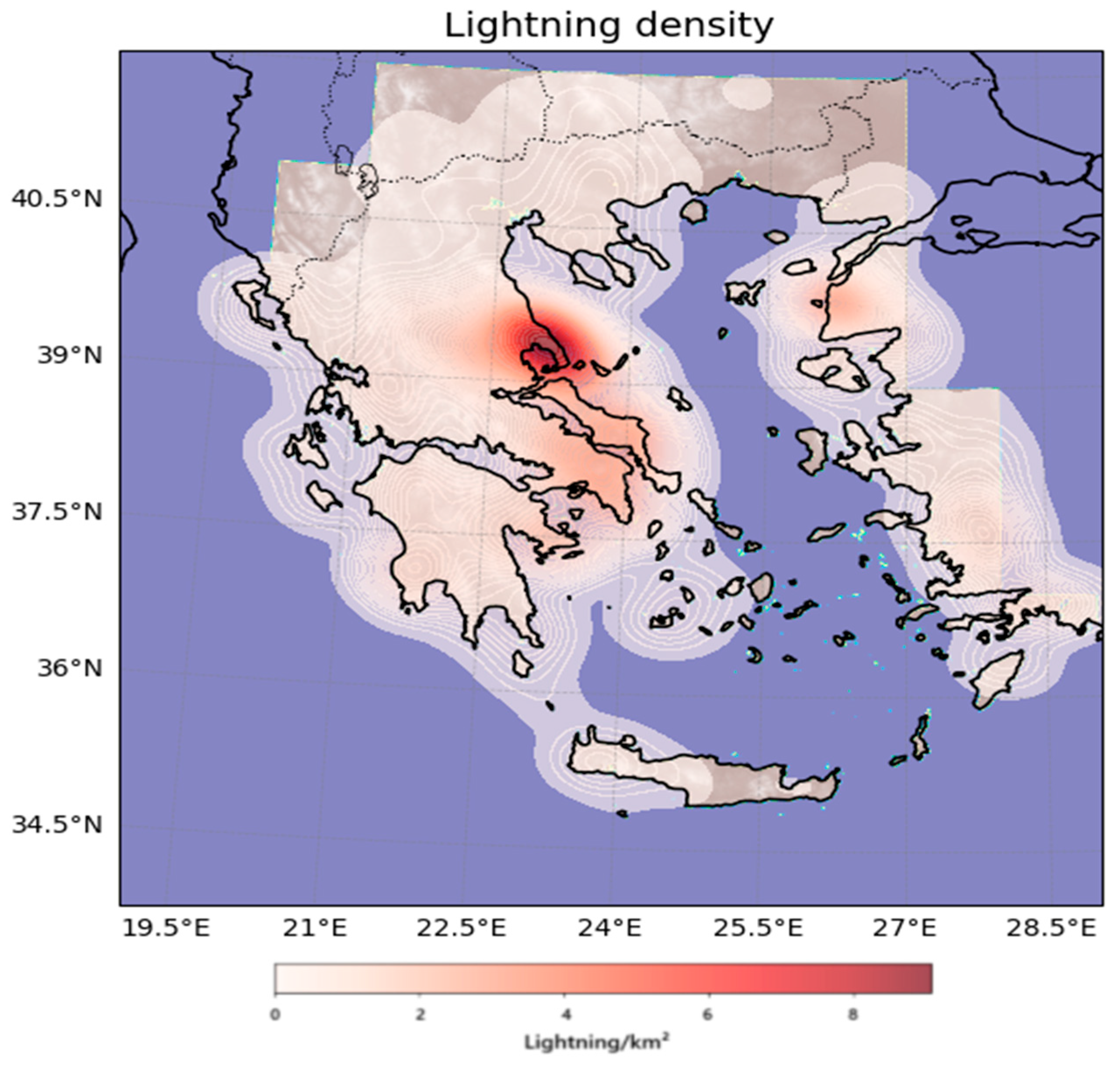
2. Data and Methodology
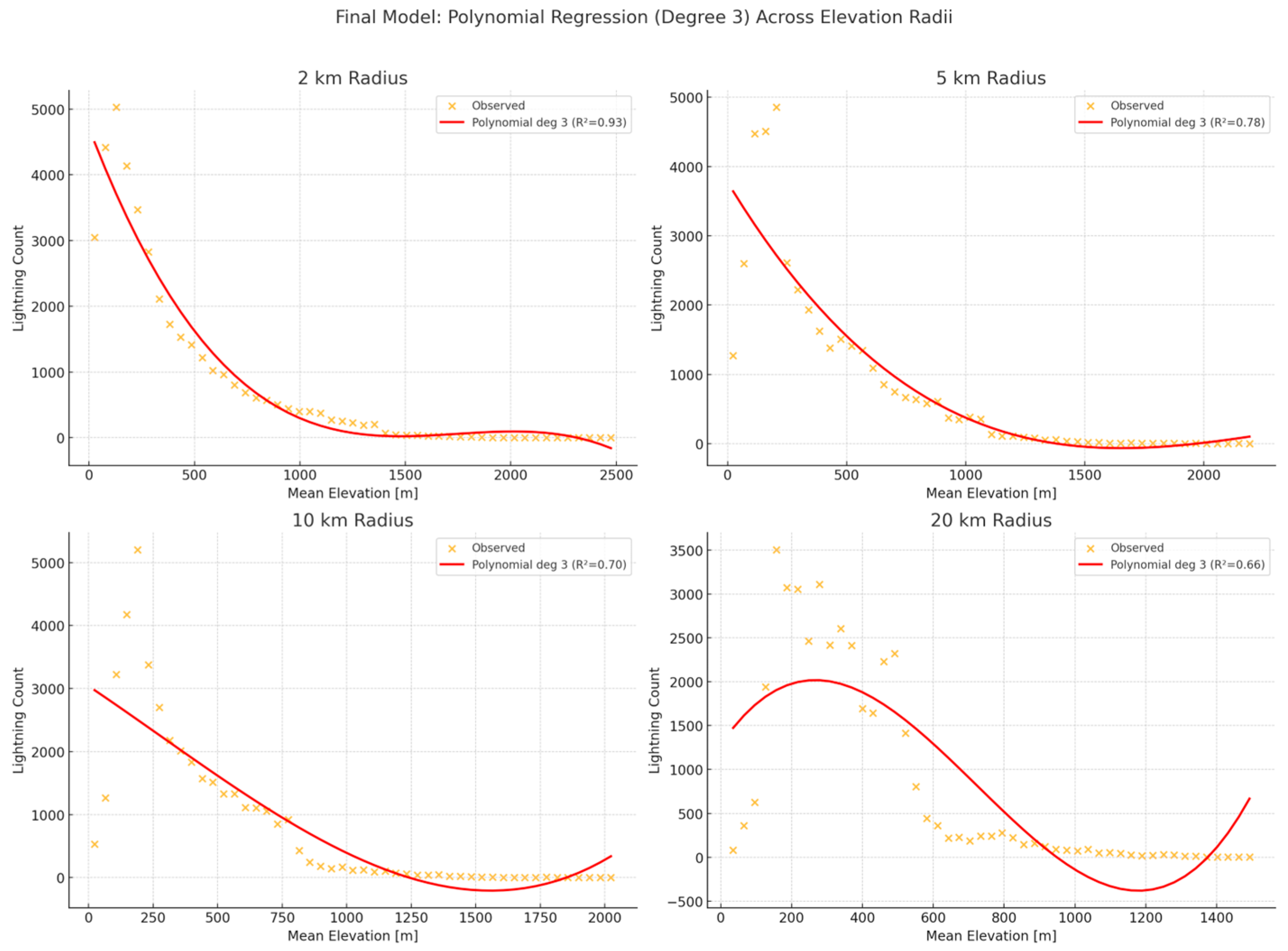
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katona, B.; Paul, M. Assessing the influence of complex terrain on severe convective environments in northeastern Alabama. Weather. Forecast. 2021, 36, 1003–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, M.; Rotunno, R.; Germann, U.; Berne, A. Supercell Thunderstorms in Complex Topography—How Mountain Valleys with Lakes Can Increase Occurrence Frequency. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2024, 152, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.M.; Lin, Y.-L. The Effects of Orographic Geometry on Supercell Thunderstorms. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.00579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshbaum, D.J.; Adler, B.; Kalthoff, N.; Barthlott, C.; Serafin, S. Moist orographic convection: Physical mechanisms and links to surface-exchange processes. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.M. Detecting soil moisture impacts on convective initiation in Europe. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 4631–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Kuang, Z. Why does deep convection have different sensitivities to temperature perturbations in the lower versus upper troposphere? J. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 76, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fankhauser, J.C.; Crook, N.A.; Tuttle, J.; Miller, L.J.; Wade, C.G. Initiation of deep convection along boundary layer convergence lines in a semitropical environment. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1995, 123, 291–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshbaum, D.J.; Dale, R.D. Factors governing cellular convection in orographic precipitation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 61, 682–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demko, J.C.; Geerts, B. A numerical study of the evolving convective boundary layer and orographic circulation around the Santa Catalina Mountains in Arizona. Part II: Interaction with deep convection. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2010, 138, 3603–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Ren, Y.; Fu, S.; Xue, H. Statistics of isolated deep convection initiation and its relation to topography in the North China area. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2023, 128, e2022JD037949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhans, W.; Gohm, A.; Zängl, G. The orographic impact on patterns of embedded convection during the August 2005 Alpine flood. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 2092–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.; Rosenfeld, D.; Madden, N.; Gerlach, J.; Gears, N.; Atkinson, L.; Dunnemann, N.; Frostrom, G.; Antonio, M.; Biazon, B. Contrasting convective regimes over the Amazon: Implications for cloud electrification. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, LBA 50-1–LBA 50-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, B.; Fang, M.; Ghate, V. Exploring stratocumulus cloud-top entrainment processes and parameterizations by using Doppler cloud radar observations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 73, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houze Jr, R.A. Orographic effects on precipitating clouds. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, C.D. Mountain Meteorology: Fundamentals and Applications; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Banta, R.M. Daytime boundary-layer evolution over mountainous terrain. Part 1: Observations of the dry circulations. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1984, 112, 340–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banta, R.M.; Barker Schaaf, C. Thunderstorm genesis zones in the Colorado Rocky Mountains as determined by traceback of geosynchronous satellite images. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1987, 115, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS EROS Archive–Digital Elevation–Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) 1 Arc-Second Global. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/centers/eros/science/usgs-eros-archive-digital-elevation-shuttle-radar-topography-mission-srtm-1 (accessed on 9 February 2025).
- De Meij, A.; Ojha, N.; Singh, N.; Singh, J.; Poelman, D.R.; Pozzer, A. The Impact of High-Resolution SRTM Topography and Corine Land Cover on Lightning Calculations in WRF. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, L.; Whitworth, M.; Pepin, N.; Dorling, S. A comprehensive review of datasets and methodologies employed to produce thunderstorm climatologies. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 2463–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, A.M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Using remote sensing and GIS to detect and monitor urban land use change in Dhaka Metropolitan of Bangladesh during 1960–2005. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 150, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nastos, P.T.; Feloni, E.; Paraskevas, A.; Matsangouras, I.T. Meteorological and Remote Sensing Analysis of the Severe Storm “Daniel” over Greece. In Proceedings of the European Geosciences Union General Assembly 2024 (EGU24), Vienna, Austria, 14–19 April 2024; p. 12908. [Google Scholar]
- Göbel, M.; Serafin, S.; Rotach, M.W. Adverse impact of terrain steepness on thermally driven initiation of orographic convection. Weather. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 4, 725–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arsenis, S.T.; Samos, I.; Nastos, P.T. Orographic Effect’s Correlation with Convection During a Low-Pressure System Passage over Greece in September 2023. Environ. Earth Sci. Proc. 2025, 35, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025035037
Arsenis ST, Samos I, Nastos PT. Orographic Effect’s Correlation with Convection During a Low-Pressure System Passage over Greece in September 2023. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings. 2025; 35(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025035037
Chicago/Turabian StyleArsenis, Sotirios T., Ioannis Samos, and Panagiotis T. Nastos. 2025. "Orographic Effect’s Correlation with Convection During a Low-Pressure System Passage over Greece in September 2023" Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings 35, no. 1: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025035037
APA StyleArsenis, S. T., Samos, I., & Nastos, P. T. (2025). Orographic Effect’s Correlation with Convection During a Low-Pressure System Passage over Greece in September 2023. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings, 35(1), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025035037







