Strategies to Mitigate Risks in Building Information Modelling Implementation: A Techno-Organizational Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Literature Review
1.2. Theoretical Framework
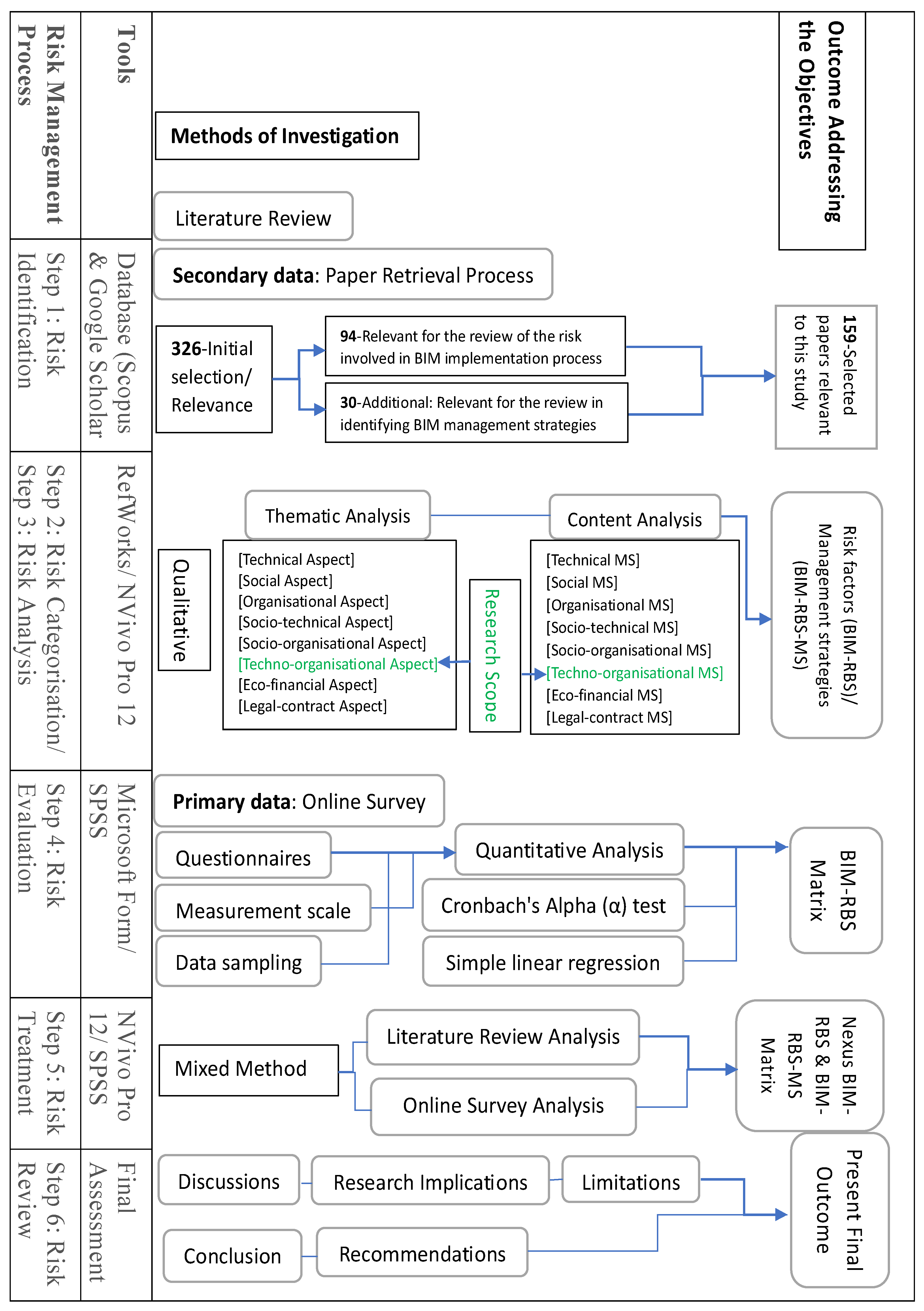
2. Methodology
2.1. Research Design
2.2. Paper Retrieval Process (Step 1–3)
2.3. Online Survey (Step 4)
- Variables and Scales: Nominal (N) Gender and Age; Ordinal (O) Level of BIM experience, BIM-RBS as the outcome variable and shares the same properties as the dependent variables; String (S) BIM-RBS-MS as the intervening variable that transmit the effect of an independent variable on a dependent variable.
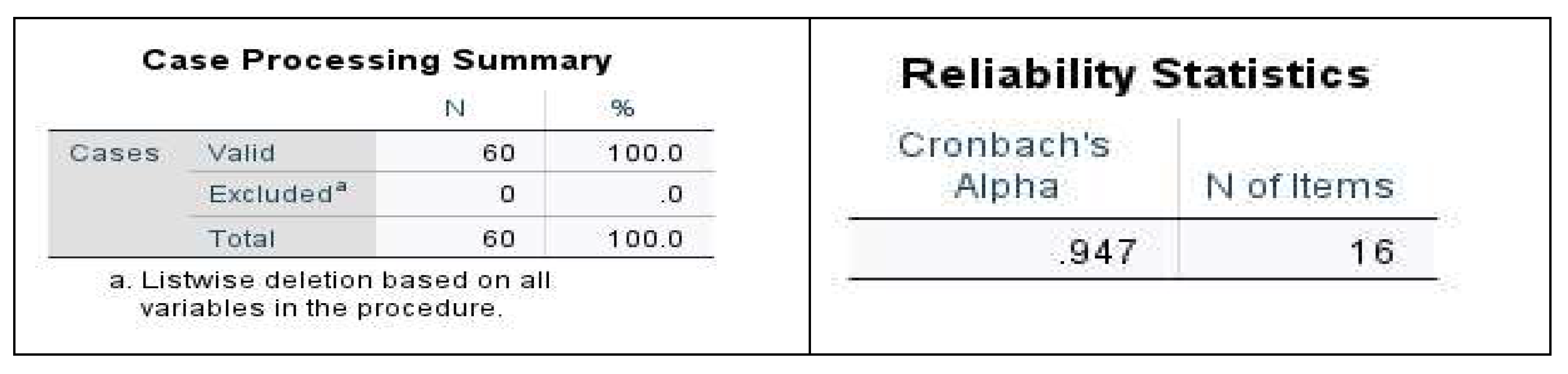
- Cronbach’s Alpha (α) test (CA): was employed to measure internal consistency/reliability of the survey scale. It assessed the reliability of multiple Likert-scale questions determining the magnitude of risk factors (BIM-RBS). Various thresholds were applied and the test procedure involved [Click Analyze > Scale > Reliability Analysis > select the variables > ensuring the model says ‘Alpha’ > then click OK]. The results are shown in Section 3.2.
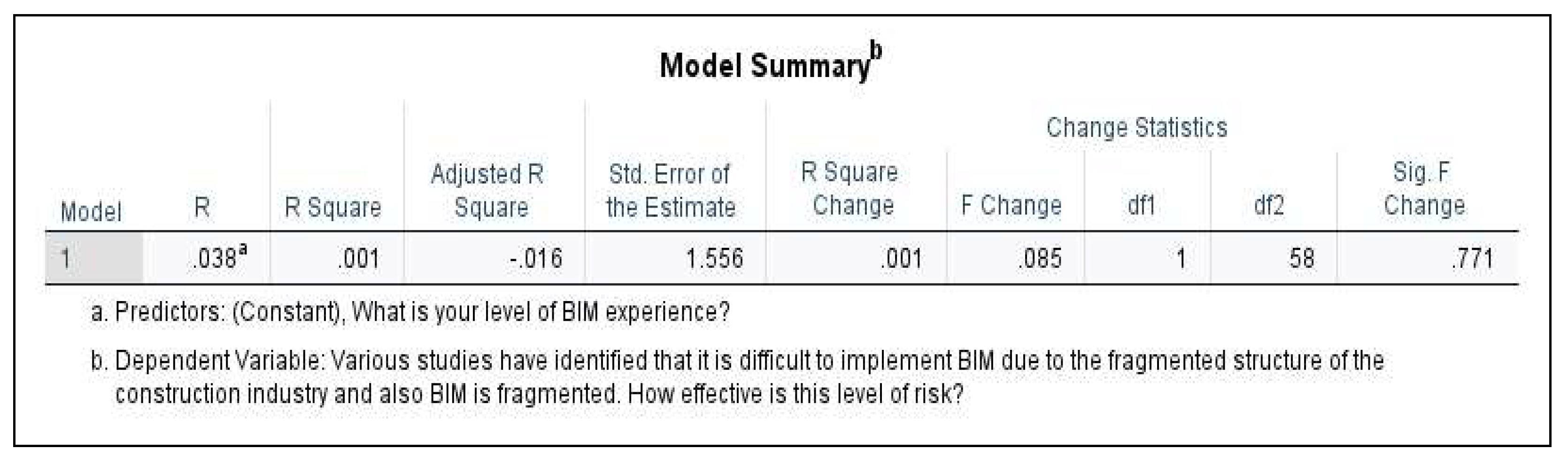
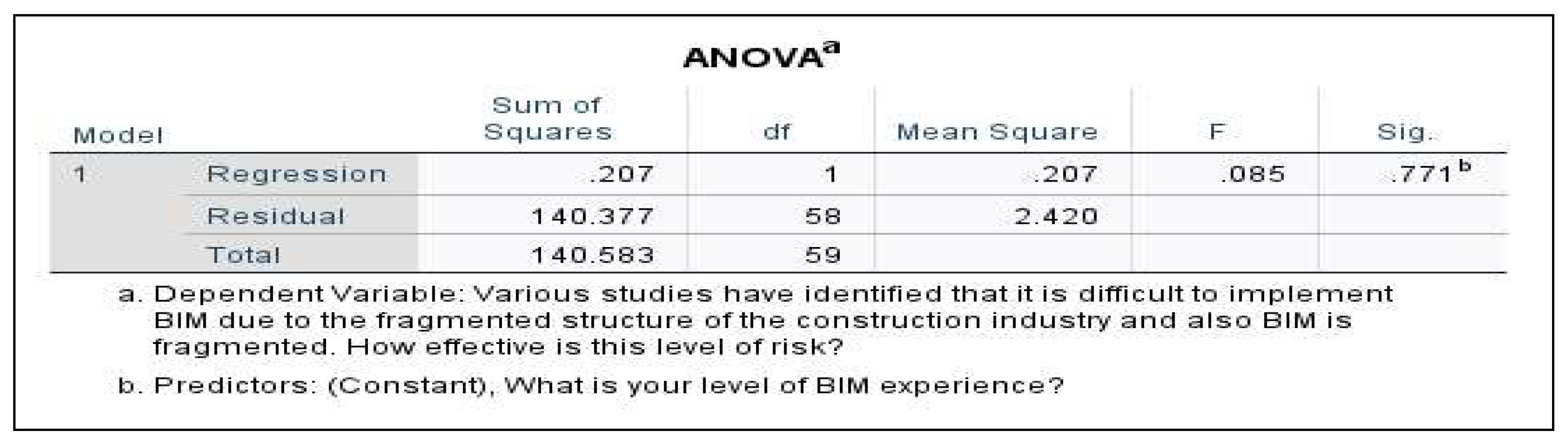
- Simple linear regression (SLR): attempts to predict the outcome variable (BIM-RBS) using the predictor variable (Level of BIM experience). The test procedure involved [Click Analyze > Regression > Linear > select outcome variable and move to the ‘Dependent’ box > select predictor variable and move to the ‘Block 1 of 1’ box > Select Statistics > click Estimates, Confidence Intervals, Model Fit, R Squared Change, and Descriptives]. See results in Section 3.2.
2.4. Mix-Method Analysis (Step 5)
3. Results
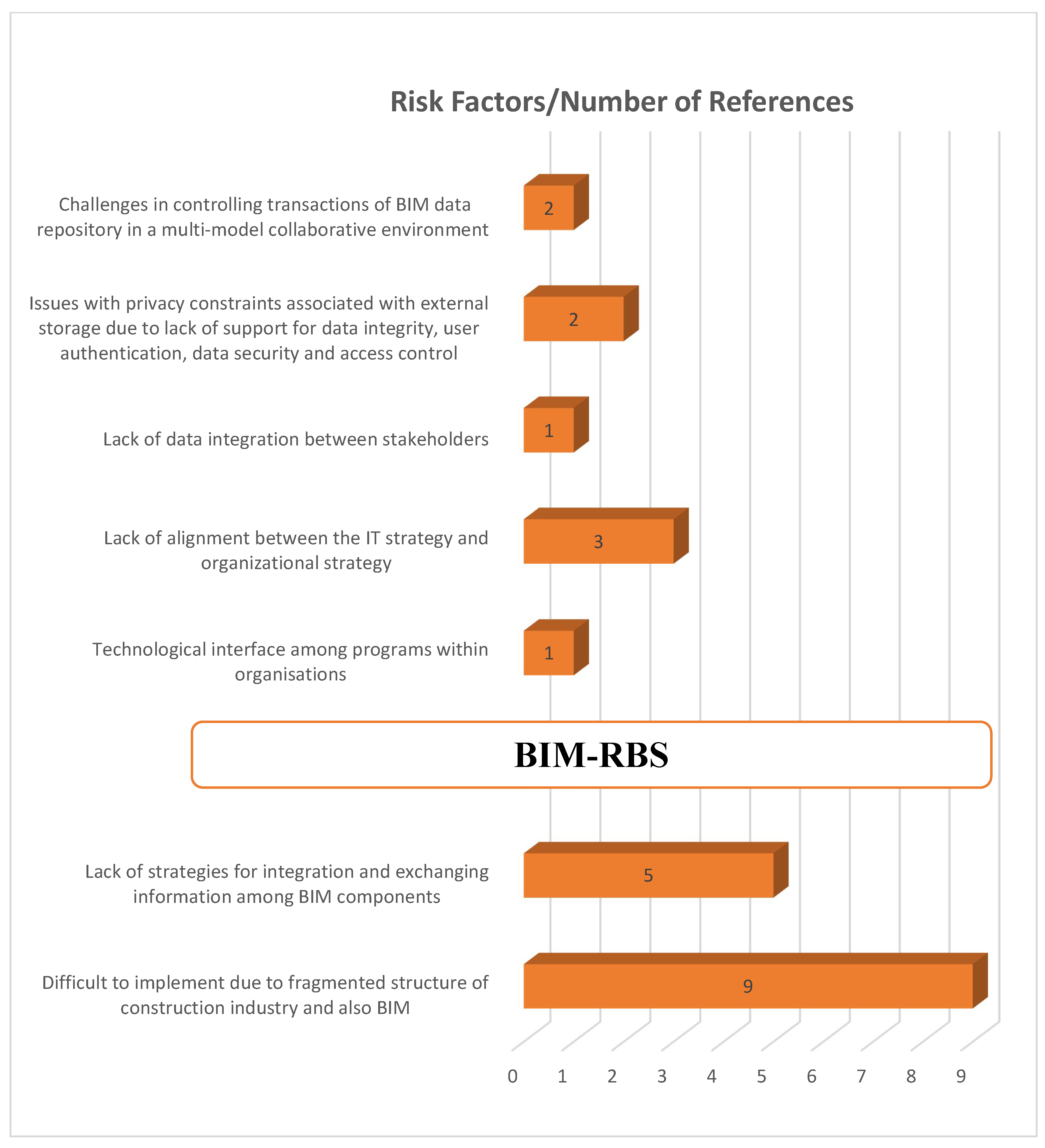
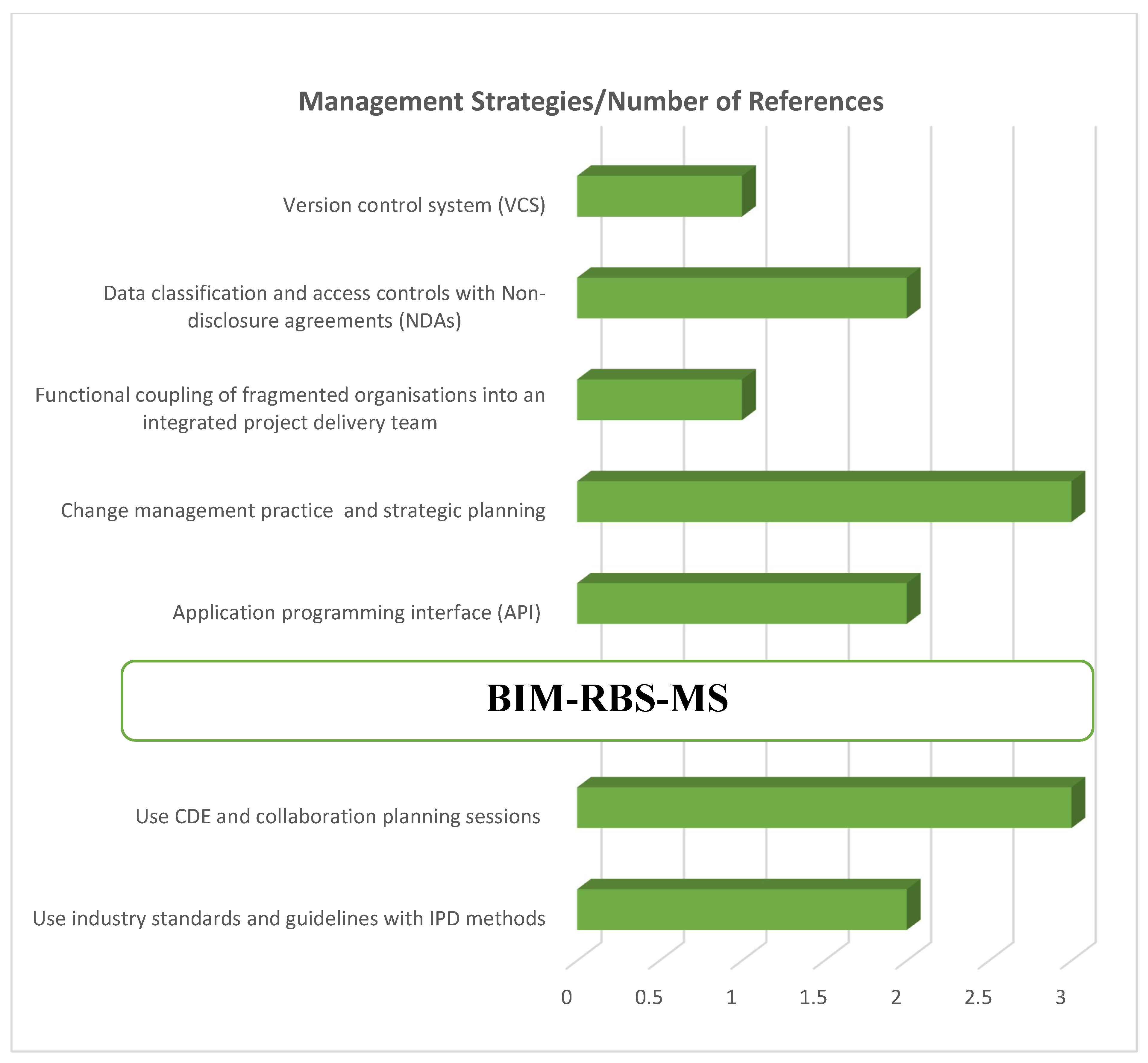
3.1. Secondary Data Analysis (Literature Review)
3.2. Primary Data Analysis (Online Survey)
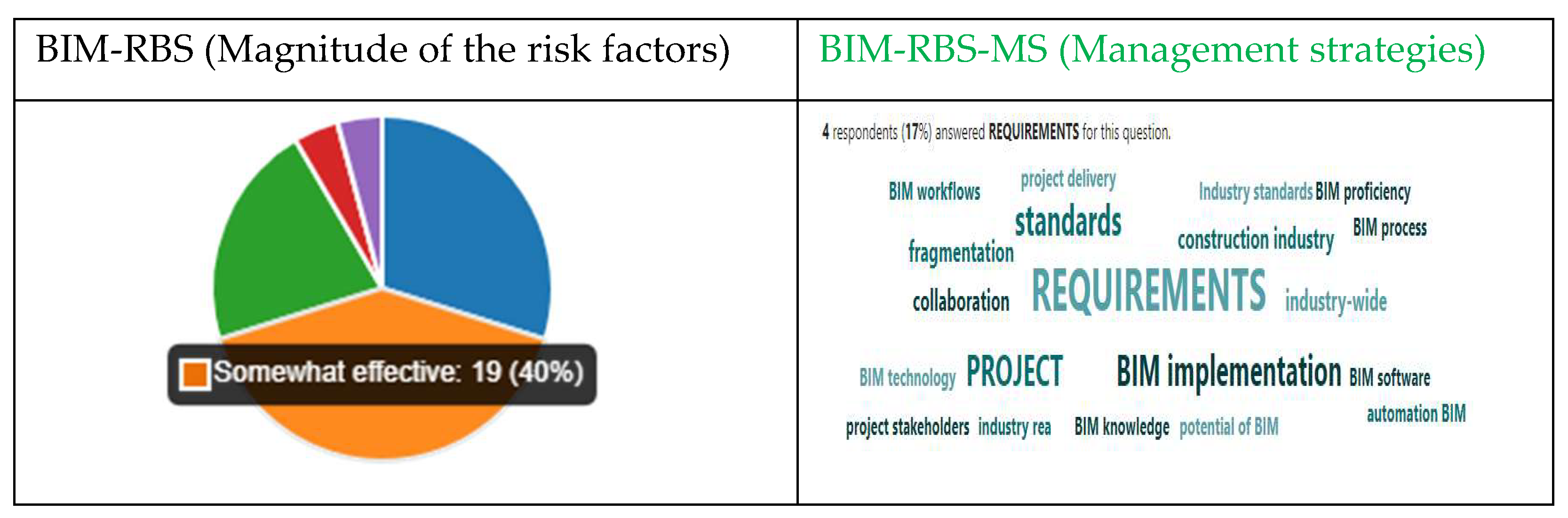
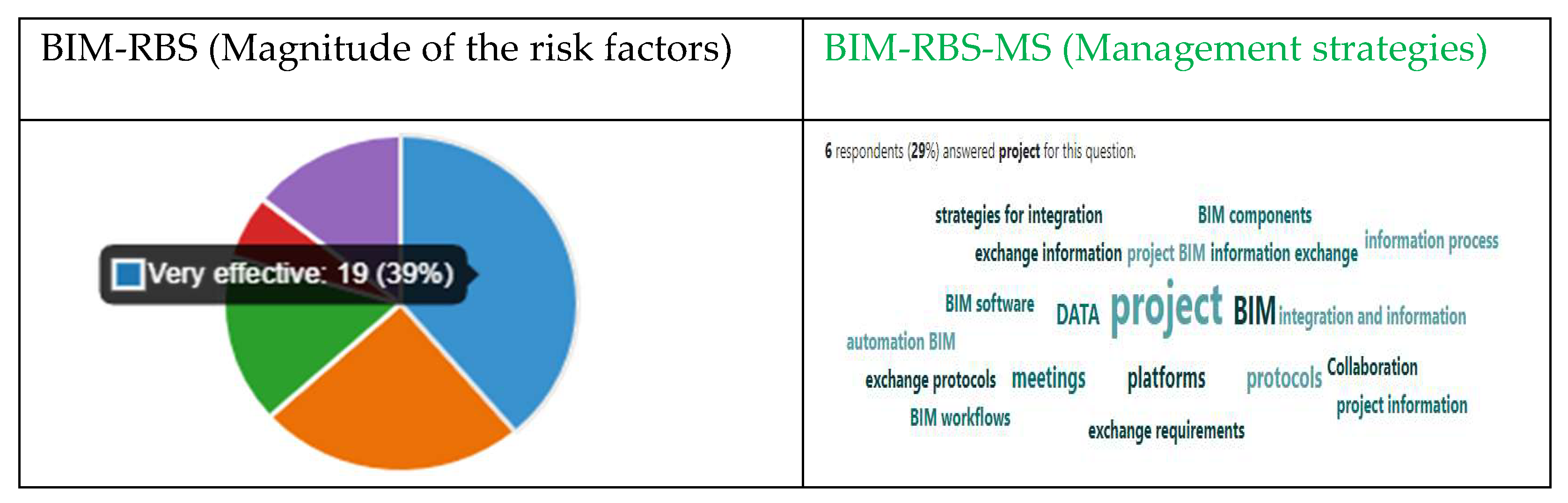
- Analyzing for risk magnitude (BIM-RBS) and management strategies (BIM-RBS-MS)
3.3. Findings
4. Discussions
4.1. Conclusions
4.2. Recommendations
- Socio-organizational Aspect
- Eco-financial perspective
- Legal-contractual perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duran, Ö.; Elnokly, A. Collaborative Approach to Design: Case-study of Future-Proofing A Paragraph 80 House. In Proceedings of the 18th IBPSA Conference, Shanghai, China, 4–6 September 2023; pp. 1497–1504. [Google Scholar]
- Kadume, N.H.; Naji, H.I. Building Schedule Risks Simulation by Using BIM with Monte Carlo Technique. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 856, 012059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshfetrat, R.; Sarvari, H.; Chan, D.W.; Rakhshanifar, M. Critical risk factors for implementing building information modelling (BIM): A Delphi-based survey. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2022, 22, 2375–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlovska, M.; Klosova, D.; Strukova, Z. Impact of Industry 4.0 Platform on the Formation of Construction 4.0 Concept: A Literature Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zairul, M.; Zaremohzzabieh, Z. Thematic Trends in Industry 4.0 Revolution Potential towards Sustainability in the Construction Industry. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, M.; Lin, C.; Chen, R.; Weng, M.; Jim, C.Y. Integrated BIM-IoT platform for carbon emission assessment and tracking in prefabricated building materialization. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 215, 108122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, M.; Ji, W. Development and application of a digital twin model for Net zero energy building operation and maintenance utilizing BIM-IoT integration. Energy Build. 2025, 328, 115170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, D.M.; Gáspár, L.; Maya, R.A. Optimizing Sustainability in Bridge Projects: A Framework Integrating Risk Analysis and BIM with LCSA According to ISO Standards. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alreshidi, E.; Mourshed, M.; Rezgui, Y. Requirements for cloud-based BIM governance solutions to facilitate team collaboration in construction projects. Requir. Eng. 2018, 23, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Kiviniemi, A.; Jones, S.W. Developing a tailored RBS linking to BIM for risk management of bridge projects. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2016, 23, 727–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshabshiri, A.; Ghanim, A.; Hussien, A.; Maksoud, A.; Mushtaha, E. Integration of Building Information Modelling and Digital Twins in the Operation and Maintenance of a Building Lifecycle: A Bibliometric Analysis Review. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 99, 111541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.H.; Kamal, E.M.; Fizal, M.F. A Systematic Literature Review: Implementing Building Information Modelling (BIM) for TVET Educators in Malaysia. J. Adv. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2025, 49, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavón, R.M.; Alberti, M.G.; Álvarez, A.A.A.; Cepa, J.J. Bim-based Digital Twin development for university Campus management. Case study ETSICCP. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 262, 125696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, X.; Kang, B.G.; Xie, J.; Hancock, C. Building Information Modelling (BIM)-enabled Facility Management (FM) of Nursing Homes in China: A Systematic Review. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 99, 111580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, J. Generative AIBIM: An automatic and intelligent structural design pipeline integrating BIM and generative AI. Inf. Fusion 2025, 114, 102654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okika, M.C.; Vermeulen, A.; Pretorius, J.H.C. A Systematic Approach to Identify and Manage Interface Risks between Project Stakeholders in Construction Projects. CivilEng 2024, 5, 89–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, A.A.; Ansari, R.; Taherkhani, R.; Hosseini, M.R. Developing a novel cash flow risk analysis framework for construction projects based on 5D BIM. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 103341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasser, M.; Rashid, I.A.; Nagy, A.M.; Elbehairy, H.S. Integrated model for BIM and risk data in construction projects. Eng. Res. Express 2022, 4, 045044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymański, P. Risk management in construction projects. Procedia Eng. 2017, 208, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei-Zohan, S.A.; Gheibi, M.; Chahkandi, B.; Mousavi, S.; Khaksar, R.Y.; Behzadian, K. A new integrated agent-based framework for designing building emergency evacuation: A BIM approach. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2023, 93, 103753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenya, L.; Aminudin, E.; Mohd, S.; Yap, L.S. Intelligent risk management in construction projects: Systematic Literature Review. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 72936–72954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mat Ya’acob, I.A.; Mohd Rahim, F.A.; Zainon, N. Risk in Implementing Building Information Modelling (BIM) in Malaysia Construction Industry: A Review. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 65, 03002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górecki, J. Big Data as a Project Risk Management Tool. In Risk Management Treatise for Engineering Practitioners; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 26–49. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, P.C.; Wei, J.; Ting, H.I.; Lo, T.P.; Long, D.; Chang, L.M. Dynamic Analysis of Construction Safety Risk and Visual Tracking of Key Factors based on Behaviour-based Safety and Building Information Modelling. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 23, 4155–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Kiviniemi, A.; Jones, S.W. A review of risk management through BIM and BIM-related technologies. Saf. Sci. 2017, 97, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganbat, T.; Chong, H.; Liao, P.; Wu, Y. A Bibliometric Review on Risk Management and Building Information Modelling for International Construction. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018, 2018, 8351679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, T.; van Meerveld, H.; Vossebeld, N.; Adriaanse, A. Aligning building information model tools and construction management methods. Autom. Constr. 2012, 22, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wu, P.; Wang, X. Risk paths in BIM adoption: Empirical study of China. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2018, 25, 1170–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.; Love, P.E.D.; Mewburn, J.; Stobaus, C.; Ramanayaka, C. Building information modelling in construction: Insights from collaboration and change management perspectives. Prod. Plan. Control 2018, 29, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, M.; Ekholm, A. A BIM-Info delivery protocol. Australas. J. Constr. Econ. Build. 2012, 12, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, S. Building Information Modelling (BIM): Trends, Benefits, Risks, and Challenges for the AEC Industry. Leadersh. Manag. Eng. 2011, 11, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossick, C.S.; Neff, G. Organizational Divisions in BIM-Enabled Commercial Construction. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2010, 136, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku DDES, K.; Taiebat, M. BIM Experiences and Expectations: The Constructors’ Perspective. J. Constr. Educ. Res. 2011, 7, 175–197. [Google Scholar]
- Tomek, A.; Matejka, P. The impact of BIM on risk management as an argument for its implementation in a construction company. Procedia Eng. 2014, 85, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, T.; Petri, I.; Rezgui, Y.; Rana, O. Management of Collaborative BIM Data by Federating Distributed BIM Models. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2017, 31, 04017009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamadu, A.-M.; Mahdjoubi, L.; Booth, C.; Manu, P.; Manu, E. Building information modelling (BIM) capability and delivery success on construction projects. Constr. Innov. 2019, 19, 170–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanda, G.; Amin, M.; Soehari, T.D. Investment, Returns, and Risk of Building Information Modelling (BIM) Implementation in Indonesia’s Construction Project. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2019, 9, 5159–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskil-Leitan, R.; Gurevich, U.; Reychav, I. BIM management measure for an effective green building project. Buildings 2020, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, W.J. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative and Mixed Methods Approaches, 2nd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Khosrowshahi, F.; Arayici, Y. Roadmap for implementation of BIM in the UK construction industry. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2012, 19, 610–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLone, W.H.; McLean, E.R. The DeLone and McLean Model of Information Systems Success: A Ten-Year Update. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2003, 19, 9–30. [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt, H.J. Applied organization change in industry: Structural, technical and human approaches. In New Perspectives in Organizational Research; Cooper, W.W., Leavitt, H.J., Shelly, M.W., Eds.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1964; pp. 55–71. [Google Scholar]
- Merschbrock, C.; Hosseini, M.; Martek, I.; Arashpour, M.; Mignone, G. Collaborative Role of Sociotechnical Components in BIM-Based Construction Networks in Two Hospitals. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 2018, 34, 05018006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnokaly, A.; Dogonyaro, I. Framework to assess connection of risk factors and management strategies in Building Information Modelling. Acad. Eng. 2024, 1, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.; Osanloo, A. Understanding, selecting, and integrating a theoretical framework in dissertation research: Creating the blueprint for your “House”. Adm. Issues J. 2014, 4, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivunja, C. Distinguishing between Theory, Theoretical Framework, and Conceptual Framework: A Systematic Review of Lessons from the Field. Int. J. High. Educ. 2018, 7, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sackey, E.; Tuuli, M.; Dainty, A. Sociotechnical systems approach to BIM implementation in a multidisciplinary construction context. J. Manag. Eng. 2015, 31, A4014005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraee, M.; Hosseini, M.R.; Papadonikolaki, E.; Palliyaguru, R.; Arashpour, M. Collaboration in BIM-based construction networks: A bibliometric-qualitative literature review. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2017, 35, 1288–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, G.; Müller, R. Literature Review Expectations of Project Management Journal®. Proj. Manag. J. 2020, 51, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Succar, B.; Sher, W.; Williams, A. Measuring BIM performance: Five metrics. Archit. Eng. Des. Manag. 2012, 8, 120–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, D.M.I. Research design. In Research in Social Science: Interdisciplinary Perspectives; Social Research Foundation: Kanpur, India, 2016; pp. 68–84. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Feng, Y.; Pienaar, J.; O’Brien, D. Modelling paths of risks associated with BIM implementation in architectural, engineering and construction projects. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2017, 60, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksenova, G.; Kiviniemi, A.; Kocaturk, T.; Lejeune, A. From Finnish AEC knowledge ecosystem to business ecosystem: Lessons learned from the national deployment of BIM. Constr. Manag. Econ. 2019, 37, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, K. NVivo. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2022, 110, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blay, K.B.; Tuuli, M.M.; France-Mensah, J. Managing change in BIM-Level 2 projects: Benefits, challenges, and opportunities. Built Environ. Proj. Asset Manag. 2019, 9, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, A.; Forgues, D.; Staub-French, S. Understanding the impact of BIM on collaboration: A Canadian case study. Build. Res. Inf. 2017, 45, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhong, B.; Wu, S.; Luo, H. Construction risk knowledge management in BIM using ontology and semantic web technology. Saf. Sci. 2016, 87, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imoudu Enegbuma, W.; Godwin Aliagha, U.; Nita Ali, K. Preliminary building information modelling adoption model in Malaysia: A strategic information technology perspective. Constr. Innov. 2014, 14, 408–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyedele, L.O.; Regan, M.; von Meding, J.; Ahmed, A.; Ebohon, O.J.; Elnokaly, A. Reducing waste to landfill in the UK: Identifying impediments and critical solutions. World J. Sci. Technol. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 10, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feist, S.; Ferreira, B.; Leitão, A. Collaborative algorithmic-based building information modelling. Protocols, Flows and Glitches. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference of the Association for Computer-Aided Architectural Design Research in Asia (CAADRIA), Suzhou, China, 5–8 April 2017; pp. 613–623. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, K.-F.; Wu, Z.-H.; Huang, S.-C. Identifying and assessing critical risk factors for BIM projects: Empirical study. Autom. Constr. 2014, 45, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, L.; Manion, L.; Morrison, K. Research Methods in Education; Routledge: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, K.N.; Alhajlah, H.H.; Kassem, M.A. Collaboration and risk in building information modelling (BIM): A systematic literature review. Buildings 2022, 12, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganbat, T.; Chong, H.-Y.; Liao, P.-C.; Lee, C.-Y. A Cross-Systematic Review of Addressing Risks in Building Information Modelling-Enabled International Construction Projects. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2019, 26, 899–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadou, M. An overview of benefits and challenges of building information modelling (BIM) adoption in UK residential projects. Constr. Innov. 2019, 19, 298–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, L.; Wang, Y. The combination of BIM technology with the whole life cycle of green building. World J. Eng. Technol. 2021, 9, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqar, A.; Qureshi, A.H.; Alaloul, W.S. Barriers to building information modelling (BIM) deployment in small construction projects: Malaysian construction industry. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Kiviniemi, A.; Jones, S.; Walsh, J. Risk Information Management for Bridges by Integrating Risk Breakdown Structure into 3D/4D BIM. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 23, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, D.M.; Gáspár, L.; Bencze, Z.; Maya, R.A. The Role of BIM in Managing Risks in Sustainability of Bridge Projects: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, M.J.; Abdul Rahman, A. GIS and BIM integration at data level: A review. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 42, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabejamaat, S.; Ahmadi, H.; Barmayehvar, B. Boosting large-scale construction project risk management: Application of the impact of building information modelling, knowledge management, and sustainable practices for optimal productivity. Energy Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2284–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Song, J. The relation of perceived benefits and organizational supports to user satisfaction with building information model (BIM). Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 68, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yitmen, I.; Almusaed, A.; Alizadehsalehi, S. Facilitating Construction 5.0 for smart, sustainable and resilient buildings: Opportunities and challenges for implementation. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 2024. Available online: https://www.emerald.com/insight/2046-6099.htm (accessed on 20 February 2025). [CrossRef]
- Bensalah, M.; Elouadi, A.; Mharzi, H. Overview: The opportunity of BIM in railway. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 2019, 8, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Techno-Organisational Aspect | Magnitude of Risk Factors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Severity→ | Very Low Risk | Low Risk | Medium Risk | High Risk | Very High Risk |
| Difficult to implement due to fragmented structure of construction industry and also BIM | 4 | 4 | 21 | 40 | 30 |
| Lack of strategies for integration and exchanging information among BIM components | 14 | 6 | 16 | 24 | 39 |
| Lack of alignment between the IT strategy and organizational strategy | 6 | 8 | 23 | 29 | 33 |
| Privacy constraints associated with external storage | 7 | 7 | 14 | 27 | 45 |
| Average (%) | 7.75 | 6.25 | 18.5 | 30 | 36.75 |
| LSTM | Equilibrium state | <<<<<<<< >>>>>>>> | Disequilibrium state | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dogonyaro, I.; Elnokaly, A. Strategies to Mitigate Risks in Building Information Modelling Implementation: A Techno-Organizational Perspective. Intell. Infrastruct. Constr. 2025, 1, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/iic1020005
Dogonyaro I, Elnokaly A. Strategies to Mitigate Risks in Building Information Modelling Implementation: A Techno-Organizational Perspective. Intelligent Infrastructure and Construction. 2025; 1(2):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/iic1020005
Chicago/Turabian StyleDogonyaro, Ibrahim, and Amira Elnokaly. 2025. "Strategies to Mitigate Risks in Building Information Modelling Implementation: A Techno-Organizational Perspective" Intelligent Infrastructure and Construction 1, no. 2: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/iic1020005
APA StyleDogonyaro, I., & Elnokaly, A. (2025). Strategies to Mitigate Risks in Building Information Modelling Implementation: A Techno-Organizational Perspective. Intelligent Infrastructure and Construction, 1(2), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/iic1020005








