Abstract
Obesity has become a global epidemic, contributing to various metabolic diseases. Despite existing therapies, the need to investigate new molecular targets to combat obesity-associated pathologies persists. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK-3), a serine/threonine kinase with two paralogs (GSK-3α and GSK-3β), has emerged as a critical player in obesity-associated metabolic pathologies such as type 2 diabetes (T2D), and cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). However, its ubiquitous dynamic expression and complex context-dependent signaling pathways present challenges in understanding its precise role in metabolic perturbations. In the present review, we will highlight the specific role and the proposed mechanisms via which the two GSK-3 paralogs impact obesity-associated pathologies such as T2D, diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM), and cognitive impairment, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). We will also highlight studies delineating the role of GSK-3s using either GSK-3 inhibitors or non-pharmacological compounds to inhibit/taper GSK-3 activity in metabolic diseases. Thus, the primary goal of this review is to highlight recent findings delineating the regulation/dysregulation of GSK-3α/β in tissues such as heart, liver, skeletal muscle, pancreas, brain, and adipose tissue that undergo morphological and metabolic changes with diet-induced obesity which predisposes obese individuals to numerous devastating chronic conditions by GSK-3 overactivity.
1. Introduction
Obesity has reached epidemic proportions worldwide and is associated with an increased incidence of numerous metabolic disorders, including insulin resistance and insulin insufficiency leading to type 2 diabetes (T2D); cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) such as diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM), heart failure (HF), and atherosclerosis; certain types of cancers such as breast, colon, colorectal, ovarian, and pancreatic cancer; and cognitive impairment, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), to list a few [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. Thus, current available therapies to counter the onslaught of metabolic diseases associated with obesity are inadequate. Hence, there is an urgent need to investigate molecules dysregulated in obesity to combat obesity-associated pathologies and their potential as a therapy against metabolic perturbations.
Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3s (GSK-3s), with their central role in organ development and cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and lipid and glucose homeostasis, are ubiquitous in their impact on our well-being. These serine/threonine kinases (GSK-3α/GSK-3β) have been implicated in numerous studies in human and animal models, and are linked to metabolic disorders including T2D, CVDs, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases such as AD (Figure 1) [10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. Identified in 1980, it was shown to regulate glycogen synthase (GS), a rate-limiting glycogen synthesis enzyme [17]. However, it is becoming clear and is now well accepted that GSK-3α and GSK-3β are critical for controlling many other signaling pathways and numerous other cellular processes essential for homeostasis [10,18,19,20,21]
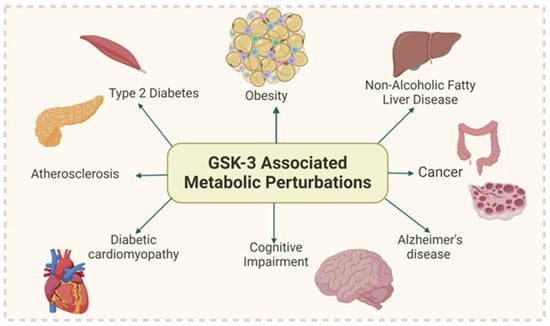
Figure 1.
GSK-3 overactivity is implicated in numerous metabolic disorders (Created with BioRender.com).
GSK-3 has two paralogs, α and β, which are products of two separate genes located on chromosome 19 (encodes GSK-3α) and chromosome 3 (encodes GSK-3β). The two paralogs of GSK-3 share 98% sequence homology in their kinase domain but differ in their N and C terminal [17]. Overall, the two GSK-3s are 85% identical, and hence, it is not surprising that several studies indicate overlapping effects of the two GSK-3s in various pathologies. Interestingly, despite homology, the two paralogs have been demonstrated to elicit distinct phenotypes in numerous pathologies [15,21,22]. So far, the two GSK-3s acting on at least 40 substrates have been shown to mediate their broad range of functions in metabolic pathologies via multiple signaling pathways such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) signaling, Wnt, Hedgehog, Notch, transforming growth factor-beta (TGFβ), nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT), and agonists that act via stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) [23]. These pathways regulate a variety of cellular functions. The cAMP signaling pathway plays a role in metabolism, hormonal response, gene transcription, and neurotransmission. Wnt, Hedgehog, and Notch pathways are involved in neurogenesis, cell motility, apoptosis, cell differentiation, proliferation, and embryonic development. TGFβ signaling regulates cell growth, differentiation, tissue repair, immune responses, and embryonic development [24]. When these pathways become dysregulated, disrupted crosstalk can contribute to disease development. One or more of these pathways are implicated in conditions such as diabetes, CVDs, Alzheimer’s disease, mood disorders and various cancers. Given its wide range of pathway involvement and substrate interactions, GSK-3 also plays a role in regulating these processes. Another exciting feature of this kinase is that it is constitutively active in an unstimulated state. Its dynamic regulation is dependent on (i) its phosphorylation status at Ser 21 (GSK-3α) and Ser 9 (GSK-3β) in response to insulin through a phosphatidylinositol 3 (PI-3) kinase/protein kinase B (PKB, also termed Akt)-dependent manner [17] or other kinases including PKC, protein kinase A (PKA), integrin-linked kinase (ILK), p70S6K, and p90RSK; (ii) cellular localization (cytoplasm, nucleus, or mitochondria) and (iii) its post-translational modifications [3,25,26].
Several studies using either a pharmacological approach or animal models have been conducted to determine the role of the two GSK-3s in obesity-associated metabolic perturbations. However, this has been daunting given its ubiquitous expression, complex signaling, and the two similar paralogs. We do not yet know the precise molecular mechanisms via which GSK-3s causes metabolic perturbations, including obesity-associated glucose intolerance, diabetic cardiomyopathy, cardiac dysfunction, certain types of cancer, and neurodegeneration. Additionally, the role and regulation of specific GSK-3 paralogs (α and β) in peripheral tissues critical for glucose homeostasis with high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity are unclear. Hence, numerous studies using either genetic or pharmacological approaches, including those from our group, are investigating the role and regulation of specific GSK-3 paralogs in tissues such as the heart, liver, skeletal muscle, brain, pancreas, and adipose tissue in HFD-induced metabolic disorders. In the present review, we will focus on studies using either a pharmacological or genetic approach to discern the role of the two GSK-3s in tissues that undergo morphological and metabolic changes with diet-induced obesity which predisposes obese individuals to numerous devastating chronic conditions by GSK-3 overactivity.
2. Regulation of GSK-3s in Heart
Heart metabolic pathophysiology has been linked to increased lipid accumulation from higher saturated fatty acids found in high-fat diets (HFDs), which increase the risk of HF and CVD. The most common form of HF is cardiomyopathy, where obesity induces lipotoxic cardiomyopathy by causing lipid accumulation in cardiomyocytes (CM), leading to cardiac dysfunction. A recent study by Nakamura et al. shows that GSK-3α, not GSK-3β, promotes fatty acid uptake and storage, leading to lipotoxic cardiomyopathy. Increased GSK-3α expression promotes PPARα (Ser280) phosphorylation, which increases transcription of PPARα target genes associated with fatty acid uptake and storage. Specifically, cardiac-specific knockdown of GSK-3α or replacement of PPARα Ser280 with Ala conferred resistance to lipotoxicity in the hearts. Interestingly, PPARα ligands and fibrates inhibited the interaction of GSK-3α with the ligand-binding domain of PPARα, thereby reversing GSK-3α-mediated lipotoxicity [27]. Previous studies have also demonstrated the role of GSK-3s in atherosclerosis via vascular endoplasmic reticulum stress [28]. A recent study indicated the role of macrophage-specific GSK-3α in atherosclerosis in low-density lipoprotein receptor (Ldlr-/-) knockout mice fed an HFD. Macrophage-specific female GSK-3α-deficient mice, not GSK-3β, had reduced plaque volume, increased plaque stability, and reduced plaque inflammation, suggesting a protective role of GSK-3α inhibition against HFD-induced atherosclerosis [29]. Endothelial–mesenchymal transition (EndMT) is a major contributor of osteoprogenitors to vascular calcification, a common feature of atherosclerotic plaques. A recent study by Cai et al. demonstrated that GSK-3β inhibition reduced EndMT and atherosclerotic plaque in Apoe-/- mice fed a Western diet [30]. Abnormal GSK-3 activity with high-fat feeding, in addition to promoting cardiomyopathy and atherosclerosis, is shown to alter cardiac function and exacerbate cardiac remodeling in diet-induced obesity models. In the heart, numerous studies indicate a role of GSK-3s in processes critical for cardiac function such as regulating cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, cardiomyocyte proliferation, apoptosis, aging, mitochondrial biogenesis, and myofilament calcium sensitivity and contraction kinetics [3,21,31,32,33,34,35]. One of the pathways through which GSK-3β alters cardiac function is the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is known to correct vascular defects, promote angiogenesis, and reduce vessel permeability by stabilizing β-catenin. GSK-3β marks β-catenin for proteasomal degradation via phosphorylation, thus inhibiting the protective effects of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in the heart. Pigs induced with metabolic syndrome symptoms and cardiovascular ischemia while on an HFD demonstrated elevated myocardial perfusion ratios and capillary and arteriole density after using the GSK-3β inhibitor. Additionally, they identified several angiogenic, cell survival, and cell differentiation pathways through which GSK-3β inhibition could have an effect, including the β-catenin signaling and Akt/FoxO1 (forkhead box O1) pathways [36]. Wang et al. also demonstrated the protective role of GSK-3β inhibition using an anti-inflammatory/antioxidant protein, metallothionein (MT). Activation (dephosphorylation) of GSK-3β was evidenced in the hearts of wild-type diabetic mice but not cardiac-specific metallothionein-overexpressing transgenic diabetic mice. GSK-3β inhibition mediated defensive changes in cardiac energy metabolism, inflammation, nitrosative damage, and remodeling in diabetes [37] A recent review by Cai et al. summarizes the benefits of MT and zinc in diabetic hearts against cardiac remodeling and dysfunction. Treatment of diabetic mice with zinc showed the preservation of phosphorylation levels of insulin-mediated glucose metabolism-related Akt2 and GSK-3β and even rescued cardiac pathogenesis induced by global deletion of the Akt2 (AKT serine/threonine kinase 2) gene in an MT-dependent manner. These results suggest that zinc protection from DCM is through MT induction and insulin signaling sensitization [38]. Iron death plays a significant role in obesity-related cardiac dysfunction. It has been reported that saturated fatty acids found in HFDs can mediate cardiac myocyte iron death [39]. Using celastrol (Cel), a bioactive compound isolated from the herb Tripterygium wilfordii, which has a protective influence on cardiovascular diseases, the investigators demonstrated that Cel-induced resistance against HFD-induced cardiotoxicity by targeting the Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway [40]. Another group reported similar observations with HFD feeding using Sestrin 2 (SESN2), a potential antioxidant. Obese patients are susceptible to adriamycin (ADR)-induced cardiotoxicity. The results revealed that obesity decreased SESN2 expression in ADR-exposed hearts. Additionally, obesity may predispose patients to ADR-induced cardiotoxicity, which was probably associated with inhibiting protein kinase B (PKB/Akt), GSK-3β phosphorylation, and subsequently blocking nuclear localization of nuclear factor erythroid-2 related factor 2 (NRF2), ultimately resulting in cardiac oxidative damage. However, these destructive cascades and cardiac oxidative damage effects induced by HFD/sodium palmitate combined with ADR were blocked by overexpression of SESN2 [41].
Our group studied GSK-3β’s role in HFD-induced cardiac dysfunction using Cre-loxP genetic recombination in mouse cardiomyocytes, which shows contrasting phenotypes depending on whether the deletion occurs before or after establishing chronic obesity. On the control diet, cardiomyocyte (CM)-specific GSK-3β-knockout (CM-GSK-3β-KO) mice exhibited no alteration in cardiac function compared with the control mice. Interestingly, CM-GSK-3α compensated for the loss of CM-GSK-3β, as evidenced by significantly reduced GSK-3αs21 phosphorylation (activation), resulting in a preserved canonical Wnt/β-catenin ubiquitination pathway and cardiac function. However, this protective compensatory mechanism was lost with HFD, leading to excessive accumulation of β-catenin in HFD-fed CM-GSK-3β-KO hearts, resulting in adverse ventricular remodeling and cardiac dysfunction. These results suggest that cardiac GSK-3β is crucial to protect against obesity-induced adverse ventricular remodeling and cardiac dysfunction [42]. Compared to the developing obesity model, deleting CM-GSK-3β in obese animals did not adversely affect cardiac function. Significantly, deleting GSK-3β in CMs improved glucose clearance in obese CM-GSK-3β KO animals compared to the controls [43]. GSK-3β’s role in the heart is complex. Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in patients with T2D, and many therapeutic strategies to mitigate cardiac dysfunction are inefficient in T2D due to their compromised function in the presence of other molecules such as GSK-3β. In a recent study, Fengxiang et al. investigated the role of GSK-3β/mitsugumin 53 (MG53) regulation in diabetic hearts, which are susceptible to ischemia. As an integral component of cell membrane repair machinery, MG53 is important for cardioprotection induced by ischemia preconditioning and postconditioning. However, it also impairs insulin signaling via its E3 ligase activity-mediated ubiquitination-dependent degradation of IR (insulin receptor) and IRS1 (insulin receptor substrate 1) and its myokine function-induced allosteric blockage of IR. GSK-3β mediates MG53S255 phosphorylation and E3 ligase activity. To minimize the harmful effects of activated MG53 S255, they generated an MG53-S255A mutant and markedly reduced ischemia-reperfusion-induced myocardial acute damage and subsequent aberrant remodeling, thus separating its detrimental metabolic effects from beneficial actions [44]. While the above studies are only a snapshot of GSK-3’s role in HFD-induced cardiac pathologies, a recent review by Umbarkar et al. [21] highlights the specific role of the two GSK-3s in obesity-associated cardiometabolic pathologies.
These studies indicate a distinct role of the two GSK-3 paralogs in cardiometabolic pathologies. Hence, there is an urgent need to revisit ongoing potential therapeutic approaches when using GSK-3 inhibitors as a possible therapy for cardiometabolic perturbations induced by obesity.
3. Regulation of GSK-3 in Liver
Germline deletion of GSK-3α displays enhanced glucose and insulin sensitivity and reduced fat mass. Fasted and glucose-stimulated hepatic glycogen content was enhanced in GSK-3α KO mice, whereas muscle glycogen was unaltered. Insulin-stimulated PKB/Akt and GSK-3β phosphorylation were higher in GSK-3α KO livers than wild-type littermates and IRS-1 expression was markedly increased [11]. These results suggested a role of liver-GSK-3α in glucose homeostasis. Surprisingly, the investigators did not see any differences in glucose tolerance or insulin sensitivity in liver-specific GSK-3α KO mice compared to wild-type littermates [45]. Additionally, liver-specific GSK-3β inhibition did not affect glucose homeostasis in normal physiology. Liver-specific GSK-3β KO mice are glucose- and insulin-tolerant and display “normal” metabolic characteristics and insulin signaling [19], suggesting a role of other tissues in the phenotype observed in GSK-3α KO mice. While liver-specific GSK-3α/β KO models do not indicate a role of liver GSK-3s in normal physiology (chow diet), studies indicate a protective role of liver GSK-3 inhibition in obesity-associated liver metabolic pathologies such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). NAFLD is the most common cause of chronic liver disease in Western countries and is predicted to become also the most frequent indication for liver transplantation by 2030. Over the last decade, the clinical burden of NAFLD is not only confined to liver-related morbidity and mortality but there is now growing evidence that NAFLD is a multisystem disease affecting extra-hepatic organs and regulatory pathways. For example, NAFLD increases the risk of T2D, CVD, cardiac diseases, and chronic kidney disease (CKD) [46]. Hence, a search for compounds with low toxicity and high efficacy, which includes some natural compounds, has been ongoing as a potential therapy for numerous chronic liver conditions, including NAFLD. In a recent study, bavachin, a flavonoid, suppressed palmitic acid/oleic acid or high glucose/high insulin-induced increases in the expression of fatty acid synthesis-related genes and the number and size of lipid droplets. Furthermore, bavachin treatment markedly elevated the phosphorylation levels of AKT and GSK-3β, improving the insulin signaling activity in the cells [47]. Another study investigated the anti-diabetic effects of pro-biotics, Lactobacillus acidophilus KLDS1.1003 and KLDS1.0901. Oral administration of L. acidophilus KLDS1.1003 and KLDS1.0901 for six weeks significantly improved the epithelial barrier function, which in turn lowered pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-8, TNF-α, and IL-1β in liver and colon tissue, and prevented liver and colon tissue injuries to some extent. Additionally, L. acidophilus treatment regulated the expression of genes related to glucose and lipid metabolism. The two tested strains down-regulated the expression of GSK-3β, fatty acid synthase, and up-regulated the expression of PKB/Akt [48]. Wang et al. demonstrated a protective role of GSK-3 down-regulation in T2D using a polysaccharide galactoxyloglucan (GXG) from an edible medicinal plant. GXG-mediated up-regulation of hepatic IRS1-PI3K-Akt phosphorylation followed by the down-regulation of FoxO1/GSK-3β phosphorylation contributed to the enhanced glycogen synthesis and decreased gluconeogenesis by GXG, suggesting that the response of insulin-mediated IRS1-PI3K-Akt-FoxO1/GSK-3β signaling to GXG might be the required mechanism for the GXG-ameliorated development of T2D [49]. A recent study by Fan et al. indicated a role of GSK-3β in glucocorticoid (GC)-induced NAFLD [50], especially in light of evidence that points to a relation between increased GC exposure and weight gain [51]. Another recent study tested the efficacy of mung bean sprouts in improving the infiltration of inflammatory cytokines, insulin sensitivity, glucose transport, and oxidative stress in a high-fat diet/streptozotocin (HFD/STZ) mouse model. The results from the study indicate an upregulated Glucose Transporter Type 4 (GLUT4) transporter andNRF2, a transcription factor that regulates the cellular defense against toxic and oxidative insults through the expression of genes involved in oxidative stress response and drug detoxification [52] and down-regulated GSK-3β via activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, promoting the production of antioxidant enzymes to reduce oxidative stress [53]. In recent years, numerous studies have investigated the role of vitamins in glucose homeostasis. Kuang et al. investigated the role of vitamin A (VA) in the development of metabolic abnormalities associated with the intake of HFD in Sprague-Dawley rats. VA deficiency attenuated HFD-induced obesity, and VA status altered the expression levels of proteins required for glucose metabolism and insulin signaling, concluding that VA status contributes to regulating hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism in an HFD setting and may regulate hepatic carbohydrate metabolism. VA-deficient HFD rats had higher protein levels of GSK-3α and lower levels of GSK-3β, but not glycogen synthase, than VA-sufficient HFD rats. VA-deficient HFD rats had higher hepatic levels of IRS-1, insulin receptor β-subunit, mitogen-activated protein kinase proteins, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α mRNA, and lower levels of IRS-2 protein than VAS-sufficient HFD rats [54].
Thus, these recent studies using either a flavonoid, pro-biotic, an antioxidant, or vitamin indicate a protective role of GSK-3 inhibition in maintaining liver homeostasis with HFD-induced obesity.
4. Regulation of GSK-3 in Skeletal Muscle
Numerous studies have indicated the role of GSK-3s in insulin-responsive peripheral tissue, such as skeletal muscle (SM), with total GSK-3 activity elevated in T2D human skeletal muscle [55]. GSK-3 inhibition in the SM of insulin-resistant Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) rats enhanced insulin action on glucose transport, oral glucose tolerance, whole-body insulin sensitivity, and IRS-1-dependent insulin signaling [12,56]. Importantly, tissue and paralog-specific experimentation revealed skeletal muscle-specific regulation of GSK-3β on a control diet. Skeletal muscle-specific GSK-3β KO mice display improved glucose tolerance coupled with enhanced insulin-stimulated glycogen synthase regulation and glycogen deposition [19]. On the other hand, over-expression of skeletal GSK-3β in male mice resulted in impaired glucose tolerance despite raised insulin levels, consistent with the possibility that elevated levels of skeletal GSK-3 in T2D are partly responsible for insulin resistance [57]. In addition, in human non-diabetic skeletal muscle, siRNA against GSK-3β (60–70% reduction in GSK-3β expression) increased glycogen synthase activity in the absence of insulin and increased insulin action [58]. In contrast, skeletal muscle-specific GSK-3α KO mice displayed no differences in glucose tolerance or insulin sensitivity [45].
Interestingly, natural compounds used in several studies demonstrate a shielding effect against insulin resistance via skeletal GSK-3 modulation. Baicalin, a natural bioactive compound, attenuates insulin resistance and skeletal muscle ectopic fat storage by modulating the skeletal muscle AMPK pathway and Akt/GSK-3β pathway [59]. Interestingly, testosterone attenuated insulin resistance in HFD-mediated T2D. Importantly, GSK-3β gene expression was reduced in the skeletal muscle of HFD-fed mice [60].
GSK-3β is known to modulate myogenic differentiation and adult muscle growth negatively. Using a pharmacological and genetic approach, Zhenyu et al. demonstrated that GSK-3β inhibition augmented myotube formation and increased levels of muscle regulatory factors and muscle-specific protein expression [61]. Thus, these studies indicate GSK-3β as the dominant GSK-3 isoform in skeletal muscle.
Abnormal mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in skeletal muscle is a sapping feature of chronic pathologies, including T2D. Data from non-muscle tissue suggests that GSK-3β represses mitochondrial biogenesis and inhibits PPAR-γ coactivator 1 (PGC-1), a master regulator of cellular oxidative metabolism. Hence, using skeletal muscle-specific GSK-3β KO mice, Theeuwes et al. investigated the role of GSK-3β in skeletal oxidative metabolism. Inactivation of GSK-3β up-regulates skeletal muscle mitochondrial metabolism and increases the expression levels of PGC-1 signaling constituents. Additionally, GSK-3β inhibition protects against inactivity-induced reductions in muscle metabolic gene expression [62]. Another proposed mechanism for the dysregulation of glucose homeostasis in T2D is HFD-induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Using a mouse model of high-fat-induced obesity and insulin resistance, Quin et al. investigated the role of the ketogenic diet in ameliorating skeletal muscle insulin resistance and the underlying mechanism associated with ER stress. A ketogenic diet ameliorated HFD-induced insulin resistance in skeletal muscle, partially mediated by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress. The insulin sensitization effect is associated with up-regulation of the Akt/GSK3β pathway and the increase in the number of Glut4 proteins on the cell membrane, suggesting a role of skeletal GSK-β in HFD-induced ER stress-associated insulin resistance [63].
Thus, important roles of skeletal GSK-3s in processes perturbed with obesity include glucose transport, insulin sensitivity, myogenesis, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and oxidative metabolism.
5. Regulation of GSK-3 in Pancreas
T2D is a complex disease with concurrent systemic insulin resistance, β-cell dysfunction, and insufficient functional β-cell mass. Pancreatic activity and GSK-3’s role in T2D are interconnected when understanding glucose tolerance and insulin effectiveness. Pancreatic β-cells secrete insulin, and in normal physiology, this secreted peptide hormone lowers blood glucose levels by binding to its receptors in insulin-sensitive peripheral tissues. When insulin resistance becomes chronic, partial β-cell mass reduction in the pancreas occurs, which is a hallmark sign in T2D patients. Using isolated, human adult pancreatic islets, Stein et al. demonstrated that GSK-3 inhibition enhanced pancreatic β-cell proliferation by reducing p27 expression, which is an important cell cycle regulatory protein to halt cell division, thus suggesting a role for GSK-3β in β-cell proliferation [64]. Previous research by Liu et al. has demonstrated that a combination of GSK-3 inhibition and nutrient activation of mTOR contributes to enhanced DNA synthesis, cell cycle progression, and proliferation of human β-cells, suggesting that identification of therapeutic agents that appropriately regulate GSK-3 and mTOR signaling may provide a feasible and available approach to enhance human islet growth and proliferation [65]. Additionally, GSK-3β deletion in pancreatic β-cells increased β-cell mass, leading to higher insulin levels and improved glucose tolerance even when fed an HFD. The increased cell mass was accompanied by increased proliferation and reduced apoptosis. Molecular mechanisms for this phenotype include increased levels of IRS1 and IRS2 proteins and phospho-AKT, suggesting signaling through the insulin receptor/PI3K/Akt pathways and increased islet PDX1 (pancreatic transcription factor critical for pancreas formation and β-cell function) [10]. Importantly, GSK3-dependent mechanisms modulate Ser61 and/or Ser66 phosphorylation of IPF1/PDX1. Phosphorylation of those serine residues seems to affect IPF1/PDX1 protein stability critically [66]. Inhibition of the enzyme protects β-cells against cell death due to high glucose and palmitic acid concentrations, with evidence of β-cell replication. Mussmann et al. treated isolated rat islets with structurally diverse small molecule GSK3 inhibitors. GSK-3β inhibition increased β-cell replication by 2–3-fold relative to the control, suggesting that GSK3 is a regulator of β-cell replication and survival and that specific inhibitors of GSK3 may have practical applications in β-cell regenerative therapies [67]. Moreover, the ability of β-cells to secrete insulin in response to glucose was restored almost completely by pharmacological inhibition of GSK3, suggesting the potential of GSK-3 as a therapy for T2D [68].
Activated macrophages (M1) are elevated in pancreatic islets, and the resulting inflammatory response significantly contributes to β-cell failure during obesity and T2D. Quian et al. investigated the mechanisms that compromise glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from pancreatic islets with HFD. Their results indicate a crosstalk between activated macrophages in obesity and islet proteins involved in insulin secretion. Specifically, obese islets of HFD mice exhibit impaired insulin secretion via the impaired SIRT2-mediated Akt/GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway. Specifically, SIRT2 inactivation in HFD-fed obese islets decreased Akt activation, leading to β-catenin (essential for insulin secretion) inhibition via GSK-3β activation [69]. Chronic HF feeding containing saturated fatty acids such as palmitic acid (PA) is associated with β-cell failure and compromised glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Using PA in cultured β-cells and islets, Aggarwal et al. demonstrated that chronic exposure to lipids leads to reduced viability and inhibition of cell cycle progression concurrent with the downregulation of a pro-growth/survival kinase Akt, independent of glucose. PA’s Akt down-regulation correlates with the induction of mTOR/S6K activity. Inhibiting mTOR activity with rapamycin-induced Raptor and restoring Akt activity allow β-cells to gain the proliferation capacity lost after HFD exposure [70].
One of the primary causes for β-cell mass reduction in T2D is β-cell apoptosis [71]. In a recent study, Li et al. elucidated the mechanism underlying HFD-induced β-cell apoptosis via Mcl-1 (an anti-apoptotic oncoprotein) regulation. PA with lipotoxic dose activates AMPK, inhibiting ERK-stimulated Mcl-1Thr163 phosphorylation. Meanwhile, AMPK blocked Akt activity to release Akt inhibition on GSK-3β, followed by GSK-3β-initiated Mcl-1Ser159 phosphorylation. Also, AMPK inhibited the activity of mTORC1, resulting in a lower level of Mcl-1. Thus, dual modulation of mTORC1 activity and Mcl-1 expression led to β-cell apoptosis and impaired insulin secretion [72].
These studies highlight the harmful role of GSK-3β in pancreatic islets, organs vital for secreting hormones involved in glucose homeostasis via regulating proteins critical for β-cell survival and proliferation.
6. Regulation of GSK-3 in Brain
While the role of GSK-3 in all aspects of brain function is well accepted, new studies implicate GSK-3s in obesity-associated cognitive impairment.
GSK-3 plays a pivotal role in regulating various cellular processes implicated in the onset of several brain disorders, including neuronal death and neurodegenerative conditions [73]. Studies consistently highlight GSK-3β as the predominant isoform within the brain [74]. One of the first studies to demonstrate the role of GSK-3β in high-fat diet-induced obesity was by Benzler et al. Using leptin-deficient Lepob/ob mice, they showed that intracerebroventricular injection of a GSK-3β inhibitor acutely improves glucose tolerance in these mice. The beneficial effect of the GSK-3β inhibitor was dependent on hypothalamic signaling via PI3K, a critical intracellular mediator of both leptin and insulin action. Conversely, neuron-specific overexpression of GSK-3β in the mediobasal hypothalamus exacerbated hyperphagia, obesity, and impairment of glucose tolerance induced by an HFD while having little effect in controls fed standard chow [75]. GSK-3β’s impact on brain disorders is diverse. It is involved in (a) modulating the Wnt pathway, whereby it phosphorylates β-catenin, hampering its ability to activate transcription factors crucial for neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity, and neuronal function [76]; (b) driving the hyperphosphorylation of Tau protein and the formation of neurofibrillary tangles (NFT), processes associated with memory decline [75]; (c) promoting the accumulation of Aβ (amyloid-β), a hallmark feature of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias [75]; and (d) acting as a critical mediator of inflammation and apoptosis, thus contributing to neuronal loss in neurodegeneration [77]. Notably, a previous study demonstrated Tau hyperphosphorylation in the hippocampus of transgenic Tet/GSK-3β mice, leading to cognitive impairment even with no filament formation [78]. Additionally, investigations into down-regulating transgene expression through tetracycline administration to Tet/GSK-3β mice revealed that eliminating this transgene mitigates neuronal apoptosis and enhances brain function [79]. Tau (a microtubule-associated protein) hyperphosphorylation and aggregation are widely considered pathological events in plentiful neurodegenerative diseases, including AD, frontotemporal dementia, and progressive supranuclear palsy [80,81]; accumulation of hyperphosphorylation tau is involved in synaptic neurotoxicity, neurodegeneration, and cognitive impairments [80,82,83]. In a recent study, 9-month-old male C57BL/6 mice fed an HFD for 10 months exhibited a decline in mental function. Mechanistically, this decline was attributed to Tau hyperphosphorylation in the hippocampus and cortex, along with an activation of GSK-3β [80]. Lithium, a GSK-3 inhibitor, is commonly used to treat patients with bipolar disorder. In a recent study, HFD feeding with lithium-supplemented drinking water for 12 weeks reduced prefrontal cortex GSK3 activity and improved insulin sensitivity [84]. Intracellular Fibroblast growth factor 11(Fgf 11) is one of the key players in regulating energy balance. Lentiviral injection of Fgf11 shRNA into the arcuate nucleus of the mouse hypothalamus decreased weight gain and fat mass, increased brown adipose tissue thermogenesis, and improved glucose and insulin intolerances under high-fat diet conditions. Fgf11 was expressed in the neuropeptide Y (NPY)-expressing neurons, and Fgf11 knockdown considerably decreased Npy expression and projection. Mechanistically, FGF11 regulated Npy gene expression through the GSK-3/cAMP response element-binding protein pathway [85].
7. Regulation of GSK-3 in Adipose Tissue
Obesity is associated with excessive adipose accumulation that can lead to worsening pathologies. Glucose intolerance and insulin resistance from obesity can lead to T2D, but how adipose GSK-3 is involved in these conditions is still being considered. Mice fed an HFD exhibit increased GSK-3 activity in adipose tissue and a rapid rise in plasma blood glucose levels, indicating that excessive adipose accumulation can lead to glucose intolerance and insulin resistance [14]. Weight loss, on the other hand, is demonstrated to reduce both GSK-3 isoform expressions in adipose tissue [86]. Current understanding in lipid accumulation can be seen with mice exhibiting hypercortisolism from excess glucocorticoids and GSK-3 levels. Elevated adipose GSK-3β and hexose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase expression contributed to 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1-mediated hypercortisolism associated with visceral adiposity [87].
Findings from a study revealed that GSK-3 induces adipogenesis by enhancing the expression and function of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 and secreted frizzled-related proteins. Inhibition of GSK-3 has been shown to halt the differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes, thereby impeding adipogenesis. GSK-3 also contributes to adipogenesis via its involvement in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, triggering inflammatory responses in adipose tissues and promoting inflammation [88]. Adipose-based uncoupling protein 1 (UCP-1) thermogenesis has shown promise in the fight against obesity. To investigate the GSK-3 regulation of UCP-1, Geromella et al. looked at the expression of UCP-1 in differentiating 3T3-L1 cells treated with GSK-3 inhibitor lithium chloride (LiCl). They saw a significant increase in inhibitory serine9 phosphorylation of GSK-3β with LiCl treatment associated with an increase in UCP1 and proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha content, supporting the role of GSK3 in negatively regulating UCP1 expression in adipocytes. In adipose, LiCl treatment inhibited GSK3 in inguinal white adipose tissue (iWAT) but not in brown adipose tissue under chow-fed conditions, which led to an increase in UCP1 in iWAT and a beiging-like effect with a multilocular phenotype. However, they did not see the beiging-like effect and increase in UCP1 in mice fed an HFD, as LiCl could not overcome the ensuing overactivation of GSK3 [89]. These findings agree with our findings in GSK-3β heterozygous mice (unpublished data), where we saw a protective effect (improved glucose clearance) of GSK-3β inhibition with acute obesity induced by HF feeding (60% kcal from fat for 4 weeks). However, this protective effect was lost with chronic HFD feeding (16 weeks). A recent study by Zhu et al. delineated the mechanism via which HFD induces insulin resistance. Proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin1-β (IL-1β) secreted from adipocytes with chronic HF feeding lead to peripheral insulin resistance in insulin-sensitive tissue. Mechanistically, palmitic acid, the primary saturated fatty acid in the HF diet, inactivated AMPK and led to decreased GSK-3β phosphorylation, at least partially through reducing Akt activity, which ultimately blocked the antioxidant pathway. In contrast, Docosahexaenoic acid, the most abundant n-3 PUFA in fat-1 adipose tissue, reversed this process by inducing Akt phosphorylation [90]. Furthermore, mice fed an HFD and given a GSK-3β inhibitor had higher glucose infusion rates, glycogen synthase activity ratios and net glycogen synthesis, higher plasma glucose disappearance, improved peripheral insulin sensitivity, and lower endogenous glucose production than HFD only [91].
8. Systemic Regulation of GSK-3
To investigate the specific role of GSK-3s in HFD-induced metabolic perturbations, we created a novel global conditional GSK-3-KO mouse model that allowed us to delete GSK-3α/β globally in a temporal manner. On an HFD, GSK-3α-KO mice had a significantly lower body weight and modest improvement in glucose tolerance compared to their littermate controls. In contrast, GSK-3β-deletion-mediated improved glucose tolerance was evident much earlier in the timeline and extended up to twelve weeks post-HFD. However, this protective effect was blunted after chronic HFD (sixteen weeks) when GSK-3β KO mice had a significantly higher body weight than controls. Importantly, GSK-3β KO mice on a control diet maintained a significant improvement in glucose tolerance even after sixteen weeks [22].
9. Conclusions
GSK-3 is a critical enzyme that has shed light into further understanding metabolic pathologies that underlie metabolic syndrome and related diseases (Figure 2 and Table 1). Genetically deleting or enzymatically inhibiting each ortholog has brought forth the distinct roles of the two GSK-3 in specific tissues and organs, such as heart, adipose, brain, skeletal muscle, and pancreas. While there are some studies (Figure 3) that have directly investigated the tissue-specific role of the two GSK-3s in diet-induced obesity models using HFD feeding, more studies are warranted to determine the specific role of the two orthologs in tissues such as adipose, skeletal, and liver wherein GSK-3 activity/expression has been shown to be dysregulated, predisposing individuals to obesity-associated pathologies including T2D. Additionally, while systemic GSK-3 inhibition is a crucial advancement in delineating the specific roles of the two GSK-3s in glucose metabolism under an HFD, homozygous genetic deletion is different from the level of inhibition seen with pharmacological agents. Therefore, future studies examining systemic heterozygous deletion in animal models are important for our understanding of the role of GSK-3s, which would mimic the level of inhibition generally seen with pharmacological agents.
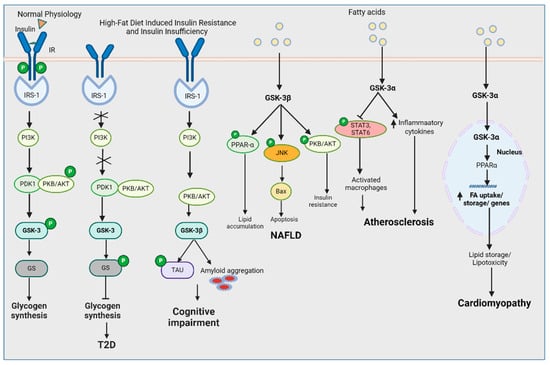
Figure 2.
GSK-3 regulation in HFD-induced pathologies (created with BioRender.com).

Table 1.
Studies demonstrating the role of GSK-3 in metabolic perturbations.
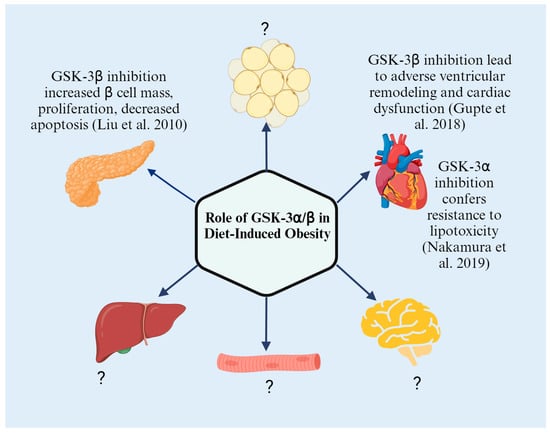
Figure 3.
Tissue-specific role of GSK-3s in HFD-induced metabolic perturbations (Created with BioRender.com) [10,27,42].
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No data was used for the research described in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicting interests to disclose in relation to this work.
References
- Choi, S.E.; Jang, H.J.; Kang, Y.; Jung, J.G.; Han, S.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, K.W. Atherosclerosis induced by a high-fat diet is alleviated by lithium chloride via reduction of VCAM expression in ApoE-deficient mice. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2010, 53, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piche, M.E.; Tchernof, A.; Despres, J.P. Obesity Phenotypes, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1477–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, J.; Di, L.J. Glycogen synthesis and beyond, a comprehensive review of GSK3 as a key regulator of metabolic pathways and a therapeutic target for treating metabolic diseases. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 946–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakoori, A.; Mai, W.; Miyashita, K.; Yasumoto, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Ooi, A.; Kawakami, K.; Minamoto, T. Inhibition of GSK-3 beta activity attenuates proliferation of human colon cancer cells in rodents. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1388–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcea, G.; Manson, M.M.; Neal, C.P.; Pattenden, C.J.; Sutton, C.D.; Dennison, A.R.; Berry, D.P. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta; a new target in pancreatic cancer? Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2007, 7, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ougolkov, A.V.; Fernandez-Zapico, M.E.; Savoy, D.N.; Urrutia, R.A.; Billadeau, D.D. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta participates in nuclear factor kappaB-mediated gene transcription and cell survival in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2076–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallamadi, P.R.; Esari, D.; Addi, U.R.; Kesavan, R.; Putcha, U.K.; Nagini, S.; Reddy, G.B. Obesity Associated with Prediabetes Increases the Risk of Breast Cancer Development and Progression—A Study on an Obese Rat Model with Impaired Glucose Tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, P.; Sachan, N.; Pal, D. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK-3) Inhibitors as a New Lead for Treating Breast and Ovarian Cancer. Curr. Drug Targets 2021, 22, 1548–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guil-Luna, S.; Rivas-Crespo, A.; Navarrete-Sirvent, C.; Mantrana, A.; Pera, A.; Mena-Osuna, R.; Toledano-Fonseca, M.; Garcia-Ortiz, M.V.; Villar, C.; Sanchez-Montero, M.T.; et al. Clinical significance of glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) expression and tumor budding grade in colorectal cancer: Implications for targeted therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tanabe, K.; Baronnier, D.; Patel, S.; Woodgett, J.; Cras-Meneur, C.; Permutt, M.A. Conditional ablation of Gsk-3beta in islet beta cells results in expanded mass and resistance to fat feeding-induced diabetes in mice. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 2600–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacAulay, K.; Doble, B.W.; Patel, S.; Hansotia, T.; Sinclair, E.M.; Drucker, D.J.; Nagy, A.; Woodgett, J.R. Glycogen synthase kinase 3alpha-specific regulation of murine hepatic glycogen metabolism. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksen, E.J.; Kinnick, T.R.; Teachey, M.K.; O’Keefe, M.P.; Ring, D.; Johnson, K.W.; Harrison, S.D. Modulation of muscle insulin resistance by selective inhibition of GSK-3 in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 284, E892–E900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaidanovich, O.; Eldar-Finkelman, H. The role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2002, 6, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldar-Finkelman, H.; Schreyer, S.A.; Shinohara, M.M.; LeBoeuf, R.C.; Krebs, E.G. Increased glycogen synthase kinase-3 activity in diabetes- and obesity-prone C57BL/6J mice. Diabetes 1999, 48, 1662–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, F.; Woodgett, J.R. Emerging roles of GSK-3alpha in pathophysiology: Emphasis on cardio-metabolic disorders. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2020, 1867, 118616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciniegas Ruiz, S.; Rippin, I.; Eldar-Finkelman, H. Prospects in GSK-3 Signaling: From Cellular Regulation to Disease Therapy. Cells 2022, 11, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacAulay, K.; Woodgett, J.R. Targeting glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) in the treatment of Type 2 diabetes. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2008, 12, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Fajol, A.; Hoene, M.; Zhang, B.; Schleicher, E.D.; Lin, Y.; Calaminus, C.; Pichler, B.J.; Weigert, C.; Haring, H.U.; et al. PI3K-resistant GSK3 controls adiponectin formation and protects from metabolic syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5754–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Doble, B.W.; MacAulay, K.; Sinclair, E.M.; Drucker, D.J.; Woodgett, J.R. Tissue-specific role of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in glucose homeostasis and insulin action. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 6314–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frame, S.; Zheleva, D. Targeting glycogen synthase kinase-3 in insulin signalling. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2006, 10, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umbarkar, P.; Ruiz Ramirez, S.Y.; Toro Cora, A.; Tousif, S.; Lal, H. GSK-3 at the heart of cardiometabolic diseases: Isoform-specific targeting is critical to therapeutic benefit. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2023, 1869, 166724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupte, M.; Tousif, S.; Lemon, J.J.; Toro Cora, A.; Umbarkar, P.; Lal, H. Isoform-Specific Role of GSK-3 in High Fat Diet Induced Obesity and Glucose Intolerance. Cells 2022, 11, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormier, K.W.; Woodgett, J.R. Recent advances in understanding the cellular roles of GSK-3. F1000Research 2017, 6, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCubrey, J.A.; Rakus, D.; Gizak, A.; Steelman, L.S.; Abrams, S.L.; Lertpiriyapong, K.; Fitzgerald, T.L.; Yang, L.V.; Montalto, G.; Cervello, M.; et al. Effects of mutations in Wnt/beta-catenin, hedgehog, Notch and PI3K pathways on GSK-3 activity-Diverse effects on cell growth, metabolism and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 2942–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervello, M.; Augello, G.; Cusimano, A.; Emma, M.R.; Balasus, D.; Azzolina, A.; McCubrey, J.A.; Montalto, G. Pivotal roles of glycogen synthase-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2017, 65, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domoto, T.; Pyko, I.V.; Furuta, T.; Miyashita, K.; Uehara, M.; Shimasaki, T.; Nakada, M.; Minamoto, T. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta is a pivotal mediator of cancer invasion and resistance to therapy. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1363–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Liu, T.; Husain, S.; Zhai, P.; Warren, J.S.; Hsu, C.P.; Matsuda, T.; Phiel, C.J.; Cox, J.E.; Tian, B.; et al. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3alpha Promotes Fatty Acid Uptake and Lipotoxic Cardiomyopathy. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1119–1134.e1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; De Sarno, P.; Jope, R.S. Central role of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced caspase-3 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 44701–44708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Mastrogiacomo, L.; Fulmer, M.; Shi, Y.; Werstuck, G.H. Deletion of Macrophage-Specific Glycogen Synthase Kinase (GSK)-3alpha Promotes Atherosclerotic Regression in Ldlr(-/-) Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; Ma, J.A.; Ji, J.; Bostrom, K.I.; Yao, Y. GSK3beta Inhibition Ameliorates Atherosclerotic Calcification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, H.; Ahmad, F.; Woodgett, J.; Force, T. The GSK-3 family as therapeutic target for myocardial diseases. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Su, X.; Xu, L.; Chang, C.; Yao, Y.; Komal, S.; Cha, X.; Zang, M.; Ouyang, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inhibition alleviates activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in myocardial infarction. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2020, 149, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, A.M.; Qaisar, R.; Al-Tamimi, A.O.; Jayakumar, M.N.; Woodgett, J.R.; Koch, W.J.; Ahmad, F. Cardiomyocyte-GSK-3beta deficiency induces cardiac progenitor cell proliferation in the ischemic heart through paracrine mechanisms. J. Cell Physiol. 2022, 237, 1804–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Maejima, Y.; Shirakabe, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Ikeda, Y.; Sadoshima, J.; Zhai, P. Ser9 phosphorylation of GSK-3beta promotes aging in the heart through suppression of autophagy. J. Cardiovasc. Aging 2021, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X.; Ren, Y.; Jiao, S.; Zhu, Q.; Guo, D.; Xia, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; et al. Qishen granule attenuates cardiac fibrosis by regulating TGF-beta /Smad3 and GSK-3beta pathway. Phytomedicine 2019, 62, 152949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potz, B.A.; Sabe, A.A.; Elmadhun, N.Y.; Clements, R.T.; Robich, M.P.; Sodha, N.R.; Sellke, F.W. Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3beta Inhibition Improves Myocardial Angiogenesis and Perfusion in a Swine Model of Metabolic Syndrome. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e003694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, W.; Xue, W.; Tan, Y.; Hein, D.W.; Li, X.K.; Cai, L. Inactivation of GSK-3beta by metallothionein prevents diabetes-related changes in cardiac energy metabolism, inflammation, nitrosative damage, and remodeling. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Tan, Y.; Watson, S.; Wintergerst, K. Diabetic cardiomyopathy—Zinc preventive and therapeutic potentials by its anti-oxidative stress and sensitizing insulin signaling pathways. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2023, 477, 116694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Si, L.; Bian, J.; Pan, C.; Guo, W.; Qin, P.; Zhu, W.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, K. Adipose tissue macrophage-derived exosomes induce ferroptosis via glutathione synthesis inhibition by targeting SLC7A11 in obesity-induced cardiac injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 182, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wei, K.; Si, L.; Zhao, X.; Shao, Y. Celastrol confers ferroptosis resistance via AKT/GSK3beta signaling in high-fat diet-induced cardiac injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 200, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Wang, J.; Xiao, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, G.; Guo, H.; Guo, Y.; et al. SESN2-Mediated AKT/GSK-3beta/NRF2 Activation to Ameliorate Adriamycin Cardiotoxicity in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2024, 40, 598–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupte, M.; Tumuluru, S.; Sui, J.Y.; Singh, A.P.; Umbarkar, P.; Parikh, S.S.; Ahmad, F.; Zhang, Q.; Force, T.; Lal, H. Cardiomyocyte-specific deletion of GSK-3beta leads to cardiac dysfunction in a diet induced obesity model. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 259, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupte, M.; Umbarkar, P.; Singh, A.P.; Zhang, Q.; Tousif, S.; Lal, H. Deletion of Cardiomyocyte Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Beta (GSK-3beta) Improves Systemic Glucose Tolerance with Maintained Heart Function in Established Obesity. Cells 2020, 9, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, F.; Wang, Y.; Shan, D.; Guo, S.; Chen, G.; Jin, L.; Zheng, W.; Feng, H.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. Blocking MG53(S255) Phosphorylation Protects Diabetic Heart From Ischemic Injury. Circ. Res. 2022, 131, 962–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Macaulay, K.; Woodgett, J.R. Tissue-specific analysis of glycogen synthase kinase-3alpha (GSK-3alpha) in glucose metabolism: Effect of strain variation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. NAFLD: A multisystem disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62 (Suppl. S1), S47–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Lin, L.; Yuan, Q.Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.M.; Tang, K.C.; Guo, M.Y.; Dong, T.Y.; Han, W.; et al. Bavachin protects against diet-induced hepatic steatosis and obesity in mice. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 1416–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Li, N.; Shi, J.; Li, H.; Yue, Y.; Jiao, W.; Wang, N.; Song, Y.; Huo, G.; Li, B. Lactobacillus acidophilus alleviates type 2 diabetes by regulating hepatic glucose, lipid metabolism and gut microbiota in mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5804–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Li, Q.M.; Yu, N.J.; Chen, W.D.; Zha, X.Q.; Wu, D.L.; Pan, L.H.; Duan, J.; Luo, J.P. Dendrobium huoshanense polysaccharide regulates hepatic glucose homeostasis and pancreatic beta-cell function in type 2 diabetic mice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 211, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Huang, L.; Wang, M.; Kuang, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, X. GPAT3 deficiency attenuates corticosterone-caused hepatic steatosis and oxidative stress through GSK3beta/Nrf2 signals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengton, R.; Iyer, A.M.; van der Valk, E.S.; Hoogeveen, E.K.; Meijer, O.C.; van der Voorn, B.; van Rossum, E.F.C. Variation in glucocorticoid sensitivity and the relation with obesity. Obes. Rev. 2022, 23, e13401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Ru, X.; Wen, T. NRF2, a Transcription Factor for Stress Response and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Wang, K.; Xia, J.; Qian, D.; Guo, J.; Zhong, L.; Tang, D.; Chen, X.; Peng, W.; Chen, Y.; et al. Natural exosomes-like nanoparticles in mung bean sprouts possesses anti-diabetic effects via activation of PI3K/Akt/GLUT4/GSK-3beta signaling pathway. J. Nanobiotechnology 2023, 21, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, H.; Wei, C.H.; Wang, T.; Eastep, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, G. Vitamin A status affects weight gain and hepatic glucose metabolism in rats fed a high-fat diet. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoulina, S.E.; Ciaraldi, T.P.; Mudaliar, S.; Mohideen, P.; Carter, L.; Henry, R.R. Potential role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in skeletal muscle insulin resistance of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2000, 49, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokken, B.B.; Sloniger, J.A.; Henriksen, E.J. Acute selective glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition enhances insulin signaling in prediabetic insulin-resistant rat skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 288, E1188–E1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, N.J.; Arch, J.R.; Clapham, J.C.; Coghlan, M.P.; Corcoran, S.L.; Lister, C.A.; Llano, A.; Moore, G.B.; Murphy, G.J.; Smith, S.A.; et al. Development of glucose intolerance in male transgenic mice overexpressing human glycogen synthase kinase-3beta on a muscle-specific promoter. Metabolism 2004, 53, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaraldi, T.P.; Carter, L.; Mudaliar, S.; Henry, R.R. GSK-3beta and control of glucose metabolism and insulin action in human skeletal muscle. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2010, 315, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.L.; Li, H.X.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y.Q.; Lv, H.M.; Dong, S.Q.; Luo, E.F.; Gu, M.B.; Liu, H. Baicalin attenuates high fat diet-induced insulin resistance and ectopic fat storage in skeletal muscle, through modulating the protein kinase B/Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta pathway. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 14, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Khan, J.; Kumar, R.; Surolia, A.; Gupta, S. Testosterone supplementation improves insulin responsiveness in HFD fed male T2DM mice and potentiates insulin signaling in the skeletal muscle and C2C12 myocyte cell line. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Shi, X.M.; Zhang, W. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta attenuates glucocorticoid-induced suppression of myogenic differentiation in vitro. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theeuwes, W.F.; Gosker, H.R.; Langen, R.C.J.; Pansters, N.A.M.; Schols, A.; Remels, A.H.V. Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK-3beta) enhances mitochondrial biogenesis during myogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864 Pt B, 2913–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Jiang, L.; You, Y.; Ni, H.; Ma, L.; Lin, X.; Wang, Z.; Yan, W.; Xiao, X.; Li, X.; et al. Ketogenic diet ameliorates high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance in mouse skeletal muscle by alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 702, 149559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, J.; Milewski, W.M.; Hara, M.; Steiner, D.F.; Dey, A. GSK-3 inactivation or depletion promotes beta-cell replication via down regulation of the CDK inhibitor, p27 (Kip1). Islets 2011, 3, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Remedi, M.S.; Pappan, K.L.; Kwon, G.; Rohatgi, N.; Marshall, C.A.; McDaniel, M.L. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 and mammalian target of rapamycin pathways contribute to DNA synthesis, cell cycle progression, and proliferation in human islets. Diabetes 2009, 58, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, M.J.; Selander, L.; Carlsson, L.; Edlund, H. Phosphorylation marks IPF1/PDX1 protein for degradation by glycogen synthase kinase 3-dependent mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 6395–6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussmann, R.; Geese, M.; Harder, F.; Kegel, S.; Andag, U.; Lomow, A.; Burk, U.; Onichtchouk, D.; Dohrmann, C.; Austen, M. Inhibition of GSK3 promotes replication and survival of pancreatic beta cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 12030–12037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, F.; Seelig, A.; Humphrey, S.J.; Krahmer, N.; Volta, F.; Reggio, A.; Marchetti, P.; Gerdes, J.; Mann, M. Phosphoproteomics Reveals the GSK3-PDX1 Axis as a Key Pathogenic Signaling Node in Diabetic Islets. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1422–1432.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.; Yang, Y.; Tang, N.; Wang, J.; Sun, P.; Yang, N.; Chen, F.; Wu, T.; Sun, T.; Li, Y.; et al. M1 macrophage-derived exosomes impair beta cell insulin secretion via miR-212-5p by targeting SIRT2 and inhibiting Akt/GSK-3beta/beta-catenin pathway in mice. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 2037–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.; Peng, Z.; Zeng, N.; Silva, J.; He, L.; Chen, J.; Debebe, A.; Tu, T.; Alba, M.; Chen, C.Y.; et al. Chronic Exposure to Palmitic Acid Down-Regulates AKT in Beta-Cells through Activation of mTOR. Am. J. Pathol. 2022, 192, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Mellado-Gil, J.M.; Bahn, Y.J.; Pathy, S.M.; Zhang, Y.E.; Rane, S.G. Protection from beta-cell apoptosis by inhibition of TGF-beta/Smad3 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.Y.; Liu, L.Z.; Xin, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Z.; Yi, J.; Dong, M. Downregulation of mTORC1 and Mcl-1 by lipid-oversupply contributes to islet beta-cell apoptosis and dysfunction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2023, 1868, 159332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Sintes, R.; Hernandez, F.; Lucas, J.J.; Avila, J. GSK-3 Mouse Models to Study Neuronal Apoptosis and Neurodegeneration. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muneer, A. Wnt and GSK3 Signaling Pathways in Bipolar Disorder: Clinical and Therapeutic Implications. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2017, 15, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzler, J.; Ganjam, G.K.; Kruger, M.; Pinkenburg, O.; Kutschke, M.; Stohr, S.; Steger, J.; Koch, C.E.; Olkrug, R.; Schwartz, M.W.; et al. Hypothalamic glycogen synthase kinase 3beta has a central role in the regulation of food intake and glucose metabolism. Biochem. J. 2012, 447, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, C.; Killick, R.; Lovestone, S. The GSK3 hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2008, 104, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turenne, G.A.; Price, B.D. Glycogen synthase kinase3 beta phosphorylates serine 33 of p53 and activates p53’s transcriptional activity. BMC Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, F.; Borrell, J.; Guaza, C.; Avila, J.; Lucas, J.J. Spatial learning deficit in transgenic mice that conditionally over-express GSK-3beta in the brain but do not form tau filaments. J. Neurochem. 2002, 83, 1529–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, T.; Hernandez, F.; Avila, J.; Lucas, J.J. Full reversal of Alzheimer’s disease-like phenotype in a mouse model with conditional overexpression of glycogen synthase kinase-3. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 5083–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Gong, X.; Ye, R.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Bao, J. Long-Term High-Fat Diet Consumption Induces Cognitive Decline Accompanied by Tau Hyper-Phosphorylation and Microglial Activation in Aging. Nutrients 2023, 15, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, M.; Yin, X.; Chen, K.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Cao, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, D. The role of pathological tau in synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s diseases. Transl. Neurodegener. 2021, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correction for Sen et al., Sulfhydration of AKT triggers Tau-phosphorylation by activating glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2114879118. [CrossRef]
- Hoover, B.R.; Reed, M.N.; Su, J.; Penrod, R.D.; Kotilinek, L.A.; Grant, M.K.; Pitstick, R.; Carlson, G.A.; Lanier, L.M.; Yuan, L.L.; et al. Tau mislocalization to dendritic spines mediates synaptic dysfunction independently of neurodegeneration. Neuron 2010, 68, 1067–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenech, R.K.; Hamstra, S.I.; Finch, M.S.; Ryan, C.R.; Marko, D.M.; Roy, B.D.; Fajardo, V.A.; MacPherson, R.E.K. Low-Dose Lithium Supplementation Influences GSK3beta Activity in a Brain Region Specific Manner in C57BL6 Male Mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2023, 91, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.H.; Kim, K.; Cho, H.C.; Lee, J.; Kim, E.K. Silencing of hypothalamic FGF11 prevents diet-induced obesity. Mol. Brain 2022, 15, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaraldi, T.P.; Oh, D.K.; Christiansen, L.; Nikoulina, S.E.; Kong, A.P.; Baxi, S.; Mudaliar, S.; Henry, R.R. Tissue-specific expression and regulation of GSK-3 in human skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 291, E891–E898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Yu, F.; Wu, Y.; Wang, W.; Adaku, U.; Lutfy, K.; Friedman, T.C.; et al. Increased glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and hexose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase expression in adipose tissue may contribute to glucocorticoid-induced mouse visceral adiposity. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Di, L. GSK3-activated STAT5 regulates expression of SFRPs to modulate adipogenesis. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 4714–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geromella, M.S.; Ryan, C.R.; Braun, J.L.; Finch, M.S.; Maddalena, L.A.; Bagshaw, O.; Hockey, B.L.; Moradi, F.; Fenech, R.K.; Ryoo, J.; et al. Low-dose lithium supplementation promotes adipose tissue browning and sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca(2+) ATPase uncoupling in muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Zhang, J.J.; Cen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, F.; Gu, K.P.; Yang, H.T.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zou, Z.Q. High Endogenously Synthesized N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Fat-1 Mice Attenuate High-Fat Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation via Akt/GSK-3beta/TXNIP Pathway. Molecules 2022, 27, 6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.; Hao, C.M.; Redha, R.; Wasserman, D.H.; McGuinness, O.P.; Breyer, M.D. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibition improves insulin-stimulated glucose metabolism but not hypertension in high-fat-fed C57BL/6J mice. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).