Differential Expression of AURKA, AURKB, and PLK1 Modulates Clinical Outcomes and Survival in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Characterization of Study Participants
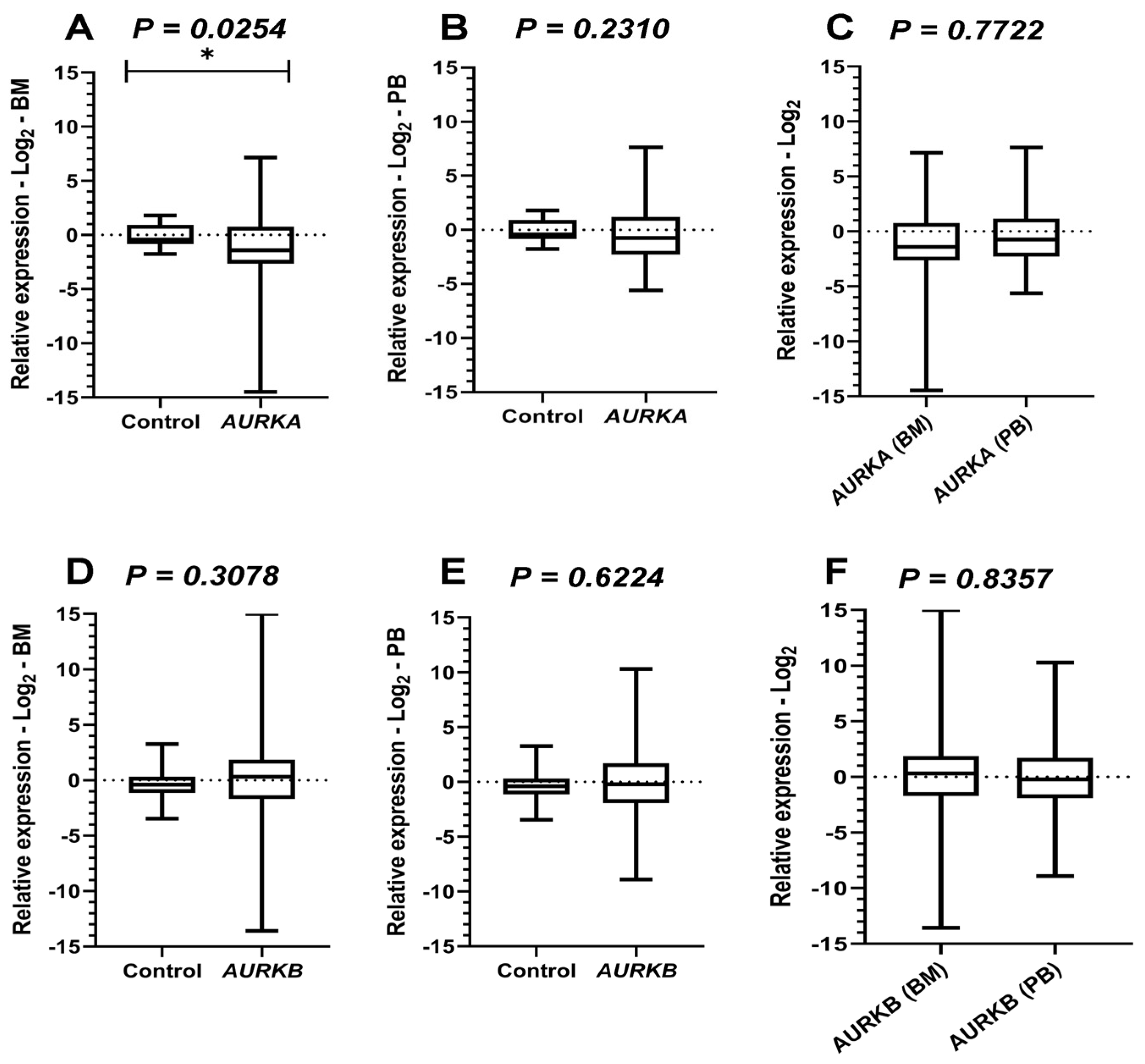
2.2. Expression of Aurora Kinases in Samples from AML Patients
2.3. Expression of PLK1 in Samples from AML Patients and Its Potential Application as a Molecular Marker of Disease Presence
2.4. Paired Comparative Analyses of AURKA, AURKB and PLK1 Expression
2.5. Correlation Analysis Associated with AURKA, AURKB, and PLK1
2.6. Mortality Rates and Survival Analysis of Study Participants
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biological Samples
4.2. Eligibility Criteria
4.3. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
4.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| CML | Chonic myeloid leukemia |
| ALL | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| CLL | Chonic lymphoblastic leukemia |
| AURK | Aurora kinase |
| PLK | Polo-like kinase |
| BORA | BORA aurora kinase A activator |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| WBC | White blood cell |
| NR | No result |
| BM | Bone marrow |
| PB | Peripheral blood |
| Log2 | Base 2 logarithmic scale |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| HSC | Hematopoietic stem cells |
| CXCL12 | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12 |
| IL-7 | Interleukin-7 |
| IL-12 | Interleukin-12 |
| G-CSF | Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| IGF1 | Insulin-like growth factor 1 |
| AIP1 | Aurora-A-interacting protein 1 |
| ELN | European Leukemia Net |
| FOXM1 | Forkhead box M1 |
| E2F | Transcription factor E2F |
| MDS | Myelodysplastic syndrome |
| CoMMpass | Relating Clinical Outcomes in Multiple Myeloma to Personal Assessment of Genetic Profiles |
| RT-qPCR | Real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction |
| RT-PCR | Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction |
| FC | Fold change |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase |
| AKT | AKT serine/threonine kinase |
| mTOR | Mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| P70S6K | p70S6 protein kinase |
| RPL15 | Ribosomal protein L15 |
| P38MAPK | p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| FLT3 | fms related receptor tyrosine kinase 3 |
| RUNX1 | RUNX family transcription factor 1 |
| RUNX1T1 | RUNX1 partner transcriptional co-repressor 1 |
| PML | PML nuclear body scaffold |
| RARA | Retinoic acid receptor alpha |
| NPM1 | Nucleophosmin 1 |
| H3S10 | Histone H3 serine |
| KDM6B | Lysine demethylase 6B |
| MYC | MYC proto-oncogene |
| TRKC | Neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase 3 |
| Twist | Transcriptor fator Twist-1 |
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| mRNA | Messenger RNA |
| PARP | Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase |
References
- Narayanan, D.; Weinberg, O.K. How I Investigate Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2020, 42, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döhner, H.; Wei, A.H.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Craddock, C.; DiNardo, C.D.; Dombret, H.; Ebert, B.L.; Fenaux, P.; Godley, L.A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of AML in Adults: 2022 Recommendations from an International Expert Panel on Behalf of the ELN. Blood 2022, 140, 1345–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shallis, R.M.; Wang, R.; Davidoff, A.; Ma, X.; Zeidan, A.M. Epidemiology of Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Recent Progress and Enduring Challenges. Blood Rev. 2019, 36, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, C.M.; Perl, A.E. Management of Primary Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia in the Era of Targeted Therapies. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.H.; Chen, C.M.; Wang, C.Y.; Hsu, W.W.Y.; Chen, H.M.; Ko, B.S.; Hsiao, F.Y. The Epidemiology, Treatment Patterns, Healthcare Utilizations and Costs of Acute Myeloid Leukaemia (AML) in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, G.; Cai, X.; Liu, Y.; Qian, B.; Li, D. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Acute Myeloid Leukemia, 1990-2021: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Biomark. Res. 2024, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucena-Araujo, A.R.; de Oliveira, F.M.; Leite-Cueva, S.D.; dos Santos, G.A.; Falcao, R.P.; Rego, E.M. High Expression of AURKA and AURKB Is Associated with Unfavorable Cytogenetic Abnormalities and High White Blood Cell Count in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2011, 35, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenson, B.; Crispino, J.D. The Aurora Kinases in Cell Cycle and Leukemia. Oncogene 2015, 34, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asteriti, I.A.; De Mattia, F.; Guarguaglini, G. Cross-Talk between AURKA and Plk1 in Mitotic Entry and Spindle Assembly. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, C.B.; Da Silva, E.L.; Nogueira, B.M.D.; Da Silva, J.B.S.; Filho, M.O.D.M.; Montenegro, R.C.; De Moraes, M.E.A.; Moreira-Nunes, C.A. The Relevance of Aurora Kinase Inhibition in Hematological Malignancies. Cancer Diagn. Progn. 2021, 1, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Heesbeen, R.G.H.P.; Raaijmakers, J.A.; Tanenbaum, M.E.; Halim, V.A.; Lelieveld, D.; Lieftink, C.; Heck, A.J.R.; Egan, D.A.; Medema, R.H. Aurora A, MCAK, and Kif18b Promote Eg5-Independent Spindle Formation. Chromosoma 2017, 126, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joukov, V.; De Nicolo, A. Aurora-PLK1 Cascades as Key Signaling Modules in the Regulation of Mitosis. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaar4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Li, J.; Yan, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, W.; Chu, E.; Wei, N. Emerging Roles of Aurora-A Kinase in Cancer Therapy Resistance. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 2826–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.J.; Shu, L.P.; Zhou, Z.W.; Yang, T.; Duan, W.; Zhang, X.; He, Z.X.; Zhou, S.F. Inhibition of Aurora Kinases Induces Apoptosis and Autophagy via AURKB/P70S6K/RPL15 Axis in Human Leukemia Cells. Cancer Lett. 2016, 382, 215–230, Correction in Cancer Lett. 2025, 27, 218039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.P.; Yang, Y.X.; Liu, Q.L.; Zhou, Z.W.; Pan, S.T.; He, Z.X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, T.; Pan, S.Y.; Duan, W.; et al. The Pan-Inhibitor of Aurora Kinases Danusertib Induces Apoptosis and Autophagy and Suppresses Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2015, 9, 1027–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.L.; Schindler, K. Specialize and Divide (Twice): Functions of Three Aurora Kinase Homologs in Mammalian Oocyte Meiotic Maturation. Trends Genet. 2017, 33, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira-Nunes, C.A.; Mesquita, F.P.; Portilho, A.J.d.S.; Júnior, F.A.R.M.; Maués, J.H.d.S.; Pantoja, L.d.C.; Wanderley, A.V.; Khayat, A.S.; Zuercher, W.J.; Montenegro, R.C.; et al. Targeting Aurora Kinases as a Potential Prognostic and Therapeutical Biomarkers in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla, A.; Cirillo, L.; Thomas, Y.; Gotta, M.; Pintard, L.; Santamaria, A. Mitotic Entry: The Interplay between Cdk1, Plk1 and Bora. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 3177–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, I.; Basheer, N.; Hasan, G.M.; Afzal, M.; Hassan, M.I. Polo-like Kinase 1 as an Emerging Drug Target: Structure, Function and Therapeutic Implications. J. Drug Target. 2021, 29, 168–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalous, J.; Aleshkina, D. Multiple Roles of PLK1 in Mitosis and Meiosis. Cells 2023, 12, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goroshchuk, O.; Kolosenko, I.; Vidarsdottir, L.; Azimi, A.; Palm-Apergi, C. Polo-like Kinases and Acute Leukemia. Oncogene 2019, 38, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Cárcer, G. The Mitotic Cancer Target Polo-Like Kinase 1: Oncogene or Tumor Suppressor? Genes 2019, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renner, A.G.; Dos Santos, C.; Recher, C.; Bailly, C.; Créancier, L.; Kruczynski, A.; Payrastre, B.; Manenti, S. Polo-like Kinase 1 Is Overexpressed in Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Its Inhibition Preferentially Targets the Proliferation of Leukemic Cells. Blood 2009, 114, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.N.; Li, Z.H.; Zhao, H.; Tao, Y.F.; Xu, L.X.; Lu, J.; Cao, L.; Du, X.J.; Sun, L.C.; Zhao, W.L.; et al. Molecular Targeting of the Oncoprotein PLK1 in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia: RO3280, a Novel PLK1 Inhibitor, Induces Apoptosis in Leukemia Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 1266–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimony, S.; Stahl, M.; Stone, R.M. Acute Myeloid Leukemia: 2023 Update on Diagnosis, Risk-Stratification, and Management. Am. J. Hematol. 2023, 98, 502–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabellini, N.; Tomlinson, B.; Cullen, J.; Shanahan, J.; Waite, K.; Montero, A.J.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Hamerschlak, N. Sex Differences in Adults with Acute Myeloid Leukemia and the Impact of Sex on Overall Survival. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 6711–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Li, A.; Zhou, L.; Chu, Q.; Song, Y.; Wu, K.; Wu, K. The Global Burden and Attributable Risk Factor Analysis of Acute Myeloid Leukemia in 195 Countries and Territories from 1990 to 2017: Estimates Based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalidi, H.S.; Medeiros, L.J.; Chang, K.L.; Brynes, R.K.; Slovak, M.L.; Arber, D.A. The Immunophenotype of Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia: High Frequency of Lymphoid Antigen Expression and Comparison of Immunophenotype, French-American-British Classification, and Karyotypic Abnormalities. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1998, 109, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Majeti, R. Biology and Relevance of Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells. Blood 2017, 129, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basharat, M.; Khan, S.A.; Din, N.U.; Ahmed, D. Immunophenotypic Characterisation of Morphologically Diagnosed Cases of Acute Myeloid Leukaemia (AML). Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 35, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haferlach, T.; Schmidts, I. The Power and Potential of Integrated Diagnostics in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 188, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessoa, F.M.C.d.P.; Machado, C.B.; Barreto, I.V.; Sampaio, G.F.; Oliveira, D.d.S.; Ribeiro, R.M.; Lopes, G.S.; de Moraes, M.E.A.; Filho, M.O.d.M.; de Souza, L.E.B.; et al. Association between Immunophenotypic Parameters and Molecular Alterations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, S.; Penrhyn-Lowe, S.; Venkitaraman, A.R. AURORA-A Amplification Overrides the Mitotic Spindle Assembly Checkpoint, Inducing Resistance to Taxol. Cancer Cell 2003, 3, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meraldi, P.; Honda, R.; Nigg, E.A. Aurora-A Overexpression Reveals Tetraploidization as a Major Route to Centrosome Amplification in P53-/- Cells. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, K.; Kudryavtseva, E.; Fomicheva, Y.; Churkina, I.; Lomaia, E.; Girshova, L.; Osipov, Y.; Zaritskey, A. Shift of N-MYC Oncogene Expression in AML Patients Carrying the FLT3-ITD Mutation. Pathophysiology 2023, 30, 296–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Hao, M.; Dong, K.; Shen, J.; Wang, X.; Lin, F.; Liu, L.; Wei, J.; Liang, Y.; Yang, J.; et al. AEG-1 Overexpression Is Essential for Maintenance of Malignant State in Human AML Cells via up-Regulation of Akt1 Mediated by AURKA Activation. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 1438–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Cho, H.; Oh, H.; Kim, J.Y.; Seo, S.B. AURKA Suppresses Leukemic THP-1 Cell Differentiation through Inhibition of the KDM6B Pathway. Mol. Cells 2018, 41, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Hirano, I.; Okinaka, K.; Takemura, T.; Yokota, D.; Ono, T.; Shigeno, K.; Shibata, K.; Fujisawa, S.; Ohnishi, K. The FOXM1 Transcriptional Factor Promotes the Proliferation of Leukemia Cells through Modulation of Cell Cycle Progression in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 2012–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Menon, H.; Jootar, S.; Saikia, T.; Kwak, J.Y.; Sohn, S.K.; Park, J.S.; Jeong, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Radotinib in Chronic Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients with Resistance or Intolerance to BCR-ABL1 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Haematologica 2014, 99, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennis, S.; Conforte, A.; O’Reilly, E.; Takanlu, J.S.; Cichocka, T.; Dhami, S.P.; Nicholson, P.; Krebs, P.; Broin, P.Ó.; Szegezdi, E. Cell-Cell Interactome of the Hematopoietic Niche and Its Changes in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. iScience 2023, 26, 106943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Hao, S.; Liu, Y.; Pang, Y.; Ma, S.; Dong, F.; Xu, J.; Zheng, G.; Li, S.; Yuan, W.; et al. Leukemic Marrow Infiltration Reveals a Novel Role for Egr3 as a Potent Inhibitor of Normal Hematopoietic Stem Cell Proliferation. Blood 2015, 126, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Plum, P.S.; Gockel, I.; Thieme, R. Pan-Cancer Analysis and in Vitro Validation of the Oncogenic and Prognostic Roles of AURKA in Human Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1186101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsby, E.; Walsh, V.; Pepper, C.; Burnett, A.; Mills, K. Effects of the Aurora Kinase Inhibitors AZD1152-HQPA and ZM447439 on Growth Arrest and Polyploidy in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cell Lines and Primary Blasts. Haematologica 2008, 93, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazarlou, F.; Kadkhoda, S.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Emerging Role of Let-7 Family in the Pathogenesis of Hematological Malignancies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 144, 112334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Shen, N.; Wicha, M.S.; Luo, M. The Roles of the Let-7 Family of MicroRNAs in the Regulation of Cancer Stemness. Cells 2021, 10, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacioppo, R.; Rad, D.; Pagani, G.; Gandellini, P.; Lindon, C. Post-Transcriptional Control Drives Aurora Kinase A Expression in Human Cancers. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0310625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacioppo, R.; Akman, H.B.; Tuncer, T.; Erson-Bensan, A.E.; Lindon, C. Differential Translation of MRNA Isoforms Underlies Oncogenic Activation of Cell Cycle Kinase Aurora A. eLife 2023, 12, e87253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, J.A.E.G.; Lima, K.; Coelho-Silva, J.L.; de Melo Alves-Paiva, R.; Moreno, N.C.; Vicari, H.P.; de Souza Santos, F.P.; Hamerschlak, N.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V.; Traina, F.; et al. Reversine Exerts Cytotoxic Effects through Multiple Cell Death Mechanisms in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cell. Oncol. 2020, 43, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Garcia, M.; Wang, S.; Chen, C.W. Therapeutic Target Discovery Using High-Throughput Genetic Screens in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cells 2020, 9, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmakumar, D.; Chandraprabha, V.R.; Gopinath, P.; Vimala Devi, A.R.T.; Anitha, G.R.J.; Sreelatha, M.M.; Padmakumar, A.; Sreedharan, H. A Concise Review on the Molecular Genetics of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2021, 111, 106727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.F.; Luo, S.K.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Xu, D.R.; Wang, L.H.; Yan, M.; Wang, X.R.; Wan, X.B.; Zheng, F.M.; et al. Aurora Kinase Inhibitory VX-680 Increases Bax/Bcl-2 Ratio and Induces Apoptosis in Aurora-A-High Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2008, 111, 2854–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.K.; Noh, E.K.; Jeong, Y.K.; Ju, L.J.; Sung, J.Y.; Yu, H.M.; Cheon, J.; Koh, S.J.; Min, Y.J.; Choi, Y.; et al. Radotinib Inhibits Mitosis Entry in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells via Suppression of Aurora Kinase A Expression. Tumour. Biol. 2019, 41, 1010428319848612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Xu, A.; Huang, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhu, H.; Yang, B.; Shao, X.; He, Q.; Ying, M. The Role of Autophagy in Targeted Therapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Autophagy 2021, 17, 2665–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X. Kinases Involved in Both Autophagy and Mitosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boss, D.S.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H.M. Clinical Experience with Aurora Kinase Inhibitors: A Review. Oncologist 2009, 14, 780–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.L.; Long, Z.J.; Wang, L.X.; Zheng, F.M.; Fang, Z.G.; Yan, M.; Xu, D.F.; Chen, J.J.; Wang, S.W.; Lin, D.J.; et al. Inhibition of MTOR Pathway Sensitizes Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells to Aurora Inhibitors by Suppression of Glycolytic Metabolism. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, M.; Quan, L.; Gui, R.; Liu, J. Alisertib Induces Apoptosis and Autophagy through Targeting the AKT/MTOR/AMPK/P38 Pathway in Leukemic Cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Brandwein, J.M. Targeting Polo-like Kinase 1 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2015, 6, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Yuan, K.; Chen, L. Molecular Biomarkers, Network Biomarkers, and Dynamic Network Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prediction of Rare Diseases. Fundam. Res. 2022, 2, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Münch, C.; Dragoi, D.; Frey, A.V.; Thurig, K.; Lübbert, M.; Wäsch, R.; Bogatyreva, L.; Hauschke, D.; Lassmann, S.; Werner, M.; et al. Therapeutic Polo-like Kinase 1 Inhibition Results in Mitotic Arrest and Subsequent Cell Death of Blasts in the Bone Marrow of AML Patients and Has Similar Effects in Non-Neoplastic Cell Lines. Leuk. Res. 2015, 39, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharow, A.; Raab, M.; Saxena, K.; Sreeramulu, S.; Kudlinzki, D.; Gande, S.; Dötsch, C.; Kurunci-Csacsko, E.; Klaeger, S.; Kuster, B.; et al. Optimized Plk1 PBD Inhibitors Based on Poloxin Induce Mitotic Arrest and Apoptosis in Tumor Cells. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 2570–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, S.; Tauchi, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Sakuta, J.; Ohyashiki, K. Efficacy of the Polo-like Kinase Inhibitor Rigosertib, Alone or in Combination with Abelson Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors, against Break Point Cluster Region-c-Abelson-Positive Leukemia Cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 20231–20240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Bai, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Lu, H. Protein Targeting Chimeric Molecules Specific for Dual Bromodomain 4 (BRD4) and Polo-like Kinase 1 (PLK1) Proteins in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 521, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolosenko, I.; Goroshchuk, O.; Vidarsdottir, L.; Björklund, A.C.; Dowdy, S.F.; Palm-Apergi, C. RNAi Prodrugs Decrease Elevated MRNA Levels of Polo-like Kinase 1 in Ex Vivo Cultured Primary Cells from Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, W.T.W.; Shin, J.S.; Roberts, T.L.; Wang, B.; Lee, C.S. Molecular Interactions of Polo-like Kinase 1 in Human Cancers. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 69, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmena, M.; Wheelock, M.; Funabiki, H.; Earnshaw, W.C. The Chromosomal Passenger Complex (CPC): From Easy Rider to the Godfather of Mitosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 789–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, K.; Chu, Y.; Dou, Z.; Jin, C.; Garcia-Barrio, M.; Liu, X.; Yao, X. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Aurora B-PLK1-MCAK Signaling Axis Orchestrates Kinetochore Bi-Orientation and Faithful Chromosome Segregation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.; Sunkel, C.E.; Conde, C. The Role of Mitotic Kinases and the RZZ Complex in Kinetochore-Microtubule Attachments: Doing the Right Link. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 787294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, D.d.P.; dos Santos, A.W.A.; Paier, C.R.K.; Ribeiro, H.L.; Costa, M.B.; Farias, I.R.; de Oliveira, R.T.G.; França, I.G.d.F.; Cavalcante, G.M.; Magalhães, S.M.M.; et al. Prognostic Importance of Aurora Kinases and Mitotic Spindle Genes Transcript Levels in Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Leuk. Res. 2018, 64, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccio, N.; Manzotti, G.; Mereu, E.; Torricelli, F.; Ronchetti, D.; Cumerlato, M.; Craparotta, I.; Di Rito, L.; Bolis, M.; Traini, V.; et al. Combinatorial Strategies Targeting NEAT1 and AURKA as New Potential Therapeutic Options for Multiple Myeloma. Haematologica 2024, 109, 4040–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, J. An Analysis of AURKB’s Prognostic and Immunological Roles across Various Cancers. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiawei, W.; Xiajun, B.; Tian, S.; Xuzheng, G.; Zhenwang, Z. Comprehensive Analysis of PLKs Expression and Prognosis in Breast Cancer. Cancer Genet. 2022, 268–269, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, J.D.; Solary, E.; Abla, O.; Akkari, Y.; Alaggio, R.; Apperley, J.F.; Bejar, R.; Berti, E.; Busque, L.; Chan, J.K.C.; et al. The 5th Edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1703–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Clinical and Laboratory Parameters | Parameter Stratification | Distribution in Absolute Numbers | Distribution in Relative Numbers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin | <10 g/dL | 61 | 87.1% |
| >10 g/dL | 9 | 12.8% | |
| WBC | ≤10,000/mm3 | 34 | 48.5% |
| <10,000 to <100,000/mm3 | 26 | 37.1% | |
| ≥100,000/mm3 | 10 | 14.2% | |
| Peripheral blood blasts | Yes | 46 | 65.7% |
| No | 24 | 34.2% | |
| Platelets | <150,000/mm3 | 63 | 90% |
| >150,000/mm3 | 7 | 10% | |
| Bone marrow blasts | ≤10% | 5 | 7.1% |
| ≤70% | 18 | 25.7% | |
| >70% | 39 | 55.7% | |
| N.R. | 8 | 11.4% | |
| LDH | ≤400 μL | 18 | 25.7% |
| >400 μL to ≤1000 μL | 33 | 47.1% | |
| >10,000 μL | 0 | 0% | |
| N.R. | 18 | 25.7% |
| Dependent Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | CI | p-Value | HR | CI | p-Value | |
| AURKA (BM) | 0.89 | 0.81–0.97 | 0.007 | 0.81 | 0.66–0.99 | 0.039 |
| AURKA (PB) | 0.92 | 0.82–1.04 | 0.187 | 0.97 | 0.87–1.08 | 0.544 |
| AURKB (BM) | 0.97 | 0.90–1.05 | 0.459 | 1.06 | 0.94–1.19 | 0.345 |
| AURKB(PB) | 0.88 | 0.80–0.98 | 0.018 | 0.87 | 0.77–0.98 | 0.021 |
| PLK1 (BM) | 0.91 | 0.83–1.00 | 0.052 | 1.04 | 0.91–1.19 | 0.559 |
| PLK1 (PB) | 0.96 | 0.90–1.02 | 0.211 | 0.98 | 0.91–1.05 | 0.505 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
da Costa Machado, A.K.; Nogueira, B.M.D.; de Sousa Oliveira, D.; Machado, C.B.; Cunha de Pinho Pessoa, F.M.; Cunha, L.S.; Barreto, I.V.; Farias, I.M.; Ribeiro, R.M.; Moreira, A.P.L.; et al. Differential Expression of AURKA, AURKB, and PLK1 Modulates Clinical Outcomes and Survival in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3040025
da Costa Machado AK, Nogueira BMD, de Sousa Oliveira D, Machado CB, Cunha de Pinho Pessoa FM, Cunha LS, Barreto IV, Farias IM, Ribeiro RM, Moreira APL, et al. Differential Expression of AURKA, AURKB, and PLK1 Modulates Clinical Outcomes and Survival in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Kinases and Phosphatases. 2025; 3(4):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3040025
Chicago/Turabian Styleda Costa Machado, Anna Karolyna, Beatriz Maria Dias Nogueira, Deivide de Sousa Oliveira, Caio Bezerra Machado, Flávia Melo Cunha de Pinho Pessoa, Leidivan Sousa Cunha, Igor Valentim Barreto, Isabelle Magalhães Farias, Rodrigo Monteiro Ribeiro, Ana Paula Lopes Moreira, and et al. 2025. "Differential Expression of AURKA, AURKB, and PLK1 Modulates Clinical Outcomes and Survival in Acute Myeloid Leukemia" Kinases and Phosphatases 3, no. 4: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3040025
APA Styleda Costa Machado, A. K., Nogueira, B. M. D., de Sousa Oliveira, D., Machado, C. B., Cunha de Pinho Pessoa, F. M., Cunha, L. S., Barreto, I. V., Farias, I. M., Ribeiro, R. M., Moreira, A. P. L., Cordeiro de Albuquerque, K. M., Gomes, M. d. P., Silva, F. A. C., Gurgel, L. A., Rodrigues, G. E. A., Vieira, R. P. G., Khayat, A. S., Van Den Berg, A. V. S., de Moraes Filho, M. O., ... Moreira-Nunes, C. A. (2025). Differential Expression of AURKA, AURKB, and PLK1 Modulates Clinical Outcomes and Survival in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Kinases and Phosphatases, 3(4), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3040025








