MicroRNA as a Potential Biomarker for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Abstract
1. Introduction
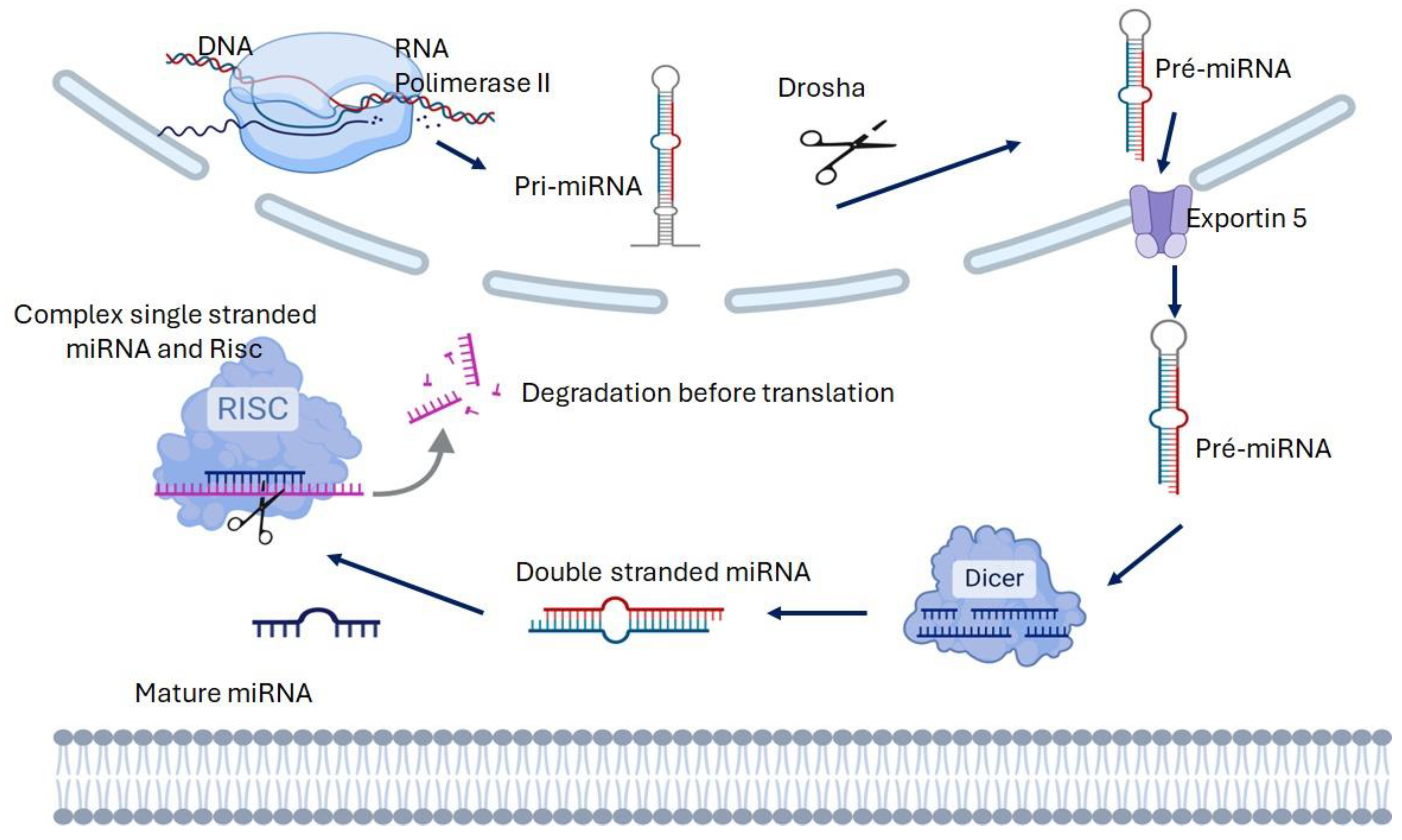
2. Biogenesis and Function of microRNA
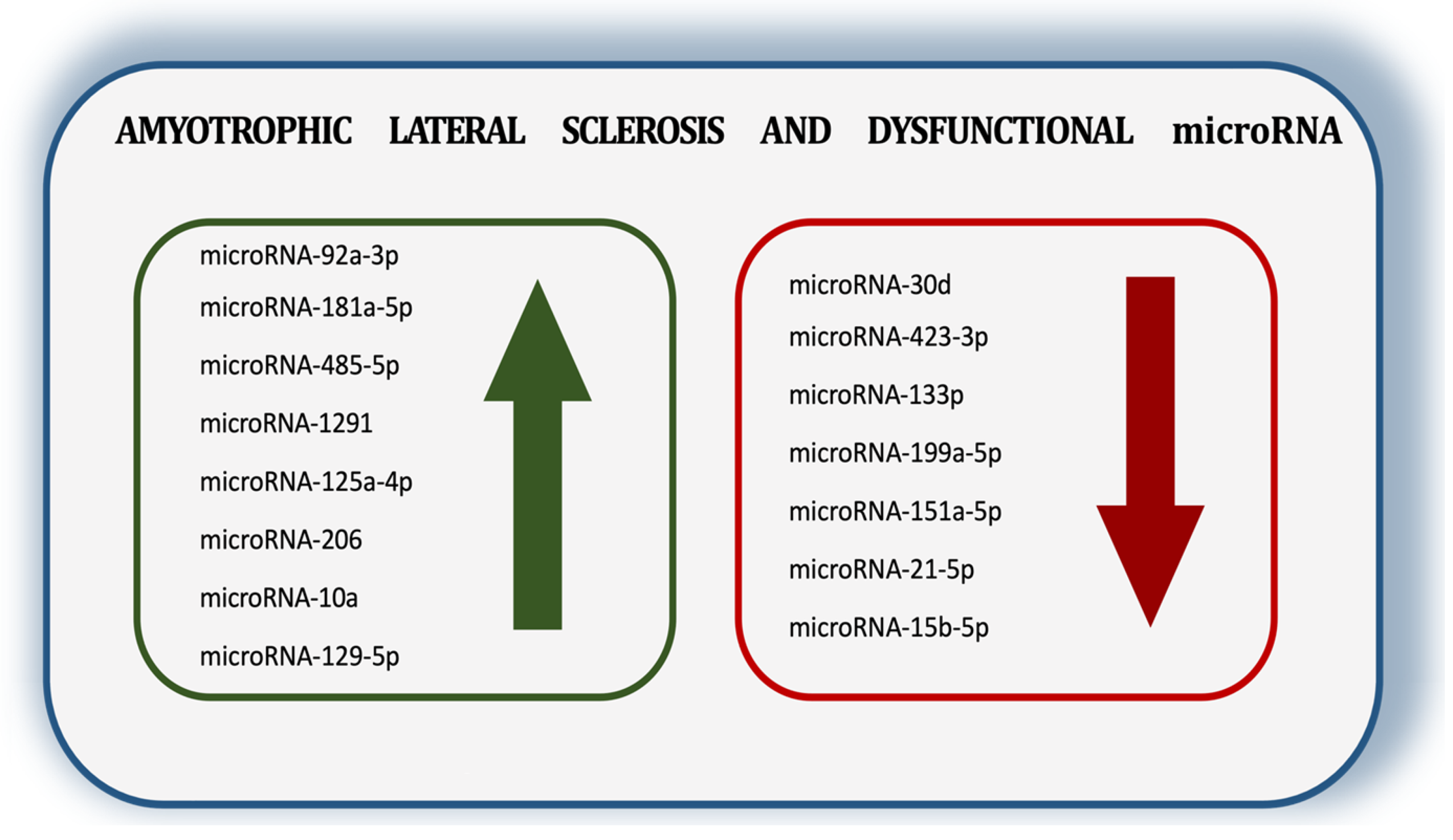
3. ALS and microRNA
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pasinelli, P.; Brown, R.H. Molecular biology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Insights from genetics. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neusch, C.; Bähr, M.; Schneider-Gold, C. Glia cells in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: New clues to understanding an old disease? Muscle Nerve. 2007, 35, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stambler, N.; Charatan, M.; Cedarbaum, J.M. Prognostic indicators of survival in ALS. Neurology 1998, 50, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, C.; Piemonte, M.E.P.; Callegaro, D.; Da Silva, H.C. Fatigue in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Frequency and associated factors. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2008, 9, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, P.N.; Abrahams, S.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Ampong, M.A.; Goldstein, L.H.; Johnson, J.; Lyall, R.; Moxham, J.; Mustfa, N.; Rio, A.; et al. The management of motor neurone disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, S32–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejzini, R.; Flynn, L.L.; Pitout, I.L.; Fletcher, S.; Wilton, S.D.; Akkari, P.A. ALS Genetics, Mechanisms, and Therapeutics: Where Are We Now? Front Neurosci. 2019, 6, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiò, A.; Logroscino, G.; Traynor, B.J.; Collins, J.; Simeone, J.C.; Goldstein, L.A.; White, L.A. Global epidemiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A systematic review of the published literature. Neuroepidemiology 2013, 41, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbott, E.O.; Malek, A.M.; Lacomis, D. The epidemiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2016, 138, 225–238. [Google Scholar]
- Peggion, C.; Scalcon, V.; Massimino, M.L.; Nies, K.; Lopreiato, R.; Rigobello, M.P.; Bertoli, A. SOD1 in ALS: Taking Stock in Pathogenic Mechanisms and the Role of Glial and Muscle Cells. Antioxidants 2022, 23, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balendra, R.; Isaacs, A.M. C9orf72-mediated ALS and FTD: Multiple pathways to disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banack, S.A.; Dunlop, R.A.; Cox, P.A. An miRNA fingerprint using neural-enriched extracellular vesicles from blood plasma: Towards a biomarker for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/motor neuron disease. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardiman, O.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Chio, A.; Corr, E.M.; Logroscino, G.; Robberecht, W.; Shaw, P.J.; Simmons, Z.; van den Berg, L.H. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2017, 5, 17071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gitler, A.D.; Shorter, J. RNA-binding proteins with prion-like domains in ALS and FTLD-U. Prion 2011, 5, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, M.A.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Ferdin, J.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs in body fluids-the mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, M.H.; Chen, L.; Fu, Y.; Wang, W.; Fu, S.W. Cell-free circulating miRNA biomarkers in cancer. J. Cancer 2012, 3, 432–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayeux, R. Biomarkers: Potential uses and limitations. NeuroRx 2004, 1, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kmetzsch, V.; Latouche, M.; Saracino, D.; Rinaldi, D.; Camuzat, A.; Gareau, T.; Le Ber, I.; Colliot, O.; Becker, E. MicroRNA signatures in genetic frontotemporal dementia and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2022, 9, 1778–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, G.; Morello, G.; La Cognata, V.; Guarnaccia, M.; Conforti, F.L.; Cavallaro, S. Dysregulated miRNAs as Biomarkers and Therapeutical Targets in Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 10, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panio, A.; Cava, C.; D’Antona, S.; Bertoli, G.; Porro, D. Diagnostic Circulating miRNAs in Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Med. 2022, 6, 861960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.P.; Brown, R.H., Jr.; Cleveland, D.W. Decoding ALS: From genes to mechanism. Nature. 2016, 10, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinchetti, P.; Rizzuti, M.; Faravelli, I.; Corti, S. MicroRNA Metabolism and Dysregulation in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 2617–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, B.C.; Peixinho, N.; Pisco, R.; Gromicho, M.; Pronto-Laborinho, A.C.; Rueff, J.; de Carvalho, M.; Rodrigues, A.S. Differential Expression of miRNAs in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 7104–7117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koike, Y.; Onodera, O. Implications of miRNAs dysregulation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Challenging for clinical applications. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 21, 1131758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharap, A.; Pokrzywa, C.; Murali, S.; Pandi, G.; Vemuganti, R. MicroRNA miR-324-3p induces promoter-mediated expression of RelA gene. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, I.; Patil, K.S.; Alves, G.; Larsen, J.P.; Møller, S.G. microRNAs as neuroregulators, biomarkers and therapeutic agents in neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 811–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Coller, J. What comes first: Translational repression or mRNA degradation? The deepening mystery of microRNA function. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 1322–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, J.J.; Bernasek, S.M.; Bakker, R.; Giri, R.; Peláez, N.; Eder, B.; Bobrowska, A.; Bagheri, N.; Nunes Amaral, L.A.; Carthew, R.W. Repressive Gene Regulation Synchronizes Development with Cellular Metabolism. Cell 2019, 178, 980–992.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xie, D.; Zhao, Q.; You, Z.H. MicroRNAs and complex diseases: From experimental results to computational models. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 22, 515–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, M.; Chen, J.; Tao, Z.; Miao, L.; Qi, X.; Wang, Y.; Ren, J. Regulatory network of miRNA on its target: Coordination between transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliminejad, K.; Khorram Khorshid, H.R.; Soleymani Fard, S.; Ghaffari, S.H. An overview of microRNAs: Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 5451–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, J.D.; Chevillet, J.R.; Kroh, E.M.; Ruf, I.K.; Pritchard, C.C.; Gibson, D.F.; Mitchell, P.S.; Bennett, C.F.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Stirewalt, D.L.; et al. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 22, 5003–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, K.C.; Palmisano, B.T.; Shoucri, B.M.; Shamburek, R.D.; Remaley, A.T. MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C. Exosomes: Secreted vesicles and intercellular communications. F1000 Biol. 2011, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogure, T.; Lin, W.L.; Yan, I.K.; Braconi, C.; Patel, T. Intercellular nanovesicle-mediated microRNA transfer: A mechanism of environmental modulation of hepatocellular cancer cell growth. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.A.; Baxter, D.H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, D.Y.; Huang, K.H.; Lee, M.J.; Galas, D.J.; Wang, K. The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Zitvogel, L.; Amigorena, S. Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X. New insight into inter-kingdom communication: Horizontal transfer of mobile small RNAs. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M.; Raposo, G. Exosomes–vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, K.C.; Remaley, A.T. Lipid-based carriers of microRNAs and intercellular communication. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2012, 23, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Hou, D.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Bian, Z.; Liang, X.; Cai, X.; et al. Exogenous plant MIR168a specifically targets mammalian LDLRAP1: Evidence of cross-kingdom regulation by microRNA. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, S.R.; Nguyen, C.; Xie, F.; Wood, J.R.; Zempleni, J. MicroRNAs are absorbed in biologically meaningful amounts from nutritionally relevant doses of cow milk and affect gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells, HEK-293 kidney cell cultures, and mouse livers. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusuma, R.J.; Manca, S.; Friemel, T.; Sukreet, S.; Nguyen, C.; Zempleni, J. Human vascular endothelial cells transport foreign exosomes from cow’s milk by endocytosis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2016, 310, C800–C807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Chu, D.; Jiang, X.; Hou, D.; Zen, K.; Zhang, C.Y. Small non-coding RNAs transfer through mammalian placenta and directly regulate fetal gene expression. Protein Cell. 2015, 6, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, M.; Paone, A.; Calore, F.; Galli, R.; Gaudio, E.; Santhanam, R.; Lovat, F.; Fadda, P.; Mao, C.; Nuovo, G.J.; et al. MicroRNAs bind to Toll-like receptors to induce prometastatic inflammatory response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 31, E2110–E2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, Y.; Morishima, Y.; Hata, T.; Shindo, A.; Murata, H.; Saito, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Shindo, K. Current progress in microRNA profiling of circulating extracellular vesicles in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A systematic review. Neurobiol. Dis. 2024, 200, 106639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.R.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Chio, A.; Hardiman, O.; Kiernan, M.C.; Rohrer, J.; Rowe, J.; Seeley, W.; Talbot, K. Genetic screening in sporadic ALS and FTD. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 1042–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, U.G.; Milla, V.; Cynthia Stafford, M.Y.; Bjourson, A.J.; Duddy, W.; Duguez, S.M.-R. A Systematic Review of Suggested Molecular Strata, Biomarkers and Their Tissue Sources in ALS. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, A.E.; Weishaupt, J.H.; Andersen, P.M.; Ludolph, A.C.; Kubisch, C. Current knowledge and recent insights into the genetic basis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Med. Genet. 2018, 30, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, R.; Chiò, A.; Traynor, B.J. Novel genes associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Diagnostic and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilmaghani, N.A.; Hussen, B.M.; Nateghinia, S.; Taheri, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Emerging role of microRNAs in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luna, N.; Turon-Sans, J.; Cortes-Vicente, E.; Carrasco-Rozas, A.; Illán-Gala, I.; Dols-Icardo, O.; Clarimón, J.; Lleó, A.; Gallardo, E.; Illa, I.; et al. Downregulation of miR-335-5P in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Can Contribute to Neuronal Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 9, 4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Wei, Q.; Ou, R.; Gu, X.; Cao, B.; Shang, H. MicroRNA-183-5p is stress-inducible and protects neurons against cell death in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 8614–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichenstein, I.; Eitan, C.; Diaz-Garcia, S.; Haim, G.; Magen, I.; Siany, A.; Hoye, M.L.; Rivkin, N.; Olender, T.; Toth, B.; et al. Human genetics and neuropathology suggest a link between miR-218 and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis pathophysiology. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaav5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffreda, A.; Nizzardo, M.; Arosio, A.; Ruepp, M.-D.; Calogero, R.; Volinia, S.; Galasso, M.; Bendotti, C.; Ferrarese, C.; Lunetta, C.; et al. miR-129-5p: A key factor and therapeutic target in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Prog. Neurobiol. 2020, 190, 101803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamala, J.M.; Arias-Carrasco, R.; Sanchez, C.; Uhrig, M.; Bargsted, L.; Matus, S.; Maracaja-Coutinho, V.; Abarzua, S.; van Zundert, B.; Verdugo, R.; et al. Genome-wide circulating microRNA expression profiling reveals potential biomarkers for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 64, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.N.; Kumar, M.; Fedele, E.; Bonanno, G.; Bonifacino, T. MicroRNA Alteration, Application as Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Approaches in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 25, 4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, L. MicroRNAs in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: From pathogenetic involvement to diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic agent development. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 3569–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacchiarelli, D.; Legnini, I.; Martone, J.; Cazzella, V.; D’Amico, A.; Bertini, E.; Bozzoni, I. miRNAs as serum biomarkers for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. EMBO Mol. Med. 2011, 3, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovanda, A.; Leonardis, L.; Zidar, J.; Koritnik, B.; Dolenc-Groselj, L.; Ristic Kovacic, S.; Curk, T.; Rogelj, B. Differential expression of microRNAs and other small RNAs in muscle tissue of patients with ALS and healthy age-matched controls. Sci. Rep. 2018, 4, 5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, I.; Hama, Y.; Matsushima, M.; Hirotani, M.; Kano, T.; Hohzen, H.; Yabe, I.; Utsumi, J.; Sasaki, H. Identification of plasma microRNAs as a biomarker of sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Mol. Brain 2015, 24, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Andrade, H.M.; de Albuquerque, M.; Avansini, S.H.; de S Rocha, C.; Dogini, D.B.; Nucci, A.; Carvalho, B.; Lopes-Cendes, I.; França, M.C., Jr. MicroRNAs-424 and 206 are potential prognostic markers in spinal onset amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 15, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrowolny, G.; Martone, J.; Lepore, E.; Casola, I.; Petrucci, A.; Inghilleri, M.; Morlando, M.; Colantoni, A.; Scicchitano, B.M.; Calvo, A.; et al. A longitudinal study defined circulating microRNAs as reliable biomarkers for disease prognosis and progression in ALS human patients. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, T.W.; Figueroa-Romero, C.; Hur, J.; Pacut, C.; Stoll, E.; Spring, C.; Lewis, R.; Nair, A.; Goutman, S.A.; Sakowski, S.A.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles in Serum and Central Nervous System Tissues Contain microRNA Signatures in Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 29, 739016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Cao, B.; Ou, R.; Hadano, S.; Shang, H.F. Aberration of miRNAs Expression in Leukocytes from Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilsland, L.G.; Sahai, E.; Kelly, G.; Golding, M.; Greensmith, L.; Schiavo, G. Deficits in axonal transport precede ALS symptoms in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 23, 20523–20528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusmini, P.; Polanco, M.J.; Cristofani, R.; Cicardi, M.E.; Meroni, M.; Galbiati, M.; Piccolella, M.; Messi, E.; Giorgetti, E.; Lieberman, A.P.; et al. Aberrant Autophagic Response in The Muscle of A Knock-in Mouse Model of Spinal and Bulbar Muscular Atrophy. Sci. Rep. 2015, 22, 15174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbiati, M.; Crippa, V.; Rusmini, P.; Cristofani, R.; Cicardi, M.E.; Giorgetti, E.; Onesto, E.; Messi, E.; Poletti, A. ALS-related misfolded protein management in motor neurons and muscle cells. Neurochem. Int. 2014, 79, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuzzo, S.; Zucca, I.; Mastropietro, A.; de Rosbo, N.K.; Cavalcante, P.; Tartari, S.; Bonanno, S.; Preite, L.; Mantegazza, R.; Bernasconi, P. Hind limb muscle atrophy precedes cerebral neuronal degeneration in G93A-SOD1 mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A longitudinal MRI study. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 231, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuzzo, S.; Bonanno, S.; Figini, M.; Scotti, A.; Zucca, I.; Minati, L.; Riva, N.; Domi, T.; Fossaghi, A.; Quattrini, A.; et al. A longitudinal DTI and histological study of the spinal cord reveals early pathological alterations in G93A-SOD1 mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 293, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrowolny, G.; Aucello, M.; Rizzuto, E.; Beccafico, S.; Mammucari, C.; Bonconpagni, S.; Belia, S.; Wannenes, F.; Nicoletti, C.; Del Prete, Z.; et al. Skeletal Muscle Is a Primary Target of SOD1G93A-Mediated Toxicity. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeffler, J.P.; Picchiarelli, G.; Dupuis, L.; De Aguilar, J.L.G. The Role of Skeletal Muscle in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malacarne, C.; Galbiati, M.; Giagnorio, E.; Cavalcante, P.; Salerno, F.; Andreetta, F.; Cagnoli, C.; Taiana, M.; Nizzardo, M.; Corti, S.; et al. Dysregulation of Muscle-Specific MicroRNAs as Common Pathogenic Feature Associated with Muscle Atrophy in ALS, SMA and SBMA: Evidence from Animal Models and Human Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 26, 5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banack, S.A.; Dunlop, R.A.; Mehta, P.; Mitsumoto, H.; Wood, S.P.; Han, M.; Cox, P.A. A microRNA diagnostic biomarker for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain Commun. 2024, 6, fcae268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado Gama, H.; Amorós, M.A.; Andrade de Araújo, M.; Sha, C.M.; Vieira, M.P.S.; Torres, R.G.D.; Souza, G.F.; Junkes, J.A.; Dokholyan, N.V.; Leite Góes Gitaí, D.; et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of dysregulated microRNAs derived from liquid biopsies as biomarkers for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024, 6, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascón, E.; Zaragoza, P.; Calvo, A.C.; Osta, R. Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Skeletal Muscle Transcriptome Analysis: A Comprehensive Examination of Differentially Expressed Genes. Biomolecules 2024, 20, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallach, T.; Mossmann, Z.J.; Szczepek, M.; Wetzel, M.; Machado, R.; Raden, M.; Miladi, M.; Kleinau, G.; Kruger, C.; Dembny, P.; et al. Microrna-100-5p and Microrna-298-5p Released from Apoptotic Cortical Neurons Are Endogenous Toll-Like Receptor 7/8 Ligands That Contribute to Neurodegeneration. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffo, P.; Catalano, S.; La Bella, V.; Conforti, F.L. Deregulation of Plasma Microrna Expression in a Tardbp-Als Family. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Ho, W.K.; Wu, B.T.; Liu, H.P.; Lin, W.Y. Mirna Profiling as a Complementary Diagnostic Tool for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivonen, J.M.; Manzano, R.; Oliván, S.; Zaragoza, P.; García-Redondo, A.; Osta, R. Microrna-206: A Potential Circulating Biomarker Candidate for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Lan, S.; Shi, X.J.; Fan, F.C.; Liu, Q.S.; Cong, L.; Cheng, Y. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Micrornas in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Brain Res. Bull. 2023, 194, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kmetzsch, V.; Anquetil, V.; Saracino, D.; Rinaldi, D.; Camuzat, A.; Gareau, T.; Jornea, L.; Forlani, S.; Couratier, P.; Wallon, D.; et al. Plasma microRNA signature in presymptomatic and symptomatic subjects with C9orf72-associated frontotemporal dementia and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musarò, A.; Dobrowolny, G.; Cambieri, C.; Libonati, L.; Moret, F.; Casola, I.; Laurenzi, G.; Garibaldi, M.; Inghilleri, M.; Ceccanti, M. MiR206 and 423-3p Are Differently Modulated in Fast and Slow-Progressing Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients. Neuromolecular Med. 2024, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, D.; Kaundal, R.K. Exploring dysregulated miRNAs in ALS: Implications for disease pathogenesis and early diagnosis. Neurol. Sci. 2024, 21, 1661–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nogueira-Machado, J.A.; da Silva Albanaz, A.T.; Rocha-Silva, F. MicroRNA as a Potential Biomarker for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). Sclerosis 2025, 3, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis3020016
Nogueira-Machado JA, da Silva Albanaz AT, Rocha-Silva F. MicroRNA as a Potential Biomarker for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). Sclerosis. 2025; 3(2):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis3020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleNogueira-Machado, José Augusto, Amanda Tábita da Silva Albanaz, and Fabiana Rocha-Silva. 2025. "MicroRNA as a Potential Biomarker for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)" Sclerosis 3, no. 2: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis3020016
APA StyleNogueira-Machado, J. A., da Silva Albanaz, A. T., & Rocha-Silva, F. (2025). MicroRNA as a Potential Biomarker for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). Sclerosis, 3(2), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis3020016





