CK2 Inhibitors Targeting Inside and Outside the Catalytic Box
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. An Overview of CK2
1.2. Structure of CK2
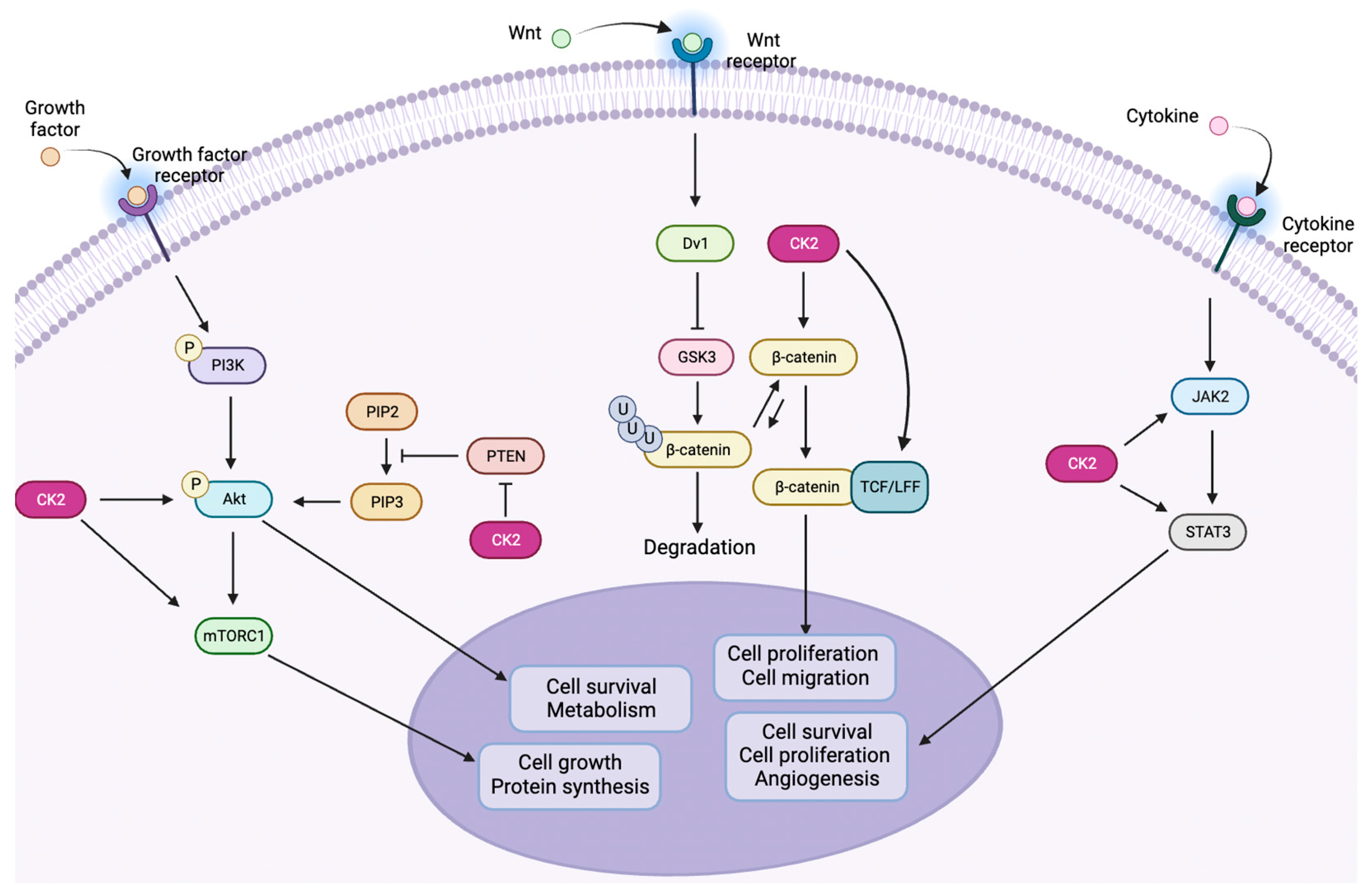
1.3. CK2 in Cancer
2. Targeting CK2 within the ATP Site
2.1. ATP-Competitive Inhibition
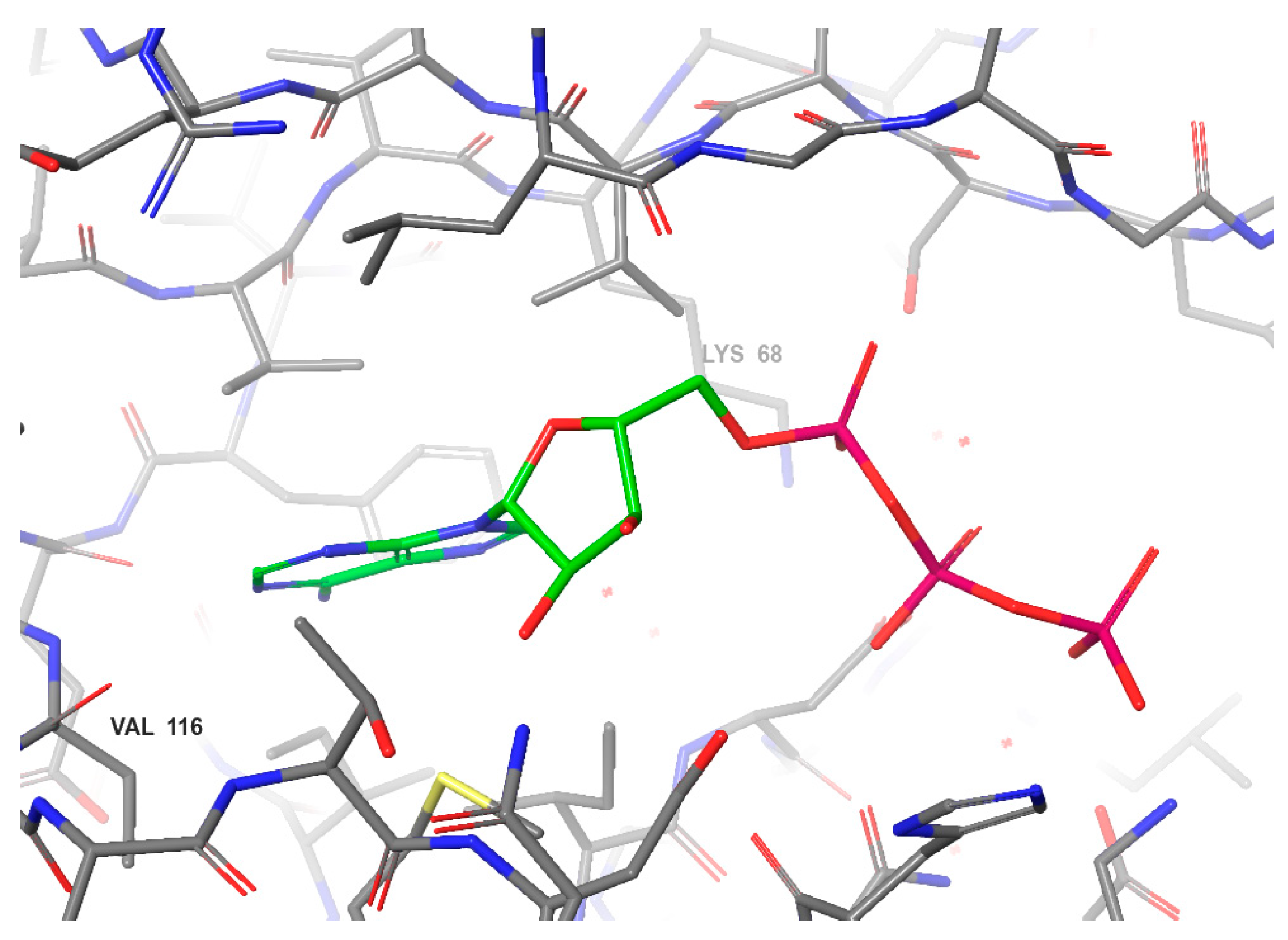
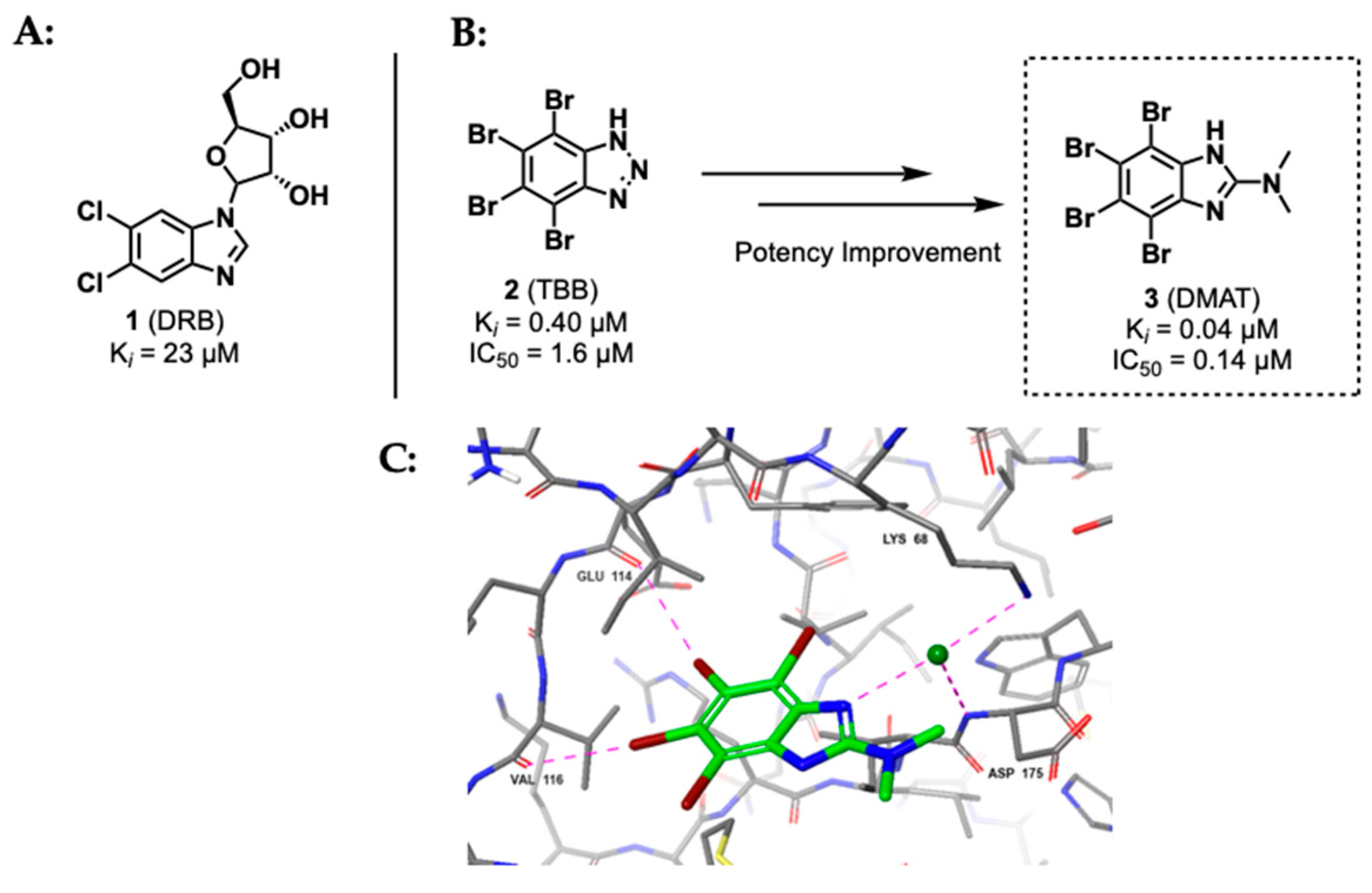
2.1.1. Polyhalogenated Benzimidazole and Benzotriazole Derivatives
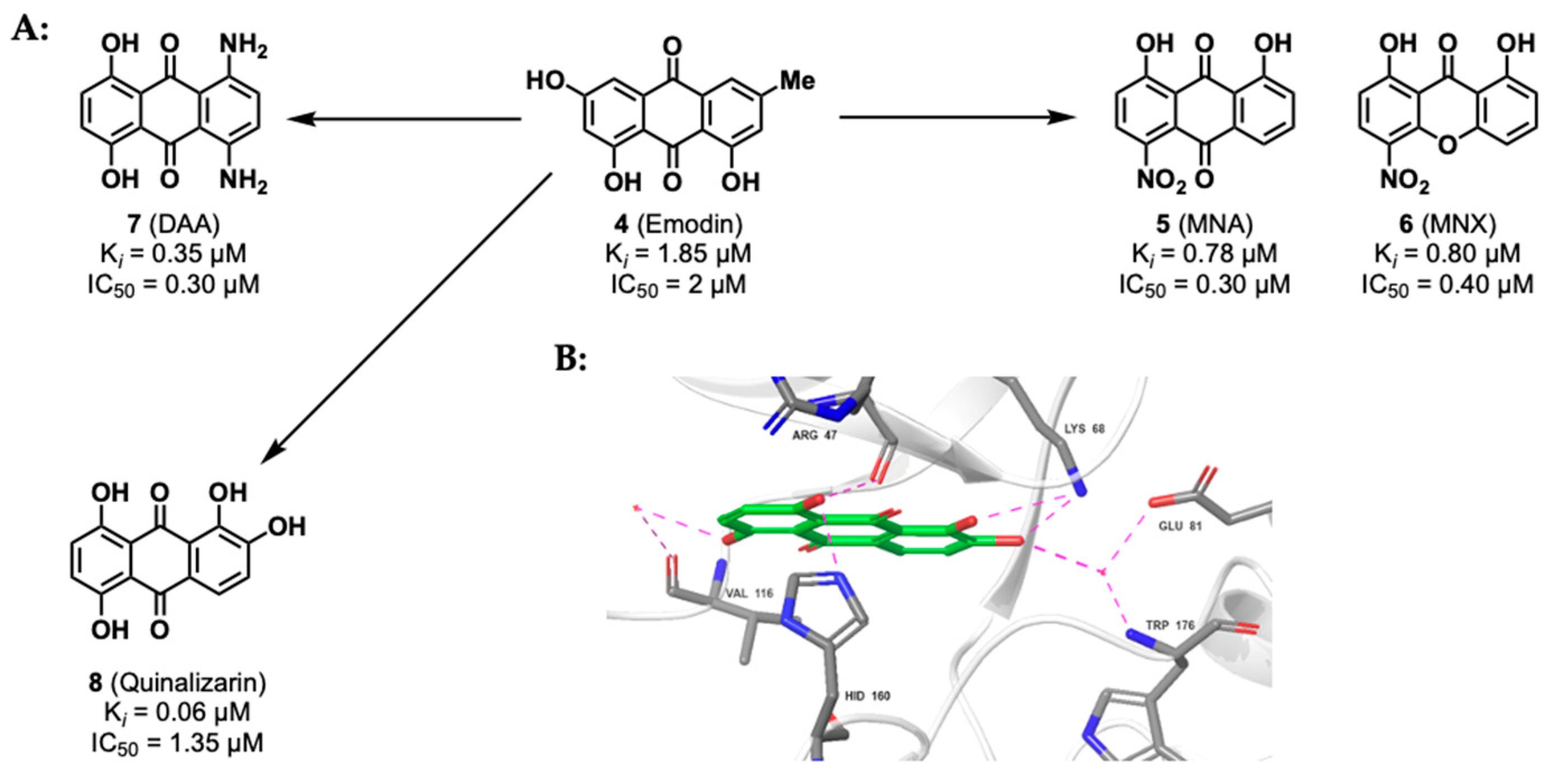
2.1.2. Anthraquinone Derivatives
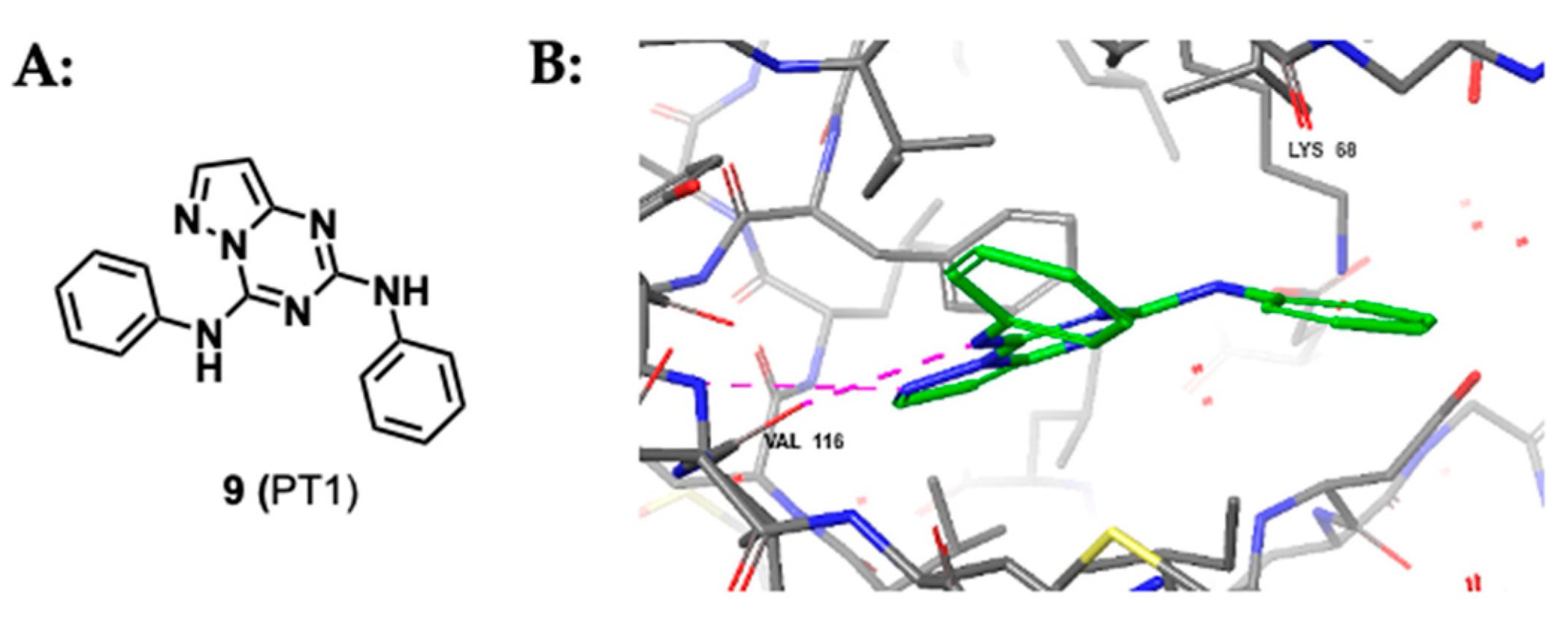
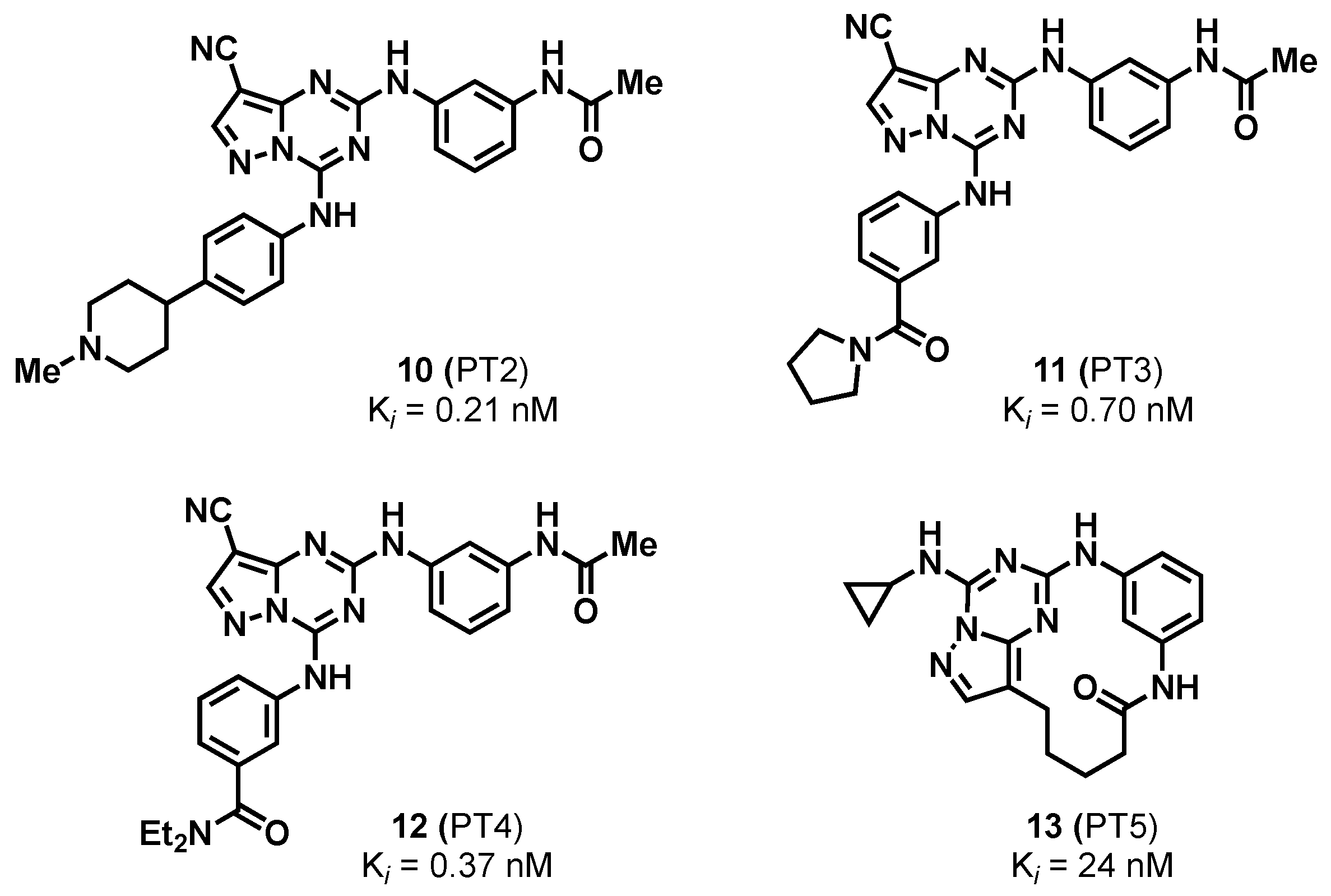
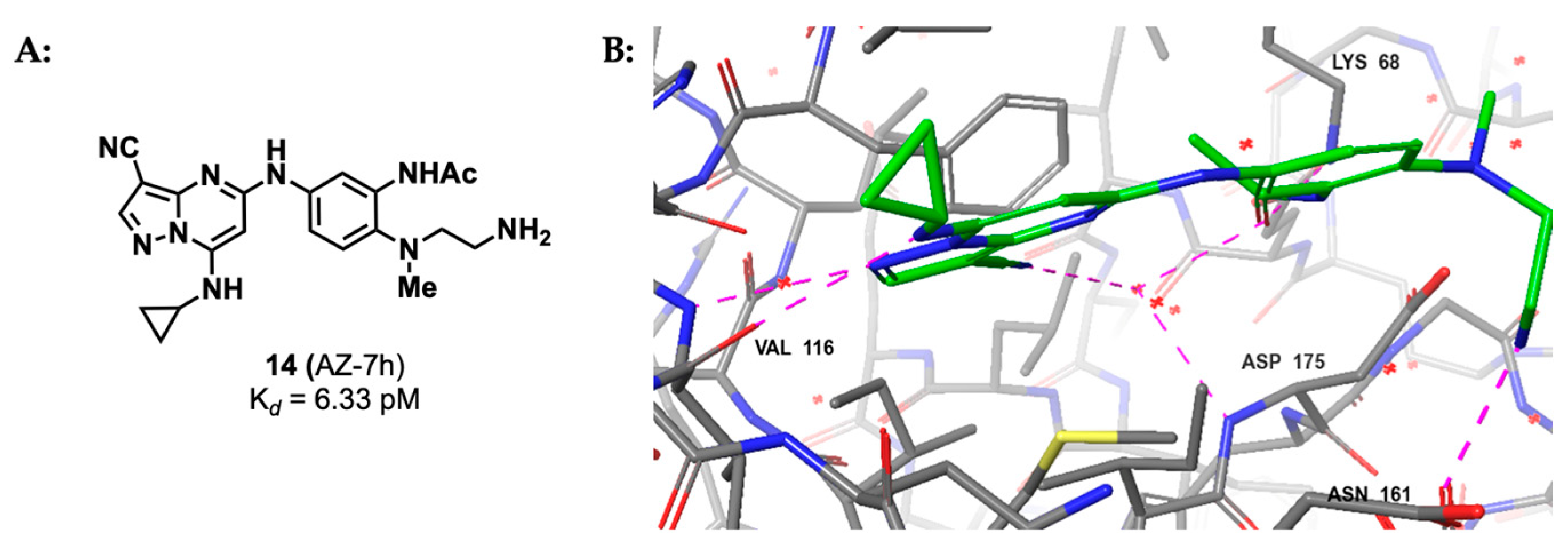
2.1.3. Pyrazolo-Triazines and Pyrazolo-Pyrimidines
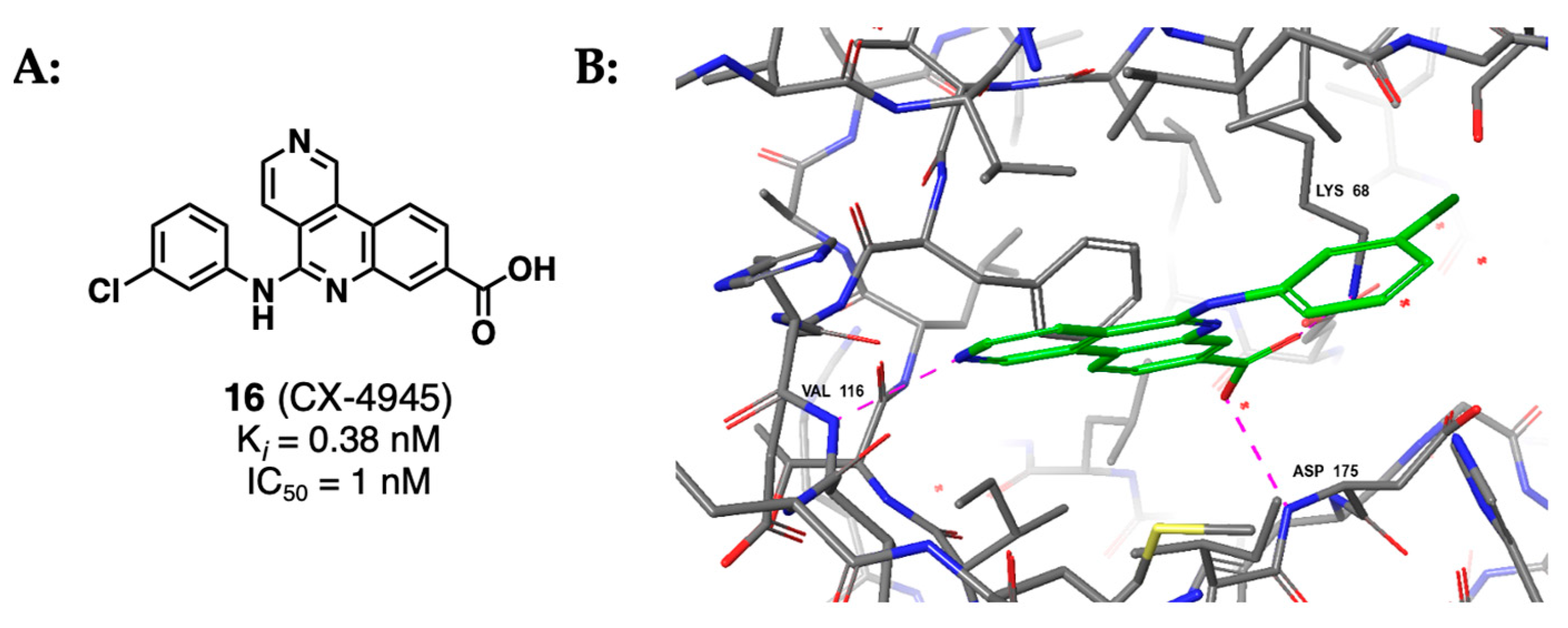
2.1.4. Indoloquinazolines Such as CX-4945
3. Extending beyond the ATP Site
3.1. Dual-Binding Ligands
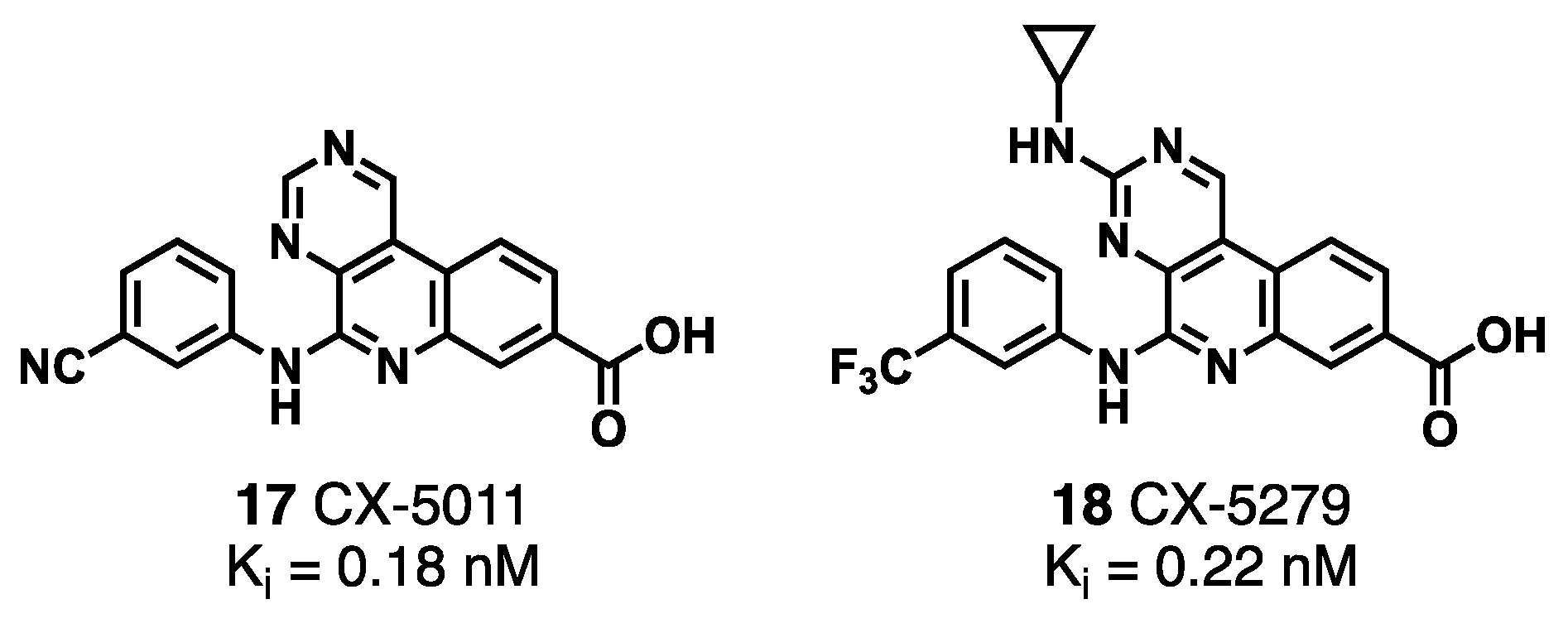
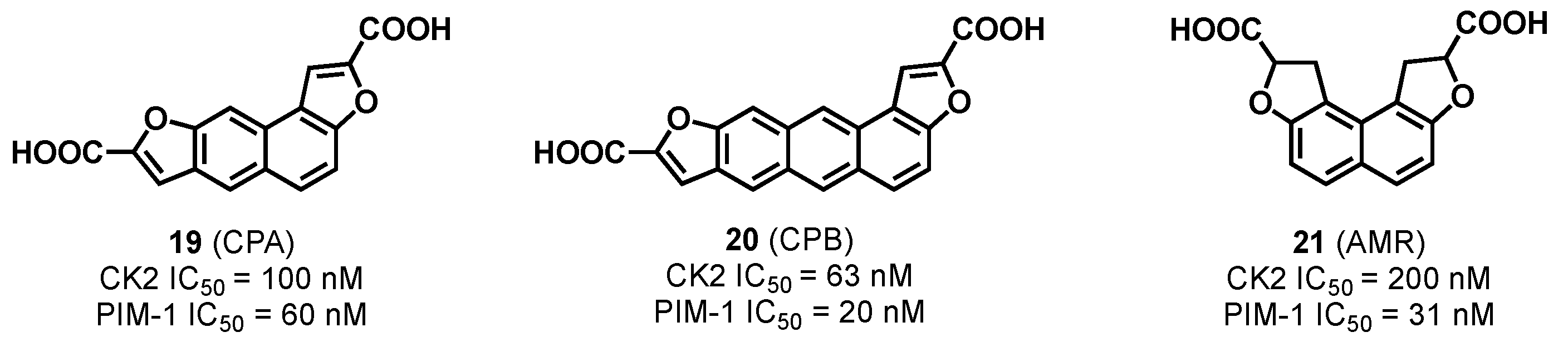
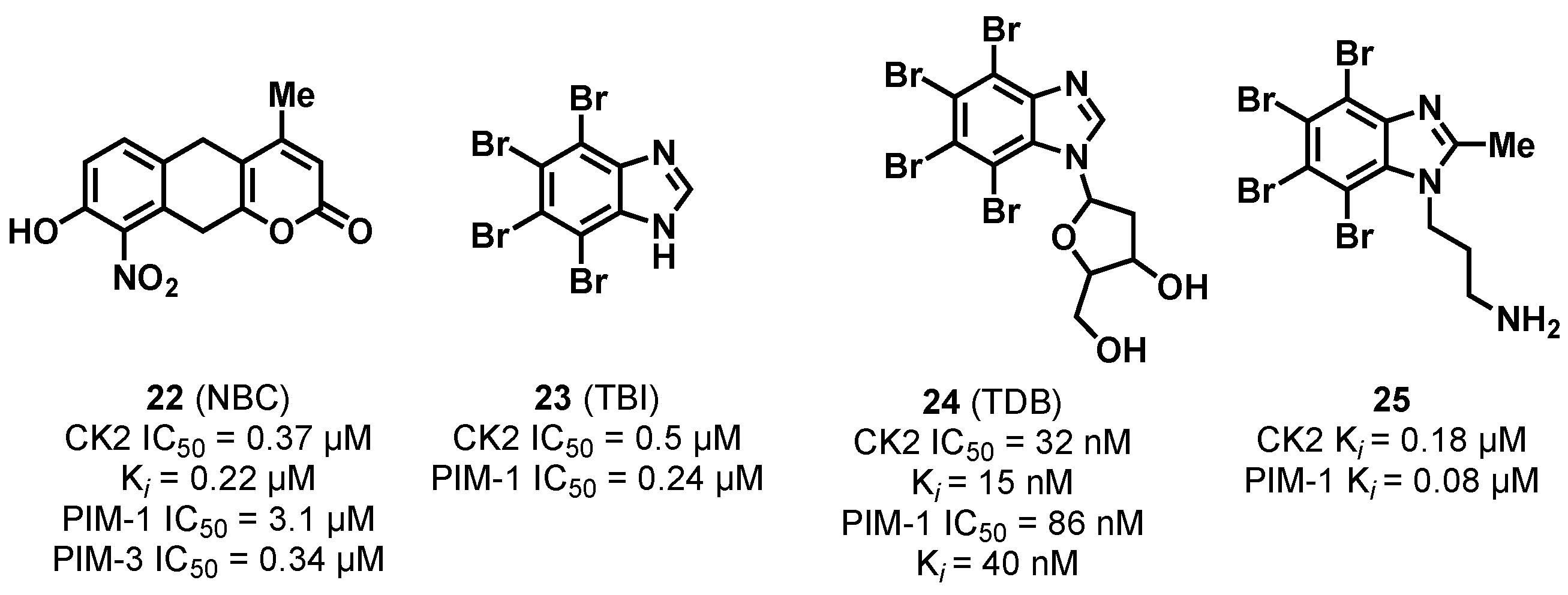
3.1.1. CK2/PIM Dual-Binding Ligands
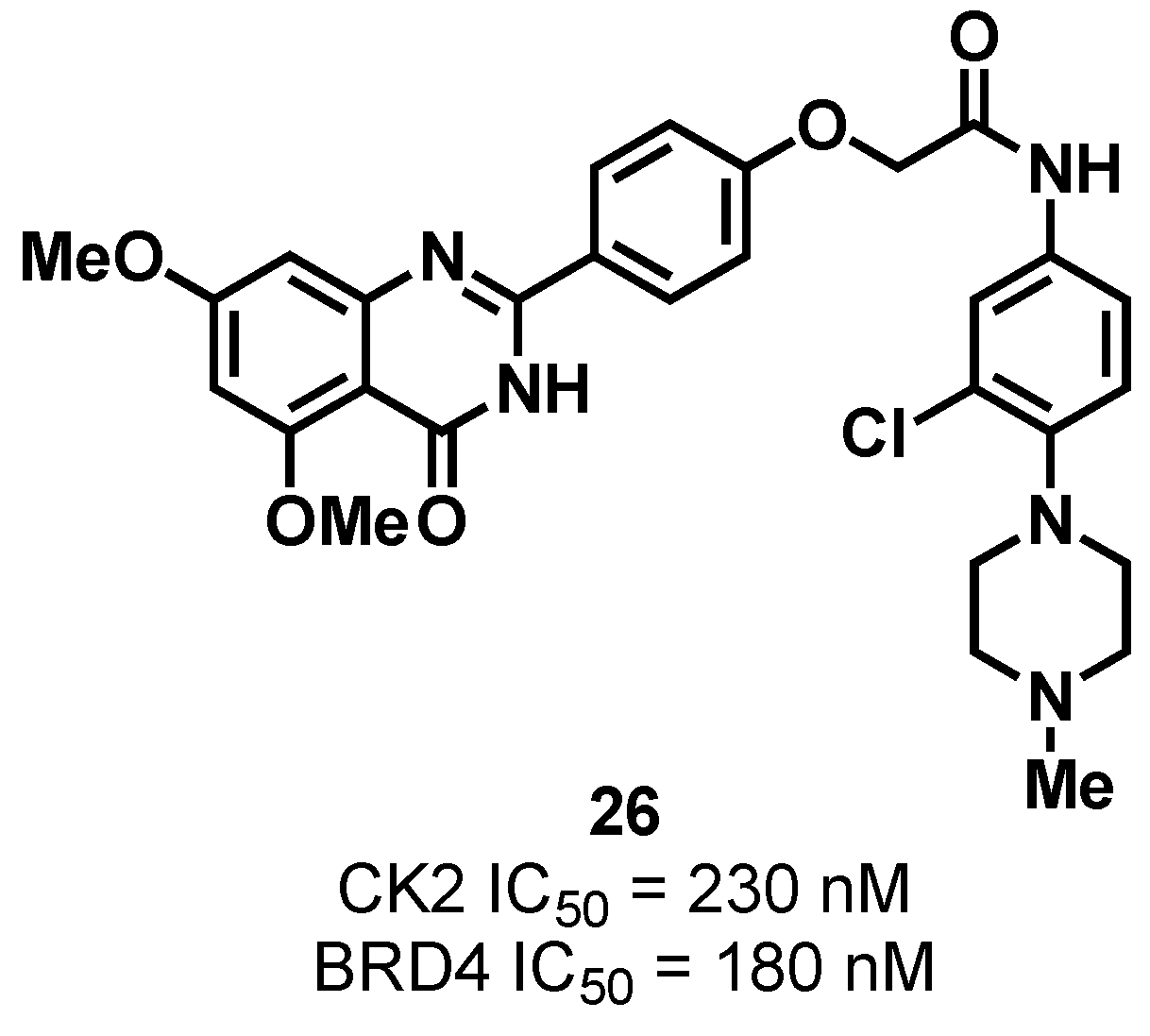
3.1.2. CK2/BRD4 Dual-Binding Ligands
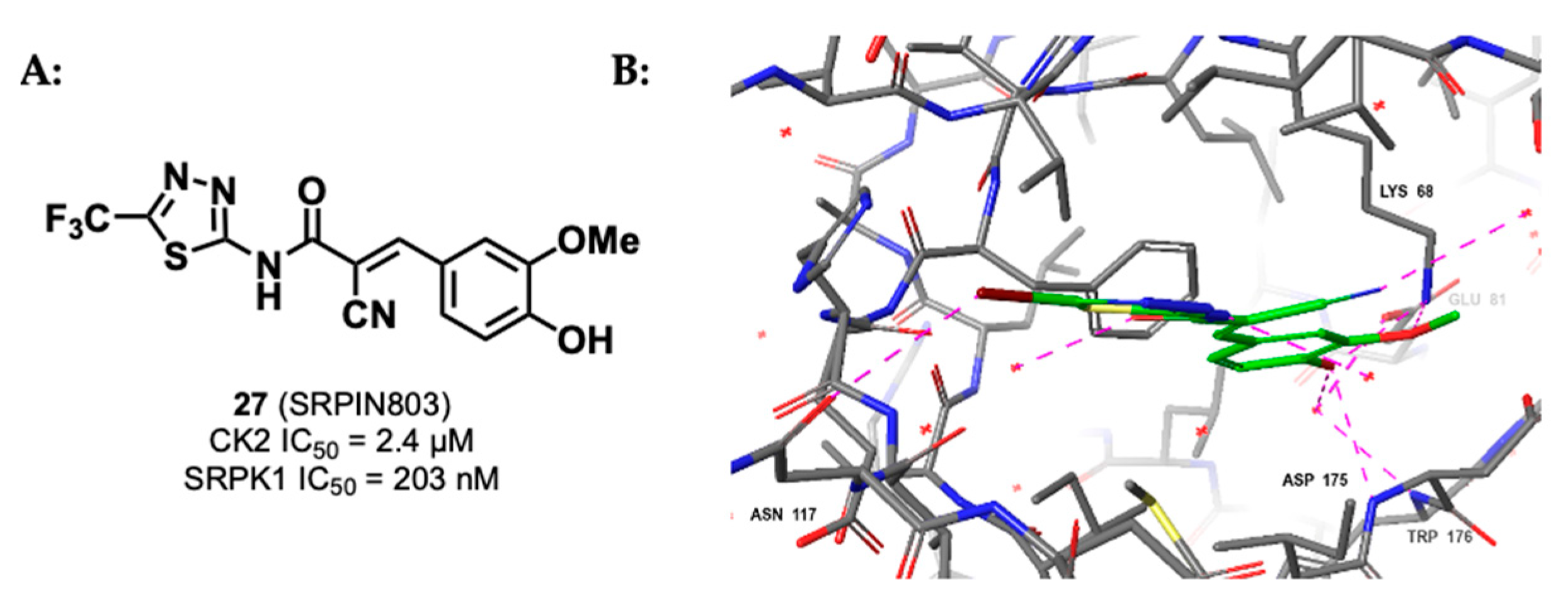
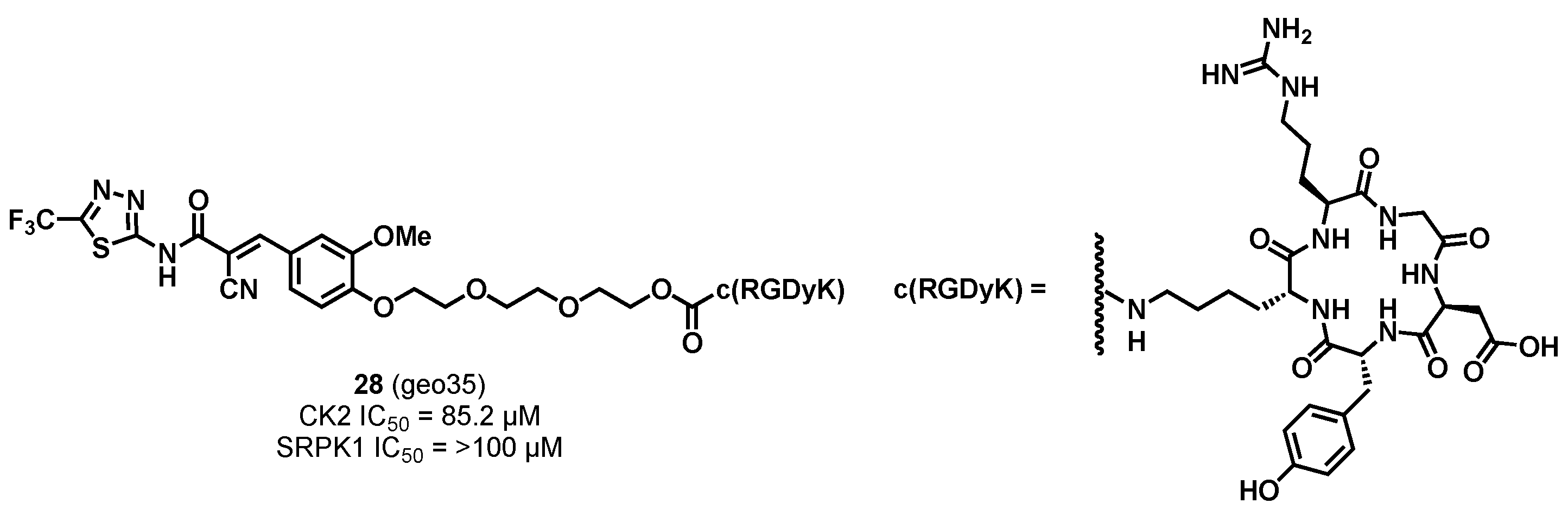
3.1.3. CK2/SRPK1 Dual Inhibitor
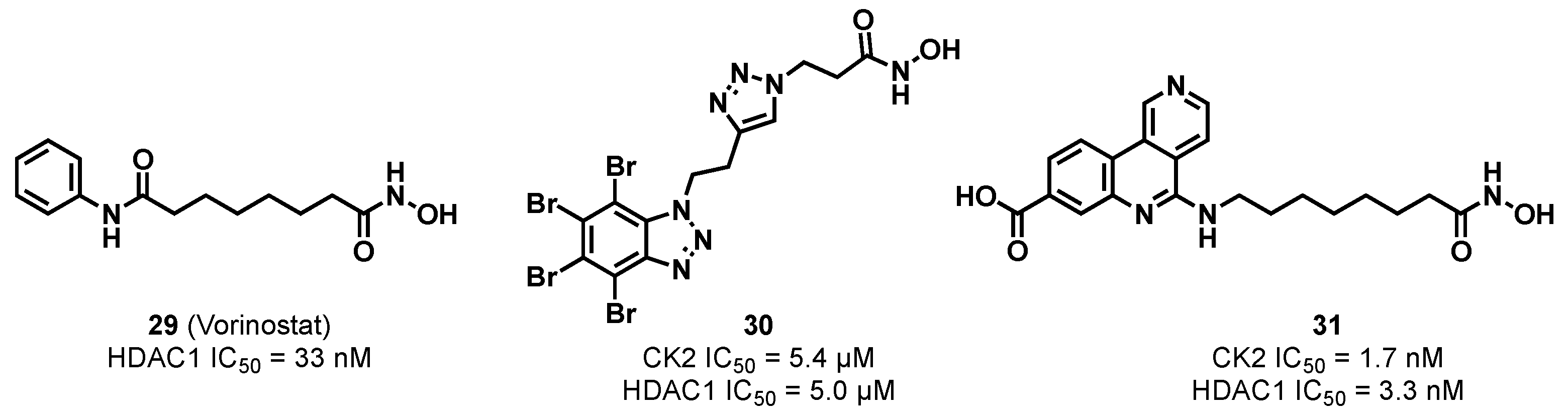
3.1.4. CK2/HDAC1 Dual Inhibitor
3.1.5. CK2/TNIK/DYRK1 Multiple Inhibitor
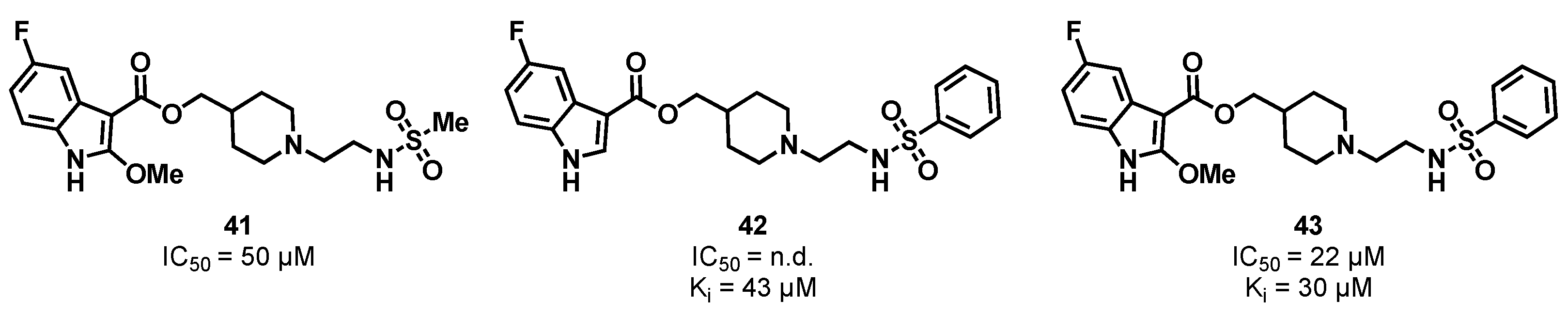
3.2. Substrate Binding Site Inhibition
3.3. Bi-Specific ATP/Substrate Competitive Inhibition
3.4. Inhibitors Acting in the αD Site
3.5. Holoenzyme Assembly Inhibition
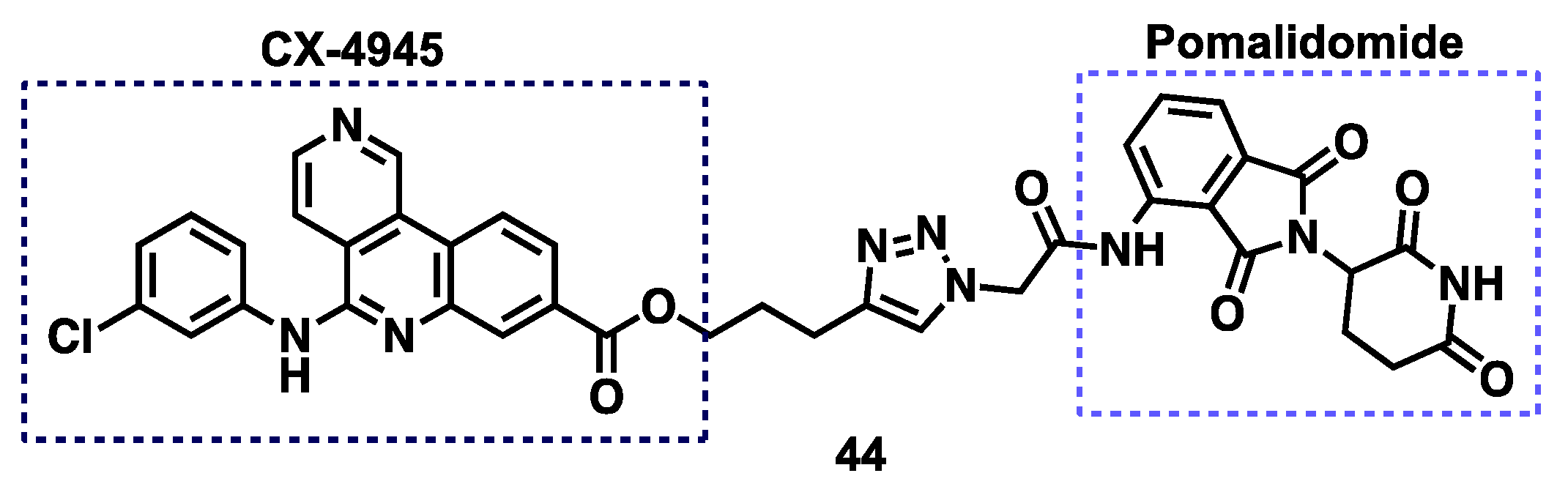
3.6. CK2 Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeras
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, Z.; Liu, H. Mapping the Protein Kinome: Current Strategy and Future Direction. Cells 2023, 12, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obsilova, V.; Obsil, T. The 14-3-3 Proteins as Important Allosteric Regulators of Protein Kinases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Small Molecule Protein Kinase Inhibitors Approved by Regulatory Agencies Outside of the United States. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 194, 106847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montenarh, M. Cellular Regulators of Protein Kinase CK2. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 342, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, N.; Neuwald, A.F. Evolutionary Constraints Associated with Functional Specificity of the CMGC Protein Kinases MAPK, CDK, GSK, SRPK, DYRK, and CK2α. Protein Sci. 2004, 13, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, G.; Kennedy, E.P. The Enzymatic Phosphorylation of Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1954, 211, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venerando, A.; Ruzzene, M.; Pinna, L.A. Casein Kinase: The Triple Meaning of a Misnomer. Biochem. J. 2014, 460, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niefind, K.; Guerra, B.; Ermakowa, I.; Issinger, O.G. Crystal structure of human protein kinase CK2: Insights into basic properties of the CK2 holoenzyme. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinna, L.A. Protein Kinase CK2: A Challenge to Canons. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roffey, S.E.; Litchfield, D.W. CK2 Regulation: Perspectives in 2021. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Cao, S.; Zhang, J. Strategies of Targeting CK2 in Drug Discovery: Challenges, Opportunities, and Emerging Prospects. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarno, S.; Ghisellini, P.; Pinna, L.A. Unique activation mechanism of protein kinase CK2. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 22509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez de Villavicencio-Díaz, T.; Mazola, Y.; Perera Negrín, Y.; Cruz García, Y.; Guirola Cruz, O.; Perea Rodríguez, S.E. Predicting CK2 Beta-Dependent Substrates Using Linear Patterns. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2015, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottardo, M.F.; Capobianco, C.S.; Sidabra, J.E.; Garona, J.; Perera, Y.; Perea, S.E.; Alonso, D.F.; Farina, H.G. Preclinical Efficacy of CIGB-300, an Anti-CK2 Peptide, on Breast Cancer Metastasic Colonization. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, B. Protein Kinase CK2 Subunits Are Positive Regulators of AKT Kinase. Int. J. Oncol. 2006, 28, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Yeh, J.; Van Waes, C. Protein Kinase CK2 Mediates Inhibitor-Kappa B Kinase and Aberrant Nuclear Factor-κB Activation by Serum Factor(s) in Head and Neck Squamous Carcinoma Cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 6722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Qin, H.; Frank, S.J.; Deng, L.; Litchfield, D.W.; Tefferi, A.; Pardanani, A.; Lin, F.-T.; Li, J.; Sha, B.; et al. A CK2-Dependent Mechanism for Activation of the JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway. Blood 2011, 118, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, H. Casein Kinase 2 Is Activated and Essential for Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 18394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Liu, Y.; Xia, R.; Tong, C.; Yue, T.; Jiang, J.; Jia, J. Casein Kinase 2 Promotes Hedgehog Signaling by Regulating Both Smoothened and Cubitus Interruptus. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 37218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Long, H.; Yang, Y.-L.; Wang, Y.; Hsieh, D.; Li, W.; Au, A.; Stoppler, H.J.; Xu, Z.; Jablons, D.M.; et al. Inhibition of CK2α Down-Regulates Notch1 Signalling in Lung Cancer Cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2013, 17, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgo, C.; D’Amore, C.; Sarno, S.; Salvi, M.; Ruzzene, M. Protein kinase CK2: A potential therapeutic target for diverse human diseases. Sig. Transduct. Target Ther. 2021, 6, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzzene, M.; Pinna, L.A. Addiction to Protein Kinase CK2: A Common Denominator of Diverse Cancer Cells? Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA—Proteins Proteom. 2010, 1804, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, M.; Montenarch, M. Subcellular localisation of protein kinase CK2. A key to its function? Cell Tissue Res. 2000, 301, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trembley, J.H.; Li, B.; Kren, B.T.; Gravely, A.A.; Caicedo-Granados, E.; Klein, M.A.; Ahmed, K. CX-4945 and siRNA-Mediated Knockdown of CK2 Improves Cisplatin Response in HPV(+) and HPV(−) HNSCC Cell Lines. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meza, C.P.Q.; Ruzeene, M. Protein Kinase CK2 and SARS-CoV-2: An Expected Interplay Story. Kinases Phosphatases 2023, 1, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breen, M.E.; Soellner, M.B. Small Molecule Substrate Phosphorylation Site Inhibitors of Protein Kinases: Approaches and Challenges. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygier, P.; Pustelny, K.; Nowak, J.; Golik, P.; Popowicz, G.M.; Plettenburg, O.; Dubin, G.; Menezes, F.; Czarna, A. Silmitasertib (CX-4945), a Clinically Used CK2-Kinase Inhibitor with Additional Effects on GSK3β and DYRK1A Kinases: A Structural Perspective. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Yun, J.-S.; Kim, W.-K.; Chun, H.-S.; Jin, H.; Cho, S.; Chang, J.H. Structural Basis for the Selective Inhibition of Cdc2-Like Kinases by CX-4945. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 6125068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iegre, J.; Atkinson, E.L.; Brear, P.D.; Cooper, B.M.; Hyvönen, M.; Spring, D.R. Chemical Probes Targeting the Kinase CK2: A Journey Outside the Catalytic Box. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, P.A.; Murray, B.W. Protein Kinase Biochemistry and Drug Discovery. Bioorg. Chem. 2011, 39, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez de Villavicencio-Diaz, T.; Rabalski, A.J.; Litchfield, D.W. Protein Kinase CK2: Intricate Relationships within Regulatory Cellular Networks. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
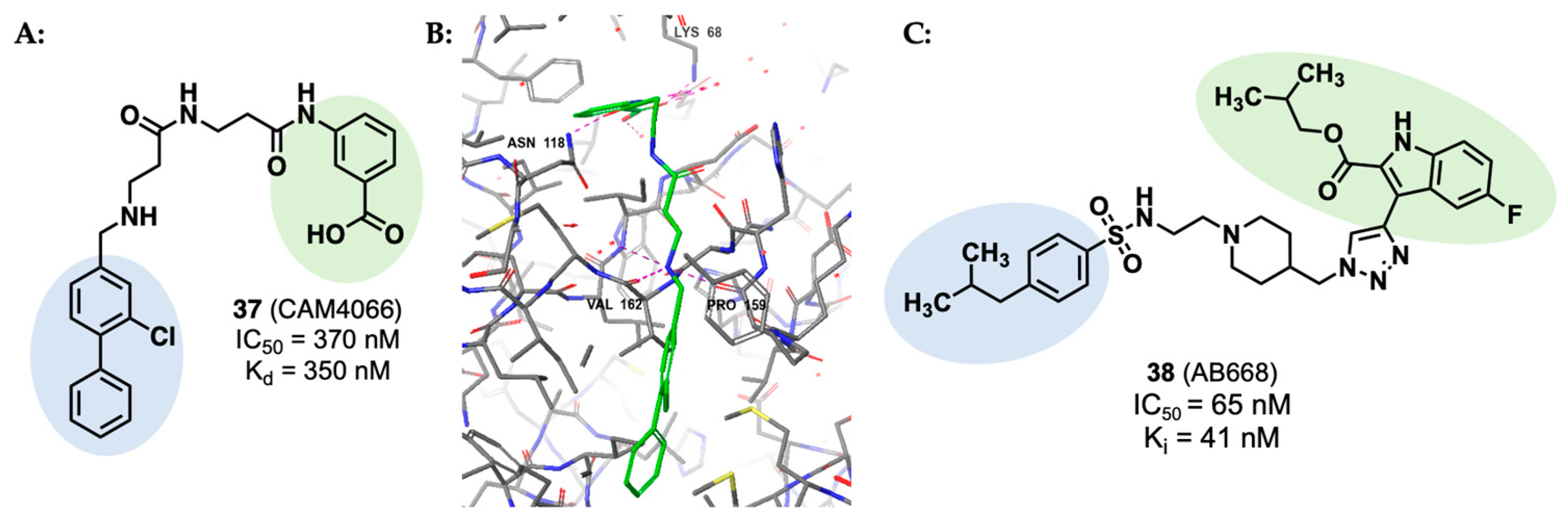
- De Fusco, C.; Brear, P.; Iegre, J.; Georgiou, K.H.; Sore, H.F.; Hyvönen, M.; Spring, D.R. A Fragment-Based Approach Leading to the Discovery of a Novel Binding Site and the Selective CK2 Inhibitor CAM4066. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niefind, K.; Guerra, B.; Pinna, L.A.; Issinger, O.-G.; Schomburg, D. Crystal Structure of the Catalytic Subunit of Protein Kinase CK2 from Zea Mays at 2.1 Å Resolution. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papinutto, E.; Ranchio, A.; Lolli, G.; Pinna, L.A.; Battistutta, R. Structural and Functional Analysis of the Flexible Regions of the Catalytic α-Subunit of Protein Kinase CK2. J. Struct. Biol. 2012, 177, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niefind, K.; Raaf, J.; Issinger, O.-G. Protein kinase CK2 in health and disease: Protein kinase CK2: From structures to insights. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lettieri, A.; Borgo, C.; Zanieri, L.; D’Amore, C.; Oleari, R.; Paganoni, A.; Pinna, L.A.; Cariboni, A.; Salvi, M. Protein Kinase CK2 Subunits Differentially Perturb the Adhesion and Migration of GN11 Cells: A Model of Immature Migrating Neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibby, A.C.; Litchfield, D.W. The Multiple Personalities of the Regulatory Subunit of Protein Kinase CK2: CK2 Dependent and CK2 Independent Roles Reveal a Secret Identity for CK2beta. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2005, 1, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litchfield, D.W. Protein kinase CK2: Structure, regulation, and role in cellular decisions of life and death. Biochem. J. 2003, 369, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filhol, O.; Martiel, J.-L.; Cochet, C. Protein Kinase CK2: A New View of an Old Molecular Complex. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trembley, J.H.; Wang, G.; Unger, G.; Slaton, J.; Ahmed, K. Protein Kinase CK2 in Health and Disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, M.M.J.; Ortega, C.E.; Sheikh, A.; Lee, M.; Abdul-Rassoul, H.; Hartshorn, K.L.; Dominguez, I. CK2 in Cancer: Cellular and Biochemical Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Target. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The Hallmarks of Cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trembley, J.H.; Kren, B.T.; Afzal, M.; Scaria, G.A.; Klein, M.A.; Ahmed, K. Protein Kinase CK2—Diverse Roles in Cancer Cell Biology and Therapeutic Promise. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2023, 478, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, R.A.; Gapany, M.; Tristani, P.; Davis, A.; Adams, G.L.; Ahmed, K. Elevated Protein Kinase CK2 Activity in Chromatin of Head and Neck Tumors: Association with Malignant Transformation. Cancer Lett. 1996, 101, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenice, S.; Davis, A.T.; Goueli, S.A.; Akdas, A.; Limas, C.; Ahmed, K. Nuclear casein kinase 2 (CK-2) activity in human normal, benign hyperplastic, and cancerous prostate. Prostate 1994, 24, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandato, E.; Manni, S.; Zaffino, F.; Semenzato, G.; Piazza, F. Targeting CK2-Driven Non-Oncogene Addiction in B-Cell Tumors. Oncogene 2016, 35, 6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Luo, H.; Zeng, Q.; Dong, Z.; Wu, D.; Liu, L. Protein Kinase CK2α Is Overexpressed in Colorectal Cancer and Modulates Cell Proliferation and Invasion via Regulating EMT-Related Genes. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-X.; Jiang, S.-S.; Zhang, X.-F.; Zhou, Z.-Q.; Pan, Q.-Z.; Chen, C.-L.; Zhao, J.-J.; Tang, Y.; Xia, J.-C.; Weng, D.-S. Protein Kinase CK2α Catalytic Subunit Is Overexpressed and Serves as an Unfavorable Prognostic Marker in Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 34800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turowec, J.P.; Vilk, G.; Gabriel, M.; Litchfield, D.W. Characterizing the Convergence of Protein Kinase CK2 and Caspase-3 Reveals Isoform-Specific Phosphorylation of Caspase-3 by CK2α’: Implications for Pathological Roles of CK2 in Promoting Cancer Cell Survival. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Ritt, D.A.; Morrison, D.K.; Der, C.J.; Cox, A.D. Protein Kinase CK2α Maintains Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase (ERK) Activity in a CK2α Kinase-Independent Manner to Promote Resistance to Inhibitors of RAF and MEK but Not ERK in BRAF Mutant Melanoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 17804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Setoguchi, T.; Tsuru, A. Inhibition of casein kinase 2 prevents growth of human osteosarcoma. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, E.L.; Iegre, J.; Brear, P.D.; Zhabina, E.A.; Hyvönen, M.; Spring, D.R. Downfalls of Chemical Probes Acting at the Kinase ATP-Site: CK2 as a Case Study. Molecules 2021, 26, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamm, I.; Folkers, K.; Shunk, C.H.; Horsfall, F.L. Inhibition of Influenza Virus Multiplication by N-Glycosides of Benzimidazoles. J. Exp. Med. 1954, 99, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandomeni, R.; Zandomeni, M.C.; Shugar, D.; Weinmann, R. Casein Kinase Type II Is Involved in the Inhibition by 5,6-Dichloro-1-Beta-D-Ribofuranosylbenzimidazole of Specific RNA Polymerase II Transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyszka, R.; Grankowski, N.; Felczak, K.; Shugar, D. Halogenated Benzimidazoles and Benzotriazoles as Selective Inhibitors of Protein Kinases CK-I and CK-II from Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Other Sources. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 208, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, R.H.; Hussung, K.F. Halogenated Benzotriazoles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957, 79, 4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, M.A.; Meggio, F.; Ruzzene, M.; Andrzejewska, M.; Kazimierczuk, Z.; Pinna, L.A. 2-Dimethylamino-4,5,6,7-Tetrabromo-1H-Benzimidazole: A Novel Powerful and Selective Inhibitor of Protein Kinase CK2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 321, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, M.A.; Bain, J.; Kazimierczuk, Z.; Sarno, S.; Ruzzene, M.; Di Maira, G.; Elliott, M.; Orzeszko, A.; Cozza, G.; Meggio, F.; et al. The Selectivity of Inhibitors of Protein Kinase CK2: An Update. Biochem. J. 2008, 415, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Pertz, V.; Zhang, B.; Kaur, P.; Shimada, H.; Groffen, J.; Kazimierczuk, Z.; Pinna, L.A.; Heisterkamp, N. Treatment of P190 Bcr/Abl Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells with Inhibitors of the Serine/Threonine Kinase CK2. Leukemia 2007, 21, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, Y.H.; Kershaw, R.M.; Humphreys, E.H.; Assis Junior, E.M.; Chaudhri, S.; Jayaraman, P.-S.; Gaston, K. CK2 Abrogates the Inhibitory Effects of PRH/HHEX on Prostate Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion and Acts through PRH to Control Cell Proliferation. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulges, A.; Witsch, E.J.; Pramanik, G.; Klein, M.; Birkner, K.; Bühler, U.; Wasser, B.; Luessi, F.; Stergiou, N.; Dietzen, S.; et al. Protein Kinase CK2 Governs the Molecular Decision between Encephalitogenic TH17 Cell and Treg Cell Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartman, J.A.; Tambar, U.K. Recent Total Syntheses of Anthraquinone-Based Natural Products. Tetrahedron 2022, 105, 132501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeczko, M.; Masłyk, M.; Kubiński, K.; Golczyk, H. Emodin, a Natural Inhibitor of Protein Kinase CK2, Suppresses Growth, Hyphal Development, and Biofilm Formation of Candida Albicans. Yeast 2017, 34, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meggio, F.; Pagano, M.A.; Moro, S.; Zagotto, G.; Ruzzene, M.; Sarno, S.; Cozza, G.; Bain, J.; Elliott, M.; Deana, A.D.; et al. Inhibition of Protein Kinase CK2 by Condensed Polyphenolic Derivatives: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 12931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozza, G. The Development of CK2 Inhibitors: From Traditional Pharmacology to in Silico Rational Drug Design. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Moliner, E.; Moro, S.; Sarno, S.; Zagotto, G.; Zanotti, G.; Pinna, L.A.; Battistutta, R. Inhibition of Protein Kinase CK2 by Anthraquinone-Related Compounds: A Structural Insight. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozza, G.; Mazzorana, M.; Papinutto, E.; Bain, J.; Elliott, M.; di Maira, G.; Gianoncelli, A.; Pagano, M.A.; Sarno, S.; Ruzzene, M.; et al. Quinalizarin as a Potent, Selective and Cell-Permeable Inhibitor of Protein Kinase CK2. Biochem. J. 2009, 421, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozza, G.; Venerando, A.; Sarno, S.; Pinna, L.A. The Selectivity of CK2 Inhibitor Quinalizarin: A Reevaluation. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, e734127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Perretta, C.; Erickson, P.; Margosiak, S.; Almassy, R.; Lu, J.; Averill, A.; Yager, K.M.; Chu, S. Structure-Based Design, Synthesis, and Study of Pyrazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]Triazine Derivatives as Potent Inhibitors of Protein Kinase CK2. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Perretta, C.; Erickson, P.; Margosiak, S.; Lu, J.; Averill, A.; Almassy, R.; Chu, S. Structure-Based Design and Synthesis of Novel Macrocyclic Pyrazolo[1,5-a] [1,3,5]Triazine Compounds as Potent Inhibitors of Protein Kinase CK2 and Their Anticancer Activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, J.E.; Chuaqui, C.; Pontz, T.W.; Lyne, P.D.; Larsen, N.A.; Block, M.H.; Chen, H.; Su, N.; Wu, A.; Russell, D.; et al. Potent and Selective Inhibitors of CK2 Kinase Identified through Structure-Guided Hybridization. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, J.E.; Alimzhanov, M.; Bao, L.; Chuaqui, C.; Denz, C.R.; Jenkins, E.; Larsen, N.A.; Lyne, P.D.; Pontz, T.; Ye, Q.; et al. Potent and Selective CK2 Kinase Inhibitors with Effects on Wnt Pathway Signaling in Vivo. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, C.I.; Drewry, D.H.; Pickett, J.E.; Tjaden, A.; Krämer, A.; Müller, S.; Gyenis, L.; Menyhart, D.; Litchfield, D.W.; Knapp, S.; et al. Development of a Potent and Selective Chemical Probe for the Pleiotropic Kinase CK2. Cell Chem. Biol. 2021, 28, 546.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licciardello, M.P.; Workman, P. A New Chemical Probe Challenges the Broad Cancer Essentiality of CK2. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 42, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, M.; Borgo, C.; Pinna, L.A.; Ruzzene, M. Targeting CK2 in Cancer: A Valuable Strategy or a Waste of Time? Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, H.W.; Drewry, D.H.; Axtman, A.D. CK2 Chemical Probes: Past, Present, and Future. Kinases Phosphatases 2023, 1, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui-Jain, A.; Drygin, D.; Streiner, N.; Chua, P.; Pierre, F.; O’Brien, S.E.; Bliesath, J.; Omori, M.; Huser, N.; Ho, C.; et al. CX-4945, an orally bioavailable selective inhibitor of protein kinase CK2, inhibits prosurvival and angiogenic signaling and exhibits antitumor efficacy. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 10288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senhwa Biosciences CX-4945 Granted Orphan Drug Designation by the US FDA in Cholangiocarcinoma. News Release. Senhwa Biosciences, Inc. January 4 2017. Available online: https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/senhwa-biosciences-cx-4945-granted-orphan-drug-designation-by-the-us-fda-in-cholangiocarcinoma-300385278.html (accessed on 14 February 2024).
- D’Amore, C.; Borgo, C.; Sarno, S.; Salvi, M. Role of CK2 Inhibitor CX-4945 in Anti-Cancer Combination Therapy—Potential Clinical Relevance. Cell. Oncol. Dordr. 2020, 43, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, H.J.; Bae, K.J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J. The Casein Kinase 2 Inhibitor, CX-4945, as an Anti-Cancer Drug in Treatment of Human Hematological Malignancies. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garuti, L.; Roberti, M.; Bottegoni, G. Multi-Kinase Inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menyhart, D.; Gyenis, L.; Jurcic, K.; Roffey, S.E.; Puri, A.; Jovanovic, P.; Szkop, K.J.; Pittock, P.; Lajoie, G.; Axtman, A.D.; et al. Comparison of CX-4945 and SGC-CK2-1 as Inhibitors of CSNK2 Using Quantitative Phosphoproteomics: Triple SILAC in Combination with Inhibitor-Resistant CSNK2. Curr. Res. Chem. Biol. 2023, 3, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistutta, R.; Cozza, G.; Pierre, F.; Papinutto, E.; Lolli, G.; Sarno, S.; O’Brien, S.E.; Siddiqui-Jain, A.; Haddach, M.; Anderes, K.; et al. Unprecedented Selectivity and Structural Determinants of a New Class of Protein Kinase CK2 Inhibitors in Clinical Trials for the Treatment of Cancer. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 8478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursu, A.; Childs-Disney, J.L.; Angelbello, A.J.; Costales, M.G.; Meyer, S.M.; Disney, M.D. Gini Coefficients as a Single Value Metric to Define Chemical Probe Selectivity. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ember, S.W.; Lambert, Q.T.; Berndt, N.; Gunawan, S.; Ayaz, M.; Tauro, M.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Cranfill, P.J.; Greninger, P.; Lynch, C.C.; et al. Potent Dual BET Bromodomain-Kinase Inhibitors as Value Added Multi-Targeted Chemical Probes and Cancer Therapeutics. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciceri, P.; Müller, S.; O’Mahony, A.; Fedorov, O.; Filippakopoulos, P.; Hunt, J.P.; Lasater, E.A.; Pallares, G.; Picaud, S.; Wells, C.; et al. Dual Kinase-Bromodomain Inhibitors for Rationally Designed Polypharmacology. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, R.M.; Bikowitz, M.J.; Chan, A.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Grassie, D.; Becker, A.; Berndt, N.; Gunawan, S.; Lawrence, N.J.; Schönbrunn, E. Differential BET Bromodomain Inhibition by Dihydropteridinone and Pyrimidodiazepinone Kinase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 15772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Magnuson, N.S. Pim kinase-dependent inhibition of c-Myc degradation. Oncogene 2008, 27, 4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchal, N.K.; Sabina, E.P. A Serine/Threonine Protein PIM Kinase as a Biomarker of Cancer and a Target for Anti-Tumor Therapy. Life Sci. 2020, 255, 117866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, S.; Finter, J.; Forde, A.J.; Kissel, S.; Schwaller, J.; Mack, T.S.; Kuhn, A.; Gray, N.; Follo, M.; Jumaa, H.; et al. PIM Kinases Are Essential for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Cell Survival (PIM2/3) and CXCR4-Mediated Microenvironmental Interactions (PIM1). Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luszczak, S.; Kumar, C.; Sathyadevan, V.K.; Simpson, B.S.; Gately, K.A.; Whitaker, H.C.; Heavey, S. PIM Kinase Inhibition: Co-Targeted Therapeutic Approaches in Prostate Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Aparicio, C.; Carnero, A. Pim Kinases in Cancer: Diagnostic, Prognostic and Treatment Opportunities. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrouchi, H.; Lakhlili, W.; Ibrahimi, A. A Review on PIM Kinases in Tumors. Bioinformation 2019, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Ramos, M.; Prudent, R.; Moucadel, V.; Sautel, C.; Barette, C.; Lafanechère, L.; Mouawad, L.; Grierson, D.; Schmidt, F.; Florent, J.; et al. New Potent Dual Inhibitors of CK2 and Pim Kinases: Discovery and Structural Insights. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarno, S.; Mazzorana, M.; Traynor, R.; Ruzzene, M.; Cozza, G.; Pagano, M.A.; Meggio, F.; Zagotto, G.; Battistutta, R.; Pinna, L.A. Structural Features Underlying the Selectivity of the Kinase Inhibitors NBC and dNBC: Role of a Nitro Group That Discriminates between CK2 and DYRK1A. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozza, G.; Sarno, S.; Ruzzene, M.; Girardi, C.; Orzeszko, A.; Kazimierczuk, Z.; Zagotto, G.; Bonaiuto, E.; Di Paolo, M.L.; Pinna, L.A. Exploiting the Repertoire of CK2 Inhibitors to Target DYRK and PIM Kinases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA—Proteins Proteom. 2013, 1834, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozza, G.; Girardi, C.; Ranchio, A.; Lolli, G.; Sarno, S.; Orzeszko, A.; Kazimierczuk, Z.; Battistutta, R.; Ruzzene, M.; Pinna, L.A. Cell-Permeable Dual Inhibitors of Protein Kinases CK2 and PIM-1: Structural Features and Pharmacological Potential. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardi, C.; Ottaviani, D.; Pinna, L.A.; Ruzzene, M. Different Persistence of the Cellular Effects Promoted by Protein Kinase CK2 Inhibitors CX-4945 and TDB. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 185736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnacki, K.; Wińska, P.; Wielechowska, M.; Łukowska-Chojnacka, E.; Tölzer, C.; Niefind, K.; Bretner, M. Biological Properties and Structural Study of New Aminoalkyl Derivatives of Benzimidazole and Benzotriazole, Dual Inhibitors of CK2 and PIM1 Kinases. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 80, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, B.; Lorenzini, E.; Ciarrocchi, A. BRD4 and Cancer: Going beyond Transcriptional Regulation. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Micco, R.; Fontanals-Cirera, B.; Low, V.; Ntziachristos, P.; Yuen, S.K.; Lovell, C.D.; Dolgalev, I.; Yonekubo, Y.; Zhang, G.; Rusinova, E.; et al. Control of Embryonic Stem Cell Identity by BRD4-Dependent Transcriptional Elongation of Super-Enhancer-Associated Pluripotency Genes. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-Y.; Lee, A.-Y.; Lai, H.-T.; Zhang, H.; Chiang, C.-M. Phospho Switch Triggers BRD4 Chromatin Binding and Activator Recruitment for Gene-Specific Targeting. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvezzi, F.; Stubbs, C.J.; Jowitt, T.A.; Dale, I.L.; Guo, X.; DeGnore, J.P.; Degliesposti, G.; Skehel, J.M.; Bannister, A.J.; McAlister, M.S. Phosphorylation-Dependent BRD4 Dimerization and Implications for Therapeutic Inhibition of BET Family Proteins. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-Y.; Lee, C.-F.; Lai, H.-T.; Yu, C.-T.; Lee, J.-E.; Zuo, H.; Tsai, S.Y.; Tsai, M.-J.; Ge, K.; Wan, Y.; et al. Opposing Functions of BRD4 Isoforms in Breast Cancer. Mol. Cell 2020, 78, 1114.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Alvarez, M.; Cristobal, I.; Luque, M.; Santos, A.; Zazo, S.; Madoz-Gurpide, J.; Carames, C.; Chiang, C.M.; Garcia-Foncillas, J.; Eroles, P.; et al. Expression of Phosphorylated BRD4 is Markedly Associated with the Activation Status of the PP2A Pathway and Shows a Strong Prognostic Value in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers 2021, 31, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, P.; Zou, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.; He, G.; Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Chiang, C.-M.; et al. Discovery of Novel Dual-Target Inhibitor of Bromodomain-Containing Protein 4/Casein Kinase 2 Inducing Apoptosis and Autophagy-Associated Cell Death for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 18025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-Q.; Duan, L.-X.; Liu, Q.-Y.; Li, H.-F.; Hu, A.-P.; Song, J.-W.; Lin, C.; Huang, B.; Yao, D.; Peng, B.; et al. Serine-Arginine Protein Kinase 1 (SRPK1) Promotes EGFR-TKI Resistance by Enhancing GSK3β Ser9 Autophosphorylation Independent of Its Kinase Activity in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Oncogene 2023, 42, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikas, I.P.; Themistocleous, S.C.; Paschou, S.A.; Tsamis, K.I.; Ryu, H.S. Serine-Arginine Protein Kinase 1 (SRPK1) as a Prognostic Factor and Potential Therapeutic Target in Cancer: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Cells 2019, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, N.; Xiao, M.; Jiang, F.; Liu, Z.; Ni, W.; Lu, C.; Ni, R.; Chen, W. SRPK1 Is a Poor Prognostic Indicator and a Novel Potential Therapeutic Target for Human Colorectal Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylonis, I.; Giannakouros, T. Protein kinase CK2 phosphorylates and activates the SR protein-specific kinase 1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 301, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morooka, S.; Hoshina, M.; Kii, I.; Okabe, T.; Kojima, H.; Inoue, N.; Okuno, Y.; Denawa, M.; Yoshida, S.; Fukuhara, J.; et al. Identification of a Dual Inhibitor of SRPK1 and CK2 That Attenuates Pathological Angiogenesis of Macular Degeneration in Mice. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 88, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonidis, G.; Dalezis, P.; Trafalis, D.; Beis, D.; Giardoglou, P.; Koukiali, A.; Sigala, I.; Nikolakaki, E.; Sarli, V. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of a c(RGDyK) Peptide Conjugate of SRPIN803. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 28379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, E.; Yoshida, M. Erasers of Histone Acetylation: The Histone Deacetylase Enzymes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a018713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.C.; Seto, E. Regulation of histone deacetylase 2 by protein kinase CK2. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 31826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubna, A.K. Vorinostat—An Overview. Indian J. Dermatol. 2015, 60, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzzene, M.; Penzo, D.; Pinna, L.A. Protein Kinase CK2 Inhibitor 4,5,6,7-Tetrabromobenzotriazole (TBB) Induces Apoptosis and Caspase-Dependent Degradation of Haematopoietic Lineage Cell-Specific Protein 1 (HS1) in Jurkat Cells. Biochem. J. 2002, 364, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.C.; Hessenauer, A.; Götz, C.; Montenarh, M. DMAT, an Inhibitor of Protein Kinase CK2 Induces Reactive Oxygen Species and DNA Double Strand Breaks. Oncol. Rep. 2009, 21, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Purwin, M.; Hernández-Toribio, J.; Coderch, C.; Panchuk, R.; Skorokhyd, N.; Filipiak, K.; de Pascual-Teresa, B.; Ramos, A. Design and Synthesis of Novel Dual-Target Agents for HDAC1 and CK2 Inhibition. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 66595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangasamy, L.; Ortín, I.; Zapico, J.M.; Coderch, C.; Ramos, A.; de Pascual-Teresa, B. New Dual CK2/HDAC1 Inhibitors with Nanomolar Inhibitory Activity against Both Enzymes. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deboever, E.; Fistrovich, A.; Hulme, C.; Dunckley, T. The Omnipresence of DYRK1A in Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vona, C.; Daniela Bezdan, D.; Islam, A.; Salichs, E.; López-Bigas, N.; Ossowski, S.; de la Luna, S. Chromatin-wide Profiling of DYRK1A Reveals a Role as a Gene-Specific RNA Polymerase II CTD Kinase. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, T.; Li, V.S.; Ng, S.S.; Taouatas, N.; Vries, R.G.; Mohammed, S.; Heck, A.J.; Clevers, H. The kinase TNIK is an essential activator of Wnt target genes. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Padgaonkar, A.A.; Baker, S.J.; Cosenza, S.C.; Rechkoblit, O.; Subbaiah, D.V.; Domingo-Domenech, J.; Bartkowski, A.; Port, E.R.; Aggarwal, A.K.; et al. Simultaneous CK2/TNIK/DYRK1 inhibition by 108600 suppresses triple negative breast cancer stem cells and chemotherapy-resistant disease. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Baker, S.J.; Reddy, E.P.; Irie, H.Y. Abstract 308: Novel Cancer Stem Cell Inhibitor 108600 Modulates Tumor Immunomicroenvironment of Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC). Cancer Res. 2022, 82, PD3-08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meggio, F.; Pinna, L.A.; Marchiori, F.; Borin, G. Polyglutamyl Peptides: A New Class of Inhibitors of Type-2 Casein Kinases. FEBS Lett. 1983, 162, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perea, S.E.; Reyes, O.; Puchades, Y.; Mendoza, O.; Vispo, N.S.; Torrens, I.; Santos, A.; Silva, R.; Acevedo, B.; López, E.; et al. Antitumor Effect of a Novel Proapoptotic Peptide that Impairs the Phosphorylation by the Protein Kinase 2 (Casein Kinase 2). Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perea, S.E.; Baladron, I.; Garcia, Y.; Perera, Y.; Lopez, A.; Soriano, J.L.; Batista, N.; Palau, A.; Hernández, I.; Farina, H.; et al. CIGB-300, a Synthetic Peptide-Based Drug That Targets the CK2 Phosphoaceptor Domain. Translational and Clinical Research. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 356, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, L.R.; Baladrón, I.; Rittoles, A.; Díaz, P.A.; Valenzuela, C.; Santana, R.; Vázquez, M.M.; García, A.; Chacón, D.; Thompson, D.; et al. Treatment with an Anti-CK2 Synthetic Peptide Improves Clinical Response in COVID-19 Patients with Pneumonia. A Randomized and Controlled Clinical Trial. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 4, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozza, G.; Zanin, S.; Sarno, S.; Costa, E.; Girardi, C.; Ribaudo, G.; Salvi, M.; Zagotto, G.; Ruzzene, M.; Pinna, L.A. Design, Validation and Efficacy of Bisubstrate Inhibitors Specifically Affecting Ecto-CK2 Kinase Activity. Biochem. J. 2015, 471, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enkvist, E.; Viht, K.; Bischoff, N.; Vahter, J.; Saaver, S.; Raidaru, G.; Issinger, O.-G.; Niefind, K.; Uri, A. A Subnanomolar Fluorescent Probe for Protein Kinase CK2 Interaction Studies. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viht, K.; Saaver, S.; Vahter, J.; Enkvist, E.; Lavogina, D.; Sinijärv, H.; Raidaru, G.; Guerra, B.; Issinger, O.-G.; Uri, A. Acetoxymethyl Ester of Tetrabromobenzimidazole-Peptoid Conjugate for Inhibition of Protein Kinase CK2 in Living Cells. Bioconjug. Chem. 2015, 26, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
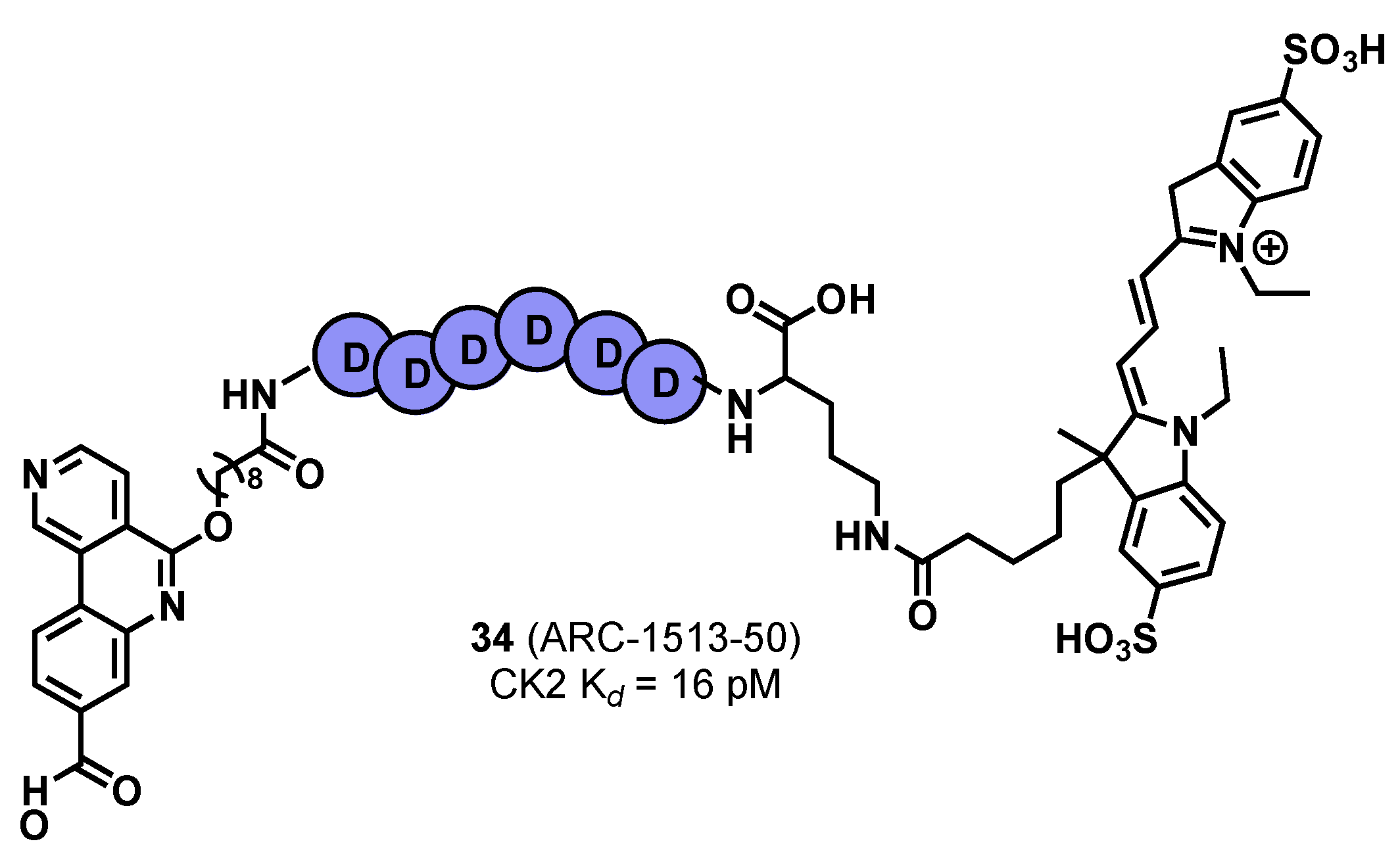
- Vahter, J.; Viht, K.; Uri, A.; Enkvist, E. Oligo-Aspartic Acid Conjugates with Benzo[c][2,6]Naphthyridine-8-Carboxylic Acid Scaffold as Picomolar Inhibitors of CK2. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brear, P.; De Fusco, C.; Hadje Georgiou, K.; Francis-Newton, N.J.; Stubbs, C.J.; Sore, H.F.; Venkitaraman, A.R.; Abell, C.; Spring, D.R.; Hyvönen, M. Specific Inhibition of CK2α from an Anchor Outside the Active Site. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 6839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, G.; Zhao, L.; Zhong, R. Identification and Biological Evaluation of CK2 Allosteric Fragments through Structure-Based Virtual Screening. Molecules 2020, 25, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancet, A.; Frem, R.; Jeanneret, F.; Mularoni, A.; Bazelle, P.; Roelants, C.; Delcros, J.G.; Guichou, J.F.; Pillet, C.; Coste, I.; et al. Cancer Selective Cell Death Induction by a Bivalent CK2 Inhibitor Targeting the ATP Site and the Allosteric αD Pocket. iScience. 2024, 27, 108903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
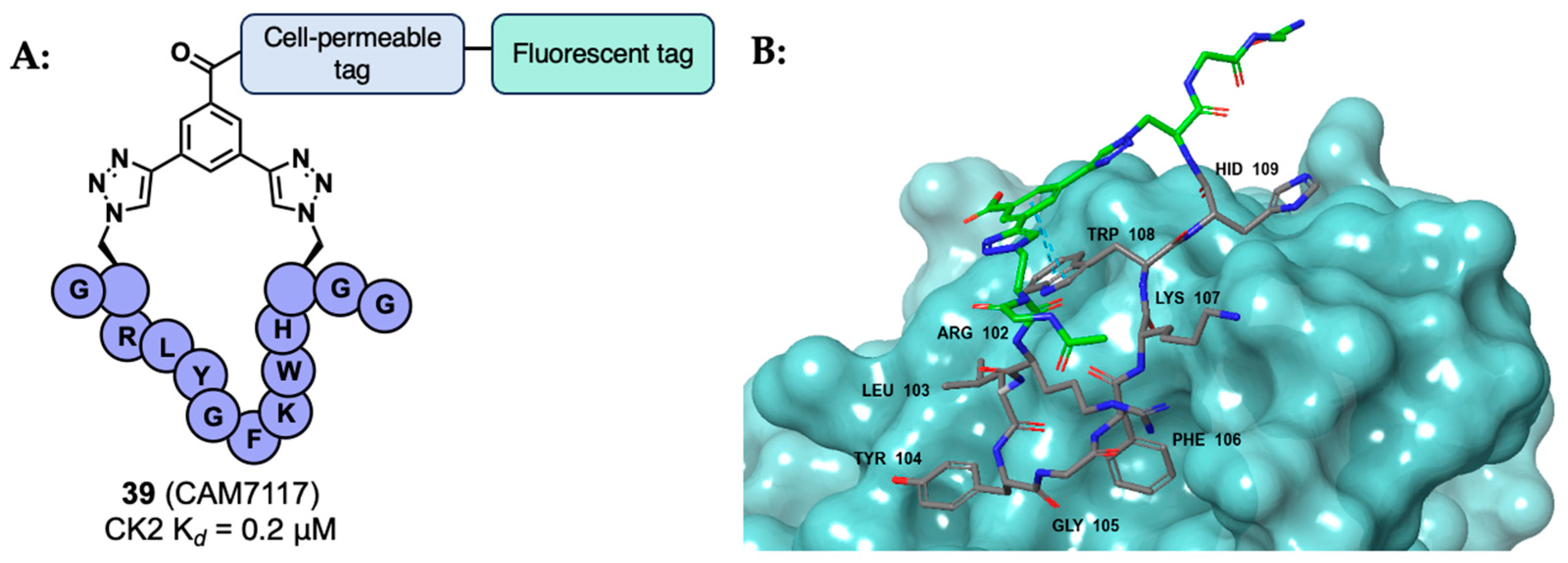
- Iegre, J.; Brear, P.; Baker, D.J.; Tan, Y.S.; Atkinson, E.L.; Sore, H.F.; Donovan, D.H.O.; Verma, C.S.; Hyvönen, M.; Spring, D.R. Efficient Development of Stable and Highly Functionalised Peptides Targeting the CK2α/CK2β Protein–Protein Interaction. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
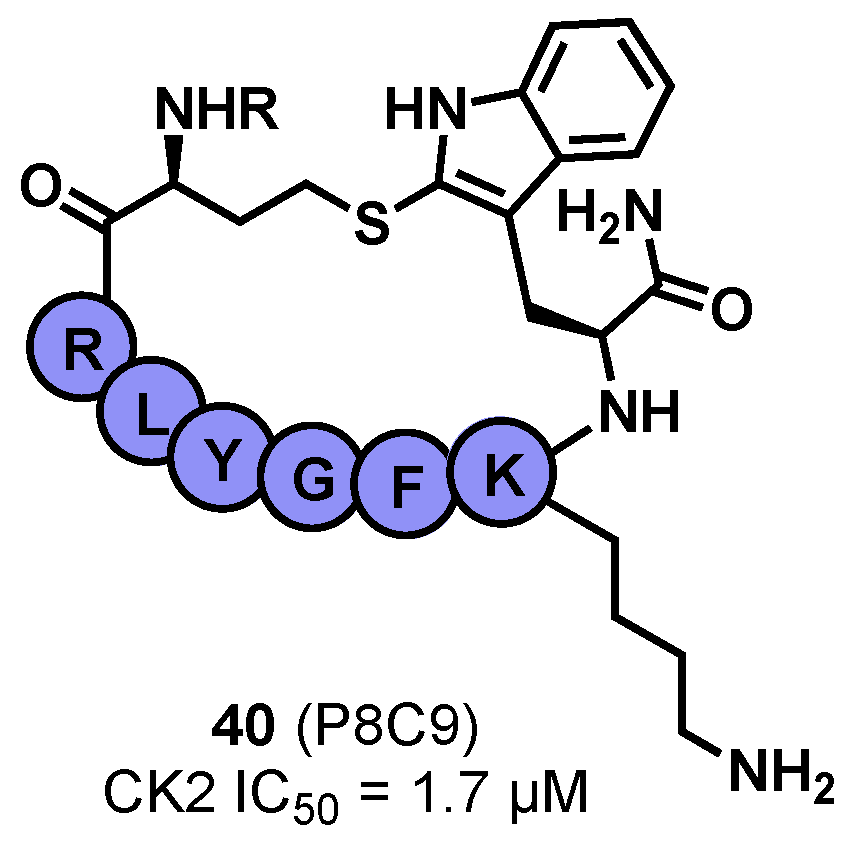
- Laudet, B.; Barette, C.; Dulery, V.; Renaudet, O.; Dumy, P.; Metz, A.; Prudent, R.; Deshiere, A.; Dideberg, O.; Filhol, O.; et al. Structure-Based Design of Small Peptide Inhibitors of Protein Kinase CK2 Subunit Interaction. Biochem. J. 2007, 408, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, E.; Iegre, J.; D’Amore, C.; Brear, P.; Salvi, M.; Hyvonen, M.; Spring, D. Development of Small Cyclic Peptides Targeting the CK2α/β Interface. ChemRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
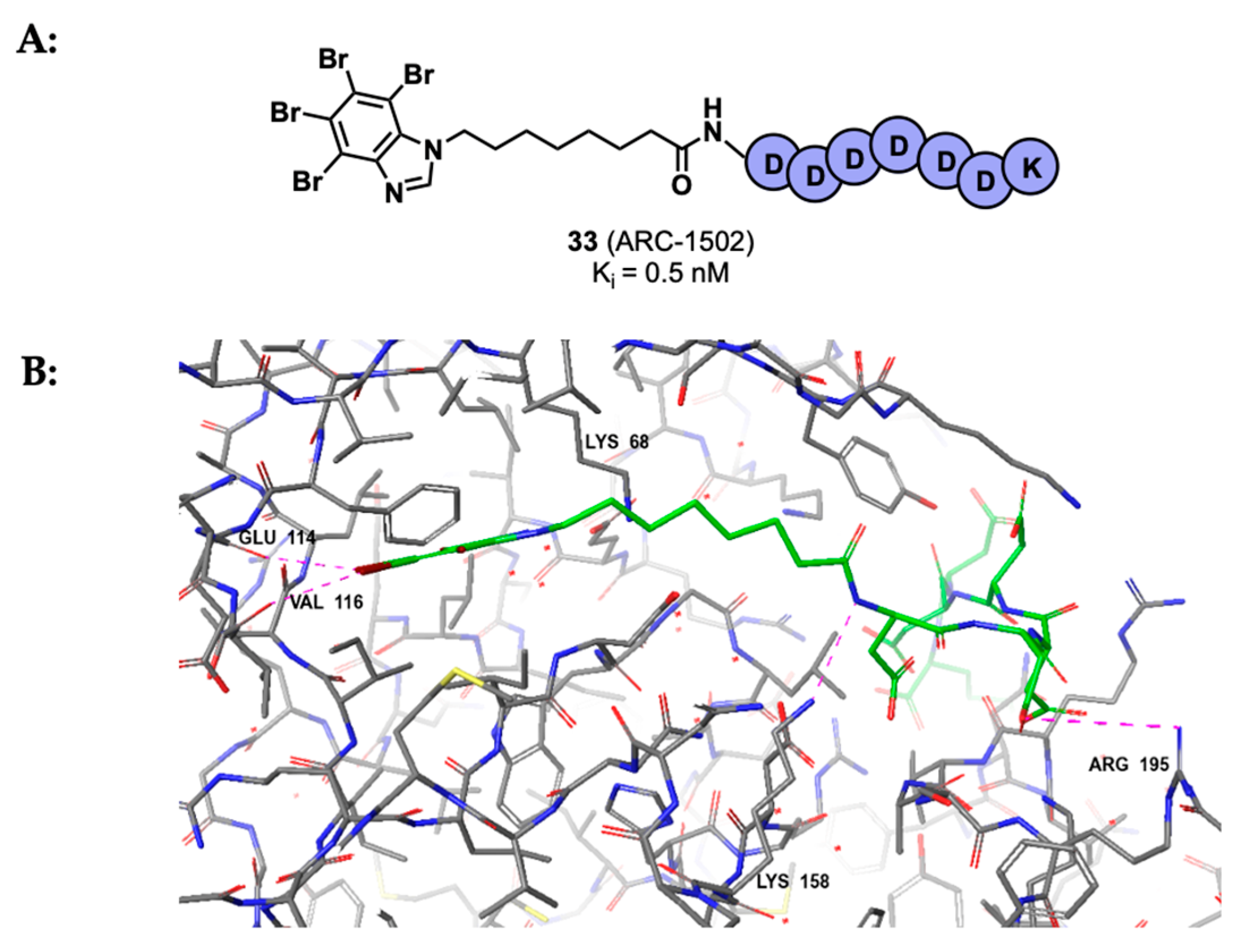
- Kufareva, I.; Bestgen, B.; Brear, P.; Prudent, R.; Laudet, B.; Moucadel, V.; Ettaoussi, M.; Sautel, C.F.; Krimm, I.; Engel, M.; et al. Discovery of Holoenzyme-Disrupting Chemicals as Substrate-Selective CK2 Inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Békés, M.; Langley, D.R.; Crews, C.M. PROTAC Targeted Protein Degraders: The Past Is Prologue. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Gao, H.; Yang, Y.; He, M.; Wu, Y.; Song, Y.; Tong, Y.; Rao, Y. PROTACs: Great Opportunities for Academia and Industry. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciechanover, A.; Schwartz, A.L. The Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway: The Complexity and Myriad Functions of Proteins Death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Chen, F.; Liu, N.; Wang, X.; Gou, S. Chemically Induced Degradation of CK2 by Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras Based on a Ubiquitin–Proteasome Pathway. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 81, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Day-Riley, S.; West, R.M.; Brear, P.D.; Hyvönen, M.; Spring, D.R. CK2 Inhibitors Targeting Inside and Outside the Catalytic Box. Kinases Phosphatases 2024, 2, 110-135. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases2020007
Day-Riley S, West RM, Brear PD, Hyvönen M, Spring DR. CK2 Inhibitors Targeting Inside and Outside the Catalytic Box. Kinases and Phosphatases. 2024; 2(2):110-135. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases2020007
Chicago/Turabian StyleDay-Riley, Sophie, Rebekah M. West, Paul D. Brear, Marko Hyvönen, and David R. Spring. 2024. "CK2 Inhibitors Targeting Inside and Outside the Catalytic Box" Kinases and Phosphatases 2, no. 2: 110-135. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases2020007
APA StyleDay-Riley, S., West, R. M., Brear, P. D., Hyvönen, M., & Spring, D. R. (2024). CK2 Inhibitors Targeting Inside and Outside the Catalytic Box. Kinases and Phosphatases, 2(2), 110-135. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases2020007






