Bioparticle Sources, Dispersion, and Influencing Factors in Rural Environmental Air
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Sites
2.2. Determination of Sampling Locations and Methods
2.3. Collected Atmospheric Particles
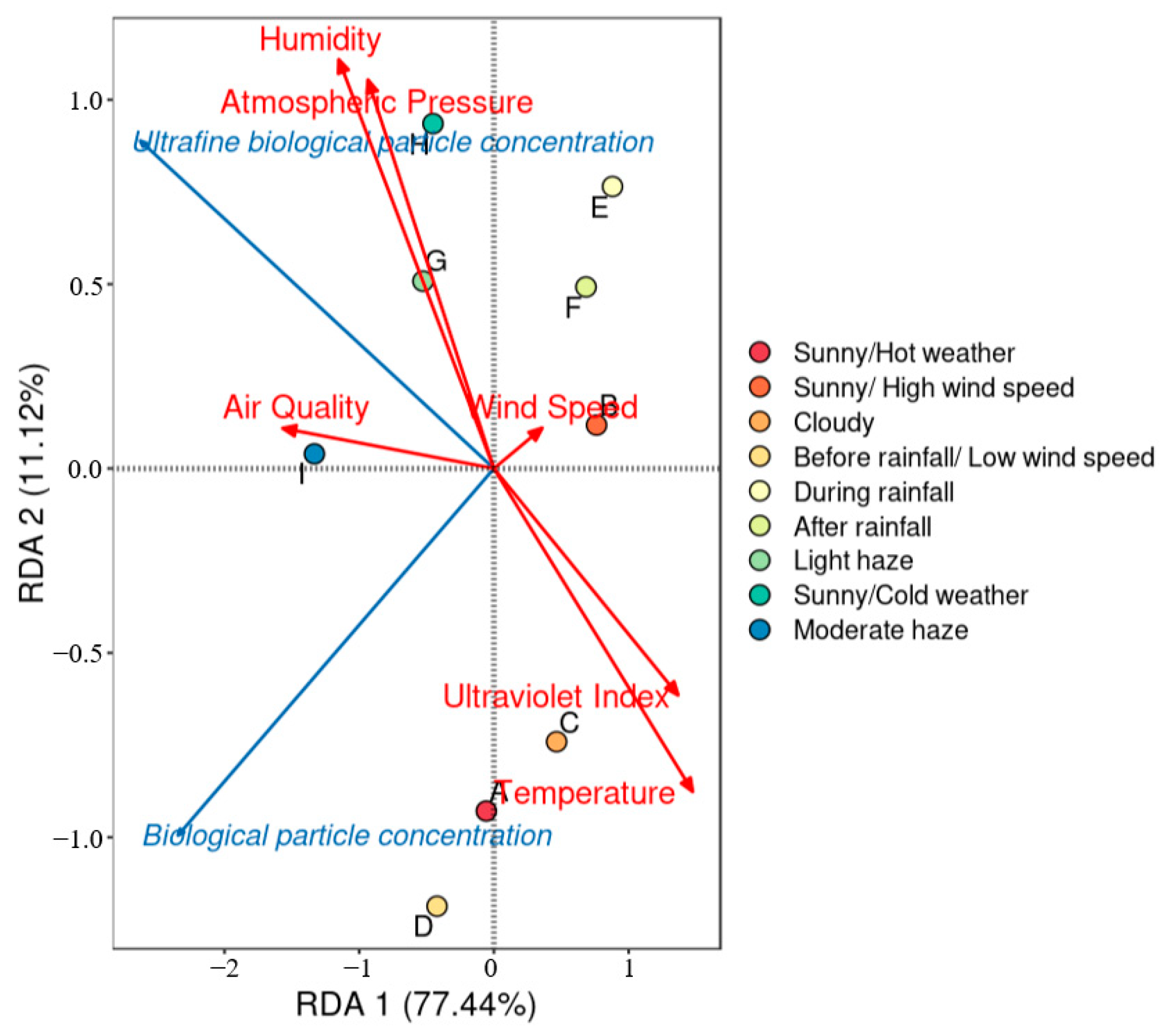
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biological Particle Dispersion Under Different Meteorological Conditions
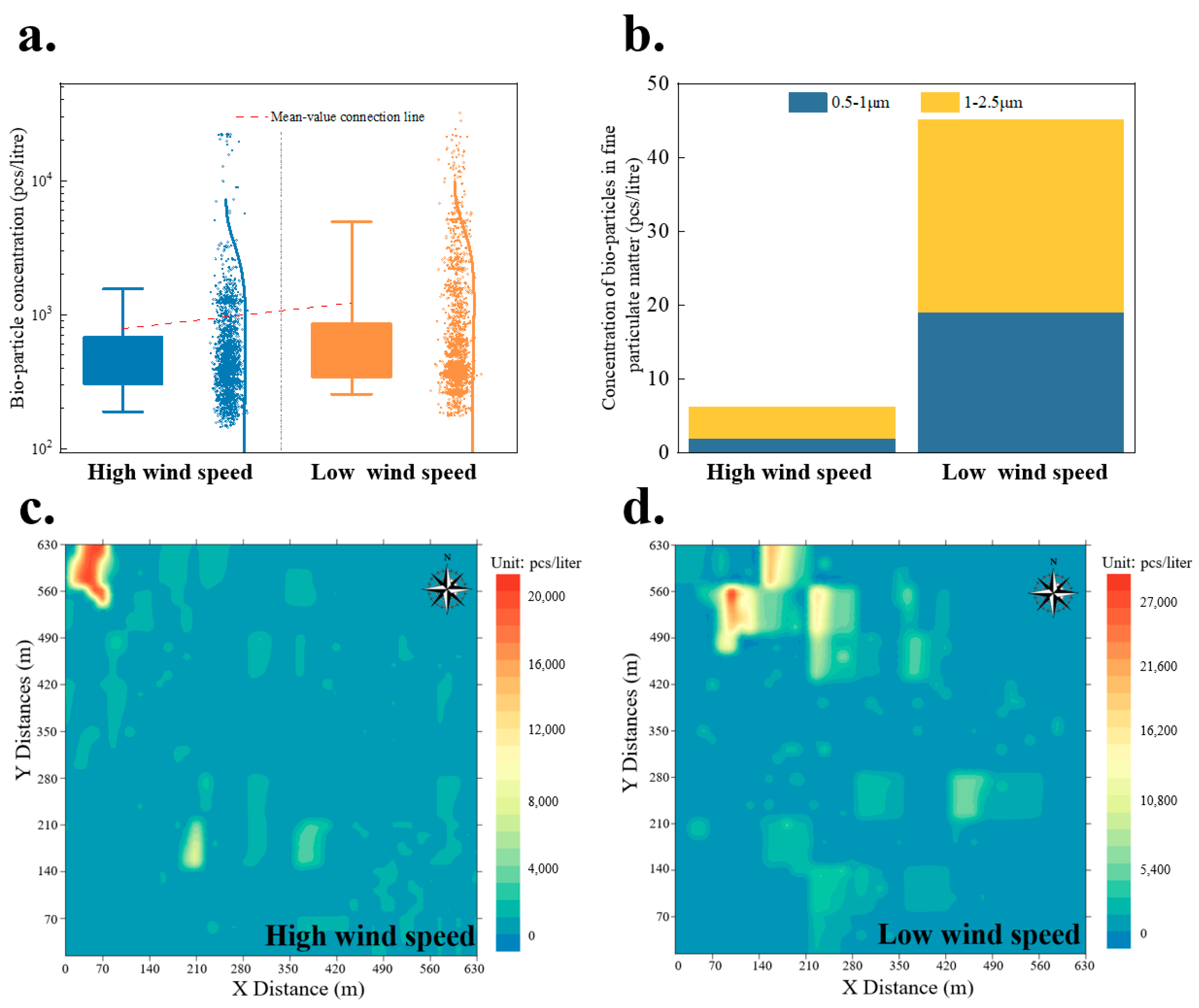
3.1.1. Low-/High-Wind-Speed Weather Conditions
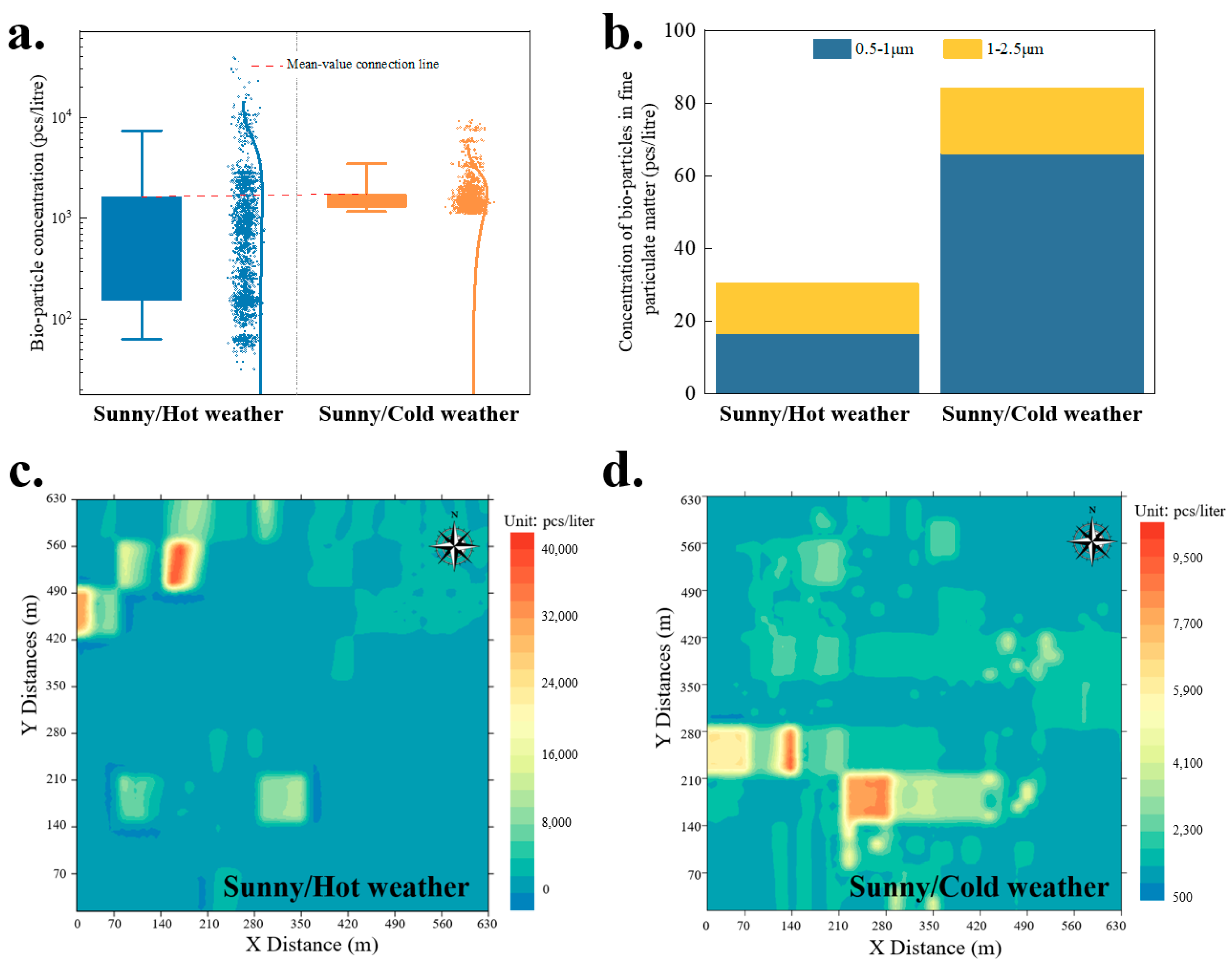
3.1.2. Low-/High-Temperature Weather Conditions
3.1.3. Cloudy Weather Conditions
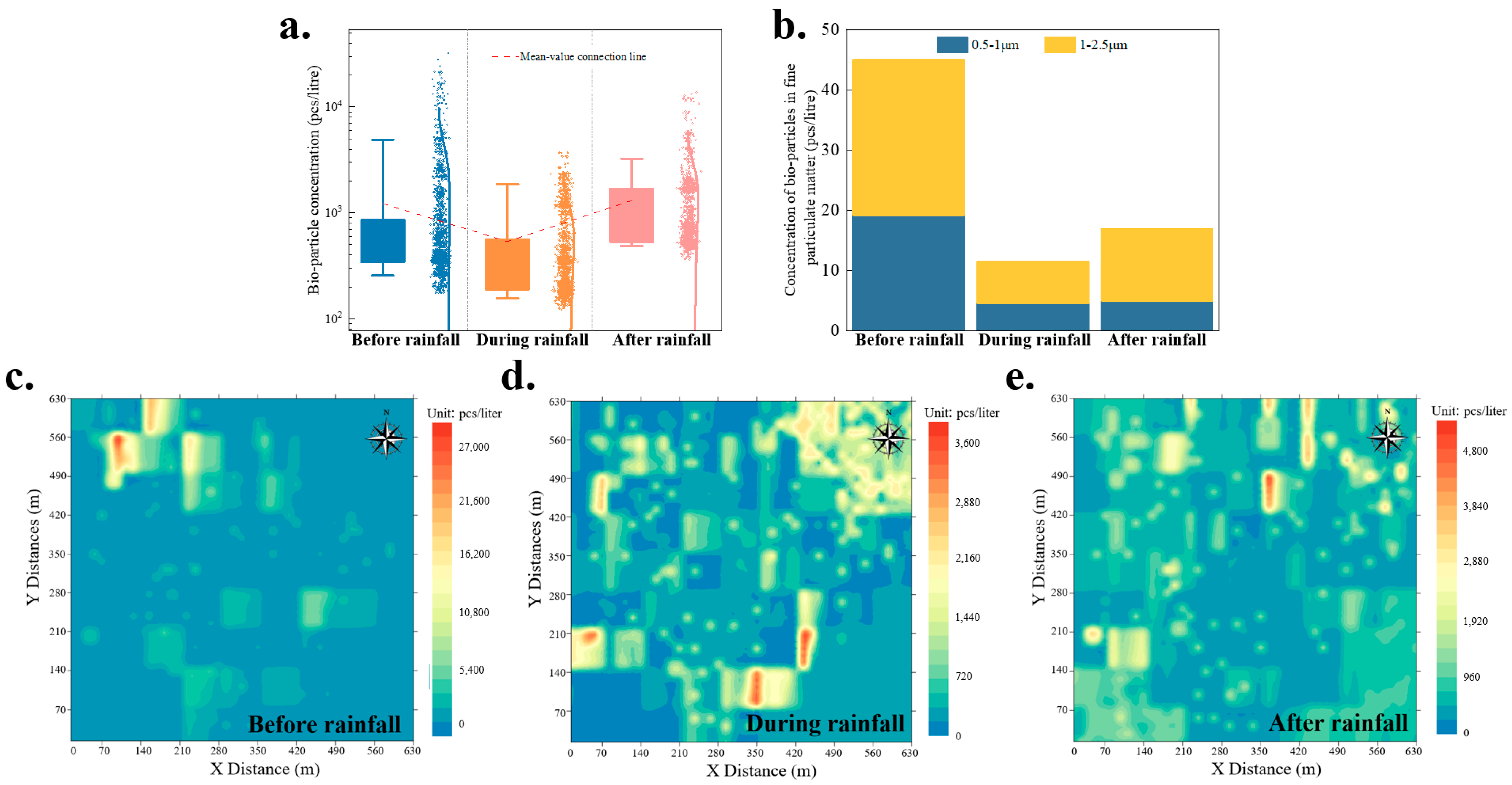
3.1.4. Rainfall Weather Conditions
3.1.5. Hazy Weather Conditions
3.2. Factors Affecting the Diffusion of Biological Particles
3.3. Analysis of Pathogenic Bacteria Escape Pathways Under Different Weather Conditions in Villages
4. Conclusions and Prospects
- Livestock farming areas in rural regions are the principal source of bioparticles, including pathogenic microorganisms. Environmental conditions such as wind speed, temperature, humidity, and precipitation significantly influence the distribution and concentration of these particles.
- Low wind speeds and cloudy or hazy weather contribute to higher concentrations and limited dispersion. Conversely, high wind speeds and rainfall events reduced bioparticle concentrations by enhancing dispersion and scavenging effects.
- Pathogenic bacteria, such as those from the Enterobacteriaceae family, exhibit specific dispersal pathways that are influenced by local environmental factors. Indoor environments in close proximity to livestock farming areas are at a high risk of contamination, posing potential health risks to rural inhabitants.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diamond, S.E.; Prileson, E.G.; Martin, R.A. Adaptation to urban environments. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2022, 51, 100893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Han, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lyu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yan, Y.; Zheng, T. Dispersion characteristics of bioaerosols during treatment of rural solid waste in northwest China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 324, 121338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; An, N.; Gu, G.C.; Yang, E.D.; Yang, H.H.; Li, C.; Yan, K. Research progress on features and characteristics of rural settlements: Literature distribution, key issues, and development trends. Buildings 2023, 13, 2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.Z.; Han, Y.P.; Liu, J.G.; Cao, Y.N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Lyu, J.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Y.X. Distribution characteristics and potential risks of bioaerosols during scattered farming. Iscience 2023, 26, 108378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.J.; Quan, J.W.; Yin, J.H.; Liu, X.W.; Yuan, Z.W.; Ma, L. High-resolution maps of intensive and extensive livestock production in China. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2023, 12, 100104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gržinić, G.; Piotrowicz-Cieślak, A.; Klimkowicz-Pawlas, A.; Górny, R.L.; Ławniczek-Wałczyk, A.; Piechowicz, L.; Olkowska, E.; Potrykus, M.; Tankiewicz, M.; Krupka, M.; et al. Intensive poultry farming: A review of the impact on the environment and human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 160014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conan, A.; Goutard, F.L.; Sorn, S.; Vong, S. Biosecurity measures for backyard poultry in developing countries: A systematic review. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.P.; Xia, J.F.; Gao, J.J.; Xu, L.Z.; Huang, Y.; Yao, L.N.; Tang, W. Measures to combat H7N9 virus infection in China: Live poultry purchasing habits, poultry handling, and living conditions increase the risk of exposure to contaminated environments. Biosci. Trends 2013, 7, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Callaghan, T.; Lueck, J.A.; Trujillo, K.L.; Ferdinand, A.O. Rural and urban differences in COVID-19 prevention behaviors. J. Rural Health 2021, 37, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning-Smith, C. The unique impact of COVID-19 on older adults in rural areas. J. Aging Soc. Policy 2020, 32, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.; Arif, A.A.; Adeyemi, O.; Ghosh, S.; Han, D. Progression of COVID-19 from urban to rural areas in the United States: A spatiotemporal analysis of prevalence rates. J. Rural Health 2020, 36, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Bassey, E.; Bos, B.; Makacha, L.; Varaden, D.; Arku, R.E.; Baumgartner, J.; Brauer, M.; Ezzati, M.; Kelly, F.J.; et al. Comparing human exposure to fine particulate matter in low and high-income countries: A systematic review of studies measuring personal PM2.5 exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otuyo, M.K.; Nadzir, M.S.M.; Latif, M.T.; Din, S.A.M. A review of personal exposure studies in selected Asian countries’ public transport microenvironments: Lessons learned and future directions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 121306–121337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.C.; Li, S.L.; Fan, C.L.; Bai, Z.G.; Yang, K.H. The impact of PM2.5 on asthma emergency department visits: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallarés, S.; Gómez, E.T.; Martínez-Poveda, Á.; Jordán, M.M. Distribution Levels of Particulate Matter Fractions (<2.5 μm, 2.5–10 μm and >10 μm) at Seven Primary Schools in a European Ceramic Cluster. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.A.; Zhang, Z.R.; Huo, Y.; Wang, X.Z.; Wang, Y.F.; Wu, J.H.; Huo, M.X. Particle size matters: Distribution, source, and seasonality characteristics of airborne and pathogenic bacteria in wastewater treatment plants. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, S.; Marshall, J.D.; Shaked, S.; Spadaro, J.V.; Nishioka, Y.; Preiss, P.; McKone, T.E.; Horvath, A.; Jolliet, O. Intake fraction for particulate matter: Recommendations for life cycle impact assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4808–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakhjirgan, P.; Kashani, H.; Kermani, M. Exposure to outdoor particulate matter and risk of respiratory diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 46, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryor, J.T.; Cowley, L.O.; Simonds, S.E. The physiological effects of air pollution: Particulate matter, physiology and disease. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 882569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.A.; Siddiqua, S.A.; Faruk, M.O.; Md Towfiqul Islam, A.R.; Salam, M.A. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the potential threats to respiratory health from microbial Bioaerosol exposures. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 122972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.P.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.W.; Li, P.Y.; Han, C.; Liu, J.X. Composition, dispersion, and health risks of bioaerosols in wastewater treatment plants: A review. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2020, 15, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, V.; Yong, K.K.; Tiong, C.K.; Ng, N.J.S.; Ni, Z. A scoping review of knowledge, awareness, perceptions, attitudes, and risky behaviors of sexually transmitted infections in Southeast Asia. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yang, K.; Yang, T.; Zhang, M.; Li, L. Bioaerosols emission and exposure risk of a wastewater treatment plant with A2O treatment process. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yang, T.; Xu, G.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Characteristics and interactions of bioaerosol microorganisms from wastewater treatment plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yang, T.; Yan, X.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Effect of aeration mode on aerosol characteristics from the same wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefzadeh, A.; Maleki, A.; Athar, S.D.; Darvishi, E.; Ahmadi, M.; Mohammadi, E.; Tang, V.T.; Kalmarzi, R.N.; Kashefi, H. Evaluation of bio-aerosols type, density, and modeling of dispersion in inside and outside of different wards of educational hospital. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 14143–14157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.K.; Zhu, X.J.; Zhang, P.Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Li, J.G. Cost-effective instant air disinfection for building ventilation system by a combination of UV and micro-static electricity. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, R. Size matters: Ultra-small and filterable microorganisms in the environment. Microbes Environ. 2020, 35, ME20025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.S.; Fan, C.L.; Lu, R.; Liu, P.X.; Wang, B.B.; Du, S.L.; Jin, C.; Deng, S.X.; Li, Y.P. Characteristics of ambient bioaerosols during haze episodes in China: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1930–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Després, V.R.; Huffman, J.A.; Burrows, S.M.; Hoose, C.; Safatov, A.S.; Buryak, G.; Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Elbert, W.; Andreae, M.O.; Pöschl, U.; et al. Primary biological aerosol particles in the atmosphere: A review. Tellus B 2012, 64, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, A.; Amo de Paz, G.A.; Rastrojo, A.; García, A.M.; Alcamí, A.; Gutiérrez-Bustillo, A.M.; Moreno, D.A. Monitoring of airborne biological particles in outdoor atmosphere. Part 2: Metagenomics applied to urban environments. Int. Microbiol. 2016, 19, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Overbeek, L.S.; Saikkonen, K. Impact of bacterial-fungal interactions on the colonization of the endosphere. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, J.; Fernandez, V.; Pontrelli, S.; Sauer, U.; Ackermann, M.; Stocker, R. A distinct growth physiology enhances bacterial growth under rapid nutrient fluctuations. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piecková, E. Adverse health effects of indoor moulds. Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 2012, 63, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.D.; Levin, P.A. Metabolism, cell growth and the bacterial cell cycle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Dai, L.H.; Ma, L.X.; Guo, R.T. Enzymatic degradation of plant biomass and synthetic polymers. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2020, 4, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amobonye, A.; Bhagwat, P.; Singh, S.; Pillai, S. Plastic biodegradation: Frontline microbes and their enzymes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, E.B.; Stamm, B.; Chan, H.K.; Maday, Y.; Stace, A.J.; Besley, E. The effect of like-charge attraction on aerosol growth in the atmosphere of titan. Icarus 2017, 291, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, P.A.; Scopel, C.O.; Jensen, E.T.; Depas, M.M.; McLellan, S.L. Detection of genetic markers of fecal indicator bacteria in Lake Michigan and determination of their relationship to Escherichia coli densities using standard microbiological methods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8305–8313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraft, H.; Watterworth, L.A. Enumeration of heterotrophs, fecal coliforms and Escherichia coli in water: Comparison of 3M Petrifilm plates with standard plating procedures. J. Microbiol. Methods 2005, 60, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.Z.; Han, Y.P.; Cao, Y.N.; Wang, Z.X.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Zheng, T.L.; Liu, J.G.; Yang, X.X. Progress in the distribution characteristics and risks of bioaerosols from anthropogenic sources. Microbiol. China 2023, 50, 667–686. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.P.; Yu, X.Z.; Cao, Y.N.; Liu, J.G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.P.; Lyu, C.L.; Li, Y.L.; Jin, X.; Zhang, Y.X.; et al. Transport and risk of airborne pathogenic microorganisms in the process of decentralized sewage discharge and treatment. Water Res. 2024, 256, 121646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghal Asghari, F.B.; Dehghani, M.H.; Dehghanzadeh, R.; Farajzadeh, D.; Yaghmaeian, K.; Mahvi, A.H.; Rajabi, A. Antibiotic resistance and antibiotic-resistance genes of Pseudomonas spp. and Escherichia coli isolated from untreated hospital wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, L.; Navarro-Gonzalez, N.; Jay-Russell, M.T.; Aminabadi, P.; Pires, A.F.A. Risk factors of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in livestock raised on diversified small-scale farms in California. Epidemiol. Infect. 2022, 150, e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Seo, J.; Jee, Y.; Kim, Y.; Sohn, J. Composition Analysis of Airborne Microbiota in Outdoor and Indoor Based on Dust Separated by Micro-sized and Nano-sized. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2023, 23, 210231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample Type | Temperature (°C) | Humidity (%) | Atmospheric Pressure (hpa) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Wind Direction | Ultraviolet Index | Air Quality (μg/m3) | Weather Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bioparticle | 23.0 | 23.0 | 891.3 | 2.7 | west | 3.7 | 89.3 | sunny/hot weather |
| 26.0 | 23.7 | 887.7 | 3.0 | west | 4.7 | 67.0 | Sunny/High wind speed | |
| 23.3 | 30.3 | 889.0 | 2.7 | northeast | 2.7 | 84.7 | cloudy | |
| 22.0 | 48.3 | 1010.1 | 1.7 | east | 2.3 | 53.0 | before rainfall/Low wind speed | |
| 23.0 | 58.7 | 1009.7 | 2.3 | east | 2.0 | 39.0 | during rainfall | |
| 25.7 | 43.0 | 1012.2 | 1.7 | east | 3.7 | 56.3 | after rainfall | |
| −17.0 | 66.0 | 1043.3 | 3.0 | southeast | 1.3 | 117.0 | light haze | |
| −11.0 | 66.7 | 1033.0 | 2.3 | southeast | 1.0 | 98.0 | sunny/cold weather | |
| −10.3 | 71.7 | 1033.0 | 2.0 | southeast | 0.7 | 187.3 | moderate haze | |
| Enterobacteriaceae | 26.4 | 30.2 | 888.6 | 2.7 | northeast | 3.2 | 59.2 | hot weather |
| 25.7 | 43.0 | 1012.2 | 1.7 | east | 3.7 | 56.3 | after rainfall | |
| −15.3 | 66.0 | 1045.3 | 4.0 | southeast | 1.0 | 162.0 | moderate haze |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, X.; Han, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Feng, W. Bioparticle Sources, Dispersion, and Influencing Factors in Rural Environmental Air. Aerobiology 2025, 3, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerobiology3020004
Yu X, Han Y, Cao Y, Liu J, Liu Z, Li Y, Feng W. Bioparticle Sources, Dispersion, and Influencing Factors in Rural Environmental Air. Aerobiology. 2025; 3(2):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerobiology3020004
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Xuezheng, Yunping Han, Yingnan Cao, Jianguo Liu, Zipeng Liu, Yilin Li, and Weiying Feng. 2025. "Bioparticle Sources, Dispersion, and Influencing Factors in Rural Environmental Air" Aerobiology 3, no. 2: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerobiology3020004
APA StyleYu, X., Han, Y., Cao, Y., Liu, J., Liu, Z., Li, Y., & Feng, W. (2025). Bioparticle Sources, Dispersion, and Influencing Factors in Rural Environmental Air. Aerobiology, 3(2), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerobiology3020004







