Multi-Omics Approaches to Understanding Therapy Resistance in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
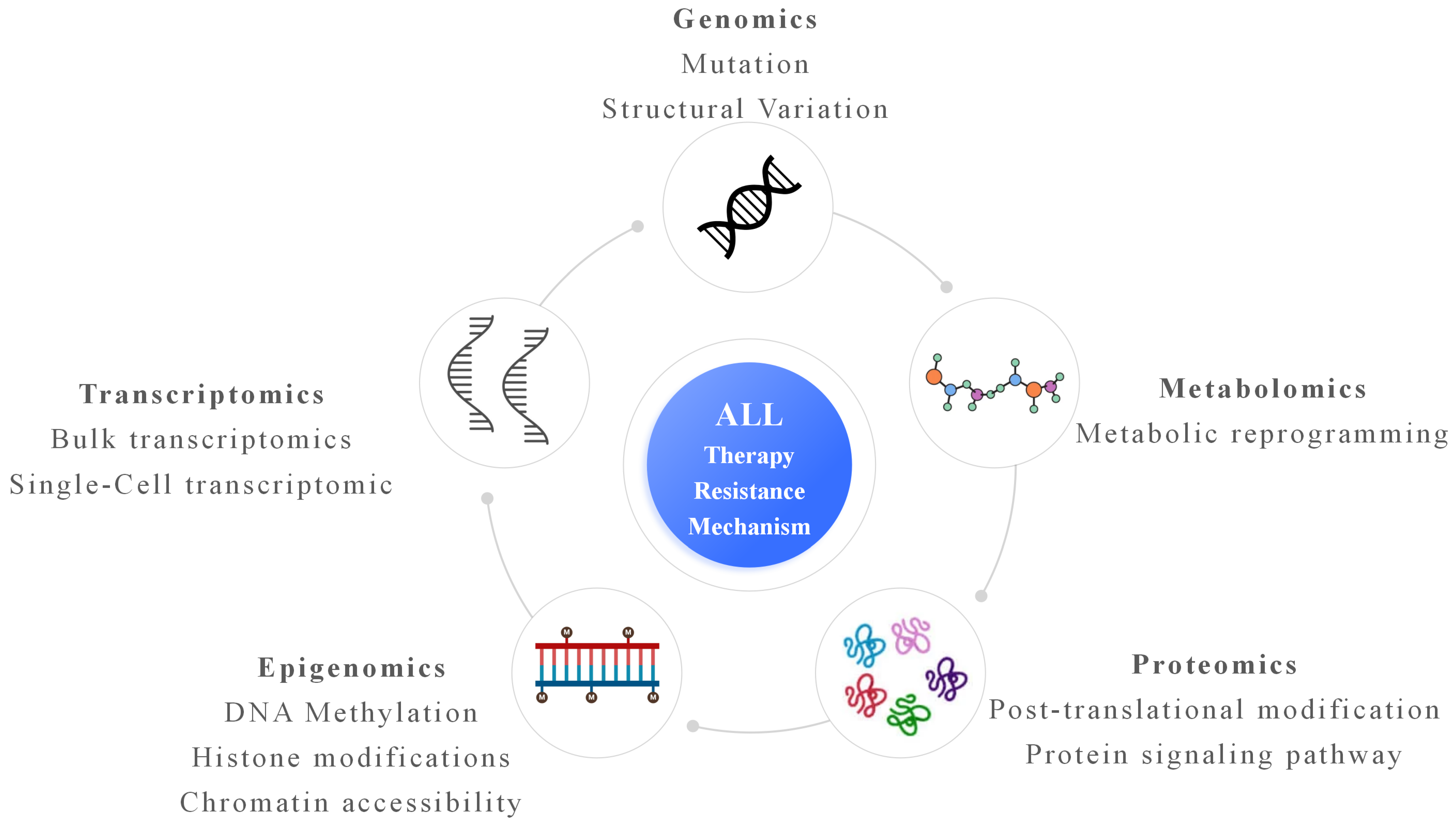
1. Introduction
2. Genomic Findings Related to Therapy Resistance in ALL
3. Transcriptomic and Single-Cell Transcriptomic Characterization in ALL
4. Epigenomic Mechanisms Underlying Resistance in ALL
5. Proteomic and Metabolomic Contributions in ALL
6. Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis and Systems Biology Approaches in ALL
7. Clinical Implications and Translational Applications in ALL
8. Future Directions and Challenges in ALL
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adomako, J.; Jiménez-Camacho, K.E.; Correa-Lara, M.V.M.; Núñez-Enriquez, J.C.; Schnoor, M. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia relapse: Biomarkers, hopes, and challenges. Trends Mol. Med. 2025, 31, 1032–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azza, E.; Ben Othmen, A.; Bahri, M.; Hsasna, R.; Ben Lakhel, R.; Ben Abdennebi, Y.; Aissaoui, L. T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Therapeutic outcomes in adolescents and young adults. Ann. Hematol. 2025, 104, 4637–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braish, J.; Kantarjian, H.; Short, N.J.; Tang, G.; Daver, N.; Kadia, T.; Senapati, J.; Jen, W.Y.; Takahashi, K.; Garris, R.; et al. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors During Frontline Therapy in Adults With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia With ABL-class Rearrangements. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2025, 26, e110–e113.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.L.; Lu, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, L.H.; Feng, H.D.; Li, B.; Jia, W.W.; Wang, J.; Hu, W.T.; Tang, X.; et al. The efficacy of blinatumomab in the treatment of pediatric B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A multicenter study. Chin. J. Pediatr. 2025, 63, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamim, H.; Jhakri, K.; Al-Shudifat, M.; Sumra, B.; Kocherry, C.; Malasevskaia, I. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell Therapy in the Treatment of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Efficacy, Safety, and Future Directions. Cureus 2025, 17, e89172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, X.; Guan, Y.; Jiang, M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, W.; Wu, Y. Molecular insights into chemotherapy resistance mediated by MLL-AF9 fusion gene in pediatric B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Biol. Chem. 2025, 301, 110321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Diz, M.; Reglero, C.; Falkenstein, C.D.; Castro, A.; Hayer, K.E.; Radens, C.M.; Quesnel-Vallières, M.; Ang, Z.; Sehgal, P.; Li, M.M.; et al. An Alternatively Spliced Gain-of-Function NT5C2 Isoform Contributes to Chemoresistance in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 3327–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gimenez, A.; Ditcham, J.E.; Azazi, D.M.A.; Giotopoulos, G.; Asby, R.; Meduri, E.; Bagri, J.; Sakakini, N.; Lopez, C.K.; Narayan, N.; et al. CREBBP inactivation sensitizes B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia to ferroptotic cell death upon BCL2 inhibition. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervoort, B.M.T.; Butler, M.; Grünewald, K.J.T.; Schenau, D.; Tee, T.M.; Lucas, L.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Boer, J.M.; Bornhauser, B.C.; Bourquin, J.P.; et al. IKZF1 gene deletions drive resistance to cytarabine in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2024, 109, 3904–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Ma, X.J.; Ying, L.L.; Tong, Y.H.; Xiang, X.P. Multi-Omics Analysis of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Identified the Methylation and Expression Differences Between BCP-ALL and T-ALL. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 622393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Y.; Zhu, S.; Peng, H.; Wang, Z. Unveiling the omics tapestry of B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Bridging genomics, metabolomics, and immunomics. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aertgeerts, M.; Meyers, S.; Gielen, O.; Lamote, J.; Dewaele, B.; Tajdar, M.; Maertens, J.; De Bie, J.; De Keersmaecker, K.; Boeckx, N.; et al. Single-cell DNA and surface protein characterization of high hyperdiploid acute lymphoblastic leukemia at diagnosis and during treatment. Hemasphere 2025, 9, e70085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narang, S.; Ghebrechristos, Y.; Evensen, N.A.; Murrell, N.; Jasinski, S.; Ostrow, T.H.; Teachey, D.T.; Raetz, E.A.; Lionnet, T.; Witkowski, M.; et al. Clonal evolution of the 3D chromatin landscape in patients with relapsed pediatric B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Witkowski, M.T.; Harris, J.; Dolgalev, I.; Sreeram, S.; Qian, W.; Tong, J.; Chen, X.; Aifantis, I.; Chen, W. Leukemia-on-a-chip: Dissecting the chemoresistance mechanisms in B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia bone marrow niche. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghantous, A.; Nusslé, S.G.; Nassar, F.J.; Spitz, N.; Novoloaca, A.; Krali, O.; Nickels, E.; Cahais, V.; Cuenin, C.; Roy, R.; et al. Epigenome-wide analysis across the development span of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Backtracking to birth. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veltri, G.; Lovisa, F.; Cortese, G.; Pillon, M.; Carraro, E.; Cesaro, S.; Provenzi, M.; Buffardi, S.; Francescato, S.; Biffi, A.; et al. Phosphoproteomic Analysis Reveals a Different Proteomic Profile in Pediatric Patients With T-Cell Lymphoblastic Lymphoma or T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 913487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, Z.; Sarno, J.; Jager, A.; Samusik, N.; Aghaeepour, N.; Simonds, E.F.; White, L.; Lacayo, N.J.; Fantl, W.J.; Fazio, G.; et al. Single-cell developmental classification of B cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia at diagnosis reveals predictors of relapse. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balduzzi, A.; Glogova, E.; Peters, C.; Sedlacek, P.; Dalle, J.H.; Locatelli, F.; Meisel, R.; Burkhardt, B.; Buechner, J.; Wachowiak, J.; et al. Impact of minimal residual disease on the outcome of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia within the FORUM Trial. Haematologica 2025, 111, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, V.W.; Sahay, S.; Vergis, J.; Weistuch, C.; Meller, J.; McCullumsmith, R.E. Pathway Analysis Interpretation in the Multi-Omic Era. BioTech 2025, 14, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormond, K.E.; Stanclift, C.; Reuter, C.M.; Carter, J.N.; Murphy, K.E.; Lindholm, M.E.; Wheeler, M.T. Researcher views on returning results from multi-omics data to research participants: Insights from The Molecular Transducers of Physical Activity Consortium (MoTrPAC) Study. BMC Med. Ethics 2025, 26, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlgren, L.; Pilheden, M.; Sturesson, H.; Song, G.; Walsh, M.P.; Yang, M.; Maillard, M.; Zhao, H.; Cheng, Z.; Singh, V.; et al. The genomic landscape of relapsed infant and childhood KMT2A-rearranged acute leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Chen, P.; Xu, Y.; Jia, P.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Li, W.; Zhen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of thirteen-gene panel with prognosis value in Multiple Myeloma. Cancer Biomark. 2023, 38, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.M.; Singh, R.; Haugen, M.; Duff, A.; Shoop, J.; Morgan, E.R.; Rossoff, J.E.; Weinstein, J.L.; Heneghan, M.B.; Badawy, S.M. Adherence to 6-Mercaptopurine (6-MP) and Habit Strength in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL). Eur. J. Haematol. 2025, 114, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kager, L.; Boztug, K. The NUDIX hydrolase NUDT5 influences purine nucleotide metabolism and thiopurine pharmacology. J. Clin. Investig. 2025, 135, e194434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazaro-Navarro, J.; Alcon, C.; Dorel, M.; Alasfar, L.; Bastian, L.; Baldus, C.; Astrahantseff, K.; Yaspo, M.L.; Montero, J.; Eckert, C. Inhibiting H3K27 Demethylases Downregulates CREB-CREBBP, Overcoming Resistance in Relapsed Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Med. 2025, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Di, S.; Nie, F.; Meng, W.; Huang, S. RPS15a knockdown impedes the progression of B-ALL by inducing p53-mediated nucleolar stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2025, 763, 151768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Leons, G.K.; Singh, V.; Naseer, S.; Ribeyron, L.; Bakhshi, S.; Gupta, R.; Gajendra, S.; Thoudam, D.S.; Sarawat, S.K.; et al. Gene expression signature of IKZF1 deleted B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia reveals a unique regulation of MUC4. Br. J. Haematol. 2025, 207, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xue, X.; Wang, H.; Hao, Y.; Yang, Q. Notch1 activation and inhibition in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia subtypes. Exp. Hematol. 2025, 148, 104771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, Y.; Ishida, T.; Masaki, A.; Murase, T.; Ohtsuka, E.; Takeshita, M.; Muto, R.; Choi, I.; Iwasaki, H.; Ito, A.; et al. Clinical significance of NOTCH1 and FBXW7 alterations in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Int. J. Hematol. 2025, 121, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalska-Sadowska, J.; Dawidowska, M.; Szarzyńska-Zawadzka, B.; Jarmuż-Szymczak, M.; Czerwińska-Rybak, J.; Machowska, L.; Derwich, K. Translocation t(8;14)(q24;q11) with concurrent PTEN alterations and deletions of STIL/TAL1 and CDKN2A/B in a pediatric case of acute T-lymphoblastic leukemia: A genetic profile associated with adverse prognosis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, e26266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studd, J.B.; Cornish, A.J.; Hoang, P.H.; Law, P.; Kinnersley, B.; Houlston, R. Cancer drivers and clonal dynamics in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia subtypes. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antić, Ž.; Yu, J.; Bornhauser, B.C.; Lelieveld, S.H.; van der Ham, C.G.; van Reijmersdal, S.V.; Morgado, L.; Elitzur, S.; Bourquin, J.P.; Cazzaniga, G.; et al. Clonal dynamics in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia with very early relapse. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2022, 69, e29361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antić, Ž.; Yu, J.; Van Reijmersdal, S.V.; Van Dijk, A.; Dekker, L.; Segerink, W.H.; Sonneveld, E.; Fiocco, M.; Pieters, R.; Hoogerbrugge, P.M.; et al. Multiclonal complexity of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia and the prognostic relevance of subclonal mutations. Haematologica 2021, 106, 3046–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahid, U.; Sagar, F.; Al Mohajer, M.; Majeed, A. Management of Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection During Intensive Chemotherapy and Stem Cell Transplantation for Leukemia: Case with Literature Review. Cureus 2018, 10, e2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Grimes, K.; Rauwolf, K.K.; Bruch, P.M.; Rausch, T.; Hasenfeld, P.; Benito, E.; Roider, T.; Sabarinathan, R.; Porubsky, D.; et al. Functional analysis of structural variants in single cells using Strand-seq. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 832–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zheng, R.; Fuda, F.; Cantu, M.D.; Koduru, P.; Jaso, J.M.; Weinberg, O.; Germans, S.; Chen, M.; Xu, J.; et al. Genomic and Clinicopathological Characterization of CRLF2-Rearranged Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2025, 72, e31507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Liu, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Yue, M.; Zhong, D.; Tang, R. Clinical features and prognosis of pediatric acute lymphocytic leukemia with JAK-STAT pathway genetic abnormalities: A case series. Ann. Hematol. 2023, 102, 2445–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, M.F.; Smadbeck, J.B.; Sharma, N.; Blackburn, P.R.; Demasi Benevides, J.; Akkari, Y.M.N.; Jaroscak, J.J.; Znoyko, I.; Wolff, D.J.; Schandl, C.A.; et al. Apparent coexistence of ETV6::RUNX1 and KMT2A::MLLT3 fusions due to a nonproductive KMT2A rearrangement in B-ALL. Leuk. Lymphoma 2022, 63, 2243–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Ham, C.G.; Van Leeuwen, F.N.; Kuiper, R.P. Treatment-related mutagenic processes in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2025, 110, 2261–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerchel, I.S.; Hoogkamer, A.Q.; Ariës, I.M.; Steeghs, E.M.P.; Boer, J.M.; Besselink, N.J.M.; Boeree, A.; van de Ven, C.; de Groot-Kruseman, H.A.; de Haas, V.; et al. RAS pathway mutations as a predictive biomarker for treatment adaptation in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2018, 32, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Waanders, E.; van Reijmersdal, S.V.; Antić, Ž.; van Bosbeek, C.M.; Sonneveld, E.; de Groot, H.; Fiocco, M.; Geurts van Kessel, A.; van Leeuwen, F.N.; et al. Upfront Treatment Influences the Composition of Genetic Alterations in Relapsed Pediatric B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Hemasphere 2020, 4, e318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.C.; Chan-Seng-Yue, M.; Ge, S.; Zeng, A.G.X.; Ng, K.; Gan, O.I.; Garcia-Prat, L.; Flores-Figueroa, E.; Woo, T.; Zhang, A.X.W.; et al. Transcriptomic classes of BCR-ABL1 lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 1186–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Lai, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, D.; Huang, J.; Zhou, D.; Li, Y.; et al. The potential role of RNA sequencing in diagnosing unexplained insensitivity to conventional chemotherapy in pediatric patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. BMC Med. Genom. 2024, 17, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Hu, D.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Wang, S. Immunometabolic Dysregulation in B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Revealed by Single-Cell RNA Sequencing: Perspectives on Subtypes and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veltri, G.; Peloso, A.; Cani, A.; Mariotto, E.; Corallo, D.; Aveic, S.; Russo, L.; Cescon, M.; Santinon, G.; Frasson, C.; et al. NFATc1 and NFATc2 regulate glucocorticoid resistance in pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia through modulation of cholesterol biosynthesis and the WNT/β-catenin pathway. Haematologica 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, M.; Chiaretti, S.; Iacobucci, I.; Tavolaro, S.; Lonetti, A.; Santangelo, S.; Elia, L.; Papayannidis, C.; Paoloni, F.; Vitale, A.; et al. AICDA expression in BCR/ABL1-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia is associated with a peculiar gene expression profile. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 152, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, C.S.; Saw, J.; Yan, F.; Boyle, J.A.; Amarasinghe, O.; Abdollahi, S.; Vo, A.N.Q.; Shields, B.J.; Mayoh, C.; McCalmont, H.; et al. Targeting LMO2-induced autocrine FLT3 signaling to overcome chemoresistance in early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2025, 39, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Du, Z.; Li, L.; Huang, J.; Liu, S.; Lu, B.; Duan, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, J.; et al. scRNA-seq reveals an immune microenvironment and JUN-mediated NK cell exhaustion in relapsed T-ALL. Cell Rep. Med. 2025, 6, 102098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Gao, G.; Xu, Y.; Jia, P.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Du, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J. Novel gene signature reveals prognostic model in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1036312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpar, D.; Wren, D.; Ermini, L.; Mansur, M.B.; van Delft, F.W.; Bateman, C.M.; Titley, I.; Kearney, L.; Szczepanski, T.; Gonzalez, D.; et al. Clonal origins of ETV6-RUNX1+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Studies in monozygotic twins. Leukemia 2015, 29, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Guillaumet-Adkins, A.; Dimitrova, V.; Yun, H.; Drier, Y.; Sotudeh, N.; Rogers, A.; Ouseph, M.M.; Nair, M.; Potdar, S.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals developmental plasticity with coexisting oncogenic states and immune evasion programs in ETP-ALL. Blood 2021, 137, 2463–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhu, S.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, X.; Xie, W.; Zhou, S.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Q.; Lin, Z.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Development of a cuproptosis-related prognostic signature to reveal heterogeneity of the immune microenvironment and drug sensitivity in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2025, 30, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullighan, C.G.; Zhang, J.; Kasper, L.H.; Lerach, S.; Payne-Turner, D.; Phillips, L.A.; Heatley, S.L.; Holmfeldt, L.; Collins-Underwood, J.R.; Ma, J.; et al. CREBBP mutations in relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature 2011, 471, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San Jose-Eneriz, E.; Agirre, X.; Rodríguez-Otero, P.; Prosper, F. Epigenetic regulation of cell signaling pathways in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Epigenomics 2013, 5, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer Hackenhaar, F.; Refhagen, N.; Hagleitner, M.; van Leeuwen, F.; Marquart, H.V.; Madsen, H.O.; Landfors, M.; Osterman, P.; Schmiegelow, K.; Flaegstad, T.; et al. CpG island methylator phenotype classification improves risk assessment in pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2025, 145, 2161–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.M.; Chen, H.Q.; Liu, L.T.; Zhang, Y.T.; Wang, J.; Zhou, D.H.; Fang, J.P.; Xu, L.H. Clinical characteristics and prognostic analysis of CDKN2A/2B gene in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A retrospective case-control study. Hematology 2025, 30, 2439606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, E.J.; Hsieh, Y.T.; Pham, J.; Zhao, Y.; Nguyen, C.; Huantes, S.; Park, E.; Naing, K.; Klemm, L.; Swaminathan, S.; et al. Small-molecule inhibition of CBP/catenin interactions eliminates drug-resistant clones in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2169–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Wong, S.H.; Kurzer, J.H.; Schneidawind, C.; Wei, M.C.; Duque-Afonso, J.; Jeong, J.; Feng, X.; Cleary, M.L. SETDB2 Links E2A-PBX1 to Cell-Cycle Dysregulation in Acute Leukemia through CDKN2C Repression. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 1166–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Tan, T.K.; Lee, D.Z.Y.; Huang, X.Z.; Ong, J.Z.L.; Kelliher, M.A.; Yeoh, A.E.J.; Sanda, T.; Tan, S.H. Oncogenic dependency on SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling factors in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2024, 38, 1906–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehtonen, J.; Teppo, S.; Lahnalampi, M.; Kokko, A.; Kaukonen, R.; Oksa, L.; Bouvy-Liivrand, M.; Malyukova, A.; Mäkinen, A.; Laukkanen, S.; et al. Single cell characterization of B-lymphoid differentiation and leukemic cell states during chemotherapy in ETV6-RUNX1-positive pediatric leukemia identifies drug-targetable transcription factor activities. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; He, B.; Bogush, D.; Schramm, J.; Singh, C.; Dovat, K.; Randazzo, J.; Tukaramrao, D.; Hengst, J.; Annageldiyev, C.; et al. Critical roles of IKAROS and HDAC1 in regulation of heterochromatin and tumor suppression in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2025, 39, 2010–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Pang, Y. Successful remission induction therapy with azacitidine and venetoclax for a treatment-naive elderly patient with ETP/myeloid mixed-phenotype acute leukemia: A case report. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1628767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumel, L.; Bernardi, F.; Picard, D.; Diaz, J.T.; Jepsen, V.H.; Hasselmann, R.; Schliehe-Diecks, J.; Bartl, J.; Qin, N.; Bornhauser, B.; et al. Proteogenomic profiling uncovers differential therapeutic vulnerabilities between TCF3::PBX1 and TCF3::HLF translocated B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2024, 109, 2290–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyczynski, M.; Vesterlund, M.; Björklund, A.C.; Zachariadis, V.; Janssen, J.; Gallart-Ayala, H.; Daskalaki, E.; Wheelock, C.E.; Lehtiö, J.; Grandér, D.; et al. Metabolic reprogramming of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells in response to glucocorticoid treatment. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordo, V.; Meijer, M.T.; Hagelaar, R.; de Goeij-de Haas, R.R.; Poort, V.M.; Henneman, A.A.; Piersma, S.R.; Pham, T.V.; Oshima, K.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. Phosphoproteomic profiling of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia reveals targetable kinases and combination treatment strategies. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Chan, W.W.; Mohi, G.; Rosenbaum, J.; Sayad, A.; Lu, Z.; Virtanen, C.; Li, S.; Neel, B.G.; Van Etten, R.A. Distinct GAB2 signaling pathways are essential for myeloid and lymphoid transformation and leukemogenesis by BCR-ABL1. Blood 2016, 127, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lai, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Yao, J.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, M.; Xu, B. Anlotinib exerts potent antileukemic activities in Ph chromosome negative and positive B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia via perturbation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 25, 101516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Garcia, F.M.; Jenkins, Y.R.; Assmann, V.D.; Paul, S.; Sharma, N.D.; Moore, C.; Ma, E.H.; Diamanti, P.; Hennequart, M.; Blagih, J.; et al. Canagliflozin synergises with serine restriction mediating anti-leukaemic effects in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Mol. Metab. 2025, 102, 102275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirs, S.; Van der Meulen, J.; Van de Walle, I.; Taghon, T.; Speleman, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Vlierberghe, P. Epigenetics in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 263, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruvolo, V.R.; Kurinna, S.M.; Karanjeet, K.B.; Schuster, T.F.; Martelli, A.M.; McCubrey, J.A.; Ruvolo, P.P. PKR regulates B56(alpha)-mediated BCL2 phosphatase activity in acute lymphoblastic leukemia-derived REH cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 35474–35485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachón-Meza, K.L.; Moreno-Cristancho, C.E.; Padilla-Agudelo, J.L.; Ramos-Murillo, A.I.; Londoño-Barbosa, D.; Salguero, G.; Sanabria-Barrera, S.M.; Chica, C.; Cruz-Rodriguez, N.; Godoy-Silva, R.D.; et al. Integration of Metabolic Profiling and Functional Genomics Suggests IGJ as a Driver of Chemoresistance in B-ALL. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2025, 72, e32068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hamaly, M.A.; Winter, E.; Blackburn, J.S. The mitochondria as an emerging target of self-renewal in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2025, 26, 2460252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hlozkova, K.; Hermanova, I.; Safrhansova, L.; Alquezar-Artieda, N.; Kuzilkova, D.; Vavrova, A.; Sperkova, K.; Zaliova, M.; Stary, J.; Trka, J.; et al. PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway alters sensitivity of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia to L-asparaginase. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakana, E.; Altman, J.K.; Glaser, H.; Donato, N.J.; Platanias, L.C. Antileukemic effects of AMPK activators on BCR-ABL-expressing cells. Blood 2011, 118, 6399–6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Liu, T.; Hao, Q.; Fang, Q.; Gong, X.; Li, Y.; Tian, Z.; Wei, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; et al. Comprehensive omics-based classification system in adult patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mol. Oncol. 2025, 19, 3578–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budak, B.; Tükel, E.Y.; Turanlı, B.; Kiraz, Y. Integrated systems biology analysis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Unveiling molecular signatures and drug repurposing opportunities. Ann. Hematol. 2024, 103, 4121–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavian, Z.; Nowzari-Dalini, A.; Stam, R.W.; Rahmatallah, Y.; Masoudi-Nejad, A. Network-based expression analysis reveals key genes related to glucocorticoid resistance in infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cell. Oncol. 2017, 40, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamrani, S.Q.; Ball, G.R.; El-Sherif, A.A.; Ahmed, S.; Mousa, N.O.; Alghorayed, S.A.; Alatawi, N.A.; Ali, A.M.; Alqahtani, F.A.; Gabre, R.M. Machine Learning for Multi-Omics Characterization of Blood Cancers: A Systematic Review. Cells 2025, 14, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Antić, Ž.; Fardzadeh, P.; Pietzsch, S.; Schröder, C.; Eberhardt, A.; van Bömmel, A.; Escherich, G.; Hofmann, W.; Horstmann, M.A.; et al. An artificial intelligence-assisted clinical framework to facilitate diagnostics and translational discovery in hematologic neoplasia. EBioMedicine 2024, 104, 105171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Houby, E.M.F. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia diagnosis using machine learning techniques based on selected features. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 28056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, A.; Ebadi, M.; Rehman, T.U.; Elhusseini, H.; Halaweish, H.; Kaiser, T.; Holtan, S.G.; Khoruts, A.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Staley, C. Compilation of longitudinal gut microbiome, serum metabolome, and clinical data in acute myeloid leukemia. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsagaby, S.A. Omics-based insights into therapy failure of pediatric B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncol. Rev. 2019, 13, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Qin, M.; Jia, C.; Wang, B.; Zhu, G.; Zheng, H. Prognostic Impact of the Level of Minimal Residual Disease Prior to Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation on Pediatric Patients With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A 10-Year Single-Center Study. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Wu, Q.F.; Ren, A.Q.; Chen, Q.; Shi, J.Z.; Li, J.P.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.J.; Tang, Y.Z.; Zhao, Y.; et al. ATF4 renders human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell resistance to FGFR1 inhibitors through amino acid metabolic reprogramming. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 2282–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Feng, B.; McClory, S.E.; de Oliveira, B.C.; Diorio, C.; Gregoire, C.; Tao, B.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Peng, L.; et al. Single-cell CAR T atlas reveals type 2 function in 8-year leukaemia remission. Nature 2024, 634, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.X. Comprehensive omics profiling in acute myeloid leukemia: From molecular landscape to clinical translation. Curr. Proteom. 2025, 22, 100028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vllahu, M.; Savarese, M.; Cantiello, I.; Munno, C.; Sarcina, R.; Stellato, P.; Leone, O.; Alfieri, M. Application of Omics Analyses in Pediatric B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aertgeerts, M.; Meyers, S.; Demeyer, S.; Segers, H.; Cools, J. Unlocking the Complexity: Exploration of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia at the Single Cell Level. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2024, 28, 727–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Khan, A.H.; Bilal, S.F.; Li, J. Deep learning approaches for resolving genomic discrepancies in cancer: A systematic review and clinical perspective. Brief. Bioinform. 2025, 26, bbaf541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Omics | Key Findings | Main Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Genomics | Relapse-associated mutations (e.g., NT5C2, CREBBP, TP53, IKZF1) and structural variants contribute to drug resistance. Relapse often arises from minor pre-existing subclones under treatment pressure. | Genetic lesions alone do not fully predict relapse; limited longitudinal samples; functional relevance of many mutations remains unclear. |
| Bulk transcriptomics | Resistant ALL shows altered expression of survival pathways, drug metabolism genes, and stemness-related programs. | Bulk data mask cellular heterogeneity; cannot identify rare resistant subpopulations. |
| Single-cell transcriptomics | Reveals heterogeneous leukemic cell states, including rare drug-tolerant populations that persist through therapy and drive relapse. | High cost; limited patient numbers; challenges for routine clinical use. |
| Epigenomics | DNA methylation changes, histone modifications, and chromatin remodeling enable transcriptional plasticity and reversible drug tolerance. | Causality difficult to establish; limited single-cell epigenomic data in ALL. |
| Proteomics | Rewired signaling pathways and altered post-translational modifications directly mediate survival and drug resistance. | Incomplete proteome coverage; scarcity of matched diagnosis–relapse samples. |
| Metabolomics | Metabolic reprogramming (e.g., increased mitochondrial metabolism) supports survival under therapeutic stress. | Strongly influenced by microenvironment; limited in vivo validation. |
| Integrated multi-omics | Cross-layer integration identifies convergent resistance pathways and improves relapse risk prediction. | Lack of standardized pipelines; limited external and prospective validation. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Zhang, J. Multi-Omics Approaches to Understanding Therapy Resistance in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Lymphatics 2026, 4, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/lymphatics4010008
Wu X, Zhang J. Multi-Omics Approaches to Understanding Therapy Resistance in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Lymphatics. 2026; 4(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/lymphatics4010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xiuyun, and Jingxin Zhang. 2026. "Multi-Omics Approaches to Understanding Therapy Resistance in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia" Lymphatics 4, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/lymphatics4010008
APA StyleWu, X., & Zhang, J. (2026). Multi-Omics Approaches to Understanding Therapy Resistance in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Lymphatics, 4(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/lymphatics4010008







