Effective Microorganism (EM) Technology for Lake Conservation and Water Quality Restoration †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Effective Microorganisms Activated Solution (EMAS)
2.2. TeMo Decomposer (TeMo)
2.3. Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB)
3. Results and Discussion
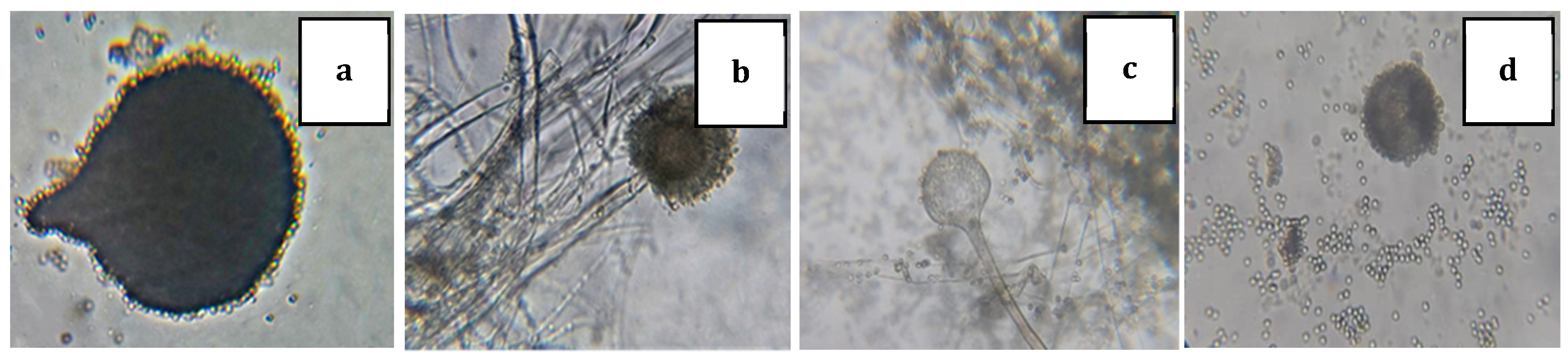
3.1. Bacteria and Fungus Identification
3.2. Lake Water Treatment Results
3.3. pH
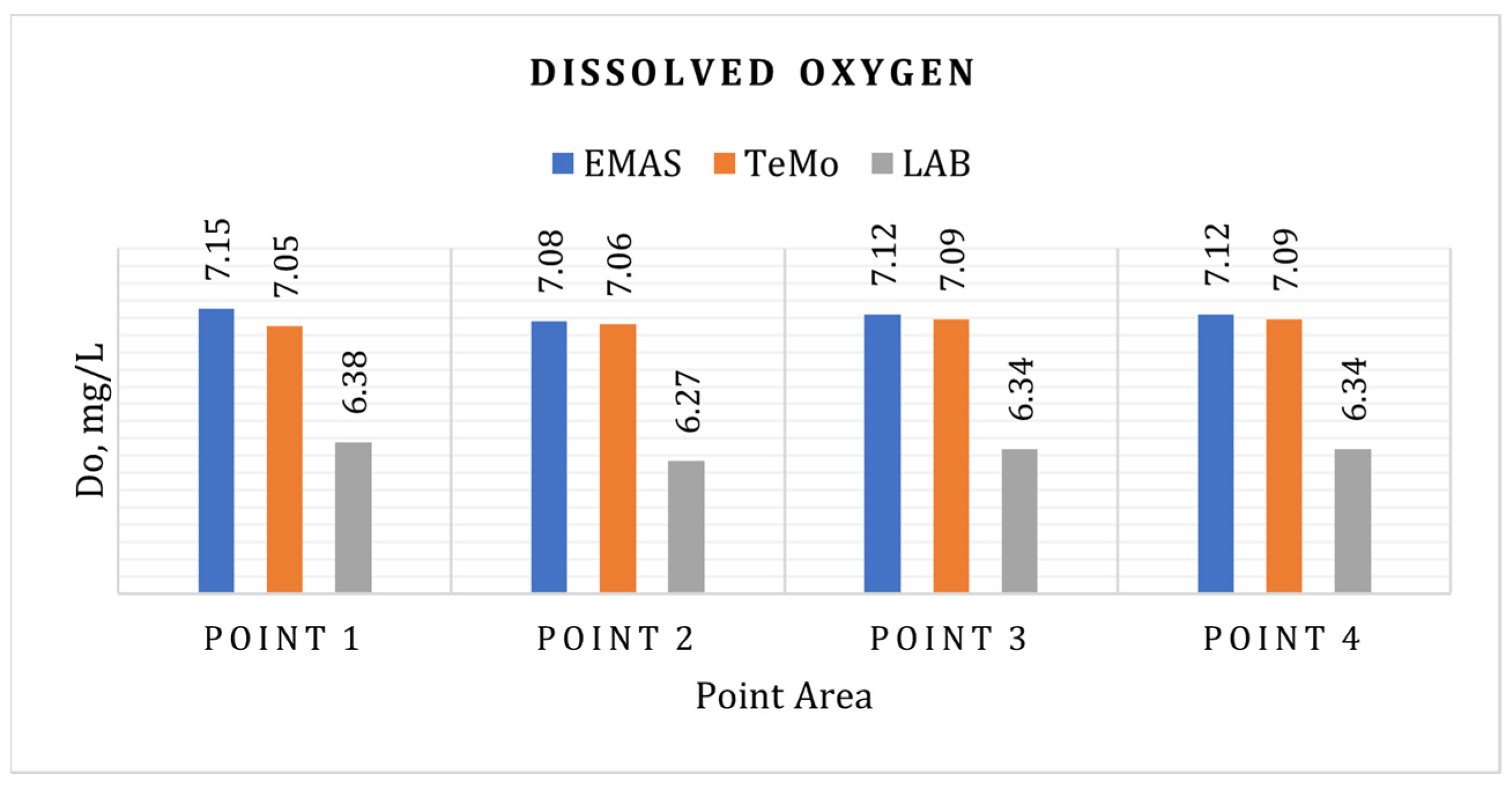
3.4. Dissolved Oxygen
3.5. Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
3.6. Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD)
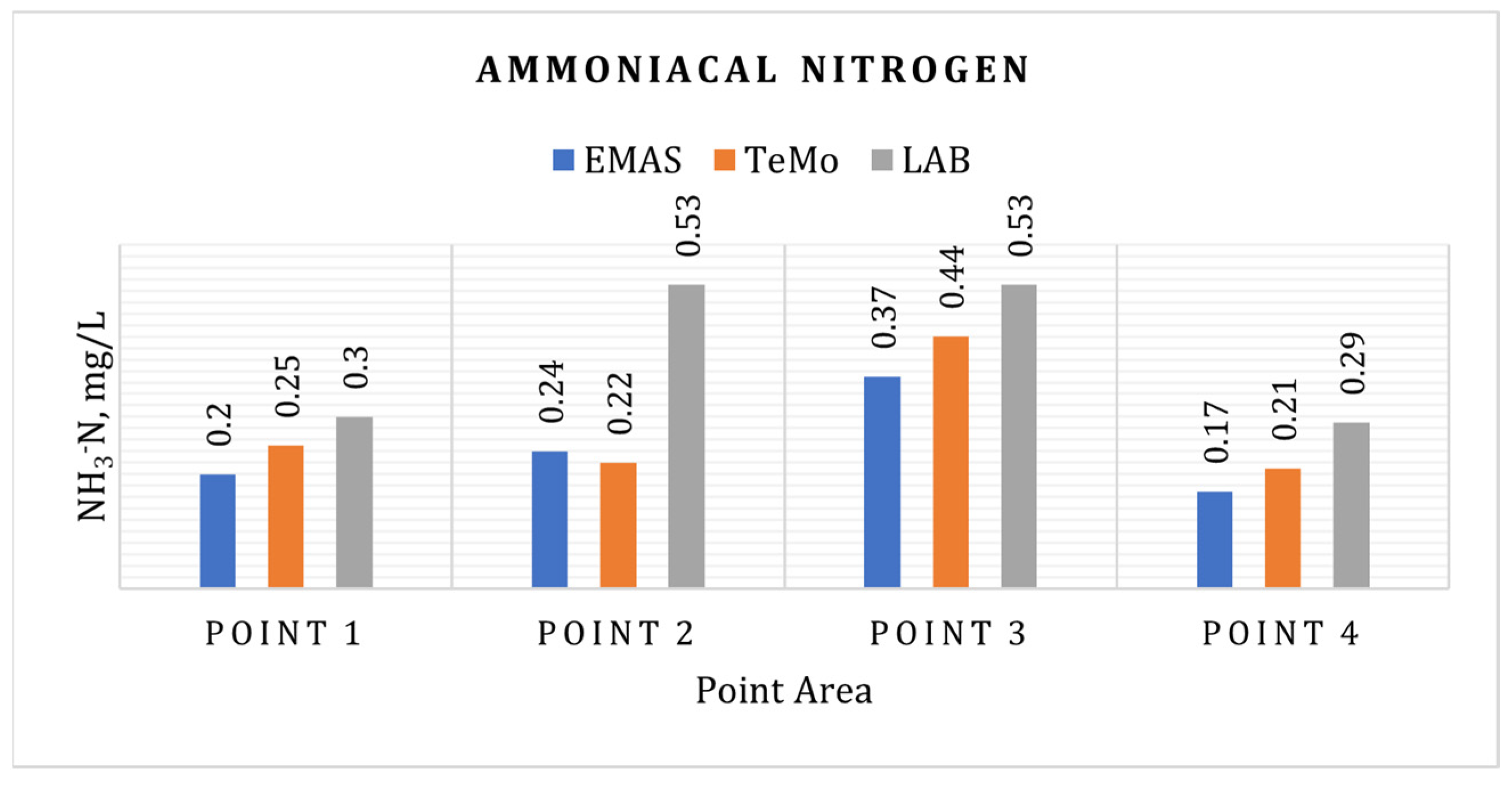
3.7. Ammoniacal Nitrogen (NH3-N)
3.8. Total Suspended Solid (TSS)
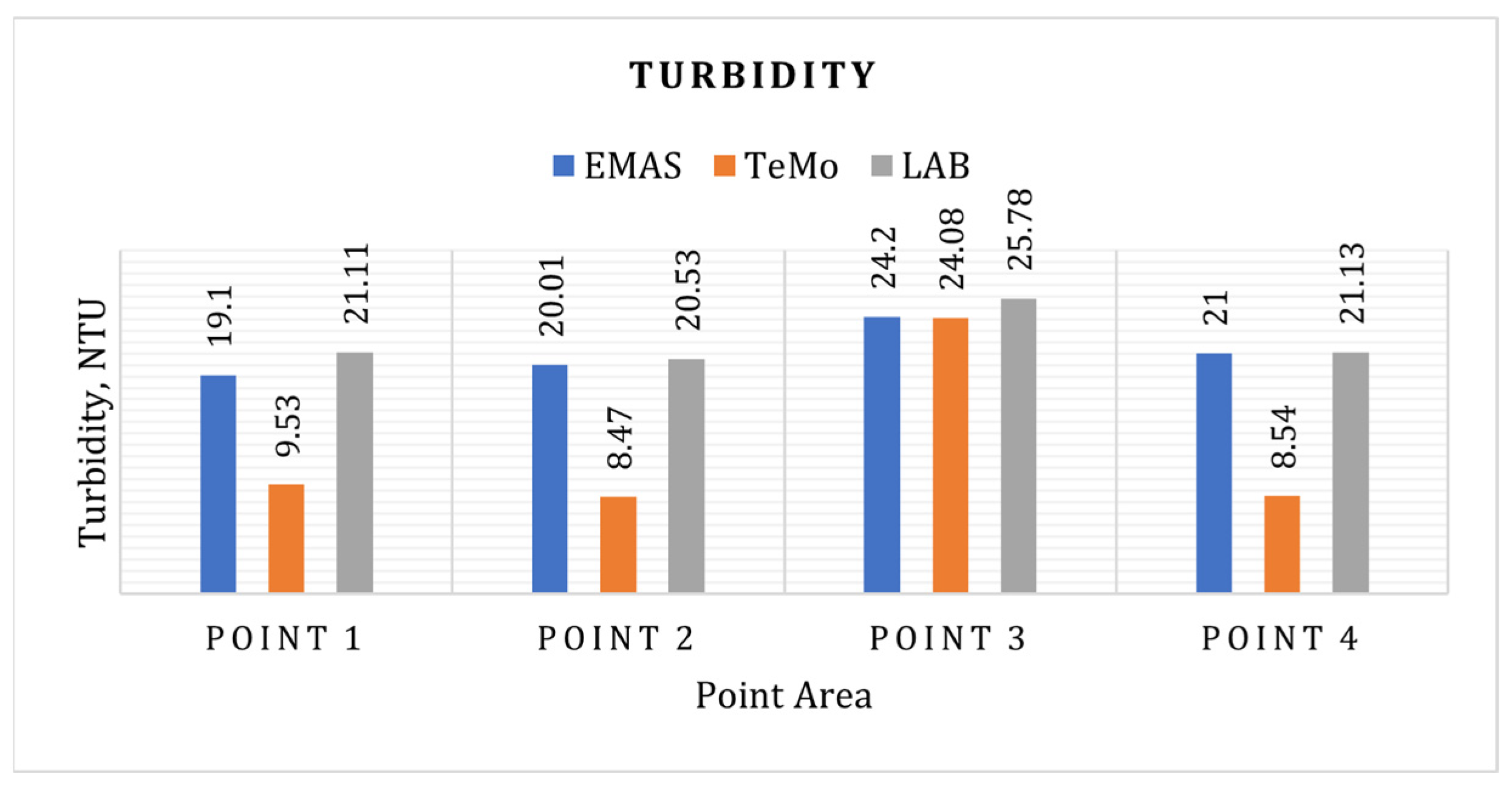
3.9. Turbidity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zakarya, I.A.; Izhar, T.N.T.; Noordin, N.M.; Ibrahim, N.; Kamaruddin, S.A. Rapid composting of food waste and yard waste with effective microorganisms (EM). IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci 2021, 920, 012028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzyński, J.; Kulkova, I.; Wierzchowski, P.S.; Wróbel, B. Response of Physicochemical and Microbiological Properties to the Application of Effective Microorganisms in the Water of the Turawa Reservoir. Water 2021, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franciosi, E.; Settanni, L.; Cavazza, A.; Poznanski, E. Biodiversity and technological potential of wild lactic acid bacteria from raw cows’ milk. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laconi, E.B.; Astuti, D.A. Fermentation of solid tempe waste using Aspergillus niger and gelatinization of liquid tempe waste using three kinds of soluble carbohydrate. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Sustainable Animal Agriculture for Developing Countries (SAADC 2011), Nakhon Rat, Thailand, 26 July 2011; Available online: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/pdf/10.5555/20113387213 (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Laconi, E. The Evaluation of Rumen Metabolism of Fries Holstein (FH) Calves Fed Biofermented Cocoa Pods Using Phanerochaete Chrysosporium. In Proceedings of the 1st International Seminar on Animal Industry, Bogor, Indonesia, 23–24 November 2009; Available online: https://repository.ipb.ac.id/handle/123456789/33821 (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Mokoena, M.P. Lactic Acid Bacteria and Their Bacteriocins: Classification, Biosynthesis and Applications against Uropathogens: A Mini-Review. Molecules 2017, 22, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anupong, W.; Jutamas, K.; On-uma, R.; Alshiekheid, M.; Sabour, A.; Krishnan, R.; Lan Chi, N.T.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Brindhadevi, K. Bioremediation competence of Aspergillus flavus DDN on pond water contaminated by mining activities. Chemosphere 2022, 304, 135250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitarek, M.; Napiórkowska-Krzebietke, A.; Mazur, R.; Czarnecki, B.; Pyka, J.; Stawecki, K.; Olech, M.; Sołtysiak, S.; Kapusta, A. Application of Effective Microorganisms Technology as a lake restoration tool—A case study of Muchawka Reservoir. J. Elem. 2017, 22, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, D.D.; Singh, G.; Majumdar, S.; Chanda, P. Challenges in developing strategies for the valorization of lignin—A major pollutant of the paper mill industry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 30, 11119–11140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Hanafiah, Z.M.; Azmi, A.R.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I.; Olivito, F.; Golemme, G.; Ilham, Z.; Jamaludin, A.A.; Razali, N.; Abdul Halim-Lim, S.; Wan Mohtar, W.H.M. Water Quality Assessment and Decolourisation of Contaminated Ex-Mining Lake Water Using Bioreactor Dye-Eating Fungus (BioDeF) System: A Real Case Study. Toxics 2024, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Sun, D.; Liu, J.; Zhu, J.; Liu, W. Recent advances and perspectives in efforts to reduce the production and application cost of microbial flocculants. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidayat, B.J.; Eriksen, N.T.; Wiebe, M.G. Acid phosphatase production by Aspergillus niger in continuous flow culture. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 254, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Type of EM & Dosages (mL) | EMAS | TeMo | LAB | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 20 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 5 | 10 | 20 | |
| After Treatment results at Point 1 | |||||||||
| WQI | 90.79 | 88.18 | 86.40 | 92.86 | 90.54 | 90.22 | 83.9 | 82.18 | 80.67 |
| Class | II | II | II | II | II | II | II | II | II |
| After Treatment results at Point 2 | |||||||||
| WQI | 89.83 | 87.57 | 87.51 | 87.76 | 87.13 | 84.55 | 81.63 | 79.9 | 77.47 |
| Class | II | II | II | II | II | II | II | II | II |
| After Treatment results at Point 3 | |||||||||
| WQI | 84.44 | 82.3 | 81.52 | 83.34 | 81.18 | 80.68 | 78.52 | 76.43 | 73.35 |
| Class | II | II | II | II | II | II | II | III | III |
| After Treatment results at Point 4 | |||||||||
| WQI | 91.41 | 88.99 | 88.97 | 88.4 | 87.34 | 86.65 | 83.87 | 83.3 | 82.64 |
| Class | II | II | II | II | II | II | II | II | II |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zakarya, I.A.; Mazwin, N.A.; Izhar, T.N.T.; Hilmi, N.A.M.; Mohamad, M. Effective Microorganism (EM) Technology for Lake Conservation and Water Quality Restoration. Environ. Earth Sci. Proc. 2025, 33, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025033001
Zakarya IA, Mazwin NA, Izhar TNT, Hilmi NAM, Mohamad M. Effective Microorganism (EM) Technology for Lake Conservation and Water Quality Restoration. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings. 2025; 33(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025033001
Chicago/Turabian StyleZakarya, Irnis Azura, Nursyazarena Azwa Mazwin, Tengku Nuraiti Tengku Izhar, Nur Adlina Mohd Hilmi, and Muna’amirah Mohamad. 2025. "Effective Microorganism (EM) Technology for Lake Conservation and Water Quality Restoration" Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings 33, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025033001
APA StyleZakarya, I. A., Mazwin, N. A., Izhar, T. N. T., Hilmi, N. A. M., & Mohamad, M. (2025). Effective Microorganism (EM) Technology for Lake Conservation and Water Quality Restoration. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings, 33(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025033001






